Sex-Biased Gene Expression and Isoform Profile of Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana by Transcriptome Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
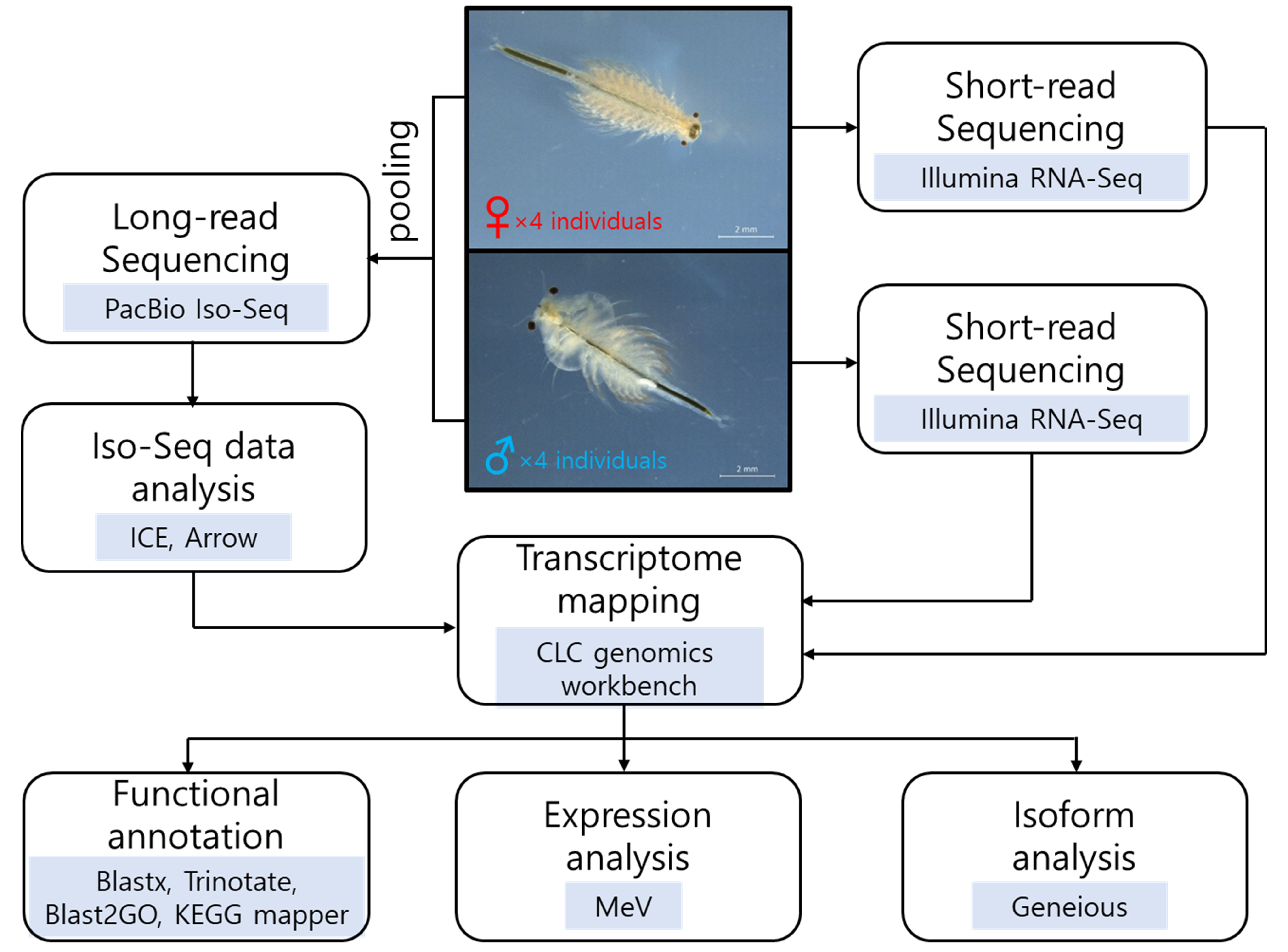
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and RNA Extraction
2.2. Iso-Seq Sequencing for Full-Length Transcripts Generation
2.3. RNA-Seq Sequencing and Mapping to Iso-Seq Data
2.4. Functional Annotation and Sex-Biased Expression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptome Sequencing Results of Female and Male A. franciscana
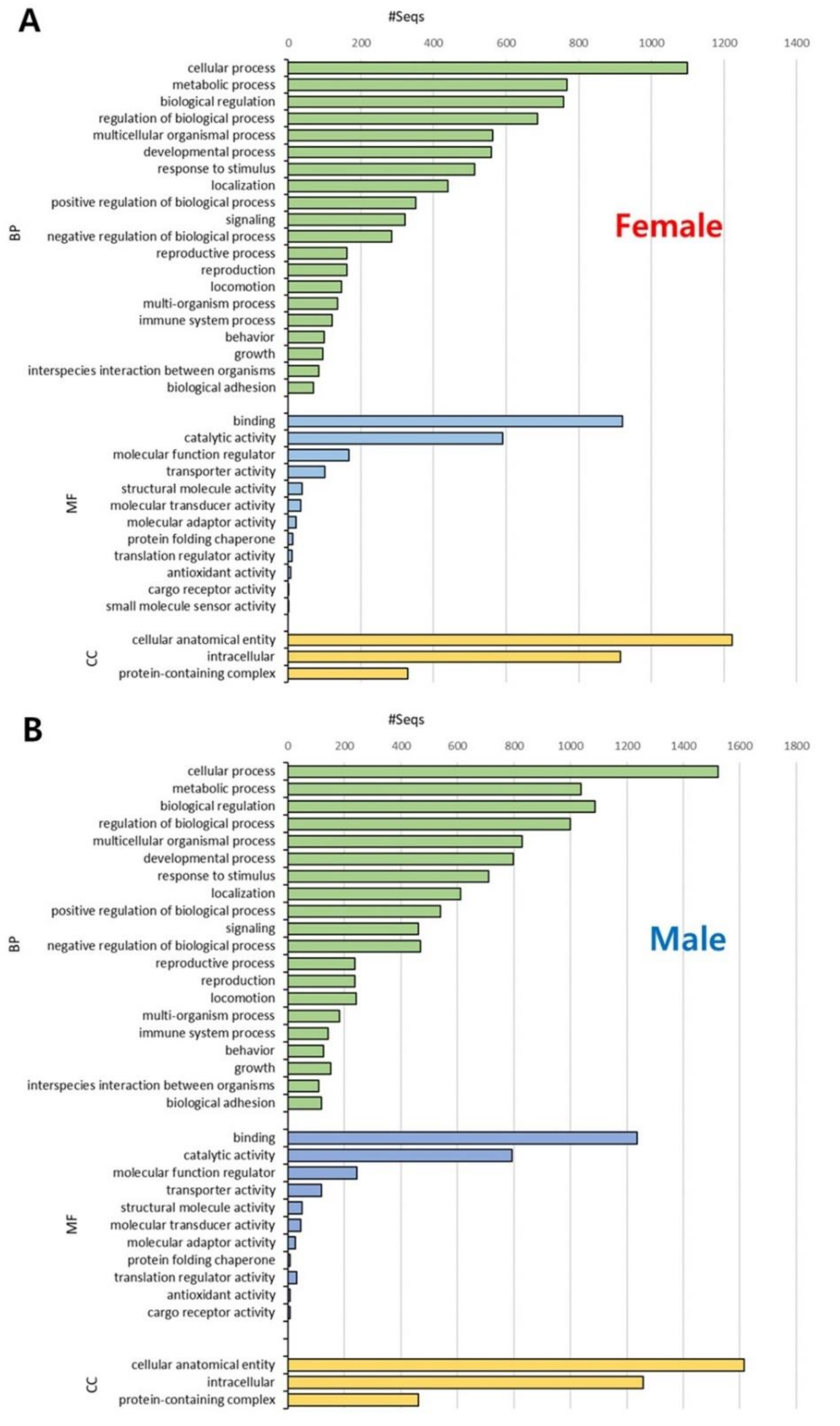
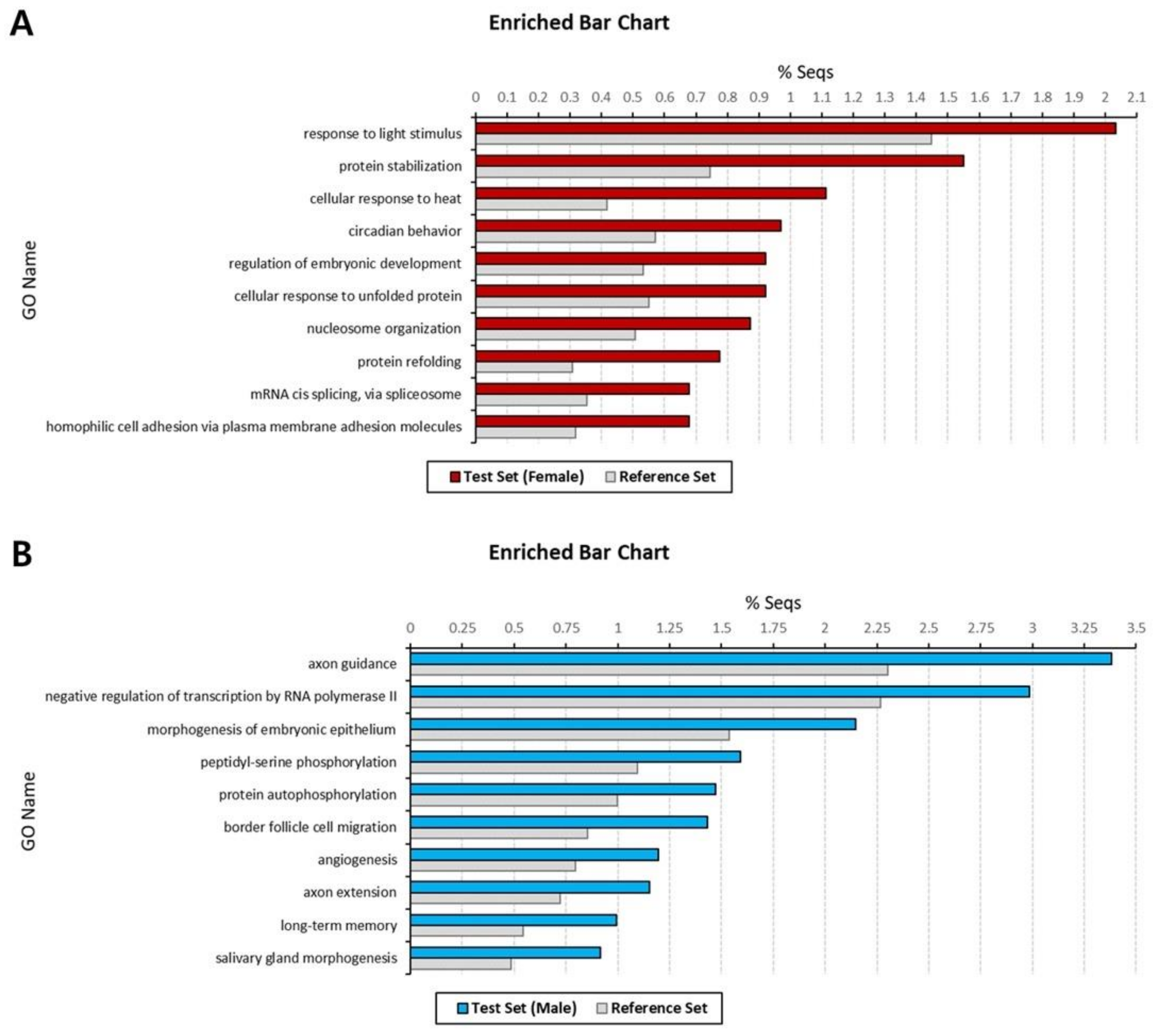
3.2. Functional Annotation and GO Enrichment Analysis
3.3. Sex-Biased Gene Expression Profile and Candidate Sex Determination Genes
3.4. Isoforms of DMRT1 and Sad Genes in A. franciscana
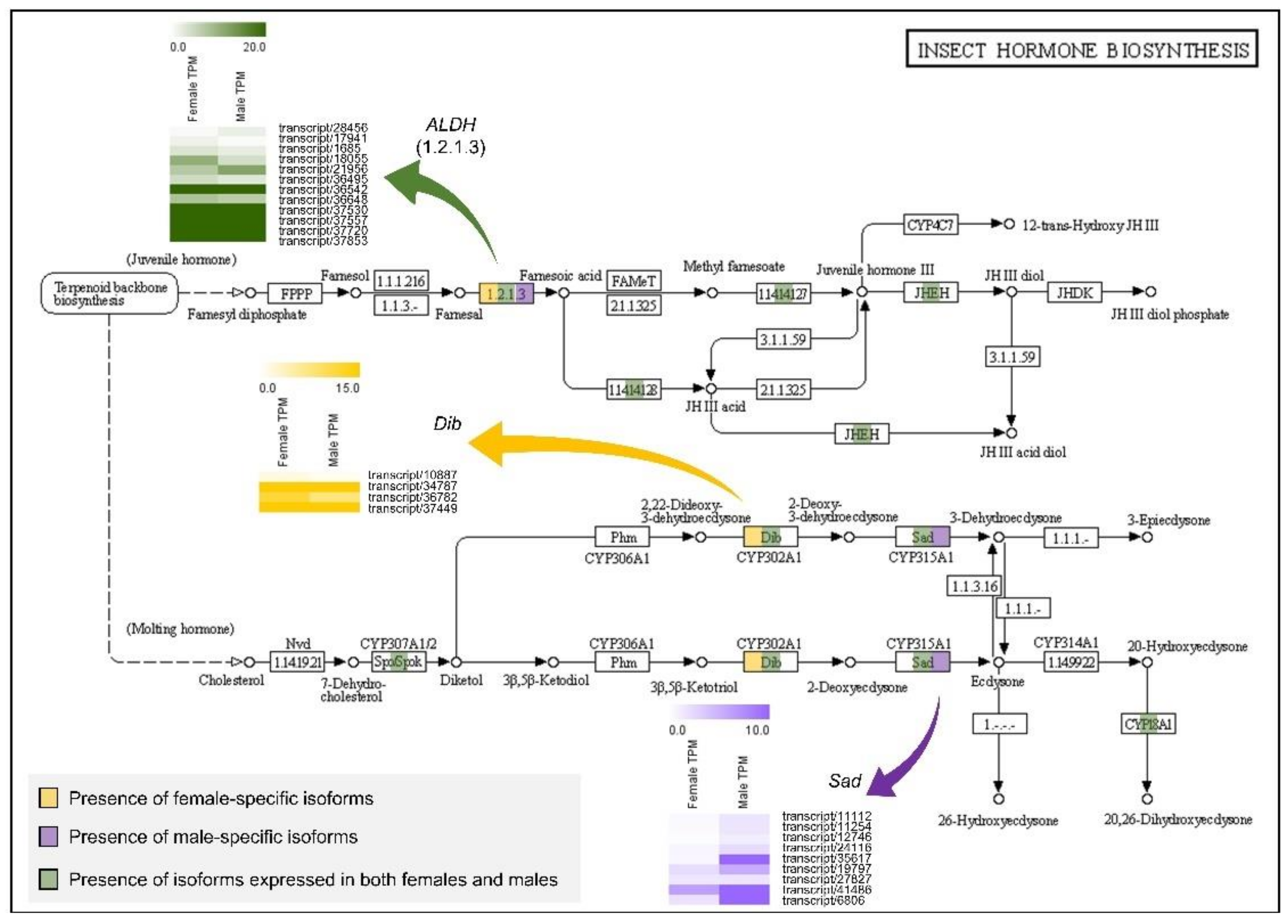
3.5. KEGG Pathway for Ecdysteroid Biosynthesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hake, L.; O’Connor, C. Genetic mechanisms of sex determination. Nat. Educ. 2008, 1, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Ye, L.; Chen, H. Sex determination and maintenance: The role of DMRT1 and FOXL2. Asian J. Androl. 2017, 19, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, A. Understanding sex determination in the mouse: Genetics, epigenetics and the story of mutual antagonisms. J. Genet. 2015, 94, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, A.J.; Goodfellow, P.N. Sex determination in humans. Bioessays 1996, 18, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.A.; Roeszler, K.N.; Ohnesorg, T.; Cummins, D.M.; Farlie, P.G.; Doran, T.J.; Sinclair, A.H. The avian Z-linked gene DMRT1 is required for male sex determination in the chicken. Nature 2009, 461, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A. Sex determination in birds: HINTs from the W sex chromosome? Sex. Dev. 2007, 1, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Sinclair, A.H. Sex determination: Insights from the chicken. Bioessays 2004, 26, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, E.; Oliver, B. Genomics of sex determination in Drosophila. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2012, 11, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waiho, K.; Fazhan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ikhwanuddin, M.; Ma, H. Comparative profiling of ovarian and testicular piRNAs in the mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Genomics 2020, 112, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, T.; Sagi, A. The “IAG-switch”—A key controlling element in decapod crustacean sex differentiation. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Liu, L.; Hui, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, Z. Primary molecular basis of androgenic gland endocrine sex regulation revealed by transcriptome analysis in Eriocheir sinensis. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Abayed, F.A.; Manor, R.; Aflalo, E.D.; Sagi, A. Screening for Dmrt genes from embryo to mature Macrobrachium rosenbergii prawns. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 282, 113205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Li, S.; Lv, X.; Xiang, J.; Sagi, A.; Manor, R.; Li, F. A putative insulin-like androgenic gland hormone receptor gene specifically expressed in male Chinese shrimp. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rotllant, G.; Nguyen, T.V.; Sbragaglia, V.; Rahi, L.; Dudley, K.J.; Hurwood, D.; Ventura, T.; Company, J.B.; Chand, V.; Aguzzi, J.; et al. Sex and tissue specific gene expression patterns identified following de novo transcriptomic analysis of the Norway lobster, Nephrops norvegicus. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chebbi, M.A.; Becking, T.; Moumen, B.; Giraud, I.; Gilbert, C.; Peccoud, J.; Cordaux, R. The genome of Armadillidium vulgare (Crustacea, Isopoda) provides insights into sex chromosome evolution in the context of cytoplasmic sex determination. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, S.F. Chromosomal Sex Determination in Mammals. In Developmental Biology, 6th ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, A.H.; Berta, P.; Palmer, M.S.; Hawkins, J.R.; Griffiths, B.L.; Smith, M.J.; Foster, J.W.; Frischauf, A.-M.; Lovell-Badge, R.; Goodfellow, P.N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature 1990, 346, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negri, I.; Pellecchia, M. Sex steroids in insects and the role of the endosymbiont Wolbachia: A new perspective. In Sex Hormones; Dubey, R., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 353–374. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M. The mechanism of sex determination in vertebrates—Are sex steroids the key-factor? J. Exp. Zool. A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2010, 313, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Loof, A. Ecdysteroids: The overlooked sex steroids of insects? Males: The black box. Insect Sci. 2006, 13, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.S.; Chang, S.A.; Mulder, E.P. Hormones in the lives of crustaceans: An overview. Am. Zool. 2001, 41, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.R.; Sieglaff, D.H.; Rees, H.H. Gonadal ecdysteroidogenesis in Arthropoda: Occurrence and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, L.I.; Rybczynski, R.; Warren, J.T. Control and biochemical nature of the ecdysteroidogenic pathway. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 883–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotllant, G.; Takac, P.; Liu, L.; Scott, G.L.; Laufer, H. Role of ecdysteroids and methyl farnesoate in morphogenesis and terminal moult in polymorphic males of the spider crab Libinia emarginata. Aquaculture 2000, 190, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, H.; Ahl, J.; Rotllant, G.; Baclaski, B. Evidence that ecdysteroids and methyl farnesoate control allometric growth and differentiation in a crustacean. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaleski, M.A.F.; Tamone, S.L. Relationship of molting, gonadosomatic index, and methyl farnesoate in male snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) from the eastern Bering Sea. J. Crustac. Biol. 2014, 34, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayanath, A.; Arath Raghavan, S.D. Profiling of methyl farnesoate in relation to female reproductive cycle in the freshwater crab, Travancoriana schirnerae Bott, 1969 (Crustacea: Gecarcinucidae). Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 64, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.-H.; Wu, Y.-S.; Chang, N.-C. The effect of steroid hormone feeds on the reproductive biology of the spiny lobster, Panulirus interruptus (J.W. Randall, 1840) (Decapoda, Palinura). Crustaceana 2015, 88, 1367–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stappen, G. Zoogeography. In Artemia: Basic and Applied Biology; Abatzopoulos, T.J., Beardmore, J.A., Clegg, J.S., Sorgeloos, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 171–224. [Google Scholar]
- Asem, A.; Eimanifar, A.; Rastegar-Pouyani, N.; Hontoria, F.; De Vos, S.; Van Stappen, G.; Sun, S.-C. An overview on the nomenclatural and phylogenetic problems of native Asian brine shrimps of the genus Artemia Leach, 1819 (Crustacea, Anostraca). ZooKeys 2020, 902, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asem, A.; Eimanifar, A.; Sun, S.C. Genetic variation and evolutionary origins of parthenogenetic Artemia (Crustacea: Anostraca) with different ploidies. Zool. Scr. 2016, 45, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatsi, S.; Baxevanis, A.D.; Kappas, I.; Deligiannidis, P.; Triantafyllidis, A.; Papakostas, S.; Bougiouklis, D.; Abatzopoulos, T.J. Is polyploidy a persevering accident or an adaptive evolutionary pattern? The case of the brine shrimp Artemia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 58, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-R.; Ye, H.-L.; Yang, J.-S.; Yang, F.; Wang, M.-R.; De Vos, S.; Vuylsteke, M.; Sorgeloos, P.; Van Stappen, G.; Bossier, P.; et al. Identification and characterization of a Masculinizer (Masc) gene involved in sex differentiation in Artemia. Gene 2017, 614, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stappen, G. Introduction, biology and ecology of Artemia. In Manual on the Production and Use of LIVE food for Aquaculture; Lavens, P., Sorgeloos, P., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996; pp. 79–106. [Google Scholar]
- Huylmans, A.K.; Toups, M.A.; Macon, A.; Gammerdinger, W.J.; Vicoso, B. Sex-biased gene expression and dosage compensation on the Artemia franciscana Z-chromosome. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Vos, S.; Bossier, P.; Van Stappen, G.; Vercauteren, I.; Sorgeloos, P.; Vuylsteke, M. A first AFLP-based genetic linkage map for brine shrimp Artemia franciscana and its application in mapping the sex locus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57585. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, S.T. The genetics of Artemia salina. II. White eye, a sex-linked mutation. Biol. Bull. 1963, 124, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawaribuchi, S.; Ito, Y.; Ito, M. Independent evolution for sex determination and differentiation in the DMRT family in animals. Biol. Open 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Watanabe, H.; Iguchi, T. Environmental sex determination in the branchiopod crustacean Daphnia magna: Deep conservation of a Doublesex gene in the sex-determining pathway. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, P.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yi, J.; Lin, W.; Guo, Z.; Xu, A.; Yang, S.; Chan, S. Potential involvement of a DMRT family member (Mr—Dsx) in the regulation of sexual differentiation and moulting in the giant river prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 3037–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.-F.; Qiu, G.-F. A novel Dmrt gene is specifically expressed in the testis of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Dev. Genes Evol. 2010, 220, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farazmand, A.; Inanloo, K.; Agh, N. Expression of DMRT family genes during gonadal differentiation in two species of Artemia (Branchiopoda, Anostraca) from Urmia Lake (Iran). Crustaceana 2010, 83, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Sakaguchi, H.; Aoki, F.; Suzuki, M.G. Functional analysis of sex-determination genes by gene silencing with LNA–DNA gapmers in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Mech. Dev. 2015, 137, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minio, A.; Massonnet, M.; Figueroa-Balderas, R.; Vondras, A.M.; Blanco-Ulate, B.; Cantu, D. Iso-Seq allows genome-independent transcriptome profiling of grape berry development. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conesa, A.; Madrigal, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Cervera, A.; McPherson, A.; Szcześniak, M.W.; Gaffney, D.J.; Elo, L.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matlin, A.J.; Clark, F.; Smith, C.W.J. Understanding alternative splicing: Towards a cellular code. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Miranda, D.; Gallardo-Escárate, C.; Valenzuela-Muñoz, V.; Farlora, R.; Gajardo, G. Sex-dependent transcriptome analysis and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery in the brine shrimp Artemia franciscana. Mar. Genomics 2014, 18, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, E.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, H. Whole genome survey and microsatellite motif identification of Artemia franciscana. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20203868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtson, D.A.; Léger, P.; Sorgeloos, P. Use of Artemia as a food source for aquaculture. In Artemia Biology; Browne, R.A., Sorgeloos, P., Trotman, C.N.A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 255–286. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, B.S.; Carvalho, F.D.; Guilhermino, L.M.; Van Stappen, G. Use of the genus Artemia in ecotoxicity testing. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lu, Y. Artemia spp. model-a well-established method for rapidly assessing the toxicity on an environmental perspective. Med. Res. Arch. 2018, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data, Version 0.11.9; Babraham Bioinformatics: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI reference sequences (RefSeq): A curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D61–D65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bryant, D.M.; Johnson, K.; DiTommaso, T.; Tickle, T.; Couger, M.B.; Payzin-Dogru, D.; Lee, T.J.; Leigh, N.D.; Kuo, T.-H.; Davis, F.G. A tissue-mapped axolotl de novo transcriptome enables identification of limb regeneration factors. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Williams, T.D.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Nueda, M.J.; Robles, M.; Talón, M.; Dopazo, J.; Conesa, A. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3420–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OmicsBox-Bioinformatics made easy. Version 1.3.11. BioBam Bioinformatics: Valencia, Spain, 2019.
- Saeed, A.; Sharov, V.; White, J.; Li, J.; Liang, W.; Bhagabati, N.; Braisted, J.; Klapa, M.; Currier, T.; Thiagarajan, M. TM4: A free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. Biotechniques 2003, 34, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, S.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W182–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y. KEGG Mapper for inferring cellular functions from protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellegren, H.; Parsch, J. The evolution of sex-biased genes and sex-biased gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsch, J.; Ellegren, H. The evolutionary causes and consequences of sex-biased gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naurin, S.; Hansson, B.; Bensch, S.; Hasselquist, D. Why does dosage compensation differ between XY and ZW taxa? Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinier, C.; Reisser, C.M.; Fields, P.; Ségard, A.; Galimov, Y.; Haag, C.R. Identification of general patterns of sex-biased expression in Daphnia, a genus with environmental sex determination. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, J.; Li, F. Sex-Specific transcriptome sequencing of zoea I larvae and identification of sex-linked genes using bulked segregant analysis in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 22, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huylmans, A.K.; López Ezquerra, A.; Parsch, J.; Cordellier, M. De novo transcriptome assembly and sex-biased gene expression in the cyclical parthenogenetic Daphnia galeata. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3120–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rewitz, K.; Rybczynski, R.; Warren, J.T.; Gilbert, L.I. The Halloween genes code for cytochrome P450 enzymes mediating synthesis of the insect moulting hormone. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, M.; Tsuji, T.; Tanaka, S.; Shiotsuki, T.; Jouraku, A.; Miura, K.; Vea, I.M.; Minakuchi, C. Sex-specific expression profiles of ecdysteroid biosynthesis and ecdysone response genes in extreme sexual dimorphism of the mealybug Planococcus kraunhiae (Kuwana). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231451. [Google Scholar]
- Emlen, D.; Nijhout, H. Hormonal control of male horn length dimorphism in Onthophagus taurus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae): A second critical period of sensitivity to juvenile hormone. J. Insect Physiol. 2001, 47, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledón-Rettig, C.C.; Zattara, E.; Moczek, A.P. Asymmetric interactions between doublesex and tissue-and sex-specific target genes mediate sexual dimorphism in beetles. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rewitz, K.F.; Gilbert, L.I. Daphnia Halloween genes that encode cytochrome P450s mediating the synthesis of the arthropod molting hormone: Evolutionary implications. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Tao, T.; Shen, X.; Zhu, D. Role of Halloween genes in ecdysteroids biosynthesis of the swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus): Implications from RNA interference and eyestalk ablation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 199, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toyota, K.; Miyakawa, H.; Hiruta, C.; Sato, T.; Katayama, H.; Ohira, T.; Iguchi, T. Sex Determination and Differentiation in Decapod and Cladoceran Crustaceans: An Overview of Endocrine Regulation. Genes 2021, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
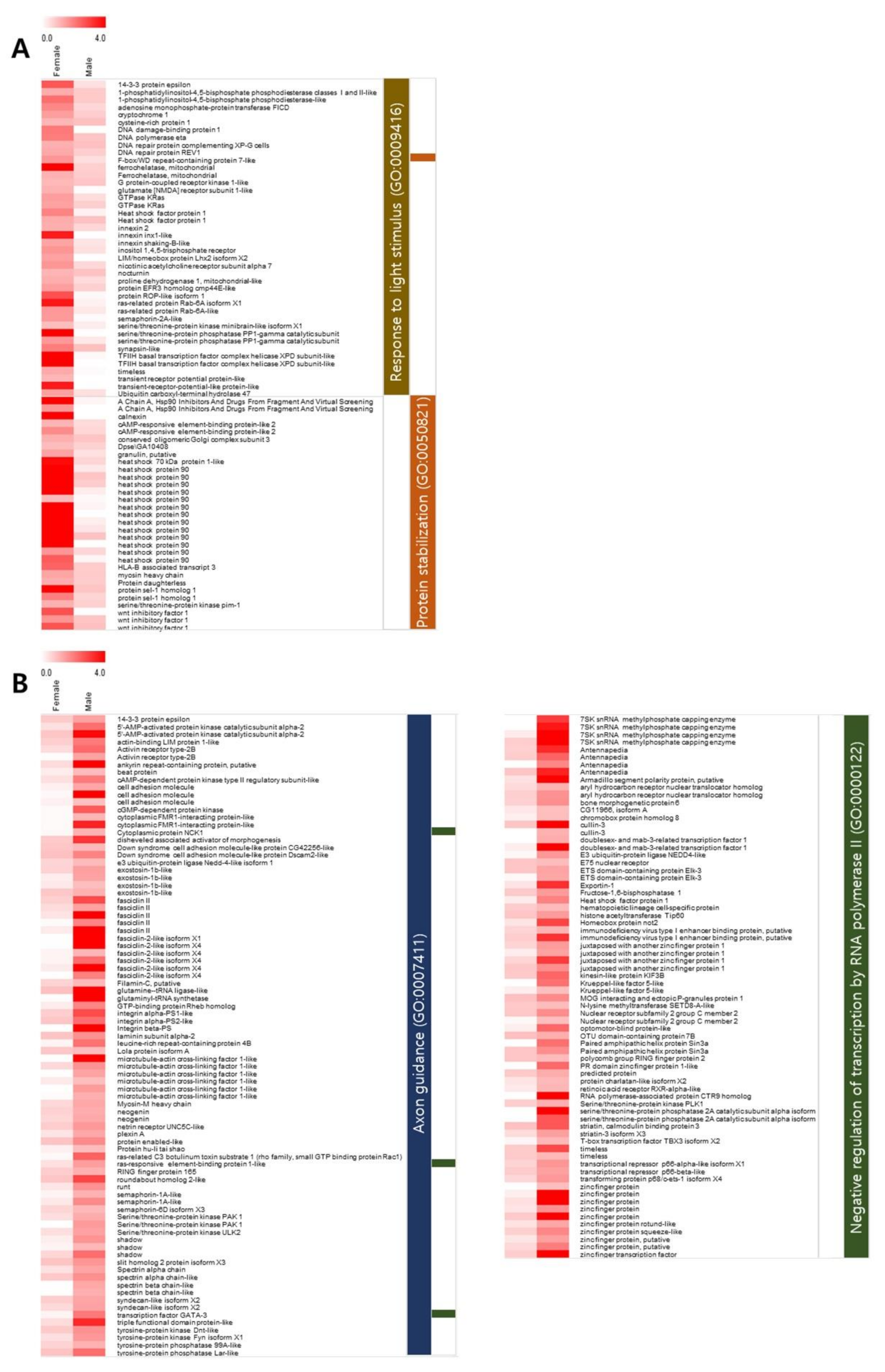
| F/M | Description | Sex-Biased Isoform | Total Isoform |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Calnexin | 3 | 7 |
| DNA damage-binding protein 1 | 1 | 5 | |
| Ferrochelatase, mitochondrial | 2 | 5 | |
| Heat shock protein 90 | 15 | 25 | |
| HLA-B associated transcript 3 | 1 | 3 | |
| Innexin inx1-like | 1 | 4 | |
| Protein ROP-like isoform 1 | 1 | 7 | |
| Ras-related protein Rab-6A isoform X1 | 2 | 7 | |
| Synapsin-like | 1 | 2 | |
| TFIIH basal transcription factor complex helicase XPD Subunit-like | 2 | 4 | |
| Male | 5’-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 | 2 | 5 |
| 7SK snRNA methylphosphate capping enzyme | 4 | 8 | |
| Armadillo segment polarity protein, putative | 1 | 5 | |
| cGMP-dependent protein kinase | 1 | 10 | |
| Cullin 3 | 2 | 4 | |
| Cytoplasmic FMR1-interacting protein-like | 2 | 2 | |
| Disheveled associated activator of morphogenesis | 1 | 4 | |
| Doublesex- and mab-3-related transcription factor 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Exportin 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| Glutamine–tRNA ligase-like | 1 | 3 | |
| Homeobox protein not2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Immunodeficiency virus type I enhancer binding protein, putative | 2 | 5 | |
| Integrin alpha-PS1-like | 1 | 2 | |
| Integrin alpha-PS2-like | 1 | 11 | |
| Integrin beta-PS | 2 | 15 | |
| Kinesin-like protein KIF3B | 1 | 3 | |
| Kruppel-like factor 5-like | 1 | 3 | |
| Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 4B | 1 | 3 | |
| Microtubule-actin cross-linking factor 1-like | 6 | 29 | |
| Optomotor-blind protein-like | 1 | 2 | |
| Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (rho family, Small GTP binding protein Rac1) | 1 | 3 | |
| RNA polymerase-associated protein CTR9 homolog | 1 | 3 | |
| Serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit alpha isoform | 2 | 8 | |
| Shadow | 5 | 7 | |
| Transcription factor GATA-3 | 1 | 4 | |
| Triple functional domain protein-like | 7 | 12 | |
| Tyrosine protein phosphatase Lar-like | 1 | 3 | |
| Zinc finger protein | 13 | 30 | |
| Zinc finger transcription factor | 1 | 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, E.; Lee, S.-J.; Choi, E.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, H. Sex-Biased Gene Expression and Isoform Profile of Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana by Transcriptome Analysis. Animals 2021, 11, 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092630
Jo E, Lee S-J, Choi E, Kim J, Lee J-H, Park H. Sex-Biased Gene Expression and Isoform Profile of Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana by Transcriptome Analysis. Animals. 2021; 11(9):2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092630
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Euna, Seung-Jae Lee, Eunkyung Choi, Jinmu Kim, Jun-Hyuck Lee, and Hyun Park. 2021. "Sex-Biased Gene Expression and Isoform Profile of Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana by Transcriptome Analysis" Animals 11, no. 9: 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092630
APA StyleJo, E., Lee, S.-J., Choi, E., Kim, J., Lee, J.-H., & Park, H. (2021). Sex-Biased Gene Expression and Isoform Profile of Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana by Transcriptome Analysis. Animals, 11(9), 2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092630







