Clustering and Correlations amongst NEFA, Selected Adipokines and Morphological Traits—New Insights into Equine Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Animals
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Population
3.2. Correlations
3.3. Linear Regression Analysis
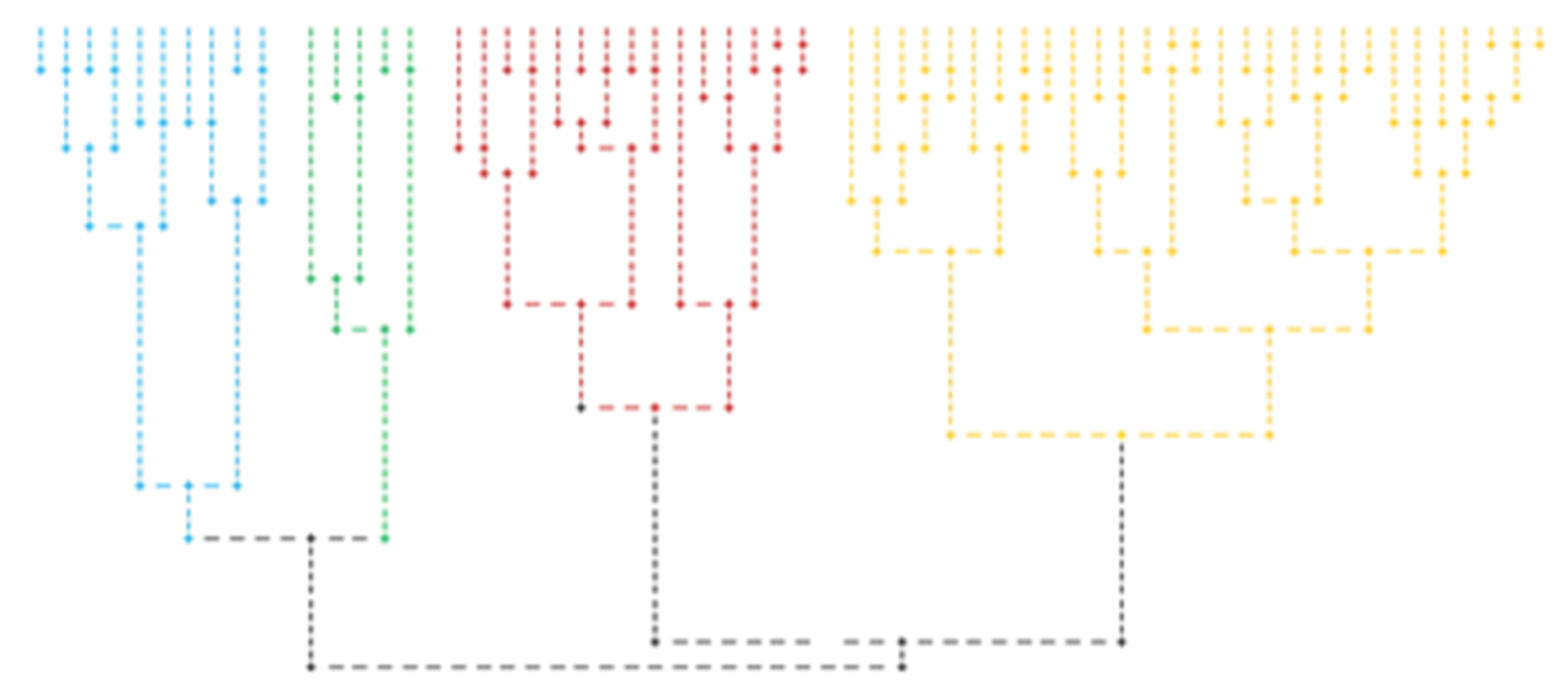
3.4. Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Després, J.P.; Lemieux, I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006, 444, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.; Keen, J.; McGowan, C. Equine metabolic syndrome. Vet. Rec. 2015, 177, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.; Jensen, M.D. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Is body structure a factor? Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1997, 8, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.L.; Zheng, X.L.; Tang, C.K. The protective functions of omentin in cardiovascular diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 448, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, R.; Ouchi, N.; Murohara, T. Adiponectin and cardiovascular disease. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K. Adipokines, myokines and cardiovascular disease. Circ. J. 2009, 73, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Taeye, B.M.; Novitskaya, T.; McGuinness, O.P.; Gleaves, L.; Medda, M.; Covington, J.W.; Vaughan, D.E. Macrophage TNF-alpha contributes to insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E713–E725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, A.J.; Hervera, M.; Hunter, L.; Holden, S.L.; Morris, P.J.; Biourge, V.; Trayhurn, P. Improvement in insulin resistance and reduction in plasma inflammatory adipokines after weight loss in obese dogs. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2009, 37, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenig, M.; McGoldrick, J.B.; De Beer, M.; Demacker, P.N.; Ferguson, D.C. Activity and tissue-specific expression of lipases and tumor-necrosis factor alpha in lean and obese cats. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2006, 30, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vick, M.M.; Adams, A.A.; Murphy, B.A.; Sessions, D.R.; Horohov, D.W.; Cook, R.F.; Shelton, B.J.; Fitzgerald, B.P. Relationships among inflammatory cytokines, obesity, and insulin sensitivity in the horse. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 85, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suagee, J.K.; Corl, B.A.; Crisman, M.V.; Pleasant, R.S.; Thatcher, C.D.; Geor, R.J. Relationships between Body Condition Score and Plasma Inflammatory Cytokines, Insulin, and Lipids in a Mixed Population of Light-Breed Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Chan, L.; Zhou, S.W. Omentin: Linking metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 12, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stulnig, T.M.; Zeyda, M. Adipokines, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. In Inflammation and Atherosclerosis; Wick, G., Grundtman, C., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012; pp. 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Nosrati-Oskouie, M.; Asghari, G.; Yuzbashian, E.; Aghili-Moghaddam, N.S.; Zarkesh, M.; Safarian, M.; Mirmiran, P. Does dietary intake impact omentin gene expression and plasma concentration? A systematic review. Lifestyle Genom. 2021, 14, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Batista, C.M.; Yang, R.Z.; Lee, M.J.; Glynn, N.M.; Yu, D.Z.; Pray, J.; Ndubuizu, K.; Patil, S.; Schwartz, A.; Kligman, M.; et al. Omentin plasma levels and gene expression are decreased in obesity. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Liu, D.; Long, M.; Ren, Y.; Pang, J.; Li, R. Changes of serum omentin levels and relationship between omentin and adiponectin concentrations in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2011, 119, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaid, N.H.; Sadik, N.A.; Ahmed, N.R.; Fayez, S.E.; Mohammed, N.A.E. Serum omentin-1 levels in type 2 diabetic obese women in relation to glycemic control, insulin resistance and metabolic parameters. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol 2018, 13, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwens, D.M.; Sell, H.; Greulich, S.; Eckel, J. The role of epicardial and perivascular adipose tissue in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, H.; Hierer, J.; Haas, O.; Forssmann, W.G. Quantification of angiotensin-converting-enzyme-mediated degradation of human chemerin 145–154 in plasma by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 2007, 362, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rourke, J.L.; Dranse, H.J.; Sinal, C.J. Towards an integrative approach to understanding the role of chemerin in human health and disease. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connysson, M.; Rhodin, M.; Jansson, A. Effects of horse housing system on energy balance during post-exercise recovery. Animals 2019, 9, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafidis, P.A.; Bakris, G.L. Non-esterified fatty acids and blood pressure elevation: A mechanism for hypertension in subjects with obesity/insulin resistance? J. Human Hypertens. 2007, 21, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breidenbach, A.; Fuhrmann, H.; Deegen, E.; Lindholm, A.; Sallmann, H.P. Studies on Equine Lipid Metabolism—2. Lipolytic Activities of Plasma and Tissue Lipases in Large Horses and Ponies. J. Vet. Med. Series A 1999, 46, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckardt, K.; Taube, A.; Eckel, J. Obesity-associated insulin resistance in skeletal muscle: Role of lipid accumulation and physical inactivity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2011, 12, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, F.H.; Huffman, D.M.; Fishman, S.; Jerschow, E.; Heo, H.J.; Atzmon, G.; Schechter, C.; Barzilai, N.; Muzumdar, R.H. Aging per se increases the susceptibility to free fatty acid–induced insulin resistance. J. Gerontol. Biol. Sci. Med. 2010, 65, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daradics, Z.; Crecan, C.M.; Rus, M.A.; Morar, I.A.; Mircean, M.V.; Cătoi, A.F.; Cecan, A.D.; Cătoi, C. Obesity-related metabolic dysfunction in dairy cows and horses: Comparison to human metabolic syndrome. Life 2021, 11, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajchenberg, B.L. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: Their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 2000, 21, 697–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, S.; Harris, P.A.; Nicol, C.J.; Rands, S.A. Variation in body condition in small groups of horses. J. Vet. Behav. 2013, 8, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.A.; Treiber, K.H.; Geor, R.J.; Douglass, L.; Harris, P.A. Prediction of incipient pasture-associated laminitis from hyperinsulinaemia, hyperleptinaemia and generalised and localised obesity in a cohort of ponies. Equine. Vet. J. 2009, 41, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, N.; Elliott, S.B.; Brandt, L.E.; Keisler, D.H. Physical characteristics, blood hormone concentrations, and plasma lipid concentrations in obese horses with insulin resistance. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 228, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, A.E.; Frank, N. ECEIM consensus statement on equine metabolic syndrome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henneke, D.R.; Potter, G.D.; Kreider, J.L.; Yeates, B.F. Relationship between condition score, physical measurements and body fat percentage in mares. Equine. Vet. J. 1983, 15, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, R.A.; Geor, R.J.; Burton Staniar, W.; Cubitt, T.A.; Harris, P.A. Apparent adiposity assessed by standardised scoring systems and morphometric measurements in horses and ponies. Vet. J. 2009, 179, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfuso, F.; Giannetto, C.; Panzera, M.F.; Fazio, F.; Piccione, G. Uncoupling Protein-1 (UCP1) in the Adult Horse: Correlations with Body Weight, Rectal Temperature and Lipid Profile. Animals 2021, 11, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Weyenberg, S.; Hesta, M.; Buyse, J.; Janssens, G.P. The effect of weight loss by energy restriction on metabolic profile and glucose tolerance in ponies. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.M.; Bayly, W.M.; Sellon, D.C. Chapter 16—disorders of the endocrine system. In Equine Internal Medicine, 4th ed.; Reed, S.M., Bayly, W.M., Sellon, D.C., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1029–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Geelen, S.N.; Jansen, W.L.; Sloet van Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan, M.M.; Breukink, H.J.; Beynen, A.C. Fat feeding increases equine heparin-released lipoprotein lipase activity. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2001, 15, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaue, D.; Schedlbauer, C.; Starzonek, J.; Gittel, C.; Brehm, W.; Einspanier, A.; Vervuert, I. Effects of body weight gain on insulin and lipid metabolism in equines. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2019, 68, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, M.; Zambito, J.; Spooner, H.; Barnes, K. Effect of weight loss on lipid metabolism in the mature horse (814.4). FASEB J. 2014, 28, 814.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.A.; McCutcheon, L.J.; George, L.A.; Smith, T.L.; Frank, N.; Geor, R.J. Effects of diet-induced weight gain on insulin sensitivity and plasma hormone and lipid concentrations in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt-Phillips, S.E.; Owens, K.M.; Dowler, L.E.; Cloninger, M.T. Assessment of resting insulin and leptin concentrations and their association with managerial and innate factors in horses. J. Equine. Vet. Sci. 2010, 30, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gimenez, T.; De Blas, I.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Diez de Castro, E.; Aguirre-Pascasio, C.N. Endocrine, morphometric, and ultrasonographic characterization of neck adiposity in Andalusian horses. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleasant, R.S.; Suagee, J.K.; Thatcher, C.D.; Elvinger, F.; Geor, R.J. Adiposity, plasma insulin, leptin, lipids, and oxidative stress in mature light breed horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auyyuenyong, R.; Henze, A.; Ungru, J.; Schweigert, F.J.; Raila, J.; Vervuert, I. Determination of lipid profiles in serum of obese ponies before and after weight reduction by using multi-one-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 117, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laat, M.A.; Hampson, B.A.; Sillence, M.N.; Pollitt, C.C. Sustained, low-intensity exercise achieved by a dynamic feeding system decreases body fat in ponies. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.M.; Ribeiro, D.S.; Cota, L.O.; Leme, F.O.; Carvalho, A.M.; Faleiros, R.R. Changes in metabolic and physiological biomarkers in Mangalarga Marchador horses with induced obesity. Vet. J. 2021, 270, 105627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.C.; McMillan, C.J.; Snead, E.R.; Takada, K.; Chelikani, P.K. Association of circulating adipokine concentrations with indices of adiposity and sex in healthy, adult client owned cats. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, P.H.P.; Nurahmi, N.; Esa, T.; Kurniawan, L.B. Omentin-1 levels in obesity. Ind. J. Clin. Path Med. Lab. 2021, 28, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, R.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, R.; Terakura, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Ikeda, N.; Higuchi, A.; Terasaki, H.; Kihara, S.; Murohara, T. Omentin as a novel biomarker of metabolic risk factors. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2012, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.Y.; Guo, L.; Li, Q. Changes of serum omentin-1 levels in normal subjects and in patients with impaired glucose regulation and with newly diagnosed and untreated type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 88, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoté, X.; Gómez-Zorita, S.; López-Yoldi, M.; Milton-Laskibar, I.; Fernández-Quintela, A.; Martínez, J.A.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Portillo, M.P. Role of omentin, vaspin, cardiotrophin-1, TWEAK and NOV/CCN3 in obesity and diabetes development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cătoi, A.F.; Suciu, Ş.; Pârvu, A.E.; Copăescu, C.; Galea, R.F.; Buzoianu, A.D.; Vereşiu, I.A.; Cătoi, C.; Pop, I.D. Increased chemerin and decreased omentin-1 levels in morbidly obese patients are correlated with insulin resistance, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Clujul Med. 2014, 87, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jialal, I.; Devaraj, S.; Kaur, H.; Adams-Huet, B.; Bremer, A.A. Increased chemerin and decreased omentin-1 in both adipose tissue and plasma in nascent metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E514–E517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Metabolic Parameters | Sensitivity | Detection Range | Inter-Assay Coefficient of Variability | Intra-Assay Coefficient of Variability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) | 1.0 µmol/L | 10–600 µmol/L | <15% | <10% |
| Horse total cholesterol | 0.026 mmol/L | 0.05–30 mmol/L | <10% | <8% |
| Horse insulin | 3.1 µIU/mL | 6.25–400 µIU/mL | <12% | <8% |
| Horse omentin | 1.0 ng/mL | 3.12–100 ng/mL | <15% | <15% |
| Horse chemerin | 5.0 ng/mL | 31.2–1000 ng/mL | <15% | <15% |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of horses (N) | 71 |
| Age (years) | 9.0 (8.0; 12.5) |
| Sex, male (n, %) | 27 (38.0%) |
| Bodyweight (kg) | 600.0 (425.0; 700.0) |
| Body condition score | 8.0 (7.0; 9.0) |
| Cresty neck score | 4.0 (3.0; 5.0) |
| NEFA (μmol/L) | 420.1 ± 82.8 |
| Omentin (ng/mL) | 14.3 (10.2; 16.6) |
| Chemerin (ng/mL) | 283.0 (219.3; 348.7) |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.9 (1.8; 3.3) |
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | 55.4 (40.4; 77.8) |
| NEFA | Total Cholesterol | Insulin | Omentin | Chemerin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | |
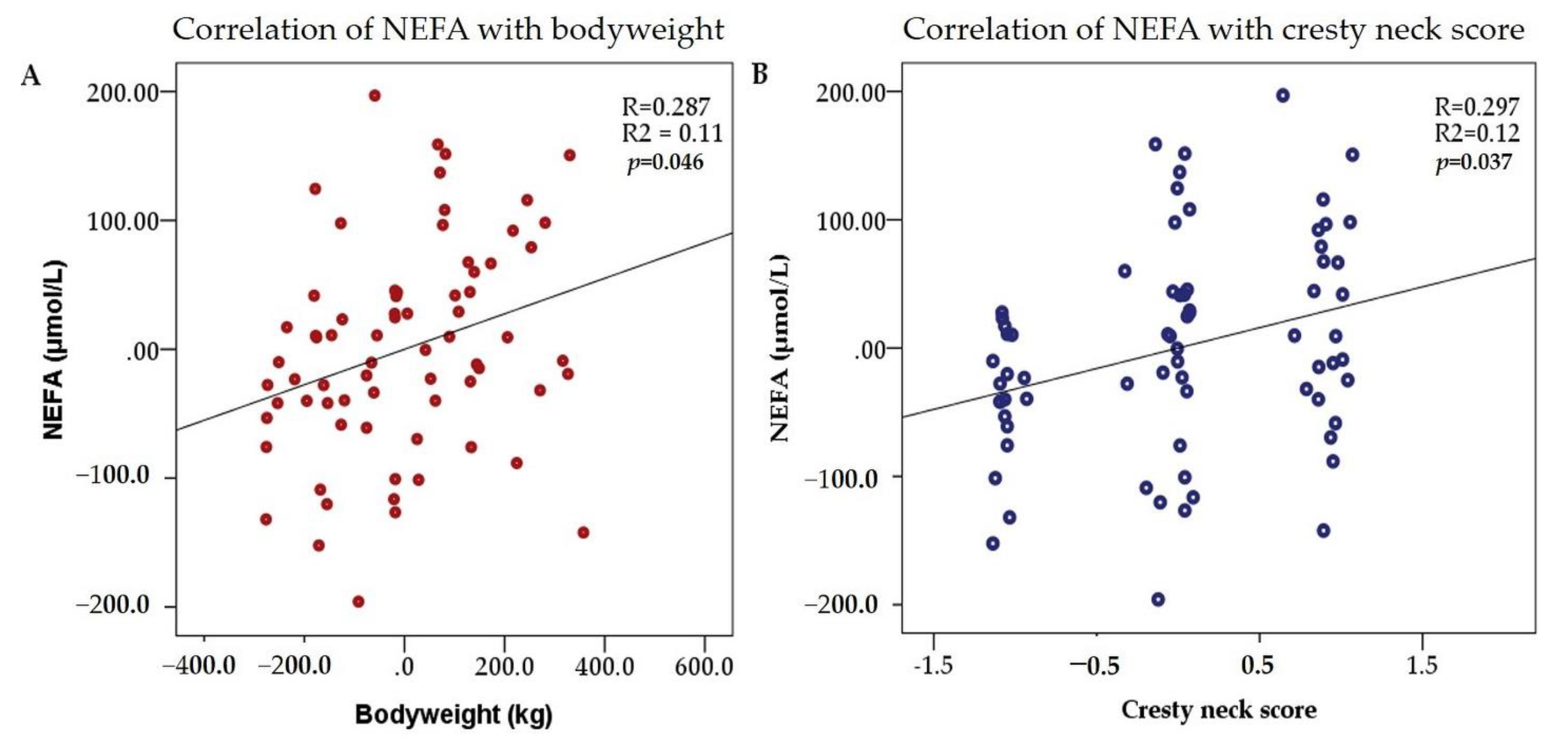
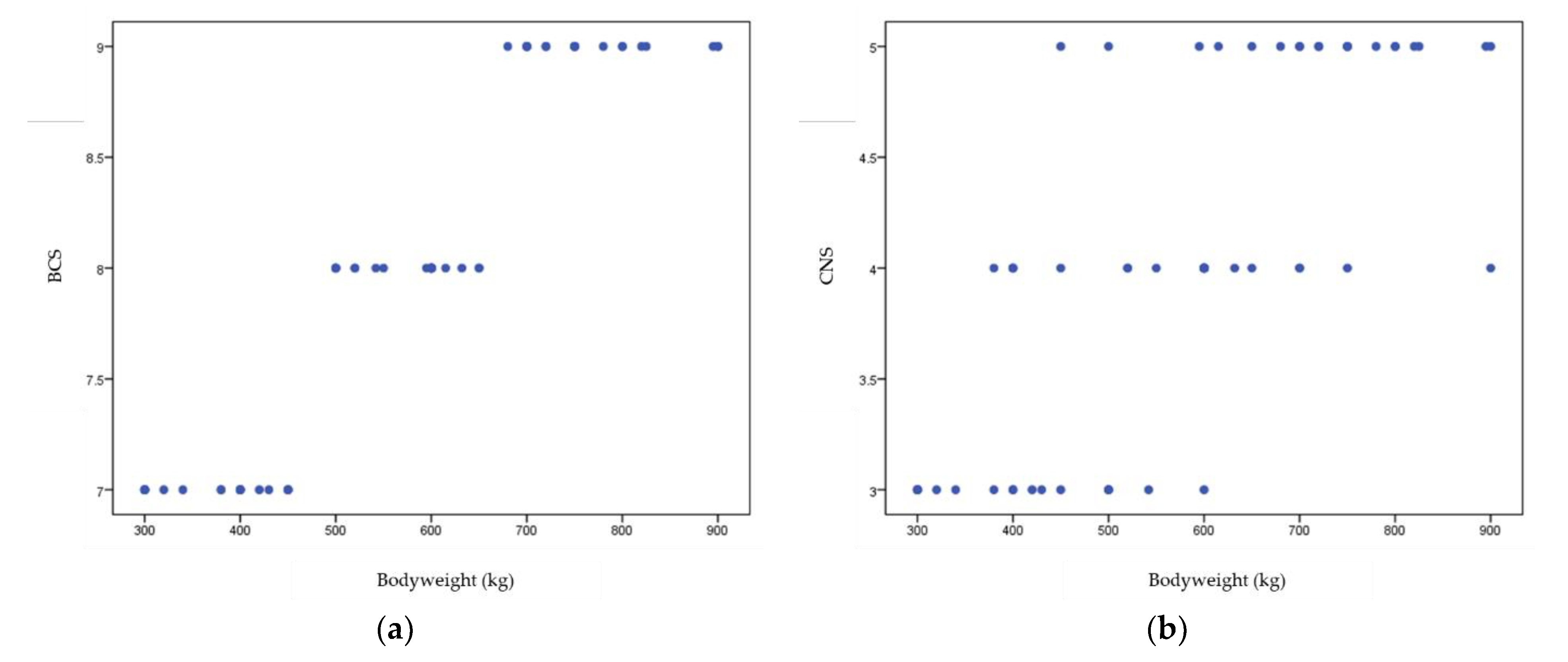
| Bodyweight | 0.322 | 0.006 | 0.262 | 0.027 | 0.066 | 0.587 | 0.213 | 0.075 | 0.157 | 0.192 |
| Age | −0.271 | 0.022 | −0.01 | 0.995 | −0.176 | 0.143 | 0.078 | 0.520 | −0.177 | 0.147 |
| Body condition score | 0.295 | 0.013 | 0.187 | 0.117 | 0.063 | 0.602 | 0.197 | 0.099 | 0.204 | 0.087 |
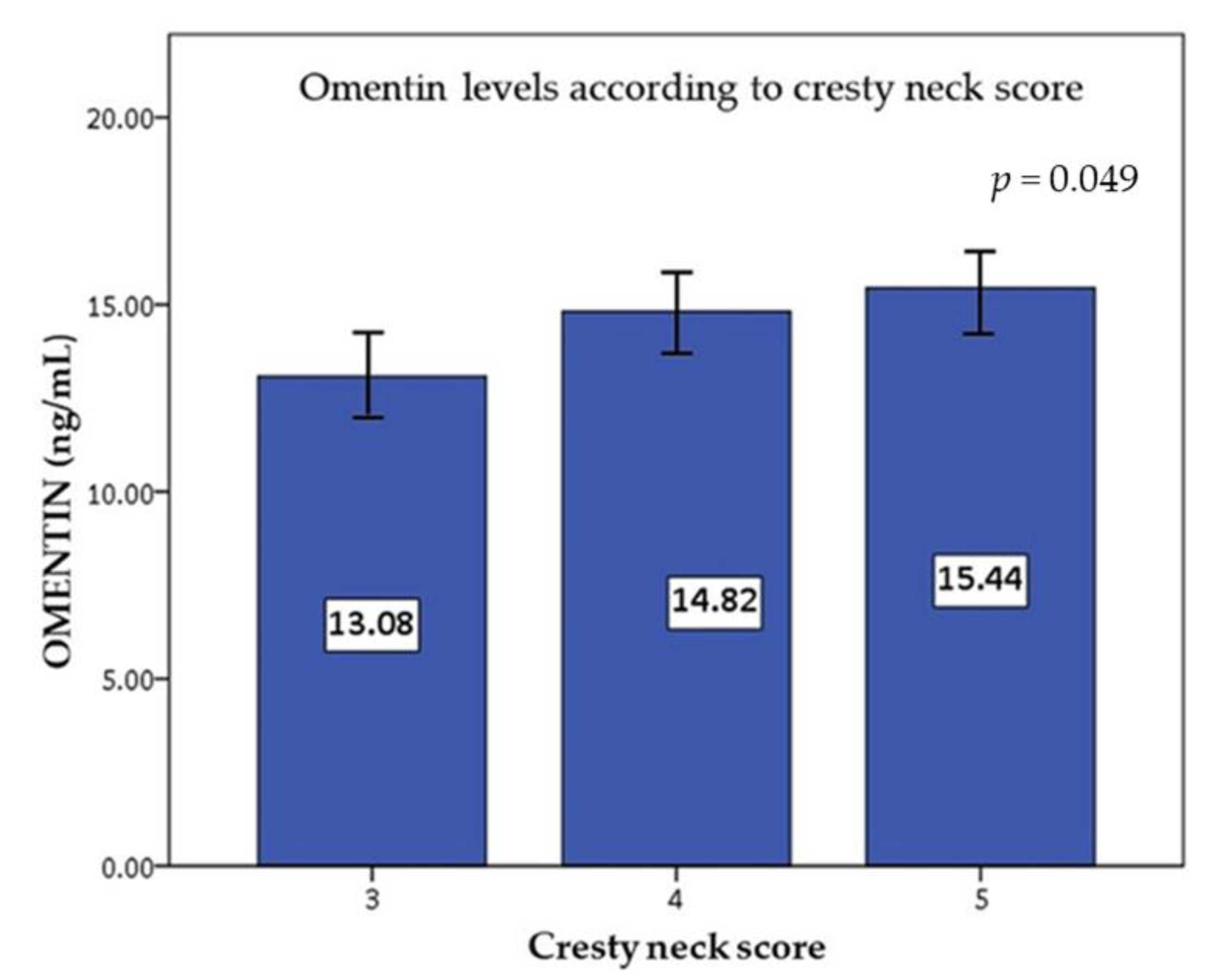
| Cresty neck score | 0.267 | 0.024 | 0.172 | 0.152 | −0.021 | 0.864 | 0.234 | 0.049 | 0.212 | 0.076 |
| Model | Variable | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | Beta | |||
| Model 1 | (Constant) | 380.09 | 52.40 | 0.000 | |
| Bodyweight | 0.139 | 0.056 | 0.287 | 0.016 | |
| Sex | −9.487 | 16.049 | −0.069 | 0.556 | |
| Age | −2.126 | 1.863 | −0.131 | 0.258 | |
| Model 2 | (Constant) | 354.26 | 58.74 | 0.000 | |
| Cresty neck score | 31.83 | 12.401 | 0.297 | 0.013 | |
| Sex | −18.783 | 15.863 | −0.136 | 0.241 | |
| Age | −2.700 | 1.865 | −0.167 | 0.152 | |
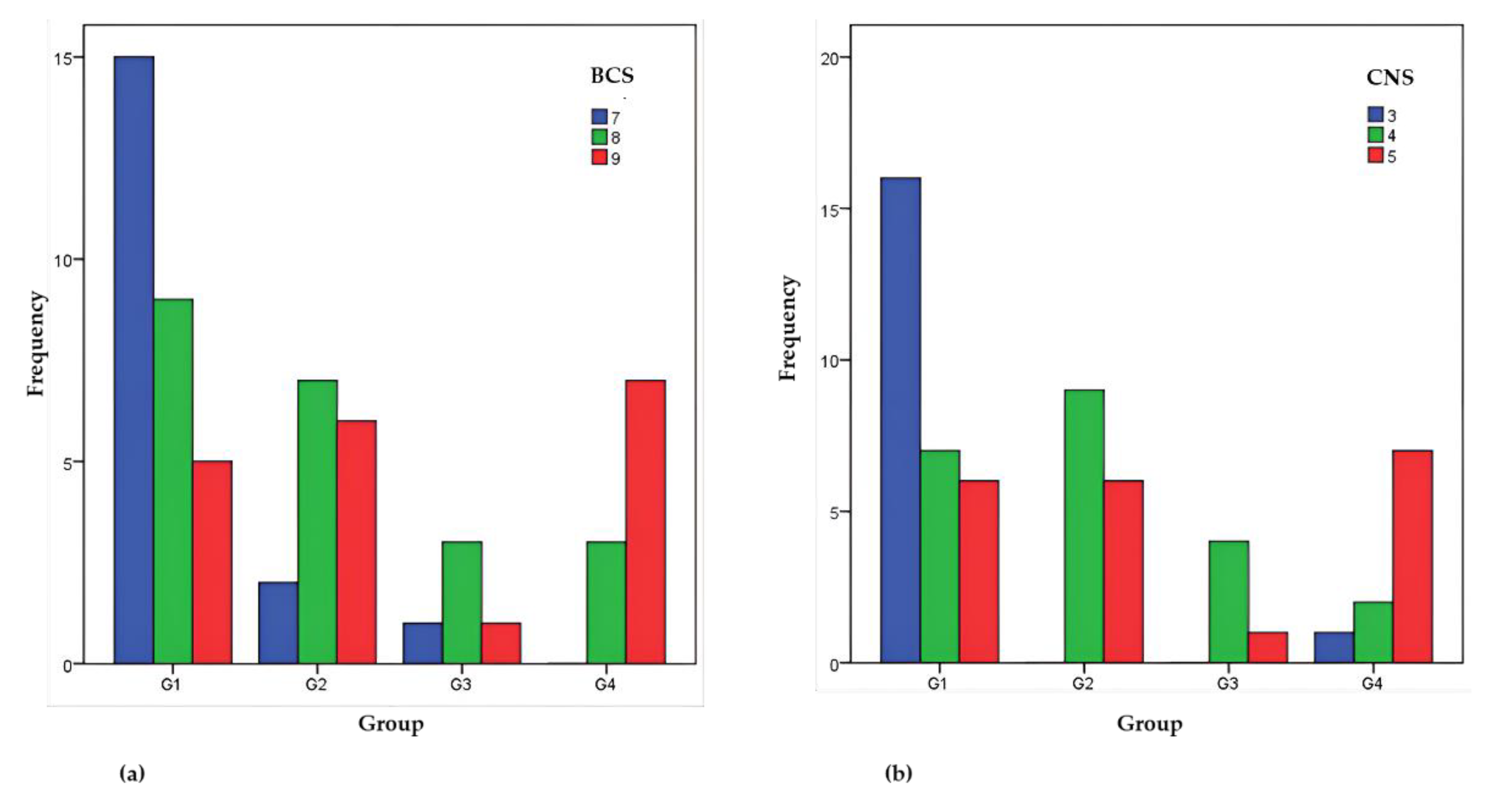
| Variable | Group | N | m | σ | F(3, 55) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1 | 29 | 10.69 | 2.67 | 1.854 | 0.148 |
| 2 | 15 | 10.07 | 5.86 | |||
| 3 | 5 | 6.10 | 3.75 | |||
| 4 | 10 | 12.30 | 7.99 | |||
| Bodyweight (kg) | 1 | 29 | 495.69 | 152.54 | 7.310 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 15 | 641.67 | 130.22 | |||
| 3 | 5 | 586.40 | 154.03 | |||
| 4 | 10 | 720.20 | 137.21 | |||
| NEFA (μmol/L) | 1 | 29 | 381.14 | 46.11 | 20.961 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 15 | 486.46 | 35.87 | |||
| 3 | 5 | 370.47 | 57.59 | |||
| 4 | 10 | 468.40 | 63.67 | |||
| Omentin (ng/mL) | 1 | 29 | 12.04 | 3.65 | 9.492 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 15 | 12.90 | 3.90 | |||
| 3 | 5 | 13.34 | 4.85 | |||
| 4 | 10 | 19.24 | 3.08 | |||
| Chemerin (ng/mL) | 1 | 29 | 250.02 | 54.96 | 23.952 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 15 | 232.93 | 97.05 | |||
| 3 | 5 | 500.40 | 40.73 | |||
| 4 | 10 | 399.37 | 110.82 | |||
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1 | 29 | 3.02 | 0.80 | 3.427 | 0.023 |
| 2 | 15 | 2.71 | 1.31 | |||
| 3 | 5 | 1.63 | 0.33 | |||
| 4 | 10 | 2.50 | 0.80 | |||
| Insulin (μIU/mL) | 1 | 29 | 50.57 | 26.40 | 0.494 | 0.688 |
| 2 | 15 | 55.89 | 29.51 | |||
| 3 | 5 | 62.63 | 38.43 | |||
| 4 | 10 | 60.03 | 20.29 |
| Group | Ranks Average | |
|---|---|---|
| BCS | CNS | |
| Group 1 | 22.69 | 22.09 |
| Group 2 | 35.03 | 36.90 |
| Group 3 | 29.60 | 32.70 |
| Group 4 | 43.85 | 41.25 |
| χ2(3) p | 14.715 0.002 | 14.671 0.002 |
| BCS | CNS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bodyweight | ρ | 0.944 | 0.745 |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| BCS | ρ | 1.000 | 0.704 |
| p | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daradics, Z.; Niculae, M.; Crecan, C.M.; Lupșan, A.F.; Rus, M.A.; Andrei, S.; Ciobanu, D.M.; Cătoi, F.A.; Pop, I.D.; Mircean, M.V.; et al. Clustering and Correlations amongst NEFA, Selected Adipokines and Morphological Traits—New Insights into Equine Metabolic Syndrome. Animals 2022, 12, 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202863
Daradics Z, Niculae M, Crecan CM, Lupșan AF, Rus MA, Andrei S, Ciobanu DM, Cătoi FA, Pop ID, Mircean MV, et al. Clustering and Correlations amongst NEFA, Selected Adipokines and Morphological Traits—New Insights into Equine Metabolic Syndrome. Animals. 2022; 12(20):2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202863
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaradics, Zsofia, Mihaela Niculae, Cristian Mihăiță Crecan, Alexandru Florin Lupșan, Mirela Alexandra Rus, Sanda Andrei, Dana Mihaela Ciobanu, Florinela Adriana Cătoi, Ioana Delia Pop, Mircea Valerian Mircean, and et al. 2022. "Clustering and Correlations amongst NEFA, Selected Adipokines and Morphological Traits—New Insights into Equine Metabolic Syndrome" Animals 12, no. 20: 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202863
APA StyleDaradics, Z., Niculae, M., Crecan, C. M., Lupșan, A. F., Rus, M. A., Andrei, S., Ciobanu, D. M., Cătoi, F. A., Pop, I. D., Mircean, M. V., & Cătoi, C. (2022). Clustering and Correlations amongst NEFA, Selected Adipokines and Morphological Traits—New Insights into Equine Metabolic Syndrome. Animals, 12(20), 2863. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202863









