Effects of Dietary Supplementation of gEGF on the Growth Performance and Immunity of Broilers
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
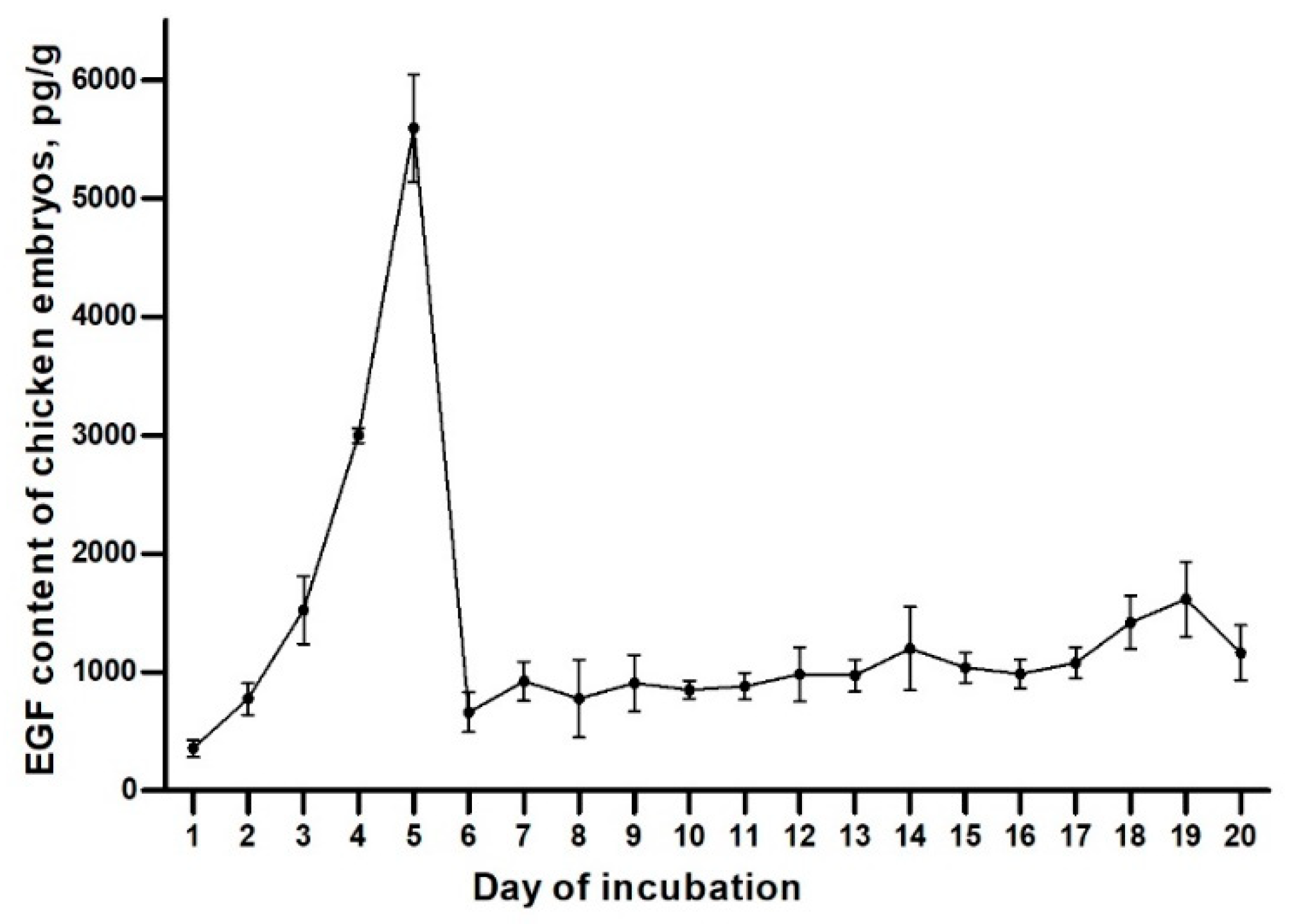
2.1. EGF Content of Chicken Embryos during the Incubation
2.2. Crude Isolation of gEGF
2.3. Effect of Crude Extract of gEGF on the Growth and Development of Broilers
2.3.1. Animals and Experimental Treatments
2.3.2. Body Measurements and Blood Sampling
2.3.3. Serum Biochemical Indices
2.3.4. Antioxidant Capacity
2.3.5. Immune Performance
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. EGF Content of Chicken Embryos during the Incubation
3.2. Growth Performance
3.3. Serum Biochemical Indices
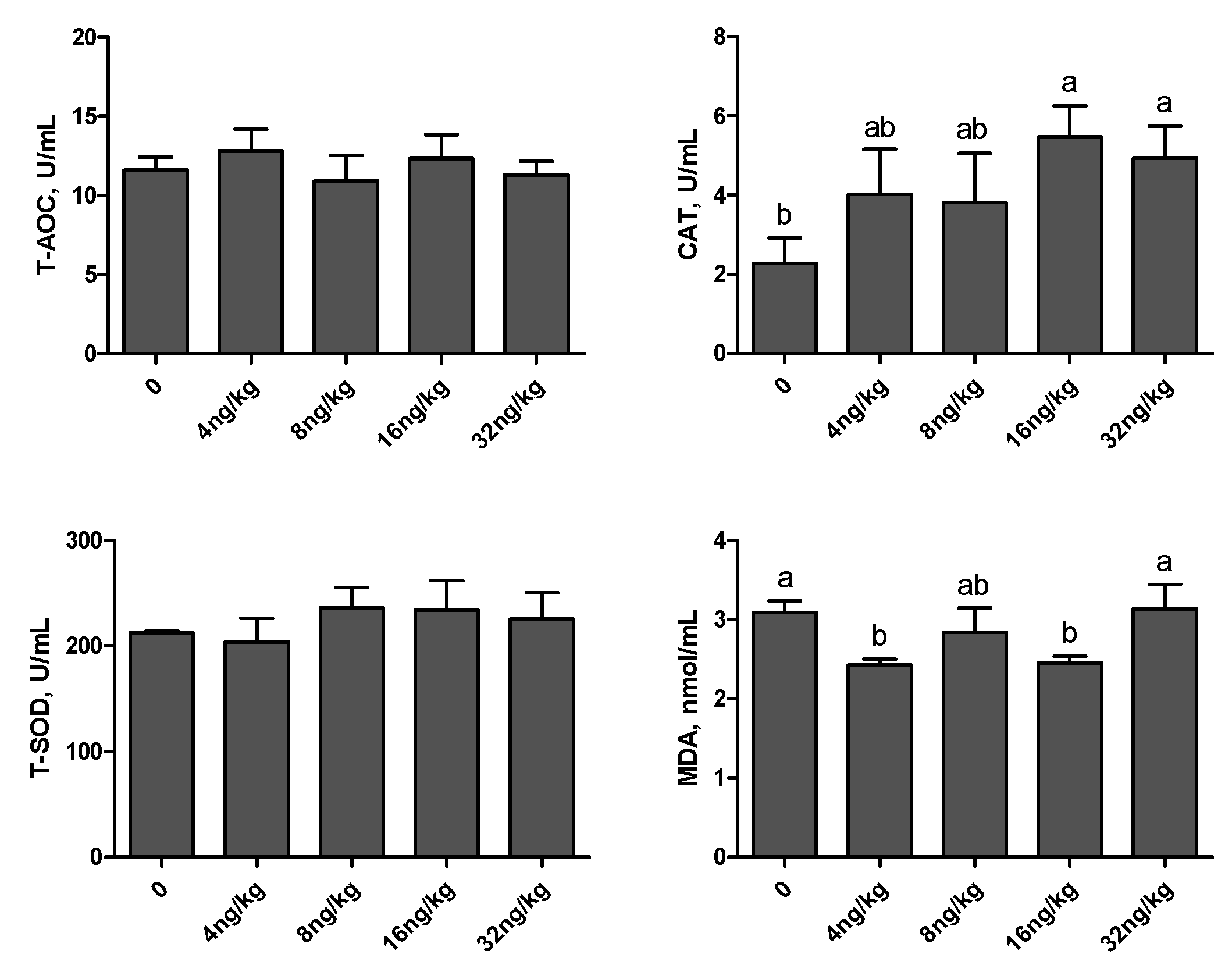
3.4. Antioxidant Capacity Indices
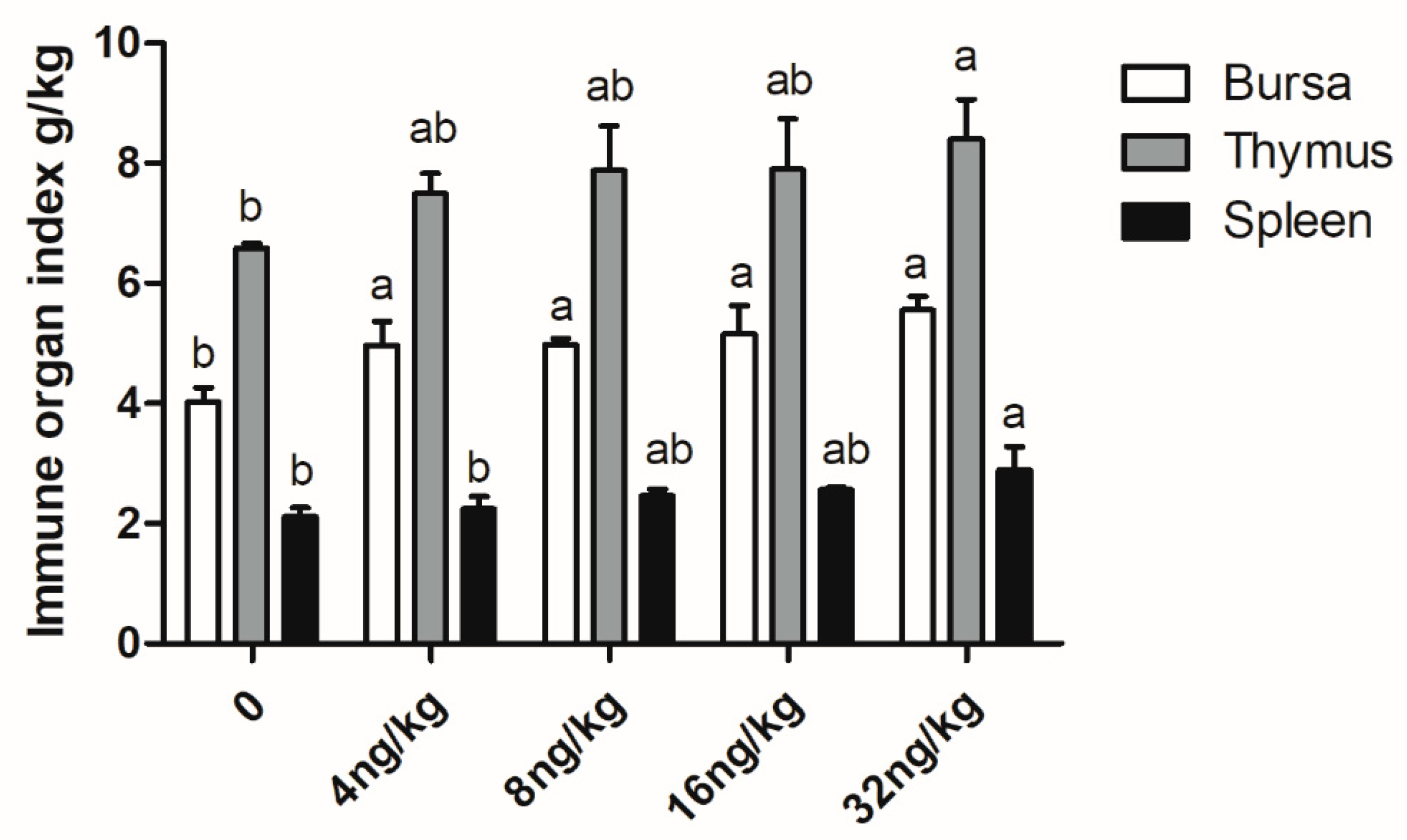
3.5. Immune Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, J.; Nam, K.C.; Shim, K.S.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, A. Comparison of the quality characteristics of chicken breast meat from conventional and animal welfare farms under refrigerated storage. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, A.E.; Abdel-Wareth, A.A.A.; Saleh, A.A.; Amer, S.A. Are the energy matrix values of the different feed additives in broiler chicken diets could be summed? BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAOSTAT. Livestock Poultry Production. 2019. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/ (accessed on 31 March 2021).
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365, eaaw1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, L.A.; Ricci, P.F. Causal regulations vs. political will: Why human zoonotic infections increase despite precautionary bans on animal antibiotics. Environ. Int. 2007, 34, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagrán-de la Mora, Z.; Nuño, K.; Vázquez-Paulino, O.; Avalos, H.; Castro-Rosas, J.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.; Angulo, C.; Ascencio, F.; Villarruel-López, A. Effect of a synbiotic mix on intestinal structural changes, and salmonella typhimurium and clostridium perfringens colonization in broiler chickens. Animals 2019, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Ma, C.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Su, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Feed-additive probiotics accelerate yet antibiotics delay intestinal microbiota maturation in broiler chicken. Microbiome 2017, 5, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrian, A.M.; Smith, M.H.; Rooyen, J.V.; Martínez-López, B.; Plank, M.N.; Smith, W.A.; Conrad, P.A. A community-based One Health education program for disease risk mitigation at the human-animal interface. One Health 2018, 5, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongbo, Y.; Li, W.; Yunxia, X.; Xiaolu, W.; Zhilin, W.; Xuefen, Y.; Kaiguo, G.; Zongyong, J. Effects of lactobacillus reuteri LR1 on the growth performance, intestinal morphology, and intestinal barrier function in weaned pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; She, R.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, K.S.; Luo, D.; Yue, Z.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Effects of pig antibacterial peptides on growth performance and intestine mucosal immune of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlstra, R.T.; Odle, J.; Donovan, S.M. Intestinal effects of milkborne growth factors in neonates of agricultural importance. J. Anim. Sci. 1996, 74, 2509–2509. [Google Scholar]
- Bedford, A.; Huynh, E.; Fu, M.; Zhu, C.; Wey, D.; De Lange, C.; Li, J. Growth performance of early-weaned pigs is enhanced by feeding epidermal growth factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis fermentation product. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.M.; Crenshaw, J.D.; Polo, J. The biological stress of early weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Fouhse, J.M.; Tiwari, U.P.; Li, L.; Willing, B.P. Dietary fiber and intestinal health of monogastric animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, G.; Dong, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Lu, W. Quercetin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal oxidative stress in broiler chickens through activation of Nrf2 pathway. Molecules 2020, 25, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, P.A.; Goodlad, R.A.; Fitzgerald, A.J.; Mandir, N.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Berlanga-Acosta, J.; Playford, R.J.; Forbes, A.; Walters, J.R.F. Intestinal growth in parenterally-fed rats induced by the combined effects of glucagon-like peptide 2 and epidermal growth factor. J. Parenter Enteral. Nutr. 2005, 29, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedford, A.; Chen, T.; Huynh, E.; Zhu, C.; Medeiros, S.; Wey, D.; De Lange, C.; Li, J. Epidermal growth factor containing culture supernatant enhances intestine development of early-weaned pigs in vivo: Potential mechanisms involved. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 196–197, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, F.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Ding, X.; Xiong, X.; Yin, Y. Effects of dietary supplementation with epidermal growth factor on nutrient digestibility, intestinal development and expression of nutrient transporters in early-weaned piglets. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.X.; Zhu, F.; Li, J.Z.; Li, Y.L.; Ding, X.Q.; Yin, J.; Xiong, X.; Yang, H.S. Epidermal growth factor promotes intestinal secretory cell differentiation in weaning piglets via Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Animal 2020, 14, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, P.; Shi, S.; Li, X.; Shi, D.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y. Expression of gallus epidermal growth factor (gEGF) with food-grade lactococcus lactis expression system and its biological effects on broiler chickens. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J. Biol. Chem. 1962, 237, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.R., Jr.; Cohen, S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 7609–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, R.H.; Cohen, S.; Orth, D.N. Epidermal growth factor: Identification of a new hormone in human urine. Science 1975, 189, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, T.T.; Tam, Y.Y.; Kong, Y.C.; Belew, M.C.; Porath, J. Isolation of the epidermal growth factor from the shrew submaxillary gland. FEBS Lett. 1985, 187, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.N.; Kuo, T.Y.; Chen, M.C.; Tang, T.Y.; Liu, F.H.; Weng, C.F. Expression of porcine epidermal growth factor in Pichia pastoris and its biology activity in early-weaned piglets. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Xu, S.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Z.; Che, L.; Xue, B.; Wu, D. Recombinant porcine epidermal growth factor-secreting Lactococcus lactis promotes the growth performance of early-weaned piglets. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dong, X.; Yao, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, C. Separating and Extracting Chicken Embryo EGF for Preparing Animal Intestinal Mucosal Nutrition Repair Agent Comprises e.g. Harvesting Hatching Chicken Embryo, Removing Shell by Adding Acetic Acid Solution, Homogenizing and Centrifuging. CN107252001-A; CN107252001-B, CN107252001-A 17, October 2017, A23K-050/30 201777 Pages: 6 Chinese CN107252001-B 29 November 2019 A23K-050/30 201994 Chinese. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1x3n0c30yk290tp0jt150p208f533215&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 13 May 2021). (In Chinese).
- Huang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Tang, D.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; et al. The chicken gut metagenome and the modulatory effects of plant-derived benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Microbiome 2018, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, W.; Yasugi, S.; Stern, C.D.; Fukuda, K. Fate and plasticity of the endoderm in the early chick embryo. Dev. Biol. 2006, 289, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krischek, C.; Janisch, S.; Naraballobh, W.; Brunner, R.; Wimmers, K.; Wicke, M. Altered incubation temperatures between embryonic Days 7 and 13 influence the weights and the mitochondrial respiratory and enzyme activities in breast and leg muscles of broiler embryos. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2016, 83, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huycke, T.R.; Tabin, C.J. Chick midgut morphogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 62, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xiong, X.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Effects of weaning on intestinal crypt epithelial cells in piglets. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, G.; Mouri, N.; Warburton, D.; Thomas, D.W. EGF regulates early embryonic mouse gut development in chemically defined organ culture. Pediatric Res. 2000, 48, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhong, Z.; Zhu, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gorgels, T.G.M.F.; Berendschot, T.T.J.M. Effects of dietary supplementation with epidermal growth factor-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae on duodenal development in weaned piglets. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L. Analysis of the duodenal microbiotas of weaned piglet fed with epidermal growth factor-expressed Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, P.K.; Bose, M.; Harish, D. Changes in certain haematological parameters in a siluroid cat fish Clarias batrachus (Linn) exposed to cadmium chloride. Pollut. Res. 2002, 21, 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Yao, W.; Li, J.; Shao, Y.; He, Q.; Xia, J.; Huang, F. Dietary garcinol supplementation improves diarrhea and intestinal barrier function associated with its modulation of gut microbiota in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentina, M.; Giacomo, L.; Michele, V.; Grazia, G.; Francesca, P.; Luigi, I. Serum levels of ochratoxin A in dogs with chronic kidney disease (CKD): A retrospective study. J. Vet. Med Sci. 2017, 79, 440–447. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, K.; Yathiraj, S.; Ramachandra, S.G. Serum cystatin-C as a marker for renal dysfunction and its correlation with creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN). J. Commonw. Vet. Assoc. 2011, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyer, H.; Oster, M.; Wittenburg, D.; Murani, E.; Wimmers, K. Genetic contribution to variation in blood calcium, phosphorus, and alkaline phosphatase activity in PigsData_Sheet_1.pdf. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channar, P.A.; Afzal, S.; Ejaz, S.A.; Saeed, A.; Larik, F.A.; Mahesar, P.A.; Lecka, J.; Sévigny, J.; Erben, M.F.; Iqbal, J. Exploration of carboxy pyrazole derivatives: Synthesis, alkaline phosphatase, nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase and nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase inhibition studies with potential anticancer profile. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 156, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, G.; Groenendaal, F. Anti-oxidant strategies. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007, 12, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.H.; Wang, L.; He, H.Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, Y.R. Expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in low osmolar contrast-induced nephropathy in rats and the effect of N-acetylcysteine. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3175–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kang, P.; Zhang, L.; Hou, Y.; Ding, B.; Wu, G. Effects of L-proline on the Growth Performance, and Blood Parameters in Weaned Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged Pigs. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnesr, S.S.; Elwan, H.A.M.; Xu, Q.Q.; Xie, C.; Dong, X.Y.; Zou, X.T. Effects of in ovo injection of sulfur-containing amino acids on heat shock protein 70, corticosterone hormone, antioxidant indices, and lipid profile of newly hatched broiler chicks exposed to heat stress during incubation. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaopeng, T.; Bo, L.; Xiangrong, W.; Qifang, Y.; Rejun, F. Epidermal growth factor, through alleviating oxidative stress, protect IPEC-J2 cells from lipopolysaccharides-induced apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 848. [Google Scholar]
- Berghman, L.R. Immune responses to improving welfare. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2216–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.K.; Rao, S.S.R.; Raju, M.V.; Sharma, S.S. Effect of probiotic (Lactobacillus sporogenes) feeding on egg production and quality, yolk cholesterol and humoral immune response of White Leghorn layer breeders. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 88, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.A. Canine IgA and IgA deficiency: Implications for immunization against respiratory pathogens. Can. Vet. J. La Rev. Vet. Can. 2019, 60, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Hennicke, J.; Schwaigerlehner, L.; Grünwald-Gruber, C.; Bally, I.; Ling, W.L.; Thielens, N.; Reiser, J.B.; Kunert, R. Transient pentameric IgM fulfill biological function-Effect of expression host and transfection on IgM properties. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shujin, W.; Chunhua, G.; Lin, Z.; Zhengfan, Z.; Yanling, H.; Jiabao, Y.; Xue, B.; Kuanmin, Y. Comparison of the biological activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiae-expressed intracellular EGF, extracellular EGF, and tagged EGF in early-weaned pigs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7125–7135. [Google Scholar]
- Suszko, A.; Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B. Influence of polysaccharide fractions isolated from Caltha palustris L. on the cellular immune response in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice. A comparison with methotrexate. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, C.E.; Demaries, S.L.; Iacampo, S.; Ratcliffe, M.J. Development of B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin molecules that lack V(D)J-encoded determinants in the avian embryo bursa of fabricius. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10806–10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredients | Content (%) | Nutrition Level 2 | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 62.35 | Metabolizable energy, MJ/kg | 11.68 |
| Soybean meal | 24.00 | Crude protein, % | 18.90 |
| Wheat middlings | 4.00 | Lysine, % | 0.93 |
| Cottonseed meal | 4.00 | Methionine, % | 0.43 |
| Fish meal | 2.00 | Threonine, % | 0.71 |
| Premix 1 | 1.00 | Arginine, % | 1.25 |
| CaCO3 | 1.20 | Total phosphorus, % | 0.65 |
| CaHPO4 | 1.10 | Calcium, % | 0.74 |
| NaCl | 0.35 | ||
| Total | 100.00 |
| Item | Control | gEGF Crude Extract (ng/kg) | p-Value | SEM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | ||||
| ADG, g | 7.44 b | 7.83 a | 7.65 a,b | 7.78 a | 7.53 a,b | 0.012 | 0.10 |
| ADFI, g | 16.4 b | 17.4 a | 17.1 a,b | 17.3 a | 16.7 a,b | 0.019 | 0.29 |
| F/g | 2.20 | 2.22 | 2.23 | 2.23 | 2.21 | 0.96 | 0.05 |
| Item | Control | gEGF Crude Extract (ng/kg) | p-Value | SEM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | ||||
| TP, g/L | 37.4 | 38.2 | 36.3 | 39.6 | 37.6 | 0.39 | 1.57 |
| ALB, g/L | 17.4 | 18.7 | 17.6 | 19.3 | 17.4 | 0.13 | 0.80 |
| UA, mmol/L | 1.36 a | 1.11 b | 1.14 b | 0.96 b | 1.14 b | 0.001 | 10.67 |
| BUN, mmol/L | 2.24 | 1.82 | 1.90 | 1.79 | 1.90 | 0.11 | 0.16 |
| Ca, mmol/L | 2.07 | 2.38 | 2.25 | 2.2 | 2.36 | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| P, mmol/L | 0.49 | 0.56 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.23 | 0.03 |
| AKP, U/L | 0.87 c | 1.38 b,c | 1.72 b | 2.76 a | 1.52 b,c | <0.001 | 2.48 |
| GOT, U/L | 36.7 a | 21.9 b | 20.3 b | 21.6 b | 34.1 a | <0.001 | 2.39 |
| GPT, U/L | 2.21 | 1.93 | 1.93 | 1.90 | 1.88 | 0.48 | 0.29 |
| Item | Control | gEGF Crude Extract (ng/kg) | p-Value | SEM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | ||||
| IgA, μg/mL | 244 b | 314 a,b | 318 a | 342 a | 311 a,b | 0.011 | 21.26 |
| IgG, μg/mL | 677 | 711 | 765 | 752 | 738 | 0.66 | 63.26 |
| IgM, μg/mL | 1788 b | 2118 a | 2122 a | 2104 a,b | 2034 a,b | 0.028 | 96.81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Yao, J.; Bai, L.; Sun, C.; Lu, J. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of gEGF on the Growth Performance and Immunity of Broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11051394
Zhou J, Yao J, Bai L, Sun C, Lu J. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of gEGF on the Growth Performance and Immunity of Broilers. Animals. 2021; 11(5):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11051394
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jianyong, Jingyi Yao, Luhong Bai, Chuansong Sun, and Jianjun Lu. 2021. "Effects of Dietary Supplementation of gEGF on the Growth Performance and Immunity of Broilers" Animals 11, no. 5: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11051394
APA StyleZhou, J., Yao, J., Bai, L., Sun, C., & Lu, J. (2021). Effects of Dietary Supplementation of gEGF on the Growth Performance and Immunity of Broilers. Animals, 11(5), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11051394






