Equine Hepacivirus: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis of Serological and Biomolecular Prevalence and a Phylogenetic Update
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Equine Viral Hepatitis: Overview
2. Equine Hepacivirus (EqHV)
2.1. Classification
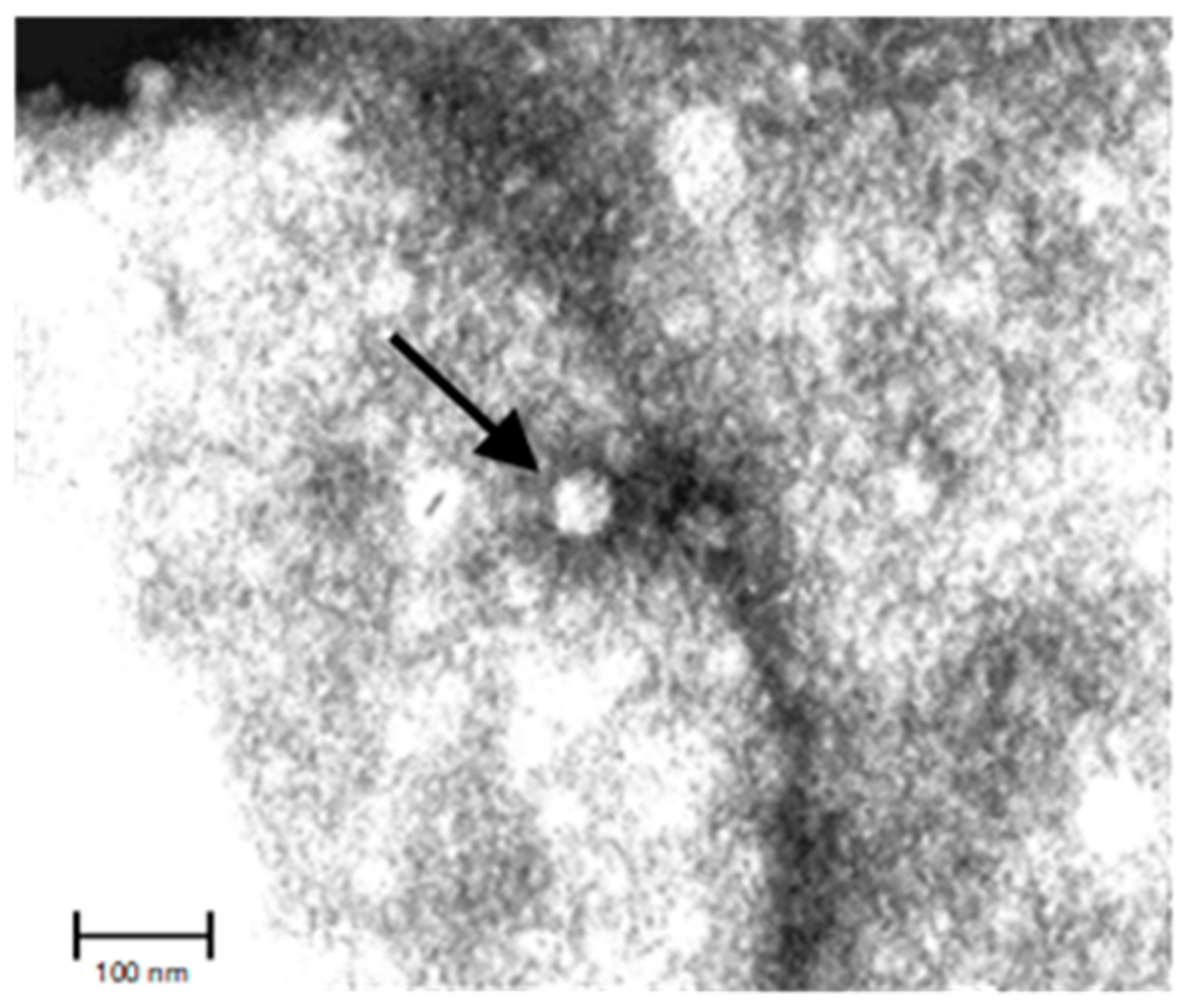
2.2. Viral Structure
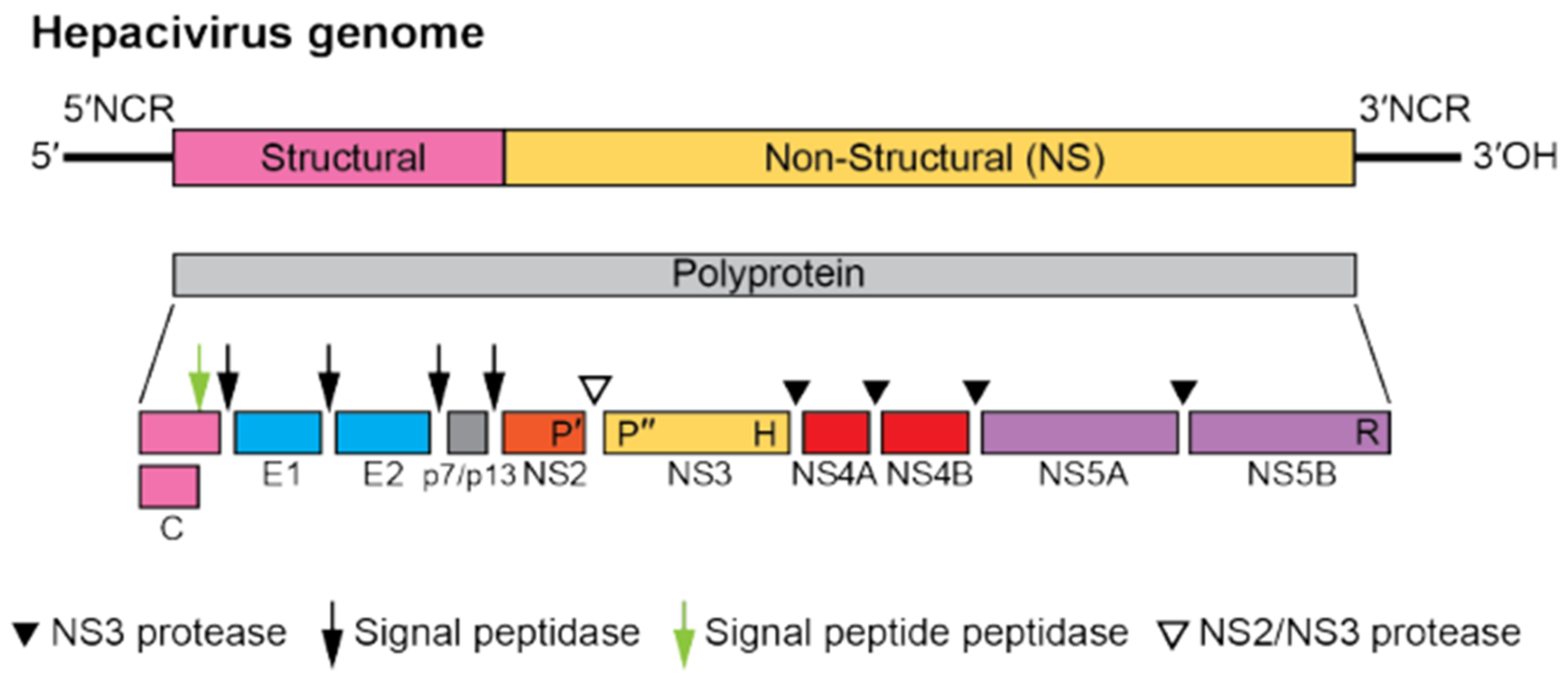
2.3. Viral Genome
2.4. Viral Replication
3. Epidemiology
3.1. Routes of Transmission
3.1.1. Vertical Transmission
3.1.2. Horizontal Transmission
3.1.3. Parenteral Transmission
The Relevance of Parenteral Transmission, Horse Serum, and Plasma
3.1.4. Other Routes of Transmission (Insect-Mediated and Sexual)
4. Geographical Distribution, Viral Prevalence, and Seroprevalence
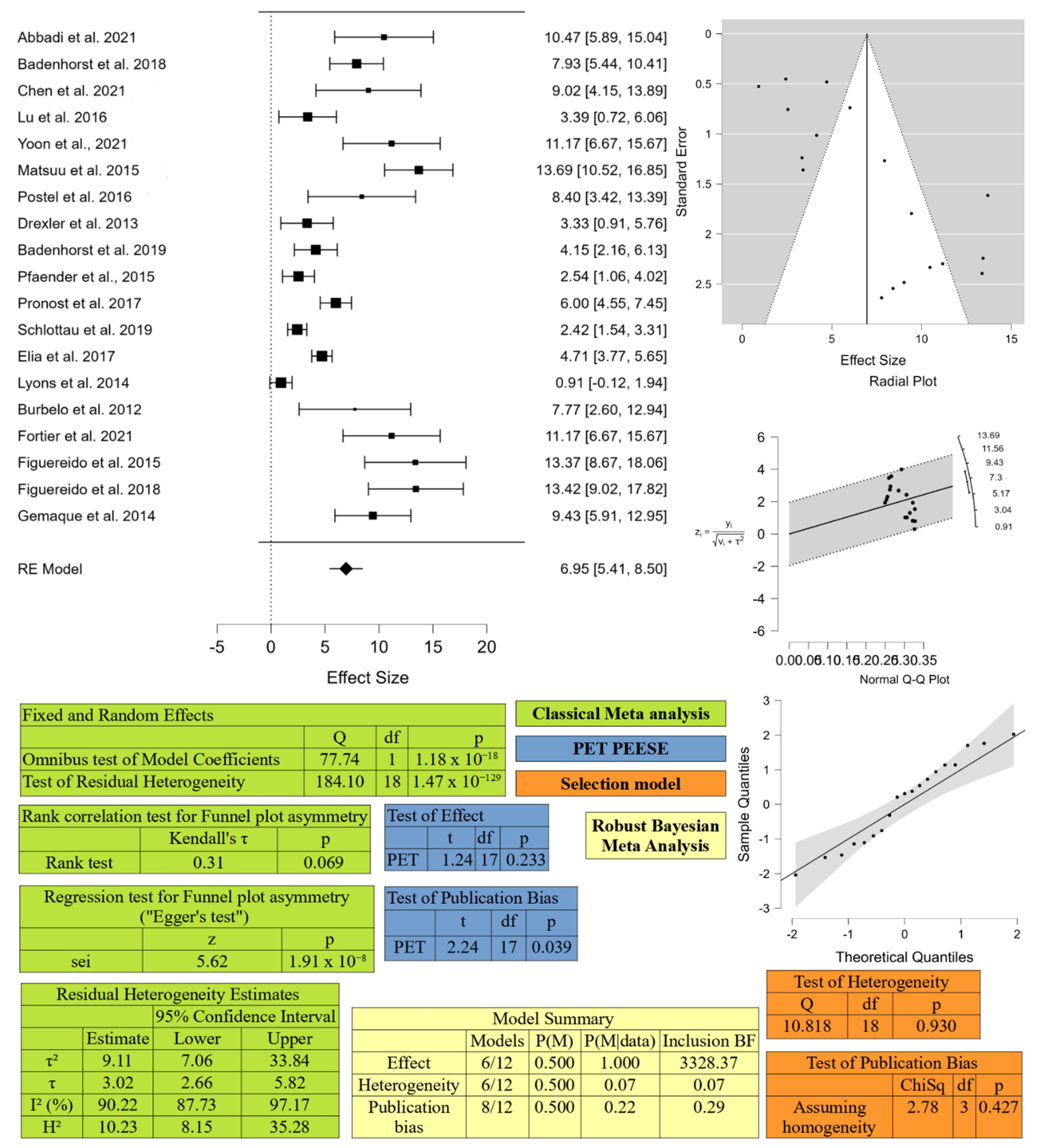
4.1. Meta-Analysis
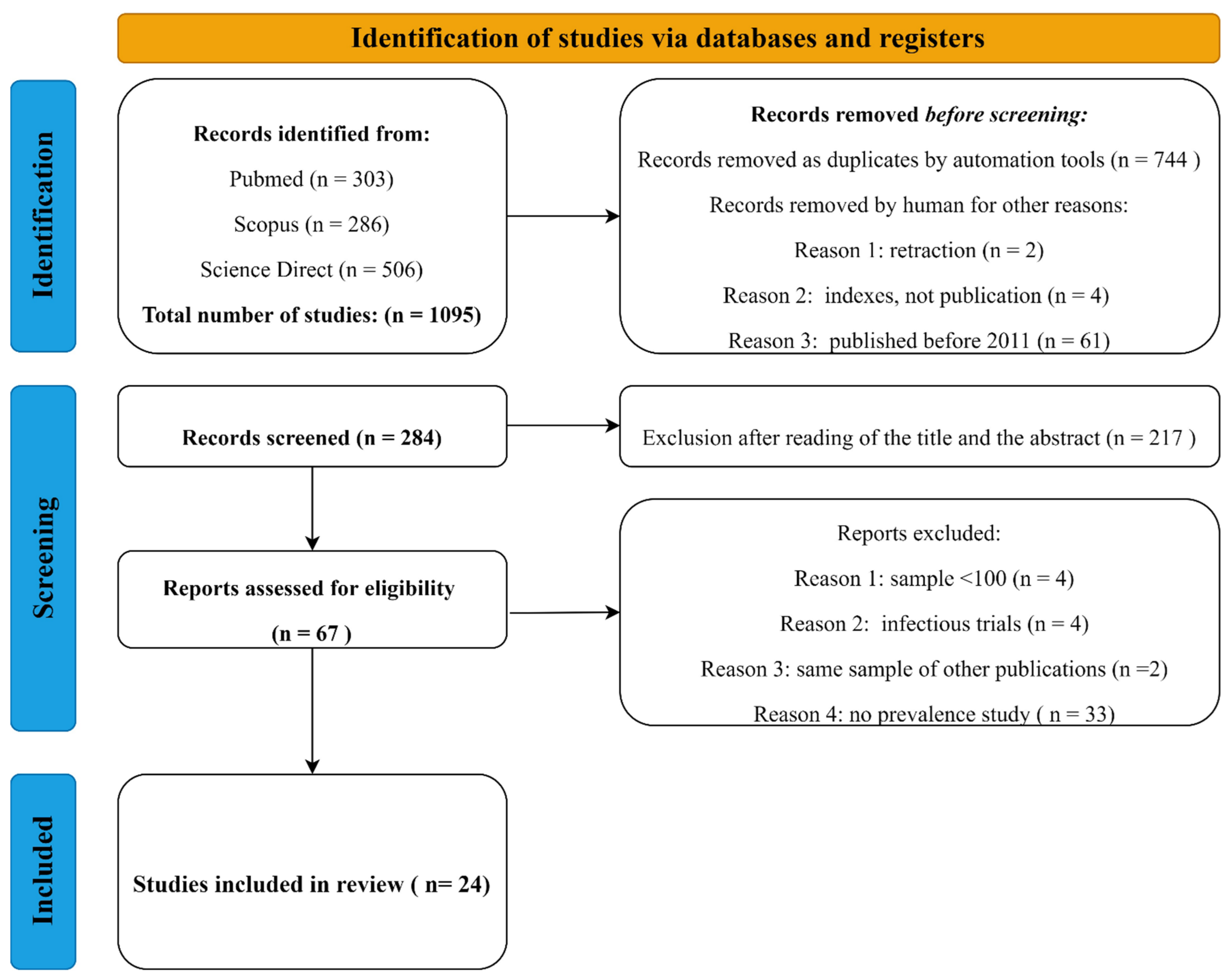
4.1.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
4.1.2. Data Extraction
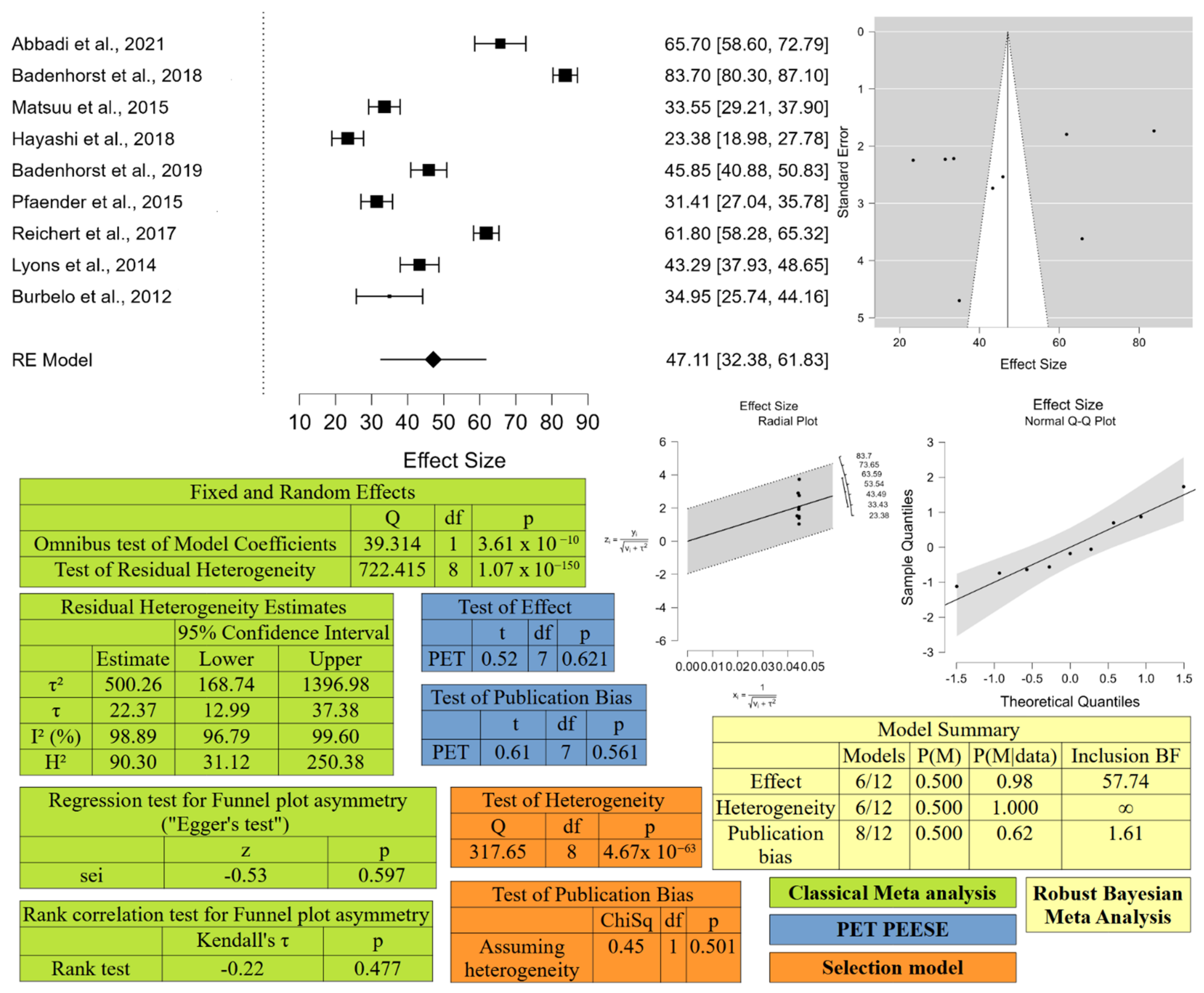
4.1.3. Meta-Analysis
5. Individual Risk Factors
5.1. Age
5.2. Breed
5.3. Sex
5.4. Production Category
6. Herd Management Risk Factors
7. EqHV Clinical Presentation
7.1. Hepaciviruses Infection: A Brief Summary
7.2. Acute and Chronic Infection in Horses
7.3. Infection Steps: Protection against Reinfection
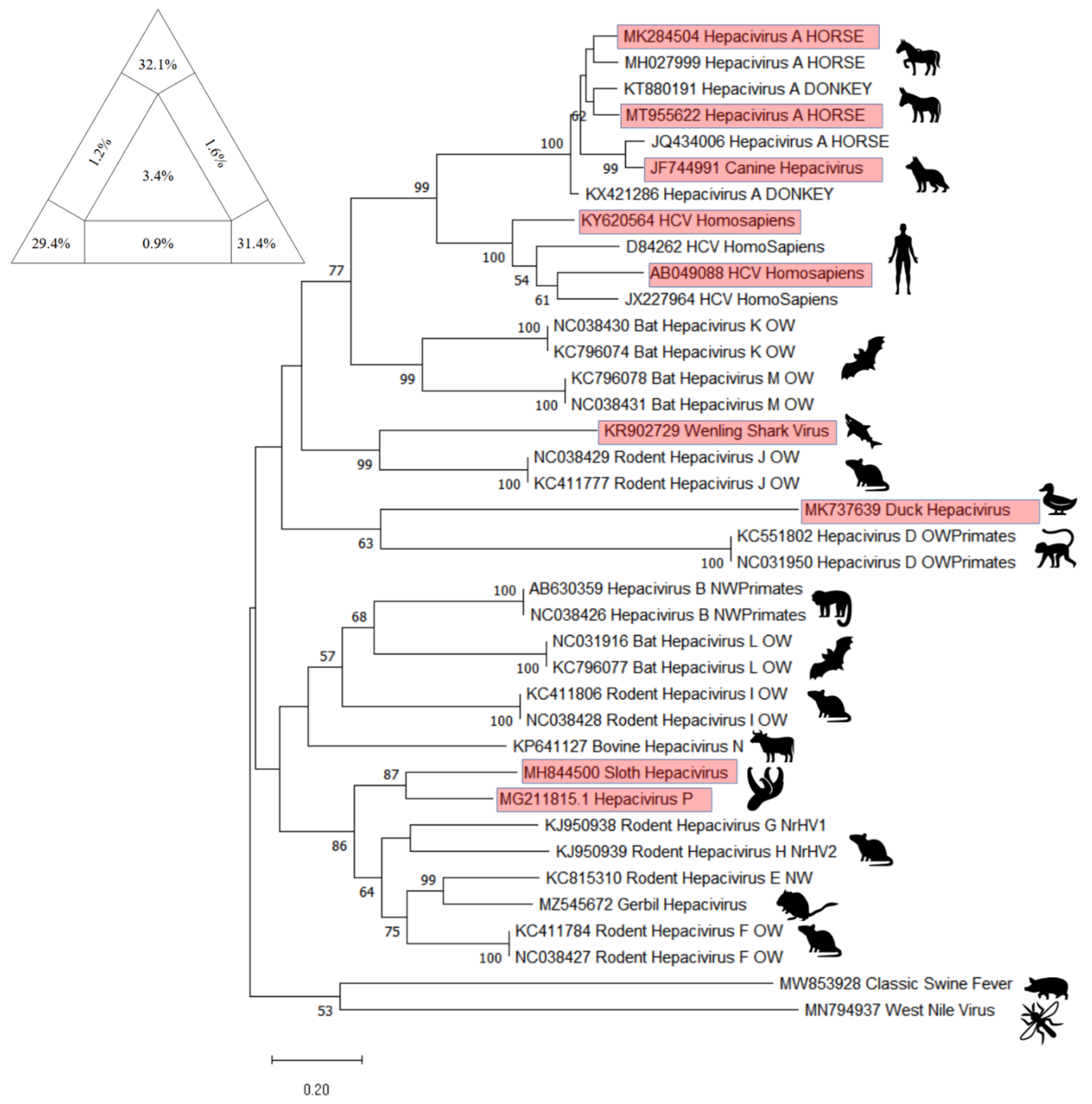
8. Cross-Species Transmission
EqHV Cross-Species Transmission
9. Laboratory Diagnosis and Therapy
9.1. Laboratory Diagnosis
9.1.1. Serological Methods
9.1.2. Biomolecular Methods
9.1.3. Other Methods
9.2. Therapy
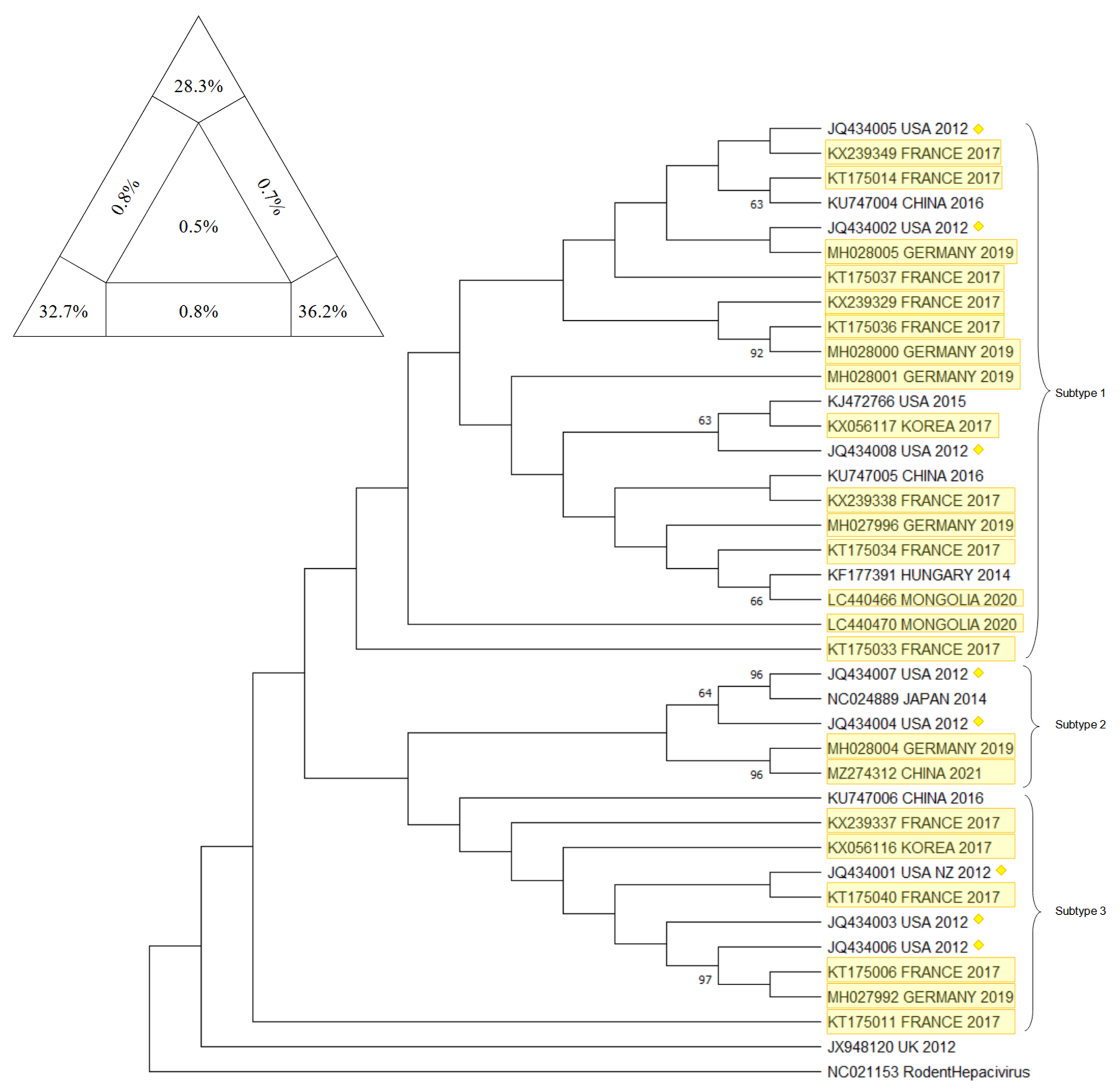
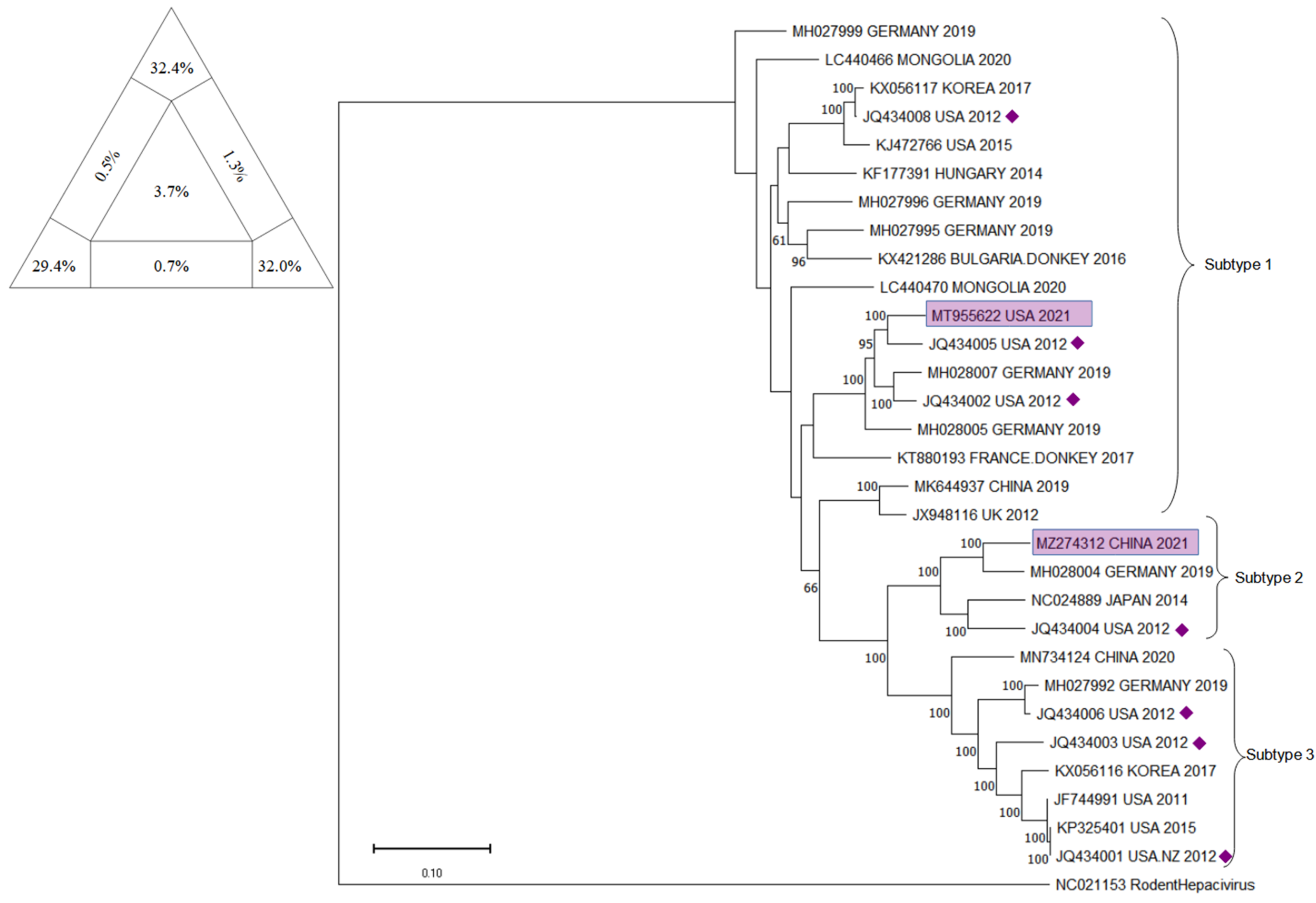
10. Phylogenetic Analysis
11. EqHV as a Model for HCV
12. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burbelo, P.D.; Dubovi, E.J.; Simmonds, P.; Medina, J.L.; Henriquez, J.A.; Mishra, N.; Wagner, J.; Tokarz, R.; Cullen, J.M.; Iadarola, M.J.; et al. Serology-Enabled Discovery of Genetically Diverse Hepaciviruses in a New Host. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6171–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Simmonds, P.; Cullen, J.M.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Medina, J.L.; Giannitti, F.; Nishiuchi, E.; Brock, K.V.; Burbelo, P.D.; Rice, C.M.; et al. Identification of a Pegivirus (GB Virus-Like Virus) That Infects Horses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7185–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Stapleton, J.T.; et al. Proposed update to the taxonomy of the genera Hepacivirus and Pegivirus within the Flaviviridae family. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2894–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divers, T.J.; Tennant, B.C.; Kumar, A.; McDonough, S.; Cullen, J.M.; Bhuva, N.; Jain, K.; Chauhan, L.S.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Lipkin, W.I.; et al. A new parvovirus associated with serum hepatitis in horses following inoculation of a common equine biological. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasche, A.; Lehmann, F.; Goldmann, N.; Nagel, M.; Moreira-Soto, A.; Nobach, D.; de Oliveira Carneiro, I.; Osterrieder, N.; Greenwood, A.D.; Steinmann, E.; et al. A hepatitis B virus causes chronic infections in equids worldwide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2013982118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Smith, D.B.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses—ICTV Family: Flaviviridae. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports/ictv_online_report/positive-sense-rna-viruses/w/flaviviridae (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Kapoor, A.; Simmonds, P.; Gerold, G.; Qaisar, N.; Jain, K.; Henriquez, J.A.; Firth, C.; Hirschberg, D.L.; Rice, C.M.; Shields, S.; et al. Characterization of a canine homolog of hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11608–11613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, T.J. Flaviviruses: General Features. In Encyclopedia of Virology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerold, G.; Bruening, J.; Weigel, B.; Pietschmann, T. Protein interactions during the Flavivirus and hepacivirus life cycle. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2017, 16, S75–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, T.K.H.; Kapoor, A.; Nishiuchi, E.; Brock, K.V.; Yu, Y.; Andrus, L.; Gu, M. Characterization of nonprimate hepacivirus and construction of a functional molecular clone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses—ICTV Family: Flaviviridae Genus: Hepacivirus. Available online: https://ictv.global/report/chapter/flaviviridae/flaviviridae/hepacivirus (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Hartlage, A.S.; Cullen, J.M.; Kapoor, A. The Strange, Expanding World of Animal Hepaciviruses. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, A.; Sander, A.L.; Corman, V.M.; Drexler, J.F. Evolutionary biology of human hepatitis viruses. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnow, P.; Sagan, S.M. Unraveling the Mysterious Interactions between Hepatitis C Virus RNA and Liver-Specific MicroRNA-122. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Luna, J.M.; Chung, H.; Nishiuchi, E.; Scull, M.A.; Echeverría, N.; Ricardo-Lax, I.; Kapoor, A.; Lipkin, I.W.; et al. miRNA independent hepacivirus variants suggest a strong evolutionary pressure to maintain miR-122 dependence. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.E.; Wolfisberg, R.; Fahnøe, U.; Patel, R.S.; Trivedi, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, H.; Nielsen, L.; McDonough, S.P.; Bukh, J.; et al. Pathogenesis, MicroRNA-122 Gene-Regulation, and Protective Immune Responses after Acute Equine Hepacivirus Infection. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1148–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, G.; Maza, N.; Pankovics, P.; Boros, Á. Non-primate hepacivirus infection with apparent hepatitis in a horse—Short communication. Acta Vet. Hung. 2014, 62, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaender, S.; Cavalleri, J.M.V.; Walter, S.; Doerrbecker, J.; Campana, B.; Brown, R.J.P.; Burbelo, P.D.; Postel, A.; Hahn, K.; Anggakusuma; et al. Clinical course of infection and viral tissue tropism of hepatitis C virus-like nonprimate hepaciviruses in horses. Hepatology 2015, 61, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, G.; Lanave, G.; Lorusso, E.; Parisi, A.; Trotta, A.; Buono, R.; Martella, V.; Decaro, N.; Buonavoglia, C. Equine hepacivirus persistent infection in a horse with chronic wasting. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1354–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaender, S.; Walter, S.; Grabski, E.; Todt, D.; Bruening, J.; Romero-brey, I. Immune protection against reinfection with nonprimate hepacivirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2430–E2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.E.; Kapoor, A.; Kumar, A.; Tennant, B.C.; Laverack, M.A.; Beard, L.; Delph, K.; Davis, E.; Schott, H.; Lascola, K.; et al. Viral testing of 18 consecutive cases of equine serum hepatitis: A prospective study (2014–2018). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegtmeyer, B.; Echelmeyer, J.; Pfankuche, V.M.; Puff, C.; Todt, D.; Fischer, N.; Durham, A.; Feige, K.; Baumgärtner, W.; Steinmann, E.; et al. Chronic equine hepacivirus infection in an adult gelding with severe hepatopathy. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 5, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, J.D.; Evanoff, R.; Wilkinson, T.E.; Divers, T.J.; Knowles, D.P.; Mealey, R.H. Experimental transmission of equine hepacivirus in horses as a model for hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gather, T.; Walter, S.; Pfaender, S.; Todt, D.; Feige, K.; Steinmann, E.; Cavalleri, J.M.V. Acute and chronic infections with nonprimate hepacivirus in young horses. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Lkhagvasuren, D.; Wakita, T.; Oyunsuren, T.; Mizokami, M. Prevalence of equine hepacivirus infection in Mongolia. Virus Res. 2020, 282, 197940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gather, T.; Walter, S.; Todt, D.; Pfaender, S.; Brown, R.J.P.; Postel, A.; Becher, P.; Moritz, A.; Hansmann, F.; Baumgaertner, W.; et al. Vertical transmission of hepatitis C virus-like nonprimate hepacivirus in horses. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2540–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronost, S.; Fortier, C.; Marcillaud-Pitel, C.; Tapprest, J.; Foursin, M.; Saunier, B.; Pitel, P.H.; Paillot, R.; Hue, E.S. Further evidence for in utero transmission of equine hepacivirus to foals. Viruses 2019, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronost, S.; Hue, E.; Fortier, C.; Foursin, M.; Fortier, G.; Desbrosse, F.; Rey, F.; Pitel, P.-H.; Saunier, B. Identification of equine hepacivirus infections in France: Facts and Physiopathological insights. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2016, 39, S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronost, S.; Fortier, C.; Hue, E.; Desbrosse, F.; Foursin, M.; Fortier, G.; Saunier, B.; Pitel, P.H. Hépacivirus, pégivirus, TDAV: Une nouvelle triade de virus hépatiques chez le cheval? Prat. Vétérinaire Équine 2018, 197, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Altan, E.; Li, Y.; Sabino-Santos, G.; Sawaswong, V.; Barnum, S.; Pusterla, N.; Deng, X.; Delwart, E. Viruses in Horses with Neurologic and Respiratory Diseases. Phys. Act. Rehabil. Life-Threat. Illn. 2019, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Park, T.; Kim, A.; Song, H.; Park, B.; Ahn, H.; Go, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; et al. First report of equine parvovirus-hepatitis and equine hepacivirus co-infection in horses in Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.; Kapoor, A.; Sharp, C.; Schneider, B.S.; Wolfe, N.D.; Culshaw, G.; Corcoran, B.; McGorum, B.C.; Simmonds, P. Nonprimate hepaciviruses in domestic horses, United Kingdom. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postel, A.; Cavalleri, J.M.V.; Pfaender, S.; Walter, S.; Steinmann, E.; Fischer, N.; Feige, K.; Haas, L.; Becher, P. Frequent presence of hepaci and pegiviruses in commercial equine serum pools. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 182, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paim, W.P.; Weber, M.N.; Cibulski, S.P.; da Silva, M.S.; Puhl, D.E.; Budaszewski, R.F.; Varela, A.P.M.; Mayer, F.Q.; Canal, C.W. Characterization of the viral genomes present in commercial batches of horse serum obtained by high-throughput sequencing. Biologicals 2019, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wu, P.; Fu, C.; Li, S. Identification and genetic characterization of hepacivirus and pegivirus in commercial equine serum products in China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, T.L.; Tegtmeyer, B.; Postel, A.; Cavalleri, J.-M.V.; Todt, D.; Stang, A.; Steinmann, E. Equine Parvovirus-Hepatitis Frequently Detectable in Commercial Equine Serum Pools. Viruses 2019, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S.; Kapoor, A.; Schneider, B.S.; Wolfe, N.D.; Culshaw, G.; Corcoran, B.; Durham, A.E.; Burden, F.; McGorum, B.C.; Simmonds, P. Viraemic frequencies and seroprevalence of non-primate hepacivirus and equine pegiviruses in horses and other mammalian species. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abbadi, I.; Lkhider, M.; Kitab, B.; Jabboua, K.; Zaidane, I.; Haddaji, A.; Nacer, S.; Matsuu, A.; Pineau, P.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; et al. Non-primate hepacivirus transmission and prevalence: Novel findings of virus circulation in horses and dogs in Morocco. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 93, 104975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pybus, O.G.; Thézé, J. Hepacivirus cross-species transmission and the origins of the hepatitis C virus. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Attar, L.M.R.; Mitchell, J.A.; Brooks Brownlie, H.; Priestnall, S.L.; Brownlie, J. Detection of non-primate hepaciviruses in UK dogs. Virology 2015, 484, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenhorst, M.; De Heus, P.; Auer, A.; Rümenapf, T.; Tegtmeyer, B.; Kolodziejek, J.; Nowotny, N.; Steinmann, E.; Cavalleri, J.M.V. No evidence of mosquito involvement in the transmission of equine hepacivirus (flaviviridae) in an epidemiological survey of Austrian horses. Viruses 2019, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.F.; Corman, V.M.; Müller, M.A.; Lukashev, A.N.; Gmyl, A.; Coutard, B.; Adam, A.; Ritz, D.; Leijten, L.M.; van Riel, D.; et al. Evidence for Novel Hepaciviruses in Rodents. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, G.; Lanave, G.; Lorusso, E.; Parisi, A.; Cavaliere, N.; Patruno, G.; Terregino, C.; Decaro, N.; Martella, V.; Buonavoglia, C. Identification and genetic characterization of equine hepaciviruses in Italy. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronost, S.; Hue, E.; Fortier, C.; Foursin, M.; Fortier, G.; Desbrosse, F.; Rey, F.A.; Pitel, P. Prevalence of Equine Hepacivirus Infections in France and Evidence for Two Viral Subtypes Circulating Worldwide. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, C.; Campe, A.; Walter, S.; Pfaender, S.; Welsch, K.; Ruddat, I.; Sieme, H.; Feige, K.; Steinmann, E.; Cavalleri, J.M.V. Frequent occurrence of nonprimate hepacivirus infections in Thoroughbred breeding horses—A cross-sectional study for the occurrence of infections and potential risk factors. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 203, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlottau, K.; Fereidouni, S.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Molecular identification and characterization of nonprimate hepaciviruses in equines. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badenhorst, M.; de Heus, P.; Auer, A.; Tegtmeyer, B.; Stang, A.; Dimmel, K.; Kubacki, J.; Bachofen, C.; Steinmann, E.; Cavalleri, J.M.V. Active equine parvovirus-hepatitis infection is most frequently detected in Austrian horses of advanced age. Eq. Vet. J. 2022, 54, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badenhorst, M.; Tegtmeyer, B.; Todt, D.; Guthrie, A.; Feige, K. First detection and frequent occurrence of Equine Hepacivirus in horses on the African continent. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 223, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemaque, B.S.; Souza de Souza, A.J.; Soares, M.D.C.P.; Malheiros, A.P.; Silva, A.L.; Alves, M.M.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Ferreira de Figueiredo, H.; Ribeiro, D.B.; et al. Hepacivirus infection in domestic horses, Brazil, 2011–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 2011–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.S.; Lampe, E.; do Espírito-Santo, M.P.; do Amaral Mello, F.C.; de Almeida, F.Q.; de Lemos, E.R.S.; Godoi, T.L.O.S.; Dimache, L.A.G.; dos Santos, D.R.L.; Villar, L.M. Identification of two phylogenetic lineages of equine hepacivirus and high prevalence in Brazil. Vet. J. 2015, 206, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.S.; Lampe, E.; de Albuquerque, P.P.L.F.; Chalhoub, F.L.L.; de Filippis, A.M.B.; Villar, L.M.; Cruz, O.G.; Pinto, M.A.; de Oliveira, J.M. Epidemiological investigation and analysis of the NS5B gene and protein variability of non-primate hepacivirus in several horse cohorts in Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 59, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kasai, H.; Yamashita, A.; Okuyama-Dobashi, K.; Yasumoto, J.; Maekawa, S.; Enomoto, N.; Okamoto, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Morimatsu, M.; et al. Hallmarks of Hepatitis C Virus in Equine Hepacivirus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13352–13366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuu, A.; Hobo, S.; Ando, K.; Sanekata, T.; Sato, F.; Endo, Y.; Amaya, T.; Osaki, T.; Horie, M.; Masatani, T.; et al. Genetic and serological surveillance for non-primate hepacivirus in horses in Japan. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 179, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Sun, L.; Xu, T.; He, D.; Wang, Z.; Ou, S.; Jia, K.; Yuan, L.; Li, S. First description of hepacivirus and pegivirus infection in domestic Horses in China: A study in guangdong province, heilongjiang province and Hong Kong district. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Moon, H.W.; Sung, H.W.; Kwon, H.M. First identification and phylogenetic analysis of equine hepacivirus in Korea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 49, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Tanaka, T.; Moriishi, K.; Hirayama, K.; Yamada, A.; Hotta, K. Seroepidemiology of non-primate hepacivirus (NPHV) in japanese native horses. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Ou, J.; Sun, Y.; Wu, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, S. Natural recombination of equine hepacivirus subtype 1 within the NS5A and NS5B genes. Virology 2019, 533, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ou, J.; Cai, S.; Ji, J.; Ren, Z.; Shao, R.; Li, S. First identification and genomic characterization of equine hepacivirus sub-type 3 strain in China. Virus Genes 2020, 56, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, Z.; Zhong, L.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Lu, G. First identification and genomic characterization of equine hepacivirus subtype 2 in China. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 3221–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, C.; El-hage, C.; Hue, E.; Sutton, G.; Pitel, M.; Jeffers, K.; Bamford, N.; Oden, E.; Paillot, R.; Fortier, C.; et al. Hepatitis viruses: Prevalence of equine parvovirus-hepatitis virus and equine hepacivirus in France and Australia. Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoš, F.; Maier, M.; Quintana, D.S.; Wagenmakers, E.-J. Adjusting for Publication Bias in JASP and R: Selection Models, PET-PEESE, and Robust Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci. 2022, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Jones, J.H.; Hornof, W.J.; Miles, J.A.; Longworth, K.E.; Willits, N.H. Effects of road transport on indices of stress in horses. Equine Vet. J. 1996, 28, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandin, T. Assessment of Stress during Handling and Transport. J. Anim. Sci. 1997, 75, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.L.; Irvine, C.H.G. The effect of social stress on adrenal axis activity in horses: The importance of monitoring corticosteroid-binding globulin capacity. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 157, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stull, C.L.; Rodiek, A.V. Physiological responses of horses to 24 hours of transportation using a commercial van during summer conditions. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 78, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Biau, S.; Möstl, E.; Becker-Birck, M.; Morillon, B.; Aurich, J.; Faure, J.M.; Aurich, C. Changes in cortisol release and heart rate variability in sport horses during long-distance road transport. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2010, 38, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badenhorst, M.; Page, P.; Ganswindt, A.; Laver, P.; Guthrie, A.; Schulman, M. Detection of equine herpesvirus-4 and physiological stress patterns in young Thoroughbreds consigned to a South African auction sale. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaender, S.; Walter, S.; Todt, D.; Behrendt, P.; Doerrbecker, J.; Wölk, B.; Engelmann, M.; Gravemann, U.; Seltsam, A.; Steinmann, J.; et al. Assessment of cross-species transmission of hepatitis C virus-related non-primate hepacivirus in a population of humans at high risk of exposure. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2636–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaender, S.; Brown, R.J.P.; Pietschmann, T.; Steinmann, E. Natural reservoirs for homologs of hepatitis C virus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopper, J.J.; Schott, H.C.; Divers, T.J.; Mullaney, T.; Huang, L.; Noland, E.; Smedley, R. Theiler’s disease associated with administration of tetanus antitoxin contaminated with nonprimate (equine) hepacivirus and equine parvovirus-hepatitis virus. Equine Vet. Educ. 2020, 32, e5–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, C.; Martinot, A.J.; Jones, R.A.; Varner, V.; Reeves, R.K. Hepatic immunopathology during occult Hepacivirus re-infection. Virology 2017, 512, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Jin, M.; Feng, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D. A highly divergent hepacivirus-like flavivirus in domestic ducks. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Soto, A.; Arroyo-Murillo, F.; Sander, A.L.; Rasche, A.; Corman, V.; Tegtmeyer, B.; Steinmann, E.; Corrales-Aguilar, E.; Wieseke, N.; Avey-Arroyo, J.; et al. Cross-order host switches of hepatitis C-related viruses illustrated by a novel hepacivirus from sloths. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.T.; Nie, S.M.; Chang, W.H.; Zhou, H.; Xu, L.; Sun, Y.X.; Shi, W.F.; Li, C.X. Identification of a novel hepacivirus in Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) from Shaanxi, China. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Vasilakis, N.; Tian, J.-H.; Li, C.-X.; Chen, L.-J.; Eastwood, G.; Diao, X.-N.; Chen, M.-H.; Chen, X.; et al. Divergent Viruses Discovered in Arthropods and Vertebrates Revise the Evolutionary History of the Flaviviridae and Related Viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, P.L.; Firth, C.; Conte, J.M.; Williams, S.H.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.M.; Anthony, S.J.; Ellison, J.A.; Gilbert, A.T.; Kuzmin, I.V.; Niezgoda, M.; et al. Bats are a major natural reservoir for hepaciviruses and pegiviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8194–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martinis, C.; Cardillo, L.; Esposito, C.; Viscardi, M.; Barca, L.; Cavallo, S.; D’Alessio, N.; Martella, V.; Fusco, G. First identification of bovine hepacivirus in wild boars. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thézé, J.; Lowes, S.; Parker, J.; Pybus, O.G. Evolutionary and phylogenetic analysis of the hepaciviruses and pegiviruses. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2996–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Walter, S.; Rasche, A.; Moreira-Soto, A.; Pfaender, S.; Bletsa, M.; Corman, V.M.; Aguilar-Setien, A.; García-Lacy, F.; Hans, A.; Todt, D.; et al. Differential Infection Patterns and Recent Evolutionary Origins of Equine Hepaciviruses in Donkeys. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01711-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals Chapter 1.1.6. “Principles and Methods of Validation of Diagnostic Assays for Infectious Diseases”. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/1.01.06_VALIDATION.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals 2022 Chapter 2.2.3. “Development and Optimisation of Nucleic Acid Detection Assays”. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/2.02.03_NAD_ASSAYS.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2022).
- Scheel, T.K.H.; Simmonds, P.; Kapoor, A.; Disease, I.; Sciences, M.; Kingdom, U. Surveying the global virome: Identification and characterization of HCV-related animal hepaciviruses. Antivir. Res. 2015, 115, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.A.; Strimmer, K.; Vingron, M.; Von Haeseler, A. TREE-PUZZLE: Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Simmonds, P.; Scheel, T.K.H.; Hjelle, B.; Cullen, J.M.; Burbelo, P.D.; Chauhan, L.V.; Duraisamy, R.; Sanchez Leon, M.; Jain, K.; et al. Identification of rodent homologs of hepatitis C virus and pegiviruses. Mbio 2013, 4, e00216-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Iwata, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Nakao, K.; Hatahara, T.; Ohta, Y.; Kanai, K.; Maruo, H.; Baba, K.; et al. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1b sequences from fifteen patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: The ‘progression score’ revisited. Hep. Res. 2001, 20, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Pedergnana, V.; Ip, C.L.C.; Magri, A.; Von Delft, A.; Bonsall, D.; Chaturvedi, N.; Bartha, I.; Smith, D.; Nicholson, G.; et al. Genome-to-genome analysis highlights the effect of the human innate and adaptive immune systems on the hepatitis C virus. Nat. Gen. 2017, 49, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, U.; Santos, P.D.; Groschup, M.H.; Hattendorf, C.; Eiden, M.; Höper, D.; Eisermann, P.; Keller, M.; Michel, F.; Klopfleisch, R.; et al. West Nile virus epidemic in Germany triggered by epizootic emergence. Viruses 2020, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report. Hepatitis C Fact Sheet. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Berggren, K.A.; Suzuki, S.; Ploss, A. Animal models used in hepatitis C virus research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartlage, A.S.; Kapoor, A. Hepatitis c virus vaccine research: Time to put up or shut up. Viruses 2021, 13, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, B.C.; Limeira, C.H.; Dos Anjos, D.M.; Nogueira, D.B.; de Andrade Morais, D.; Falcão, B.M.R.; Alves, C.J.; de Sousa, A.B.S.C.; Silva, M.L.C.R.; de Azevedo, S.S. Global Prevalence of RNA-Positive Horses for Hepacivirus (EqHV): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 114, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hepacivirus Species | A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
| Previous identifier | Canine HV, NPHV, EqHV | GBV-B | HCV | Guereza Hepacivirus | Rodent Hepacivirus | Rodent Hepacivirus | Norway Rat HV 1 |
| Host | Horse (Dog?) | NW primates | Human | OW Primate | NW Rodent | OW Rodent | Global Rodent |
| Hepacivirus species | H | I | J | K | L | M | N |
| Previous identifier | Norway Rat HV 2 | Rodent Hepacivirus | Rodent Hepacivirus | Bat Hepacivirus | Bat Hepacivirus | Bat Hepacivirus | Bovine Hepacivirus |
| Host | Global Rodent | OW Rodent | OW Rodent | OW bat | OW bat | OW bat | Cow |
| Continent | Country | Tested Species | Prevalences (Only Horses) | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCR (%) | Serum (%) | ||||
| Europe | Italy | Horse, Donkey | 91/1932 (4.7%) | n.d. | Elia et al., 2017 [44] |
| Hungary | Horse | 1/1 (100%) | n.d. | Reuter et al., 2014 [18] | |
| UK | Horse | 3/142 (2.1%) | n.d. | Lyons et al., 2012 [33] | |
| UK | Horse, Donkey | 3/328 (<1%) | 142/328 (43.3%) | Lyons et al., 2014 [38] | |
| Germany | Horse | 7/210 (3.3%) | n.d. | Drexler et al., 2013 [43] | |
| Germany | Horse | 11/433 (2.5%) | 136/433 (31.4%) | Pfaender et al., 2015 [19] | |
| Germany | Horse | 10/119 (8.4%) | n.d. | Postel et al., 2016 [34] | |
| Germany | Horse | 134/733 (18.2%) | 453/733 (61.8%) | Reichert et al., 2017 [46] | |
| Germany | Horse | 28/1155 (2.4%) | n.d. | Schlottau et al., 2019 [47] | |
| Austria | Horse | 16/386 (4.15%) | 177/386 (45.9%) | Badenorst et al., 2019 [42] | |
| Austria | Horse, Donkey | 1/259 (0.38%) | n.d. | Badenorst et al., 2021 [48] | |
| France | Horse | 69/1229 (5.6%) | n.d. | Pronost et al., 2016 [29] | |
| France | Horse, Thoroughbreds | 62/1033 (6.2%) | n.d. | Pronost et al., 2017 [45] | |
| Africa | South Africa | Horse, Thoroughbreds | 36/454 (7.9%) | 380/454 (83.70%) | Badenhorst et al., 2018 [49] |
| Marocco | Horse | 18/172 (10.50%) | 113/172 (65.70%) | Abbadi et al., 2021 [39] | |
| North America | US | Horse | 8/103 (7.7%) | 36/103 (34.9%) | Burbelo et al., 2012 [1] |
| US | Horse | 2/14 (14.28%) | n.d. | Tomlinson et al., 2019 [22] | |
| South America | Brazil | Horse, Donkey, Mule | 25/265 (9.4%) | n.d. | Gemaque et al., 2014 [50] |
| Brazil | Horse, Donkey | 27/202 (13.4%) | n.d. | Figuereido et al., 2015 [51] | |
| Brazil | Horse | 31/231 (13.4%) | n.d. | Figuereido et al., 2018 [52] | |
| Asia | China | Horse, Donkey, Mule | 6/177 (3.4%) | n.d. | Lu et al., 2016 [55] |
| China | Horse | 6/13 (46.2%) | n.d. | Lu et al., 2019 [58] | |
| China | Horse, Warmblood | 19/60 (3.2%) | n.d. | Wu et al., 2020 [59] | |
| China | Horse | 12/133 (9%) | n.d. | Chen et al., 2021 [60] | |
| Mongolia | Horse | 141/299 (47.1%) | n.d. | Date et al., 2020 [26] | |
| Japan | Horse | 11/31 (35.6%) | 7/31 (22.6%) | Tanaka et al., 2014 [53] | |
| Japan | Horse, Thoroughbreds | 62/453 (13.7%) | 152/453 (33.5%) | Matsuu et al., 2015 [54] | |
| Japan | Indigenous breed horses | n.d. | 83/355 (23.9%) | Hayashi et al., 2018 [57] | |
| Korea | Horse, Thoroughbreds | 14/74 (18.9%) | n.d. | Kim et al., 2017 [56] | |
| Korea | Horse | 13/160 (8.1%) | n.d. | Yoon et al., 2021 [32] | |
| Oceania | Australia | Horse | 21/188 (11.2%) | n.d. | Fortier et al., 2021 [61] |
| References | Species | Altered Values | Reference Intervals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lyons et al., 2012 [33] | Horse | ↑ GGT | GGT < 40 U/mL |
| Ramsay et al., 2015 [24] | Horse | ↑ GGT | GGT 14–40 U/L |
| ↑ SDH | SDH 4–14 U/L | ||
| Scheel et al., 2015 [11] | Horse | ↑ GLDH | GLDH 1–8 U/L |
| ↑ GGT | GGT 8–29 U/L | ||
| ↑ AST | AST 199–374 U/L | ||
| ↑ SDH | SDH 0–11 U/L | ||
| Gather et al., 2016 [25] | Horse | ↑ GLDH | GLDH < 6 U/L |
| ↑ GGT | GGT < 20 U/L | ||
| ↑ AST | AST < 170 U/L | ||
| Pfaender et al., 2017 [21] | Horse | ↑ GLDH | GLDH < 6 U/L |
| ↑ GGT | GGT < 20 U/L | ||
| ↑ AST | AST < 170 U/L | ||
| Tomlinson et al., 2021 [17] | Horse | ↑ GLDH | n.d. |
| ↑ GGT | n.d. | ||
| ↑ AST | n.d. | ||
| ↑ SDH | n.d. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pacchiarotti, G.; Nardini, R.; Scicluna, M.T. Equine Hepacivirus: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis of Serological and Biomolecular Prevalence and a Phylogenetic Update. Animals 2022, 12, 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192486
Pacchiarotti G, Nardini R, Scicluna MT. Equine Hepacivirus: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis of Serological and Biomolecular Prevalence and a Phylogenetic Update. Animals. 2022; 12(19):2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192486
Chicago/Turabian StylePacchiarotti, Giulia, Roberto Nardini, and Maria Teresa Scicluna. 2022. "Equine Hepacivirus: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis of Serological and Biomolecular Prevalence and a Phylogenetic Update" Animals 12, no. 19: 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192486
APA StylePacchiarotti, G., Nardini, R., & Scicluna, M. T. (2022). Equine Hepacivirus: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis of Serological and Biomolecular Prevalence and a Phylogenetic Update. Animals, 12(19), 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12192486






