Porcine Milk-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Intestinal Immunoglobulin Production through pIgR
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles Isolation
2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Particle Size and Protein Concentration Analysis
2.3. Animal Experiments and Sample Collection
2.4. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.5. Milk sEVs Treatment in IPEC-J2 Cells
2.6. Bioinformatics Analysis and Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.7. Cell Transfection
2.8. Validation of PM-sEVs circRNAs
2.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.10. Immunofluorescence
2.11. Gene Expression Analysis Using qRT-PCR
2.12. Western Blotting Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
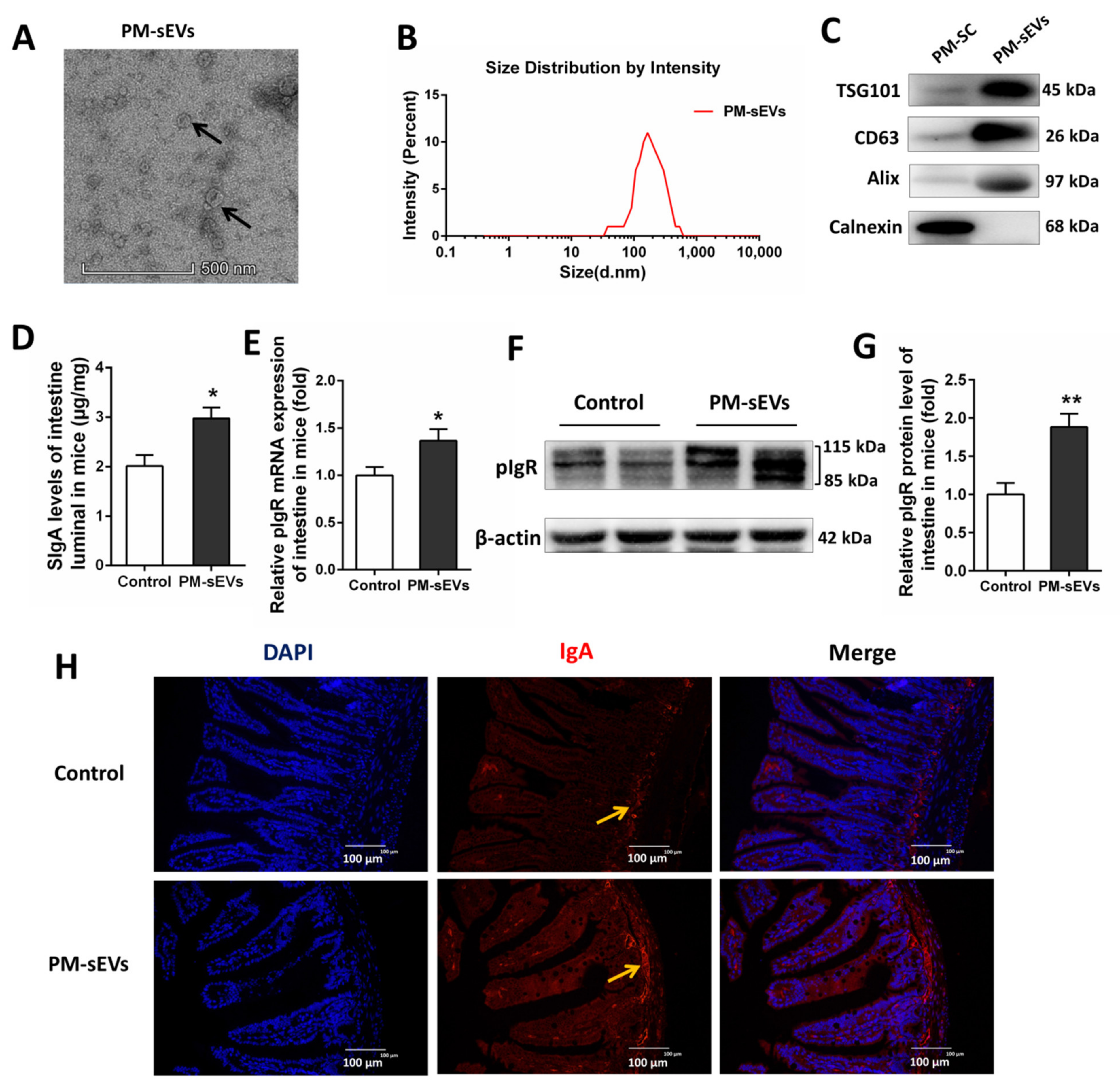
3.1. Identification of PM-sEVs
3.2. PM-sEVs Promote Intestinal Secretory IgA (SIgA) Levels in Mice and Piglet
3.3. PM-sEVs Promote pIgR Levels in IPEC-J2 Cells
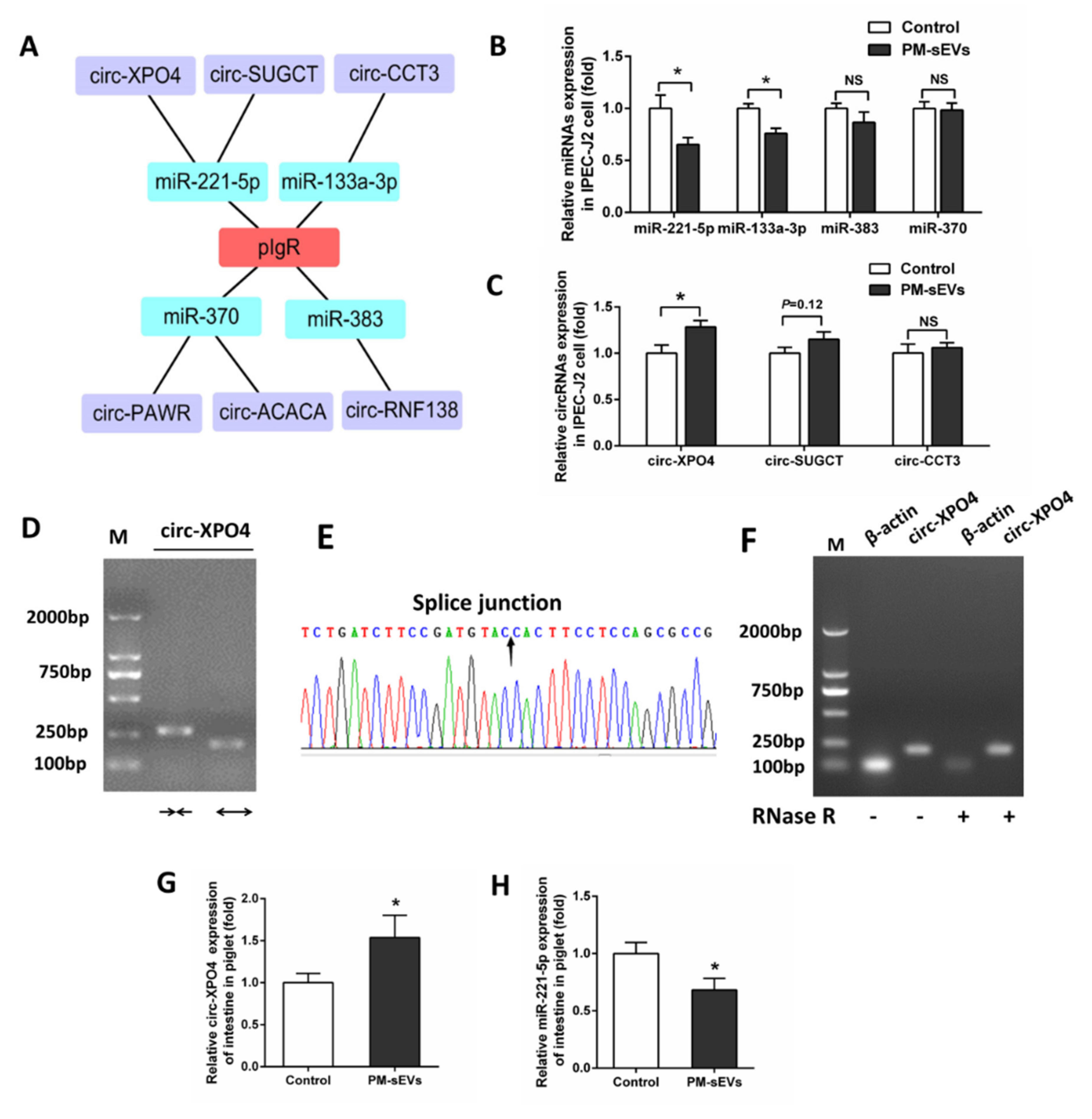
3.4. PM-sEVs Influence Noncoding RNA Expression Levels in IPEC-J2 Cells and Piglet Intestine
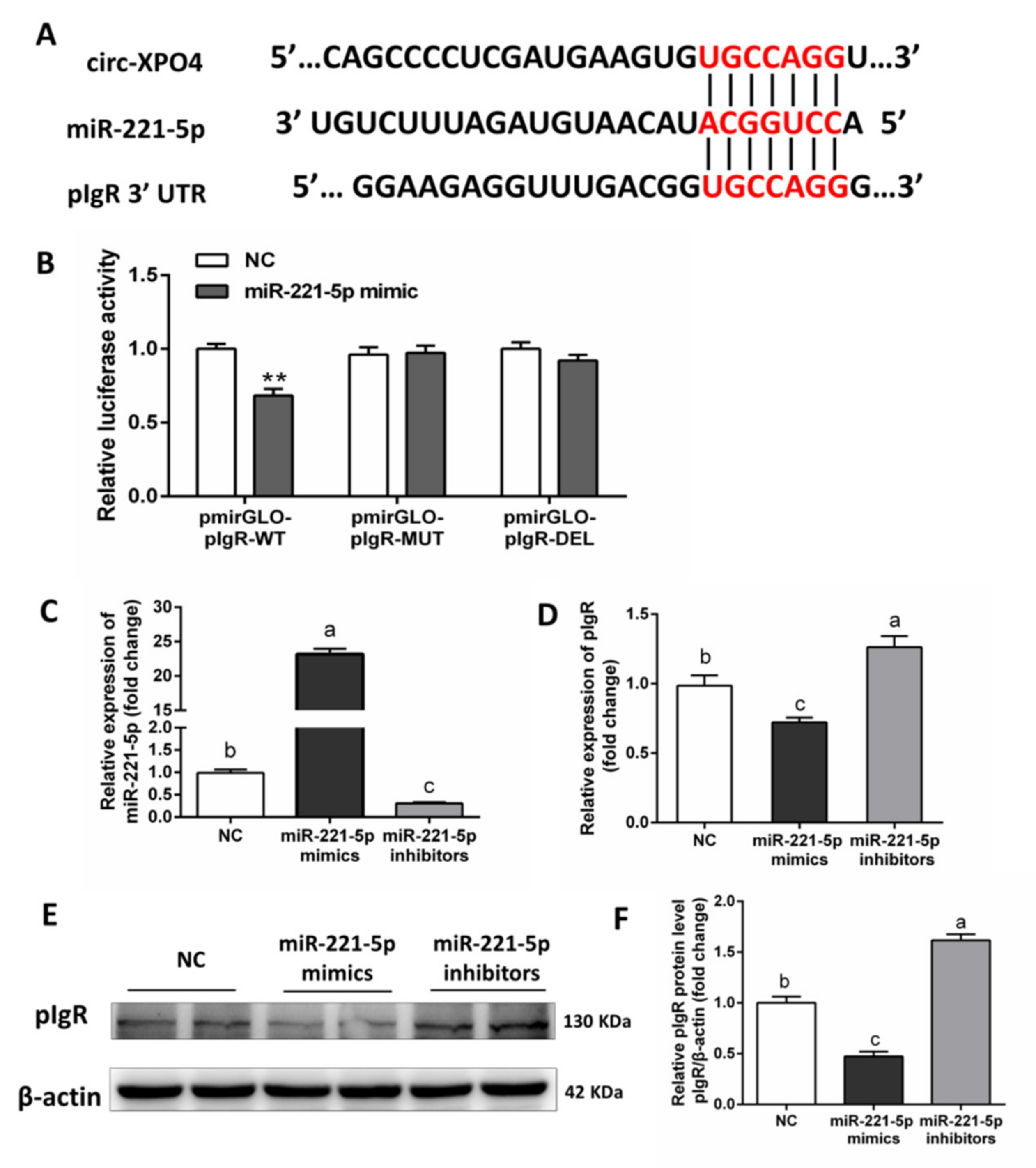
3.5. Validation of pIgR as a Direct Target of miR-221-5p in IPEC-J2 Cells
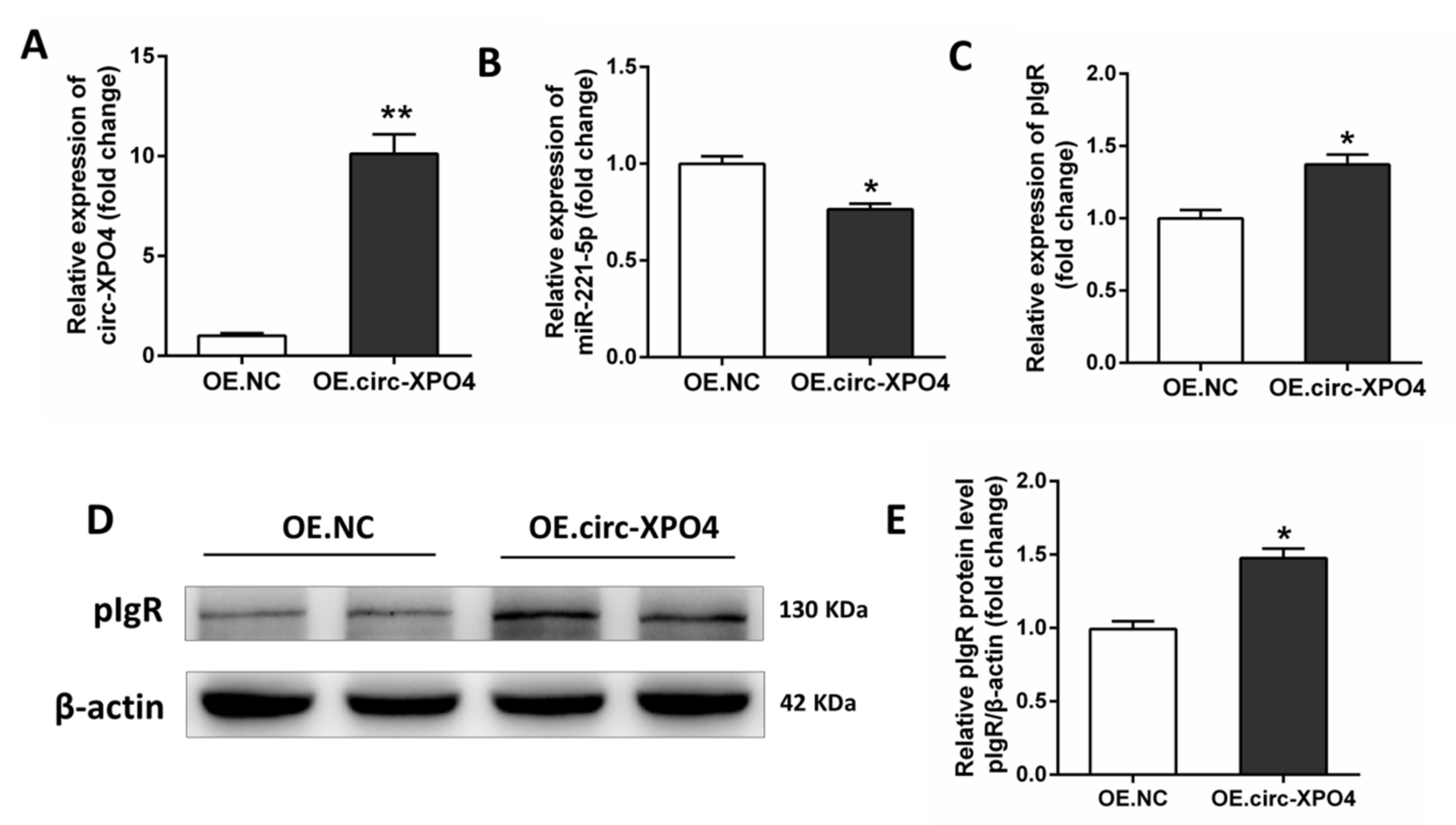
3.6. Circ-XPO4 Regulates pIgR Expression via miR-221-5p in IPEC-J2 Cells
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SIgA | Secretory immunoglobulin A |
| PM-sEVs | Porcine milk small extracellular vesicles |
| PIgR | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor |
| IEC | Intestinal epithelial cell |
| SC | Secretory component |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
References
- Zeng, B.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Luo, J.; Xi, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Dietary Soy Protein Isolate Attenuates Intestinal Immunoglobulin and Mucin Expression in Young Mice Compared with Casein. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O. New concepts in the generation and functions of IgA. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantis, N.J.; Rol, N.; Corthesy, B. Secretory IgA’s complex roles in immunity and mucosal homeostasis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, F.E.; Kaetzel, C.S. Regulation of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor and IgA transport: New advances in environmental factors that stimulate pIgR expression and its role in mucosal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.E.C.; Frantz, A.L.; Rogier, E.W.; Johansen, F.E.; Kaetzel, C.S. Regulation of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor by the classical and alternative NF-kappa B pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Hida, M.; Kohgo, T.; Fukunaga, Y. Changes in salivary and fecal secretory IgA in infants under different feeding regimens. Pediatr. Int. 2009, 51, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Chen, T.; Luo, J.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Xi, Q.-Y.; Jiang, Q.-Y.; Sun, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.-L. Biological Characteristics and Roles of Noncoding RNAs in Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Nutr. 2020, nmaa124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Riopel, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Dong, Y.; Birmingham, A.; Seo, J.B.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Wollam, J.; Hernandez-Carretero, A.; Fu, W.; et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Derived Exosomal miRNAs Can Modulate In Vivo and In Vitro Insulin Sensitivity. Cell 2017, 171, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Du, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Liang, J.; Wang, W.; Lv, Q.; Qin, C.; Chu, H.; Wang, M.; et al. Exosome-transmitted long non-coding RNA PTENP1 suppresses bladder cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, T.; Ge, S.; Liu, Y.; Bai, M.; Zhu, K.; Fan, Q.; Li, J.; Ning, T.; Tian, F.; et al. Exosome circRNA secreted from adipocytes promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting deubiquitination-related USP7. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2844–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Chen, T.; Xie, M.-Y.; Luo, J.-Y.; He, J.-J.; Xi, Q.-Y.; Sun, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.-L. Exploration of long noncoding RNA in bovine milk exosomes and their stability during digestion in vitro. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6726–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, H.; Kosaka, N.; Shimizu, T.; Sekine, K.; Ochiya, T.; Takase, M. Bovine milk contains microRNA and messenger RNA that are stable under degradative conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, P.; Vashisht, M.; Golla, N.; Shandilya, S.; Onteru, S.K.; Singh, D. Milk miRNAs encapsulated in exosomes are stable to human digestion and permeable to intestinal barrier in vitro. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 34, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, A.; Miyake, H.; Li, B.; Lee, C.; Ermini, L.; Koike, Y.; Chen, Y.; Maattanen, P.; Zani, A.; Pierro, A. Breast milk-derived exosomes promote intestinal epithelial cell growth. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Patel, M.; Williams, S.; Arora, H.; Sims, B. Human breast milk-derived exosomes attenuate cell death in intestinal epithelial cells. Innate Immun. 2018, 24, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, D.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Xiao, T.-T. Protective Effects of Human Milk-Derived Exosomes on Intestinal Stem Cells Damaged by Oxidative Stress. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 0963689720912690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Hock, A.; Wu, R.Y.; Minich, A.; Botts, S.R.; Lee, C.; Antounians, L.; Miyake, H.; Koike, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Bovine milk-derived exosomes enhance goblet cell activity and prevent the development of experimental necrotizing enterocolitis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H.; Tsuda, M.; Sato, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Namba, K.; Takeda, Y. Bovine milk exosomes contain microRNA and mRNA and are taken up by human macrophages. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2920–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Du, X.; Li, J.; Lonnerdal, B. Human milk exosomes and their microRNAs survive digestion in vitro and are taken up by human intestinal cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, S.; Upadhyaya, B.; Mutai, E.; Desaulniers, A.T.; Cederberg, R.A.; White, B.R.; Zempleni, J. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Kittana, H.; Shu, J.; Kachman, S.D.; Cui, J.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Zempleni, J. Dietary Depletion of Milk Exosomes and Their MicroRNA Cargos Elicits a Depletion of miR-200a-3p and Elevated Intestinal Inflammation and Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 9 Expression in Mdr1a-/- Mice. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2019, 3, nzz122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xi, Q.-Y.; Ye, R.-S.; Cheng, X.; Qi, Q.-E.; Wang, S.-B.; Shu, G.; Wang, L.-N.; Zhu, X.-T.; Jiang, Q.-Y.; et al. Exploration of microRNAs in porcine milk exosomes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xie, M.-Y.; Sun, J.-J.; Ye, R.-S.; Cheng, X.; Sun, R.-P.; Wei, L.-M.; Li, M.; Lin, D.-L.; Jiang, Q.-Y.; et al. Porcine milk-derived exosomes promote proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-Y.; Hou, L.-J.; Sun, J.-J.; Zeng, B.; Xi, Q.-Y.; Luo, J.-Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.-L. Porcine Milk Exosome MiRNAs Attenuate LPS-Induced Apoptosis through Inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappa B and p53 Pathways in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9477–9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-Y.; Chen, T.; Xi, Q.-Y.; Hou, L.-J.; Luo, J.-Y.; Zeng, B.; Li, M.; Sun, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.-L. Porcine milk exosome miRNAs protect intestinal epithelial cells against deoxynivalenol-induced damage. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 175, 113898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Chen, T.; Luo, J.; Xie, M.; Wei, L.; Xi, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Exploration of Long Non-coding RNAs and Circular RNAs in Porcine Milk Exosomes. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Bai, M.; Ning, T.; Deng, T.; Liu, R.; Fan, Q.; Zhu, K.; Li, J.; et al. Exosome-delivered circRNA promotes glycolysis to induce chemoresistance through the miR-122-PKM2 axis in colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betel, D.; Koppal, A.; Agius, P.; Sander, C.; Leslie, C. Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, J.; Rehmsmeier, M. RNAhybrid: microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W451–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Jose Alcaraz, M.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiferman, A.; Shu, J.; Upadhyaya, B.; Cui, J.; Zempleni, J. Storage of Extracellular Vesicles in Human Milk, and MicroRNA Profiles in Human Milk Exosomes and Infant Formulas. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhang, R.; Qian, T.; Peng, X.; He, W.; Zheng, S.; Cao, Y.; Pierro, A.; Shen, C. A comparison of exosomes derived from different periods breast milk on protecting against intestinal organoid injury. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2019, 35, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, C.; Galley, J.; Elbahrawy, M.; Wang, Y.; Farrell, A.; Brigstock, D.; Besner, G.E. Human Breast Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in the Protection Against Experimental Necrotizing Enterocolitis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2020, 55, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Mohammed-Geba, K.; Tawfic, A.A.; El-Magd, M.A. Camel milk exosomes modulate cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress and immuno-toxicity in rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7523–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Hao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yi, H. Oral Administration of Bovine Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Alters the Gut Microbiota and Enhances Intestinal Immunity in Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1901251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, D.; Dorodnykh, D.; Avdeenko, N.V.; Nekliudov, N.A.; Garssen, J.; Elolimy, A.A.; Petrou, L.; Simpson, M.R.; Yeruva, L.; Munblit, D. Perspective: The Role of Human Breast-Milk Extracellular Vesicles in Child Health and Disease. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 12, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O.; Slack, E. IgA and the intestinal microbiota: The importance of being specific. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Paz, H.A.; Sadri, M.; Cui, J.; Kachman, S.D.; Fernando, S.C.; Zempleni, J. Dietary bovine milk exosomes elicit changes in bacterial communities in C57BL/6 mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G618–G624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pozo-Acebo, L.; Lopez de las Hazas, M.-C.; Margolles, A.; Davalos, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, A. Eating microRNAs: Pharmacological opportunities for cross-kingdom regulation and implications in host gene and gut microbiota modulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2218–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Song, D.; Cao, X.; Wu, R.; Liu, B.; Ye, W.; Wu, J.; Yue, X. Comparative proteomic analysis of milk-derived exosomes in human and bovine colostrum and mature milk samples by iTRAQ-coupled LC-MS/MS. Food Res. Int. 2017, 92, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Xi, Q.-Y.; Sun, J.-J.; Ye, R.-S.; Cheng, X.; Sun, R.-P.; Wang, S.-B.; Shu, G.; Wang, L.-N.; Zhu, X.-T.; et al. Revelation of mRNAs and proteins in porcine milk exosomes by transcriptomic and proteomic analysis. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, B.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Xie, M.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Sun, J.; Xi, Q.; Chen, T.; et al. Porcine Milk-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Intestinal Immunoglobulin Production through pIgR. Animals 2021, 11, 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061522
Zeng B, Wang H, Luo J, Xie M, Zhao Z, Chen X, Wang D, Sun J, Xi Q, Chen T, et al. Porcine Milk-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Intestinal Immunoglobulin Production through pIgR. Animals. 2021; 11(6):1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061522
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Bin, Hailong Wang, Junyi Luo, Meiying Xie, Zhengjiang Zhao, Xingping Chen, Dongyang Wang, Jiajie Sun, Qianyun Xi, Ting Chen, and et al. 2021. "Porcine Milk-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Intestinal Immunoglobulin Production through pIgR" Animals 11, no. 6: 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061522
APA StyleZeng, B., Wang, H., Luo, J., Xie, M., Zhao, Z., Chen, X., Wang, D., Sun, J., Xi, Q., Chen, T., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Porcine Milk-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Intestinal Immunoglobulin Production through pIgR. Animals, 11(6), 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061522






