On Gram-Positive- and Gram-Negative-Bacteria-Associated Canine and Feline Skin Infections: A 4-Year Retrospective Study of the University Veterinary Microbiology Diagnostic Laboratory of Naples, Italy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Informed Consent
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Data Management
2.5. Statistical Analysis
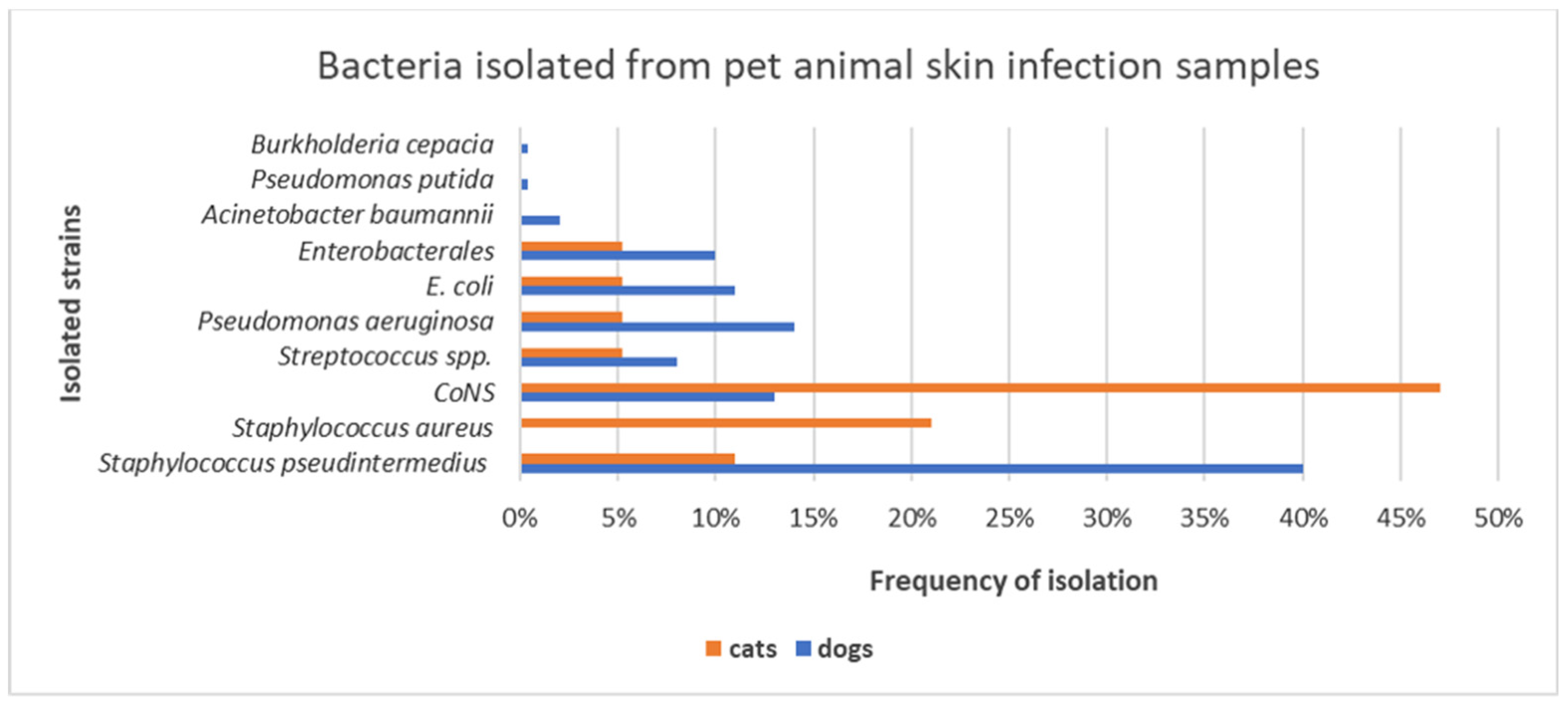
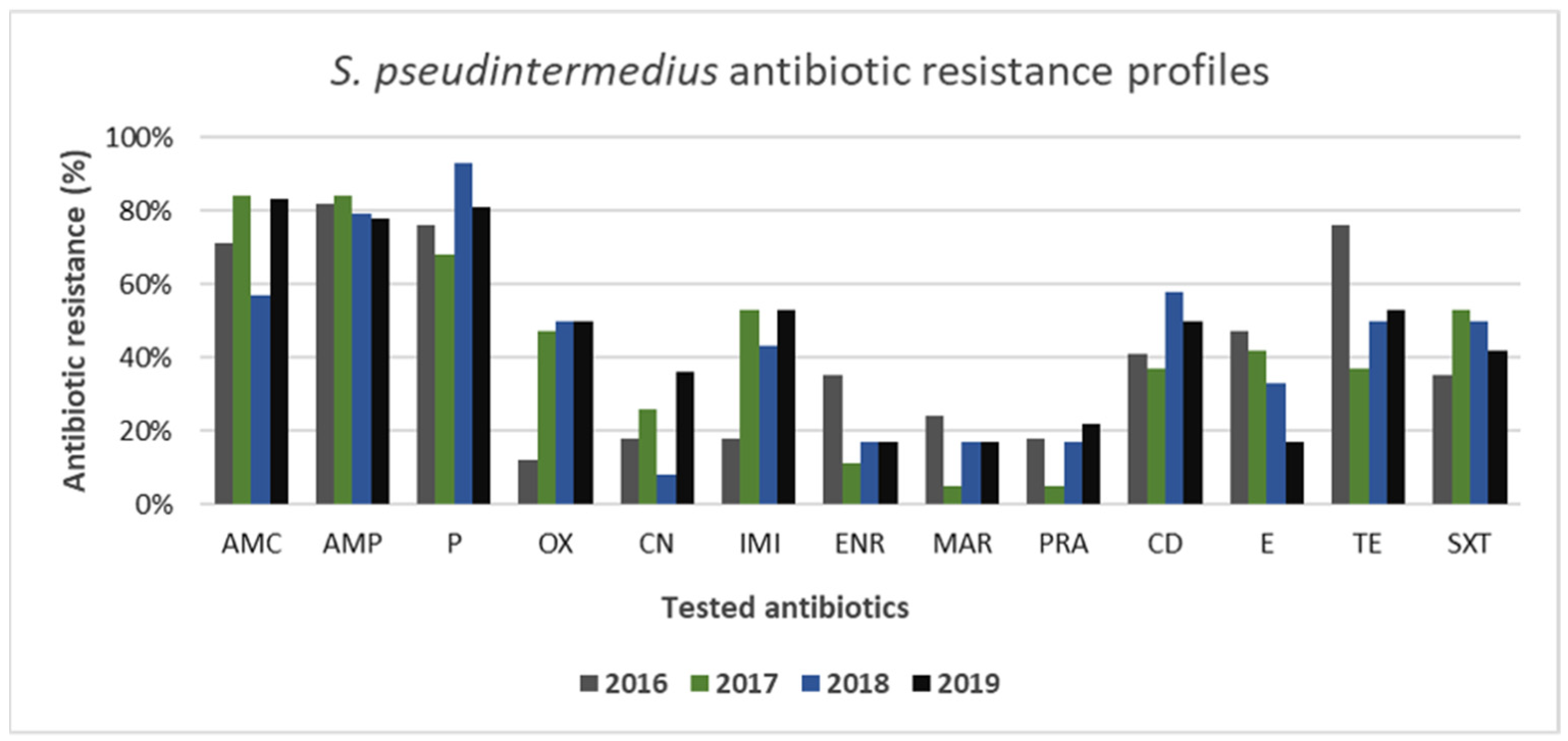
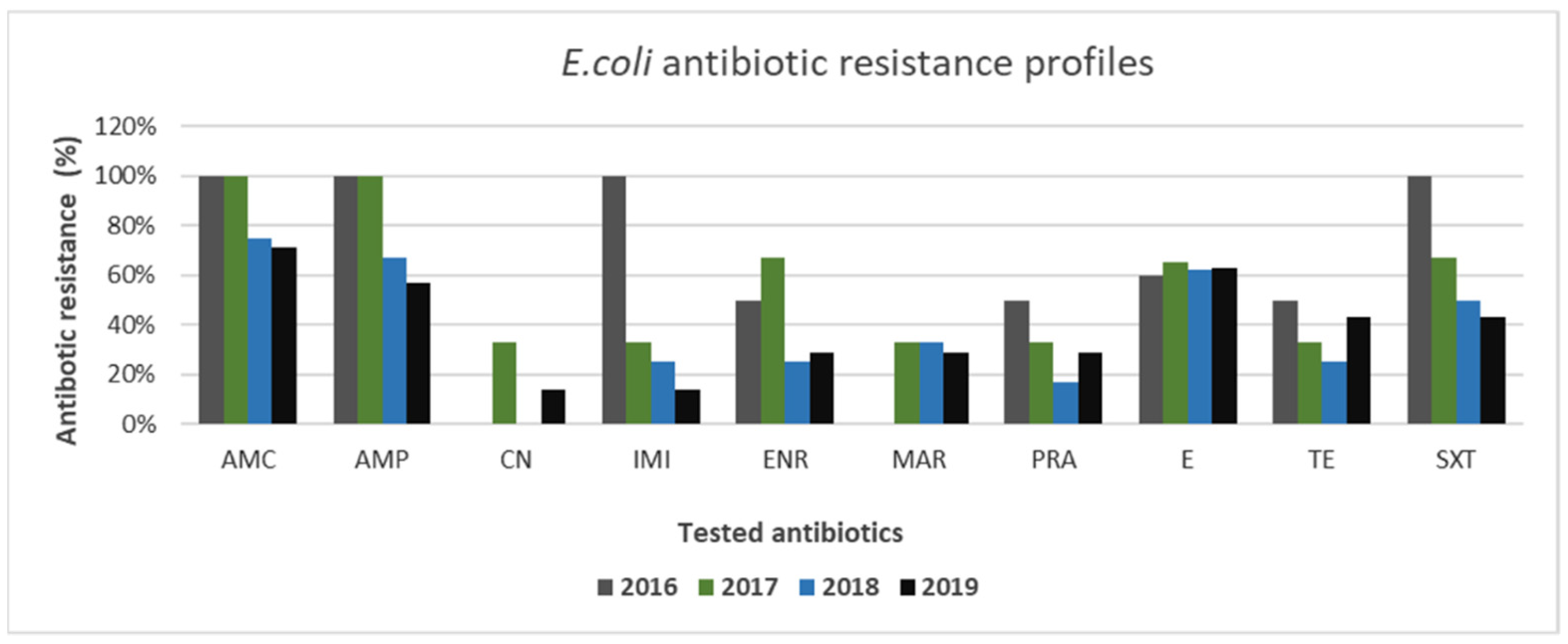
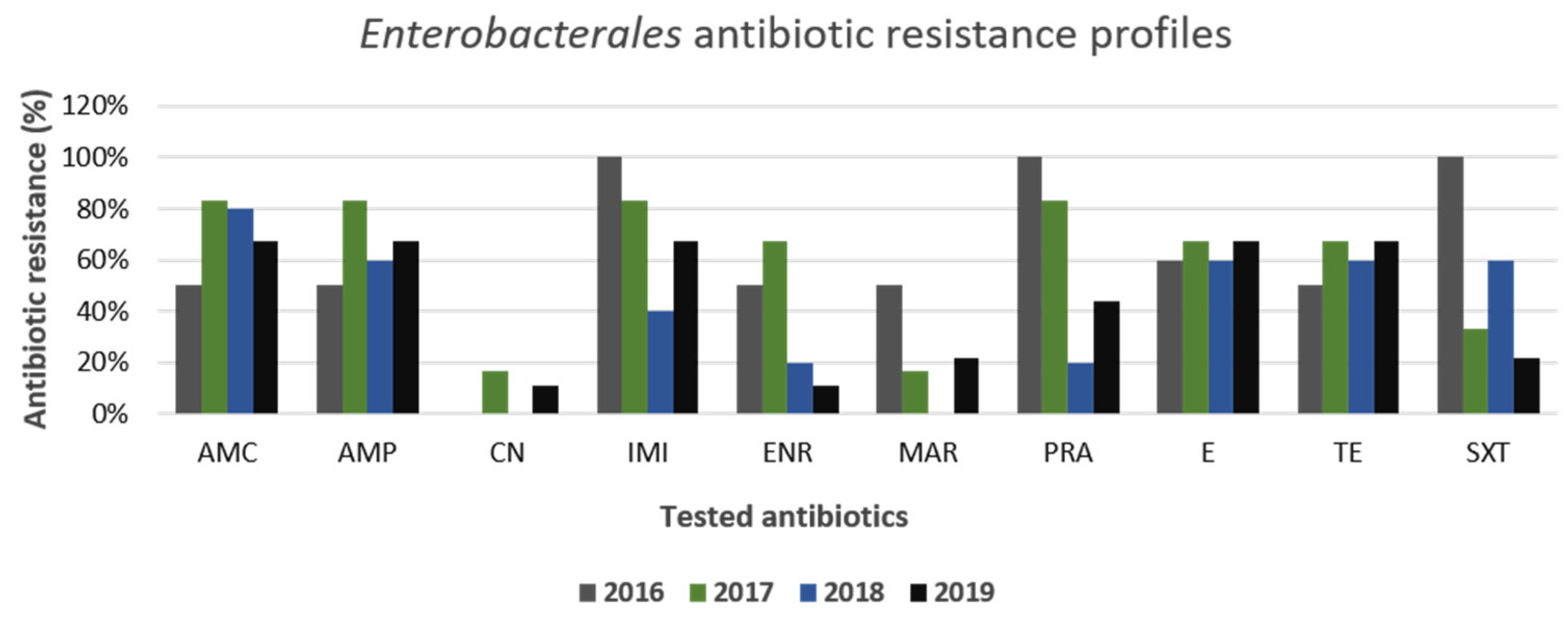
3. Results
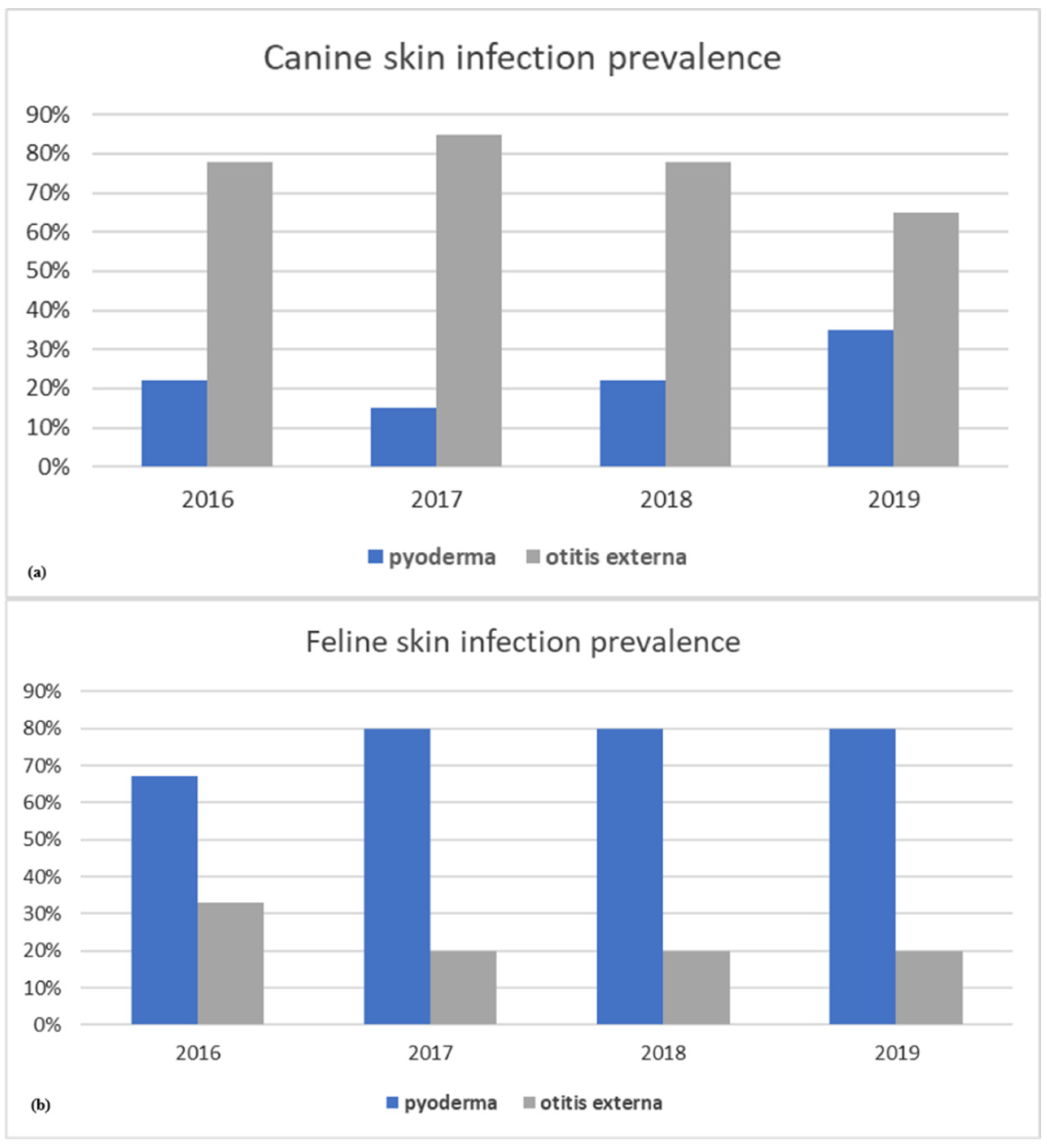
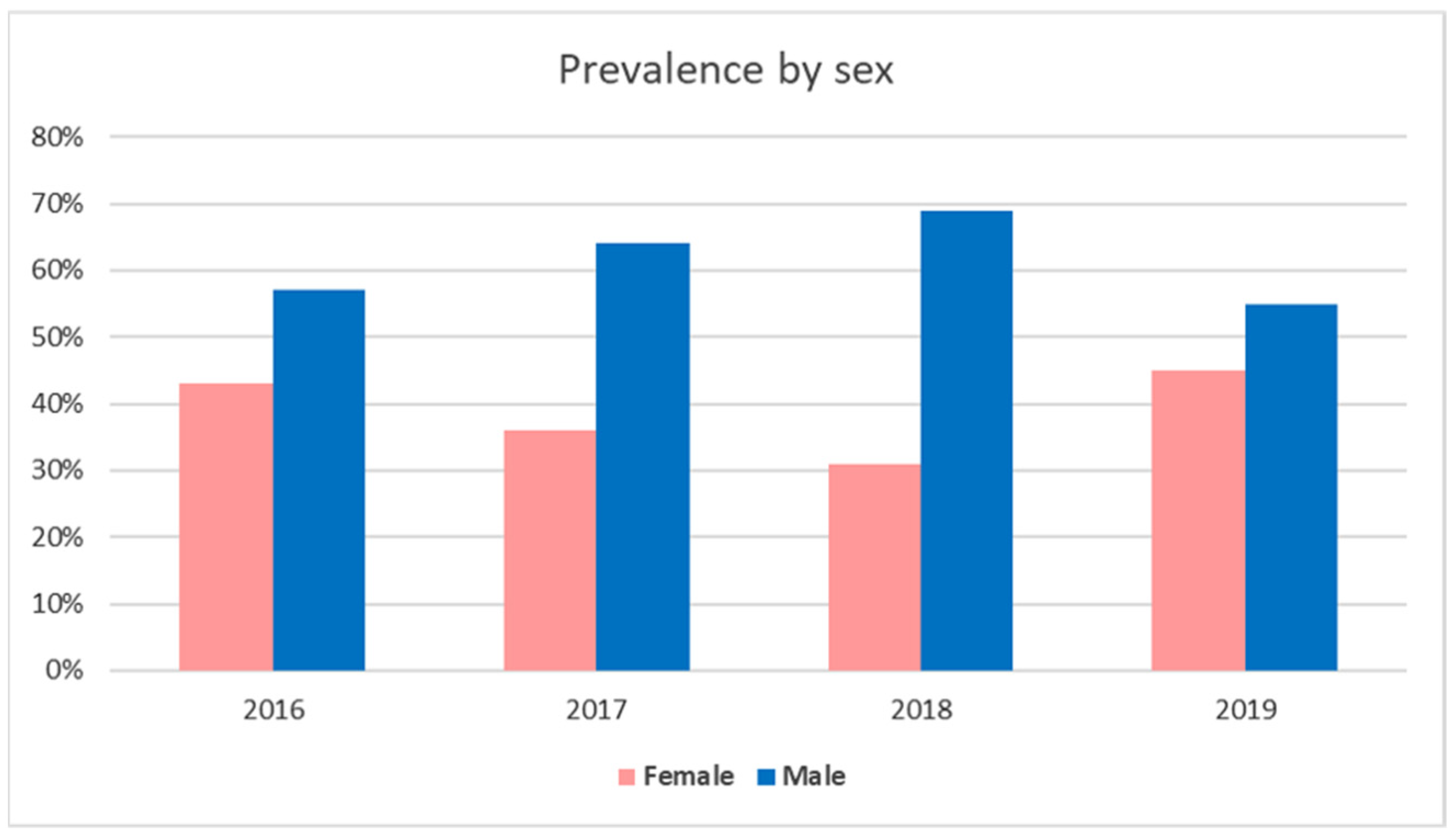
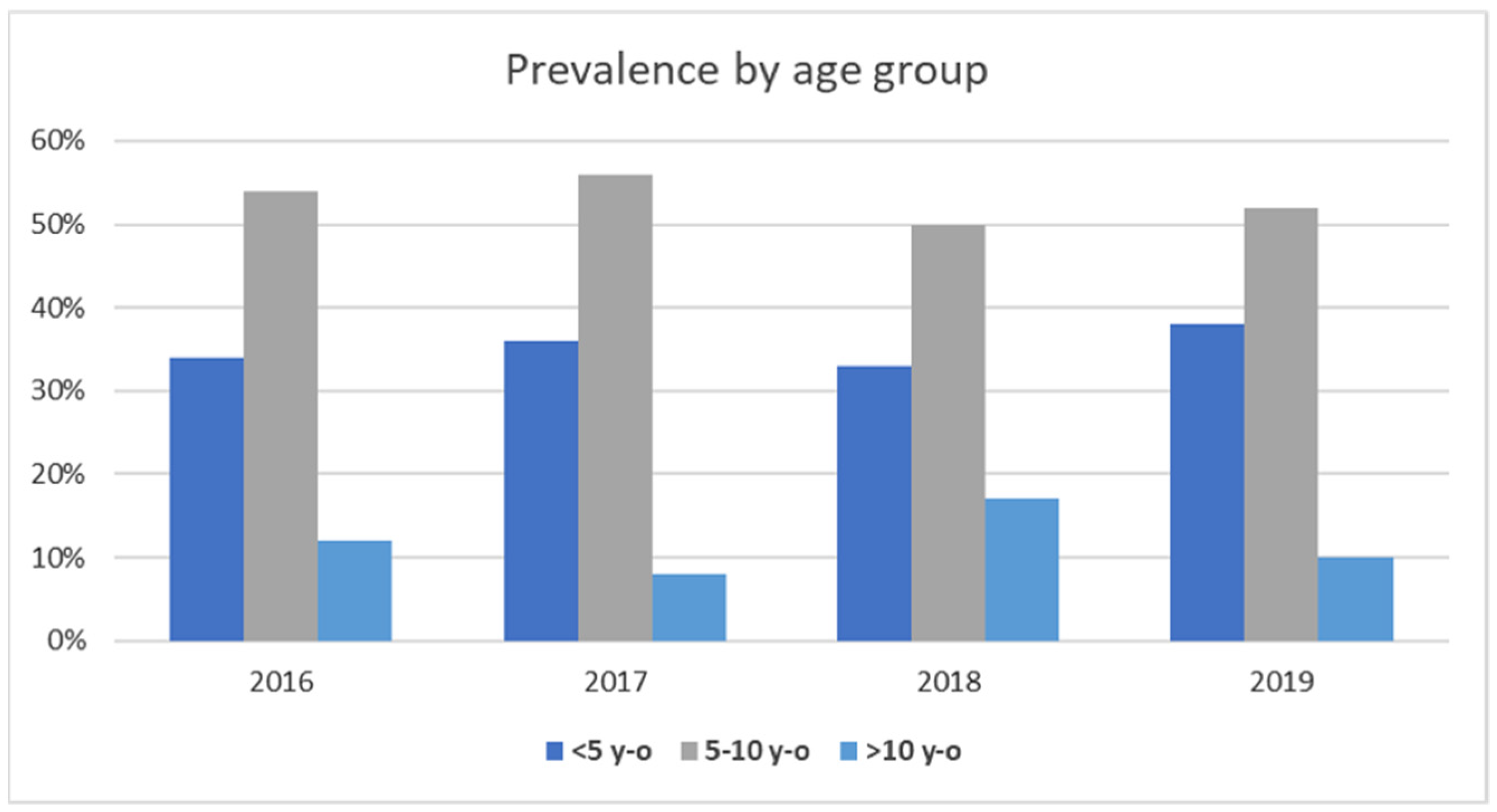
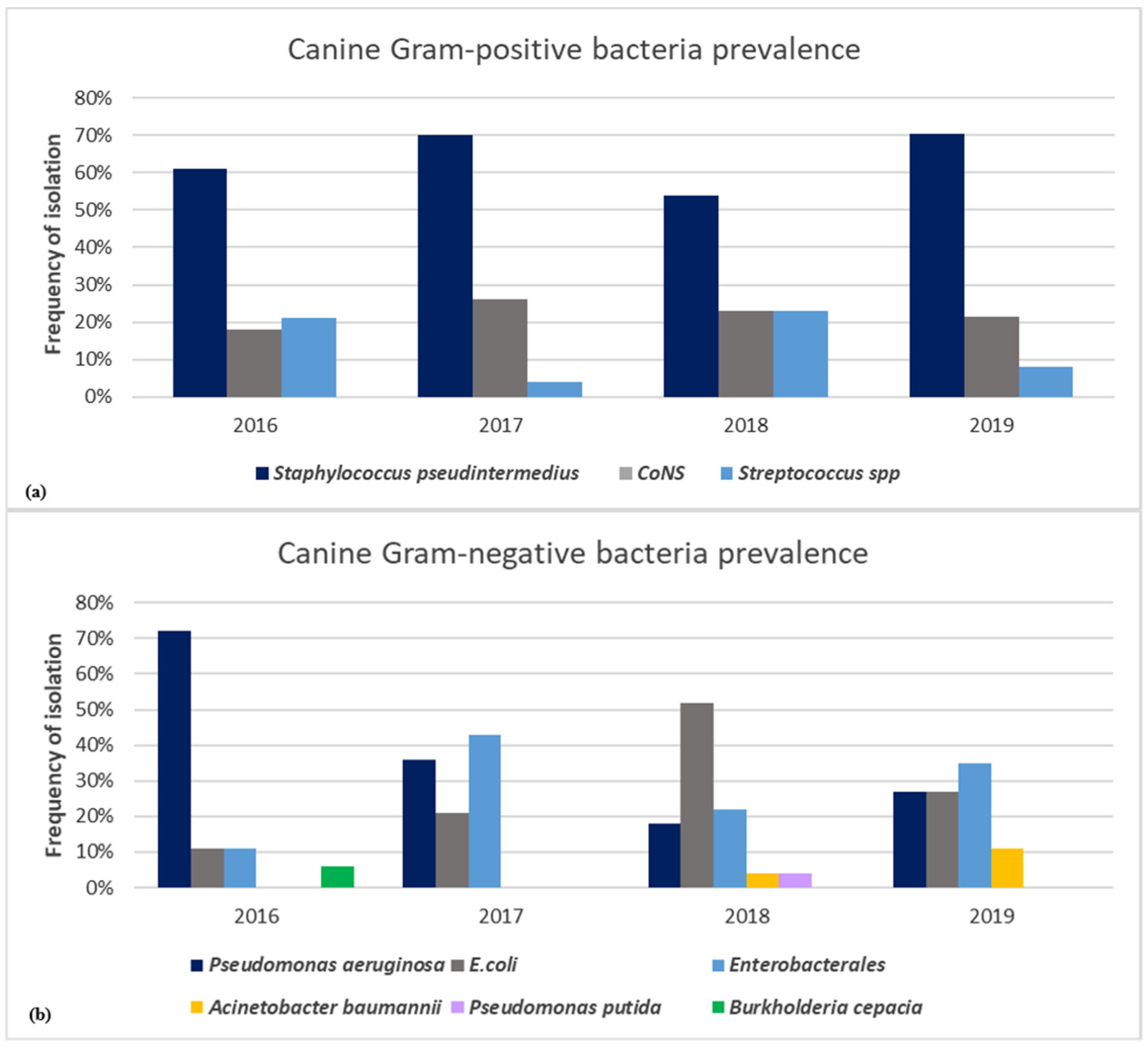
3.1. Gram-Positive- and Gram-Negative-Bacteria-Associated Pet Animal Skin Infections
3.2. Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria Antibiotic Resistance Profiles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marsella, R.; De Benedetto, A. Atopic Dermatitis in Animals and People: An Update and Comparative Review. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsella, R. Advances in our understanding of canine atopic dermatitis. Vet. Dermatol. 2021. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaminami, H.; Okamura, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Wajima, T.; Murayama, N.; Noguchi, N. Prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant staphylococci in nares and affected sites of pet dogs with superficial pyoderma. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, L.; Nocera, F.P.; Mallardo, K.; Nizza, S.; Masturzo, E.; Fiorito, F.; Iovane, G.; Catalanotti, P. An update on microbiological causes of canine otitis externa in Campania Region, Italy. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fernández, R.; Durán, I.; Molina-López, R.A.; Darwich, L. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria isolated from cats and dogs from the Iberian Peninsula. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 621597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.Y.; Hickey, E.E.; Page, S.W.; Trott, D.J.; Hill, P.B. Biofilm production by pathogens associated with canine otitis externa, and the antibiofilm activity of ionophores and antimicrobial adjuvants. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 42, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, R.F.; Boysen, L.; Jessen, L.R.; Guardabassi, L.; Damborg, P. Diversity of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in carriage sites and skin lesions of dogs with superficial bacterial folliculitis: Potential implications for diagnostic testing and therapy. Vet. Dermatol. 2018, 29, 291-e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menandro, M.L.; Dotto, G.; Mondin, A.; Martini, M.; Ceglie, L.; Pasotto, D. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from symptomatic companion animals in Northern Italy: Clonal diversity and novel sequence types. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 66, 101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocera, F.P.; Parisi, A.; Corrente, M.; De Martino, L. Evidence of new sequence types of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Italy. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 23, 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- Rampacci, E.; Bottinelli, M.; Stefanetti, V.; Hyatt, D.R.; Sgariglia, E.; Coletti, M.; Passamonti, F. Antimicrobial susceptibility survey on bacterial agents of canine and feline urinary tract infections: Weight of the empirical treatment. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 13, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, P.; Tsagkaraki, E.; Athanasaki, A.; Tsioutis, C.; Gikas, A. Gram-negative bacteria as emerging pathogens affecting mortality in skin and soft tissue infections. Hippokratia 2018, 22, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, A.; Alcorn, J.R.; Cole, L.K.; Kowalski, J.J. Pyoderma caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in dogs: 20 cases. Vet. Dermatol. 2006, 17, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banovic, F.; Koch, S.; Robson, D.; Jacob, M.; Olivry, T. Deep pyoderma caused by Burkholderia cepacia complex associated with ciclosporin administration in dogs: A case series. Vet. Dermatol. 2015, 26, 287-e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escher, M.; Vanni, M.; Intorre, L.; Caprioli, A.; Tognetti, R.; Scavia, G. Use of antimicrobials in companion animal practice: A retrospective study in a veterinary teaching hospital in Italy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, S.N.; Goggs, R.; Lhermie, G.; Lalonde-Paul, D.F.; Menard, J. Antimicrobial prescribing practices in small animal emergency and critical care. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirollo, C.; Nocera, F.P.; Piantedosi, D.; Fatone, G.; Della Valle, G.; De Martino, L.; Cortese, L. Data on before and after the traceability system of Veterinary antimicrobial prescriptions in small animals at the University Veterinary Teaching Hospital of Naples. Animals 2021, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Beltrán, D.A.; Villar, D.; López-Osorio, S.; Ferguson, D.; Monsalve, L.K.; Chaparro-Gutiérrez, J.J. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in bacterial isolates from dogs and cats in a Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory in Colombia from 2016–2019. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocera, F.P.; Mancini, S.; Najar, B.; Bertelloni, F.; Pistelli, L.; De Filippis, A.; Fiorito, F.; De Martino, L.; Fratini, F. Antimicrobial activity of some essential oils against methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius-associated pyoderma in dogs. Animals 2020, 10, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Reflection Paper on the Risk of Antimicrobial Resistance Transfer from Companion Animals; Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/reflection-paper-risk-antimicrobial-resistance-transfer-companion-animals_en.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2015).
- Damborg, P.; Broens, E.M.; Chomel, B.B.; Guenther, S.; Pasmans, F.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Weese, J.S.; Wieler, L.H.; Windahl, U.; Vanrompay, D.; et al. Bacterial zoonoses transmitted by household pets: State-of-the-art and future perspectives for targeted research and policy actions. J. Comp. Path. 2016, 155, S27–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standard for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 3rd ed.; Clinical Laboratory and Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- EUCAST. The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 7.1. 2017. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, K.H.; Rantala, M.H.; Viita-Aho, T.K.; Vainio, O.M.; Kaartinen, L.A. Condition-based use of antimicrobials in cats in Finland: Results from two surveys. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, L.A.; Williams, N.; Clegg, P.; Callaby, R.; Nuttall, T.; Coyne, K.; Pinchbeck, G.; Dawson, S. Cross-sectional survey of antimicrobial prescribing patterns in UK small animal veterinary practice. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 104, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, A.; Linek, M.; Moodley, A.; Guardabassi, L.; Sung, J.M.; Winkler, M.; Weiss, R.; Lloyd, D.H. First report of multiresistant, mecA-positive Staphylococcus intermedius in Europe: 12 cases from a veterinary dermatology referral clinic in Germany. Vet. Dermatol. 2007, 18, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.W.; Vogelnest, L.J. Feline superficial pyoderma: A retrospective study of 52 cases (2001–2011). Vet. Dermatol. 2012, 23, 448-e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Llyod, H.D.; Howell, S.A.; Noble, W.C. 2002. Investigation into the potential pathogenicity of Staphylococcus felis in a cat. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, P.B.; Lo, A.; Eden, C.A.; Huntley, S.; Morey, V.; Ramsey, S.; Richardson, C.; Smith, D.J.; Sutton, C.; Taylor, M.D.; et al. Survey of the prevalence, diagnosis and treatment of dermatological conditions in small animals in general practice. Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icen, H.; Yesilmen, S. Staphylococcal pyoderma in a cat: A case report. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2008, 7, 1332–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Misic, A.M.; Davis, M.F.; Tyldsley, A.S.; Hodkinson, B.P.; Tolomeo, P.; Hu, B.; Nachamkin, I.; Lautenbach, E.; Morris, D.O.; Griceet, E.A. The shared microbiota of humans and companion animals as evaluated from Staphylococcus carriage sites. Microbiome 2015, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qekwana, D.N.; Oguttu, J.W.; Sithole, F.; Odoi, A. Burden and predictors of S. aureus and S. pseudintermedius infections among dogs presented at an academic veterinary hospital in South Africa (2007–2012). PeerJ 2017, 5, e3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awosile, B.B.; Mcclure, J.T.; Saab, M.E.; Heider, L.C. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria isolated from cats and dogs from the Atlantic Provinces, Canada from 1994–2013. Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 885–893. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffers, J.G. Topical therapy for drug-resistant pyoderma in small animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small. Anim. Pract. 2013, 43, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, R.; Proverbio, D.; Bagnagatti De Giorgi, G.; Della Pepa, A.; Spada, E. Prevalence of otitis externa in stray cats in northern Italy. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2014, 16, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiblu, M.A.; Ellraiss, O.M.; Karim, E.S.; Elmishri, R.A.; Duro, E.M.; Altaeb, A.A.; Bennour, E.M. Otodectic and bacterial etiology of feline otitis externa in Tripoli, Libya. Open Vet. J. 2021, 10, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.D.; Walker, R.D.; Bowman, M.M.; Schott, H.C., 2nd; Rosser, E.J., Jr. Frequency of isolation and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Staphylococcus intermedius and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from canine skin and ear samples over a 6-year period (1992–1997). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2002, 38, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyskova, P.; Vydrzalova, M.; Mazurova, J. Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria and yeasts isolated from healthy dogs and dogs with otitis externa. J. Vet. Med. 2007, 54, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budgen, D.L. Identification and antibiotic susceptibility of bacterial isolates from dogs with otitis externa in Australia. Austr. Vet. J. 2013, 91, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, P. Canine superficial bacterial folliculitis: Current understanding of its etiology, diagnosis and treatment. Vet. J. 2014, 199, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, L.R.; MacLennan, B.; Korven, R.; Rawlings, T.A. Epidemiological study of dogs with otitis externa in Cape Breton, Nova Scotia. Can. Vet. J. 2017, 58, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, A.; Lloyd, D.H. What has changed in canine pyoderma? A narrative review. Vet. J. 2018, 235, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourély, C.; Cazeau, G.; Jarrige, N.; Leblond, A.; Madec, J.Y.; Haenni, M.; Gay, E. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of bacteria isolated from dogs with otitis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocera, F.P.; Meroni, G.; Fiorito, F.; De Martino, L.; Martino, P.A. Occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of canine Staphylococcus pseudintermedius strains isolated from two different Italian university veterinary hospitals. Vet. Ital. 2020, 56, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, J.P.; Anderson, K.L.; Correa, M.T.; Lyman, R.; Ruffin, F.; Reller, L.B.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Transmission of MRSA between companion animals and infected human patients presenting to outpatient medical care facilities. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Sanz, E.; Torres, C.; Lozano, C.; Zarazaga, M. High diversity of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius lineages and toxigenic traits in healthy pet-owning household members. Underestimating normal household contact? Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 36, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, T.P.; Damborg, P.; Moodley, A.; Guardabassi, L. Systematic review on global epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: Inference of population structure from Multilocus sequence typing data. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kolk, J.H.; Endimiani, A.; Graubner, C.; Gerber, V.; Perreten, V. Acinetobacter in veterinary medicine, with an emphasis on Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 16, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocera, F.P.; Addante, L.; Capozzi, L.; Bianco, A.; Fiorito, F.; De Martino, L.; Parisi, A. Detection of a novel clone of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from a dog with otitis externa. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 101471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocera, F.P.; Attili, A.R.; De Martino, L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Its clinical significance in Human and Veterinary Medicine. Pathogens 2021, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafei, R.; Hamze, M.; Pailhoriès, H.; Eveillard, M.; Marsollier, L.; Joly-Guillou, M.-L.; Dabboussi, F.; Kempf, M. Extrahuman epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii in Lebanon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2359–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilini, F.; Turba, M.E.; Pasquali, F.; Mion, D.; Romagnoli, N.; Zambon, E.; Terni, D.; Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D.D.; Parisi, A.; et al. Hospitalized pets as a source of carbapenem-resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenni, M.; de Moraes, N.A.; Châtre, P.; Médaille, C.; Moodley, A.; Madec, J.Y. Characterisation of clinical canine meticillin-resistant and meticillin-susceptible Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in France. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2014, 2, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osland, A.M.; Vestby, L.K.; Fanuelsen, H.; Schau Slettemeås, J.; Sunde, M. Clonal diversity and biofilm-forming ability of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, A.; Damborg, P.; Nielsen, S.S. Antimicrobial resistance in methicillin susceptible and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius of canine origin: Literature review from 1980 to 2013. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanetti, V.; Bietta, A.; Pascucci, L.; Marenzoni, M.L.; Coletti, M.; Franciosini, M.P.; Passamonti, F.; Casagrande Proietti, P. Investigation of the antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius strains isolated from canine pyoderma. Vet. Ital. 2017, 53, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grönthal, T.; Eklund, M.; Thomson, K.; Piiparinen, H.; Sironen, T.; Rantala, M. Antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and the molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant S. pseudintermedius in small animals in Finland. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, N.C.; Moodley, A.; Ghibaudo, G.; Guardabassi, L. Carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in small animal veterinarians: Indirect evidence of zoonotic transmission. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Duijkeren, E.; Kamphuis, M.I.C.; Mije, V.; Laarhoven, L.M.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Houwers, D.J. Staphylococcus pseudintermedius between infected dogs and cats and contact pets, humans and the environment in households and veterinary clinics. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 150, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, H.; Jasni, A.S.; Jamaluddin, T.Z.M.T.; Ibrahim, R. A Review of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome mec (SCCmec) Types in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CoNS) Species. Malays J. Med. Sci. 2017, 24, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Z.; Plésiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekić, S.; Matanović, K.; Šeol, B. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from dogs with otitis externa. Vet. Rec. 2011, 169, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, H.; Coles, M.; Poole, D.; Lund, L.; Page, R. Update on antimicrobial susceptibilities of bacterial isolates from canine and feline otitis externa. Can. Vet. J. 2006, 47, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubin, J.; Walker, R.D.; Blickenstaff, K.; Bodeis-Jones, S.; Zhao, S. Antimicrobial resistance and genetic characterization of fluoroquinolone resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from canine infections. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 131, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, C.; de Jong, A.; Moyaert, H.; El Garch, F.; Janes, R.; Klein, U.; Morrissey, I.; Thiry, J.; Youala, M. Antimicrobial susceptibility monitoring of dermatological bacterial pathogens isolated from diseased dogs and cats across Europe (ComPath results). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, P.M. Antimicrobial therapy of skin and ear infections. Can. Vet. J. 1996, 37, 695–699. [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann, P.; Dortet, L.; Poirel, L. Carbapenem resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: Here is the storm! Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.P.; Woodford, N. Global spread of antibiotic resistance: The example of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM)-mediated carbapenem resistance. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently. 2017. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 18 June 2018).
- Kroemer, S.; El Garch, F.; Galland, D.; Petit, J.L.; Woehrle, F.; Boulouis, H.J. Antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria isolated from infections in cats and dogs throughout Europe (2002–2009). Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 37, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Law 2017 No. 167 of 20 November 2017 on Traceability of Veterinary Medicines and Medicated Feeds for the Achievement of the Objectives Stated in Directives 2001/82/EC and 90/167/EEC; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017.


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nocera, F.P.; Ambrosio, M.; Fiorito, F.; Cortese, L.; De Martino, L. On Gram-Positive- and Gram-Negative-Bacteria-Associated Canine and Feline Skin Infections: A 4-Year Retrospective Study of the University Veterinary Microbiology Diagnostic Laboratory of Naples, Italy. Animals 2021, 11, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061603
Nocera FP, Ambrosio M, Fiorito F, Cortese L, De Martino L. On Gram-Positive- and Gram-Negative-Bacteria-Associated Canine and Feline Skin Infections: A 4-Year Retrospective Study of the University Veterinary Microbiology Diagnostic Laboratory of Naples, Italy. Animals. 2021; 11(6):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061603
Chicago/Turabian StyleNocera, Francesca Paola, Monica Ambrosio, Filomena Fiorito, Laura Cortese, and Luisa De Martino. 2021. "On Gram-Positive- and Gram-Negative-Bacteria-Associated Canine and Feline Skin Infections: A 4-Year Retrospective Study of the University Veterinary Microbiology Diagnostic Laboratory of Naples, Italy" Animals 11, no. 6: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061603
APA StyleNocera, F. P., Ambrosio, M., Fiorito, F., Cortese, L., & De Martino, L. (2021). On Gram-Positive- and Gram-Negative-Bacteria-Associated Canine and Feline Skin Infections: A 4-Year Retrospective Study of the University Veterinary Microbiology Diagnostic Laboratory of Naples, Italy. Animals, 11(6), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061603







