Simple Summary
Vertebrate hosts, especially wild living animals, are pivotal to the circulation and maintenance of Borrelia spp. Mesocarnivores are involved in Lyme disease ecology in sylvatic and suburban ecosystems. In this study, we aimed to examine the relative importance of six medium-sized carnivore species, raccoon, red fox, raccoon dog, European badger, pine marten and stone marten, as hosts of Borrelia spp. and investigated their role in this spirochaete’s transmission cycle. We also aimed to trace the reservoir competence of these invasive and native predators and the eco-epidemiology of Borrelia spp. in the context of a dilution effect. In all examined carnivore species, the occurrence of Borrelia was recorded, and the results suggest that raccoons may play a role as reservoir hosts for these spirochaetal bacteria. The role of invasive species seems to be worthy of further analysis with reference to the circulation of vector-borne pathogens as well as in the context of the “dilution effect” hypothesis.
Abstract
Wild living mesocarnivores, both introduced and native species, are able to adapt well to peri-urban environments, facilitating cross-species pathogen transmission with domestic animals, and potentially humans. Individual tissue samples derived from 284 specimens of six carnivore species, i.e., raccoon, raccoon dog, red fox, European badger, pine marten and stone marten, were used for molecular investigations with the nested PCR method. The animals were sampled in the Ruszów Forest District (Poland). We aimed to examine the relative importance of the studied mesocarnivores as hosts of Borrelia spp. and investigated their role in this spirochaete’s transmission cycle. We also aimed to trace the reservoir competence of these invasive and native predators and borreliosis eco-epidemiology in the context of a dilution effect. The overall prevalence of Borrelia spp. in the tested carnivores was 8.8%. Almost all of the consensus sequences of the partial flaB gene shared identity with a sequence of specific Borrelia species, i.e., B. afzelii, B. garinii and B. burgdorferi. Our results suggest that raccoons may play a role as reservoir hosts for these spirochaetal bacteria. The role of invasive species seems to be worthy of further analysis with reference to the circulation of vector-borne pathogens as well as in the context of the “dilution effect” hypothesis.
1. Introduction
The genus Borrelia comprises arthropod-borne spirochetes which are pathogens of human and animals. Vertebrate hosts, especially wild living animals [1], are pivotal to the circulation and maintenance of Borrelia spp. The level of competence varies between hosts, with rodents appearing to be important hosts [2,3], whereas, e.g., roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) seem to be zooprophylactic or “dilution” hosts [4]. According to the dilution effect hypothesis, diverse host communities inhibit the parasite abundance through various mechanisms, such as regulating populations of susceptible hosts or interfering with parasite transmission [5,6,7]. Nevertheless, the role of carnivores as hosts in Borrelia spp. ecology remains unclear. The current knowledge of the complex interaction between this diverse pathogen and its vectors as well as different reservoir and non-reservoir hosts is still incomplete.
Mesocarnivores such as raccoon (Procyon lotor), red fox (Vulpes vulpes), raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides), European badger (Meles meles), pine marten (Martes martes) and stone marten (Martes foina) serve as hosts for several tick species [8,9,10,11] and their significant involvement in Lyme disease ecology in sylvatic and suburban ecosystems is likely. The castor bean tick (Ixodes ricinus) is known as one of the main vectors of Borrelia spp. in Central Europe and has quite often been found on these animals [12,13,14].
In Poland, raccoons and raccoon dogs are considered invasive and alien species [15]. They may introduce new pathogens to the environment and may serve as potential hosts for many infectious agents important to domestic animals and humans. Some of the predators have a direct impact on the host competence, e.g., red foxes reduce, by hunting, populations of rodents, being one of the most numerous reservoirs of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. [16].
Here, we aimed to examine the importance of six medium-sized native and invasive species of carnivore hosts of Borrelia spp. with overlapping ranges and to investigate their role in the spirochaete transmission cycle. We also aimed to check the reservoir competence of these predators and to study the borreliosis eco-epidemiology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
A total of 586 tissue samples (ear, spleen, liver) derived from 284 specimens of six carnivore species, i.e., raccoon (n = 51), raccoon dog (n = 50), red fox (n = 50), European badger (n = 53), pine marten (n = 27) and stone marten (n = 53), were used for molecular study (Table 1). The animals were sampled in the Ruszów Forest District (Poland), in the west part of the Lower Silesian Wilderness, being the largest lowland forest complex in Europe and the unique location of co-occurrence of the native and invasive carnivore species in Europe. The tissue samples obtained through collaboration with other projects were collected mainly during a predator control operation carried out as a part of the capercaillie (Tetrao urogallus) reintroduction program in the Lower Silesian Forest [17,18]. The tissue samples were delivered to the laboratory of the Department of Parasitology, University of Wrocław, and stored at −20 °C.

Table 1.
Tissue samples of carnivore hosts used in the present study.
2.2. Molecular Analyses
DNA was extracted using the Bio-Trace DNA Purification Kit (EURx, Poland), following the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA concentrations were estimated with a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Nanodrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA). The molecular detection of Borrelia spp. was performed in three steps, i.e., (1) qPCRs on all obtained tissue samples of invasive (raccoon and raccoon dog) and native species (red fox); (2) nested PCRs targeting the flaB gene on selected samples of all carnivore species co-occurring in the study area; (3) conventional PCR targeting the 5S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region on positive samples for the flaB gene.
Firstly, qPCR with the ospA gene as a marker and primers and probes such as B-OspA_modF, B-OspA_borAS and B-OspAmodPatto was applied [19,20]. The qPCR was performed on all tissue samples (ear, liver and spleen) obtained from raccoons, raccoon dogs and red foxes. The presence of Borrelia spp. DNA was determined by the amplification of a 600 bp fragment of the flaB gene in nested PCR, with two primer sets: 132f, 905r and 220f, 824r [21]. As the qPCR results were confirmed by nested PCRs, we performed only nested PCRs for other co-occurring carnivore species such as badgers and pine and stone martens (mustelids). In the last step, the flaB-positive samples were further examined using conventional PCR assays amplifying parts of the 5S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region (IGS) with primers IGS_A and IGS_B [22]. Negative controls with nuclease-free distilled water as well as positive controls (B. afzelii from Ixodes ricinus) were included in each PCR reaction. In the PCRs, we followed the protocols described in the above-mentioned literature.
All nested PCR-positive amplicons were purified using Exo-BAP (EURx) and sequenced in both directions by Macrogen (Amsterdam, the Netherlands) with the primers used for DNA amplification. The nucleotide sequences were edited using DNA Baser Sequence Assembly software (Heracle BioSoft, Mioveni, Romania) and compared to each other and with corresponding sequences deposited in GenBank using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) program (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 30 September 2022). The representative sequences were deposited in GenBank under accession numbers OP559180–OP559187.
3. Results
The samples obtained from skin (ear), spleen and liver of raccoons, raccoon dogs and foxes were checked for the presence of Borrelia DNA using qPCR and nested PCR (14 vs. 16). Apart from one case, all positive samples were obtained for ear isolates (16/151; 10.6%). The only other sample, which proved to be positive in the qPCR, originated from raccoon liver. Following the results obtained for raccoons, raccoon dogs and foxes, the nested PCRs was performed for co-occurring mustelids only. The overall prevalence of Borrelia spp. In all tested carnivores was 8.8%, considering skin samples (25/284) (Table 2), and the infection rates varied significantly between these host species. Almost all consensus sequences of the partial flaB gene which were analyzed with the BLAST method revealed shared identity with a sequence of specific Borrelia species, i.e., B. afzelii (23), B. garinii (1) and B. burgdorferi (1) (Figure 1).

Table 2.
Borrelia species identified in samples obtained from wild living mesocarnivores based on flaB gene.
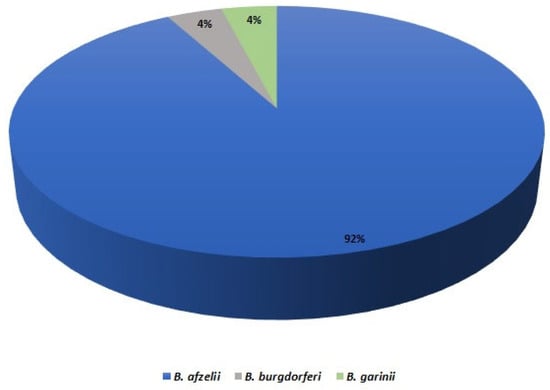
Figure 1.
Distribution of Borrelia species identified in examined carnivores.
The highest prevalence (23.5%) was observed for raccoons (12/51) as compared to raccoon dogs and red foxes with a single positive sample (prevalence of 2% each) (Table 2). The majority of positive samples were Borrelia afzelii (100% identity with, e.g., CP018262, DQ016619, KF894068, KX646195), one sample from fox was identified as B. garinii (100% homology with a few sequences, i.e., KF894068, MF150061).
The badgers proved to be more susceptible to Borrelia infection. Of 53 tested skin samples, eight were positive (15.1%), while DNA of Borrelia sp. was found in two samples obtained from pine marten (27 tested, i.e., 7.4%) and one from stone marten (53 tested, i.e., 1.9%). The BLAST analysis of seven sequences showed 100% similarity to several Borrelia afzelii sequences; one was 100% identical to a Borrelia burgdorferi sequence (acc. no. KF836508) from Ixodes ricinus from Poland (Lower Silesia) and 99.8% identical to other sequences (KX646200, KR782218) from I. ricinus from Poland as well as one sequence (acc. no. CP077727) from Belarus.
The interspecific divergence of IGS sequences of Borrelia afzelii was 0.0–2.3% (0–6 bp out of 264 bp), and three groups could be distinguished when analyzing the nucleotide similarity. The comparison between these lines and the homological sequences available in GenBank showed 100% to 99.2% similarity to samples derived from humans (CP018262, CP002933, JX888444), Ixodes ticks from Russia, Estonia, Germany (CP009212, KX418638, AY772053, MW489224, OL848283) as well as to sequences obtained from rodent tissues from France and Romania (KY273112, KY123663).
4. Discussion
The majority of data on Borrelia spp. in raccoons originate from the USA and are based on the results of serological testing [23,24,25,26]. Additionally, the results of studies carried out by Tufts et al. [27] showed the presence of B. burgdorferi s.l. in 2.6% of examined samples. Serological studies concerning this spirochaetal infection in raccoons from introduced areas, carried out in Japan, revealed the presence of B. afzelii (0.1%) and B. garinii (0.1%) [27,28]. Our results, with the first molecular evidence of B. afzelii infection, attaining 24.0% in the European population of introduced raccoons, indicate this carnivore as a potential reservoir host for the aforementioned spirochaetal species.
Molecular studies carried out by Wodecka et al. [10] on European raccoon dogs in Poland revealed that 11.9% of tested animals were positive for B. garinii (dominant species), followed by B. afzelii and B. valaisiana. Our survey indicated a much lower level of Borrelia infection—2.0% in raccoon dogs, being detected as B. afzelii only. On the other hand, a study carried out in South Korea, on native carnivores, resulted in the first report of Borrelia theileri (0.7%) in raccoon dogs [29].
In the present study, badgers yielded a higher prevalence of Borrelia spp. (15.1%) compared to other tested species of native carnivores, although Borrelia afzelii and B. burgdorferi were detected as well. Research by Wodecka et al. [10] provided evidence for Borrelia infection in badgers with a similar level of prevalence. Analyses of all PCR-positive blood, ear biopsy and liver samples revealed that 12% of badgers were infected with borreliae. Gern and Sell [30] detected the presence of both B. afzelii and B. valaisiana in 19.4% of tissue samples from the ears of badgers in Switzerland. The PCR-positive tissue samples identified in badgers revealed that they were infected exclusively with B. afzelii. In contrast, during research conducted in Belgium and the Netherlands, Borrelia burgdorferi (s.l.) was detected in 0.9% of liver samples of European badgers [11].
DNA of B. burgdorferi (s.l.) was found in tissues of other musteloid species, i.e., stone and pine martens. Borrelia burgdorferi (s.l.) was detected in 3.9% of spleen samples of pine martens and 2.9% of ear biopsies of stone martens [11]. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first molecular identification of B. afzelii in stone marten (7.4%) and in pine marten (1.9%).
To date, there have been only a few reports from Europe on the occurrence of B. burgdorferi s.l. in tissues of red foxes in Germany [31,32], Romania [33], Norway [34] and Poland [35]. Results of our study showed that the prevalence of Borrelia spp. was 2.0% and B. garinii was the only species detected in red foxes in this survey. Borrelia garinii was also solely noticed in foxes in Germany, but the recorded prevalence was much higher—24% [31]. In Poland, the analysis of tissues of 243 animals showed that 23.5% of them contained DNA of Borrelia spp., whereas B. garinii was identified in 91% of the infected foxes [35]. On the other hand, only B. afzelii and B. burgdorferi were detected in tissues of red foxes in Romania [33].
5. Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the few and the most comprehensive studies undertaken to assess the importance of introduced and native carnivores in the ecology of Borrelia spp. worldwide. In all examined carnivore species, the occurrence of Borrelia was recorded. We identified B. afzelii (the most abundant genospecies), B. garinii and B. burgdorferi in studied animals. The highest level of Borrelia prevalence estimated in raccoons suggests they can play a role as reservoir hosts for these spirochaetal bacteria. The significance of invasive species is worth further analysis, with special reference to the circulation of vector-borne pathogens as well as in the context of the “dilution effect” hypothesis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H., A.P-M.; methodology, J.H., K.B.-G.; material collection, M.P.; molecular study, K.J., K.B-G.; results analysis; J.H., K.B.-G., A.P-M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H., K.J., K.B.-G., A.P.-M., writing—review and editing, J.H., A.P.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was partially financed by the National Science Centre, Poland, under the MINIATURA-2 project (grant no. 2018/02/X/NZ6/01983).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The approval of the Ethics Committee was not required because the material for the research was obtained from the predator control operation.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The carnivores’ carcasses were collected during the predator control operation conducted as a part of the program to reintroduce the capercaillie (Tetrao urogallus) in the Lower Silesian Forest, financed by the European Commission, the National Fund for Environmental Protection and Water Management and the Polish State Forests (grant LIFE11 NAT/PL/428). We are grateful to Janusz Kobielski, Head of the Ruszów Forest District, and Dorota Merta for their help in collecting the material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wolcott, K.A.; Margos, G.; Fingerle, V.; Becker, N.S. Host association of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato: A review. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalca, A.D.; Sándor, A.D. The role of rodents in the ecology of Ixodes ricinus and associated pathogens in Central and Eastern Europe. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmeester, T.R.; Coipan, E.C.; van Wieren, S.E.; Prins, H.H.T.; Takken, W.; Sprong, H. Few vertebrate species dominate the Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. life cycle. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Răileanu, C.; Silaghi, C.; Fingerle, V.; Margos, G.; Thiel, C.; Pfister, K.; Overzier, E. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in questing and engorged ticks from different habitat types in southern Germany. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, R.S.; Keesing, F. Biodiversity and disease risk: The case of Lyme disease. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, R.S.; Keesing, F. The function of biodiversity in the ecology of vector-borne zoonotic diseases. Can. J. Zool. 2000, 78, 2061–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civitello, D.J.; Cohen, J.; Fatima, H.; Halstead, N.T.; Liriano, J.; McMahon, T.A.; Ortega, C.N.; Sauer, E.L.; Sehgal, T.; Young, S.; et al. Biodiversity inhibits parasites: Broad evidence for the dilution effect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8667–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuda, K. Kleszcze (Acari: Ixodida) Polski. II. Systematyka i Rozmieszczenie; Polish Parasitological Society: Warsaw, Poland, 1993. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette, J.; Apperson, C.S.; Howard, P.; Evans, T.L.; Levine, J.F. Tick-raccoon associations and the potential for Lyme disease spirochete transmission in the coastal plain of North Carolina. J. Wildl. 1997, 33, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodecka, B.; Michalik, J.; Lane, R.S.; Nowak-Chmura, M.; Wierzbicka, A. Differential associations of Borrelia species with European badgers (Meles meles) and raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in western Poland. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeester, T.R.; Krawczyk, A.I.; van Leeuwen, A.D.; Fonville, M.; Montizaan, M.G.; van Den Berge, K.; Gouwy, J.; Ruyts, S.C.; Verheyen, K.; Sprong, H. Role of mustelids in the life-cycle of ixodid ticks and transmission cycles of four tick-borne pathogens. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherman, C.M.; Sándor, A.D.; Kalmár, Z.; Marinov, M.; Mihalca, A.D. First report of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in two threatened carnivores: The Marbled polecat, Vormela peregusna and the European mink, Mustela lutreola (Mammalia: Mustelidae). BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbobaniyi, A. Badgers (Meles meles) as Reservoirs of Vector-Borne Infections in the UK. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Salford, Salford, UK, 2018; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Karbowiak, G.; Stanko, M.; Miterpaková, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Víchová, B. Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) parasitizing red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Slovakia and new data about subgenus Pholeoixodes occurrence. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, K.; Jerzak, L.; Tryjanowski, P. Zwierzęta Konfliktowe w Miastach; Regionalna Dyrekcja Ochrony Środowiska: Warsaw, Poland, 2016. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.A.; Castellanos, A.A.; Schmidt, J.P.; Fischhoff, I.R.; Drake, J.M. The ecology of zoonotic parasites in the Carnivora. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 1096–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perec-Matysiak, A.; Leśniańska, K.; Buńkowska-Gawlik, K.; Merta, D.; Popiołek, M.; Hildebrand, J. Zoonotic genotypes of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in wild living invasive and native carnivores in Poland. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, J.; Perec-Matysiak, A.; Popiołek, M.; Merta, D.; Myśliwy, I.; Buńkowska-Gawlik, K. A molecular survey of spotted fever group rickettsiae in introduced raccoons (Procyon lotor). Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamšíková, Z.; Coipan, C.; Mahríková, L.; Minichová, L.; Sprong, H.; Kazimírová, M. Borrelia miyamotoi and co-infection with Borrelia afzelii in Ixodes ricinus ticks and rodents from Slovakia. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodecka, B.; Leońska, A.; Skotarczak, B. A comparative analysis of molecular markers for the detection and identification of Borrelia spirochetes in Ixodes ricinus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coipan, E.C.; Jahfari, S.; Fonville, M.; Oei, G.A.; Spanjaard, L.; Takumi, K.; Hovius, J.W.; Sprong, H. Imbalanced presence of Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. multilocus sequence types in clinical manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 42, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coipan, E.C.; Fonville, M.; Tijsse-Klasen, E.; van der Giessen, J.W.; Takken, W.; Sprong, H.; Takumi, K. Geodemographic analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato using the 5S-23S rDNA spacer region. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 17, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnarelli, L.A.; Oliver, J.H.; Hutcheson, H.J.; Anderson, J.F. Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in deer and raccoons. J. Wildl. Dis. 1991, 27, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabsley, M.J.; Murphy, S.M.; Luttrell, M.P.; Little, S.E.; Massung, R.F.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Conti, L.A.; Blackmore, C.G.; Durden, L.A. Experimental and field studies on the suitability of raccoons (Procyon lotor) as hosts for tick-borne pathogens. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2008, 8, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellaw, A.H.; Chenney, E.F.; Varela Stokes, A.S. Tick borne disease agents in various wildlife from Mississippi. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 1, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myśliwy, I.; Perec-Matysiak, A.; Hildebrand, J. Invasive raccoon (Procyon lotor) and raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) as potential reservoirs of tick-borne pathogens: Data review from native and introduced areas. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufts, D.M.; Goodman, L.B.; Benedict, M.C.; Davis, A.D.; van Acker, M.C.; Diuk-Wasser, M. Association of the invasive Haemaphysalis longicornis tick with vertebrate hosts, other native tick vectors, and tick-borne pathogens in New York City, USA. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Kabeya, H.; Fujita, H.; Makino, T.; Asano, M.; Inoue, S.; Inokuma, H.; Nogami, S.; Maruyama, S. Serological survey of five zoonoses, scrub typhus, Japanese spotted fever, tularemia, Lyme disease, and Q fever, in feral raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Japan. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.K.; Lim, J.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, I.Y. Redescription of Haemaphysalis flava and Ixodes tanuki collected from a raccoon dog in Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 1997, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gern, L.; Sell, K. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato from the skin of the European badger (Meles meles) in Switzerland. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, G.; Dimpfl, B.; Finkbeiner-Weber, B.; Liebisch, A.; Frosch, M. The red fox (Vulpes vulpes) a reservoir competent host for Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Tick-Borne Pathogens at the Host-Vector Interface: A Global Perspective, Kruger National Park, South Africa, 28 August–1 September 1995; p. 238. [Google Scholar]
- Heidrich, J.; Schönberg, A.; Steuber, S.; Nöckler, K.; Schulze, P.; Voigt, W.P.; Schein, E. Investigation of skin samples from red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in eastern Brandenburg (Germany) for the detection of Borrelia burgdorferi s. l. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. 1999, 289, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrache, M.O.; Matei, I.A.; Ionică, A.M.; Kalmár, Z.; D’Amico, G.; Sikó-Barabási, S.; Ionescu, D.T.; Gherman, C.M.; Mihalca, A.D. Molecular detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato genospecies in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Romania. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysterud, A.; Stigum, V.M.; Jaarsma, R.I.; Sprong, H. Genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato detected in 16 mammal species and questing ticks from northern Europe. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodecka, B.; Michalik, J.; Grochowalska, R. Red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) are exposed to high diversity of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato species infecting fox-derived Ixodes ticks in West-Central Poland. Pathogens 2022, 11, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).