Chlorinated Persistent Organic Pollutants (PCDD/Fs and PCBs) in Loggerhead Sea Turtles Stranded along the Central Adriatic Coast
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.2.1. Chemicals and Analytical Standards
2.2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.3. Instrumental Analysis
2.2.4. Quality Control
2.3. Statistical Analysis
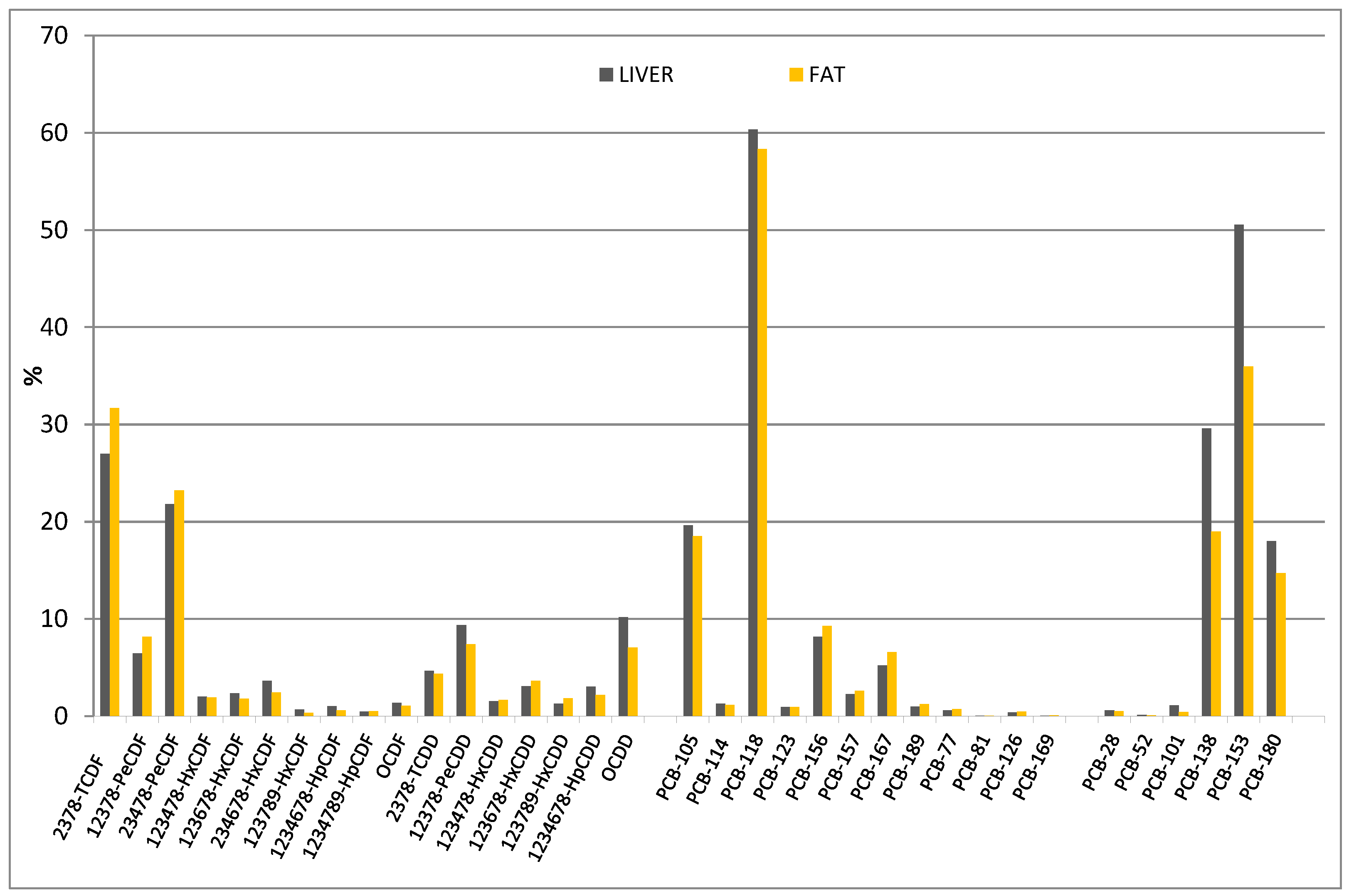
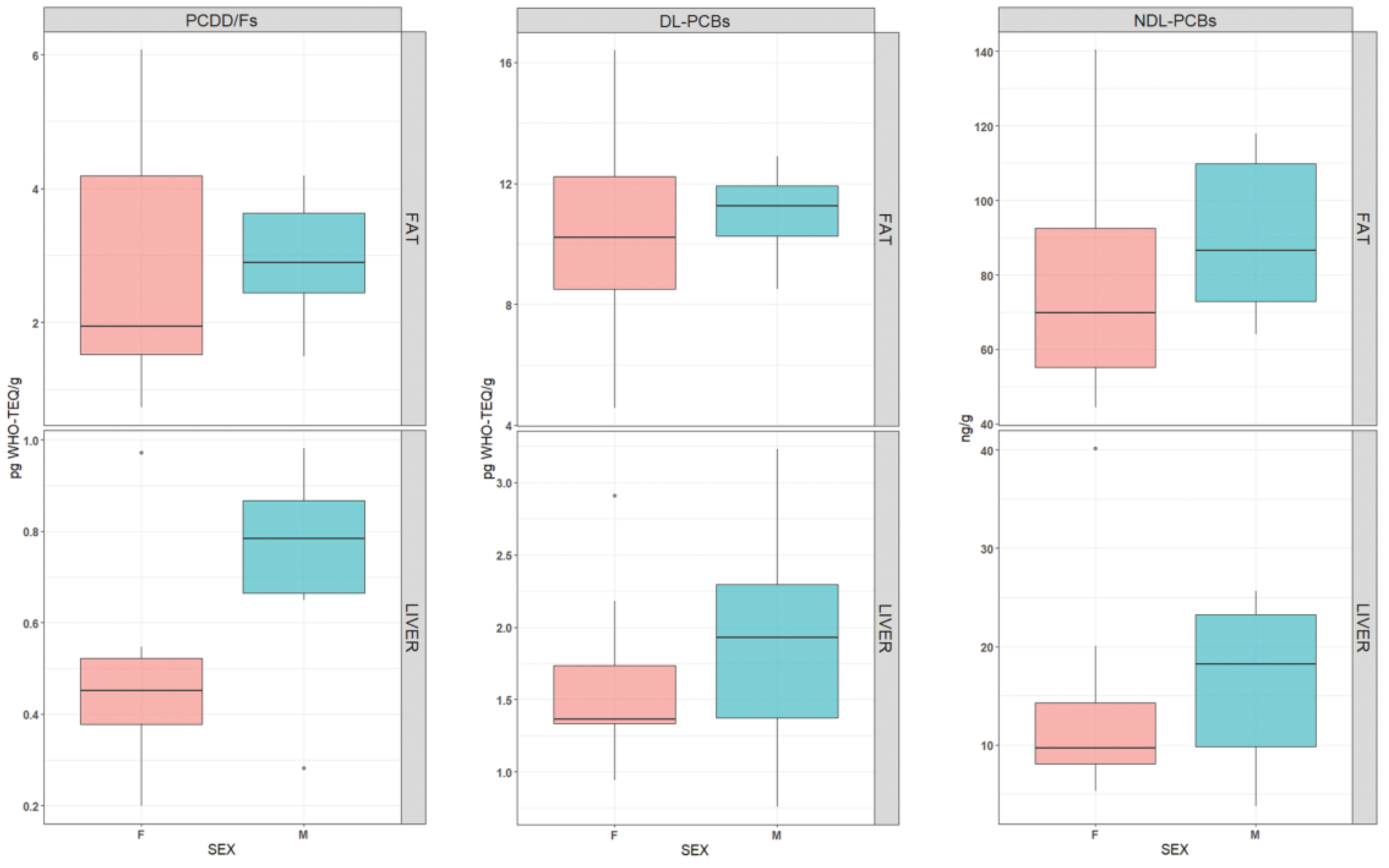
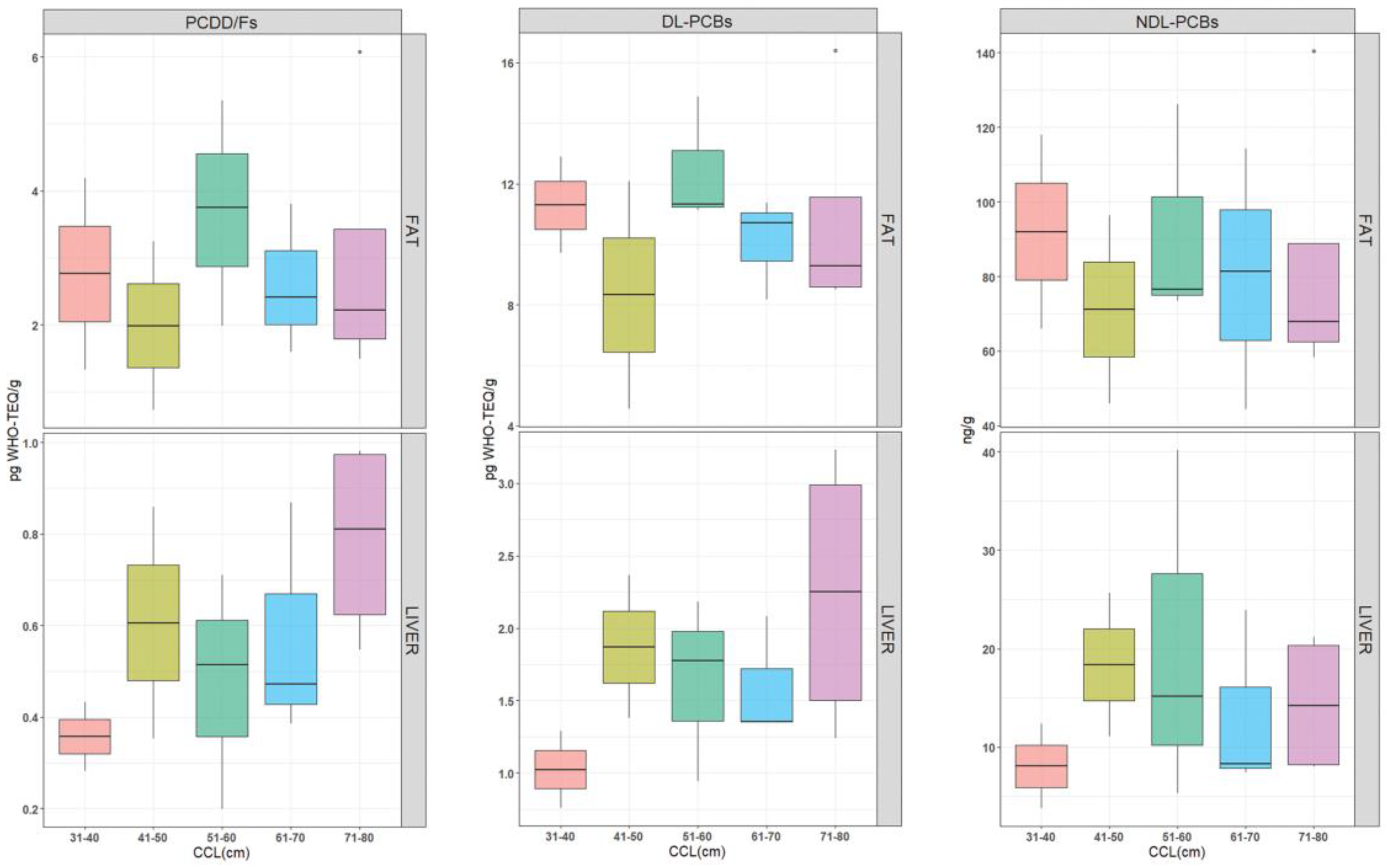
3. Results
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Contamination Levels
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.; Pan, B.; Sakkiah, S.; Yavas, G.; Ge, W.; Zou, W.; Tong, W.; Hong, H. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Food: Contamination Sources, Health Effects and Detection Methods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenreich, S.J.; Hornbuckle, K.; Jones, K.C. The Global Legacy of POPs: Special Issue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9397–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Egli, T.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. Global water pollution and human health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioxins and Their Effects on Human Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dioxins-and-their-effects-on-human-health (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Johnson, L.L.; Anulacion, B.F.; Arkoosh, M.R.; Burrows, D.G.; da Silva, D.A.M.; Dietrich, J.P.; Myers, M.S.; Spromberg, J.; Ylitalo, G.M. Effects of Legacy Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Fish—Current and Future Challenges. Fish Physiol. 2013, 33, 53–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wikoff, D.; Fitzgerald, L.; Birnbaum, L. Persistent organic pollutants: An overview. In Dioxins and Health: Including Other Persistent Organic Pollutants and Endocrine Disruptors, 3rd ed.; Schecter, A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, K.A.; Leusch, F.; van de Merwe, J.P. The current state and future directions of marine turtle toxicology research. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwacke, L.H.; Zolman, E.S.; Balmer, B.C.; De Guise, S.; George, R.C.; Hoguet, J.; Hohn, A.A.; Kucklick, J.R.; Lamb, S.; Levin, M.; et al. Anaemia, hypothyroidism and immune suppression associated with polychlorinated biphenyl exposure in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.D.; Berger, M.L.; Weijs, L.; Päpke, O.; Covaci, A. Polychlorinated biphenyls still pose significant health risks to northwest Atlantic harbor seals. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strid, A.; Jörundsdóttir, H.; Päpke, O.; Svavarsson, J.; Bergman, A. Dioxins and PCBs in Greenland shark (Somniosus microcephalus) from the North-East Atlantic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, R.; Takada, H.; Nakazawa, A.; Takahashi, A.; Ito, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Watanabe, Y.Y.; Kokubun, N.; Sato, K.; Wanless, S.; et al. Global Monitoring of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) Using Seabird Preen Gland Oil. Arch. Env. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 75, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, R.H.; LaKind, J.S. Biomonitoring of dioxins and furans: Levels and trends in humans. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 23, pp. 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.S.; Birnbaum, L.S. An Overview of the Effects of Dioxins and Dioxin-like Compounds on Vertebrates, as Documented in Human and Ecological Epidemiology. J. Environ. Sci. Health. 2009, 27, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, B.G.; Masunaga, S. CHAPTER 18-PCBs, Dioxins, and Furans: Human Exposure and Health Effects. In Handbook of Toxicology of Chemical Warfare Agents; Gupta, R.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotrigiano, G.O.; Storelli, M.M. Heavy metal, polychlorinated biphenyl and organochlorine pesticide residues in marine organisms: Risk evaluation for consumers. Vet. Res. Commun. 2003, 27, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, J.M.; Kannan, K.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Day, R.D.; Arendt, M.D.; Segars, A.L.; Kucklick, J.R. Perfluorinated compounds in the plasma of loggerhead and Kemp’s ridley sea turtles from the southeastern coast of the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9101–9108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roose, P.; Brinkman, U.A.T. Monitoring organic microcontaminants in the marine environment: Principles, programmes and progress. Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 897–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, Y.; Takada, H.; Mizukawa, K.; Hirai, H.; Iwasa, S.; Endo, S.; Mato, Y.; Saha, M.; Okuda, K.; Nakashima, A.; et al. International Pellet Watch: Global monitoring of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in coastal waters. 1. Initial phase data on PCBs, DDTs, and HCHs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.B.; Kannan, K.; Choi, H.G.; An, Y.R.; Choi, S.G.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, Z.G. Concentrations and accumulation features of PCDDs, PCDFs and dioxin-like PCBs in cetaceans from Korean coastal waters. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, S.; Caliani, I.; Giannetti, M.; Marsili, L.; Maltese, S.; Coppola, D.; Bianchi, N.; Campani, T.; Ancora, S.; Caruso, C.; et al. First ecotoxicological assessment of Caretta caretta (Linnaeus, 1758) in the Mediterranean Sea using an integrated nondestructive protocol. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Canzanella, S.; Iaccarino, D.; Bruno, T.; Esposito, E.; Di Nocera, F.; Arienzo, M.; Ferrara, L.; Gallo, P. Levels of non-dioxin-like PCBs (NDL-PCBs) in liver of loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) from the Tyrrhenian Sea (Southern Italy). Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domènech, F.; Aznar, F.J.; Raga, J.A.; Tomás, J. Two decades of monitoring in marine debris ingestion in loggerhead sea turtle, Caretta caretta, from the western Mediterranean. Env. Pollut. 2019, 244, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission EUR 26113 EN-Joint Research Centre-Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Marine Strategy Framework Directive Technical Subgroup on Marine Litter. In Guidance on Monitoring of Marine Litter in European Seas; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013.
- Margaritoulis, D.; Argano, R.; Baran, I.; Bentivegna, F.; Bradai, M.N.; Camiñas, J.A.; Casale, P.; De Metrio, G.; Demetropoulos, A.; Gerosa, G. Chapter 11-Loggerhead turtles in the Mediterranean Sea: Present knowledge and conservation perspectives. In Loggerhead Sea Turtles; Bolten, A.B., Ed.; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 175–198. [Google Scholar]
- Clukey, K.E.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Balazs, G.H.; Work, T.M.; Li, Q.X.; Bachman, M.J.; Lynch, J.M. Persistent organic pollutants in fat of three species of Pacific pelagic longline caught sea turtles: Accumulation in relation to ingested plastic marine debris. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.M. Exposure to and effects of persistent organic pollutants. In The Biology of Sea Turtles, 1st ed.; Wyneken, J., Lohmann, K.J., Musick, J.A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2013; Volume III, Chapter 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckenzie, C.; Godley, B.J.; Furness, R.W.; Wells, D.E. Concentrations and patterns of organochlorine contaminants in marine turtles from Mediterranean and Atlantic waters. Mar. Environ. Res. 1999, 47, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, P.; Abbate, G.; Freggi, D.; Conte, N.; Oliverio, M.; Argano, R. Foraging ecology of loggerhead sea turtles Caretta caretta in the central Mediterranean Sea: Evidence for a relaxed life history model. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 372, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ilio, S.; Mattei, D.; Blasi, M.F.; Alimonti, A.; Bogialli, S. The occurrence of chemical elements and POPs in loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta): An overview. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2011, 62, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoca, D.; Arculeo, M.; Barreca, S.; Buscemi, S.; Caracappa, S.; Gentile, A.; Persichetti, M.F.; Pace, A. Chasing phthalates in tissues of marine turtles from the Mediterranean sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoca, D.; Arculeo, M.; Vecchioni, L.; Cambera, I.; Visconti, G.; Melfi, R.; Arizza, V.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; Buscemi, S.; Pace, A. Can phthalates move into the eggs of the loggerhead sea turtle Caretta caretta? The case of the nests on the Linosa Island in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2021, 168, 112395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savoca, D.; Arculeo, M.; Arizza, V.; Pace, A.; Melfi, R.; Caracappa, S.; Caracappa, G.; Vullo, C.; Cambera, I.; Visconti, G.; et al. Impact of Heavy Metals in Eggs and Tissues of C. caretta along the Sicilian Coast (Mediterranean Sea). Environments 2022, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camiñas, J.A.; Kaska, Y.; Hochscheid, S.; Casale, P.; Panagopoulou, A.; Báez, J.C.; Alcázar, E. Conservation of Marine Turtles in the Mediterranean Sea; IUCN: Grand, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ramírez, P.; Espín, S.; Navas, I.; Martínez-López, E.; Jiménez, P.; María-Mojica, P.; Peñalver, J.; García-Fernández, A.J. Mercury and Organochlorine Pesticides in Tissues of Loggerhead Sea Turtles (Caretta caretta) Stranded Along the Southwestern Mediterranean Coastline (Andalusia, Spain). Bull Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Determinazione Dir. Regione Abruzzo n. DG/21/167 del 31.12.2014 “Applicazione Nella Regione Abruzzo del Reg. CE 1069/2009 Recante: “Norme Sanitarie Relative ai Sottoprodotti di O.A. Non Destinati al Consumo Umano”. Available online: http://bura.regione.abruzzo.it/ (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- DCA Regione Molise n.67 del 22/05/2019 “Procedura Regionale per la Gestione Delle Segnalazioni di Carcasse di Tartarughe Marine o di Cetacei Ritrovate sul Litorale Molisano, e del Ritrovamento di Animali Marini Vivi, Feriti e/o in Difficoltà”. Available online: https://www3.regione.molise.it/flex/cm/pages/ServeBLOB.php/L/IT/IDPagina/16448. (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Poppi, L.; Marchiori, E. Dissection Techniques and Notions in “Sea Turtle Management Manual”; Poppi, L., Di Bello, A., Eds.; Genesi Design: Venice, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Diletti, G.; Ceci, R.; De Benedictis, A.; Migliorati, G.; Scortichini, G. Determination of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in feed and foods of animal origin by gas chromatography and high resolution mass spectrometry. Vet. Ital. 2007, 43, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ceci, R.; Diletti, G.; Bellocci, M.; Chiumiento, F.; D’Antonio, S.; De Benedictis, A.; Leva, M.; Pirito, L.; Scortichini, G.; Fernandes, A.R. Brominated and chlorinated contaminants in food (PCDD/Fs, PCBs, PBDD/Fs PBDEs): Simultaneous determination and occurrence in Italian produce. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diletti, G.; Ceci, R.; De Benedictis, A.; Leva, M.; Migliorati, G.; Pirito, L.; Vairano, I.; Fernandes, A.R. Polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and furans (PBDD/Fs) in Italian food: Occurrence and dietary exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 139916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Denison, M.; De Vito, M.; Farland, W.; Feeley, M.; Fiedler, H.; Hakansson, H.; Hanberg, A.; Haws, L.; et al. The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and Mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) n. 2017/644 of 5 April 2017, “Laying down Methods of Sampling and Analysis for the Control of Levels of Dioxins, Dioxin-like PCBs and Non-Dioxin-Like PCBs in Certain Foodstuffs and Repealing Regulation (EU) No 589/2014”. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32017R0644#:~:text=Commission%20Regulation%20(EU)%202017%2F,(Text%20with%20EEA%20relevance.%20). (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.r-project.org/index.html (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Storelli, M.M.; Zizzo, N. Occurrence of organochlorine contaminants (PCBs, PCDDs and PCDFs) and pathologic findings in loggerhead sea turtles, Caretta caretta, from the Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambiase, S.; Serpe, F.P.; Pilia, M.; Fiorito, F.; Iaccarino, D.; Gallo, P.; Esposito, M. Polychlorinated organic pollutants (PCDD/Fs and DL-PCBs) in loggerhead (Caretta caretta) and green (Chelonia mydas) turtles from Central-Southern Tyrrhenian Sea. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, M.M.; Barone, G.; Marcotrigiano, G.O. Polychlorinated biphenyls and other chlorinated organic contaminants in the tissues of Mediterranean loggerhead turtle Caretta caretta. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 373, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, B.; Maslov, L.; Romanić, S.H.; Gračan, R.; Krauthacker, B.; Holcer, D.; Tvrtković, N. Accumulation of organochlorine contaminants in loggerhead sea turtles, Caretta caretta, from the eastern Adriatic Sea. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammilleri, G.; Calvaruso, E.; Pantano, L.; Cascio, G.L.; Randisi, B.; Macaluso, A.; Vazzana, M.; Caracappa, G.; Giangrosso, G.; Vella, A.; et al. Survey on the presence of non–dioxine-like PCBs (NDL-PCBs) in loggerhead turtles (Caretta caretta) stranded in south Mediterranean coasts (Sicily, Southern Italy). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2997–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, C.C.; Hendriks, A.J.; Ragas, A.M.; Vermeiren, P. Internal and maternal distribution of persistent organic pollutants in sea turtle tissues: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10012–10024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Risk for animal and human health related to the presence of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs in feed and food. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diletti, G.; Scortichini, G.; Abete, M.C.; Binato, G.; Candeloro, L.; Ceci, R.; Chessa, G.; Conte, A.; Di Sandro, A.; Esposito, M.; et al. Intake estimates of dioxins and dioxin-like polychlorobiphenyls in the Italian general population from the 2013-2016 results of official monitoring plans in food. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayarri, S.; Baldassarri, L.T.; Iacovella, N.; Ferrara, F.; Di Domenico, A. PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBs and DDE in edible marine species from the Adriatic Sea. Chemosphere 2001, 43, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scortichini, G.; Diletti, G.; Forti, A.F.; Migliorati, G. Dioxin contamination of food in Italy: An overview of the situation 1999–2000. Vet. Ital. 2004, 40, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
| Pool | Number of Carcasses | Sexual Maturity | CCL Range (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | iF | 31–40 |
| 2 | 1 | iF | 41–50 |
| 3 | 8 | iF | 51–60 |
| 4 | 2 | F | 51–60 |
| 5 | 2 | iF | 61–70 |
| 6 | 5 | F | 61–70 |
| 7 | 1 | iF | 71–80 |
| 8 | 3 | F | 71–80 |
| 9 | 5 | iM | 31–40 |
| 10 | 3 | iM | 41–50 |
| 11 | 4 | iM | 51–60 |
| 12 | 2 | iM | 61–70 |
| 13 | 1 | iM | 71–80 |
| 14 | 2 | M | 71–80 |
| Pool | Lipid | PCDD/Fs | DL-PCBs | NDL-PCBs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | pg WHO-TEQ g−1 | pg WHO-TEQ g−1 | ng g−1 | ||
| Female | 1 | 2.8 | 0.43 | 1.3 | 12 |
| 2 | 1.6 | 0.35 | 1.4 | 11 | |
| 3 | 1.7 | 0.51 | 2.2 | 40 | |
| 4 | 3.4 | 0.20 | 0.94 | 5.3 | |
| 5 | 8.9 | 0.47 | 1.4 | 7.4 | |
| 6 | 3.5 | 0.39 | 1.4 | 8.3 | |
| 7 | 8.1 | 0.55 | 1.6 | 8.3 | |
| 8 | 2.7 | 0.97 | 2.9 | 20 | |
| 9 | 1.5 | 0.28 | 0.76 | 3.8 | |
| 10 | 1.8 | 0.86 | 2.4 | 26 | |
| Male | 11 | 3.5 | 0.71 | 1.8 | 15 |
| 12 | 8.2 | 0.87 | 2.1 | 24 | |
| 13 | 1.8 | 0.65 | 1.2 | 8.0 | |
| 14 | 3.3 | 0.98 | 3.2 | 21 |
| Pool | Lipid | PCDD/Fs | DL-PCBs | NDL-PCBs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | pg WHO-TEQ g−1 | pg WHO-TEQ g−1 | ng g−1 | ||
| Female | 1 | 52 | 1.3 | 9.7 | 66 |
| 2 | 22 | 0.73 | 4.6 | 46 | |
| 3 | 72 | 5.4 | 15 | 126 | |
| 4 | 68 | 2.0 | 11 | 73 | |
| 5 | 91 | 1.6 | 8.2 | 44 | |
| 6 | 86 | 3.8 | 12 | 81 | |
| 7 | 61 | 1.9 | 8.6 | 58 | |
| 8 | 88 | 6.1 | 16 | 140 | |
| 9 | 44 | 4.2 | 13 | 118 | |
| 10 | 63 | 3.3 | 12 | 96 | |
| Male | 11 | 64 | 3.8 | 11 | 77 |
| 12 | 72 | 2.4 | 11 | 114 | |
| 13 | 68 | 1.5 | 8.5 | 64 | |
| 14 | 87 | 2.6 | 9.9 | 72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Renzo, L.; Ceci, R.; D’Antonio, S.; Di Francesco, G.; Di Giacinto, F.; Ferri, N.; Giansante, C.; Leva, M.; Mariani, G.; Olivieri, V.; et al. Chlorinated Persistent Organic Pollutants (PCDD/Fs and PCBs) in Loggerhead Sea Turtles Stranded along the Central Adriatic Coast. Animals 2022, 12, 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223177
Di Renzo L, Ceci R, D’Antonio S, Di Francesco G, Di Giacinto F, Ferri N, Giansante C, Leva M, Mariani G, Olivieri V, et al. Chlorinated Persistent Organic Pollutants (PCDD/Fs and PCBs) in Loggerhead Sea Turtles Stranded along the Central Adriatic Coast. Animals. 2022; 12(22):3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223177
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Renzo, Ludovica, Roberta Ceci, Silvia D’Antonio, Gabriella Di Francesco, Federica Di Giacinto, Nicola Ferri, Carla Giansante, Manuela Leva, Giulia Mariani, Vincenzo Olivieri, and et al. 2022. "Chlorinated Persistent Organic Pollutants (PCDD/Fs and PCBs) in Loggerhead Sea Turtles Stranded along the Central Adriatic Coast" Animals 12, no. 22: 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223177
APA StyleDi Renzo, L., Ceci, R., D’Antonio, S., Di Francesco, G., Di Giacinto, F., Ferri, N., Giansante, C., Leva, M., Mariani, G., Olivieri, V., Pulsoni, S., Salini, R., Scortichini, G., Tammaro, G., & Diletti, G. (2022). Chlorinated Persistent Organic Pollutants (PCDD/Fs and PCBs) in Loggerhead Sea Turtles Stranded along the Central Adriatic Coast. Animals, 12(22), 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223177







