Virulence Genes and In Vitro Antibiotic Profile of Photobacterium damselae Strains, Isolated from Fish Reared in Greek Aquaculture Facilities
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Culture Media
2.3. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Photobacterium bacteria
2.4. Detection of the Virulence Factors
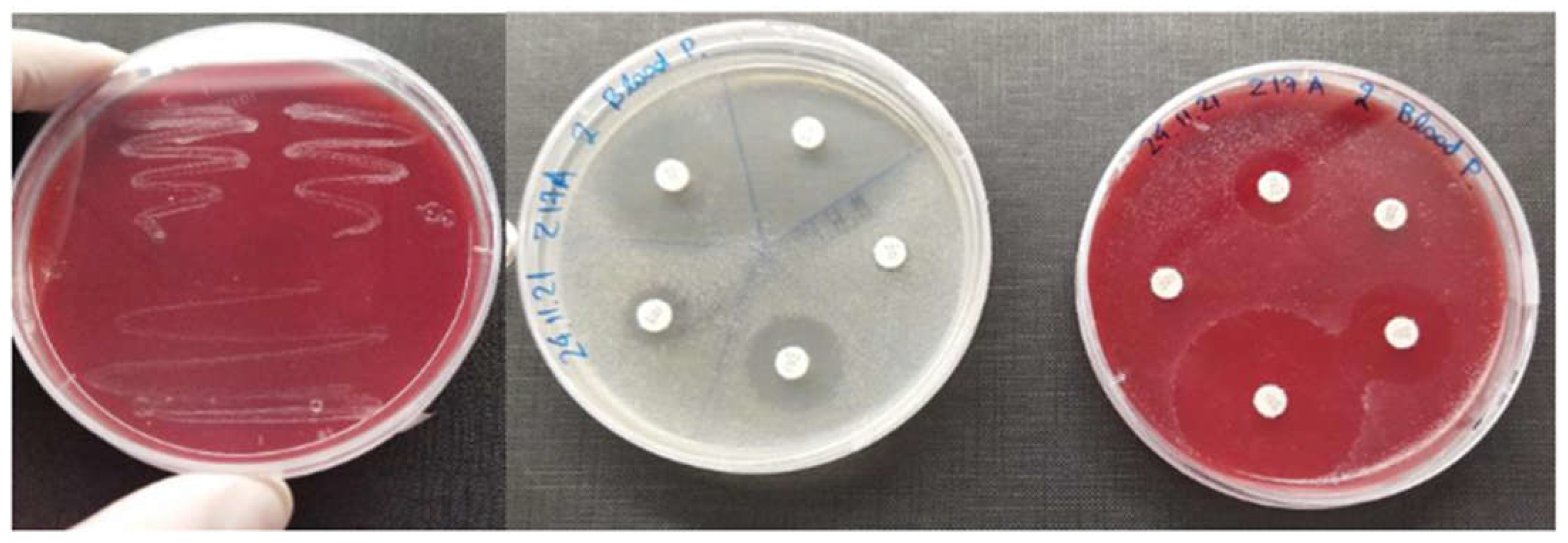
2.5. Antibiogram
3. Results
3.1. Pathogenicity, Bacterial Culture, Molecular Identification, and Presence of Virulence Factors
3.2. Virulence Factors Detected
3.3. Antibiogram
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, J.L.; Asche, F.; Garlock, T.; Chu, J. Aquaculture: Its role in the future of food. Front. Econ. Glob. 2017, 17, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, R.D.; Bean, T.P.; Macqueen, D.J.; Gundappa, M.K.; Jin, Y.H.; Jenkins, T.L.; Selly, S.L.C.; Martin, S.A.M.; Stevens, J.R.; Santos, E.M.; et al. Harnessing genomics to fast-track genetic improvement in aquaculture. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattos, A.; Chaligiannis, I.; Papadopoulos, D.; Giantsis, I.A.; Petridou, E.I.; Vafeas, G.; Staikou, A.; Michaelidis, B. How Safe to Eat Are Raw Bivalves? Host Pathogenic and Public Health Concern Microbes within Mussels, Oysters, and Clams in Greek Markets. Foods 2021, 10, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Subasinghe, R.P.; Arthur, J.R.; Ogawa, K.; Chinabut, S.; Adlard, R.; Tan, Z.; Shariff, M. Disease and health management in Asian aquaculture. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 132, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Sánchez, T.; Mora-Sánchez, B.; Balcázar, J.L. Biological Approaches for Disease Control in Aquaculture: Advantages, Limitations and Challenges. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, A.; Abunna, F. Maintenance of Fish Health in Aquaculture: Review of Epidemiological Approaches for Prevention and Control of Infectious Disease of Fish. Vet. Med. Int. 2018, 2018, 5432497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial disease in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, K.D.; Harvell, C.D.; Conrad, J.M.; Friedman, C.S.; Kent, M.L.; Kuris, A.M.; Powell, E.N.; Rondeau, D.; Saksida, S.M. Infectious diseases affect marine fisheries and aquaculture economics. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romalde, J. Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida: An integrated view of a bacterial fish pathogen. Int. Microbiol. 2002, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toranzo, A.E.; Magariños, B.; Romalde, J.L. A review of the main bacterial fish diseases in mariculture systems. Aquaculture 2005, 246, 37–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Cheng, T.; Wang, P.; Chen, S. Genotypic diversity, and molecular and pathogenic characterization of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida isolated from different fish species in Taiwan. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magariños, B.; Osorio, C.R.; Toranzo, A.E.; Romalde, J.L. Applicability of Ribotyping for Intraspecific Classification and Epidemiological Studies of Photobacterium damsela subsp. piscicida. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 20, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakopoulos, V.; Peric, Z.; Rodger, H.; Adams, A.; Richards, R. First Report of Fish Pasteurellosis from Malta. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1997, 9, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.M.; Abd-Elsalam, R.M.; Marzouk, M.S. Molecular and Immunohistochemical Diagnosis of Photobacterium damselae Subspecies piscicida During Naturally Occurring Disease in Egypt. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2015, 46, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baseggio, L.; Silayeva, O.; Engelstädter, J.; Barnes, A.C. The Evolution of a Specialized, Highly Virulent Fish Pathogen through Gene Loss and Acquisition of Host-Specific Survival Mechanisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e00222-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagana, P.; Caruso, G.; Minutoli, E.; Zaccone, R.; Delia, S. Susceptibility to antibiotics of vibrio spp. and Photobacterium damsela ssp. piscicida strains isolated from italian aquaculture farms. New Microbiol. 2011, 34, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Steele, J.C.; Meng, X.Z. Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C. Heavy use of prophylactic antibiotics in aquaculture: A growing problem for human and animal health and for the environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepi, M.; Focardi, S. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquaculture and climate change: A challenge for health in the mediterranean area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A.K.; Meyer, M.T.; Boxall, A.B.A. A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 725–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapkota, A.; Sapkota, A.R.; Kucharski, M.; Burke, J.; McKenzie, S.; Walker, P.; Lawrence, R. Aquaculture practices and potential human health risks: Current knowledge and future priorities. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hektoen, H.; Berge, J.A.; Hormazabal, V.; Yndestad, M. Persistence of antibacterial agents in marine sediments. Aquaculture 1995, 133, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serwecińska, L. Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health. Water 2020, 12, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of resistant bacteria at very low antibiotic concentrations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Evolution of antibiotic resistance at non-lethal drug concentrations. Drug Resist. Updat. 2012, 15, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Larsson, D.G.J. Concentrations of antibiotics predicted to select for resistant bacteria: Proposed limits for environmental regulation. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Díaz, J.A.; Fumanal, M.; Do Vale, A.; Fernández-Díaz, C.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Balebona, M.C. Transcription of iviat and virulence genes in photobacterium damselae subsp. Piscicida infecting solea senegalensis. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdikaris, C.; Paschos, I. Organic aquaculture in Greece: A brief review. Rev. Aquac. 2010, 2, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, V.; Feidantsis, K.; Papadopoulos, D.; Lattos, A.; Georgoulis, I.; Michaelidis, B.; Giantsis, I.A. Natural-like pigmentation in cultured fish stocks, not only a matter of nutrition. A review of Salmonidae and Sparidae families, with a particular focus on the red porgy Pagrus pagrus. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 2942–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, C.R.; Collins, M.D.; Toranzo, A.E.; Barja, J.L.; Romalde, J.L. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis of Photobacterium damselae and nested PCR method for rapid detection of the causative agent of fish pasteurellosis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2942–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.A.; Reich, C.I.; Sharma, S.; Weisbaum, J.S.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J. Critical Evaluation of Two Primers Commonly Used for Amplification of Bacterial 16S rRNA Genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattos, A.; Bitchava, K.; Giantsis, I.A.; Theodorou, J.A.; Batargias, C.; Michaelidis, B. The implication of vibrio bacteria in the winter mortalities of the critically endangered Pinna nobilis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, M.P.; Patel, J.B.; Burnhman, C.-A.; ZImmer, B.L. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically Standard, Approval CDM-A. M07 Methods Dilution Antimicrob. Susceptibility Tests Bact. Grow Aerob. 2018, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Reverter, M.; Sarter, S.; Caruso, D.; Avarre, J.-C.; Combe, M.; Pepey, E.; Pouyaud, L.; Vega-Heredía, S.; De Verdal, H.; Gozlan, R.E. Aquaculture at the crossroads of global warming and antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Marques, A.; Nunes, M.L. Impact of climate change in Mediterranean aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2012, 4, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Feidantsis, K.; Georgoulis, I.; Giantsis, I.A.; Karagiannis, D.; Theodorou, J.A.; Staikou, A.; Michaelidis, B. Pathophysiological responses of pinna nobilis individuals enlightens the etiology of mass mortality situation in the mediterranean populations. Cells 2021, 10, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morash, A.J.; Alter, K. Effects of environmental and farm stress on abalone physiology: Perspectives for abalone aquaculture in the face of global climate change. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 8, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Lim, P.; Kause, A.; Mulder, H.A.; Olesen, I. Breeding and genetics symposium: Climate change and selective breeding in aquaculture. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 1801–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcogliese, D.J. The impact of climate change on the parasites and infectious diseases of aquatic animals. OIE Rev. Sci. Tech. 2008, 27, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattos, A.; Giantsis, I.A.; Karagiannis, D.; Theodorou, J.A.; Michaelidis, B. Gut Symbiotic Microbial Communities in the IUCN Critically Endangered Pinna nobilis Suffering from Mass Mortalities, Revealed by 16S rRNA Amplicon NGS. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafferty, K.D. Calling for an ecological approach to studying climate change and infectious diseases. Ecology 2009, 90, 932–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.; Folli, M.; Klinck, J.; Ford, S.; Miller, J. The relationship between increasing sea-surface temperature and the northward spread of Perkinsus marinus (Dermo) disease epizootics in oysters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 46, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burreson, E.M.; Ford, S.E. A review of recent information on the Haplosporidia, with special reference to Haplosporidium nelsoni (MSX disease). Aquat. Living Resour. 2004, 17, 499–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascarano, M.C.; Stavrakidis-Zachou, O.; Mladineo, I.; Thompson, K.D.; Papandroulakis, N.; Katharios, P. Mediterranean aquaculture in a changing climate: Temperature effects on pathogens and diseases of three farmed fish species. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korun, J.; Timur, G. The first pasteurellosis case in cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) at low marine water temperatures in Turkey. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2005, 57, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Vale, A.; Costa-Ramos, C.; Silva, A.; Silva, D.S.P.; Gärtner, F.; dos Santos, N.M.S.; Silva, M.T. Systemic macrophage and neutrophil destruction by secondary necrosis induced by a bacterial exotoxin in a Gram-negative septicaemia. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, A.D.; Pereira, C.; Osorio, C.R.; dos Santos, N.M.S. The Apoptogenic Toxin AIP56 Is Secreted by the Type II Secretion System of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Toxins 2017, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Vale, A.; Silva, M.T.; Dos Santos, N.M.S.; Nascimento, D.S.; Reis-Rodrigues, P.; Costa-Ramos, C.; Ellis, A.E.; Azevedo, J.E. AIP56, a novel plasmid-encoded virulence factor of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida with apoptogenic activity against sea bass macrophages and neutrophils. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 58, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Vale, A.; Cabanes, D.; Sousa, S. Bacterial toxins as pathogen weapons against phagocytes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, I.L.; Teixeira, A.; Loureiro, I.; Lisboa, J.; Saraiva, A.; dos Santos, N.M.S.; Vale, A.D. Susceptibility of Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) to AIP56, an AB-Type Toxin Secreted by Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Toxins 2022, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.T.; Do Vale, A.; Dos Santos, N.M.N. Secondary necrosis in multicellular animals: An outcome of apoptosis with pathogenic implications. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.S.; Pereira, L.M.G.; Moreira, A.R.; Ferreira-da-Silva, F.; Brito, R.M.; Faria, T.Q.; Zornetta, I.; Montecucco, C.; Oliveira, P.; Azevedo, J.E.; et al. The Apoptogenic Toxin AIP56 Is a Metalloprotease A-B Toxin that Cleaves NF-κb P65. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Liu, X.W.; Feng, L.; Jiang, W.D.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Shi, H.Q.; Zhou, X.Q.; Liu, Y. (2-Carboxyethyl) dimethylsulfonium bromide supplementation in non-fish meal diets for on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Beneficial effects on immune function of the immune organs via modulation of NF-κB and TOR signalling pathway. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 107, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magariños, B.; Romalde, J.L.; Noya, M.; Barja, J.L.; Toranzo, A.E. Adherence and invasive capacities of the fish pathogen Pasteurella piscicida. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 138, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Díaz, J.A.; Fumanal, M.; Viguera, E.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Balebona, M.C. Use of in vivo induced technology to identify antigens expressed by Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida during infection of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 64, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandy, M.; Butler, A. Microbial Iron Acquisition: Marine and Terrestrial Siderophores. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4580–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, F.; Boiani, R.; Serafini, G.; Bianconi, I.; Dominici, S.; Gorini, F.; Magnani, M. Expression, purification, and characterization of the recombinant putative periplasmic hemin-binding protein (hutb) of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1180–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, A.; Montaos, M.A.; Rivas, A.J.; Balado, M.; Osorio, C.R.; Rodríguez, J.; Lemos, M.L.; Jiménez, C. Structure and biosynthetic assembly of piscibactin, a siderophore from Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida, predicted from genome analysis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5693–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, C.R.; Rivas, A.J.; Balado, M.; Fuentes-Monteverde, J.C.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C.; Lemos, M.L.; Waldor, M.K. A transmissible plasmid-borne pathogenicity island confers piscibactin biosynthesis in the fish pathogen Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 5867–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, C.R.; Juiz-Río, S.; Lemos, M.L. A siderophore biosynthesis gene cluster from the fish pathogen Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida is structurally and functionally related to the Yersinia high-pathogenicity island. Microbiology 2006, 152, 3327–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Río, S.J.; Osorio, C.R.; Lemos, M.L. Heme uptake genes in human and fish isolates of Photobacterium damselae: Existence of hutA pseudogenes. Arch. Microbiol. 2005, 183, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.-Y.; Pak, M.; Kish, R.; Kajihara, K.; Brown, E.J. A Mycobacterial Operon Essential for Virulence In Vivo and Invasion and Intracellular Persistence in Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Lun, S.; Guo, H.; Ammerman, N.C.; Geiman, D.E.; Bishai, W.R. Rv2190c, an NlpC/P60 Family Protein, Is Required for Full Virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, H.; Matsuyama, S.-I. Sorting of lipoproteins to the outer membrane in E. coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1693, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs-Simon, A.; Titball, R.W.; Michell, S.L. Lipoproteins of Bacterial Pathogens. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.-Y.-D.; Zhu, D.; Giles, M.; Daniell, T.; Neilson, R.; Yang, X.-R. Does reduced usage of antibiotics in livestock production mitigate the spread of antibiotic resistance in soil, earthworm guts, and the phyllosphere? Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriol-González, C.; Domingo-Calap, P. Phage therapy in livestock and companion animals. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaplewski, L.; Bax, R.; Clokie, M.; Dawson, M.; Fairhead, H.; Fischetti, V.A.; Foster, S.; Gilmore, B.F.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Harper, D.; et al. Alternatives to antibiotics-a pipeline portfolio review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa Shamsuzzaman, M.; Kumar Biswas, T. Aqua chemicals in shrimp farm: A study from south-west coast of Bangladesh. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillehaug, A.; Lunestad, B.; Grave, K. Epidemiology of bacterial diseases in Norwegian aquaculture–A description based on antibiotic prescription data for the ten-year period 1991 to 2000. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 53, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burridge, L.; Weis, J.S.; Cabello, F.; Pizarro, J.; Bostick, K. Chemical use in salmon aquaculture: A review of current practices and possible environmental effects. Aquaculture 2010, 306, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, L.-O.; Effarizah, M.E.; Goni, A.M.; Rusul, G. Antibiotic Application and Emergence of Multiple Antibiotic Resistance (MAR) in Global Catfish Aquaculture. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulijwa, R.; Rupia, E.J.; Alfaro, A.C. Antibiotic use in aquaculture, policies and regulation, health and environmental risks: A review of the top 15 major producers. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyssen, A.; Ollevier, F. In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida to 15 different antimicrobial agents. Aquaculture 2001, 200, 259–269 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
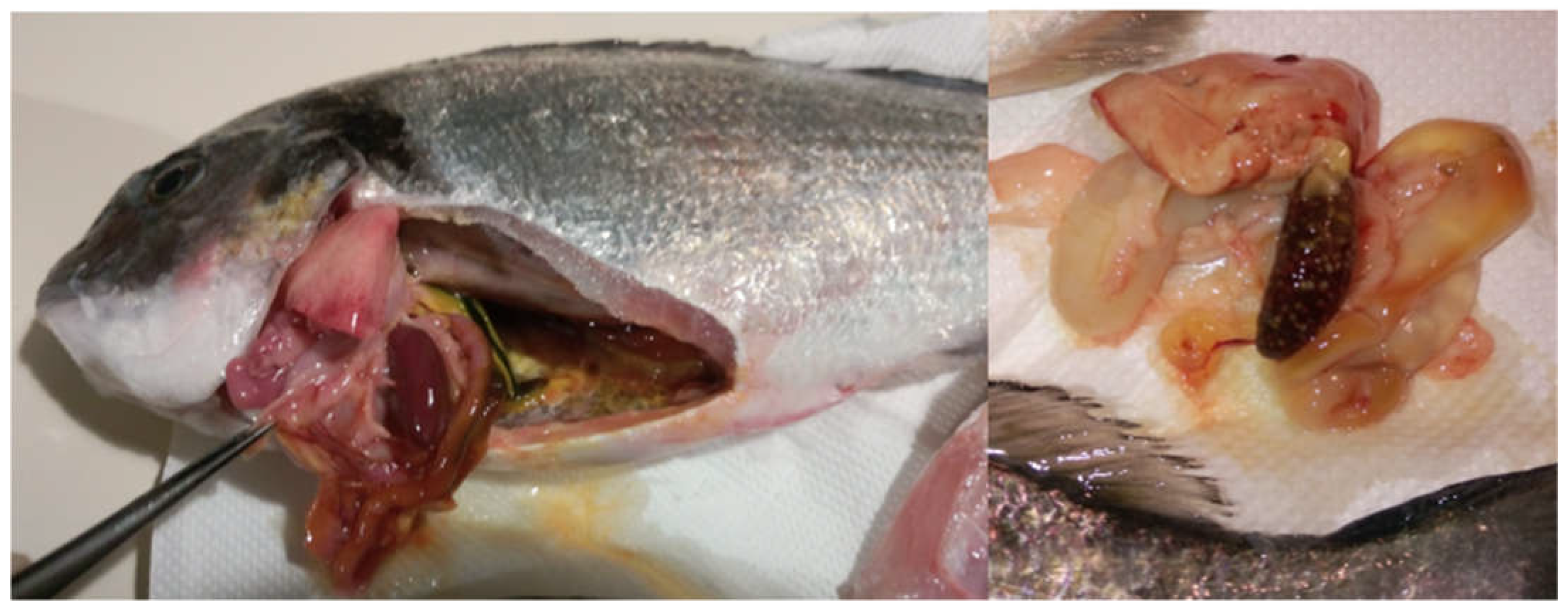
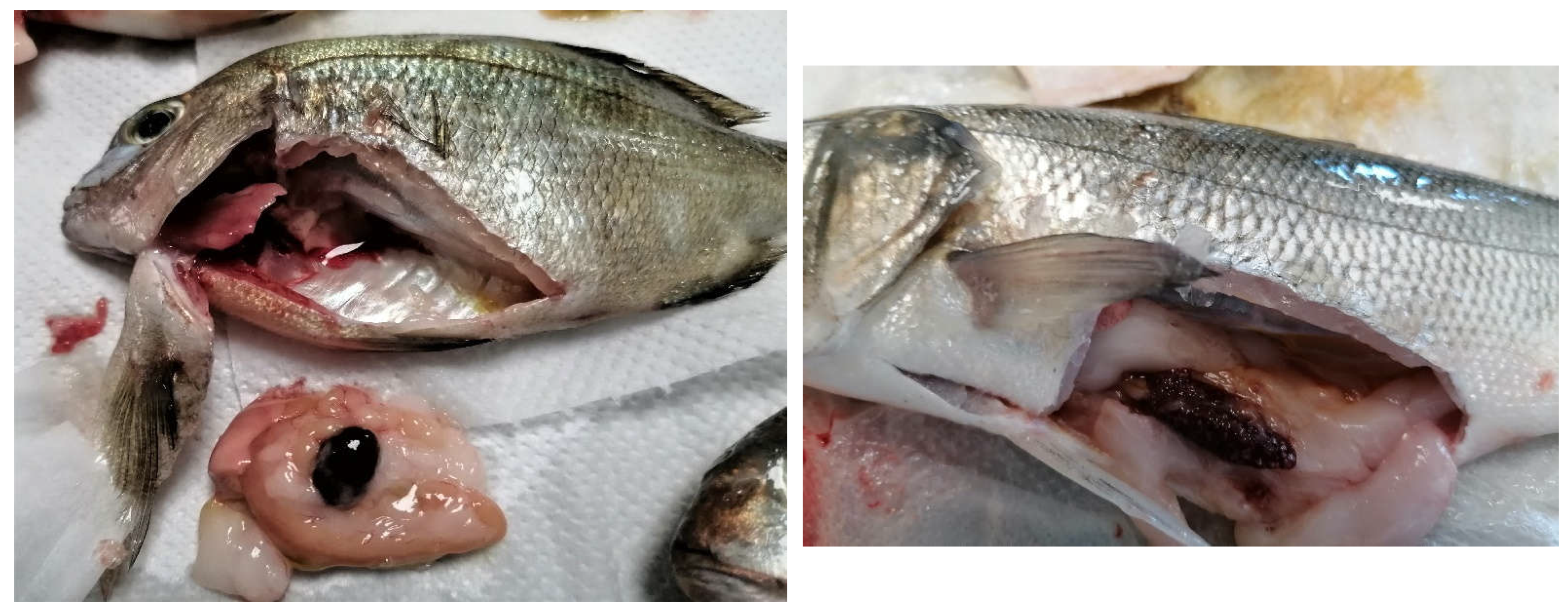



| Sampling Code | Molecular Identification | Collection Period | Seawater Temperature (°C) | Location | Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 222 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | October 2019 | 24 | Thesprotia | sea bass |
| 407 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | November 2021 | 21 | Thesprotia | red porgy |
| 354 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | October 2020 | 22 | Chalkidiki | sea bass |
| 415 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | November 2021 | 21 | Thesprotia | red porgy |
| 120 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | October 2019 | 25 | Evia | sea bass |
| 214 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | October 2019 | 22 | Chalkidiki | sea bream |
| 355 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | October 2020 | 25 | Thesprotia | red porgy |
| 367 | P. damselae sbsp. damselae | October 2020 | 24 | Thesprotia | sea bass |
| 228 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | December 2020 | 21 | Aegean Sea | sea bream |
| 399 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | November 2021 | 23 | Peloponnisos | sea bass |
| 406 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | November 2021 | 23 | Peloponnisos | sea bass |
| 400 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | November 2021 | 22 | Peloponnisos | sea bass |
| 371 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | December 2021 | 17 | Thesprotia | sea bream |
| 417 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | November 2021 | 23 | Peloponnisos | sea bream |
| 405 | P. damselae sbsp. piscicida | November 2021 | 20 | Thesprotia | red porgy |
| Photobacterium damselae sbsp. Piscicida | Virulence Genes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Isolated Strain | Aip56 | pdp-0080 | hutB | p55 | hutD |
| 222 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 407 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 354 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 415 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 120 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 214 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 355 | - | + | + | + | + |
| 367 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 228 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 399 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 406 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 400 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 371 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 417 | + | + | + | + | + |
| 405 | + | + | + | + | + |
| Cephalosporin | Penicillins | Aminoglycosides | Macrolide | Sulfonamide | Phenicol | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STRAIN | CTX | AMP | AX | S | GM | E | SXT | FFC |
| 120 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 214 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 222 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 228 | S | S | S | R | S | S | R | S |
| 354 | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 355 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 367 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 371 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 399 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 400 | R | S | S | I | S | S | S | S |
| 405 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 406 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 407 | S | R | S | I | S | S | S | S |
| 415 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 417 | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| Fluoroquinolones | Tetracycline | Aminocoumarin | Quinolones | Antimycobacterials | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STRAIN | SPECIES | CIP | ENR | TE | NV | NA | RD | O/129 | Nitrofurantoin (F) |
| 120 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 214 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 222 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 228 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | I | I | S | S | S | S |
| 354 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 355 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 367 | P. damselae subsp. damselae | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 371 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 399 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 400 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 405 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 406 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 407 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | R |
| 415 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 417 | P. damselae subsp. piscicida | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lattos, A.; Giantsis, I.A.; Tsavea, E.; Kolygas, M.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Bitchava, K. Virulence Genes and In Vitro Antibiotic Profile of Photobacterium damselae Strains, Isolated from Fish Reared in Greek Aquaculture Facilities. Animals 2022, 12, 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223133
Lattos A, Giantsis IA, Tsavea E, Kolygas M, Athanassopoulou F, Bitchava K. Virulence Genes and In Vitro Antibiotic Profile of Photobacterium damselae Strains, Isolated from Fish Reared in Greek Aquaculture Facilities. Animals. 2022; 12(22):3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLattos, Athanasios, Ioannis A. Giantsis, Eleni Tsavea, Markos Kolygas, Fotini Athanassopoulou, and Konstantina Bitchava. 2022. "Virulence Genes and In Vitro Antibiotic Profile of Photobacterium damselae Strains, Isolated from Fish Reared in Greek Aquaculture Facilities" Animals 12, no. 22: 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223133
APA StyleLattos, A., Giantsis, I. A., Tsavea, E., Kolygas, M., Athanassopoulou, F., & Bitchava, K. (2022). Virulence Genes and In Vitro Antibiotic Profile of Photobacterium damselae Strains, Isolated from Fish Reared in Greek Aquaculture Facilities. Animals, 12(22), 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12223133






