Investigation of Parasitic Infection in Crocodile Lizards (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) Using High-Throughput Sequencing
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. PCR Amplification and DNA Sequencing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
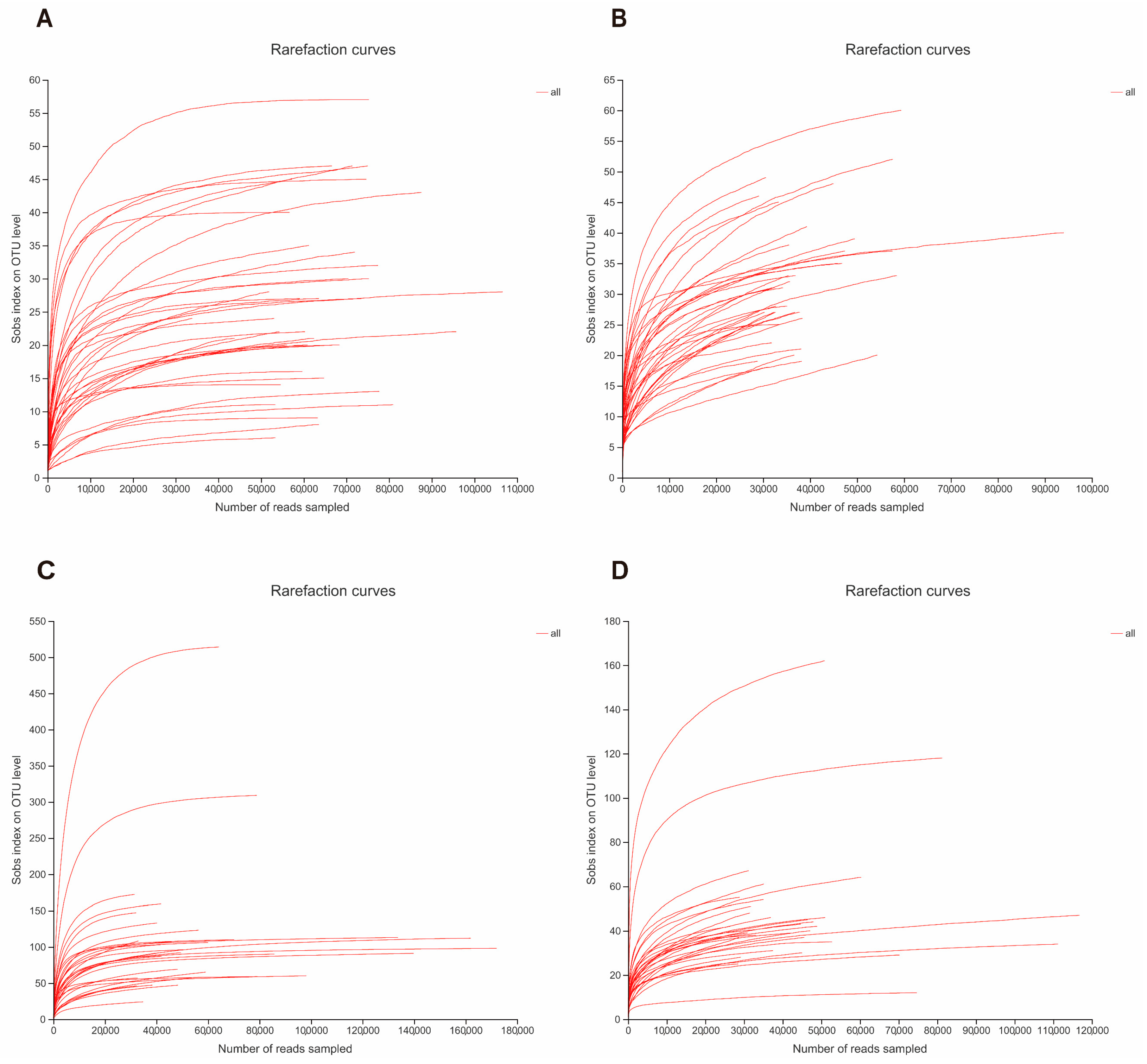
3.1. Observed Rarefaction Curves
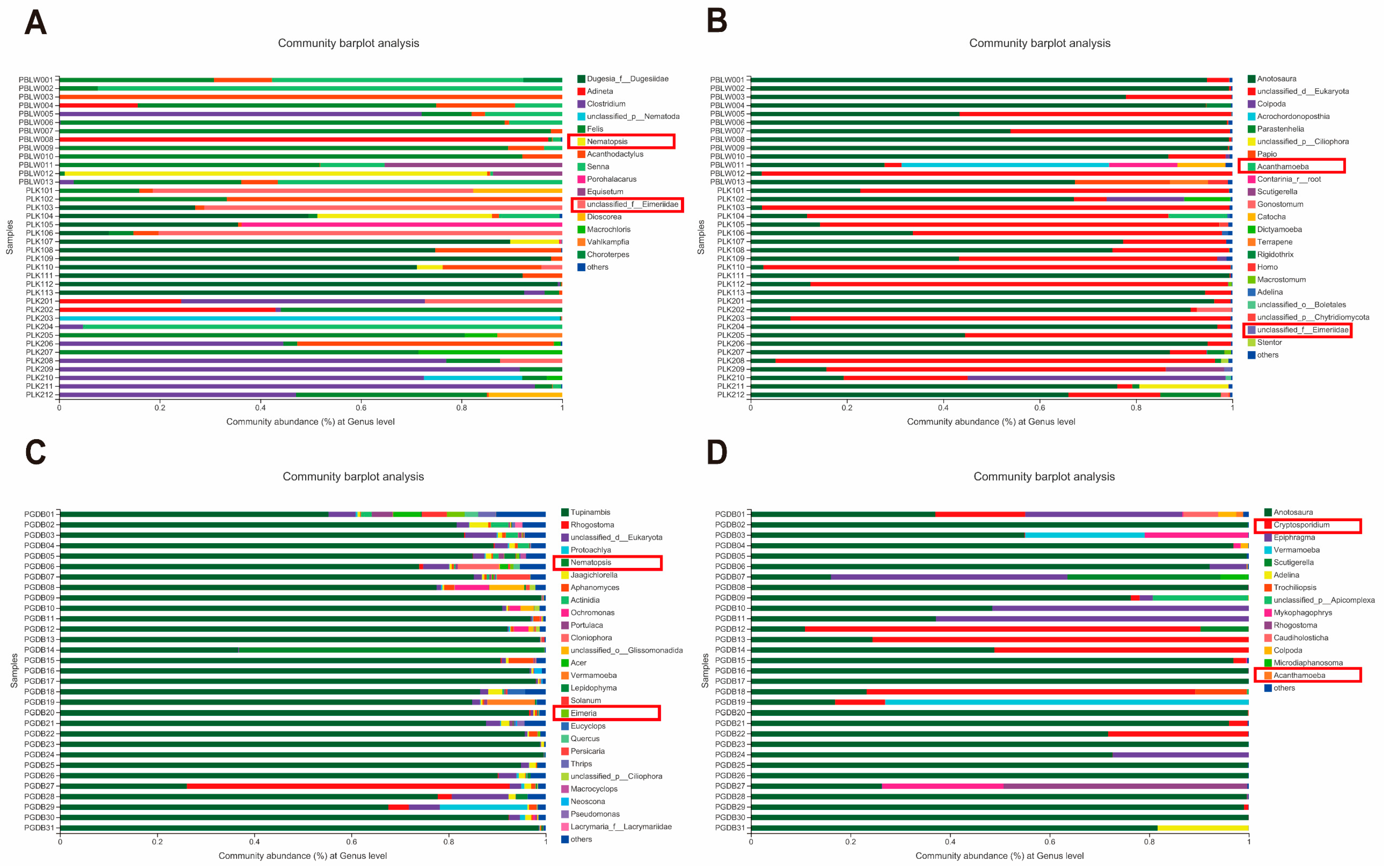
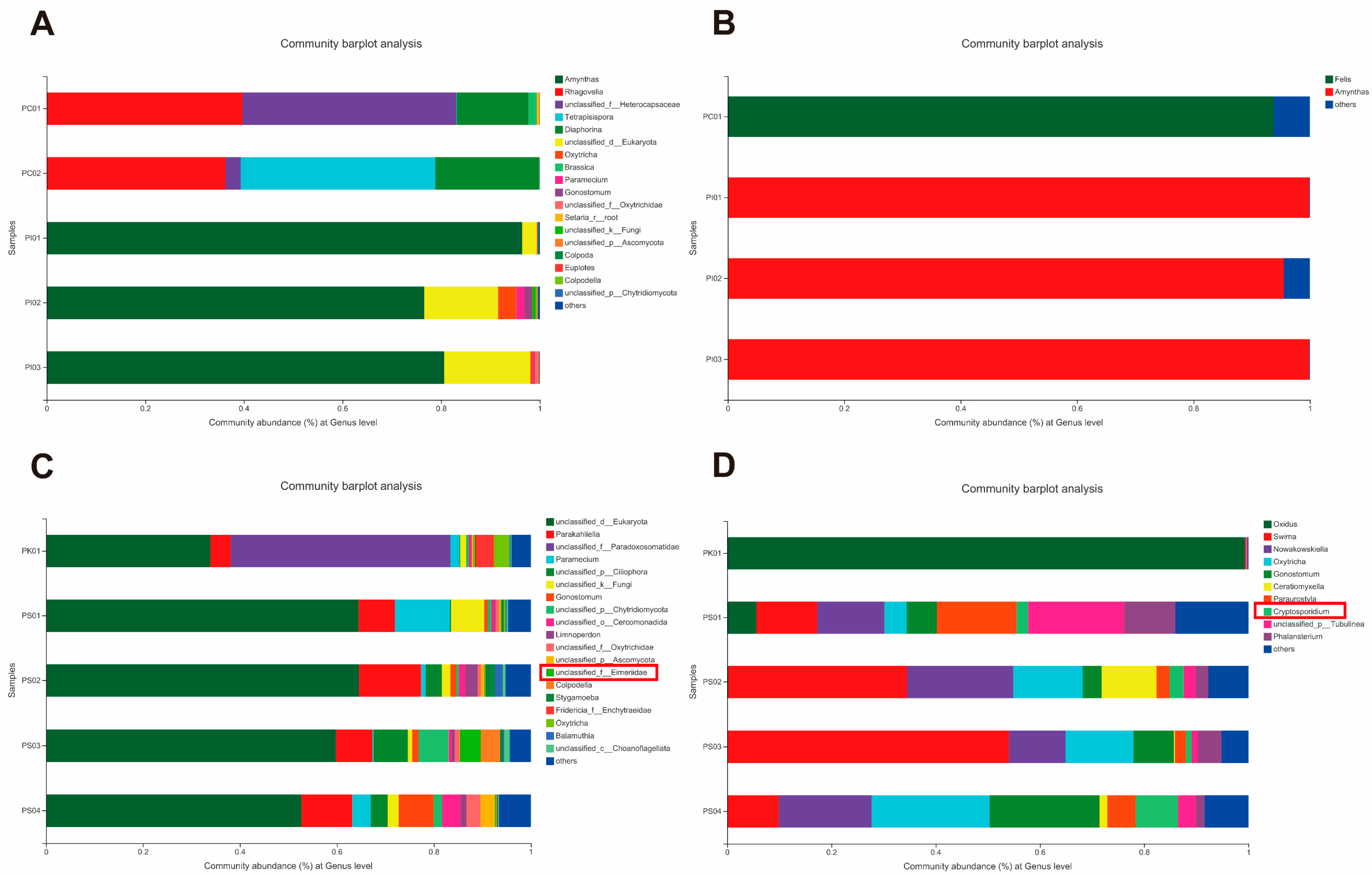
3.2. Analysis of Parasite Community Composition
3.3. Analysis of Parasitic Infection
3.4. Source of Crocodile Lizard Parasites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Redford, K.H.; Segre, J.A.; Salafsky, N.; del Rio, C.M.; McAloose, D. Conservation and the Microbiome. Conserv. Biol. 2012, 26, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rull, V. Biodiversity crisis or sixth mass extinction? Does the current anthropogenic biodiversity crisis really qualify as a mass extinction? EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, C.J. Preserving Australian native fauna: Zoo-based breeding programs as part of a more unified strategic approach. Aust. J. Zool. 2013, 61, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, N.F.R.; Derrickson, S.R.; Beissinger, S.R.; Wiley, J.W.; Smith, T.B.; Toone, W.D.; Miller, B. Limitations of Captive Breeding in Endangered Species Recovery. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratti, G.; Stranieri, A.; Giordano, A.; Oltolina, M.; Bonacina, E.; Magnone, W.; Morici, M.; Ravasio, G.; Paltrinieri, S.; Lauzi, S. Molecular Detection of Feline Coronavirus in Captive Non-Domestic Felids from Zoological Facilities. Animals 2022, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Wu, Q.; Qin, X.; Yang, C.; Luo, S.; He, J.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, Z. Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the Skin Ulcer Disease of Crocodile Lizards (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) and Probiotics as the Control Measure. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 850684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Ma, J.E.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, L.M.; He, N.; Liu, H.Y.; Luo, S.Y.; Wu, Z.J.; Han, R.C.; et al. Diets Alter the Gut Microbiome of Crocodile Lizards. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schingen, M.; Minh Duc, L.; Hanh Thi, N.; Cuong The, P.; Quynh Quy, H.; Truong Quang, N.; Ziegler, T. Is there more than one Crocodile Lizard? An Integrative Taxonomic Approach Reveals Vietnamese and Chinese Shinisaurus crocodilurus Represent Separate Conservation and Taxonomic Units. Zool. Gart. 2016, 85, 240–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheelings, T.F.; Lightfoot, D.; Holz, P. Prevalence of Salmonella in Australian reptiles. J. Wildl. Dis. 2011, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.S.; Liang, X.X.; Yang, M.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Chen, J.P.; Du, W.G.; Li, H.; Sun, B.J. Captivity Influences Gut Microbiota in Crocodile Lizards (Shinisaurus crocodilurus). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, L.M.; Ma, J.G.; He, N.; Liu, H.Y.; Han, R.C.; Li, H.M.; Wu, Z.J.; Chen, J.P. Identification of Austwickia chelonae as cause of cutaneous granuloma in endangered crocodile lizards using metataxonomics. Peerj 2019, 7, e6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Lin, L.B.; Huang, M.W.; Zang, Y.A.; Chen, J.P. Genome Sequence of Morganella morganii DG56-16, Isolated from Shinisaurus crocodilurus. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01301–e01318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norval, G.; Ross, K.E.; Sharrad, R.D.; Gardner, M.G. Taking stock: A review of the known parasites of the sleepy lizard, Tiliqua rugosa (Gray, 1825), a common lizard endemic to Australia. Trans. R. Soc. South Aust. 2019, 143, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.; Paparini, A.; Jian, F.C.; Robertson, I.; Ryan, U. Public health significance of zoonotic Cryptosporidium species in wildlife: Critical insights into better drinking water management. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Wildl. 2016, 5, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownstein, D.G.; Strandberg, J.D.; Montali, R.J.; Bush, M.; Fortner, J. Cryptosporidium in snakes with hypertrophic gastritis. Vet. Pathol. 1977, 14, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Rea, J.; Gonzalez-Morales, J.C.; Fajardo, V.; Megia-Palma, R.; Bastiaans, E.; Manjarrez, J. Phenological variation in parasite load and inflammatory response in a lizard with an asynchronous reproductive cycle. Sci. Nat. 2022, 109, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, M.J.; Smallridge, C.J.; Bull, C.M.; Komdeur, J. Susceptibility to infection by a haemogregarine parasite and the impact of infection in the Australian sleepy lizard Tiliqua rugosa. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, A.; Maruyama, H.; Kikuchi, T. A novel method to assess the biodiversity of parasites using 18S rDNA Illumina sequencing; parasitome analysis method. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, R.; Hino, A.; Tsai, I.J.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Yoshida, A.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Maruyama, H.; Kikuchi, T. Assessment of Helminth Biodiversity in Wild Rats Using 18S rDNA Based Metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiang, J.H.; Shahzad, M.; Zhang, H.; Mehmood, K.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, X.D.; Luo, H.Q.; Tong, X.L.; Li, J.K. Revealing the parasitic infection in diarrheic yaks by piloting high-throughput sequencing. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylezich, C.; Caccio, S.M.; Walochnik, J.; Beer, M.; Hoper, D. Untargeted metagenomics shows a reliable performance for synchronous detection of parasites. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porazinska, D.L.; Giblin-Davis, R.M.; Faller, L.; Farmerie, W.; Kanzaki, N.; Morris, K.; Powers, T.O.; Tucker, A.E.; Sung, W.; Thomas, W.K. Evaluating high-throughput sequencing as a method for metagenomic analysis of nematode diversity. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porazinska, D.L.; Sung, W.; Giblin-Davis, R.M.; Thomas, W.K. Reproducibility of read numbers in high-throughput sequencing analysis of nematode community composition and structure. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.H.; Kong, Q.Y.; Li, X.H.; Xu, W.X.; Mao, C.Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Song, W.B.; Huang, J. The Effects of DNA Extraction Kits and Primers on Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Community in Freshwater Sediments. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.M.; Chen, C.C.; Huffman, M.A. Entamoeba spp. in wild formosan rock macaques (Macaca Cyclopis) in an area with frequent human-macaque contact. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Goebel, B.M. Taxonomic Note: A Place for DNA-DNA Reassociation and 16S rRNA Sequence Analysis in the Present Species Definition in Bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1994, 44, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.X.; Colwell, R.K.; Chang, J. Estimating the species accumulation curve using mixtures. Biometrics 2005, 61, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.K.; Mao, C.X.; Chang, J. Interpolating, extrapolating, and comparing incidence-based species accumulation curves. Ecology 2004, 85, 2717–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.; Lewis, M.; Ostendorf, B. Additive partitioning of rarefaction curves: Removing the influence of sampling on species-diversity in vegetation surveys. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.J.; Zhong, X.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Xu, H.L. An approach to detecting species diversity of microfaunas in colonization surveys for marine bioassessment based on rarefaction curves. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 88, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Park, K.M.; Yang, E.J.; Joo, H.M.; Jeon, M.; Kang, S.H.; Choi, H.G.; Park, M.H.; Min, G.S.; Kim, S. Patchy-distributed ciliate (Protozoa) diversity of eight polar communities as determined by 454 amplicon pyrosequencing. Anim. Cells Syst. 2015, 19, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilio, G.; Koella, J.C. Sequential co-infections drive parasite competition and the outcome of infection. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabbott, N.A. The Influence of Parasite Infections on Host Immunity to Co-infection with Other Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L.; Su, X.Z.; Lu, F.L. The Roles of Type I Interferon in Co-infections With Parasites and Viruses, Bacteria, or Other Parasites. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Acremont, V.; Kilowoko, M.; Kyungu, E.; Philipina, S.; Sangu, W.; Kahama-Maro, J.; Lengeler, C.; Cherpillod, P.; Kaiser, L.; Genton, B. Beyond Malaria—Causes of Fever in Outpatient Tanzanian Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.L.; Zhang, V.; Werder, R.B.; Best, S.E.; Sebina, I.; James, K.R.; Faleiro, R.J.; Rivera, F.D.; Amante, F.H.; Engwerda, C.R.; et al. Coinfection with Blood-Stage Plasmodium Promotes Systemic Type I Interferon Production during Pneumovirus Infection but Impairs Inflammation and Viral Control in the Lung. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej-Sobocinska, M.; Demiaszkiewicz, A.W.; Pyziel, A.M.; Kowalczyk, R. Increased Parasitic Load in Captive-Released European Bison (Bison bonasus) has Important Implications for Reintroduction Programs. EcoHealth 2018, 15, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oosterhout, C.; Smith, A.M.; Hanfling, B.; Ramnarine, I.W.; Mohammed, R.S.; Cable, J. The guppy as a conservation model: Implications of parasitism and inbreeding for reintroduction success. Conserv. Biol. J. Soc. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, K.S.; Swan, R.A.; Morgan-Ryan, U.M.; Friend, J.A.; Elliot, A. Cryptosporidium muris infection in bilbies (Macrotis lagotis). Aust. Vet. J. 2003, 81, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Q.; Karim, M.R.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, L.X. Review on parasites of wild and captive giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca): Diversity, disease and conservation impact. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Wildl. 2020, 13, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiczigel, J.; Rozsa, L. Do small samples underestimate mean abundance? It depends on what type of bias we consider. Folia Parasitol. 2017, 64, 025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Luo, Y.H. Many Yaoshan crocodile lizards were discovered in the Daguishan Forest Farm’s Beilou branch. Guangxi For. 2003, 6, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Inclan-Rico, J.M.; Siracusa, M.C. First Responders: Innate Immunity to Helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.B.; Marshall, R.N.; La Ragione, R.M.; Catchpole, J. A new method for the experimental production of necrotic enteritis and its use for studies on the relationships between necrotic enteritis, coccidiosis and anticoccidial vaccination of chickens. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 90, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Fayer, R.; Ryan, U.; Upton, S.J. Cryptosporidium taxonomy: Recent advances and implications for public health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 72–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecker, N.J.; Braithwaite, S.L.; Topp, E.; Edge, T.; Lapen, D.R.; Wilkes, G.; Robertson, W.; Medeiros, D.; Sensen, C.W.; Neumann, N.F. Tracking host sources of Cryptosporidium spp. in raw water for improved health risk assessment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3945–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ning, J.J. Behavioral Time Budget and Diet of the Chinese Crocodile Lizard (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) in the Luokeng Nature Reserve, Guangdong. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.J.; Zeng, Z.G.; Xing, K.F.; Li, S.R.; Yang, C.S.; Du, W.G. Behavioural thermoregulation by the endangered crocodile lizard (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) in captivity. J. Therm. Biol. 2020, 93, 102731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Lopez, R.; Bourret, V.; Loiseau, C. Is Host Selection by Mosquitoes Driving Vector Specificity of Parasites? A Review on the Avian Malaria Model. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, P.G.; Hart, C.A.; Trees, A.J. In vitro activity of antimicrobial agents against the endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 47, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P. The Study on Scientific Raise and Management in Semi-Released and Reintroduce Nature Test of the Shinisaurus crocodilurus Ahl. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi Normal University, Guangxi, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Cao, X.F.; Deng, L.; Li, W.; Huang, X.M.; Lan, J.C.; Xiao, Q.C.; Zhong, Z.J.; Feng, F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Epidemiology of Cryptosporidium infection in cattle in China: A review. Parasite 2017, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, R.S.; Wang, X.J.; Huang, Y.; Mu, G.D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jia, H.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Han, X.G.; et al. Sheep as a Potential Source of Zoonotic Cryptosporidiosis in China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00086-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Wang, H.; Li, L.M.; Wu, Z.J.; Chen, J.P. Genetic Diversity and Population Demography of the Chinese Crocodile Lizard (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, R.A.; Knudsen, R.; Blasco-Costa, I.; Dunn, A.M.; Hytterod, S.; Hansen, H. Determinants of parasite distribution in Arctic charr populations: Catchment structure versus dispersal potential. J. Helminthol. 2019, 93, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumaine, J.E.; Tandel, J.; Striepen, B. Cryptosporidium parvum. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, C.D.; Reyes-Batlle, M.; Pinero, J.E.; Martinez-Carretero, E.; Valladares, B.; Streete, D.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Lindo, J.F. Isolation and molecular characterization of Acanthamoeba genotypes in recreational and domestic water sources from Jamaica, West Indies. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D.R.; Hoberg, E.P. How will global climate change affect parasite-host assemblages? Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.A.; Escobar, C.E. Potentially emergent vector-borne diseases in the Mediterranean and their possible relationship with climate change. Emergencias 2011, 23, 386–393. [Google Scholar]
- Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R. Effects of Climate and Climate Change on Vectors and Vector-Borne Diseases: Ticks Are Different. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couso-Perez, S.; Ares-Mazas, E.; Gomez-Couso, H. A review of the current status of Cryptosporidium in fish. Parasitology 2022, 149, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C.A.; Smith, A. Zoonotic enteric protozoa. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, R.M.; Davies, A.P. Minireview: Clinical cryptosporidiosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kik, M.J.L.; van Asten, A.; Lenstra, J.A.; Kirpensteijn, J. Cloaca prolapse and cystitis in green iguana (Iguana iguana) caused by a novel Cryptosporidium species. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimming, B.; Pattanatanang, K.; Sanyathitiseree, P.; Inpankaew, T.; Kamyingkird, K.; Pinyopanuwat, N.; Chimnoi, W.; Phasuk, J. Molecular Identification of Cryptosporidium Species from Pet Snakes in Thailand. Korean J. Parasitol. 2016, 54, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerace, E.; Lo Presti, V.D.M.; Biondo, C. Cryptosporidium Infection: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Differential Diagnosis. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 9, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanis, P.; Kourenti, C.; Smith, H. Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: A worldwide review of outbreaks and lessons learnt. J. Water Health 2007, 5, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Ryan, U.M.; Graczyk, T.K.; Limor, J.; Li, L.; Kombert, M.; Junge, R.; Sulaiman, I.M.; Zhou, L.; Arrowood, M.J.; et al. Genetic diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. in captive reptiles. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Qi, R.; Han, H.J.; Liu, J.W.; Qin, X.R.; Fang, L.Z.; Zhou, C.M.; Gong, X.Q.; Lei, S.C.; Yu, X.J. Molecular identification and phylogenetic analysis of Cryptosporidium, Hepatozoon and Spirometra in snakes from central China. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Wildl. 2019, 10, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketzis, J.K.; Vercruysse, J.; Stromberg, B.E.; Larsen, M.; Athanasiadou, S.; Houdijk, J.G.M. Evaluation of efficacy expectations for novel and non-chemical helminth control strategies in ruminants. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 139, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Infection Rate of Different Parasites (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Site | Sample Number | Positive Sample Number | Infection Rate (%) | Eimeria | Cryptosporidium | Nematopsis | Acanthamoeba |
| Gandong | 31 | 14 | 45.16 | 16.13 (5/31) | 38.71 (12/31) | 3.23 (1/31) | 6.45 (2/31) |
| Luokeng | 25 | 8 | 32.00 | 24.00 (6/25) | - | 12.00 (3/25) | 4.00 (1/25) |
| Beilou | 13 | 1 | 7.69 | - | - | 7.69 (1/13) | - |
| Total | 69 | 23 | 33.33 | 15.94 a (11/69) | 17.39 a (12/69) | 7.25 a (5/69) | 4.35 a (3/69) |
| Infection Rate of Different Parasites (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | Sample Number | Positive Sample Number | Infection Rate (%) | Eimeria | Cryptosporidium | Nematopsis | Acanthamoeba |
| Captive | 56 | 22 | 39.29 a | 19.64 (11/56) | 21.43 (12/56) | 7.14 (4/56) | 5.36 (3/56) |
| Wild | 13 | 1 | 7.69 a | - | - | 7.69 (1/13) | - |
| Infection Rate of Different Parasites (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locality | Sample Number | Positive Sample Number | Infection Rate (%) | Eimeria | Cryptosporidium | Nematopsis | Acanthamoeba |
| Daguishan | 44 | 15 | 34.09 | 11.36 (5/44) | 27.27 a (12/44) | 4.55 (2/44) | 4.55 (2/44) |
| Luokeng | 25 | 8 | 32.00 | 24.00 (6/25) | - | 12.00 (3/25) | 4.00 (1/25) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, C.; He, N.; He, J.; Luo, W.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z. Investigation of Parasitic Infection in Crocodile Lizards (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) Using High-Throughput Sequencing. Animals 2022, 12, 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202726
Zeng Y, Xiong Y, Yang C, He N, He J, Luo W, Chen Y, Zeng X, Wu Z. Investigation of Parasitic Infection in Crocodile Lizards (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) Using High-Throughput Sequencing. Animals. 2022; 12(20):2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202726
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Yongru, Yi Xiong, Chunsheng Yang, Nan He, Jiasong He, Wenxian Luo, Yaohuan Chen, Xiaochen Zeng, and Zhengjun Wu. 2022. "Investigation of Parasitic Infection in Crocodile Lizards (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) Using High-Throughput Sequencing" Animals 12, no. 20: 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202726
APA StyleZeng, Y., Xiong, Y., Yang, C., He, N., He, J., Luo, W., Chen, Y., Zeng, X., & Wu, Z. (2022). Investigation of Parasitic Infection in Crocodile Lizards (Shinisaurus crocodilurus) Using High-Throughput Sequencing. Animals, 12(20), 2726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12202726





