Ultrasonography of Parasitic Diseases in Domestic Animals: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Ultrasound AND veterinary AND parasitology.
- Ultrasonography AND veterinary AND parasitology.
- Ultrasound AND (parasites OR parasitology) AND (small animals OR ruminants OR swine OR horses OR equids).
- Ultrasound AND veterinary AND (nematodes OR cestodes OR trematodes).
- Ultrasound AND animals AND (nematodes OR cestodes OR trematodes).
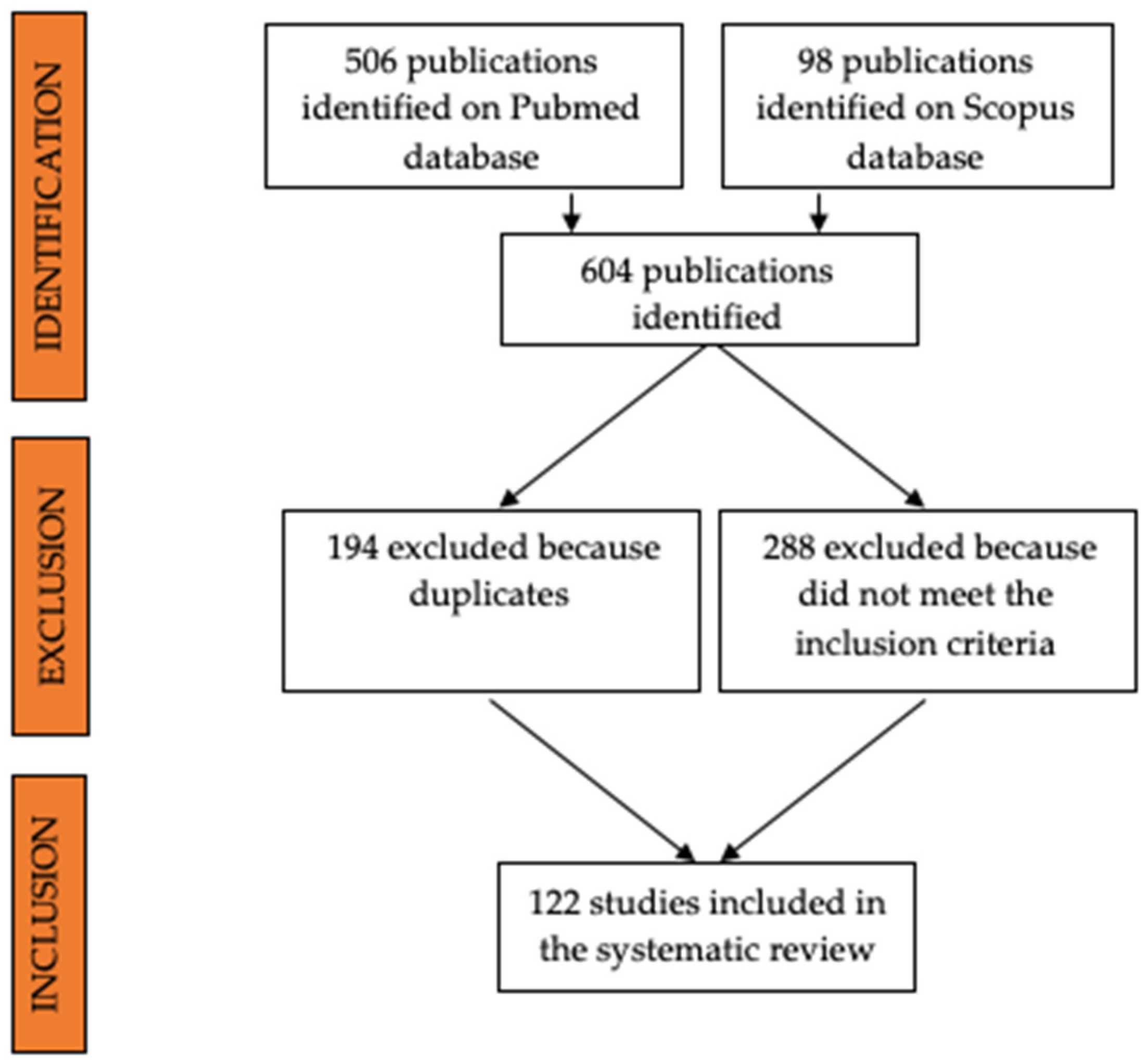
3. Results
3.1. Cestodes
3.2. Nematodes
3.3. Trematodes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ndao, M. Diagnosis of Parasitic Diseases: Old and New Approaches. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2009, 2009, 278246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenopoulos, K.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Papadopoulos, E. Sonoparasitology: An alternative approach to parasite detection in sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 152, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.M. Development, advances and applications of diagnostic ultrasound in animals. Vet. J. 2006, 171, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Urbani, C.; Jiamin, Q.; Vuitton, D.A.; Dongchuan, Q.; Heath, D.D.; Craig, P.S.; Zheng, F.; Schantz, P.M. Control of echinococcosis and cysticercosis: A public health challenge to international cooperation in China. Acta Trop. 2003, 86, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, G.A.; Carmena, D. A review of the global prevalence, molecular epidemiology and economics of cystic echinococcosis in production animals. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 192, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplazes, P.; Rinaldi, L.; Alvarez Rojas, C.A.; Torgerson, P.R.; Harandi, M.F.; Romig, T.; Antolova, D.; Schurer, J.M.; Lahmar, S.; Cringoli, G.; et al. Global Distribution of Alveolar and Cystic Echinococcosis. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 315–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romig, T. Epidemiology of echinococcosis. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2003, 388, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seimenis, A. Overview of the epidemiological situation on echinococcosis in the Mediterranean region. Acta Trop. 2003, 85, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, P.R. Economic effects of echinococcosis. Acta Trop. 2003, 85, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.L. Ultrasonography of echinococcal cysts. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1973, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicary, F.R.; Cusick, G.; Shirley, I.M.; Blackwell, R.J. Ultrasound and abdominal hydatid disease. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1977, 71, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, C.N.L.; Vuitton, D.A.; Gharbi, H.A.; Caremani, M.; Frider, B.; Brunettii, E.; Perdomo, R.; Schantz, P.M.; Felice, C.; Teggi, A.; et al. International classification of ultrasound images in cystic echinococcosis for application in clinical and field epidemiological settings. Acta Trop. 2003, 85, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson, A.D.; Wachira, T.M.; Zeyhle, E.E.; Fine, A.; Mwangi, T.W.; Smith, G. The use of ultrasound to study the prevalence of hydatid cysts in the right lung and liver of sheep and goats in Turkana, Kenya. Int. J. Parasitol. 1996, 26, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnera, E.A.; Zanzottera, E.M.; Pereyra, H.; Franco, A.J. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of ovine cystic echinococcosis. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2001, 42, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahmar, S.; Chéhida, F.B.; Pétavy, A.F.; Hammou, A.; Lahmar, J.; Ghannay, A.; Gharbi, H.A.; Sarciron, M.E. Ultrasonographic screening for cystic echinococcosis in sheep in Tunisia. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 143, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi, H.A.; Hassine, W.; Brauner, M.W.; Dupuch, K. Ultrasound examination of the hydatic liver. Radiology 1981, 139, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, F.; Varcasia, A.; Pipia, A.P.; Sanna, G.; Pinna Parpaglia, M.L.; Corda, A.; Romig, T.; Scala, A. Ultrasound as a monitoring tool for cystic echinococcosis in sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 203, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, G.; Guccione, J.; Di Loria, A.; Bosco, A.; Pepe, P.; Prisco, F.; Cringoli, G.; Paciello, O.; Rinaldi, L.; Ciaramella, P. Fast focus ultrasound liver technique for the assessment of cystic echinococcosis in sheep. Animals 2021, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmar, S.; Sarciron, M.E.; Chehida, F.B.; Hammou, A.; Gharbi, H.A.; Gherardi, A.; Lahmar, J.; Ghannay, A.; Pétavy, A.F. Cystic hydatic disease in sheep: Treatment with percutaneous aspiration and injection with dipeptide methyl ester. Vet. Res. Commun. 2006, 30, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, V.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, B.B.; Randhawa, C.S.; Uppal, S.K. Stridor and emphysema due to cystic echinococcosis in cattle and buffalo intermediate hosts in Punjab, India. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2017, 10, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson Sage, A.; Wachira, T.M.; Zeyhle, E.E.; Weber, E.P.; Njoroge, E.; Smith, G. Evaluation of diagnostic ultrasound as a mass screening technique for the detection of hydatid cysts in the liver and lung of sheep and goats. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; Elrashidy, M. Ultrasonographic features of the liver with cystic echinococcosis in sheep. Vet. Rec. Open 2014, 1, e000004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sagkan-Ozturk, A.; Durgut, R.; Ozturk, O.H. Oxidant/antioxidant status in lambs and sheep with liver and lung cystic echinococcosis diagnosed by ultrasonography and necropsy. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 208, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cringoli, G.; Pepe, P.; Bosco, A.; Maurelli, M.P.; Baldi, L.; Ciaramella, P.; Musella, V.; Buonanno, M.L.; Capuano, F.; Corrado, F.; et al. An integrated approach to control Cystic Echinococcosis in southern Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 290, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armua-Fernandez, M.T.; Castro, O.F.; Crampet, A.; Bartzabal, Á.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Grimm, F.; Deplazes, P. First case of peritoneal cystic echinococcosis in a domestic cat caused by Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto (genotype 1) associated to feline immunodeficiency virus infection. Parasitol. Int. 2014, 63, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, H.G.; Maglioco, A.; Gertiser, M.L.; Ferreyra, M.P.; Ferrari, F.; Klinger, E.; Barbery Venturi, M.S.; Agüero, F.A.; Fuchs, A.G.; Jensen, O. First report of cystic echinococcosis caused by Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto/G1 in Felis catus from the Patagonian region of Argentina. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konyaev, S.V.; Yanagida, T.; Ivanov, M.V.; Ruppel, V.V.; Sako, Y.; Nakao, M.; Ito, A. The first report on cystic echinococcosis in a cat caused by Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto (G1). J. Helminthol. 2012, 86, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, P.; Masu, G.; Dei Giudici, S.; Pintus, D.; Peruzzu, A.; Piseddu, T.; Santucciu, C.; Cossu, A.; Demurtas, N.; Masala, G. Cystic echinococcosis in a domestic cat (Felis catus) in Italy. Parasite 2018, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scharf, G.; Deplazes, P.; Kaser-Hotz, B.; Borer, L.; Hasler, A.; Haller, M.; Flückiger, M. Radiographic, ultrasonographic, and computed tomographic appearance of alveolar echinococcosis in dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2004, 45, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, M.; Geissbühler, U.; Howard, J.; Gottstein, B.; Spreng, D.; Frey, C.F. Clinical presentation, diagnosis, therapy and outcome of alveolar echinococcosis in dogs. Vet. Rec. 2015, 177, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geigy, C.A.; Kühn, K.; Rütten, M.; Howard, J.; Grimm, F.; Rohrer Bley, C. Unusual presentation of alveolar echinococcosis as prostatic and paraprostatic cysts in a dog. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antolová, D.; Víchová, B.; Jarošová, J.; Gál, V.; Bajuzík, B. Alveolar echinococcosis in a dog; Analysis of clinical and histological findings and molecular identification of Echinococcus multilocularis. Acta Parasitol. 2018, 63, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delling, C.; Böttcher, D.; Cabrera-García, I.A.; Kiefer, I.; Helm, C.; Daugschies, A.; Heilmann, R.M. Clinical, pathological and parasitological examinations of a German spaniel with alveolar echinococcosis, Germany, 2018. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 20, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajac, A.; Fairman, D.; McGee, E.; Wells, B.; Peregrine, A.; Jenkins, E.; LeRoith, T.; St John, B. Alveolar echinococcosis in a dog in the eastern United States. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heier, A.; Geissbühler, U.; Sennhauser, D.; Scharf, G.; Kühn, N. A case of alveolar hydatid disease in a dog: Domestic animals as rare incidental intermediate hosts for Echinococcus multilocularis. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2007, 149, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabattani, S.; Marliani, A.F.; Roncaroli, F.; Zucchelli, M.; Zini, A.; Calbucci, F.; Chiodo, F. Cerebral coenurosis: Case illustration. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varcasia, A.; Tamponi, C.; Ahmed, F.; Cappai, M.G.; Porcu, F.; Mehmood, N.; Dessì, G.; Scala, A. Taenia multiceps coenurosis: A review. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunta, M.L.; Evangelisti, M.A.; Burrai, G.P.; Columbano, N.; Ligios, C.; Varcasia, A.; Scala, A.; Passino, E.S. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and skull of sheep with cerebral coenurosis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Altonaga, J.R.; Diez, A.; Gonzalo, J.M.; Asuncion Orden, M. Correlation between MRI, computed tomographic findings and clinical signs in a case of ovine coenurosis. Vet. Rec. 2000, 146, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crilly, J.P.; Politis, A.P.; Hamer, K. Use of ultrasonographic examination in sheep veterinary practice. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 152, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Athar, H.; Fazili, M.u.R.; Mir, A.Q.; Gugjoo, M.B.; Ahmad, R.A.; Khan, H.M. Ultrasonography: An affordable diagnostic tool for precisely locating Coenurosis cyst in sheep And goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2018, 169, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, M.L.; McAllister, H.; Healy, A. Ultrasound as an aid to Coenurus cerebralis cyst localisation in a lamb. Vet. Rec. 1989, 124, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, D. Ultrasound diagnosis and surgical treatment of coenurosis (GID) in bengal goat (Capra hircus) at chittagong metropolitan area, Chittagong, Bangladesh. Sci. J. Vet. Adv. 2013, 2, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, A.; McCowan, C.; Hardman, C.; Stanley, R. Taenia serialis causing exophthalmos in a pet rabbit. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2002, 5, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, B.J.; Hollingsworth, S.R.; Osofsky, A.; Tell, L.A. Taenia coenurus in the orbit of a chinchilla. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2007, 10, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corda, A.; Dessì, G.; Varcasia, A.; Carta, S.; Tamponi, C.; Sedda, G.; Scala, M.; Marchi, B.; Salis, F.; Scala, A.; et al. Acute visceral cysticercosis caused by Taenia hydatigena in lambs: Ultrasonographic findings. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Garcia, S.C.; De Aluja, A.S.; Aguilar, R.E.M. Use of ultrasound to diagnose porcine cysticercosis. Vet. México 2007, 38, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Flecker, R.H.; Pray, I.W.; Santivaňez, S.J.; Ayvar, V.; Gamboa, R.; Muro, C.; Moyano, L.M.; Benavides, V.; Garcia, H.H.; O’Neal, S.E. Assessing Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Porcine Cysticercosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brody, A.; Kloer, T.B.; Rush, R.T.; Harris, L.J.; Griffin, L.R.; Sadar, M.J. Ultrasonographic features of mesenteric cysticercosis in a domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2020, 61, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfanti, U.; Bertazzolo, W.; Pagliaro, L.; Demarco, B.; Venco, L.; Casiraghi, M.; Bandi, C. Clinical, cytological and molecular evidence of Mesocestoides sp. infection in a dog from Italy. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 2004, 51, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venco, L.; Kramer, L.; Pagliaro, L.; Genchi, C. Ultrasonographic features of peritoneal cestodiasis caused by Mesocestoides sp. in a dog and in a cat. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2005, 46, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrescu, V.F.; Morganti, G.; Moretti, G.; Birettoni, F.; Cafiso, A.; Bufalari, A.; Lepri, E.; Caivano, D.; Porciello, F. Severe Pleural Effusion in a Dog Affected by Larval Mesocestodiasis. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2020, 40, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, S.; Corda, A.; Tamponi, C.; Dessì, G.; Nonnis, F.; Tilocca, L.; Cotza, A.; Knoll, S.; Varcasia, A.; Scala, A. Clinical forms of peritoneal larval cestodiasis by Mesocestoides spp. in dogs: Diagnosis, treatment and long term follow-up. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasur-Landau, D.; Salant, H.; Levin-Gichon, G.; Botero-Anug, A.M.; Zafrany, A.; Mazuz, M.L.; Baneth, G. Urinary incontinence associated with Mesocestoides vogae infection in a dog. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiide, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Yamaya, Y.; Uwasawa, A.; Miyoshi, A.; Yamada, K.; Watari, T.; Nogami, S. Case report: First confirmed case of canine peritoneal larval cestodiasis caused by Mesocestoides vogae (syn. M. corti) in Japan. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 201, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venco, L.; Mihaylova, L.; Boon, J.A. Right Pulmonary Artery Distensibility Index (RPAD Index). A field study of an echocardiographic method to detect early development of pulmonary hypertension and its severity even in the absence of regurgitant jets for Doppler evaluation in heartworm-infec. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 206, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badertscher, R.R.; Losonsky, J.M.; Paul, A.J.; Kneller, S.K. Two-dimensional echocardiography for diagnosis of dirofilariasis in nine dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1988, 193, 843–846. [Google Scholar]
- Corda, A.; Tamponi, C.; Meloni, R.; Varcasia, A.; Parpaglia, M.L.P.; Gomez-Ochoa, P.; Scala, A. Ultrasonography for early diagnosis of Toxocara canis infection in puppies. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.; Kawooya, M.; Esterre, P.; Ravaoalimalala, V.E.; Roth, J.; Thomas, A.K.; Roux, J.; Seitz, H.M.; Doehring, E. In vivo and in vitro studies on the sonographical detection of Ascaris lumbricoides. Pediatr. Radiol. 1997, 27, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Mansoor, N.; Quraishy, S.; Ilyas, M.; Hussain, S. Ultrasonographic appearance of Ascaris lumbricoides in small bowel. J. Ultrasound Med. 2001, 20, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.K.; Donoghue, E.M.; Stephens, M.L.; Stowe, C.J.; Donecker, J.M.; Fenger, C.K. An ultrasonographic scoring method for transabdominal monitoring of ascarid burdens in foals. Equine Vet. J. 2016, 48, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierantozzi, M.; Di Giulio, G.; Traversa, D.; Aste, G.; Di Cesare, A. Aberrant peritoneal localization of Dirofilaria repens in a dog. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2017, 10, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigger, A.; Peppler, C.; Kramer, M. Ultrasonographic appearance of intestinal roundworms in a dog and a cat. Vet. Rec. 2007, 161, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.T. Dirofilaria immitis in cats: Diagnosis and management. Compend. Contin. Educ. Vet. 2008, 30, 393–400, quiz 400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Atkins, C.E.; DeFrancesco, T.C.; Coats, J.R.; Sidley, J.A.; Keene, B.W. Heartworm infection in cats: 50 cases (1985–1997). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atkins, C.E.; Arther, R.G.; Ciszewski, D.K.; Davis, W.L.; Ensley, S.M.; Guity, P.S.; Chopade, H.; Hoss, H.; Settje, T.L. Echocardiographic quantification of Dirofilaria immitis in experimentally infected cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 158, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFrancesco, T.C.; Atkins, C.E.; Miller, M.W.; Meurs, K.M.; Keene, B.W. Use of echocardiography for the diagnosis of heartworm disease in cats: 43 cases (1985–1997). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venco, L.; Calzolari, D.; Mazzocchi, D.; Morini, S.; Genchi, C. The use of echocardiography as a diagnostic tool for detection of feline heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) infections. Feline Pract. 1998, 26, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, C.; Venco, L.; Simon, F.; Genchi, C. Feline heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) infection: Detection of specific IgG for the diagnosis of occult infections. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 70, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selcer, B.A.; Newell, S.M.; Mansour, A.E.; McCall, J.W. Radiographic and 2-D echocardiographic findings in eighteen cats experimentally exposed to D. immitis via mosquito bites. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 1996, 37, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, H.; Kato, K.; Sasaki, T.; Koyama, S.; Kotani, T.; Fukata, T. Echocardiographic diagnosis of dirofilariasis in a ferret. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2000, 41, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litster, A.L.; Atwell, R.B. Feline heartworm disease: A clinical review. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, J.W. Dirofilariasis in the domestic ferret. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 1998, 13, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Tasker, S.; Hartmann, K.; Belák, S.; Addie, D.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Egberink, H.; Frymus, T.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hosie, M.; et al. Dirofilarioses in cats: European guidelines from the ABCD on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020, 22, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.R.; Nutter, F.B.; Kyles, A.E.; Atkins, C.E.; Sellon, R.K. Systemic arterial dirofilariasis in five dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1997, 11, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goggin, J.M.; Biller, D.S.; Rost, C.M.; DeBey, B.M.; Ludlow, C.L. Ultrasonographic identification of Dirofilaria immitis in the aorta and liver of a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1997, 210, 1635–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Grimes, J.A.; Scott, K.D.; Edwards, J.F. Aberrant heartworm migration to the Abdominal aorta and systemic arteriolitis in a dog presenting with vomiting and hemorrhagic diarrhea. Can. Vet. J. 2016, 57, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Oldach, M.S.; Gunther-Harrington, C.T.; Balsa, I.M.; McLarty, E.M.; Wakeman, K.A.; Phillips, K.L.; Honkavaara, J.; Visser, L.C.; Stern, J.A. Aberrant migration and surgical removal of a heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis) from the femoral artery of a cat. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifur, L.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Montiani-Ferreira, F. Epidemiological aspects of filariosis in dogs on the coast of Paraná state, Brazil: With emphasis on Dirofilaria immitis. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 122, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, N.; Yamane, I.; Takemura, N. Comparison of canine heartworm removal rates using flexible alligator forceps guided by transesophageal echocardiography and fluoroscopy. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano-Parreño, B.; Carretón, E.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Falcón-Cordón, S.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Evaluation of pulmonary hypertension and clinical status in dogs with heartworm by Right Pulmonary Artery Distensibility Index and other echocardiographic parameters. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, Y.W.; Choi, H.J. Comparison of radiographic and echocardiographic features between small and large dogs with heartworm disease. J. Vet. Clin. 2019, 36, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maerz, I. Clinical and diagnostic imaging findings in 37 rescued dogs with heartworm disease in Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Parreño, B.; Carretón, E.; Caro-Vadillo, A.; Falcón-Cordón, S.; Falcón-Cordón, Y.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Pulmonary hypertension in dogs with heartworm before and after the adulticide protocol recommended by the American Heartworm Society. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 236, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novo Matos, J.; Malbon, A.; Dennler, M.; Glaus, T. Intrapulmonary arteriovenous anastomoses in dogs with severe Angiostrongylus vasorum infection: Clinical, radiographic, and echocardiographic evaluation. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2016, 18, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradies, P.; Sasanelli, M.; Capogna, A.; Mercadante, A.; Rubino, G.T.R.; Bussadori, C.M. Is Pulmonary Hypertension a Rare Condition Associated to Angiostrongylosis in Naturally Infected Dogs? Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2021, 43, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corda, A.; Carta, S.; Varcasia, A.; Tamponi, C.; Evangelisti, M.A.; Scala, A.; Pinna Parpaglia, M.L. Pulmonary arterial response to Angiostrongylus vasorum in naturally infected dogs: Echocardiographic findings in two cases. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estèves, I.; Tessier, D.; Dandrieux, J.; Polack, B.; Carlos, C.; Boulanger, V.; Muller, C.; Pouchelon, J.L.; Chetboul, V. Reversible pulmonary hypertension presenting simultaneously with an atrial septal defect and angiostrongylosis in a dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, A.P.; Chetboul, V.; Tessier-Vetzel, D.; Sampedrano, C.C.; Aletti, E.; Pouchelon, J.L. Severe pulmonary arterial hypertension due to Angiostrongylosus vasorum in a dog. Can. Vet. J. 2006, 47, 792–795, PMID 16933559. [Google Scholar]
- Glaus, T.; Schnyder, M.; Dennler, M.; Tschuor, F.; Wenger, M.; Sieber-Ruckstuhl, N. Natural infection with Angiostrongylus vasorum: Characterisation of 3 dogs with pulmonary hypertension. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2010, 152, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crisi, P.E.; Traversa, D.; Di Cesare, A.; Luciani, A.; Civitella, C.; Santori, D.; Boari, A. Irreversible pulmonary hypertension associated with Troglostrongylus brevior infection in a kitten. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 102, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirven, M.; Szatmári, V.; Van Den Ingh, T.; Nijsse, R. Reversible pulmonary hypertension associated with lungworm infection in a young cat. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2012, 14, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzosi, T.; Perrucci, S.; Parisi, F.; Morelli, S.; Maestrini, M.; Mennuni, G.; Traversa, D.; Poli, A. Fatal Pulmonary Hypertension and Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure in a Kitten Infected with Aelurostrongylus abstrusus. Animals 2020, 10, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczinski, S.; Pinard, J.; Ferrouillet, C.; Veillette, M. Echocardiographic findings in a goat with cor pulmonale secondary to chronic parasitic pneumonia. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2010, 152, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brianti, E.; Gaglio, G.; Giannetto, S.; Annoscia, G.; Latrofa, M.S.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Traversa, D.; Otranto, D. Troglostrongylus brevior and Troglostrongylus subcrenatus (Strongylida: Crenosomatidae) as agents of broncho-pulmonary infestation in domestic cats. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Traversa, D.; Guglielmini, C. Feline aelurostrongylosis and canine angiostrongylosis: A challenging diagnosis for two emerging verminous pneumonia infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 157, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuca, L.; Meomartino, L.; Piantedosi, D.; Cortese, L.; Cringoli, G.; Rinaldi, L.; Lamagna, B. Irreversible Ocular Lesions in a Dog With Angiostrongylus Vasorum Infection. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2019, 36, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venco, L.; Colaneri, G.; Formaggini, L.; De Franco, M.; Rishniw, M. Utility of thoracic ultrasonography in a rapid diagnosis of angiostrongylosis in young dogs presenting with respiratory distress. Vet. J. 2021, 271, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, L.; Cortese, L.; Meomartino, L.; Pagano, T.B.; Pepe, P.; Cringoli, G.; Papparella, S. Angiostrongylus vasorum: Epidemiological, clinical and histopathological insights. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traversa, D.; Di Cesare, A.; Meloni, S.; Frangipane di Regalbono, A.; Milillo, P.; Pampurini, F.; Venco, L. Canine angiostrongylosis in Italy: Occurrence of Angiostrongylus vasorum in dogs with compatible clinical pictures. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzocchi, S.; Lendner, M.; Piseddu, E.; Sebastiani, V.; Morabito, S.; Daugschies, A.; Pantchev, N. Nodular presentation of Dirofilaria repens infection in a cat mimicking a fibrosarcoma. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 46, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lia, R.P.; Mutafchiev, Y.; Veneziano, V.; Giannelli, A.; Abramo, F.; Santoro, M.; Latrofa, M.S.; Cantacessi, C.; Martin, C.; Otranto, D.; et al. Filarial infection caused by Onchocerca boehmi (Supperer, 1953) in a horse from Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franchini, D.; Giannelli, A.; Di Paola, G.; Cortes, H.; Cardoso, L.; Lia, R.P.; Campbell, B.E.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Lenoci, D.; Assad, E.A.; et al. Image diagnosis of zoonotic onchocercosis by Onchocerca lupi. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 203, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, V.; Maia, C.; Pereira, A.; Gonçalves, N.; Caruso, M.; Martin, C.; Cardoso, L.; Campino, L.; Scandale, I.; Otranto, D. Evaluation of oxfendazole in the treatment of zoonotic Onchocerca lupi infection in dogs. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giannelli, A.; Baldassarre, V.; Ramos, R.A.N.; Lia, R.P.; Furlanello, T.; Trotta, M.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Baneth, G.; Otranto, D. Spirocerca lupi infection in a dog from southern Italy: An “old fashioned” disease? Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2391–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merhavi, N.; Segev, G.; Dvir, E.; Peery, D. Ultrasonography is insensitive but specific for detecting aortic wall abnormalities in dogs infected with Spirocerca lupi. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, A.; Loxton, A.J.; Heydenrych, J.J.; Abdurahman, K.E. Sonographic diagnosis of biliary ascariasis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1982, 139, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuroo, M.S.; Zargar, S.A.; Mahajan, R.; Bhat, R.L.; Javid, G. Sonographic appearances in biliary ascariasis. Gastroenterology 1987, 93, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, R.J. Ultrasonography of intestinal ascaris. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1990, 18, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmen, M.N.; Oğuzkurt, L.; Ahmet, B.; Akata, D.; Akhan, O. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of intestinal ascariasis. Pediatr. Radiol. 1995, 25, S171–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venier, F.; Compagnone, K.; Kerins, A.; Rosa, C. Common bile duct obstruction caused by a helminth in a cat in the UK: Ultrasonographic findings, histopathology and outcome. J. Feline Med. Surg. Open Rep. 2021, 7, 205511692098439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cribb, N.C.; Coté, N.M.; Bouré, L.P.; Peregrine, A.S. Acute small intestinal obstruction associated with Parascaris equorum infection in young horses: 25 cases (1985–2004). N. Z. Vet. J. 2006, 54, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatz, A.J.; Segev, G.; Steinman, A.; Berlin, D.; Milgram, J.; Kelmer, G. Surgical treatment for acute small intestinal obstruction caused by Parascaris equorum infection in 15 horses (2002–2011). Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 2012, 44, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Steen, L.; Pardon, B.; Sarre, C.; Valgaeren, B.; Van Hende, D.; Vlaminck, L.; Deprez, P. Intestinal obstruction by Toxocara vitulorum in a calf. Vlaams Diergeneeskd. Tijdschr. 2014, 83, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, J.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Yurlova, N.; Pedrassani, D.; Yoshikawa, M.; Nawa, Y. Dioctophyme renale (Goeze, 1782) (Nematoda, Dioctophymidae) parasitic in mammals other than humans: A comprehensive review. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 81, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.L.D.R.; Bracarense, A.P.F.R.L.; dos Reis, A.C.F.; Yamamura, M.H.; Headley, S.A. Giant kidney worm (Dioctophyma renale) infections in dogs from Northern Paraná, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, C.B.; Santos, M.C.S.; de Andrade, P.S.C. Ectopic dioctophymosis in a dog–Clinical, diagnostic and pathological challenges of a silent disease. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 78, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caye, P.; Perera, S.C.; Mendes, C.B.d.M.; Sanches, M.C.; Salame, J.P.; Robaldo, G.F.; Brun, M.V.; Rappeti, J.C.d.S. Ectopic Dioctophyme renale in the thoracic and abdominal cavities associated with renal parasitism in a dog. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 80, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paras, K.L.; Miller, L.; Verocai, G.G. Ectopic infection by Dioctophyme renale in a dog from Georgia, USA, and a review of cases of ectopic dioctophymosis in companion animals in the Americas. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2018, 14, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahal, S.C.; Mamprim, M.J.; Oliveira, H.S.; Mesquita, L.R.; Faria, L.G.; Takahira, R.K.; Matsubara, L.M.; Agostinho, F.S. Ultrasonographic, computed tomographic, and operative findings in dogs infested with giant kidney worms (Dioctophyme renale). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 244, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, C.B. Dioctophyme renale (Goeze, 1782) diagnosis in companion animals: Let’s not overlook ultrasonography! Parasitol. Int. 2022, 87, 2021–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, V.L.; Medeiros, F.P.; July, J.R.; Raso, T.F. Dioctophyma renale in a dog: Clinical diagnosis and surgical treatment. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, M.; Cardoso, L.; Teixeira, M.; Agut, A. Imaging diagnosis–Dioctophyma renale in a dog. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2008, 49, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butti, M.J.; Gamboa, M.I.; Terminiello, J.D.; Franchini, G.R.; Giorello, A.N.; Maldonado, L.L.; Kamenetzky, L.; Luna, M.F.; Lopez Merlo, M.; Radman, N.E. Dioctophyme renale in a domestic cat (Felis catus): Renal location and nephrectomy. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2019, 18, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrassani, D.; Wendt, H.; Rennau, E.A.; Pereira, S.T.; Wendt, S.B.T. Dioctophyme renale Goeze, 1782 in a cat with a supernumerary kidney. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2014, 23, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, M.A.; Coop, R.L.; Wall, R.L. Parassitologia E Malattie Parassitarie Degli Animali, 1st ed.; EMSI: Rome, Italy, 2010; ISBN 8886669755. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.K.; Jang, H.J.; Choi, B.I.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, T.K.; Won, H.J.; Kim, Y., II; Cho, S.Y. Experimental hepatobiliary fascioliasis in rabbits: A radiology-pathology correlation. Investig. Radiol. 1999, 34, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo-Orden, M.; Millán, L.; Álvarez, M.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Jiménez, R.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Diagnostic imaging in sheep hepatic fascioliasis: Ultrasound, computer tomography and magnetic resonance findings. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 90, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.R.; Sargison, N.D.; Macrae, A.; Rhind, S.R. An outbreak of subacute fasciolosis in Soay sheep: Ultrasonographic biochemical and histological studies. Vet. J. 2005, 170, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, M. Ultrasonographic findings in cattle and buffaloes with chronic hepatic fascioliosis. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Damaty, H.M.; Mahmmod, Y.S.; Gouda, S.M.; Sobhy, N.M. Epidemiological and ultrasonographic investigation of bovine fascioliasis in smallholder production system in Eastern Nile Delta of Egypt. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 158, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S.; Mohammadi, T. Ultrasonographic Liver Findings in a Sheep Flock Involved in Chronic Fasciolosis. Iran. J. Vet. Med. 2019, 13, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.J.; O’Brien, P.J.; Wolfe, A.; Hoey, S.; Chandler, C.; Rhodes, V.; Carty, C.I.; Piras, I.M.; Ryan, E.G. Acute fasciolosis in an alpaca: A case report. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimini, A.; Ricci, M.; Gigliotti, P.E.; Pugliese, L.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Danieli, R.; Schillaci, O. Medical Imaging in the Diagnosis of Schistosomiasis: A Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardorff, R.; Eriksen, L.; Nielsen, D.H.; Johansen, M.V. Validation of ultrasonography for hepatic schistosomiasis using a porcine Schistosoma japonicum model. Acta Trop. 2003, 85, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, A.M.; Davenport, A.; Moshnikova, V.S.; Gilmour, L.J.; Fabiani, M.; Bishop, M.A.; Cook, A.K. Heterobilharzia americana infection in dogs: A retrospective study of 60 cases (2010–2019). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvitko-White, H.L.; Sayre, R.S.; Corapi, W.V.; Spaulding, K.A. Imaging diagnosis-Heterobilharzia americana infection in a dog. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2011, 52, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corapi, W.V.; Ajithdoss, D.K.; Snowden, K.F.; Spaulding, K.A. Multi-organ involvement of Heterobilharzia americana infection in a dog presented for systemic mineralization. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moshnikova, V.S.; Gilmour, L.J.; Cook, A.K.; Fabiani, M. Sonographic findings of pinpoint hyperechoic foci in the small intestine, liver, and mesenteric lymph nodes are indicative of canine Heterobilharzia americana infection. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2020, 61, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Donne, V.; McGovern, D.A.; Fletcher, J.M.; Grasperge, B.J. Cytologic Diagnosis of Heterobilharzia americana Infection in a Liver Aspirate from a Dog. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, A.K.; Charles, R.A. A review of the cat liver fluke Platynosomum fastosum Kossack, 1910 (Trematoda: Dicrocoeliidae). Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, L.; Shell, L.; Illanes, O.; Lathroum, C.; Neuville, K.; Ketzis, J. Percutaneous Ultrasound-guided Cholecystocentesis and Bile Analysis for the Detection of Platynosomum spp.-Induced Cholangitis in Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima, R.L.; Pacheco, R.d.C.; Mendonça, A.J.; Néspoli, P.E.B.; Morita, L.H.M.; de Almeida, A.d.B.P.F.; Sousa, V.R.F. Platynosomum fastosum in domestic cats in Cuiabá, Midwest region of Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2021, 24, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unruh, D.H.; King, J.E.; Eaton, R.D.; Allen, J.R. Parasites of dogs from Indian settlements in northwestern Canada: A survey with public health implications. Can. J. Comp. Med. 1973, 37, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lemetayer, J.D.; Snead, E.C.; Starrak, G.S.; Wagner, B.A. Multiple liver abscesses in a dog secondary to the liver fluke Metorchis conjunctus treated by percutaneous transhepatic drainage and alcoholization. Can. Vet. J. 2016, 57, 605–609. [Google Scholar]
- Amarir, F.; Rhalem, A.; Sadak, A.; Raes, M.; Oukessou, M.; Saadi, A.; Bouslikhane, M.; Gauci, C.G.; Lightowlers, M.W.; Kirschvink, N.; et al. Control of cystic echinococcosis in the Middle Atlas, Morocco: Field evaluation of the EG95 vaccine in sheep and cesticide treatment in dogs. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightowlers, M.W.; Lawrence, S.B.; Gauci, C.G.; Young, J.; Ralston, M.J.; Maas, D.; Heath, D.D. Vaccination against hydatidosis using a defined recombinant antigen. Parasite Immunol. 1996, 18, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightowlers, M.W.; Colebrook, A.L.; Gauci, C.G.; Gauci, S.M.; Kyngdon, C.T.; Monkhouse, J.L.; Vallejo Rodriquez, C.; Read, A.J.; Rolfe, R.A.; Sato, C. Vaccination against cestode parasites: Anti-helminth vaccines that work and why. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 115, 83–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightowlers, M.W. Fact or hypothesis: Concomitant immunity in taeniid cestode infections. Parasite Immunol. 2010, 32, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macpherson, C.N.L.; Bartholomot, B.; Frider, B. Application of ultrasound in diagnosis, treatment, epidemiology, public health and control of Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis. Parasitology 2003, 127, S21–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, E.; Tamarozzi, F.; Macpherson, C.; Filice, C.; Piontek, M.S.; Kabaalioglu, A.; Dong, Y.; Atkinson, N.; Richter, J.; Schreiber-Dietrich, D.; et al. Ultrasound and Cystic Echinococcosis. Ultrasound Int. Open 2018, 4, E70–E78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulima, M.; Nahorski, W.; Gorycki, T.; Wołyniec, W.; Wąż, P.; Felczak-Korzybska, I.; Szostakowska, B.; Sikorska, K. Ultrasound images in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis and clinical stage of the disease. Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Carpio, M.; Moguilansky, S.; Costa, M.; Panomarenko, H.; Bianchi, G.; Bendersky, S.; Lazcano, M.; Frider, B.; Larrieu, E. Diagnosis of human hydatidosis. Predictive value of a rural ultrasonographic survey in an apparently healthy population. Med.-Buenos Aires 2000, 60, 466–468. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO) Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/zoonoses/infections_more/en/ (accessed on 5 May 2022).
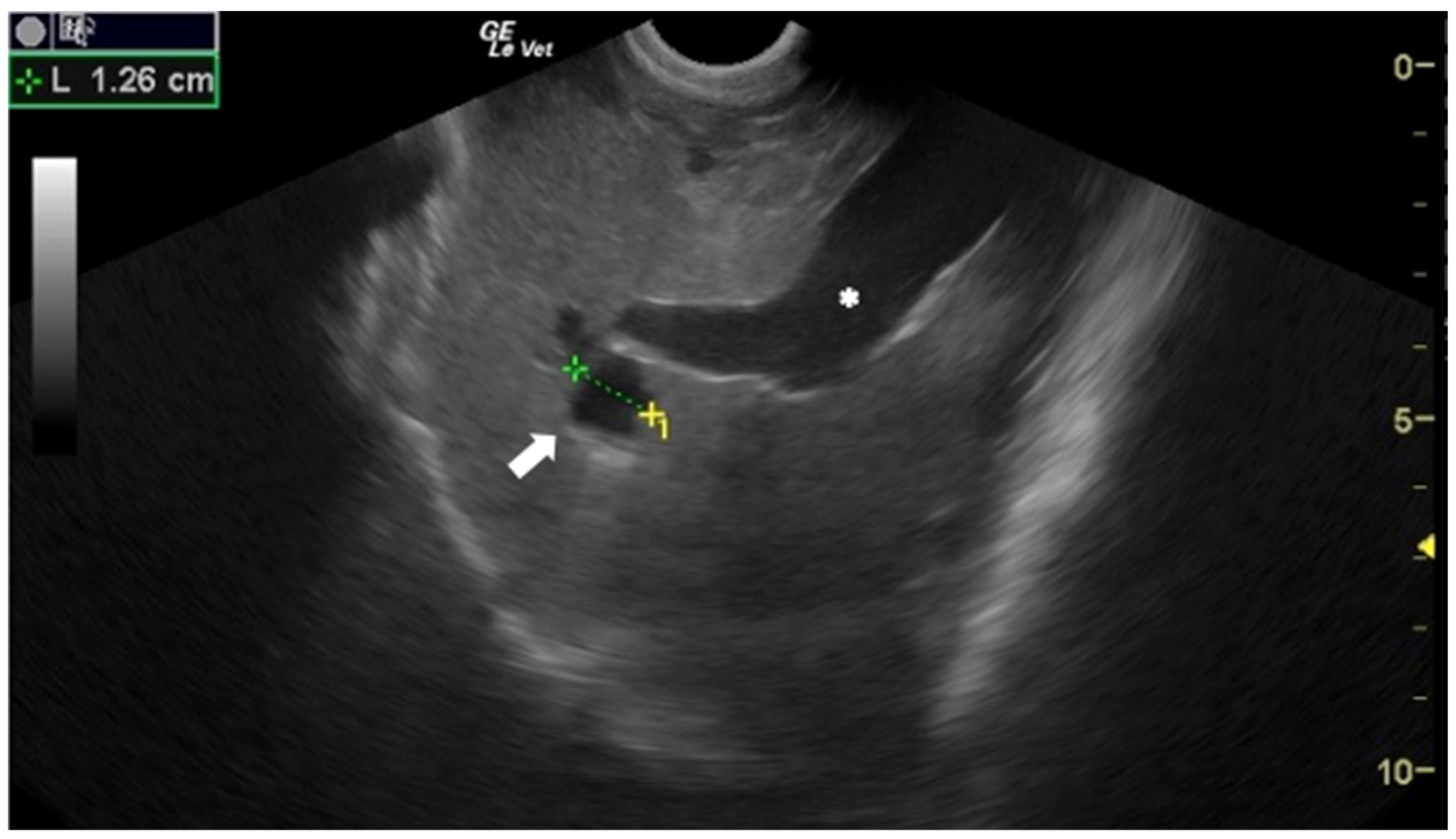
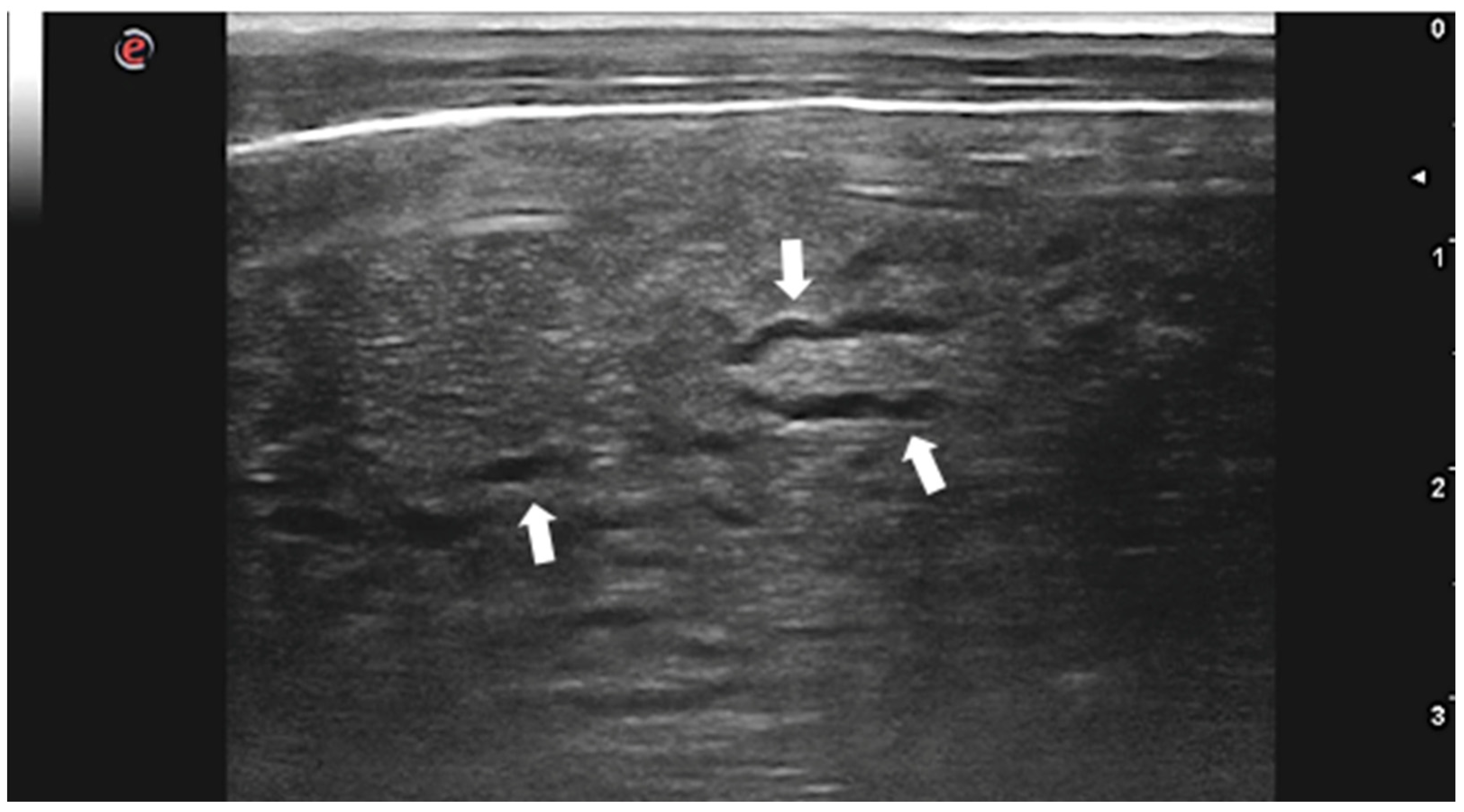
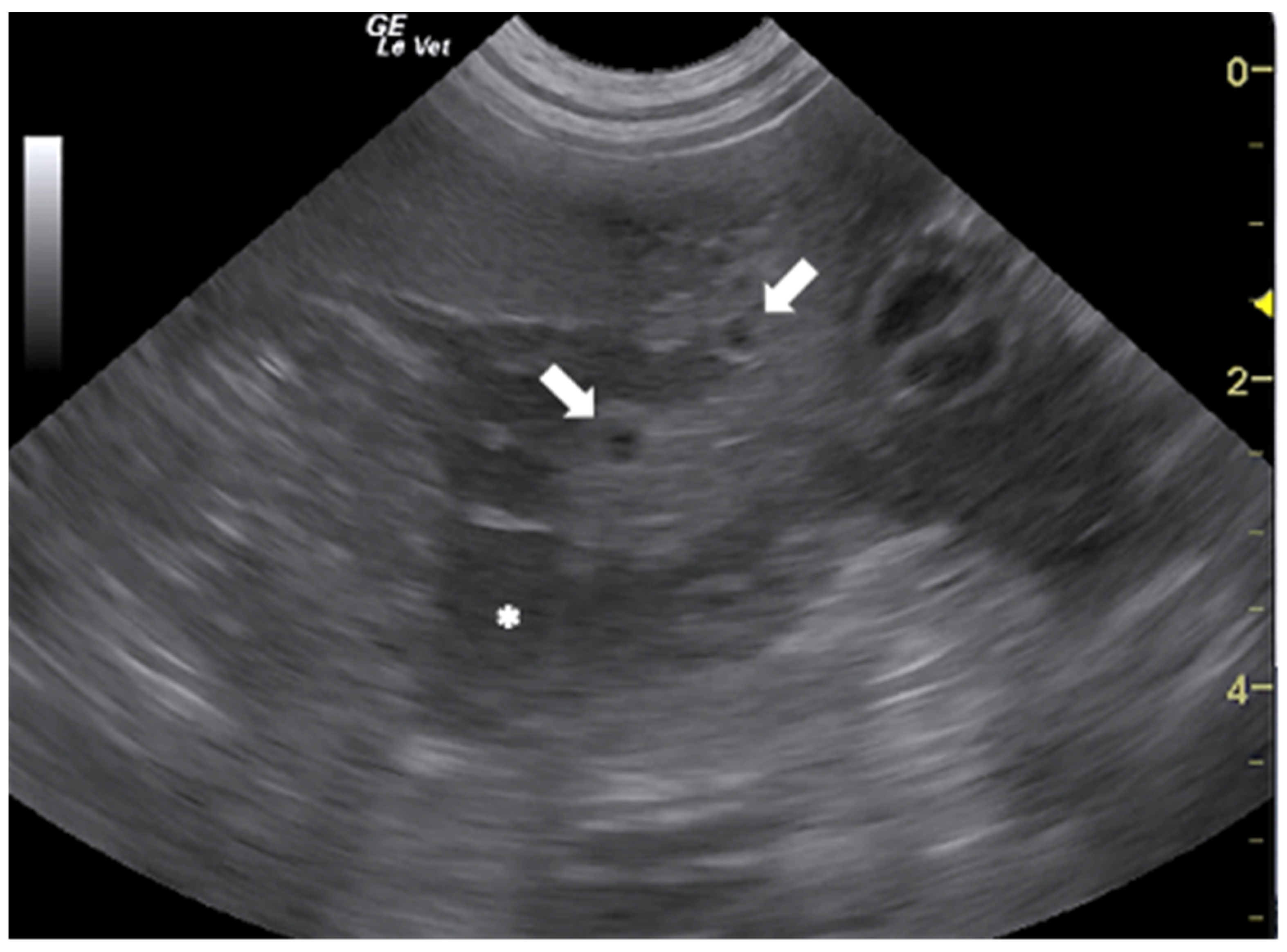
| Gharby Scheme Type | Gharby US Description | WHO Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Type I: pure fluid collection | Unilocular round shape, well-defined walls, anechoic content | CE1 Active and fertile |
| Type II: fluid collection with a split wall | Unilocular, less rounded shape, well defined contour, anechoic content, and presence of “split wall” sign. | CE3 Transitional stage |
| Type III: fluid collection with septa | Multilocular, rounded or oval shape, well defined contour, fluid collection divided by septa. | CE2 Active and fertile |
| Type IV: heterogeneous echo patterns | Roughly rounded masses with irregular contour and variable echo pattern: 1. hypoechoic with irregular echoes, 2. solid, hyperechoic, and not shadowing, 3. intermediate including hypoechoic and hyperechoic structures | CE4 Inactive |
| Type V: reflecting thick walls | Structures with hyperechoic and shadowing contour | CE5 Inactive |
| Author | Maxson Sage et al. [21] | Dore et al. [17] | Hussein et al. [22] | Borriello et al. [18] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year of study | 1996 | 2012 | 2011–2013 | 2017–2019 |
| Location | Kiserian, Kenya | Sardinia, Italy | Asyut, Egypt | Southern Italy |
| Animals | 16 sheep of I.B. 284 goats of I.B. | 129 Sarda sheep | 22 Baladi sheep | 172 sheep of different breeds |
| Wool shearing | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Probes | L 3.5 MHz | MC 8–11 MHz | L and C 3.5, 5, 8 MHz | MC 6–10 MHz |
| Duration of US | 2 min/animal | 5 min/animal | NR | 7.1 min/animal |
| Examined organs | Liver and right lung | Liver | Liver | Liver |
| Postmortem exam | All animals | All animals | 10 animals | All animals |
| Only pulmonary cysts (%) | 15.2 | 3.9 | 0 | 1.7 |
| Sensitivity (%) | 54 | 89 | 80 | 91 |
| Specificity (%) | 98 | 76 | 100 | 80 |
| PPV (%) | 81 | 82 | 100 | 80 |
| NPV (%) | 92 | 85 | 83 | 91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corda, A.; Corda, F.; Secchi, V.; Pentcheva, P.; Tamponi, C.; Tilocca, L.; Varcasia, A.; Scala, A. Ultrasonography of Parasitic Diseases in Domestic Animals: A Systematic Review. Animals 2022, 12, 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12101252
Corda A, Corda F, Secchi V, Pentcheva P, Tamponi C, Tilocca L, Varcasia A, Scala A. Ultrasonography of Parasitic Diseases in Domestic Animals: A Systematic Review. Animals. 2022; 12(10):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12101252
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorda, Andrea, Francesca Corda, Valentina Secchi, Plamena Pentcheva, Claudia Tamponi, Laura Tilocca, Antonio Varcasia, and Antonio Scala. 2022. "Ultrasonography of Parasitic Diseases in Domestic Animals: A Systematic Review" Animals 12, no. 10: 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12101252
APA StyleCorda, A., Corda, F., Secchi, V., Pentcheva, P., Tamponi, C., Tilocca, L., Varcasia, A., & Scala, A. (2022). Ultrasonography of Parasitic Diseases in Domestic Animals: A Systematic Review. Animals, 12(10), 1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12101252









