Microsatellite Characterization of Malaysian Mahseer (Tor spp.) for Improvement of Broodstock Management and Utilization
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Study Materials
2.2. Total Genomic DNA Extraction
2.3. PCR Amplification
2.4. Gel Electrophoresis and Fragment Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. SSR Genetic Diversity and Polymorphism
2.5.2. Population Differentiation, Genetic Distance and Genetic Structure
2.5.3. Genetic Relatedness
2.5.4. Population Bottleneck, Effective Population Size (Ne), and Population Assignment
3. Results
3.1. SSR Genetic Diversity and Polymorphism
3.1.1. Genetic Diversity by Population
3.1.2. Level of Inbreeding across Loci and Populations
3.1.3. Null Allele
3.2. Population Differentiation, Genetic Distance and Genetic Structure
3.2.1. Genetic Differentiation
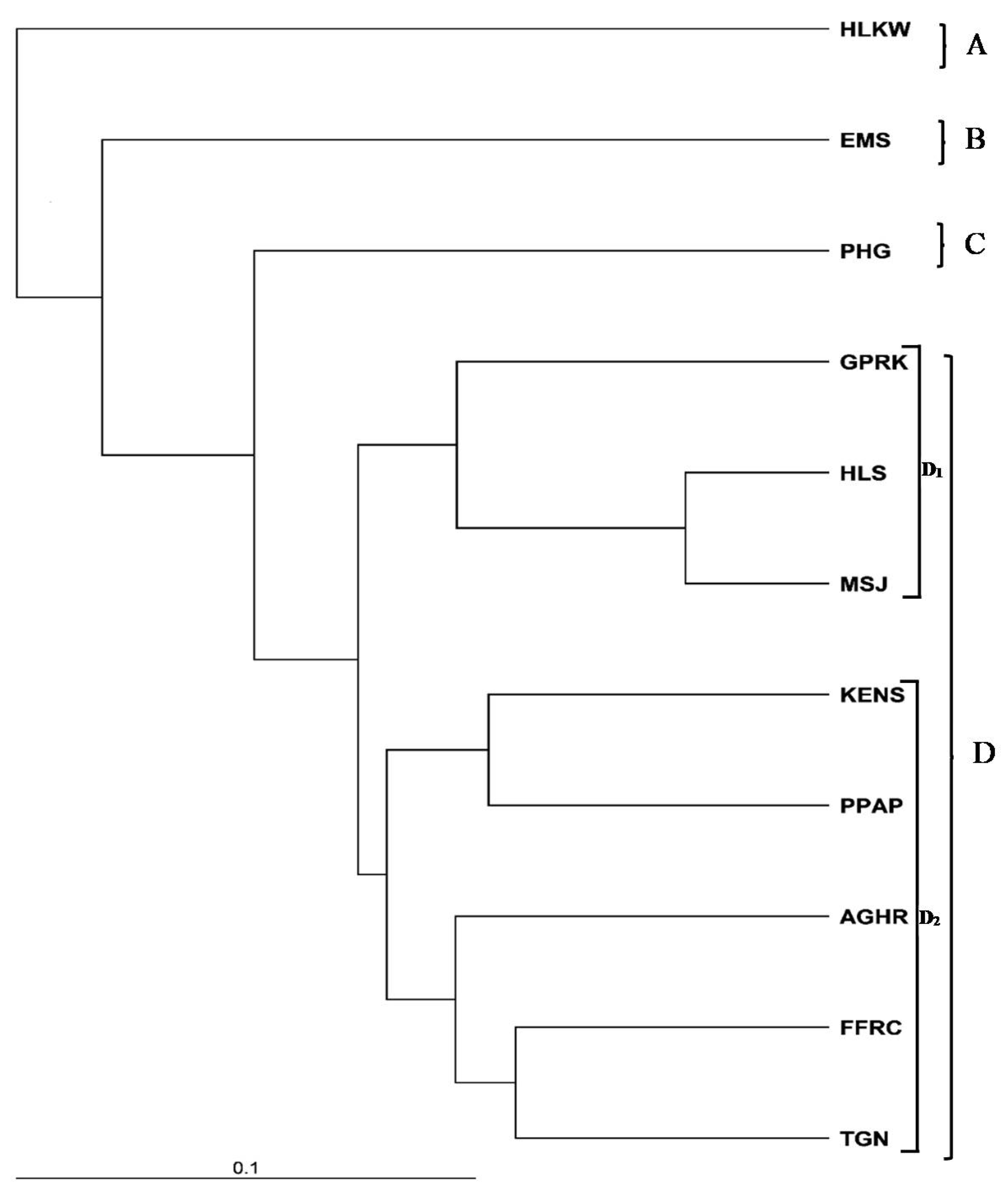
3.2.2. Genetic Distance
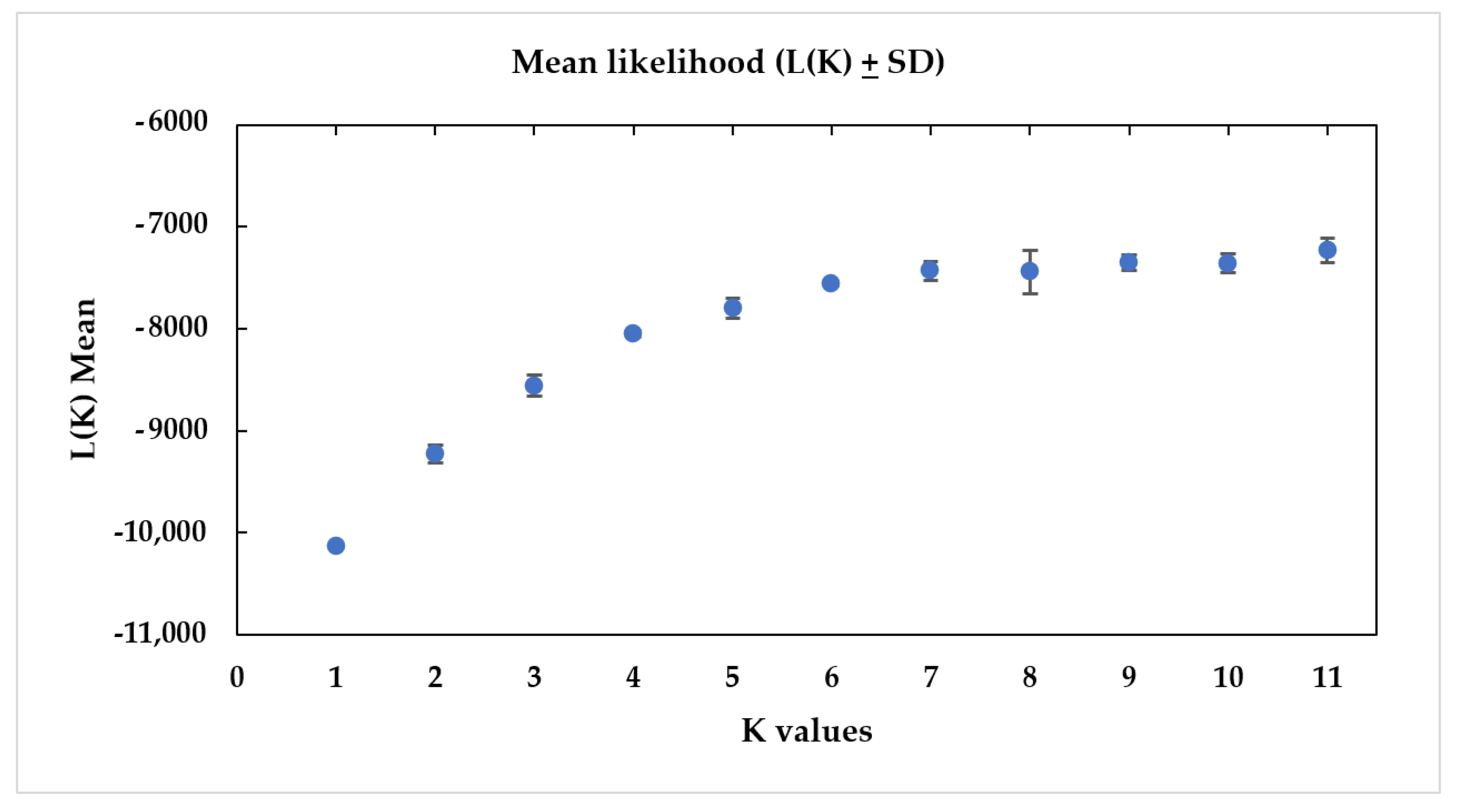
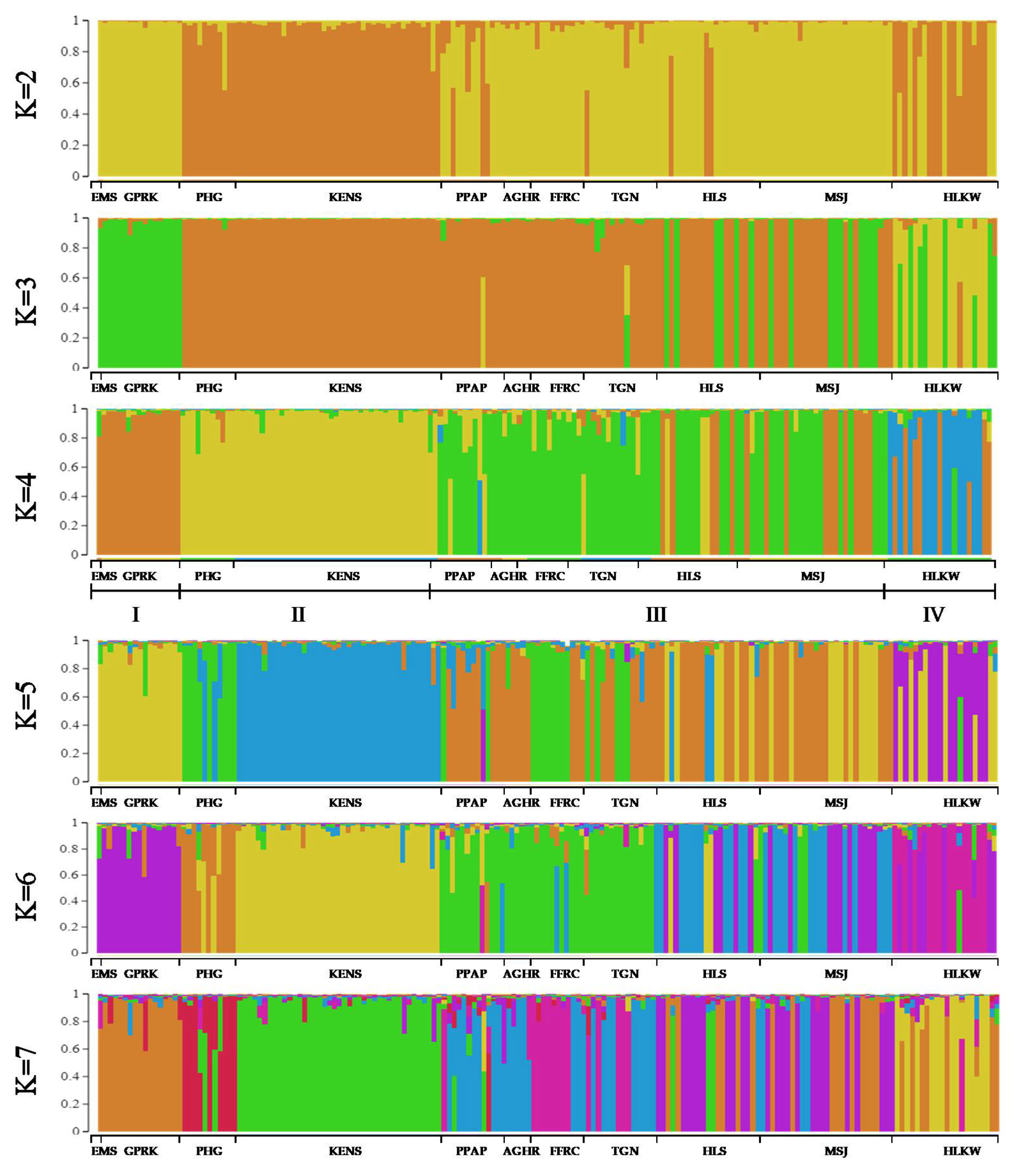
3.2.3. Genetic Structure
3.3. Genetic Relatedness among Individuals
3.4. Analysis for Bottleneck, Effective Population Size (Ne) and Population Assignment
3.4.1. Bottleneck Analysis
3.4.2. Estimation of Effective Population Size (Ne)
3.4.3. Population Assignment
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity of the Tor spp. Collection
4.2. Genetic Differentiation and Genetic Structure Analysis
4.3. Genetic Distance and Population Structure among Sampling Locations
4.4. Genetic Relatedness among Individuals
4.5. Population Bottleneck, Effective Population Size (Ne) and Population Assignment
4.6. Genetic Information and Broodstocks Management
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| SSR ID | Populations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGHR | FFRC | GPRK | HLKW | HLS | KENS | MSJ | PHG | PPAP | TGN | EMS | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | Ap | N0 | S | |
| BS02 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 173, 185 | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 189 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BS03 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 448, 450 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BS04 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 148, 150, 152, 154, 156, 160 | √ | √ | - | √ | - | - | - | - | - | √ | - | - | - | - | 140 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BS05 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 241, 257 | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 259 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BS06 | - | - | - | 232 | - | - | - | - | - | 254 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 252 | - | - | 256 | - | - | - | - | - |
| BS07 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 170 | - | - | - | - | - | 154, 156 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 232 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| BS08 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 241 | - | - | - | - | - |
| BS09 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 249 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NY01 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 233, 241, 243 | √ | - | - | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NY02 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 238, 250, 252, 254, 256, 258, 262, 266, 274 | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NY03 | - | - | - | - | √ | √ | - | √ | - | - | √ | - | - | √ | - | - | √ | √ | - | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NY04 | - | - | - | - | √ | - | 239 | - | 269 | √ | - | - | √ | - | - | √ | √ | - | √ | - | 243 | - | - | - | - | - | 275 | √ | - | - | - | - | |
| NY05 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | √ | √ | 168, 186, 188, 196, 200, 208 | √ | - | - | √ | √ | - | √ | √ | - | √ | √ | - | √ | - | - | √ | √ | - | √ | √ | - | - | - |
| NY06 | - | - | - | 168 | - | - | - | - | - | 130, 132, 136, 160, 162 | - | - | - | √ | - | - | - | - | - | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 176 | - | - | - | - | - |
| NY07 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 233 | - | - | 241 | - | - | - | - | - |
| NY08 | - | - | - | - | √ | - | √ | √ | 173, 183, 187 | √ | - | - | √ | - | - | √ | √ | 225 | √ | - | 195 | - | - | 193 | √ | - | 229 | √ | - | 177 | - | - | |
| NY09 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 243, 249, 255 | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 239 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NY10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 182 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 222 | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 188 | - | 178 | - | - | |
| NY11 | - | - | - | - | √ | - | 212 | - | - | 208, 218, 220, 254, 270, 282 | √ | - | - | √ | - | - | - | - | 262 | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 230, 256 | √ | - | - | - | - |
| NY12 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 155 | √ | - | - | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | √ | - | - | - | - |
| NY13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 162 | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 150 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| NY14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 197 | - | - | 195 | √ | √ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 52 | 14 | 7 | 0 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
References
- Kottelat, M. The fishes of the inland waters of Southeast Asia: A catalogue and core bibliography of the fishes known to occur in freshwaters, mangroves and estuaries. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2013, 27, 1–663. [Google Scholar]
- Rainboth, W.J. Fishes of the Cambodian Mekong; FAO Species Identification Field Guide for Fishery Purposes; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Publication: Rome, Italy, 1996; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Inger, R.F.; Chin, P.K. The Freshwater Fishes of North Borneo. Fieldiana Zool. 1962, 45, 1–268. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M.; Whitten, A.J.; Kartikasari, S.N.; Wirjoatmodjo, S. Freshwater Fishes of Western Indonesia and Sulawesi; Periplu: Singapore, 1993; p. 221. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsin, A.K.M.; Ambak, M.A. Freshwater Fishes of Peninsular Malaysia; Penerbit Universiti Pertanian Malaysia: Serdang, Malaysia, 1991; p. 284. [Google Scholar]
- Kottelat, M.; Pinder, A.; Harrison, A. Tor Tambra. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; 2018: E.T188012A89801879; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M.; Pinder, A.; Harrison, A. Tor Tambroides. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; 2018: E.T187939A91076554; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinder, A.C.; Britton, J.R.; Harrison, A.J.; Nautiyal, P.; Bower, S.D.; Cooke, S.J.; Raghavan, R. Mahseer (Tor spp.) fishes of the world: Status, challenges and opportunities for conservation. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2019, 29, 417–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, S.E.; Gan, H.M.; Raghavan, R.; Pinder, A.C.; Ahmad, A. Disentangling the Taxonomy of the Mahseers (Tor spp.) of Malaysia: An Integrated Approach Using Morphology, Genetics and Historical Records. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2017, 25, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.R. Fishes of the cyprinid genus Tor in the Nam Theun watershed (Mekong Basin) of Laos, with description of a new species. Raffles Bull. Zool. 1999, 47, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase (World Wide Web electronic publication version Feb 2018). In Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life, 31st May 2018; Roskov, Y., Abucay, L., Orrell, T., Nicolson, D., Bailly, N., Kirk, P.M., Bourgoin, T., DeWalt, R.E., et al., Eds.; Species 2000 Naturalis: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2018; ISSN 2405-8858. Available online: www.catalogueoflife:col (accessed on 22 June 2018).
- DOF. Annual Fisheries Statistics, 2012; Department of Fisheries Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2012.
- DOF. Annual Fisheries Statistics, 2019; Department of Fisheries Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2019.
- Kamarudin, M.S.; Ramezani-Fard, E.; Ishak, S.D.; De Cruz, C.R.; Bami, M.L.; Harris, M.H.I.; Misieng, J.D. Feeding and nutrition of endangered mahseers: A review. Keynote Paper. In International Conference of Aquaculture Indonesia; Universitas Padjajaran: Bandung, Indonesia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- DOF. Annual Fisheries Statistics, 2016; Department of Fisheries Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2016; Volume 1, p. 53.
- Ingram, B.A.; Sungan, S.; Gooley, G.; Sim, S.Y.; Tinggi, D.; De Silva, S.S. Induced spawning, larval development and rearing of two indigenous Malaysian mahseer. Tor Tambroides T. Douronensis Aquacult. Res. 2005, 36, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Ingram, B.A.; Sungan, S.; Tinggi, D.; Sim, S.Y.; Gooley, G.J.; De Silva, S.S. Observation on the growth of cage and pond reared Tor tambroides and T. douronensis in Sarawak, Malaysia. In Proceeding of the International Symposium on the Mahseer; Siraj, S.S., Christianus, A., Ng, C.K., De Silva, S.S., Eds.; Malaysian Fisheries Society: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2007; pp. 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- DOF. Annual Fisheries Statistics, 2013; Department of Fisheries Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2013.
- DOF. Annual Fisheries Statistics, 2014; Department of Fisheries Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2014.
- DOF. Annual Fisheries Statistics, 2015; Department of Fisheries Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2015.
- DOF. Annual Fisheries Statistics, 2017; Department of Fisheries Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2017; Volume 1, p. 47.
- DOF. Annual Fisheries Statistics, 2018; Department of Fisheries Malaysia: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2018; Volume 1, p. 53.
- Muchlisin, Z.A.; Batubara, A.S.; Siti-Azizah, M.N.; Adlim, M.; Hendri, A.; Fadli, N.; Muhammadarm, A.A.; Sugianto, S. Feeding habit and length weight relationship of keureling fish, Tor tambra. Valenciennes, 1842 (Cyprinidae) from the western region of Aceh Province, Indonesia. Biodiversitas 2015, 16, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmawati, L.; Azizi, A.; Sudhi, M.; Subagyo, H.A.; Hardjamulia, A. Carp genetic resources of Indonesia. In Carp Genetic Resources for Aquaculture in Asia; Penman, D.J., Gupta, M.V., Dey, M.M., Eds.; World Fish Center Technical Report: Penang, Malaysia, 2005; Volume 65, pp. 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Muchlisin, Z.A. Potency of freshwater fishes in Aceh waters as a basis for aquaculture development program. J. Iktiologi Indones. 2013, 13, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, G.J.; Danzman, R.G.; Ferguson, M.M. Relatedness determination in the absence of pedigree information in three cultured strains of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2004, 233, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.J.; Ye, R.H.; Zhang, G.F.; Zheng, R.Q. Microsatellite analysis of genetic diversity and population structure of freshwater mussel (Lamprotula leai). Zool. Res. 2015, 36, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, A.T.; Bradley, D.G.; Cunningham, E.P. Parentage and relatedness determination in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) using microsatellite markers. Aquaculture 2000, 182, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekino, M.; Sugaya, T.; Hara, M.; Taniguchi, N. Relatedness inferred from microsattelite genotypes as a tool for broodstock management of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 2004, 233, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanan, W.; Pechsiri, J.; Sonkaew, S.; Na-Nakorn, U.; Sean-In, N.; Yashiro, R. Genetic relatedness and differentiation of hatchery populations of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) (Bloch, 1790) broodstock in Thailand inferred from microsatellite genetic markers. Aquac. Res. 2015, 46, 2897–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Muneer, P.M. Application of microsatellite markers in conservation genetics and fisheries management: Recent advances in population structure analysis and conservation strategies. Gen. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 691759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esa, Y.B.; Siraj, S.S.; Rahim, K.A.A.; Daud, S.K.; Chong, H.G.M.; Guan, T.S.; Syukri, M.F. Genetic characterization of two mahseer species (Tor douronensis and Tor tambroides) using microsatellite markers from other cyprinids. Sains Malays. 2011, 40, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Esa, Y.B.; Abdul Rahim, K.A. Genetic structure and preliminary findings of cryptic diversity of the Malaysian mahseer (Tor tambroides Valenciennes: Cyprinidae) inferred from mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite analyses. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keong, R.B.P.; Siraj, S.S.; Daud, S.K. Cross species amplification of Ikan Kelah, Tor tambroides by using Mystus nemurus microsatellite markers. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2008, 31, 179–189. [Google Scholar]
- Mohindra, V.; Ranjana, A.; Khulbe, L.; Ponniah, A.G.; Lal, K.K. Microsatellite loci to assess genetic variation in Tor putitora. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2004, 20, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Baranski, M.; Rourke, M.; McPartlan, H. Characterization of microsatellite DNA markers for a mahseer species, Tor tambroides (Cyprinidae) and cross-amplification in four congeners. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T.; Na-Nakorn, U.; Sukmanomon, S.; Ziming, C.A. study on phylogeny and biogeography of mahseer species (Pisces: Cyprinidae) using sequences of three mitochondrial DNA gene regions. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siraj, S.S.; Esa, Y.B.; Keong, B.P.; Daud, S.K. Genetic characterization of the two colour-types of Kelah. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2007, 36, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Koressaar, T.; Remm, M. Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. PowerMarker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.W.; Thompson, E. Performing the exact test of Hardy-Weinberg proportion for multiple alleles. Biometrics 1992, 48, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oosterhout, C.; Hutchinson, W.F.; Wills, D.P.M.; Shipley, P. Microchecker: Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornuet, J.M.; Luikart, G. Description and power analysis of two tests for detecting recent population bottlenecks from allele frequency data. Genetics 1997, 144, 2001–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luikart, G.; Allendorf, F.W.; Cornuet, J.M.; Sherwin, W.B. Distortion of allele frequency distributions provides a test for recent population bottlenecks. J. Hered. 1997, 89, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, R.S. A bias correction for estimates of effective population size based on linkage disequilibrium at unlinked gene loci. Conserv. Genet. 2006, 7, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, R.S.; Do, C. LDNE: A program for estimating effective population size from data on linkage disequilibrium. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, F.C.; Adams, L.J.; Littlejohn, R.P.; Maddox, J.F.; Crawford, A.M. Determination of evolutionary relationships among sheep breeds using microsatellites. Genomics 1994, 22, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacHugh, D.E.; Loftus, R.T.; Cunningham, P.; Bradley, D.G. Genetic structure of seven European cattle breeds assessed using 20 microsatellite markers. Anim. Genet. 1998, 29, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Estoup, A.; Cornuet, J.M. Bayesian analysis of an admixture model with mutations and arbitrarily linked markers. Genetics 2005, 169, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, M.; Rousset, F. GENEPOP (version 1.2): Population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. J. Hered. 1995, 86, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, B.S.; Cockerham, C.C. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 1984, 38, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin, M.; Barton, N.H. A comparison of three indirect methods for estimating average levels of gene flow. Evolution 1989, 43, 1349–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Tajima, F.; Tateno, Y. Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular data. J. Mol. Evol. 1983, 19, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.D.M. TREEVIEW: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; von Holdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. COANCESTRY: A program for simulating, estimating and analysing relatedness and inbreeding coefficients. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. An estimator for pairwise relatedness using molecular markers. Genetics 2002, 160, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M. Estimation of relatedness by DNA fingerprinting. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1988, 5, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.C.; Weeks, D.E.; Chakravarti, A. Similarity of DNA fingerprints due to chance and relatedness. Hum. Hered. 1993, 43, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Ritland, K. Estimation of pairwise relatedness with molecular markers. Genetics 1999, 152, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritland, K. Estimators for pairwise relatedness and inbreeding coefficients. Genet. Res. 1996, 67, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queller, D.C.; Goodnight, K.F. Estimating relatedness using molecular markers. Evolution 1989, 43, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Triadic IBD coefficients and applications to estimating pairwise relatedness. Genet. Res. 2007, 89, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, B.G. Maximum-likelihood estimation of relatedness. Genetics 2003, 163, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fopp-Bayat, D.; Ciereszko, A. Microsatellite genotyping of cryopreserved spermatozoa for the improvement of whitefish semen cryobanking. Cryobiology 2012, 65, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jia, Y.; Huang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Li, H. Individual identification of Chinese Holstein Bull by 10 STR loci. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruett, C.; Winker, K. The Effects of Sample Size on Population Genetic Diversity Estimates in Song Sparrows Melospiza melodia. J. Avian Biol. 2008, 39, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.N.; Zhang, D.X. Effects of sample size on various genetic diversity measures in population genetic study with microsatellite DNA markers. Dong Wu Xue Bao 2004, 50, 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Dieringer, D.; Schlotterer, C. Microsatellite analyser (MSA): A platform independent analysis tool for large microsatellite data sets. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2003, 3, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, G.; Templeton, A.R.; Zarmi, Y.; Bar-David, S. Allelic richness following population founding events–A Stochastic modeling framework incorporating gene flow and genetic drift. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, R.M.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S.; Moreira, H.L.M.; Cabello, P.H.; Traub-Cseko, Y.M. Genetic diversity of wild and cultured populations of Brycon opalinus (Cuvier, 1819) (Characiforme, Characidae, Bryconiae) using microsatellites. Aquaculture 2005, 247, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castric, V.; Bernatchez, L.; Belkhir, K.; Bonhomme, F. Heterozygote deficiencies in small lacustrine populations of brook charr Salvelinus fontinalis Mitchill (Pisces, Salmonidae): A test of alternative hypotheses. Heredity 2002, 89, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, R.M.; León, F.J.G.; Mejía, O.; Ángeles, I.D.L. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in the Charal de Xochimilco Chirostoma humboldtianum. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2014, 85, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papetti, C.; Harms, L.; Jürgens, J.; Sandersfeld, T.; Koschnick, N.; Windisch, H.S.; Lucassen, M. Microsatellite markers for the notothenioid fish Lepidonotothen nudifrons and two congeneric species. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yue, G.H.; Li, Y.; Lim, L.C.; Orban, L. Monitoring the genetic diversity of three Asian arowana (Scleropages formosus) captive stocks using AFLP and microsatellites. Aquaculture 2004, 237, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookfield, J.F.Y. A simple new method for estimating null allele frequency from heterozygote deficiency. Mol. Ecol. 1996, 5, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angel, P.; Mercedes, G.; Philippe, L.; Concepcion, M.; Jose, A. Effects of fishing protection on the genetic structure of fish populations. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 129, 244–255. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Gupta, J.; Kumar, N.; Dikshit, K.; Navani, N.; Jain, P.; Nagarajan, M. Genetic variation and relationships among eight Indian riverine buffalo breed. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, M.; Wright, J.M. Microsatellite DNA in fishes. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 1997, 7, 331–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.T. Population structure in the highly fragmented range of Tor douronensis (Cyprinidae) in Sarawak, Malaysia revealed by microsatellite DNA markers. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 53, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrick, J.L. Response of forest trees to global environmental changes. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 197, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; p. 514. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, S. Systems of mating II. The effects of inbreeding on the genetic composition of a population. Genetics 1921, 6, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Variability Within and Among Natural Populations; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978; Volume 4, p. 590. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R.Q.; Ye, R.H.; Yu, Y.Y.; Yang, G. Fifteen polymorphic microsatellite markers for the giant spiny frog. Paa Spinosa Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 336–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, C.; Cuesta, J.A.; Drake, P.; Macpherson, E.; Bernatchez, L.; Marie, A.D. Null alleles are ubiquitous at microsatellite loci in the Wedge Clam (Donax trunculus). PeerJ. 2017, 18, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.J.; Tamate, H.B.; Wilson, R.; Nagata, J.; Tatsuzawa, S.; Swanson, G.S.; Pemberton, J.M.; McCullough, D.R. Bottlenecks, drift and differentiation: The population structure and demographic history of sika deer (Cervus nippon) in the Japanese archipelago. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, M.P.; Estoup, A. Microsatellite null alleles and estimation of population differentiation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, S.; Lucentini, L.; Freitas, R.; Nonnis-Marzano, F.; Ferrari, C.; Filonzi, L.; Breda, S.; Minello, F.; Figueira, E.; Argese, E. Null alleles of microsatellites for Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, J.S.; Sturmer, L.; Scarpa, J.; Austin, J.D. Assessment of genetic diversity in wild and aquaculture stocks of mercenaria mercenariain Florida. J. Shellfish Res. 2015, 34, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.M.; An, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; An, C.M.; Dong, C.M.; Hong, Y.K.; Park, J.Y. New polymorphic microsatellite markers for the Korean manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) and their application to wild populations. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 8163–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantón, A.; Arias-Pérez, A.; Méndez, J.; Freire, R. Characterization of nineteen microsatellite markers and development of multiplex PCRs for the wedge clam Donax trunculus (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 5351–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, M.; Bornelöv, S.; Kruczyk, M.; Baltzer, N.; Komorowski, J. ‘True’null allele detection in microsatellite loci: A comparison of methods, assessment of difficulties and survey of possible improvements. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, J. Effects of microsatellite null alleles on assignment testing. J. Hered. 2008, 99, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radha, P.; Sivaselvam, S.N.; Kumarasamy, P.; Kumanan, K. Genetic diversity and bottleneck analysis of kilakarsal sheep by microsatellite markers. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Frankham, R.; Ballou, J.D.; Briscoe, D.A. Introduction to Conservation Genetics, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gratton, P.; Allegrucci, G.; Sbordoni, V.; Gandolfi, A. The evolutionary jigsaw puzzle of the surviving trout (Salmo trutta L. complex) diversity in the Italian region. a multilocus bayesian approach. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 79, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.M.; McDonald, B.A. Gene flow in plant pathosystems. Annu Rev. Phytopathol. 1993, 31, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F. Genetic differentiation and estimation of gene flow from F-statistics under isolation by distance. Genetics 1997, 145, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Isolation by distance. Genetics 1943, 28, 114–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Li, S.; Pan, W.; Yao, M. Low genetic diversity and strong population structure shaped by anthropogenic habitat fragmentation in a critically endangered primate. Trachypithecus Leucocephalus Hered. 2017, 118, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paetkau, D.; Slade, R.; Burden, M.; Estoup, A. Genetic assignment methods for the direct, real-time estimation of migration rate: A simulation-based exploration of accuracy and power. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. A new method for estimating effective population sizes from a single sample of multilocus genotypes. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 2148–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliehoek, P.A.; Windig, J.J.; Van Arendonk, J.A.M.; Bijma, P. Estimating relatedness between individuals in general populations with a focus on their use in conservation programs. Genetics 2006, 173, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, F. Inbreeding and relatedness coefficients: What do they measure? Heredity 2002, 88, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Santiago, E.; Caballero, A. Prediction and estimation of effective population size. Heredity 2016, 117, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatkin, M. Gene flow in natural populations. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1985, 16, 393–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikhi, L.; Sousa, V.C.; Luisi, P.; Goossens, B.; Beaumont, M.A. The confounding effects of population structure, genetic diversity and the sampling scheme on the detection and quantification of population size changes. Genetics 2010, 186, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macbeth, G.M.; Broderick, D.; Buckworth, R.C.; Ovenden, J.R. Linkage disequilibrium estimation of effective population size with immigrants from divergent populations: A case study on spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus commerson). G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2013, 3, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, W.C.; McKay, J.K.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Allendorf, F.W. Harnessing genomics for delineating conservation units. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, S.A.; Prasanna, B.M. Analysis of Genetic Diversity in Crop Plants—Salient Statistical Tools and Considerations. Crop. Sci. 2003, 43, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, R.S.; Gaggiotti, O. What is a population? An empirical evaluation of some genetic methods for identifying the number of gene pools and their degree of connectivity. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejui, O.; Sukmanomon, S.; Na-Nakorn, U. Allozyme revealed substantial genetic diversity between hatchery stocks of Siamese fighting fish, Betta splendens, in the province of Nakornpathom, Thailand. Aquaculture 2005, 262, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na-Nakorn, U.; Moeikum, T. Genetic diversity of domesticated stocks of striped catfish, Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage 1978) in Thailand: Relevance to broodstock management regimes. Aquaculture 2009, 297, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bank, F.H.; Grober, J.P.; du Preez, H.H. A comparative biochemical genetic study of three populations of domesticated and wild African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1992, 101, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
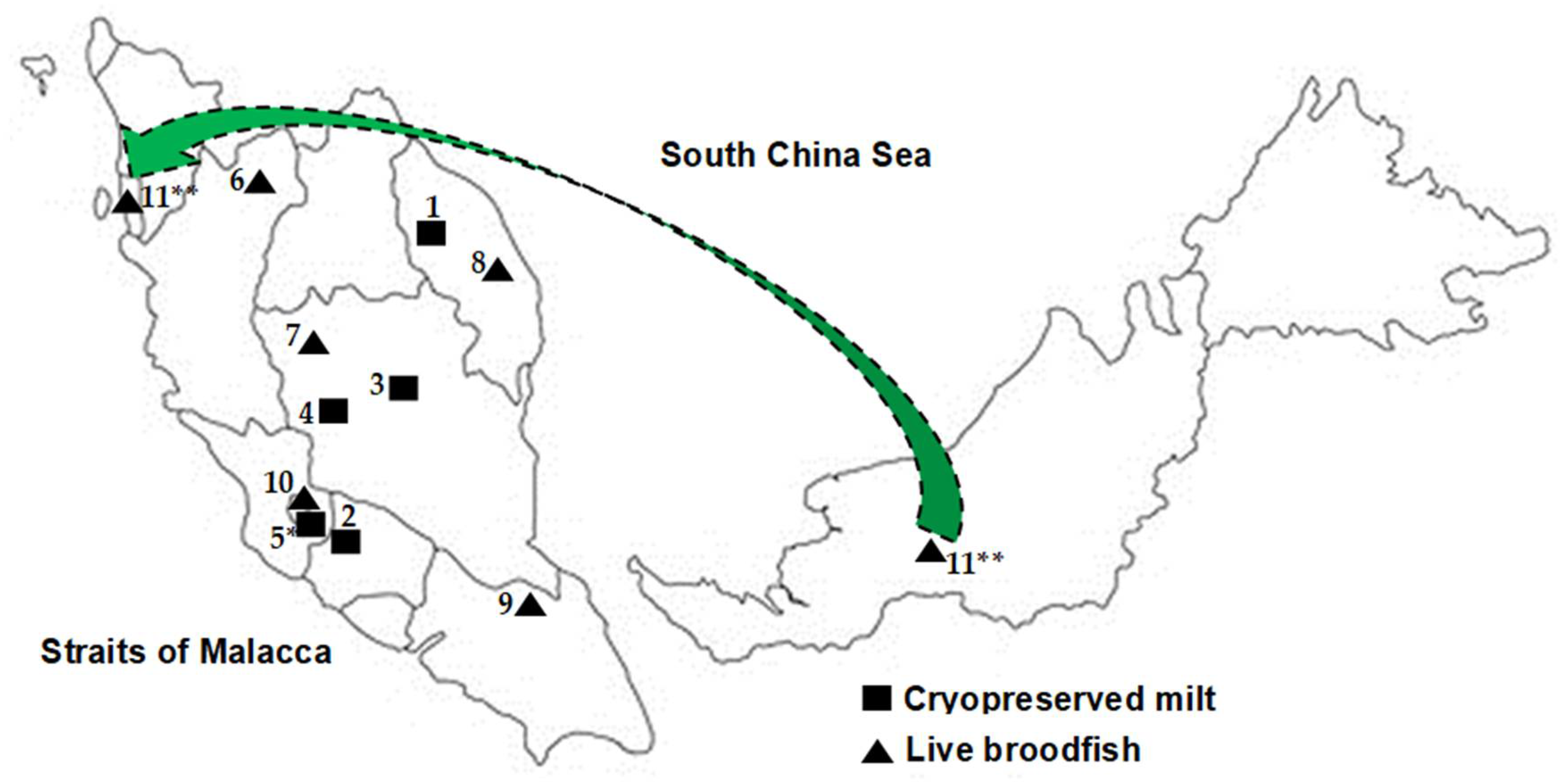
| No. | Sample Population | Population ID | Origin | Year of Collection | Sample Type | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fisheries Research Institute Glami Lemi stock | FFRC | Kenyir Lake, Terengganu | 2000–2004 | Frozen milt | 11 |
| 2 | Kg Esok, Jelebu, Negeri Sembilan | KENS | Kenaboi River, Jelebu, Negeri Sembilan | 2007–2008 | Frozen milt | 41 |
| 3 | Aquaculture Extension Center, Perlok, Jerantut, Pahang | PPAP | Pahang River | 2006–2008 | Frozen milt | 13 |
| 4 | AgroHarvest, Raub, Pahang | AGHR | Keniam River, Taman Negara | 2007–2008 | Frozen milt | 5 |
| 5 | Kelah World, Hulu Langat, Selangor a | HLKW | Imported from Sumatera, Indonesia | 2007–2008 | Frozen milt | 21 |
| 6 | Grik, Perak b | GPRK | Kejar Banding River, Perak | 2010–2011 | Scale | 16 |
| 7 | Raub, Pahang b | PHG | Jerai River, Pahang | 2016 | Scale | 11 |
| 8 | Terengganu b | TGN | Berang River, Terengganu | 2016 | Scale | 14 |
| 9 | Mersing, Johor c | MSJ | Endau Rompin, Johor | 2016–2017 | Scale | 28 |
| 10 | Hulu Langat, Selangor c | HLS | Hulu Langat River, Selangor | 2017 | Scale | 20 |
| 11 | Empurau, Sarawak c,d | EMS | Sarawak | 2017 | Scale | 1 |
| Total | 181 |
| Population ID | Ar | MAF | Ae | NG | Ap | % Polymorphic Loci | He | Ho | Fis | PIC | HWE p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFRC | 3.5000 | 0.6446 | 2.595 | 3.9545 | 2 | 77.27% | 0.4093 | 0.4008 | 0.013 | 0.3930 | 0.4304 |
| KENS | 4.0909 | 0.6896 | 2.459 | 6.2273 | 3 | 77.27% | 0.3946 | 0.4279 | −0.089 | 0.3623 | 0.2846 |
| PPAP | 4.0909 | 0.6486 | 2.311 | 4.6818 | 11 | 95.45% | 0.4315 | 0.4161 | 0.192 | 0.4144 | 0.2579 |
| HLKW | 6.6818 | 0.5097 | 2.145 | 7.8182 | 52 | 95.45% | 0.5970 | 0.4545 | 0.234 | 0.5711 | 0.0740 |
| AGHR | 2.6818 | 0.7091 | 3.792 | 2.2273 | 0 | 77.27% | 0.3264 | 0.3909 | −0.083 | 0.3161 | 0.5232 |
| HLS | 4.2727 | 0.6966 | 2.340 | 4.7273 | 0 | 77.27% | 0.3754 | 0.3273 | 0.142 | 0.3513 | 0.2455 |
| GPRK | 3.8636 | 0.6591 | 2.948 | 4.7273 | 3 | 77.27% | 0.4081 | 0.4176 | −0.003 | 0.3831 | 0.3141 |
| PHG | 2.7273 | 0.6736 | 2.226 | 3.1364 | 2 | 63.64% | 0.3676 | 0.4504 | −0.203 | 0.3395 | 0.3443 |
| MSJ | 5.0000 | 0.6412 | 2.729 | 6.1818 | 3 | 77.27% | 0.4282 | 0.3458 | 0.145 | 0.3994 | 0.1805 |
| TGN | 4.6818 | 0.6234 | 3.160 | 5.0000 | 9 | 95.45% | 0.4506 | 0.4513 | 0.023 | 0.4354 | 0.3796 |
| EMS | 1.2727 | 0.8636 | 1.273 | 1.0000 | 2 | 27.27% | 0.0682 | 0.2727 | −1.000 | 0.1023 | 1.0000 |
| Mean | 3.8967 | 0.6495 | 2.543 | 4.8682 | 76.45% | 0.4189 | 0.4083 | 0.015 | 0.3966 | 0.3667 |
| SSR Marker | Tm (°C) | Product Size (bp) | MAF | NA | NG | No. of Allele per Genotype | Ar | He | Ho | PIC | f | HWE p-Value | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS02 | 48 | 171–189 | 0.5249 | 5 | 6 | 0.8333 | 2.273 | 0.5531 | 0.8122 | 0.4589 | −0.4639 | 0.0000 ** | 3.370 |
| BS03 | 50 | 208–224 | 0.7376 | 6 | 5 | 1.2000 | 2.545 | 0.4248 | 0.5193 | 0.3924 | −0.2174 | 0.0001 ** | 1.398 |
| BS04 | 65 | 140–174 | 0.7901 | 15 | 29 | 0.5172 | 3.091 | 0.3697 | 0.1713 | 0.3656 | 0.5406 | 0.0000 ** | 0.709 |
| BS05 | 50 | 241–259 | 0.9448 | 6 | 9 | 0.6667 | 1.455 | 0.1060 | 0.0442 | 0.1046 | 0.5865 | 0.0000 ** | 0.805 |
| BS06 | 52 | 204–268 | 0.9392 | 6 | 6 | 1.0000 | 1.727 | 0.1160 | 0.1215 | 0.1135 | −0.0427 | 0.7843 | 1.348 |
| BS07 | 50 | 154–232 | 0.3812 | 9 | 11 | 0.8182 | 3.364 | 0.6692 | 0.8287 | 0.6039 | −0.2331 | 0.0000 ** | 1.363 |
| BS08 | 50 | 241–257 | 0.5746 | 4 | 5 | 0.8000 | 2.364 | 0.5063 | 0.8232 | 0.3990 | −0.6226 | 0.0000 ** | 6.433 |
| BS09 | 51 | 243–259 | 0.9061 | 6 | 7 | 0.8571 | 2.000 | 0.1750 | 0.1768 | 0.1697 | −0.0046 | 0.7765 | 3.096 |
| NY01 | 55 | 223–243 | 0.4751 | 8 | 16 | 0.5000 | 3.364 | 0.6839 | 0.3702 | 0.6430 | 0.4631 | 0.0000 ** | 0.545 |
| NY02 | 56 | 238–274 | 0.8867 | 12 | 14 | 0.8571 | 2.455 | 0.2107 | 0.1271 | 0.2082 | 0.4017 | 0.0000 ** | 0.749 |
| NY03 | 66 | 93–105 | 0.5580 | 5 | 13 | 0.3846 | 3.455 | 0.6168 | 0.2265 | 0.5749 | 0.6361 | 0.0000 ** | 0.941 |
| NY04 | 55 | 239–275 | 0.5608 | 15 | 39 | 0.3846 | 4.727 | 0.6562 | 0.3481 | 0.6416 | 0.4739 | 0.0000 ** | 0.878 |
| NY05 | 60 | 168–208 | 0.4144 | 13 | 21 | 0.6190 | 4.545 | 0.7127 | 0.3370 | 0.6728 | 0.5311 | 0.0000 ** | 1.104 |
| NY06 | 60 | 131–173 | 0.2320 | 23 | 57 | 0.4035 | 7.273 | 0.8783 | 0.8066 | 0.8706 | 0.0872 | 0.0000 ** | 0.975 |
| NY07 | 55 | 233–245 | 0.9917 | 3 | 3 | 1.0000 | 1.182 | 0.0164 | 0.0055 | 0.0164 | 0.6660 | 0.0011 * | 4.192 |
| NY08 | 66 | 173–224 | 0.1409 | 26 | 71 | 0.3662 | 8.364 | 0.9197 | 0.5304 | 0.9185 | 0.4278 | 0.0000 ** | 1.095 |
| NY09 | 58 | 239–249 | 0.8122 | 8 | 8 | 1.0000 | 2.636 | 0.3301 | 0.2486 | 0.3191 | 0.2521 | 0.0000 ** | 0.635 |
| NY10 | 66 | 174–202 | 0.1188 | 26 | 81 | 0.3210 | 9.818 | 0.9238 | 0.8564 | 0.9218 | 0.0785 | 0.0000 ** | 1.830 |
| NY11 | 60 | 201–283 | 0.1851 | 33 | 84 | 0.3929 | 10.091 | 0.9185 | 0.6630 | 0.9171 | 0.2833 | 0.0000 ** | 1.071 |
| NY12 | 65 | 151–173 | 0.2293 | 11 | 34 | 0.3235 | 4.727 | 0.8437 | 0.4751 | 0.8296 | 0.4413 | 0.0000 ** | 0.486 |
| NY13 | 64 | 150–162 | 0.9227 | 4 | 4 | 1.0000 | 1.364 | 0.1435 | 0.0110 | 0.1367 | 0.9238 | 0.0000 ** | 0.373 |
| NY14 | 65 | 183–197 | 0.4254 | 6 | 10 | 0.6000 | 2.727 | 0.6597 | 0.4088 | 0.5944 | 0.3850 | 0.0000 ** | 0.671 |
| Mean | 0.5796 | 11.36 | 24.23 | 0.6748 | 3.888 | 0.5197 | 0.4051 | 0.4942 | 0.2259 | 1.548 |
| Source of Variation | d.f. | Sum of Squares | Variance Components | Percentage of Variation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among populations | 10 | 330.674 | 0.87317 Va | 14.92 | p < 0.001 |
| Among individuals within populations | 170 | 936.019 | 0.52648 Vb | 9.00 | p < 0.001 |
| Within individuals | 181 | 806.000 | 4.96302 Vc | 76.09 | p < 0.001 |
| Total | 361 | 2072.693 | 5.85339 | 100.00 |
| Population | Moment Estimators * | Likelihood Estimators * | Correlation Coefficients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang (2002) | Lynch (1988) and Li et al. (1993) | Lynch and Ritland (1999) | Ritland (1996) | Queller and Goodnight (1989) | Wang (2007) | Milligan (2003) | ||
| AGHR | −0.199 (0.030) | −0.181 (0.035) | −0.250 (0.010) | −0.223 (0.025) | −0.249 (0.037) | 0.021 (0.001) | 0.027 (0.002) | 0.523–0.968 |
| FFRC | −0.142 (0.061) | −0.105 (0.058) | −0.100 (0.038) | −0.100 (0.036) | −0.098 (0.052) | 0.056 (0.023) | 0.065 (0.026) | 0.749–0.994 |
| GPRK | −0.058 (0.026) | −0.025 (0.028) | −0.067 (0.011) | −0.066 (0.017) | −0.066 (0.029) | 0.067 (0.008) | 0.081 (0.010) | 0.554–0.976 |
| HLKW | −0.131 (0.075) | −0.160 (0.144) | −0.050 (0.023) | −0.057 (0.059) | −0.049 (0.126) | 0.144 (0.042) | 0.155 (0.045) | 0.850–0.995 |
| HLS | −0.071 (0.145) | −0.127 (0.211) | −0.053 (0.050) | −0.055 (0.037) | −0.031 (0.164) | 0.191 (0.073) | 0.209 (0.081) | 0.820–0.996 |
| MSJ | −0.108 (0.057) | −0.095 (0.106) | −0.037 (0.025) | −0.039 (0.040) | −0.034 (0.092) | 0.144 (0.042) | 0.168 (0.050) | 0.817–0.990 |
| KENS | 0.024 (0.056) | 0.053 (0.045) | −0.025 (0.020) | −0.024 (0.016) | −0.022 (0.042) | 0.091 (0.016) | 0.113 (0.020) | 0.562–0.976 |
| PPAP | −0.079 (0.222) | −0.111 (0.399) | −0.083 (0.035) | −0.102 (0.076) | −0.009 (0.100) | 0.087 (0.021) | 0.104 (0.025) | 0.455–0.984 |
| PHG | 0.010 (0.083) | 0.039 (0.065) | −0.100 (0.050) | −0.081 (0.026) | −0.097 (0.066) | 0.120 (0.025) | 0.127 (0.027) | 0.714–0.993 |
| TGN | −0.074 (0.048) | −0.061 (0.061) | −0.077 (0.016) | −0.080 (0.019) | −0.069 (0.045) | 0.066 (0.012) | 0.080 (0.014) | 0.639–0.984 |
| Overall | −0.048 (0.040) | −0.065 (0.121) | −0.006 (0.014) | −0.007 (0.020) | 0.013 (0.055) | 0.107 (0.026) | 0.130 (0.031) | 0.531–0.986 |
| Populations | IAM | TPM | SMM | Mode Shift |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGHR | 0.3389 | 0.4816 | 0.5912 | Y |
| FFRC | 0.0101 * | 0.0797 | 0.3560 | N |
| GPRK | 0.0075 * | 0.1123 | 0.5000 | N |
| HLKW | 0.0021 * | 0.5407 | 0.9790 | N |
| HLS | 0.4633 | 0.9681 | 0.9977 | N |
| KENS | 0.0198 * | 0.5550 | 0.9716 | N |
| MSJ | 0.0224 * | 0.5367 | 0.8966 | N |
| PHG | 0.0067 * | 0.0067 * | 0.0067 * | N |
| PPAP | 0.6586 | 0.9677 | 0.9903 | N |
| TGN | 0.1602 | 0.7416 | 0.9484 | N |
| Population | N | Ne | 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) | Self-Population | Mismatched | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Number (Percentage) | Population Assigned | ||||
| AGHR | 5 | −6.1 | −8.9 | Infinite | 5 | 0 | |
| EMS | 1 | −0.3 | −0.3 | Infinite | 1 | 0 | |
| FFRC | 11 | 20.9 | 11.2 | 63.8 | 11 | 0 | |
| GPRK | 16 | −430.0 | 54.0 | Infinite | 16 | 0 | |
| HLKW | 20.9 | 14.2 | 11.1 | 18.7 | 17 | 4 (23.5%) | KENS(2), GPRK (2) |
| HLS | 20 | 9.9 | 7.1 | 13.9 | 16 | 4 (25%) | MSJ(2), GPRK (2) |
| KENS | 41 | 63.6 | 27.3 | 1162.5 | 41 | 0 | |
| MSJ | 27.9 | 19.6 | 14.2 | 28.3 | 21 | 7 (33.3%) | HLS(3), TGN(3), AGHR(1) |
| PHG | 11 | 13.8 | 5.2 | 105.7 | 11 | 0 | |
| PPAP | 13 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 13 | 0 | |
| TGN | 14 | 23.1 | 15.5 | 40.0 | 11 | 3 (27.3%) | FFRC(2), AGHR(1) |
| Total (%) | 181 | 163 (90%) | 18 (10%) | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chew, P.C.; Christianus, A.; Zudaidy, J.M.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Chong, C.M.; Tan, S.G. Microsatellite Characterization of Malaysian Mahseer (Tor spp.) for Improvement of Broodstock Management and Utilization. Animals 2021, 11, 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092633
Chew PC, Christianus A, Zudaidy JM, Ina-Salwany MY, Chong CM, Tan SG. Microsatellite Characterization of Malaysian Mahseer (Tor spp.) for Improvement of Broodstock Management and Utilization. Animals. 2021; 11(9):2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092633
Chicago/Turabian StyleChew, Poh Chiang, Annie Christianus, Jaapar M. Zudaidy, Md Yasin Ina-Salwany, Chou Min Chong, and Soon Guan Tan. 2021. "Microsatellite Characterization of Malaysian Mahseer (Tor spp.) for Improvement of Broodstock Management and Utilization" Animals 11, no. 9: 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092633
APA StyleChew, P. C., Christianus, A., Zudaidy, J. M., Ina-Salwany, M. Y., Chong, C. M., & Tan, S. G. (2021). Microsatellite Characterization of Malaysian Mahseer (Tor spp.) for Improvement of Broodstock Management and Utilization. Animals, 11(9), 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092633






