Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis Revealed Lipometabolic Disorders in Perirenal Adipose Tissue of Rabbits Subject to a High-Fat Diet
Abstract
:Simply Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Histological Examination
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) Analysis
2.6. Data Processing and Analysis
2.7. Identification and Analysis of Metabolites
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
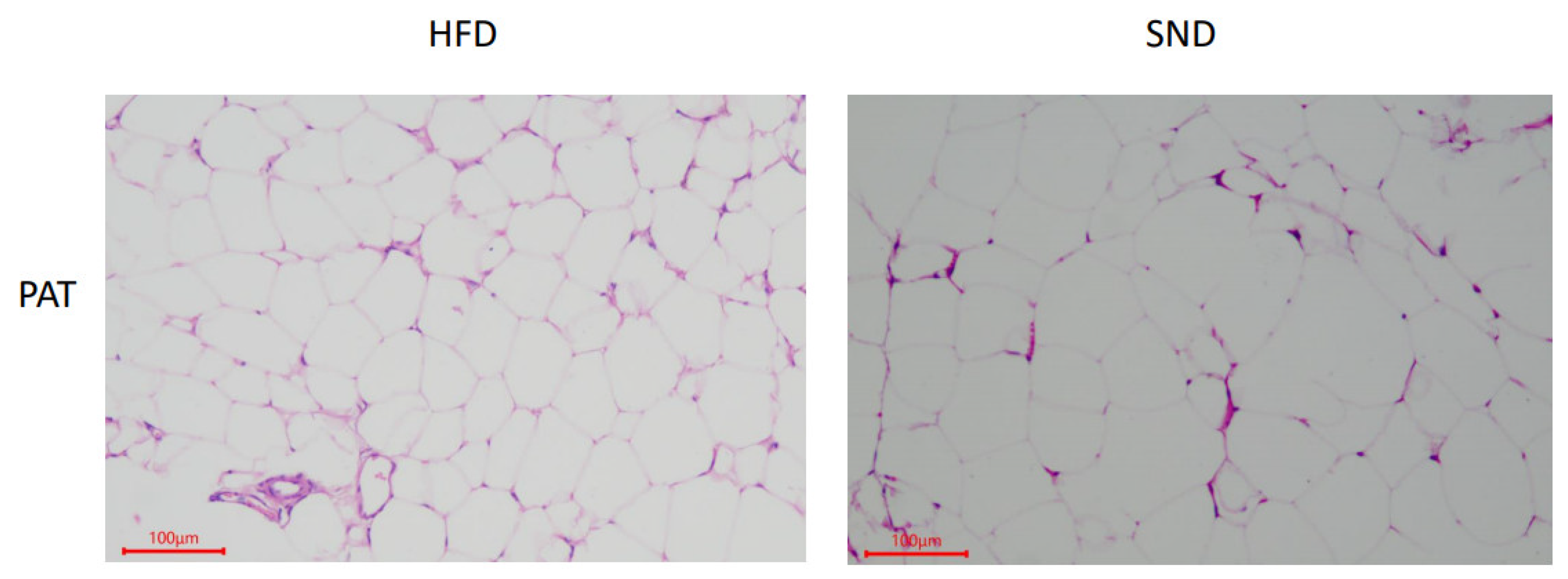
3.1. PAT Histological Observations
3.2. Quality Control of Metabolomics Data
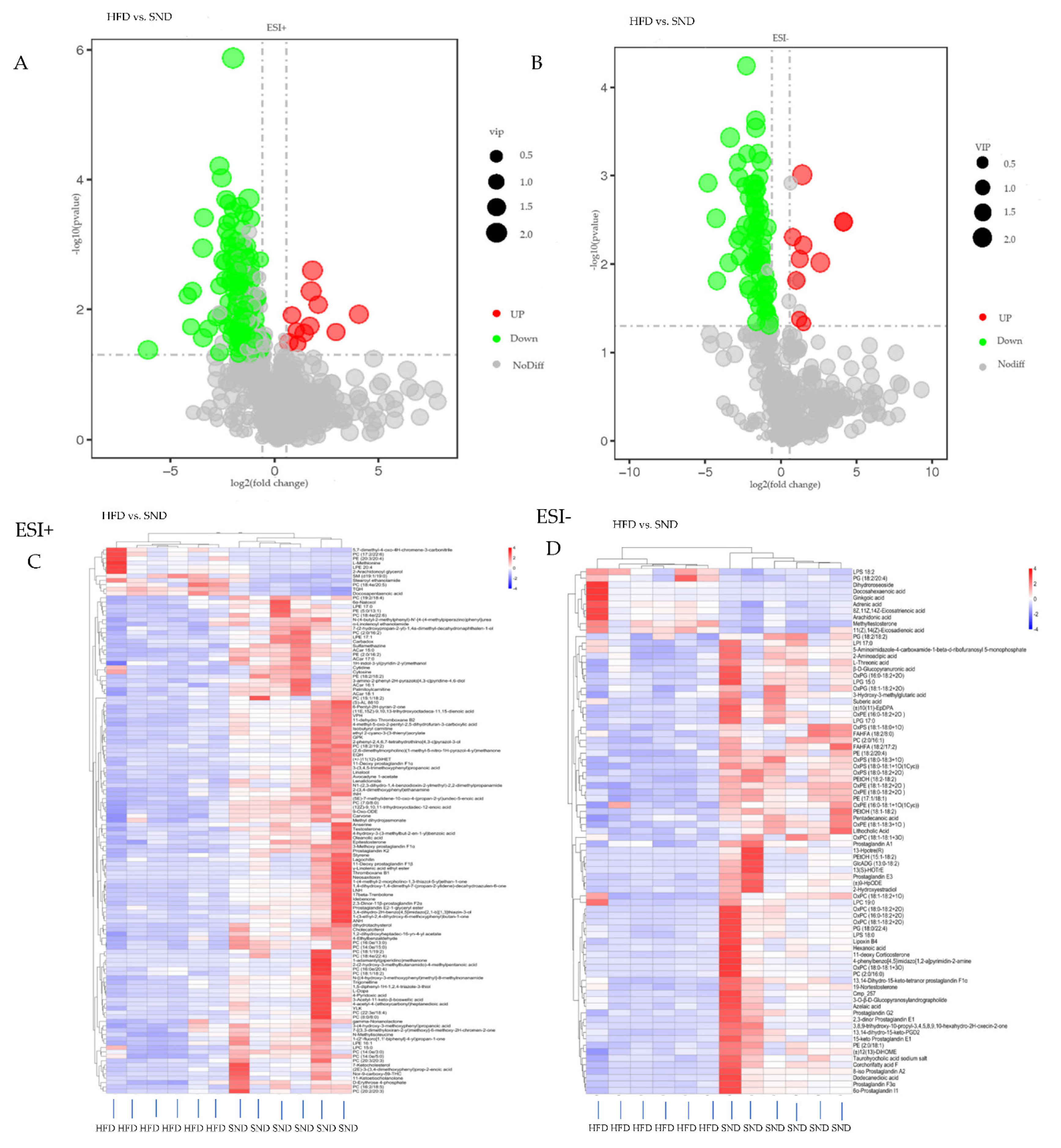
3.3. Differential Metabolites Analysis
3.4. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PAT | perirenal adipose tissue |
| HFD | high-fat diet |
| SND | standard normal diet |
| HPLC | high performance liquid chromatography |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PLS-DA | partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| FC | fold change |
| QC | quality control |
| ARA | arachidonic acid |
| PEs | phosphatidylethanolamines |
| PCs | phosphatidylcholines |
| SM | sphingomyelin |
| SMS | sphingomyelin synthase |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| SAM | s-adenosine methionine |
| SAH | methyltransferase inhibitor S-adenosylhomocysteine |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| DPA | docosapentaenoic acid |
| DHA | docosahexaenoic acid |
| PUFAs | polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| LPEs | lysophosphatidylethanolamine |
| LysoPCs/LPCs | lysophosphatidylcholines |
| Hcy | homocysteine |
| HM | homocysteine–methionine |
| LC | liquid chromatography |
| LC-MS/MS | liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| TG | triglyceride |
| KEGG | kyotoencyclopedia of genes and genomes |
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyatt, S.B.; Winters, K.P.; Dubbert, P.M. Overweight and Obesity: Prevalence, Consequences, and Causes of a Growing Public Health Problem. Am. J. Med Sci. 2006, 331, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reilly, J.J.; El-Hamdouchi, A.; Diouf, A.; Monyeki, M.A.; A Somda, S. Determining the worldwide prevalence of obesity. Lancet 2018, 391, 1773–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elobeid, M.A.; Allison, D.B. Putative environmental-endocrine disruptors and obesity: A review. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2008, 15, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLaughlin, T.; Ackerman, S.E.; Shen, L.; Engleman, E. Role of innate and adaptive immunity in obesity-associated metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Hu, F.B. Epidemiology of Obesity and Diabetes and Their Cardiovascular Complications. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Lysaght, J.; Donohoe, C.L.; Reynolds, J.V. Obesity and gastrointestinal cancer: The interrelationship of adipose and tumour microenvironments. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Patil, I.Y.; Jiang, T.; Sancheti, H.; Walsh, J.P.; Stiles, B.L.; Yin, F.; Cadenas, E. High-Fat Diet Induces Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Impairment of Synaptic Plasticity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, P.; Di Carlo, M.; Nuzzo, D. Obesity and Alzheimer’s disease: Molecular bases. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 52, 3944–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, F.S.; Rosa, J.C.; A Cunha, C.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Nascimento, C.O.D.; Oyama, L.M.; Mota, J.F. Supplementing alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) and vitamin D3 in high fat diet decrease IL-6 production in murine epididymal adipose tissue and 3T3-L1 adipocytes following LPS stimulation. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Yuan, J.; Yu, Z.; Lin, L.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhuang, P.; Whalen, M.J.; Song, B.; Wang, X.-J.; et al. FGF21 Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Cognitive Impairment via Metabolic Regulation and Anti-inflammation of Obese Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 4702–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.R.; González-Bulnes, A.; Garcia-Contreras, C.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.E.; Astiz, S.; Vazquez-Gomez, M.; Pesantez, J.L.; Isabel, B.; Salido-Ruiz, E.; González, J.; et al. The Iberian pig fed with high-fat diet: A model of renal disease in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Liu, M. Adipose tissue in control of metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 231, R77–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocquier, F.; Bonnet, M.; Faulconnier, Y.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Martin, P.; Chilliard, Y. Effects of photoperiod and feeding level on perirenal adipose tissue metabolic activity and leptin synthesis in the ovariectomized ewe. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 1998, 38, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Gang, X.; He, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, G. The Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane-Induced Insulin Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 592129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, C.M.; Prado, C.; Takane, K.K.; Lasnier, F.; Garcia-Ocana, A.; Ferre, P.; Dugail, I.; Hajduch, E. Plasma Membrane Subdomain Compartmentalization Contributes to Distinct Mechanisms of Ceramide Action on Insulin Signaling. Diabetes 2010, 59, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meikle, J.; Summers, S.A. Sphingolipids and phospholipids in insulin resistance and related metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, G.; Becattini, B. JNK at the crossroad of obesity, insulin resistance, and cell stress response. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Yang, L.; Li, P.; Hofmann, O.; Dicker, L.; Hide, W.; Lin, X.; Watkins, S.M.; Ivanov, A.R.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Aberrant lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity. Nature 2011, 473, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, C.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamboni, N.; Saghatelian, A.; Patti, G.J. Defining the metabolome: Size, flux, and regulation. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, F.; Xie, X.; Wang, R.; Hua, C. Untargeted metabonomics reveals intervention effects of chicory polysaccharide in a rat model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, S.G.B.; Gao, Z.J.; Chen, Z.; Abe, T.; Hori, S.; Fukiya, S.; Ishizuka, S.; Yokota, A.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.-P. Untargeted Lipidomic Analysis of Plasma from High.-fat Diet.-induced Obese Rats Using UHPLC-Linear Trap Quadrupole-Orbitrap MS. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Álvaro, M.; Hernández, P.; Agha, S.; Blasco, A. Correlated responses to selection for intramuscular fat in several muscles in rabbits. Meat Sci. 2018, 139, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, J.E.; Tumurbaatar, B.; D’Agostino, C.; Main, E.; Wright, T.; Dillon, E.L.; Saito, T.B.; Porter, C.; Andersen, C.R.; Brining, D.L.; et al. Effect of high-fat diet on peripheral blood mononuclear cells and adipose tissue in early stages of diet-induced weight gain. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, G.; Roco, J.; Medina, M.; Medina, A.; Peral, M.; Jerez, S. High fat diet-induced metabolically obese and normal weight rabbit model shows early vascular dysfunction: Mechanisms involved. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Elzo, M.A.; Tang, T.; Lai, T.; Ma, Y.; Gan, M.; Wang, L.; Jia, X.; et al. Growth, behavioural, serum biochemical and morphological changes in female rabbits fed high-fat diet. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 105, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, V.; De Santis, N.; Scotto, R.; Della Giustina, P.; Desideri, L.F.; Cellerino, M.; Cordano, C.; Inglese, M.; Uccelli, A.; Vagge, A.; et al. Corneal epithelial dendritic cells in patients with multiple sclerosis: An in vivo confocal microscopy study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 81, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; O’Maille, .G.; Smith, C.; Brandon, T.R.; Uritboonthai, W.; Qin, C.; Trauger, A.S.A.; Siuzdak, G. Solvent-Dependent Metabolite Distribution, Clustering, and Protein Extraction for Serum Profiling with Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heischmann, S.; Quinn, K.; Cruickshank-Quinn, C.; Liang, L.-P.; Reisdorph, R.; Reisdorph, N.; Patel, M. Exploratory Metabolomics Profiling in the Kainic Acid Rat Model Reveals Depletion of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 during Epileptogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haspel, J.A.; Chettimada, S.; Shaik, R.S.; Chu, J.-H.; Raby, B.A.; Cernadas, M.; Carey, V.; Process, V.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Ifedigbo, E.; et al. Circadian rhythm reprogramming during lung inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, N.; Liu, X.; Kong, X.; Li, S.; Jiao, Z.; Qin, Z.; Dong, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Feces and liver tissue metabonomics studies on the regulatory effect of aspirin eugenol eater in hyperlipidemic rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinert, M.; Clemmensen, C.; Hofmann, S.; Moore, M.C.; Renner, S.; Woods, S.C.; Huypens, P.; Beckers, J.; de Angelis, M.H.; Schürmann, A.; et al. Animal models of obesity and diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.-P.; Cheng, M.-L.; Hung, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Hsieh, P.-S.; Shiao, M.-S.; Chen, J.-K.; Li, D.-E.; Hung, L.-M. Docosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid are positively associated with insulin sensitivity in rats fed high-fat and high-fructose diets. J. Diabetes 2017, 9, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Fang, C.; Hayashi, S.; Hao, S.; Zhao, M.; Tsutsui, H.; Nishiguchi, S.; Sheng, J. Pu-erh tea extract ameliorates high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and insulin resistance by modulating hepatic IL-6/STAT3 signaling in mice. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiik, A.; Andersson, D.P.; Brismar, T.; Chanpen, S.; Dhejne, C.; Ekström, T.J.; Flanagan, J.N.; Holmberg, M.; Kere, J.; Lilja, M.; et al. Metabolic and functional changes in transgender individuals following cross-sex hormone treatment: Design and methods of the GEnder Dysphoria Treatment in Sweden (GETS) study. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2018, 10, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, L.; Losito, I.; Cianci, C.; Cataldi, T.R.T.R.I.; Palmisano, F. Structural characterization and profiling of lyso-phospholipids in fresh and in thermally stressed mussels by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiley, L.; Sen, A.; Heaton, J.; Proitsi, P.; García-Gómez, D.; Leung, R.; Smith, N.; Thambisetty, M.; Kloszewska, I.; Mecocci, P. Evidence of altered phosphatidylcholine metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Noh, S.; Hur, H.J.; Sung, M.J.; Hwang, J.-T.; Park, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, M.-S.; Kwon, D.Y.; et al. Metabolomic Analysis of Livers and Serum from High-Fat Diet Induced Obese Mice. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.N.; Risis, S.; Yang, C.; Meikle, P.; Staples, M.; Febbraio, M.A.; Bruce, C.R. Plasma Lysophosphatidylcholine Levels Are Reduced in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Song, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H. Preventive effects of turmeric on the high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidaemia in mice associated with a targeted metabolomic approach for the analysis of serum lysophosphatidylcholine using LC-MS/MS. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 11, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Sutter, B.M.; Wang, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Tu, B.P. A Metabolic Function for Phospholipid and Histone Methylation. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 180–193.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pories, W.J.; Dohm, G.L. Diabetes: Have We Got It All Wrong?: Hyperinsulinism as the culprit: Surgery provides the evidence. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2438–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanamatsu, H.; Ohnishi, S.; Sakai, S.; Yuyama, K.; Mitsutake, S.; Takeda, H.; Hashino, S.; Igarashi, Y. Altered levels of serum sphingomyelin and ceramide containing distinct acyl chains in young obese adults. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Peng, J.-B.; Jia, H.-M.; Cai, D.-Y.; Zhang, H.-W.; Yu, C.-Y.; Zou, Z.-M. UPLC-Q/TOF MS standardized Chinese formula Xin-Ke-Shu for the treatment of atherosclerosis in a rabbit model. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-W.; Heden, T.D.; Morris, E.M.; Fritsche, K.L.; Vieira-Potter, V.J.; Thyfault, J.P. High-Fat Diet Alters Serum Fatty Acid Profiles in Obesity Prone Rats: Implications for In Vitro Studies. Lipids 2015, 50, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonnweber, T.; Pizzini, A.; Nairz, M.; Weiss, G.; Tancevski, I. Arachidonic Acid Metabolites in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, I.L.; Lavery, P.; Agellon, S.; Rauch, F.; Murshed, M.; A Weiler, H. Arachidonic acid exacerbates diet-induced obesity and reduces bone mineral content without impacting bone strength in growing male rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 73, 108226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Inflammatory Basis of Metabolic Disease. Cell 2010, 140, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, A.M.; Olefsky, J.M. The Origins and Drivers of Insulin Resistance. Cell 2013, 152, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horas, H.; Nababan, S.; Kawano, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshida, M.; Azuma, T. Adrenic acid as an inflammation enhancer in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 623, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.-F.; Li, X.; Shi, M.; Li, D. n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Metabolic Syndrome Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N. Pro-resolving lipid mediators are leads for resolution physiology. Nature 2014, 510, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, T.; Muraoka, S.; Ogiso, T. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by estradiol and 2-hydroxyestradiol. Steroids 1996, 61, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.S.; Shah, G. High-fat diet exposure from pre-pubertal age induces polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in rats. Reproduction 2018, 155, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Shin, Y.; Lee, I.; Kim, S.Y. L-Methionine Production. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 159, 153–177. [Google Scholar]
- Bauerle, M.R.; Schwalm, E.L.; Booker, S.J. Mechanistic Diversity of Radical S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM)-dependent Methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3995–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lever, M.; Slow, S. The clinical significance of betaine, an osmolyte with a key role in methyl group metabolism. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachier, F.; Andriamihaja, M.; Blais, A. Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids and Lipid Metabolism. J. Nutr. 2020, 150 (Suppl. S1), 2524S–2531S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Gao, C.; Cueto, R.; Liu, L.; Fu, H.; Shao, Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Fang, P.; Choi, E.T.; Wu, Q.; et al. Homocysteine-methionine cycle is a metabolic sensor system controlling methylation-regulated pathological signaling. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Fernandez, M.V.; Torres-Rovira, L.; Pesantez-Pacheco, J.L.; Vazquez-Gomez, M.; Garcia-Contreras, C.; Astiz, S.; Gonzalez-Bulnes, A. A Cross-Sectional Study of Obesity Effects on the Metabolomic Profile of a Leptin-Resistant Swine Model. Metabolites 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Metabolites’ Name | Formula | M 1 | RT 2 | VIP 3 | Trend 4 and p Value (HFD vs. SND) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC (2:0/16:1) | C26H50NO8P | 595.3491 | 13.322 | 1.563966765 | ↓ ** |
| PC (2:0/16:0) | C26H52NO8P | 597.36482 | 13.637 | 1.678708 | ↓ * |
| PC (2:0/16:2) | C26H48NO8P | 533.312 | 13.083 | 1.257585 | ↓ ** |
| PC (7:0/8:0) | C23H46NO8P | 495.296 | 13.64 | 1.709003 | ↓ ** |
| PC (8:0/8:0) | C24H48NO8P | 509.3122 | 12.994 | 1.482654 | ↓ * |
| PC (14:0e/3:0) | C25H52NO7P | 509.3481 | 15.092 | 1.797233 | ↓ ** |
| PC (14:0e/5:0) | C27H56NO7P | 537.3799 | 15.604 | 1.563913 | ↓ ** |
| PC (14:0e/15:0) | C37H76NO7P | 677.5239 | 15.723 | 1.590351 | ↓ ** |
| PC (15:1/18:2) | C41H76NO8P | 741.5327 | 16.04 | 1.638059 | ↓ * |
| PC (16:0e/13:0) | C37H76NO7P | 660.4966 | 15.72 | 1.602117 | ↓ ** |
| PC (16:0e/20:4) | C44H82NO7P | 767.5806 | 16.279 | 1.665696 | ↓ * |
| PC (16:2/18:5) | C42H70NO8P | 709.5431 | 15.675 | 1.384283 | ↓ ** |
| PC (17:2/22:6) | C47H78NO8P | 815.5423 | 15.998 | 1.250684 | ↑ * |
| PC (18:1/18:2) | C44H82NO8P | 783.5737 | 16.245 | 1.218645 | ↓ * |
| PC (18:1/19:2) | C45H84NO8P | 797.5907 | 16.194 | 1.176725 | ↓ * |
| PC (18:2/19:2) | C45H82NO8P | 795.5781 | 15.76 | 2.130609 | ↓ ** |
| PC (18:4e/20:5) | C46H76NO7P | 785.5238 | 15.649 | 1.666749 | ↑ ** |
| PC (18:4e/22:6) | C48H78NO7P | 811.5374 | 15.781 | 1.790827 | ↓ ** |
| PC (19:2/18:4) | C45H78NO8P | 791.5449 | 16.305 | 1.457723 | ↓ ** |
| PC (20:2/20:3) | C48H86NO8P | 835.5957 | 15.534 | 1.313735 | ↓ * |
| PC (22:3e/18:4) | C48H84NO7P | 817.594 | 15.407 | 1.361675 | ↓ ** |
| PC (20:3/20:3) | C48H84NO8P | 833.5871 | 15.567 | 1.34977 | ↓ * |
| LPC 15:0 | C23H48NO7P | 481.3167 | 14.571 | 1.951213 | ↓ * |
| LPC 19:0 | C27H56NO7P | 597.40091 | 15.577 | 2.003144 | ↓ * |
| PE (2:0/16:2) | C23H42NO8P | 491.2647 | 13.081 | 1.33104 | ↓ ** |
| PE (5:0/13:1) | C23H44NO8P | 493.2803 | 13.564 | 1.864231 | ↓ ** |
| PE (2:0/18:1) | C25H48NO8P | 521.31072 | 14.223 | 1.958401 | ↓ ** |
| PE (17:1/18:1) | C40H76NO8P | 729.53193 | 16.438 | 2.004323 | ↓ ** |
| PE (18:2/18:2) | C41H74NO8P | 739.5142 | 16.165 | 1.086091 | ↓ * |
| PE (18:2/20:4) | C43H74NO8P | 763.50059 | 15.487 | 1.856928 | ↓ ** |
| PE (20:3/20:4) | C45H76NO8P | 789.5234 | 15.926 | 1.857655 | ↑ * |
| LPE 16:1 | C21H42NO7P | 451.2696 | 14.594 | 1.583397 | ↓ ** |
| LPE 17:0 | C22H46NO7P | 467.3011 | 14.966 | 1.396921 | ↓ ** |
| LPE 17:1 | C22H44NO7P | 465.2855 | 14.621 | 2.160675 | ↓ ** |
| LPE 20:4 | C25H44NO7P | 501.2857 | 14.407 | 1.723687 | ↑ * |
| LPS 18:2 | C24H44 N O9 P | 521.27548 | 13.894 | 1.839273 | ↑ ** |
| LPS 18:0 | C24 H48NO9 P | 525.30639 | 14.412 | 1.545101 | ↓ * |
| PG (18:2/20:4) | C44H75O10P | 794.51067 | 15.605 | 1.039475 | ↑ * |
| SM(d19:1/19:0) | C43H87N2O6P | 758.6277 | 15.612 | 1.201017 | ↑ * |
| Arachidonic acid | C20H32O2 | 304.23985 | 14.263 | 1.235326 | ↑ * |
| Adrenic acid | C22H36O2 | 332.27124 | 14.649 | 1.732588 | ↑ * |
| Docosapentaenoic acid | C22H34O2 | 330.2556 | 15.208 | 2.095414 | ↑ ** |
| Docosahexaenoic acid | C22H32O2 | 328.23993 | 14.209 | 1.90978 | ↑ ** |
| Methyltestosterone | C20H30O2 | 302.22456 | 14.414 | 2.348698 | ↑ ** |
| 2-Hydroxyestradiol | C18H24O3 | 288.17234 | 10.513 | 1.100492 | ↓ ** |
| Epitestosterone | C19H28O2 | 288.2084 | 13.648 | 1.387 | ↓ * |
| Cholecalciferol | C27H44O | 384.3388 | 15.714 | 1.61838 | ↓ ** |
| 4-Pyridoxic acid | C8H9NO4 | 183.0533 | 7.482 | 1.766454 | ↓ ** |
| L-Methionine | C5H11NO2S | 149.0511 | 1.964 | 1.568533 | ↑ * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, S.; Shao, J.; Elzo, M.A.; Tang, T.; Li, Y.; Lai, T.; Gan, M.; Ma, Y.; Jia, X.; Lai, S.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis Revealed Lipometabolic Disorders in Perirenal Adipose Tissue of Rabbits Subject to a High-Fat Diet. Animals 2021, 11, 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082289
Xia S, Shao J, Elzo MA, Tang T, Li Y, Lai T, Gan M, Ma Y, Jia X, Lai S, et al. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis Revealed Lipometabolic Disorders in Perirenal Adipose Tissue of Rabbits Subject to a High-Fat Diet. Animals. 2021; 11(8):2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082289
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Siqi, Jiahao Shao, Mauricio A. Elzo, Tao Tang, Yanhong Li, Tianfu Lai, Mingchuan Gan, Yuan Ma, Xianbo Jia, Songjia Lai, and et al. 2021. "Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis Revealed Lipometabolic Disorders in Perirenal Adipose Tissue of Rabbits Subject to a High-Fat Diet" Animals 11, no. 8: 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082289
APA StyleXia, S., Shao, J., Elzo, M. A., Tang, T., Li, Y., Lai, T., Gan, M., Ma, Y., Jia, X., Lai, S., & Wang, J. (2021). Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis Revealed Lipometabolic Disorders in Perirenal Adipose Tissue of Rabbits Subject to a High-Fat Diet. Animals, 11(8), 2289. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11082289






