Intraguild Competition between Endangered Kit Foxes and a Novel Predator in a Novel Environment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
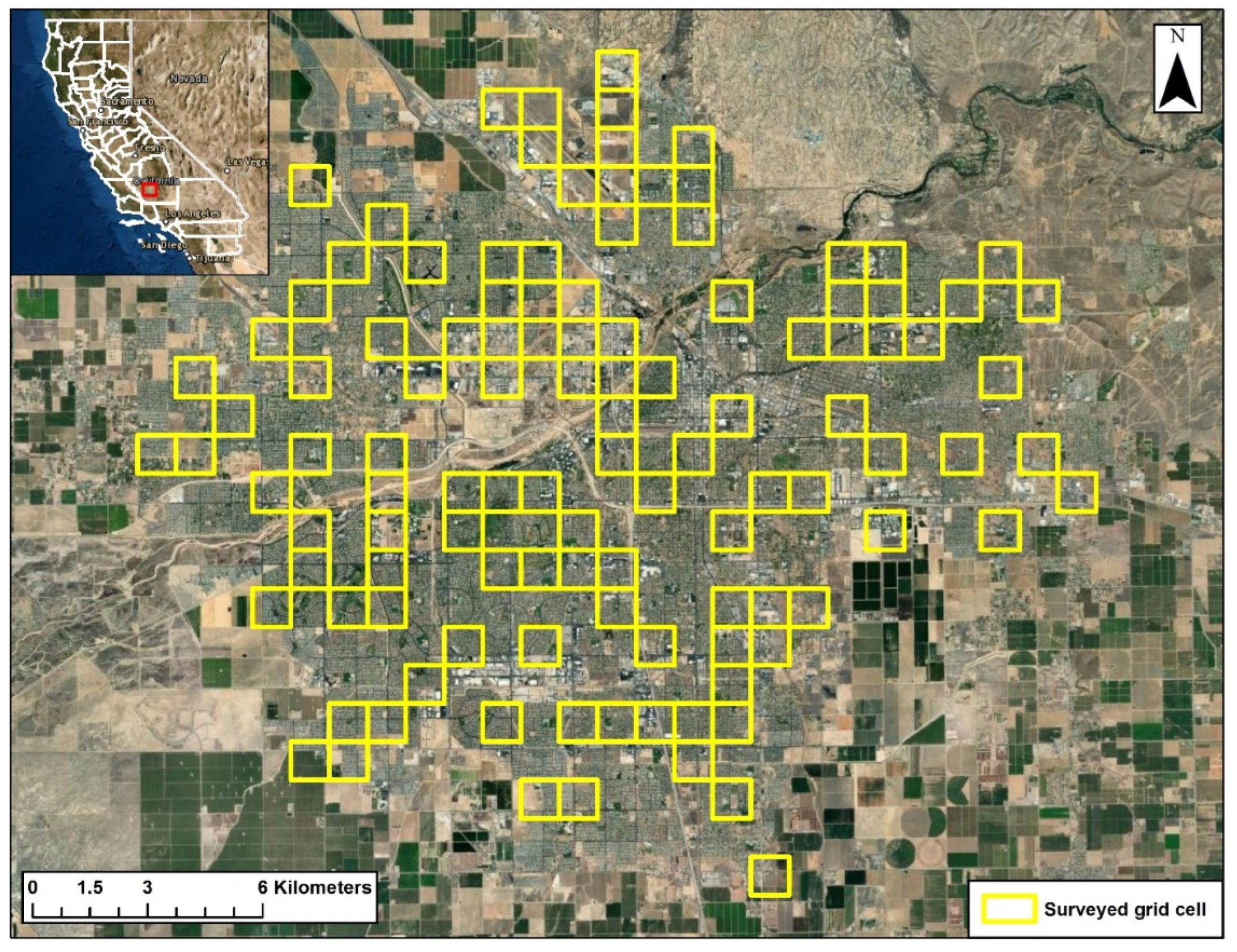
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Food Item Use
2.3. Red Fox Den Use
2.4. Spatial Overlap
2.5. Habitat Attributes
3. Results
3.1. Food Item Use
3.2. Red Fox Den Use
3.3. Spatial Overlap
3.4. Habitat Attributes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cypher, B.L.; Phillips, S.E.; Kelly, P.A. Quantity and distribution of suitable habitat for endangered San Joaquin kit foxes: Conservation implications. Canid Biol. Cons. 2013, 16, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Germano, D.J.; Rathbun, G.B.; Saslaw, L.R.; Cypher, B.L.; Cypher, E.A.; Vredenburgh, L.M. The San Joaquin desert of California: Ecologically misunderstood and overlooked. Nat. Areas J. 2011, 31, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Recovery Plan for Upland Species of the San Joaquin Valley, California; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Region 1: Portland, OR, USA, 1998.
- Cypher, B.L.; Van Horn Job, C.L. Management and conservation of San Joaquin kit foxes in urban environments. Proc. Vert. Pest Conf. 2012, 25, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cypher, B.L. Kit foxes. In Urban Carnivores: Ecology, Conflict, and Conservation; Gehrt, S.D., Riley, S.P.D., Cypher, B.L., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Cypher, B.L.; Deatherage, N.A.; Westall, T.L.; Kelly, E.C.; Phillips, S.E. Potential habitat and carrying capacity of endangered San Joaquin kit foxes in an urban environment: Implications for conservation and recovery. Urb. Ecosyst. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Species Status Assessment Report for the San Joaquin Kit Fox (Vulpes Macrotis Mutica); U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2020.
- Lewis, J.C.; Sallee, K.L.; Golighty, R.T., Jr. Introduction and range expansion of nonnative red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in California. Am. Midland Nat. 1999, 142, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinnell, J.; Dixon, J.S.; Linsdale, J.M. Furbearing Mammals of California; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Larivière, S.; Pasitschniak-Arts, M. Vulpes vulpes . Mammal. Species 1996, 537, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypher, B.L. Foxes. In Wild Mammals of North America: Biology, Management, and Conservation, 2nd ed.; Feldhamer, G.A., Thompson, B.C., Chapman, J.A., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 511–546. [Google Scholar]
- Zembal, R. Status and management of light-footed clapper rails in coastal southern California. Trans. West. Sect. Wildl. Soc. 1992, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cypher, B.L.; Clark, H.O., Jr.; Kelly, P.A.; Van Horn Job, C.; Warrick, G.W.; Williams, D.F. Interspecific interactions among mammalian predators: Implications for the conservation of endangered San Joaquin kit foxes. End. Species Update 2001, 18, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.; Caro, T. Interspecific competition and predation in American carnivore families. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2008, 20, 295–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralls, K.; White, P.J. Predation on San Joaquin kit foxes by larger canids. J. Mammal. 1995, 76, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.O., Jr.; Warrick, G.D.; Cypher, B.L.; Kelly, P.A.; Williams, D.F.; Grubbs, D.E. Competitive interactions between endangered kit foxes and nonnative red foxes. West. N. Am. Nat. 2005, 65, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Cypher, B.L.; Spencer, K.A. Competitive interactions between San Joaquin kit foxes and coyotes. J. Mammal. 1998, 79, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, G.D.; Clark, H.O., Jr.; Kelly, P.A.; Williams, D.F.; Cypher, B.L. Use of agricultural lands by San Joaquin kit foxes. West. N. Am. Nat. 2007, 67, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deatherage, N.A.; Cypher, B.L.; Westall, T.L.; Kelly, E.C. Spatiotemporal patterns of San Joaquin kit foxes and an urban canid guild. West. N. Am. Nat. 2022, 82, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work Population Review 2022, Bakersfield, California Population. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/us-cities/bakersfield-ca-population (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Bakersfield, California, Monthly Rainfall by Water Year 1889–Present. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Weather Service. Available online: https://www.wrh.noaa.gov/hnx/bfl/normals/bflh2oyr.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Moore, T.D.; Spence, L.E.; Dugnolle, C.E. Identification of the Dorsal Hairs of Some Animals of Wyoming; Wyoming Game and Fish Department: Cheyenne, WY, USA, 1974.
- Glass, B.P. Key to the Skulls of North American Mammals; Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Roest, A.I. A Key-Guide to Mammal Skulls and Lower Jaws; Mad River Press: Eureka, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, J.E.; Zar, J.H. Field and Laboratory Methods for General Ecology; Wm. C. Brown Publishers: Dubuque, IA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Cypher, B.L.; Rudd, J.L.; Westall, T.L.; Woods, L.W.; Stephenson, N.; Foley, J.E.; Richardson, D.; Clifford, D.L. Sarcoptic mange in endangered kit foxes: Case histories, diagnoses, and implications for conservation. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westall, T.L.; Cypher, B.L. Latency to first detection of kit foxes (Vulpes macrotis) during camera surveys. Canid Biol. Cons. 2017, 20, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Deatherage, N.A.; Cypher, B.L.; Murdoch, J.; Westall, T.L.; Kelly, E.C.; Germano, D.J. Urban landscape attributes affect occupancy patterns of the San Joaquin kit fox during an epizootic. Pacific Cons. Biol. 2021, 27, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Model Selection and Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Royall, R.M. Statistical Evidence: A Likelihood Paradigm; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch, J.D.; Munkhzul, T.; Buyandelger, S.; Reading, R.P.; Sillero-Zubiri, C. Seasonal food habits of corsac and red foxes in Mongolia and the potential for competition. Mammal. Biol. 2010, 75, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersteinsson, P.; Macdonald, D.W. Interspecific competition and the geographical distribution of red and arctic foxes Vulpes vulpes and Alopex lagopus. Oikos 1992, 64, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmhagen, B.; Tannerfeldt, M.; Angerbjorn, A. Food-niche overlap between arctic and red foxes. Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frafjord, K. Ecology and use of arctic fox Alopex lagopus dens in Norway: Tradition overtaken by interspecific competition? Biol. Cons. 2003, 111, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickney, A.; Obritschkewitsch, T.; Burgess, R. Shifts in fox den occupancy in the Greater Prudhoe Bay Area, Alaska. Arctic 2014, 67, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypher, B.L.; Murdoch, J.D.; Brown, A.D. Artificial dens for the conservation of San Joaquin kit foxes. Calif. Fish Wildl. J. 2021, Special CESA Issue, 416–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J.; Berry, W.H.; Eliason, J.J.; Hanson, M.T. Catastrophic decrease in an isolated population of kit foxes. Southwest. Nat. 2000, 45, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, F.; Caro, T.M. Interspecific killing among mammalian carnivores. Am. Nat. 1999, 153, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdoch, J.D.; Munkhzul, T.; Buyandelger, S.; Sillero-Zubiri, C. Survival and cause-specific mortality of Corsac and red foxes in Mongolia. J. Wildl. Manag. 2010, 74, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersteinsson, P.; Angerbjörn, A.; Frafjord, K.; Kaikusalo, A. The arctic fox in Fennoscandia and Iceland: Management problems. Biol. Cons. 1989, 49, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frafjord, K.; Becker, D.; Angerbjörn, A. Interactions between arctic and red foxes in Scandinavia—Predation and aggression. Arctic 1989, 42, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannerfeldt, M.; Elmhagen, B.; Angerbjörn, A. Exclusion by interference competition? The relationship between red and arctic foxes. Oecologia 2002, 132, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamperin, N.J.; Follmann, E.H.; Petersen, B. Interspecific killing of an arctic fox by a red fox at Prudhoe Bay, Alaska. Arctic 2006, 59, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, S.; Killengreen, S.T.; Henden, J.-A.; Yoccoz, N.G.; Ims, R.A. Disentangling the importance of interspecific competition, food availability, and habitat in species occupancy: Recolonization of the endangered Fennoscandian arctic fox. Biol. Cons. 2013, 160, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Rodrigues, C.W.; Gallant, D.; Roth, J.D.; Berteaux, D. Red foxes at their northern edge: Competition with the Arctic fox and winter movements. J. Mammal. 2022, 103, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjurlin, C.D.; Cypher, B.L.; Wingert, C.M.; Van Horn Job, C.L. Urban Roads and the Endangered San Joaquin Kit Fox; California State University-Stanislaus, Endangered Species Recovery Program: Fresno, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Westall, T.L.; Cypher, B.L.; Ralls, K.; Germano, D.J. Raising pups of urban San Joaquin kit fox: Relative roles of adult group members. West. N. Am. Nat. 2019, 79, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Road | Any paved public road carrying vehicular traffic |
| Res | Residential areas including single-family and multi-family housing |
| Und | Undeveloped parcels of various sizes within the urban landscape |
| Ind | Industrial areas including refineries, manufacturing facilities, and pipe and equipment storage yards |
| Park | Parks and green spaces such as city parks, recreational areas, golf courses, and cemeteries |
| Camp | Campuses including schools, churches, and large medical centers |
| Com | Commercial areas including office buildings, hotels, shopping centers, restaurants, and other businesses |
| Item | Frequency of Occurrence (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Kit Foxes (n = 720 Scats) | Red Foxes (n = 763 Scats) | |
| Mammals | ||
| Pocket gopher | 7.4 | 31.9 |
| California ground squirrel | 10.7 | 21.9 |
| Deer mouse | 0.3 | - |
| Rat | - | 0.1 |
| Kangaroo rat | - | 0.1 |
| Pocket mouse | - | 0.3 |
| Leporid | 2.2 | 3.4 |
| Cat | - | 0.1 |
| Kit fox | - | 0.1 |
| Birds | ||
| Unidentified bird | 14.0 | 16.0 |
| Reptiles | ||
| Unidentified lizard | 0.3 | 0.7 |
| Unidentified snake | 0.7 | 3.9 |
| Invertebrates | ||
| Jerusalem cricket | - | 0.1 |
| Grasshopper | 0.3 | - |
| Cricket | - | 0.4 |
| Cockroach | 1.8 | - |
| Beetle | 13.1 | 26.2 |
| Arachnid | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| Solpugid | - | 0.1 |
| Anthropogenic materials | ||
| Food wrappers | 22.9 | 12.2 |
| Model | Model 1 | −2LL 2 | K 3 | AICc 4 | ΔAICc | Wi 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Troad + Tres + Tund + Tcom + Tind + Tcamp + Tpark | 170.245 | 9 | 188.8766 | 0 | 0.3644 |
| 2 | Tres + Tund + Tcom + Tind + Tcamp + Tpark | 172.919 | 8 | 189.4225 | 0.5459 | 0.2773 |
| 3 | Troad + Tres + Tund + Tcom + Tind + Tpark | 174.489 | 8 | 190.9925 | 2.1159 | 0.1265 |
| 4 | Tres + Tund + Tcom + Tind + Tcamp | 177.718 | 7 | 192.1082 | 3.2317 | 0.0724 |
| 5 | Troad + Tres + Tund + Tcom + Tind + Tcamp | 176.975 | 8 | 193.4785 | 4.6019 | 0.0365 |
| Parameter Importance Weights | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troad | Tres | Tund | Tcom | Tind | Tcamp | Tpark | |
| Model 1 | 0.3644 | 0.3644 | 0.3644 | 0.3644 | 0.3644 | 0.3644 | 0.3644 |
| Model 2 | 0 | 0.2773 | 0.2773 | 0.2773 | 0.2773 | 0.2773 | 0.2773 |
| Model 3 | 0.1265 | 0.1265 | 0.1265 | 0.1265 | 0.1265 | 0 | 0.1265 |
| Model 4 | 0 | 0.0724 | 0.0724 | 0.0724 | 0.0724 | 0.0724 | 0 |
| Model 5 | 0.0365 | 0.0365 | 0.0365 | 0.0365 | 0.0365 | 0.0365 | 0 |
| Total weight | 0.5274 | 0.8771 | 0.8771 | 0.8771 | 0.8771 | 0.7506 | 0.7682 |
| Parameter | β | S.E. | Wald | df | p | Exp(β) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troad | 4.040 | 2.537 | 2.535 | 1 | 0.111 | 56.815 |
| Tres | 7.164 | 2.083 | 11.832 | 1 | <0.01 | 1291.714 |
| Tund | 6.380 | 2.137 | 8.911 | 1 | 0.003 | 589.966 |
| Tcom | −2.038 | 1.895 | 1.157 | 1 | 0.282 | 0.130 |
| Tind | 6.807 | 2.161 | 9.918 | 1 | 0.002 | 903.782 |
| Tcamp | −3.395 | 1.754 | 3.747 | 1 | 0.053 | 0.034 |
| Tpark | 5.109 | 2.014 | 6.435 | 1 | 0.011 | 165.454 |
| Intercept | −12.630 | 3.772 | 11.209 | 1 | <0.01 | 0.000 |
| % Cell Composition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attribute | Kit Fox | Red Fox | t | df | p |
| Road | 21.0 | 19.1 | −0.933 | 293 | 0.352 |
| Residential | 37.5 | 41.9 | 0.952 | 293 | 0.342 |
| Undeveloped | 19.4 | 20.4 | 0.250 | 293 | 0.803 |
| Commercial | 5.0 | 2.8 | −1.623 | 293 | 0.106 |
| Industrial | 6.3 | 8.9 | 1.207 | 293 | 0.229 |
| Campus | 5.2 | 1.9 | −2.563 | 293 | 0.011 |
| Park/green space | 3.6 | 4.1 | 0.472 | 293 | 0.637 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cypher, B.L.; Deatherage, N.A.; Westall, T.L.; Kelly, E.C. Intraguild Competition between Endangered Kit Foxes and a Novel Predator in a Novel Environment. Animals 2022, 12, 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202727
Cypher BL, Deatherage NA, Westall TL, Kelly EC. Intraguild Competition between Endangered Kit Foxes and a Novel Predator in a Novel Environment. Animals. 2022; 12(20):2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202727
Chicago/Turabian StyleCypher, Brian L., Nicole A. Deatherage, Tory L. Westall, and Erica C. Kelly. 2022. "Intraguild Competition between Endangered Kit Foxes and a Novel Predator in a Novel Environment" Animals 12, no. 20: 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202727
APA StyleCypher, B. L., Deatherage, N. A., Westall, T. L., & Kelly, E. C. (2022). Intraguild Competition between Endangered Kit Foxes and a Novel Predator in a Novel Environment. Animals, 12(20), 2727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202727







