Functional Identification of Porcine DLK1 during Muscle Development
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Samples
2.2. Cell Cultures and Reagents
2.3. Vector Construction and Transfection
2.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Expression Analysis
2.5. Proliferation Assay
2.6. Migration Assay
2.7. Immunofluorescent Staining
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
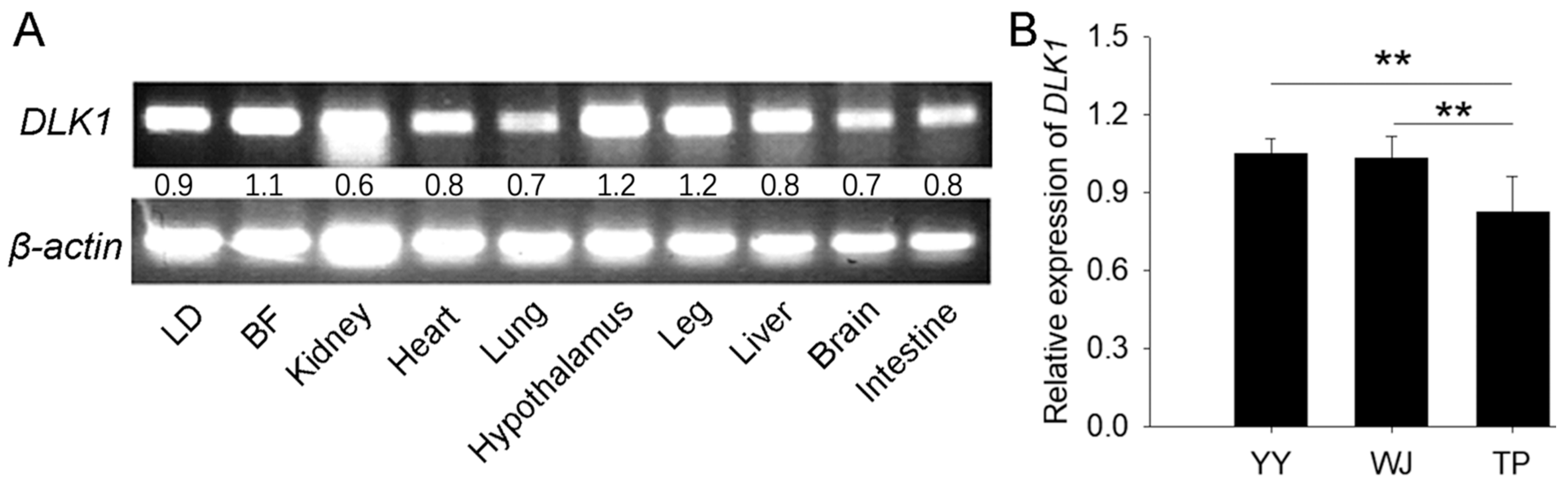
3.1. Expression of DLK1 in Tissues of Pig Embryos
3.2. DLK1 Promotes Myoblast Proliferation
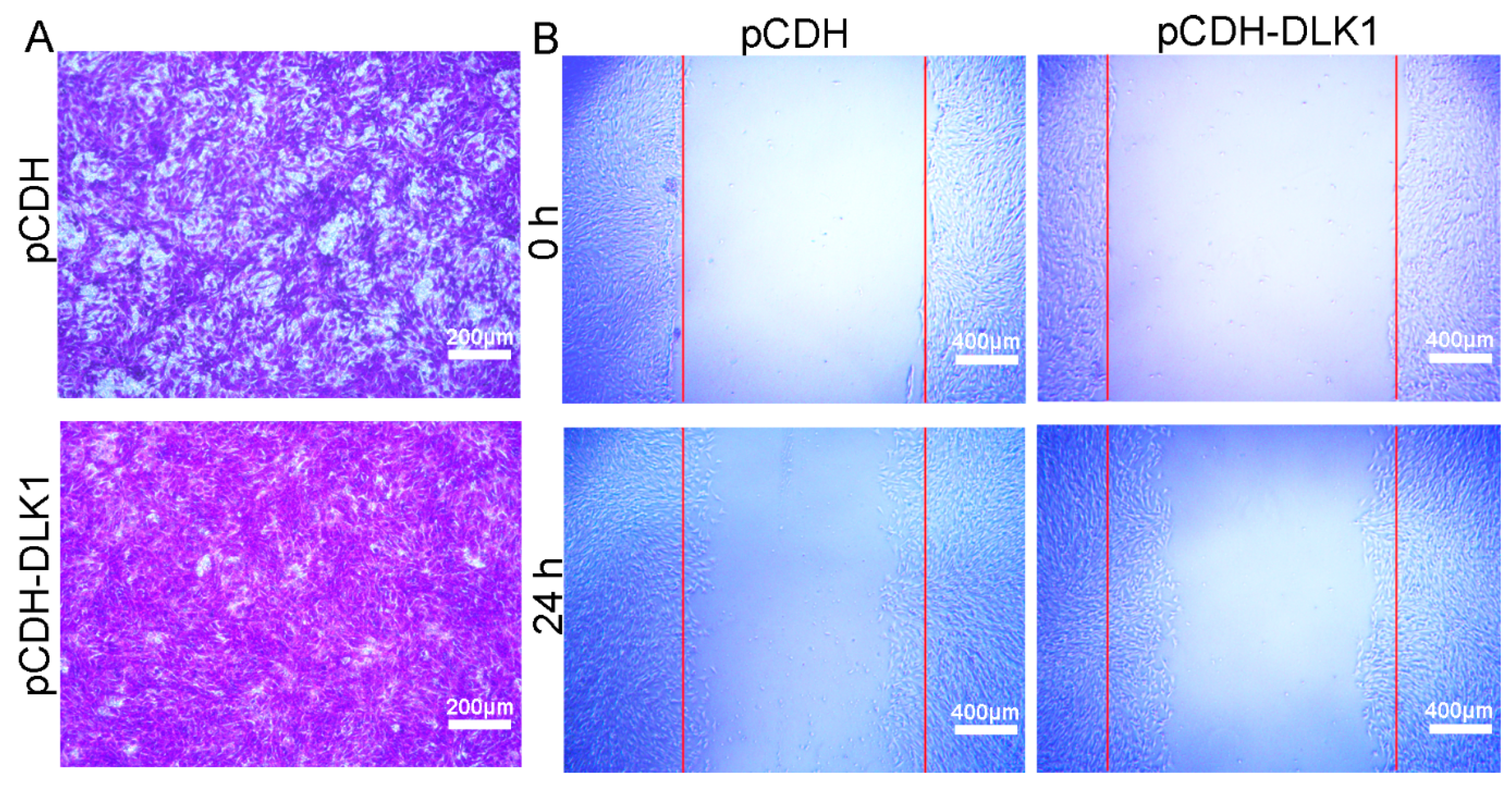
3.3. DLK1 Accelerates Myoblast Migration
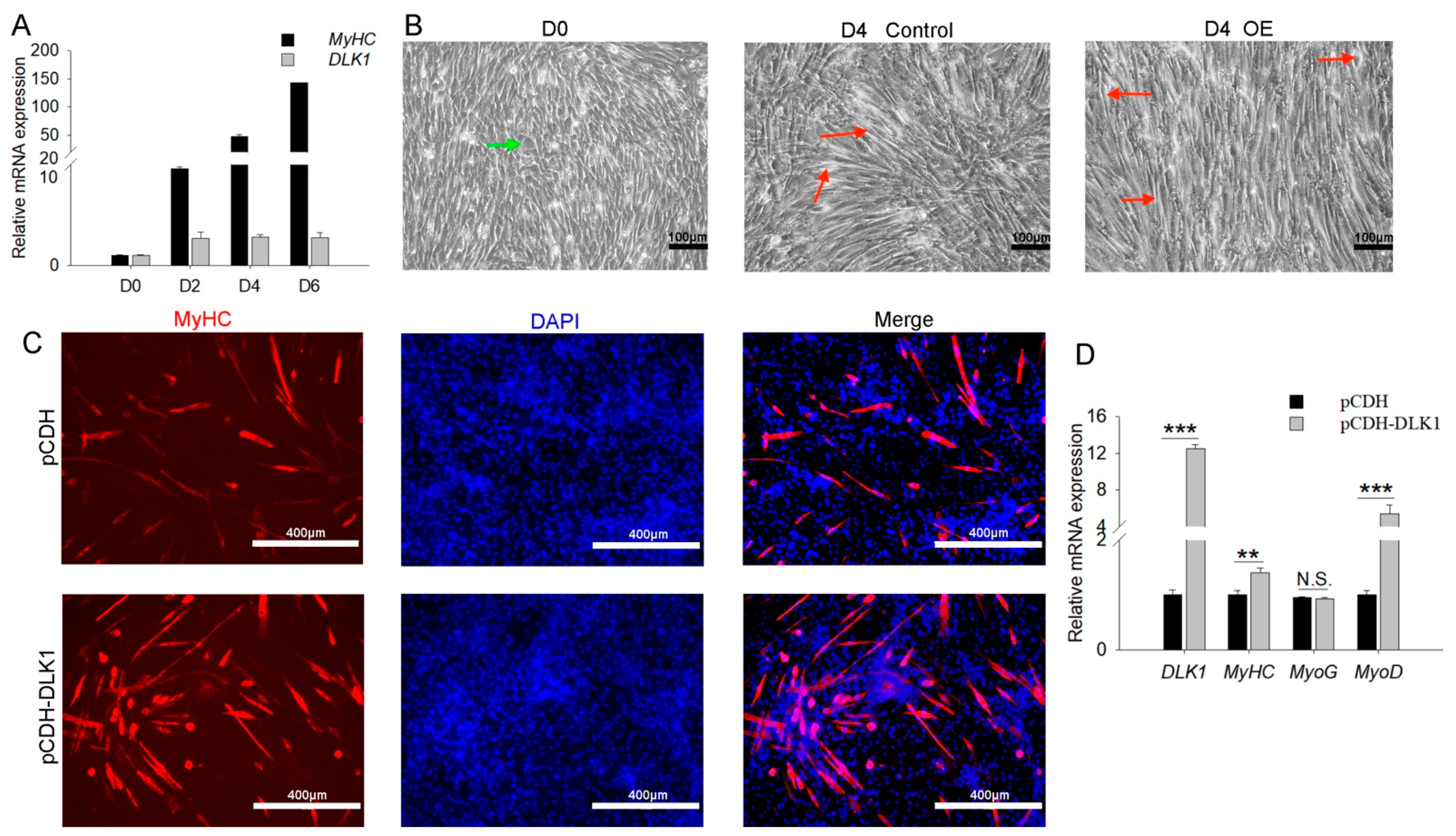
3.4. DLK1 Positively Regulates Myogenic Differentiation and Myogenin Expression
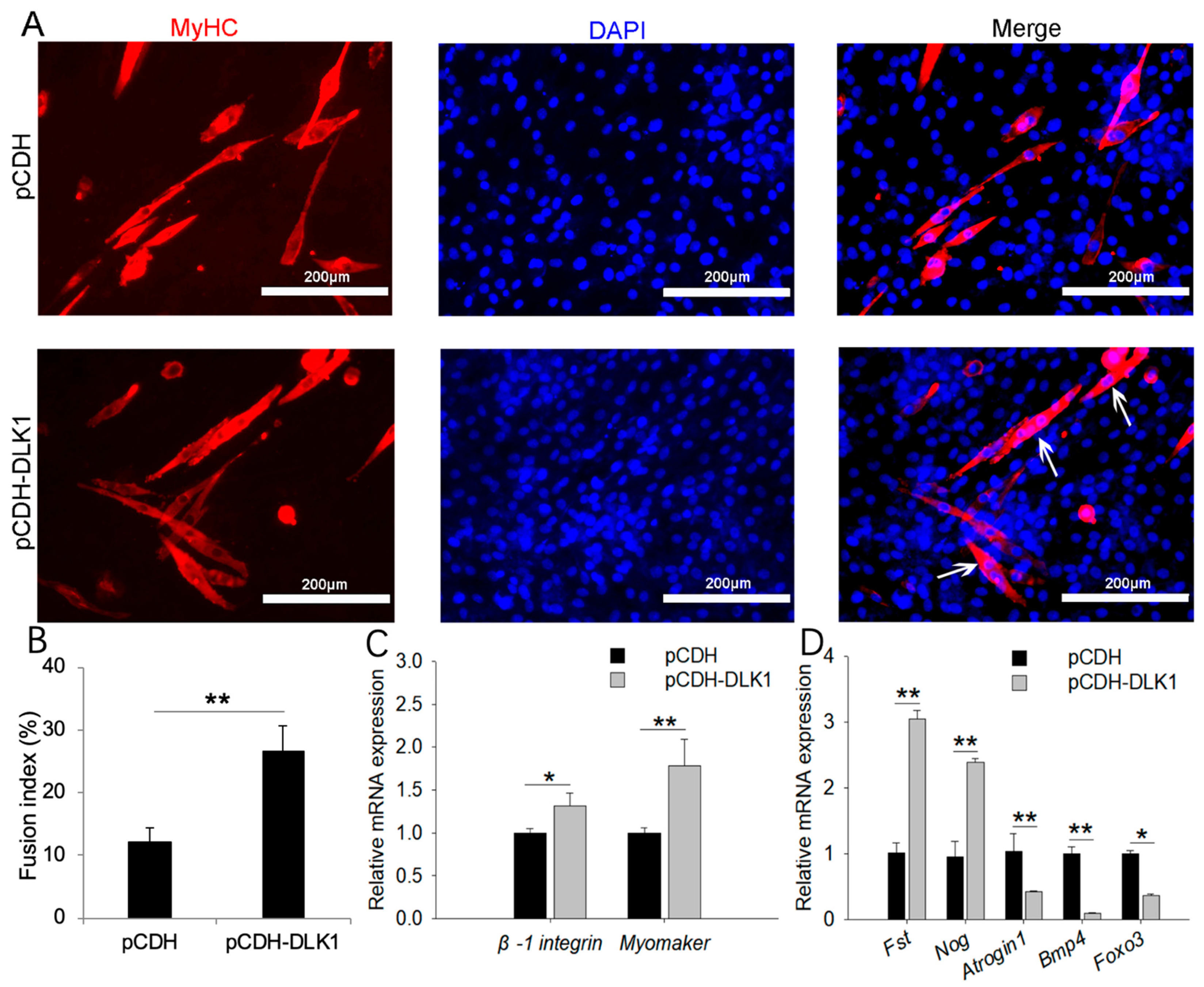
3.5. DLK1 Promotes Myogenic Fusion and Muscular Hypertrophy but Inhibits Muscle Degradation
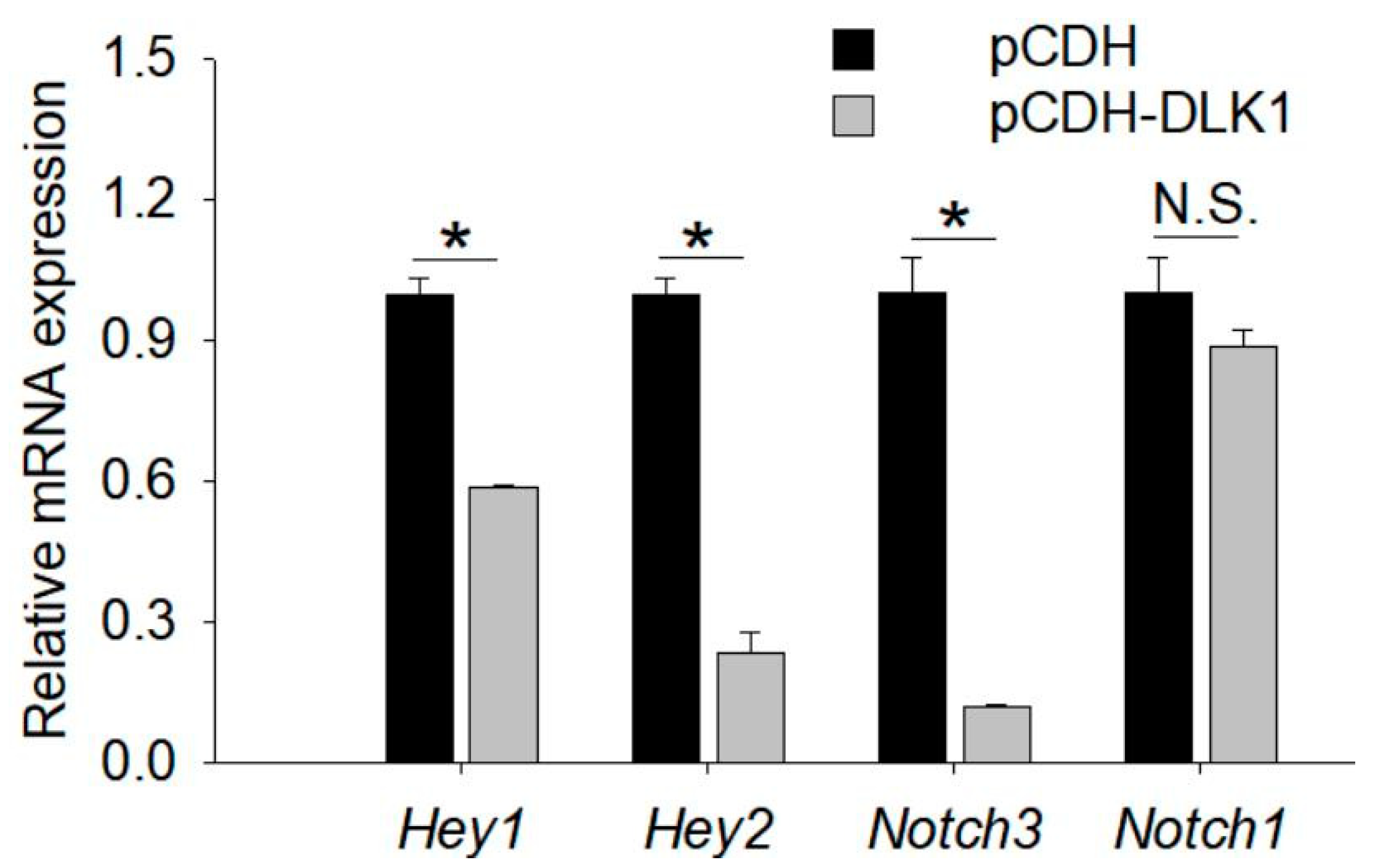
3.6. Regulatory Pathway of DLK1 on Myogenesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abe, T.; Nahar, V.K.; Young, K.C.; Patterson, K.M.; Stover, C.D.; Lajza, D.G.; Tribby, A.C.; Geddam, D.A.; Ford, M.A.; Bass, M.A.; et al. Skeletal muscle mass, bone mineral density, and walking performance in masters cyclists. Rejuvenation Res. 2014, 17, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckingham, M. Skeletal muscle development and the role of the myogenic regulatory factors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1996, 24, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadabadi, M.; Bordbar, F.; Jensen, J.; Du, M.; Guo, W. Key Genes Regulating Skeletal Muscle Development and Growth in Farm Animals. Animals 2021, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Araya, Y.; Stenhouse, C.; Salavati, M.; Dan-Jumbo, S.O.; Ho, W.; Ashworth, C.J.; Clark, E.; Esteves, C.L.; Donadeu, F.X. KLB dysregulation mediates disrupted muscle development in intrauterine growth restriction. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1771–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Qi, C.; Chen, H.; Niu, H.; Yang, J.; Kwok, K.W.H.; Dong, W. Effects of ferulic acid on muscle development and intestinal microbiota of zebrafish. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kumar, A. Supraphysiological activation of TAK1 promotes skeletal muscle growth and mitigates neurogenic atrophy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, B.O.S.; Zanella, B.T.T.; Perez, E.S.; Mareco, E.A.; Blasco, J.; Dal-Pai-Silva, M.; Garcia de la Serrana, D. Amino Acids and IGF1 Regulation of Fish Muscle Growth Revealed by Transcriptome and microRNAome Integrative Analyses of Pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) Myotubes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsley, V.; Pavlath, G.K. Forming a multinucleated cell: Molecules that regulate myoblast fusion. Cells Tissues Organs 2004, 176, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abmayr, S.M.; Pavlath, G.K. Myoblast fusion: Lessons from flies and mice. Development 2012, 139, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manneken, J.D.; Dauer, M.V.P.; Currie, P.D. Dynamics of muscle growth and regeneration: Lessons from the teleost. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 411, 112991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chal, J.; Pourquie, O. Making muscle: Skeletal myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Development 2017, 144, 2104–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.H.; Teisner, B.; Højrup, P.; Rasmussen, H.B.; Madsen, O.D.; Nielsen, B.; Skjødt, K. Studies on the isolation, structural analysis and tissue localization of fetal antigen 1 and its relation to a human adrenal-specific cDNA, pG2. Hum. Reprod. 1993, 8, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, D.B.; Kaiser, U.B. DLK1, Notch Signaling and the Timing of Puberty. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2019, 37, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, D.C.; Petersson, S.J.; Jørgensen, L.H.; Bollen, P.; Jensen, P.B.; Teisner, B.; Schroeder, H.D.; Jensen, C.H. Characterization of DLK1+ cells emerging during skeletal muscle remodeling in response to myositis, myopathies, and acute injury. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, T.; Chano, T.; Minami, K.; Okabe, H.; Okada, Y.; Okamoto, K. Imprinted DLK1 is a putative tumor suppressor gene and inactivated by epimutation at the region upstream of GTL2 in human renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J.; Cole, S.E. Multiple Dlk1 splice variants are expressed during early mouse embryogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, D.C.; Laborda, J.; Baladron, V.; Kassem, M.; Sheikh, S.P.; Jensen, C.H. Dual role of delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1) in skeletal muscle development and adult muscle regeneration. Development 2013, 140, 3743–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.H.; Meyer, M.; Schroder, H.D.; Kliem, A.; Zimmer, J.; Teisner, B. Neurons in the monoaminergic nuclei of the rat and human central nervous system express FA1/dlk. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 3959–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiuliis, J.A.; Li, B.; Lyvers-Peffer, P.A.; Moeller, S.J.; Lee, K. Alternative splicing of delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1) in the pig and human. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 145, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oczkowicz, M.; Piestrzyska-Kajtoch, A.; Piórkowska, K.; Rejduch, B.; Rózycki, M. Expression of DLK1 and MEG3 genes in porcine tissues during postnatal development. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2010, 33, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.D.; Vuocolo, T.; McDonagh, M.; Grounds, M.D.; Harper, G.S.; Cockett, N.E.; Tellam, R. Analysis of the callipyge phenotype through skeletal muscle development; association of Dlk1 with muscle precursor cells. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2008, 76, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Waddell, J.N.; Kuang, S.; Tellam, R.L.; Cockett, N.E.; Bidwell, C.A. Identification of genes directly responding to DLK1 signaling in Callipyge sheep. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crameri, R.M.; Langberg, H.; Magnusson, P.; Jensen, C.H.; Schroder, H.D.; Olesen, J.L.; Suetta, C.; Teisner, B.; Kjaer, M. Changes in satellite cells in human skeletal muscle after a single bout of high intensity exercise. J. Physiol. 2004, 558, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Velleman, S.G.; Latshaw, J.D.; Wick, M.P.; Suh, Y.; Lee, K. The ontogeny of delta-like protein 1 messenger ribonucleic acid expression during muscle development and regeneration: Comparison of broiler and Leghorn chickens. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 1427–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, L.H.; Sellathurai, J.; Davis, E.E.; Thedchanamoorthy, T.; Al-Bader, R.W.; Jensen, C.H.; Schrøder, H.D. Delta-like 1 homolog (dlk1): A marker for rhabdomyosarcomas implicated in skeletal muscle regeneration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, E.S.; Pietras, A. Emerging Roles of DLK1 in the Stem Cell Niche and Cancer Stemness. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 70, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sul, H.S. Minireview: Pref-1: Role in adipogenesis and mesenchymal cell fate. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, E.; Kuzinski, J.; Komolka, K.; Gotoh, T.; Maak, S. Localization and abundance of early markers of fat cell differentiation in the skeletal muscle of cattle during growth—Are DLK1-positive cells the origin of marbling flecks? Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smas, C.M.; Sul, H.S. Pref-1, a protein containing EGF-like repeats, inhibits adipocyte differentiation. Cell 1993, 73, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, C.J.; Burling, K.A.; Barker, P.; Hughes, I.A.; Ong, K.K.; Dunger, D.B. Pregnancy Serum DLK1 Concentrations Are Associated with Indices of Insulin Resistance and Secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e2413–e2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smas, C.M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Latasa, M.J.; Sul, H.S. Transcriptional repression of pref-1 by glucocorticoids promotes 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 12632–12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Villena, J.A.; Moon, Y.S.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.; Kang, C.; Sul, H.S. Inhibition of adipogenesis and development of glucose intolerance by soluble preadipocyte factor-1 (Pref-1). J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, J.J.; Dekkers, J.C.; Rothschild, M.F. Polar overdominant inheritance of a DLK1 polymorphism is associated with growth and fatness in pigs. Mamm. Genome Off. J. Int. Mamm. Genome Soc. 2004, 15, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.P.; Do, K.T.; Kim, J.J.; Huang, J.; Zhao, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Rothschild, M.F.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, K.S. Molecular characteristics of the porcine DLK1 and MEG3 genes. Anim. Genet. 2008, 39, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.S.; Smas, C.M.; Lee, K.; Villena, J.A.; Kim, K.H.; Yun, E.J.; Sul, H.S. Mice lacking paternally expressed Pref-1/Dlk1 display growth retardation and accelerated adiposity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5585–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, J.N.; Zhang, P.; Wen, Y.; Gupta, S.K.; Yevtodiyenko, A.; Schmidt, J.V.; Bidwell, C.A.; Kumar, A.; Kuang, S. Dlk1 is necessary for proper skeletal muscle development and regeneration. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.; Jensen, C.H.; Schroder, H.D.; Farnir, F.; Shay-Hadfield, T.; Kliem, A.; Cockett, N.; Georges, M.; Charlier, C. Ectopic expression of DLK1 protein in skeletal muscle of padumnal heterozygotes causes the callipyge phenotype. Curr. Biol. CB 2004, 14, 1858–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Uezumi, A.; Kaji, T.; Tsujikawa, K.; Andersen, D.C.; Jensen, C.H.; Fukada, S.I. Expression and Functional Analyses of Dlk1 in Muscle Stem Cells and Mesenchymal Progenitors during Muscle Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Solana, B.; Nueda, M.L.; Ruvira, M.D.; Ruiz-Hidalgo, M.J.; Monsalve, E.M.; Rivero, S.; García-Ramírez, J.J.; Díaz-Guerra, M.J.; Baladrón, V.; Laborda, J. The EGF-like proteins DLK1 and DLK2 function as inhibitory non-canonical ligands of NOTCH1 receptor that modulate each other’s activities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.D.; Tang, Y.; Lu, A.P.; Takayama, K.; Usas, A.; Wang, B.; Weiss, K.; Huard, J. The role of Notch signaling in muscle progenitor cell depletion and the rapid onset of histopathology in muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 2923–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buas, M.F.; Kadesch, T. Regulation of skeletal myogenesis by Notch. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröhl, D.; Vasyutina, E.; Czajkowski, M.T.; Griger, J.; Rassek, C.; Rahn, H.-P.; Purfürst, B.; Wende, H.; Birchmeier, C. Colonization of the satellite cell niche by skeletal muscle progenitor cells depends on Notch signals. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Shang, P.; Zhang, B.; Tian, X.; Nie, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H. Function of the Porcine TRPC1 Gene in Myogenesis and Muscle Growth. Cells 2021, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Weinlander, E.; Somnay, Y.; Harrison, A.D.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Yu, X.M.; Chen, H. The novel histone deacetylase inhibitor thailandepsin A inhibits anaplastic thyroid cancer growth. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 190, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, J.; Nagaprashantha, L.D.; Vatsyayan, R.; Awasthi, S.; Singhal, S.S. Didymin induces apoptosis by inhibiting N-Myc and upregulating RKIP in neuroblastoma. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Zhu, S.Q.; Cui, H.J. Artesunate inhibits proliferation of glioblastoma cells by arresting cell cycle. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 43, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.M.; Subramaniyam, N.; Sim, C.M.; Ge, X.; Sathiakumar, D.; McFarlane, C.; Sharma, M.; Kambadur, R. Irisin is a pro-myogenic factor that induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy and rescues denervation-induced atrophy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Jeon, S.; Ha, J.K. Guidelines for experimental design and statistical analyses in animal studies submitted for publication in the Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, P.; Wang, Z.; Chamba, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. A comparison of prenatal muscle transcriptome and proteome profiles between pigs with divergent growth phenotypes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 5277–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.A.; Pytowski, B.; Witte, L.; Hicklin, D.; Lemischka, I.R. Hematopoietic activity of a stromal cell transmembrane protein containing epidermal growth factor-like repeat motifs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4011–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, N.; Izawa, A.; Hattori, M.; Kageyama, R.; Sudo, T. dlk inhibits stem cell factor-induced colony formation of murine hematopoietic progenitors: Hes-1-independent effect. Stem Cells 2001, 19, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinose, M.; Suzuki, N.; Wang, T.; Wright, J.A.; Lannagan, T.R.M.; Vrbanac, L.; Kobayashi, H.; Gieniec, K.A.; Ng, J.Q.; Hayakawa, Y. Stromal DLK1 promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of the intestinal epithelium during development. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G506–G520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D.; Cen, J.; Gu, M. Expression of Dlk1 gene in myelodysplastic syndrome determined by microarray, and its effects on leukemia cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 22, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raghunandan, R.; Ruiz-Hidalgo, M.; Jia, Y.; Ettinger, R.; Rudikoff, E.; Riggins, P.; Farnsworth, R.; Tesfaye, A.; Laborda, J.; Bauer, S.R. Dlk1 influences differentiation and function of B lymphocytes. Stem Cells Dev. 2008, 17, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Forman, S.J.; Bhatia, R. Expression of DLK1 in hematopoietic cells results in inhibition of differentiation and proliferation. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4472–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, B.; Zhao, L.; Chen, L.; Sul, H.S. Only the large soluble form of preadipocyte factor-1 (Pref-1), but not the small soluble and membrane forms, inhibits adipocyte differentiation: Role of alternative splicing. Biochem. J. 2002, 364, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wust, S.; Drose, S.; Heidler, J.; Wittig, I.; Klockner, I.; Franko, A.; Bonke, E.; Gunther, S.; Gartner, U.; Boettger, T.; et al. Metabolic Maturation during Muscle Stem Cell Differentiation Is Achieved by miR-1/133a-Mediated Inhibition of the Dlk1-Dio3 Mega Gene Cluster. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1026–1039.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millay, D.P.; Sutherland, L.B.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. Myomaker is essential for muscle regeneration. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millay, D.P.; O’Rourke, J.R.; Sutherland, L.B.; Bezprozvannaya, S.; Shelton, J.M.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation. Nature 2013, 499, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavlakadze, T.; Grounds, M. Of bears, frogs, meat, mice and men: Complexity of factors affecting skeletal muscle mass and fat. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2006, 28, 994–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.B.; Qi, S.N.; Dong, J.Z.; Ha, X.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.W.; Yang, Y.S.; Bai, J.; Zhao, L. Salidroside induces neuronal differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells through Notch and BMP signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2014, 71, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buas, M.F.; Kabak, S.; Kadesch, T. Inhibition of myogenesis by Notch: Evidence for multiple pathways. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 218, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, T.; Hanaoka, K. Notch3 null mutation in mice causes muscle hyperplasia by repetitive muscle regeneration. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 2205–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conboy, I.M.; Rando, T.A. The regulation of Notch signaling controls satellite cell activation and cell fate determination in postnatal myogenesis. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nueda, M.L.; Baladrón, V.; Sánchez-Solana, B.; Ballesteros, M.A.; Laborda, J. The EGF-like protein dlk1 inhibits notch signaling and potentiates adipogenesis of mesenchymal cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traustadottir, G.A.; Lagoni, L.V.; Ankerstjerne, L.B.S.; Bisgaard, H.C.; Jensen, C.H.; Andersen, D.C. The imprinted gene Delta like non-canonical Notch ligand 1 (Dlk1) is conserved in mammals, and serves a growth modulatory role during tissue development and regeneration through Notch dependent and independent mechanisms. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 46, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Hao, X.; Shang, P.; Chamba, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H. Functional Identification of Porcine DLK1 during Muscle Development. Animals 2022, 12, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121523
Fu Y, Hao X, Shang P, Chamba Y, Zhang B, Zhang H. Functional Identification of Porcine DLK1 during Muscle Development. Animals. 2022; 12(12):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121523
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yu, Xin Hao, Peng Shang, Yangzom Chamba, Bo Zhang, and Hao Zhang. 2022. "Functional Identification of Porcine DLK1 during Muscle Development" Animals 12, no. 12: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121523
APA StyleFu, Y., Hao, X., Shang, P., Chamba, Y., Zhang, B., & Zhang, H. (2022). Functional Identification of Porcine DLK1 during Muscle Development. Animals, 12(12), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12121523






