A Poly(dA:dT) Tract in the IGF1 Gene Is a Genetic Marker for Growth Traits in Pigs
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Sample Collection, and Traits Evaluated
2.2. Construction of the IGF1 Promoter Luciferase Plasmid
2.3. Construction of the Overexpression Vector and siRNA for C/EBPα
2.4. Cell Transfection and Luciferase Activity Analysis
2.5. RT-PCR and Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
2.6. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assays
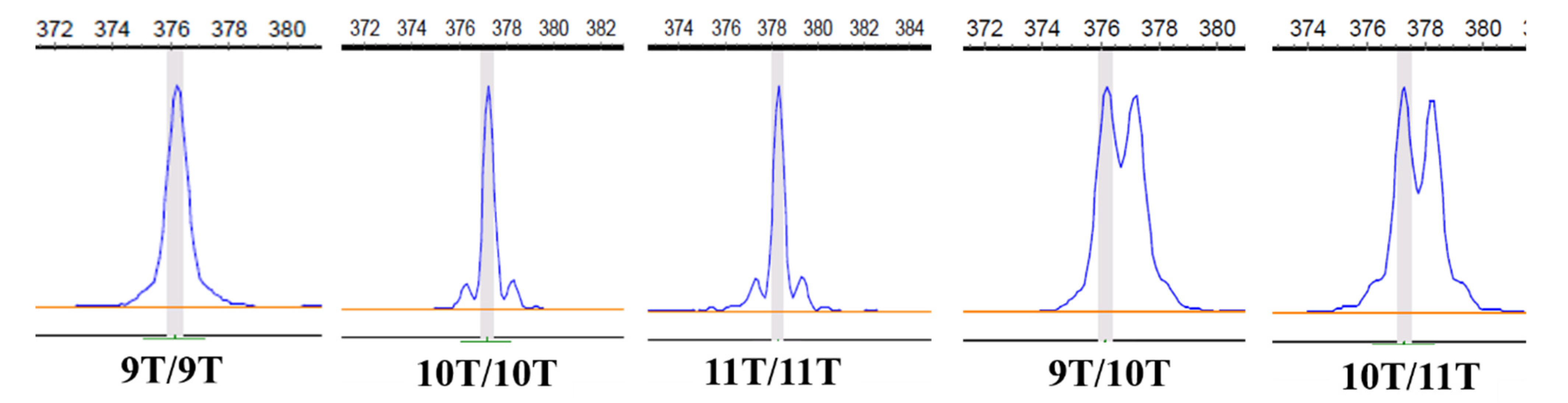
2.7. Genotyping the Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
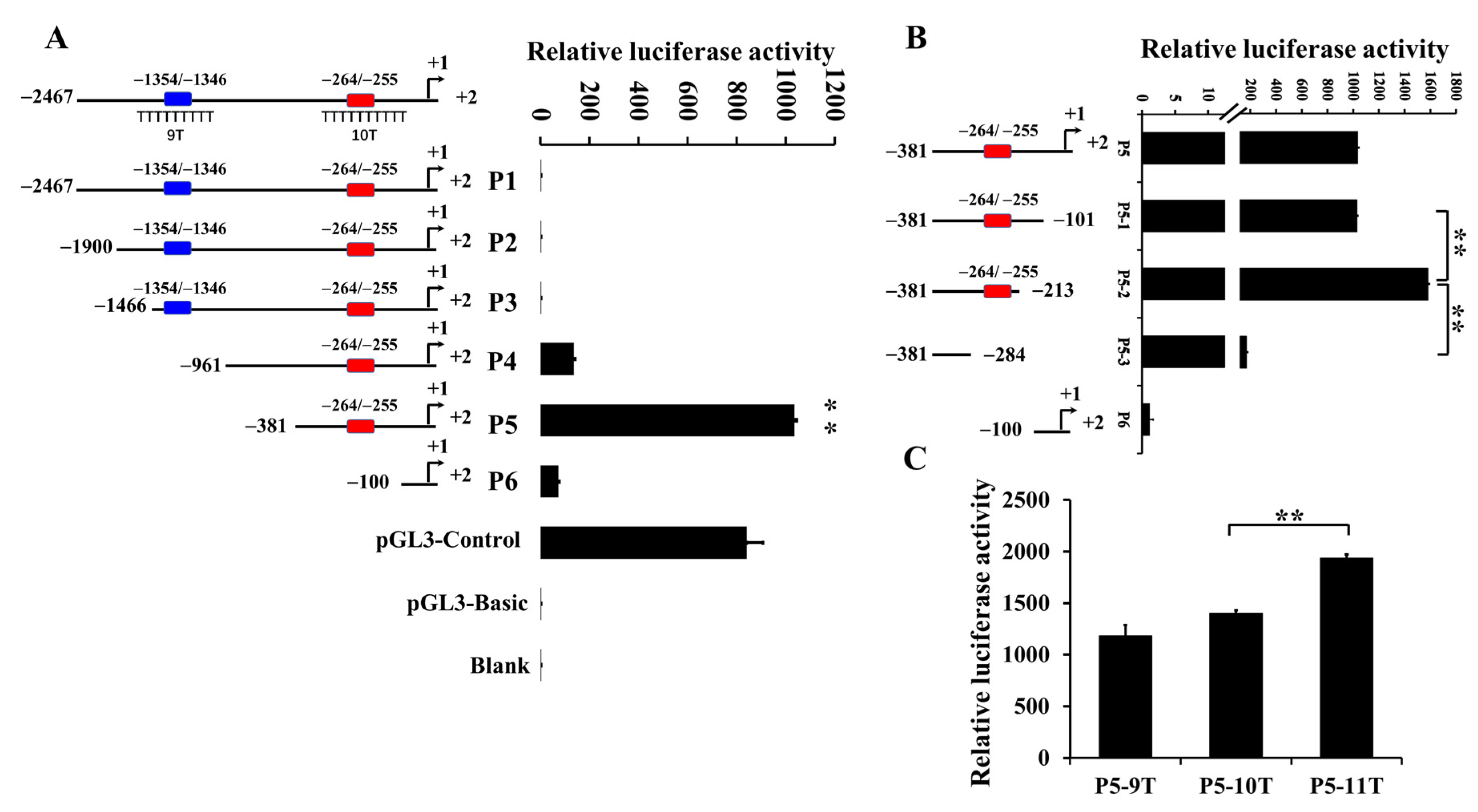
3.1. Effect of Poly(dA:dT) Tracts on IGF1 Transcription Activity
3.2. Distribution of Tract 2 Genotypes on IGF1 in Chinese Native and Commercial Breeds
3.3. Association Analysis between Tract 2 on IGF1 and the Growth Traits of Commercial Pigs
3.4. Transcription Factor C/EBPα Affects the Expression Abundance of IGF1
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rotwein, P. Insulin-like growth factor action and skeletal muscle growth, an in vivo perspective. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2003, 13, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.I.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Their Binding Proteins: Biological Actions*. Endocr. Rev. 1995, 16, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayne, S.; Hoogerbrugge, C.; Thomsen, J.; Skriver, L.; Van Buul-Offers, S.; Brande, J.V.D. Primary sequences of insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 isolated from porcine plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1991, 562, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, G.L.; Upton, F.M.; Ballard, F.J.; McNeil, K.A.; Wallace, J.C. Insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 in bovine colostrum. Sequences and biological activities compared with those of a potent truncated form. Biochem. J. 1988, 251, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinderknecht, E.; Humbel, R.E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.A.; Le Roith, D. Control of Growth by the Somatropic Axis: Growth Hormone and the Insulin-Like Growth Factors Have Related and Independent Roles. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Contreras, C.; Madsen, O.; Groenen, M.A.M.; López-García, A.; Vázquez-Gómez, M.; Astiz, S.; Núñez, Y.; Benítez, R.; Fernández, A.; Isabel, B.; et al. Impact of genotype, body weight and sex on the prenatal muscle transcriptome of Iberian pigs. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelfle, J.; Chia, D.J.; Massart-Schlesinger, M.B.; Moyano, P.; Rotwein, P. Molecular physiology, pathology, and regulation of the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-I system. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2004, 20, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, F.; Terwilliger, J.D.; Lee, K.; Segre, G.V.; Efstratiadis, A. Roles of Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 in Mouse Postnatal Growth. Dev. Biol. 2001, 229, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstratiadis, A. Genetics of mouse growth. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1998, 42, 955–976. [Google Scholar]
- Stratikopoulos, E.; Szabolcs, M.; Dragatsis, I.; Klinakis, A.; Efstratiadis, A. The hormonal action of IGF1 in postnatal mouse growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19378–19383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigenmann, J.E.; Patterson, D.F.; Froesch, E.R. Body size parallels insulin-like growth factor I levels but not growth hormone secretory capacity. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1984, 106, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunter, K.L.; Cai, W.; Johnston, D.J.; Dekkers, J.C.M. Selection to reduce residual feed intake in pigs produces a correlated response in juvenile insulin-like growth factor-I concentration1. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Casas-Carrillo, E.; Kirkpatrick, B.W.; Prill-Adams, A.; Price, S.G.; Clutter, A.C. Relationship of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 genotypes with growth and carcass traits in swine. Anim. Genet. 1997, 28, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, N.B.; Bustamante, C.D.; Chase, K.; Gray, M.M.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, L.; Padhukasahasram, B.; Karlins, E.; Davis, S.; Jones, P.G.; et al. A Single IGF1 Allele Is a Major Determinant of Small Size in Dogs. Science 2007, 316, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, P.; Morel, P.; Ambler, G.; Breier, B.; Blair, H.; McCutcheon, S. Elevating maternal insulin-like growth factor-i in mice and rats alters the pattern of fetal growth by removing maternal constraint. J. Endocrinol. 1992, 134, R1–R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clutter, A.; Jiang, R.; McCann, J.; Buchanan, D. Plasma Cholecystokinin-8 in Pigs with Divergent Genetic Potential for Feed Intake and Growth. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 1998, 15, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clutter, A.C.; Spicer, L.J.; Woltmann, M.D.; Grimes, R.W.; Hammond, J.M.; Buchanan, D.S. Plasma growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor I, and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in pigs with divergent genetic merit for postweaning average daily gain1. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, J.C.M.; Mathur, P.K.; Knol, E.F. Genetic improvement of the pig. Genet. Pig 2011, 390, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, E.; Widom, J. Poly(dA:dT) tracts: Major determinants of nucleosome organization. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, V.; Struhl, K. Poly(dA:dT), a ubiquitous promoter element that stimulates transcription via its intrinsic DNA structure. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Huang, W.; Leung, V.H.K.; Fung, S.L.M.; Ma, S.L.; Jiang, H.; Tang, N.L.S. Functional Interaction Between SNPs and Microsatellite in the Transcriptional Regulation of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cai, H.; Liu, J.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, L. Controlling AOX1 promoter strength in Pichia pastoris by manipulating poly (dA:dT) tracts. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Gao, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, J. A functional mutation at position -155 in porcine APOE promoter affects gene expression. BMC Genet. 2011, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Pan, R.-Y.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.-L.; Chen, Z.-M.; Cai, G.-Y.; Li, J.-Q.; Wu, Z.-F. Genetic parameters and trends for production and reproduction traits of a Landrace herd in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhou, X.; Qiao, X.; Wu, Q.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J. FoxA2 and p53 regulate the transcription of HSD17B1 in ovarian granulosa cells of pigs. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2020, 56, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaps, M.; Lamberson, W.R. Biostatistics for Animal Science: An Introductory Text; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Raveh-Sadka, T.; Levo, M.; Shabi, U.; Shany, B.; Keren, L.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Zeevi, D.; Sharon, E.; Weinberger, A.; Segal, E. Manipulating nucleosome disfavoring sequences allows fine-tune regulation of gene expression in yeast. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Ma, S.L.; Huang, W.; Ji, L.; Leung, V.H.K.; Jiang, H.; Yao, X.; Tang, N.L.S. The mechanism of transactivation regulation due to polymorphic short tandem repeats (STRs) using IGF1 promoter as a model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Dou, M.; Wang, X.; Han, Q.; Zhao, B.; Hu, J.; Yang, G.; Shi, X.; Li, X. Fermented corn-soybean meal elevated IGF1 levels in grower-finisher pigs1. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 5144–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Fan, B.; Tang, Z. A genome-wide scan for signatures of selection in Chinese indigenous and commercial pig breeds. BMC Genet. 2014, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estany, J.; Tor, M.; Villalba, D.; Bosch, L.; Gallardo, D.; Jiménez, N.; Altet, L.; Noguera, J.L.; Reixach, J.; Amills, M.; et al. Association of CA repeat polymorphism at intron 1 of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) gene with circulating IGF-I concentration, growth, and fatness in swine. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 31, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanesi, L.; Scotti, E.; Buttazzoni, L.; Dall’Olio, S.; Russo, V. Analysis of Association Between a Microsatellite at Intron 1 of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 (IGF1) Gene and Fat Deposition, Meat Production and Quality Traits in Italian Large White and Italian Duroc Pigs. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 12, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Jianzhong, S. Association of CA Repeat Polymorphisma tIntron1of Insulin-like Growth Factor Ⅰ Gene with Body Weight and Body Size in Shanxi White Pig. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2012, 39, 140–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N.; Owens, J.; Pringle, K.; Roberts, C. The neglected role of insulin-like growth factors in the maternal circulation regulating fetal growth. J. Physiol. 2010, 589, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letcher, R.; Simmen, R.C.; Bazer, F.W.; Simmen, F. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Expression during Early Conceptus Development in the Pig1. Biol. Reprod. 1989, 41, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Construct | Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| P1 (−2467/+2) | Sense-2467 | GGGGTACCCC CTGTTGCTGGCTCGCTCTACCC |
| P2 (−1900/+2) | Sense-1900 | GGGGTACCCC AGATGGGTGCAGTTCTTCAGCT |
| P3 (−1466/+2) | Sense-1466 | GGGGTACCCC CACCACATGACAGTGACGTTTT |
| P4 (−959/+2) | Sense-959 | GGGGTACCCC ATCTCCTACTTCGCAAAACCAA |
| P5 (−381/+2) | Sense-381 | GGGGTACCCC CCCAGCACTGTCTTCCAATCTA |
| P6 (−98/+2) | Sense-98 | GGGGTACCCC AAAATGCTTCTGTGCTCTAGTT |
| Antisense | CCGCTCGAGCGG CCCTCTTCTGGCAAAGTTATCG |
| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) | Product |
|---|---|---|
| IGF1 | F: TGCGGAGACAGGGGCTTTT | 154 bp |
| R: ACTTGGCAGGCTTGAGGGGT | ||
| C/EBPα | F: ATGAGCAGCCACCTCCAGAGCC | 168 bp |
| R: CGGGTCGATGTAGGCGCTGATGT | ||
| IGF1-ChIP | F: CCTGCGCAATGGAATAAAGT | 163 bp |
| R: ATTGGGTTGGAAGACTGCTG |
| Breed | N | Genotype Frequency | Observation Value | Theoretical Value | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9/9T | 9/10T | 10/10T | 10/11T | 9/10T | Others | 9/10T | Others | ||||
| Guanzhuang Spotted pigs | 22 | 0.18 | 0.55 | 0.27 | 0 | 12 | 10 | 10.91 | 11.09 | 0.26 | 0.61 |
| Yuedong Black pigs | 18 | 0.06 | 0.56 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 10 | 8 | 7.67 | 10.33 | 1.64 | 0.27 |
| Breed | N | Genotype Frequency | Observation Value | Theoretical Value | p | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10/10T | 10/11T | 11/11T | 10/10T | 10/11T | 11/11T | 10/10T | 10/11T | 11/11T | ||||
| Duroc | 328 | 0.48 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 157 | 128 | 43 | 148.91 | 144.19 | 34.91 | 4.13 | 0.13 |
| Large White | 225 | 0.02 | 0.33 | 0.65 | 5 | 74 | 146 | 7.84 | 68.32 | 148.84 | 1.56 | 0.46 |
| Traits | Genotype (N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10/10T (156) | 10/11T (129) | 11/11T (43) | |
| Birth weight, kg | 1.67 ± 0.08 | 1.71 ± 0.02 | 1.69 ± 0.04 |
| Body length, cm | 117.25 ± 0.31 | 117.01 ± 0.34 | 116.86 ± 0.59 |
| Average daily gain, g/day | 636.55 ± 2.87 a | 629.30 ± 3.16 ab | 617.86 ± 5.54 b |
| Days to 115 kg, day | 179.20 ± 2.63 a | 180.38 ± 2.54 ab | 184.57 ± 2.99 b |
| Average backfat thickness at 115 kg, cm | 9.69 ± 0.12 | 9.77 ± 0.13 | 9.54 ± 0.22 |
| Loin muscle area, cm2 | 42.63 ± 0.38 | 42.59 ± 0.42 | 41.92 ± 0.74 |
| Traits | Genotype (N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10/10T (5) | 10/11T (75) | 11/11T (145) | |
| Birth weight, kg | 1.48 ± 0.12 | 1.78 ± 0.04 | 1.65 ± 0.03 |
| Body length, cm | 123.54 ± 1.57 | 120.48 ± 0.43 | 120.49 ± 0.31 |
| Average daily gain, g/day | 721.15 ± 16.25 a | 679.47 ± 4.43 b | 686.54 ± 3.21 ab |
| Days to 115 kg, day | 157.31 ± 4.04 a | 167.33 ± 1.10 b | 165.52 ± 0.80 ab |
| Average backfat thickness at 115 kg, cm | 14.98 ± 1.06 | 15.17 ± 0.29 | 14.79 ± 0.21 |
| Loin muscle area, cm2 | 37.68 ± 1.73 | 40.77 ± 0.47 | 40.58 ± 0.34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, W.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Deng, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, H. A Poly(dA:dT) Tract in the IGF1 Gene Is a Genetic Marker for Growth Traits in Pigs. Animals 2022, 12, 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233316
Liao W, Wang Y, Qiao X, Zhang X, Deng H, Zhang C, Li J, Yuan X, Zhang H. A Poly(dA:dT) Tract in the IGF1 Gene Is a Genetic Marker for Growth Traits in Pigs. Animals. 2022; 12(23):3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233316
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Weili, Yifei Wang, Xiwu Qiao, Xiaoke Zhang, Haohui Deng, Caihong Zhang, Jiaqi Li, Xiaolong Yuan, and Hao Zhang. 2022. "A Poly(dA:dT) Tract in the IGF1 Gene Is a Genetic Marker for Growth Traits in Pigs" Animals 12, no. 23: 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233316
APA StyleLiao, W., Wang, Y., Qiao, X., Zhang, X., Deng, H., Zhang, C., Li, J., Yuan, X., & Zhang, H. (2022). A Poly(dA:dT) Tract in the IGF1 Gene Is a Genetic Marker for Growth Traits in Pigs. Animals, 12(23), 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12233316






