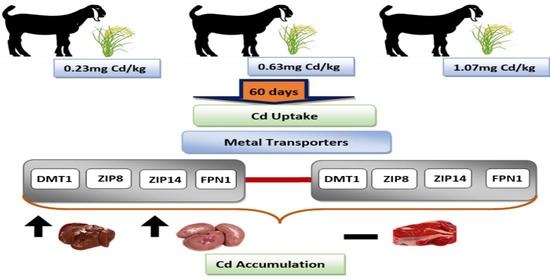
Cadmium Accumulation in the Goat Liver and Kidney Is Partially Promoted by the Upregulation of Metal Transporter Genes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
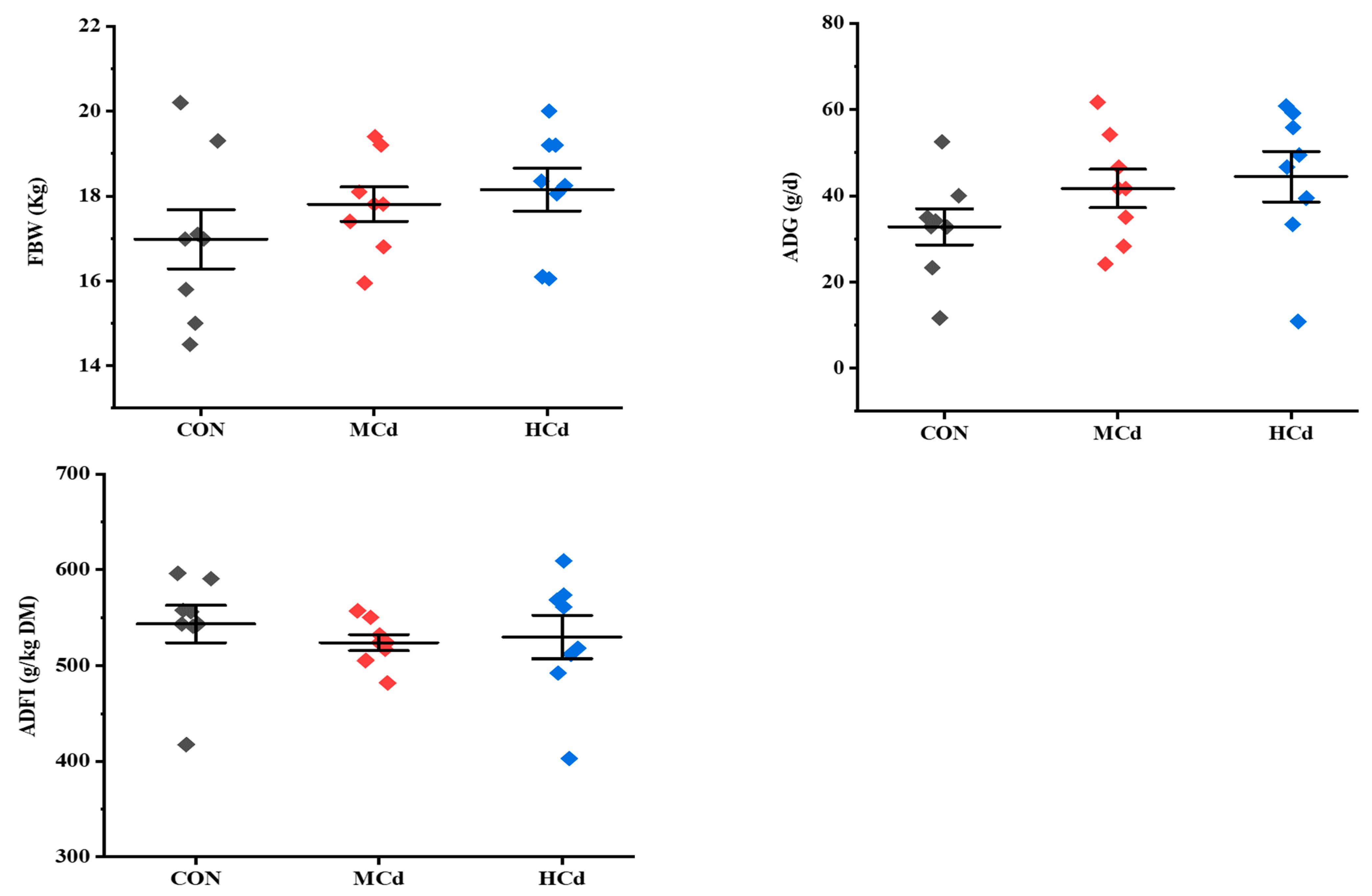
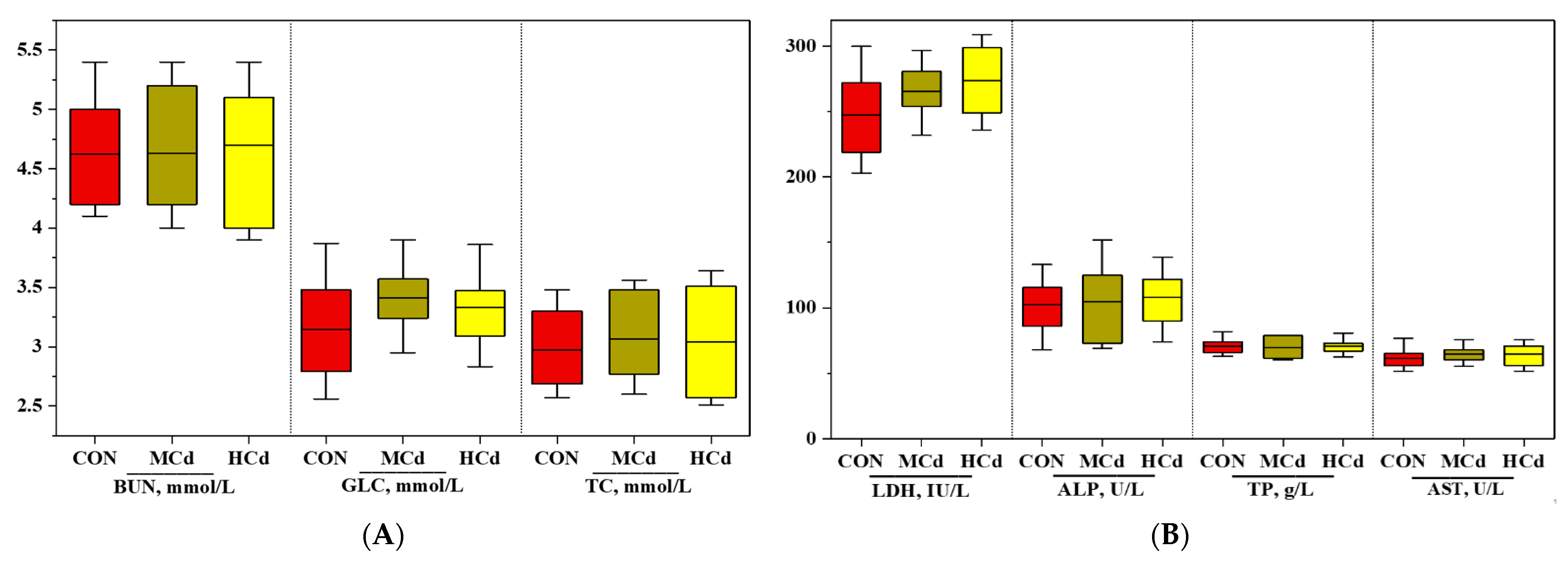
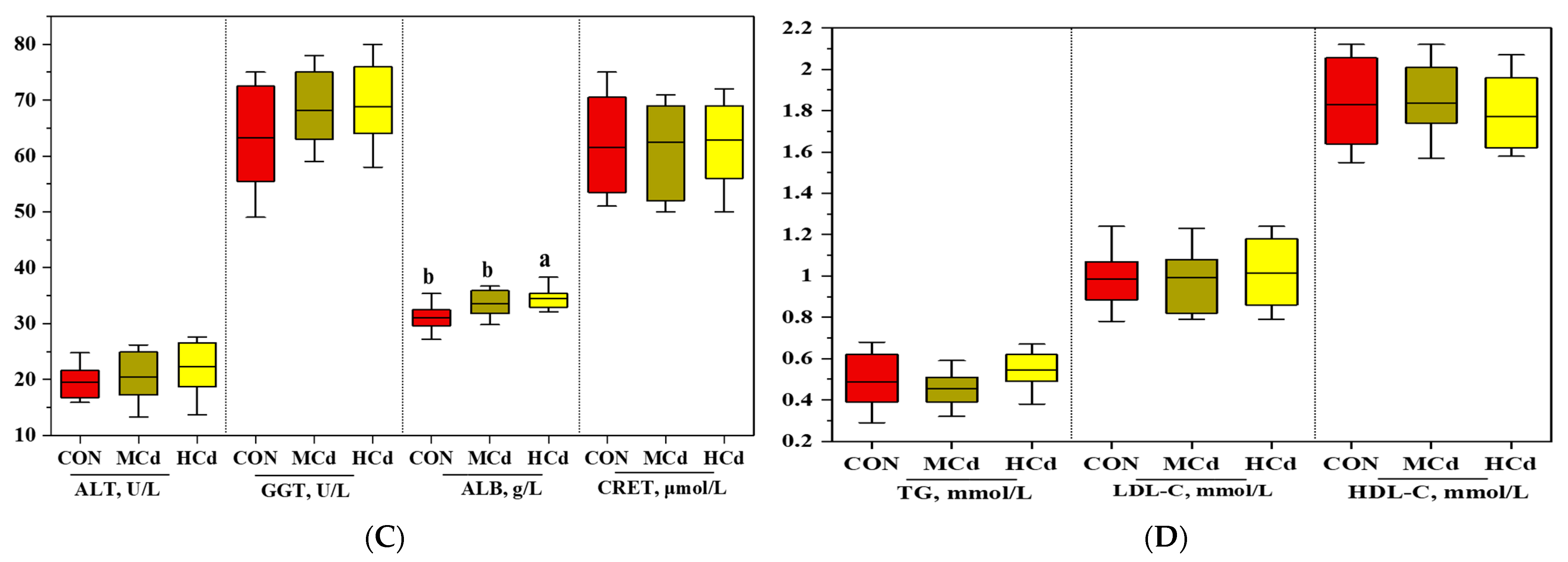
2.2. Growth Performance and Plasma Biochemical Indices
2.3. Determination of the Cd and Fe Concentration in Tissues
2.4. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.5. Gene Expression Profile
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Dietary Cd on Growth Performance and Plasma Biochemical Indices
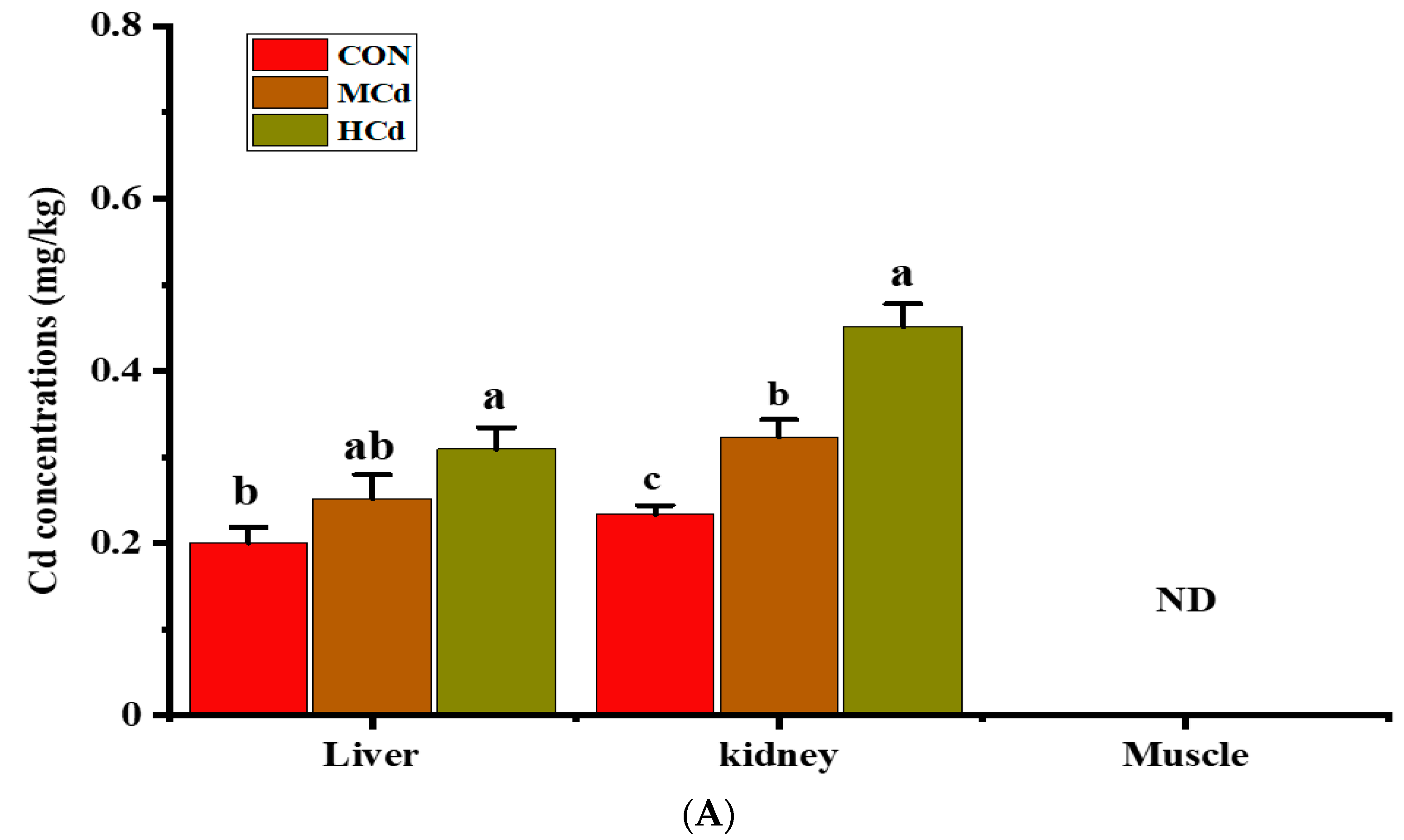
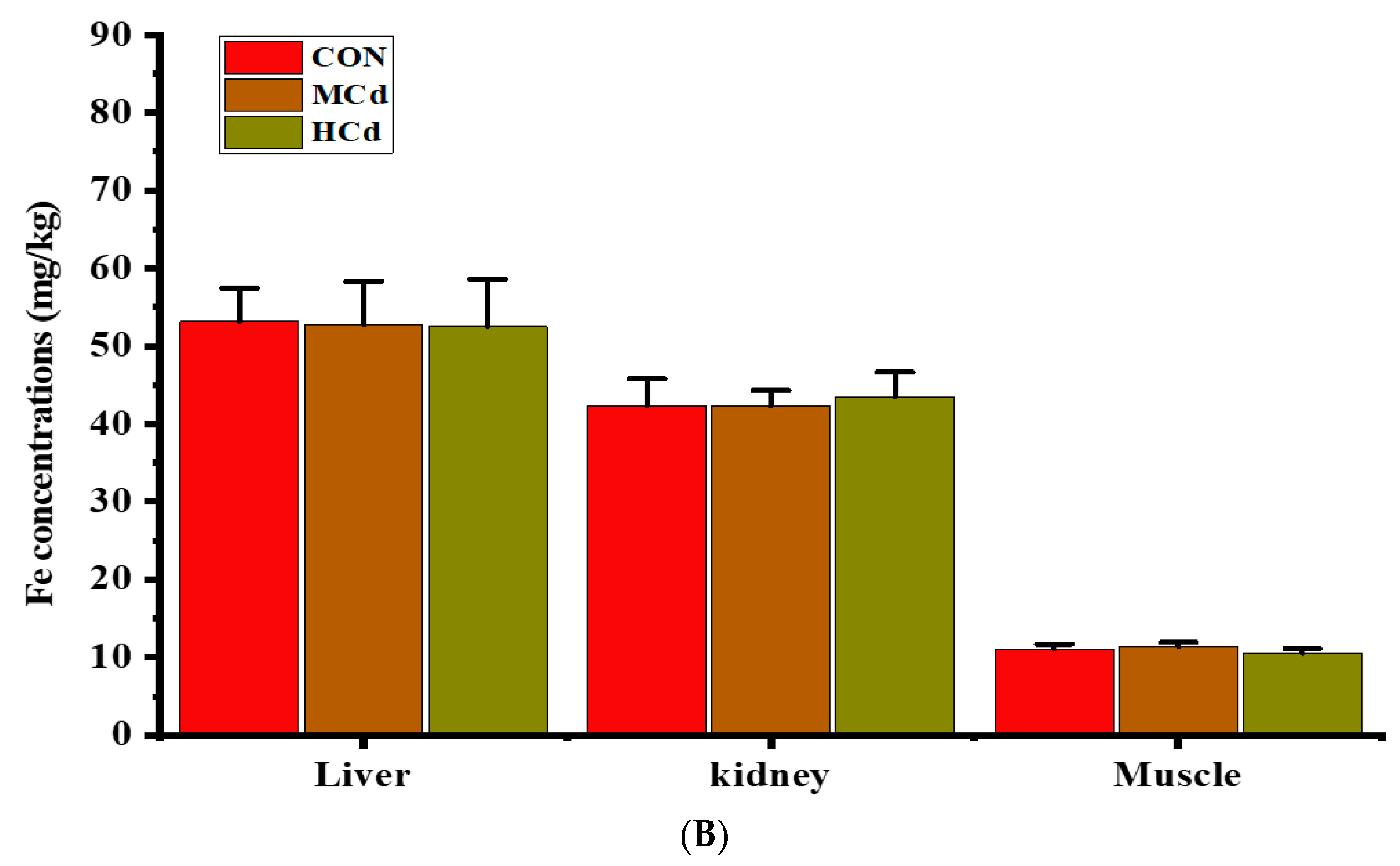
3.2. Effects of Dietary Cd on the Cd and Fe Concentrations in the Liver, Kidney and Muscle Tissues
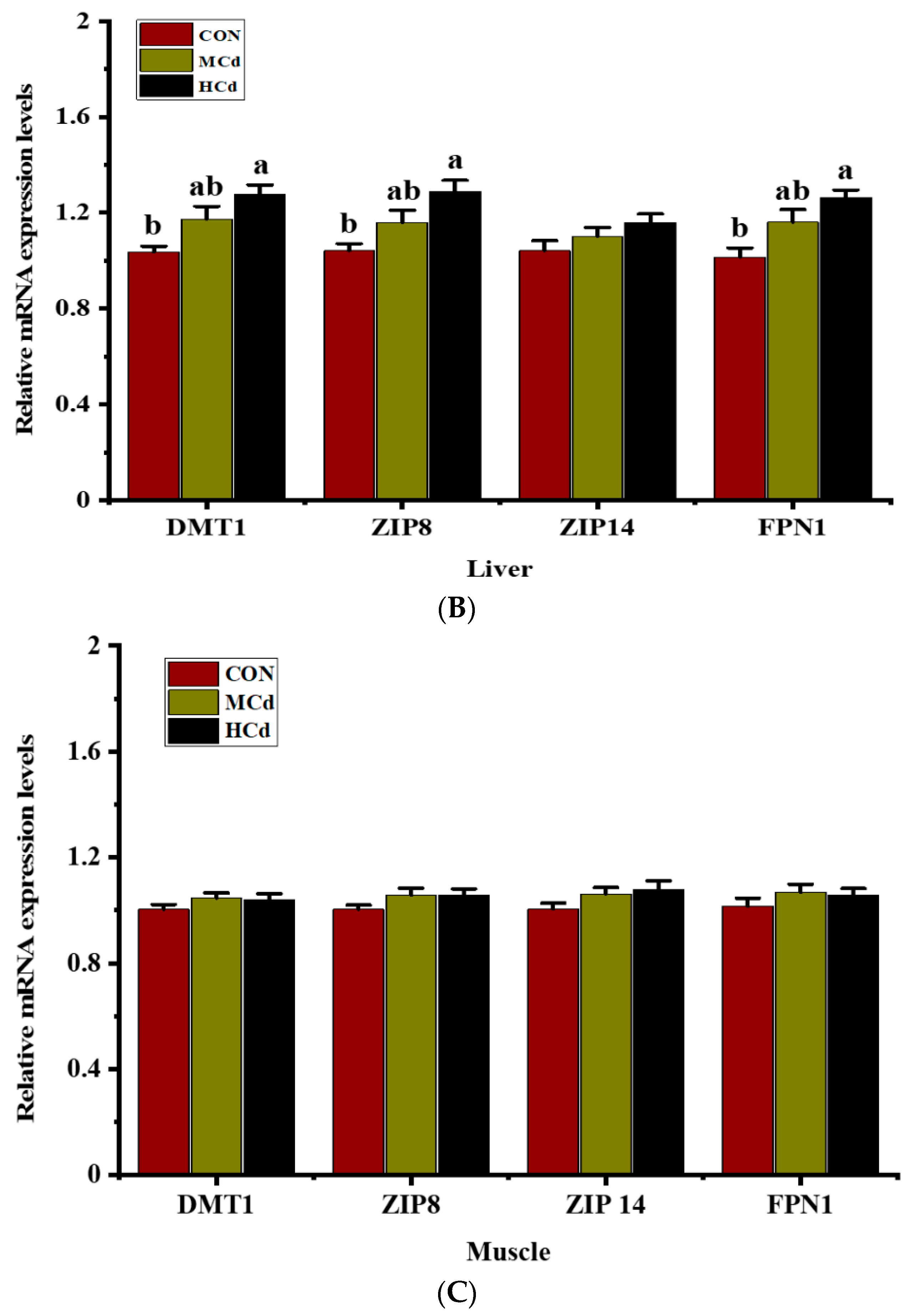
3.3. Effects of Dietary Cd on the Expression of Genes Involved in Metal Transport
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chałabis-Mazurek, A.; Rechulicz, J.; Pyz-Łukasik, R. A Food-Safety Risk Assessment of Mercury, Lead and Cadmium in Fish Recreationally Caught from Three Lakes in Poland. Animals 2021, 11, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Hill, J.; Phillips, C.J.C. The accumulation of potentially-toxic metals by grazing ruminants. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Xing, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Gu, X.; Luo, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Hu, G. Effect of Stress from Cadmium Combined with Different Levels of Molybdenum on Serum Free Radical and Expression of Related Apoptosis Genes in Goat Livers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 172, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogowska, K.A.; Monkiewicz, J.; Kaszyca, S. Correlations in cadmium concentrations in the body of the sheep poisoned subacutely and nourished with or without a supplement of detoxicating preparation. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2008, 52, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ajarem, J.S.; Hegazy, A.K.; Allam, G.A.; Allam, A.A.; Maodaa, S.N.; Mahmoud, A.M. Heavy Metal Accumulation, Tissue Injury, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Dromedary Camels Living near Petroleum Industry Sites in Saudi Arabia. Animals 2022, 12, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nriagu, J.; Boughanen, M.; Linder, A.; Howe, A.; Grant, C.; Rattray, R.; Vutchkov, M.; Lalor, G. Levels of As, Cd, Pb, Cu, Se and Zn in bovine kidneys and livers in Jamaica. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Long, M.L.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, Q.Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. Food chain transfer of cadmium and lead to cattle in a lead-zinc smelter in Guizhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 3078–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włostowski, T.; Bonda, E.; Krasowska, A. Free-ranging European bisons accumulate more cadmium in the liver and kidneys than domestic cattle in north-eastern Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 364, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKie, A.T.; Marciani, P.; Rolfs, A.; Brennan, K.; Wehr, K.; Barrow, D.; Miret, S.; Bomford, A.; Peters, T.J.; Farzaneh, F.; et al. A novel duodenal iron-regulated transporter, IREG1, implicated in the basolateral transfer of iron to the circulation. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.S.; Ueda, H.; Kihara, T.; Tanaka, K. Increased hepatic accumulation of ingested Cd is associated with upregulation of several intestinal transporters in mice fed diets deficient in essential metals. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 106, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gunshin, H.; Mackenzie, B.; Berger, U.V.; Gunshin, Y.; Romero, M.F.; Boron, W.F.; Nussberger, S.; Gollan, J.L.; Hediger, M.A. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature 1997, 388, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, D.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Park, D.W.; Choi, B.S.; Klaassen, C.D.; Park, J.D. Dietary iron regulates intestinal cadmium absorption through iron transporters in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 152, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, T.P.; He, L.; Wang, B.; Miller, M.L.; Jin, L.; Stringer, K.F.; Chang, X.; Baxter, C.S.; Nebert, D.W. Identification of mouse SLC39A8 as the transporter responsible for cadmium-induced toxicity in the testis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3401–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girijashanker, K.; He, L.; Soleimani, M.; Reed, J.M.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Dalton, T.P.; Nebert, D.W. Slc39a14 gene encodes ZIP14, a metal/bicarbonate symporter: Similarities to the ZIP8 transporter. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Soleimani, M.; Girijashanker, K.; Reed, J.M.; He, L.; Dalton, T.P.; Nebert, D.W. Cd2+ versus Zn2+ uptake by the ZIP8 HCO3−-dependent symporter: Kinetics, electrogenicity and trafficking. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troadec, M.B.; Ward, D.M.V.; Lo, E.; Kaplan, J.; De Domenico, I. Induction of FPN1 transcription by MTF-1 reveals a role for ferroportin in transition metal efflux. Blood 2010, 116, 4657–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Chung, J. Cadmium increases ferroportin-1 gene expression in J774 macrophage cells via the production of reactive oxygen species. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2009, 3, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fujishiro, H.; Yano, Y.; Takada, Y.; Tanihara, M.; Himeno, S. Roles of ZIP8, ZIP14, and DMT1 in transport of cadmium and manganese in mouse kidney proximal tubule cells. Metallomics 2012, 4, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, J.; Le Clère, K.; Daniel, C.; Sauty, M.; Nakab, L.; Chassat, T.; Dewulf, J.; Penet, S.; Carnoy, C.; Thomas, P.; et al. Chronic ingestion of cadmium and lead alters the bioavailability of essential and heavy metals, gene expression pathways and genotoxicity in mouse intestine. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Nebert, L.F.; Gálvez-Peralta, M.; Landero Figueroa, J.; Somarathna, M.; Hojyo, S.; Fukada, T.; Nebert, D.W. Comparing gene expression during cadmium uptake and distribution: Untreated versus oral Cd-treated wild-type and ZIP14 knockout mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 143, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaiman, D.; Jonah, M.M.; Miyasaki, W.; Ho, G.; Bhattacharyya, M.H. Increased metallothionein in mouse liver, kidneys, and duodenum during lactation. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 60, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zacharias, B.; Ott, H.; Drochner, W. The influence of dietary microbial phytase and copper on copper status in growing pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2003, 106, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, W.; Feng, Z.; Huang, R.; Yin, Y. Transcriptomic analysis on responses of the liver and kidney of finishing pigs fed cadmium contaminated rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2964–2972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Small Ruminants: Sheep, Goats, Cervids, and New World Camelids; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hussain, T.; Dai, C.; Li, J.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Ding, X.; Huang, J.; Ji, F.; et al. Effects of dietary energy level on growth performance, blood parameters and meat quality in fattening male Hu lambs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyew, K.; Chen, W.; Yan, Q.; He, Z.; Tan, Z. Growth of Pancreas and Intestinal Enzyme Activities in Growing Goats: Influence of a Low-Protein Diet. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhou, H.; Yang, F.; Mao, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Dai, J.; Xiao, G.; et al. Additive, dominant parental effects control the inheritance of grain cadmium accumulation in hybrid rice. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyew, K.; Yang, C.; He, Z.; Tan, Z. Low-protein diets supplemented with methionine and lysine alter the gut microbiota composition and improve the immune status of growing lambs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 8393–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lei, A.; Wang, L.; Niu, L.; Zhan, S.; Guo, J.; Cao, J.; Li, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Reference Genes for Reverse-Transcription Quantitative PCR in Goat Rumen. Animals 2021, 11, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Kuang, X. Correlation between environmental low-dose cadmium exposure and early kidney damage: A comparative study in an industrial zone vs. a living quarter in Shanghai, China. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 79, 103381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haouem, S.; Hmad, N.; Fathel, M.; El, A.; Sakly, R. Accumulation of cadmium and its effects on liver and kidney functions in rats given diet containing cadmium-polluted radish bulb. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 59, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.; Stark, B.A.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Curran, M.K.; Lean, I.J.; Hall, J.E.; Livesey, C.T. Accumulation of potentially toxic elements by sheep given diets containing soil and sewage sludge. 2. Effect of the ingestion of soils treated historically with sewage sludge. Anim. Sci. 1998, 67, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, E.A.; Canty, M.J.; More, S.J. Cadmium exposure and consequence for the health and productivity of farmed ruminants. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 101, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artacho, P.; Soto-gamboa, M.; Verdugo, C.; Nespolo, R.F. Blood biochemistry reveals malnutrition in black-necked swans (Cygnus melanocoryphus) living in a conservation priority area. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 146, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andjelkovic, M.; Djordjevic, A.B.; Antonijevic, E.; Spasojevic-kalimanovska, V.; Jovanovic, M.; Boricic, N. Toxic Effect of Acute Cadmium and Lead Exposure in Rat Blood, Liver, and Kidney. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renugadevi, J.; Prabu, S.M. Cadmium induced Hepatotoxicity in rats and the protective effect of Cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity in rats and the protective effect of naringenin. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018, 62, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovásová, E.; Rácz, O.; Cimboláková, I.; Nováková, J. Effects of Chronic Low-Dose Cadmium Exposure on Selected Biochemical and Antioxidant Parameters in Rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health-Part A Curr. Issues 2013, 76, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olisekodiaka, J.; Igbeneghu, C.A.; Onuegbu, A.J. Lipid, Lipoproteins, Total Antioxidant Status and Organ Changes in Rats Administered High Doses. Med. Princ. Pract. 2010, 21, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalska, J.; Brzóska, M.M.; Roszczenko, A.; Moniuszko-jakoniuk, J. Enhanced zinc consumption prevents cadmium-induced alterations in lipid metabolism in male rats. Chemico-Biol. Interact. 2009, 177, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, I.; Elhabiby, M.; Ashour, A.A. Toxicity of cadmium and protective effect of bee honey, vitamins C and B complex. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 32, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, T.; Mitra, P.; Singh, P.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P. Assessement of Blood Lead and Cadmium Levels in Occupationally Exposed Workers of Jodhpur, Rajasthan. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 36, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prankel, S.H.; Nixon, R.M.; Phillips, C.J.C. Meta-analysis of feeding trials investigating cadmium accumulation in the livers and kidneys of sheep. Environ. Res. 2004, 94, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Liu, J.; Choudhuri, S. Metallothionein: An intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity. Ann. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 1999, 39, 267–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waegeneers, N.; Pizzolon, J.C.; Hoenig, M.; De Temmerman, L. Accumulation of trace elements in cattle from rural and industrial areas in Belgium. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2009, 26, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressler, J.P.; Olivi, L.; Cheong, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Bannon, D. Divalent metal transporter 1 in lead and cadmium transport. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1012, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.D.; Cherrington, N.J.; Klaassen, C.D. Intestinal absorption of cadmium is associated with divalent metal transporter 1 in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 68, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leazer, T.M.; Liu, Y.; Klaassen, C.D. Cadmium absorption and its relationship to divalent metal transporter-1 in the pregnant rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2002, 185, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Girijashanker, K.; Dalton, T.P.; Reed, J.; Li, H.; Soleimani, M.; Nebert, D.W. ZIP8, member of the solute-carrier-39 (SLC39) metal-transporter family: Characterization of transporter properties. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishiro, H.; Doi, M.; Enomoto, S.; Himeno, S. High sensitivity of RBL-2H3 cells to cadmium and manganese: An implication of the role of ZIP8. Metallomics 2011, 3, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishiro, H.; Okugaki, S.; Kubota, K.; Fujiyama, T.; Miyataka, H.; Himeno, S. The role of ZIP8 down-regulation in cadmium-resistant metallothionein-null cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2009, 29, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abboud, S.; Haile, D.J. A Novel Mammalian Iron-regulated Protein Involved in Intracellular Iron Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, A.; Cutts, A.; Donovan, A.; Brownlie, A.; Zhou, Y.; Shepard, J.; Pratt, S.J.; Moynihan, J.; Paw, B.H.; Drejer, A.; et al. Positional cloning of zebrafish ferroportin1 identifies a conserved vertebrate iron exporter Positional cloning of zebrafish ferroportin1 identifies a conserved vertebrate iron exporter. Nature 2000, 403, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, N.A.; Liu, W.; Fenton, R.A.; Lee, W.; Thévenod, F.; Smith, C.P. Ferroportin 1 is expressed basolaterally in rat kidney proximal tubule cells and iron excess increases its membrane trafficking. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.J.; Shawki, A.; Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E.; Mackenzie, B. Functional properties of human ferroportin, a cellular iron exporter reactive also with cobalt and zinc. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2013, 306, C450–C459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, W.; Bowlus, C.L.; Tallkvist, J.; Lo, B.; Bowlus, C.L.; Tallk, J.; Lo, B. DMT1 and FPN1 expression during infancy: Developmental regulation of iron absorption. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G1153–G1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohrvik, H.; Oskarsson, A.; Lundh, T.; Ohrvik, H.; Skerfving, S.; Tallkvist, J. Impact of iron status on cadmium uptake in suckling piglets. Toxicology 2007, 240, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamunde, C.; Macphail, R. Metal–metal interactions of dietary cadmium, copper and zinc in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nica, D.V.; Draghici, G.A.; Andrica, F.M.; Popescu, S.; Coricovac, D.E.; Cristina, A.; Gergen, I.I.; Kovatsi, L.; Coleman, M.D.; Tsatsakis, A. Short-term effects of very low dose cadmium feeding on copper, manganese and iron homeostasis: A gastropod perspective. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 65, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Haile, D.J.; Wessling-resnick, M. Copper-induced ferroportin-1 expression in J774 macrophages is associated with increased iron efflux. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2700–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredient | % of DM |
|---|---|
| Paddy | 33.2 |
| Soybean meal | 9.6 |
| Wheat bran | 6.0 |
| Fat powder | 3.2 |
| Calcium carbonate | 0.5 |
| Calcium bicarbonate | 1.1 |
| Sodium chloride | 0.6 |
| Premix 1 | 1.0 |
| Rice straw | 45 |
| Chemical Composition 2 | % of DM |
| CP, % | 8.8 |
| NDF, % | 47 |
| ADF, % | 33.5 |
| Ca, % | 0.47 |
| Total P, % | 0.32 |
| Gene | Primers (5′~3′) | Bp | Accession | Efficiency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMT11 | Forward | TGCCTACAGTAATTCCTCAATTCCTCAG | 169 | BC113342.1 | 95.2 |
| Reverse | ATCCACAACGCTCATAAGAAGTCCTG | ||||
| ZIP81 | Forward | TTCCAGAGATGAACGATATGCTGAGAG | 115 | NM_001205630.1 | 102.6 |
| Reverse | ATGAGAAGAATGGCTGTGAATCCAGTT | ||||
| ZIP141 | Forward | AGAATGAGGAGAACGAGCAGACAGA | 182 | BC140602.1 | 108.7 |
| Reverse | TCCAATCGCCAGAGCTATGAAGTAGA | ||||
| FPN1 | Forward | AGACAGAGGCAGATTAGCAGATATGAATG | 134 | XM_018065526.1 | 104.9 |
| Reverse | CCGAAATGAAACCACAGCCAATGAC | ||||
| ACTB | Forward | CTTCCAGCCTTCCTTCCTG | 111 | NM_001314342.1 | 97.1 |
| Reverse | ACCGTGTTGGCGTAAAGGT | ||||
| GAPDH | Forward | GGGTCATCATCTCTGCACCT | 176 | XM_005680968.3 | 105.2 |
| Reverse | GGTCATAAGTCCCTCCACGA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gebeyew, K.; Jiang, C.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Tan, Z.; Han, X. Cadmium Accumulation in the Goat Liver and Kidney Is Partially Promoted by the Upregulation of Metal Transporter Genes. Animals 2022, 12, 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111408
Gebeyew K, Jiang C, Gao Q, Zhang L, Zhu H, Tian Y, Wang Q, Wei Y, Tan Z, Han X. Cadmium Accumulation in the Goat Liver and Kidney Is Partially Promoted by the Upregulation of Metal Transporter Genes. Animals. 2022; 12(11):1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111408
Chicago/Turabian StyleGebeyew, Kefyalew, Chunyu Jiang, Qinghua Gao, Liping Zhang, Hanhua Zhu, Yushi Tian, Qi Wang, Yuqing Wei, Zhiliang Tan, and Xuefeng Han. 2022. "Cadmium Accumulation in the Goat Liver and Kidney Is Partially Promoted by the Upregulation of Metal Transporter Genes" Animals 12, no. 11: 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111408
APA StyleGebeyew, K., Jiang, C., Gao, Q., Zhang, L., Zhu, H., Tian, Y., Wang, Q., Wei, Y., Tan, Z., & Han, X. (2022). Cadmium Accumulation in the Goat Liver and Kidney Is Partially Promoted by the Upregulation of Metal Transporter Genes. Animals, 12(11), 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111408