Practical Euthanasia Method for Common Sea Stars (Asterias rubens) That Allows for High-Quality RNA Sampling
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sea Star Collection and Husbandry
2.2. Sea Star Euthanasia and Sampling
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Animals
3.2. Sea Star Euthanasia
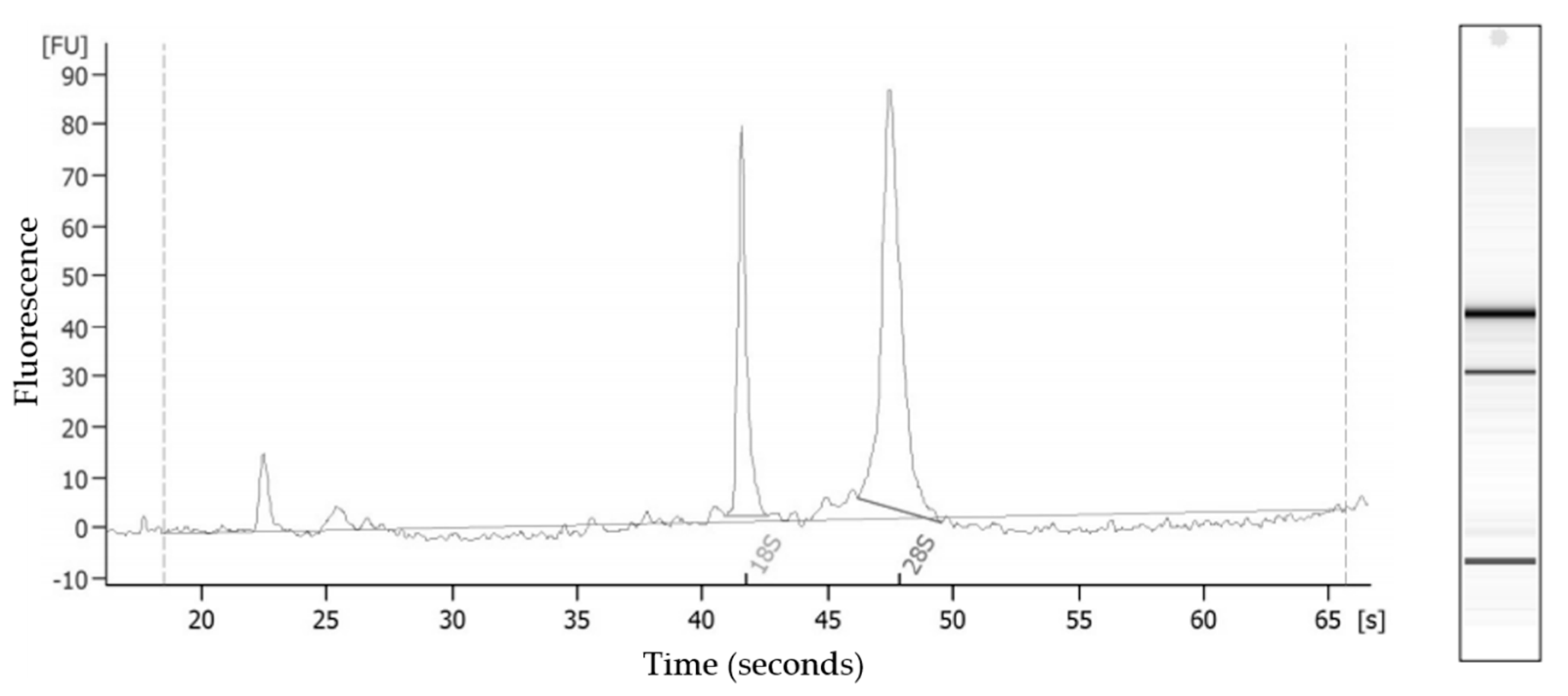
3.3. RNA Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paine, R.T. Food web complexity and species diversity. Am. Nat. 1966, 100, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dare, P.J. Notes on the swarming behaviour and population density of Asterias rubens L. (Echinodermata: Asteroidea) feeding on the mussel, Mytilus edulis. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1982, 40, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saier, B. Direct and indirect effects of seastars Asterias rubens on mussel beds (Mytilus edulis) in the Wadden Sea. J. Sea Res. 2001, 46, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Khadra, Y.; Sugni, M.; Ferrario, C.; Bonasoro, F.; Varela Coelho, A.; Martinez, P.; Candia Carnevali, M.D. An integrated view of asteroid regeneration: Tissues, cells and molecules. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 370, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candia Carnevali, M.D. Regeneration in Echinoderms: Repair, regrowth, cloning. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2006, 3, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie, I.C. Mutable collagenous tissue: Overview and biotechnological perspective. Echinodermata 2005, 39, 221–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammang, P.; Michel, A.; Van Cauwenberge, A.; Alexandre, H.; Jangoux, M. A study of the temporary adhesion of the podia in the sea star Asterias rubens (Echinodermata, Asteroidea) through their footprints. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, M.; Flammang, P.; Aranko, A.S.; Linder, M.B.; Scheibel, T.; Humenik, M.; Leclercq, M.; Surin, M.; Tafforeau, L.; Wattiez, R.; et al. Sea star-inspired recombinant adhesive proteins self-assemble and adsorb on surfaces in aqueous environments to form cytocompatible coatings. Acta Biomater. 2020, 112, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, F.S.; Oguro, C.; Komatsu, M. Sea-star (Asteroid) development. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1993, 31, 223–257. [Google Scholar]
- Vickery, M.C.L.; Vickery, M.S.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D. Utilization of a novel deuterostome model for the study of regeneration genetics: Molecular cloning of genes that are differentially expressed during early stages of larval sea star regeneration. Gene. 2001, 262, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vevers, H.G. The biology of Asterias rubens: Growth and reproduction. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1949, 28, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaymer, C.F.; Himmelman, J.H.; Johnson, L.E. Distribution and feeding ecology of the seastars Leptasterias polaris and Asterias vulgaris in the northern Gulf of St. Lawrence, Canada. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2001, 81, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, S.; Underwood, W.; Anthony, R.; Cartner, S.; Grandin, T.; Greenacre, C.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.; McCrackin, M.A.; Meyer, R.; Miller, D.; et al. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition. Available online: https://www.avma.org/sites/default/files/2020-01/2020-Euthanasia-Final-1-17-20.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Close, B.; Banister, K.; Baumans, V.; Bernoth, E.M.; Bromage, N.; Bunyan, J.; Erhardt, W.; Flecknell, P.; Gregory, N.; Hackbarth, H.; et al. Recommendations for euthanasia of experimental animals: Part 1. Lab. Anim. 1996, 30, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, J.R.; Dombrowski, D.S.; Christian, L.S.; Bayer, M.P.; Harms, C.A.; Lewbart, G.A. Tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222) sedation and anesthesia in the purple-spined sea urchin (Arbacia punctulata). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2016, 47, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewbart, G.A. Euthanasia of Ectotherms. In Fowler’s Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine Current Therapy; Elsevier Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 9, pp. 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.M. Histological studies on the digestive system of a starfish, Henricia, with notes on Tiedemann’s pouches in starfishes. Biol. Bull. 1960, 119, 371–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M. Studies on visceral regeneration in sea stars. III. Regeneration of the cardiac stomach in Asterias forbesi. Biol. Bull. 1965, 129, 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Gonzalez-Bernat, M.; Doo, S.; Foo, S.; Soars, N.; Lamare, M. Effects of ocean warming and acidification on embryos and non-calcifying larvae of the invasive sea star Patiriella regularis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 473, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eernisse, D.J.; Strathmann, M.F.; Strathmann, R.R. Henricia pumila sp. nov.: A brooding seastar (Asteroidea) from the coastal northeastern Pacific. Zootaxa 2010, 36, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurley, R.S.; Kier, W.M. The functional morphology of starfish tube feet: The role of a crossed-fiber helical array in movement. Biol. Bull. 1995, 188, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford, E.; Menge, B.A. Reproductive output and consistency of source populations in the sea star Pisaster ochraceus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 349, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.; Graba-Landry, A.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Byrne, M. Larval phenotypic plasticity in the boom-and-bust crown-of-thorns seastar, Acanthaster planci. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 539, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, E.E.; Fox, R.S.; Barnes, R.D. Echinodermata. In Invertbrate Zoology; Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning: Belmont, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 872–929. [Google Scholar]
- Jangoux, M.; van Impe, E. The annual pyloric cycle of Asterias rubens L. (Echinodermata: Asteroidea). J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 1977, 30, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Plas, A.J.; Koenderman, A.H.L.; Deibel-van Schijndel, G.J.; Voogt, P.A. Effects of oestradiol-17β on the synthesis of RNA, proteins and lipids in the pyloric caeca of the female starfish Asterias rubens. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. 1982, 73, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.A.; Lawrence, J.M. The effect of reproductive state, temperature, and salinity on DNA and RNA levels and activities of metabolic enzymes of the pyloric ceca in the sea star Luidia clathrata (Say). Physiol. Zool. 1990, 63, 1196–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadritdinova, A.F.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Krasnov, G.S.; Astakhova, L.N.; Kudryavtsev, A.A.; Mel’nikova, N.V.; Speranskaya, A.S.; Darii, M.V.; Lakunina, V.A.; et al. A new reference gene, Ef1A, for quantitative real-time PCR assay of the starfish Asterias rubens pyloric ceca. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2013, 452, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, O.; Lightfoot, S.; Schroeder, A. RNA Integrity Number (RIN)—Standardization of RNA quality control. Agil. Appl. Note 2016, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, S. Quantitation comparison of total RNA using the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer, ribogreen analysis and UV spectrometry. Agil. Appl. Note 2002, 1–8. Available online: https://hpst.cz/sites/default/files/oldfiles/quantitation-comparison-total-rna-using-agilent-2100-bioanalyzer-ribogreen-analysis-and-uv.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Mueller, O.; Hahnenberger, K.; Dittmann, M.; Herman, Y.; Dubrow, R.; Nagle, R.; Ilsley, D. A microfluidic system for high-speed reproducible DNA sizing and quantitation. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braly, L.; Brohawn, P.; Higgins, P.; Albright, C.A.; Boland, J.F. Advancing the quality control methodology to assess isolated total RNA and generated fragmented cRNA. Agil. Appl. Note 2003, 1–7. Available online: https://hpst.cz/sites/default/files/oldfiles/advancing-quality-control-methodology-assess-isolated-total-rna-and-generated-fragmented-crna.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Schroeder, A.; Mueller, O.; Stocker, S.; Salowsky, R.; Leiber, M.; Gassmann, M.; Lightfoot, S.; Menzel, W.; Granzow, M.; Ragg, T. The RIN: An RNA integrity number for assigning integrity values to RNA measurements. BMC Mol. Biol. 2006, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dybos, S.A.; Brustad, Å.W.; Rolfseng, T.; Kvam, S.; Olsen, O.E.; Halgunset, J.; Skogseth, H. RNA-Integrity and 8-Isoprostane levels are stable in prostate tissue samples upon long-term storage at −80 °C. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2021, 19, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 4110 Determination of anions by ion chromatography. 2018. Available online: https://www.standardmethods.org/doi/10.2105/SMWW.2882.070 (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- U.S. EPA. Method 6010D (SW-846): Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/esam/epa-method-6010d-sw-846-inductively-coupled-plasma-atomic-emission-spectrometry (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Garcia-Reyero, N.; Barber, D.S.; Gross, T.S.; Johnson, K.G.; Sepúlveda, M.S.; Szabo, N.J.; Denslow, N.D. Dietary exposure of largemouth bass to OCPs changes expression of genes important for reproduction. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pantin, C.F.A. Narcotization. In Notes on Microscopical Technique for Zoologists; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1946; pp. 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Heasman, M.P.; O’Connor, W.A.; Frazer, A.W.J. Induction of anaesthesia in the commercial scallop, Pecten fumatus Reeve. Aquaculture 1995, 131, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culloty, S.C.; Mulcahy, M.F. An evaluation of anaesthetics for Ostrea edulis (L.). Aquaculture 1992, 107, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suquet, M.; De Kermoysan, G.; Araya, R.G.; Queau, I.; Lebrun, L.; Le Souchu, P.; Mingant, C. Anesthesia in Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Aquat. Living Resour. 2009, 22, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butt, D.; O’Connor, S.J.; Kuchel, R.; O’Connor, W.A.; Raftos, D.A. Effects of the muscle relaxant, magnesium chloride, on the Sydney rock oyster (Saccostrea glomerata). Aquaculture 2008, 275, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Salmón, H.; Davis, M. Inducing relaxation in the queen conch Strombus gigas (L.) for cultured pearl production. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, S.; Sadok, S.; Abed, A. El Assessment of magnesium chloride as an anaesthetic for adult sea urchins (Paracentrotus lividus): Incidence on mortality and spawning. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler-Struben, H.M.; Brophy, S.M.; Johnson, N.A.; Crook, R.J. In vivo recording of neural and behavioral correlates of anesthesia induction, reversal, and euthanasia in cephalopod molluscs. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, A.M.; Stoskopf, M.K. Evaluation of euthanasia of moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) using simple salt solutions. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2019, 50, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquer-Sunyer, R.; Duarte, C.M. Threholds for hypoxia for marine biodiversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15452–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theede, H.; Ponat, A.; Hiroki, K.; Schlieper, C. Studies on the resistance of marine bottom invertebrates to oxygen-deficiency and hydrogen sulphide. Mar. Biol. 1969, 2, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B. Nerve, Muscle, Synapse; McGraw-Hill Book Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett, W.J.; Haxby, E.J.; Male, D.A. Magnesium: Physiology and pharmacology. Brit. J. Anaesthesia. 1999, 83, 302–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, T.Y.; You, H.J.; Cho, C.K.; Choi, H.R.; Kim, Y.B.; Shin, Y.S.; Yang, H.S. Effects of magnesium chloride on rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade and sugammadex reversal in an isolated rat phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm preparation: An in-vitro study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 35, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewbart, G.A.; Mosley, C. Clinical Anesthesia and Analgesia in Invertebrates. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2012, 21, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groelz, D.; Sobin, L.; Branton, P.; Compton, C.; Wyrich, R.; Rainen, L. Non-formalin fixative versus formalin-fixed tissue: A comparison of histology and RNA quality. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Balzac, C.A.; García-Arrarás, J.E. Echinoderm Nervous System. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia, Neuroscience; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hyman, L. The Invertebrates: Echinodermata; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Cobb, J.L.S. The nervous systems of Echinodermata: Recent results and new approaches. In The Nervous Systems of Invertebrates: An Evolutionary and Comparative Approach; Breidbach, O., Kutsch, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Volume 72, pp. 407–424. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert, E.E.; Fox, R.S.; Barnes, R.D. Invertebrate Zoology; A Functional Evolutionary Approach; Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning: Belmont, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Leys, S.P. Elements of a “nervous system” in sponges. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mather, J.A.; Dickel, L. Cephalopod complex cognition. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2017, 16, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunkel, C.; Lewbart, G.A. Anesthesia and analgesia of invertebrates. In Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals; Fish, R.E., Brown, M.J., Danneman, P.J., Karas, A.Z., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 535–545. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.R.; Nossov, P.C.; Apland, J.P.; Filbert, M.G. Anesthetic agents for use in the invertebrate sea snail, Aplysia californica. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1996, 35, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, D.; Von Keyserlingk, M.A.G.; Richards, J.G.; Weary, D.M. Conditioned place avoidance of zebrafish (Danio rerio) to three chemicals used for euthanasia and anaesthesia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sykes, A.V.; Baptista, F.D.; Gonçalves, R.A.; Andrade, J.P. Directive 2010/63/EU on animal welfare: A review on the existing scientific knowledge and implications in cephalopod aquaculture research. Rev. Aquac. 2012, 4, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Andrews, P.L.R.; Hawkins, P.; Louhimies, S.; Ponte, G.; Dickel, L. Cephalopod research and EU Directive 2010/63/EU: Requirements, impacts and ethical review. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 447, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, L.U. Pain in aquatic animals. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elwood, R.W. Pain and suffering in invertebrates? ILAR J. 2011, 52, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinkwater, E.; Robinson, E.J.H.; Hart, A.G. Keeping invertebrate research ethical in a landscape of shifting public opinion. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, S.; Llenos, I.C.; Dulay, J.R.; Elashoff, M.; Martínez-Murillo, F.; Miller, C.L. Quality control for microarray analysis of human brain samples: The impact of postmortem factors, RNA characteristics, and histopathology. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2007, 165, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbeaud, S.; Graudens, E.; Boulanger, V.; Barlet, X.; Zaborski, P.; Eveno, E.; Mueller, O.; Schroeder, A.; Auffray, C. Towards standardization of RNA quality assessment using user-independent classifiers of microcapillary electrophoresis traces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, C.; Hammerle-Fickinger, A.; Riedmaier, I.; Pfaffl, M.W. mRNA and microRNA quality control for RT-qPCR analysis. Methods. 2010, 50, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleige, S.; Walf, V.; Huch, S.; Prgomet, C.; Sehm, J.; Pfaffl, M.W. Comparison of relative mRNA quantification models and the impact of RNA integrity in quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, L.; Salinas-Riester, G.; Grade, M.; Jung, K.; Jo, P.; Emons, G.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Gaedcke, J.; Beißbarth, T. Impact of RNA degradation on gene expression profiling. BMC Med. Genom. 2010, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trabzuni, D.; Ryten, M.; Walker, R.; Smith, C.; Imran, S.; Ramasamy, A.; Weale, M.E.; Hardy, J. Quality control parameters on a large dataset of regionally dissected human control brains for whole genome expression studies. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kishimura, H.; Ojima, T.; Hayashi, K.; Nishita, K. cDNA cloning and sequencing of phospholipase A2 from the pyloric ceca of the starfish Asterina pectinifera. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.—B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 126, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agilent Technologies Bioanalyzer System—Troubleshooting Section. Bioanal. User Meet. 2013, 1–36. Available online: https://cpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com/blog.uta.edu/dist/4/4833/files/2020/08/Bioanalyzer_Troubleshooting.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2021).
| ID | Diameter (cm) | Weight (g) | Sex | Time (min) | RIN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14.6 | 77.2 | F | 4 | NP |
| 2 | 10.3 | 43.5 | F | 3 | 7.3 |
| 3 | 13.1 | 55.8 | M | 6 | NP |
| 4 | 11.0 | 39.4 | M | 2 | NP |
| 5 | 15.0 | 65.9 | M | 3 | 9.8 |
| 6 | 15.4 | 74.5 | F | 3 | 9.5 |
| 7 | 15.5 | 71.3 | F | 4 | 9.0 |
| 8 | 14.2 | 50.7 | F | 3 | 9.3 |
| 9 | 14.7 | 64.8 | F | 2 | NP |
| 10 | 13.3 | 53.8 | M | 3 | 8.8 |
| 11 | 13.5 | 66.1 | F | 3 | 8.4 |
| 12 | 16.0 | 64.8 | M | 6 | NP |
| 13 | 14.1 | 55.4 | M | 7 | 9.3 |
| 14 | 15.1 | 71.3 | F | 5 | 8.3 |
| 15 | 12.1 | 41.3 | M | 4 | 6.8 |
| Sample | Cl− (mg/L) | Na+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | Osmolality (mmol/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tank Water | 15,017.0 | 9224.0 | 1496.0 | 381.0 | 466.0 | 809.0 |
| 75 g/L MgCl2 | 18,527.0 | 49.0 | 6557.0 | 165.0 | 23.0 | 802.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wahltinez, S.J.; Kroll, K.J.; Nunamaker, E.A.; Denslow, N.D.; Stacy, N.I. Practical Euthanasia Method for Common Sea Stars (Asterias rubens) That Allows for High-Quality RNA Sampling. Animals 2021, 11, 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11071847
Wahltinez SJ, Kroll KJ, Nunamaker EA, Denslow ND, Stacy NI. Practical Euthanasia Method for Common Sea Stars (Asterias rubens) That Allows for High-Quality RNA Sampling. Animals. 2021; 11(7):1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11071847
Chicago/Turabian StyleWahltinez, Sarah J., Kevin J. Kroll, Elizabeth A. Nunamaker, Nancy D. Denslow, and Nicole I. Stacy. 2021. "Practical Euthanasia Method for Common Sea Stars (Asterias rubens) That Allows for High-Quality RNA Sampling" Animals 11, no. 7: 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11071847
APA StyleWahltinez, S. J., Kroll, K. J., Nunamaker, E. A., Denslow, N. D., & Stacy, N. I. (2021). Practical Euthanasia Method for Common Sea Stars (Asterias rubens) That Allows for High-Quality RNA Sampling. Animals, 11(7), 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11071847






