Random Regression Model for Genetic Evaluation and Early Selection in the Iranian Holstein Population
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Model
2.3. Prediction of Breeding Values
2.4. Estimation of Genetic Parameters
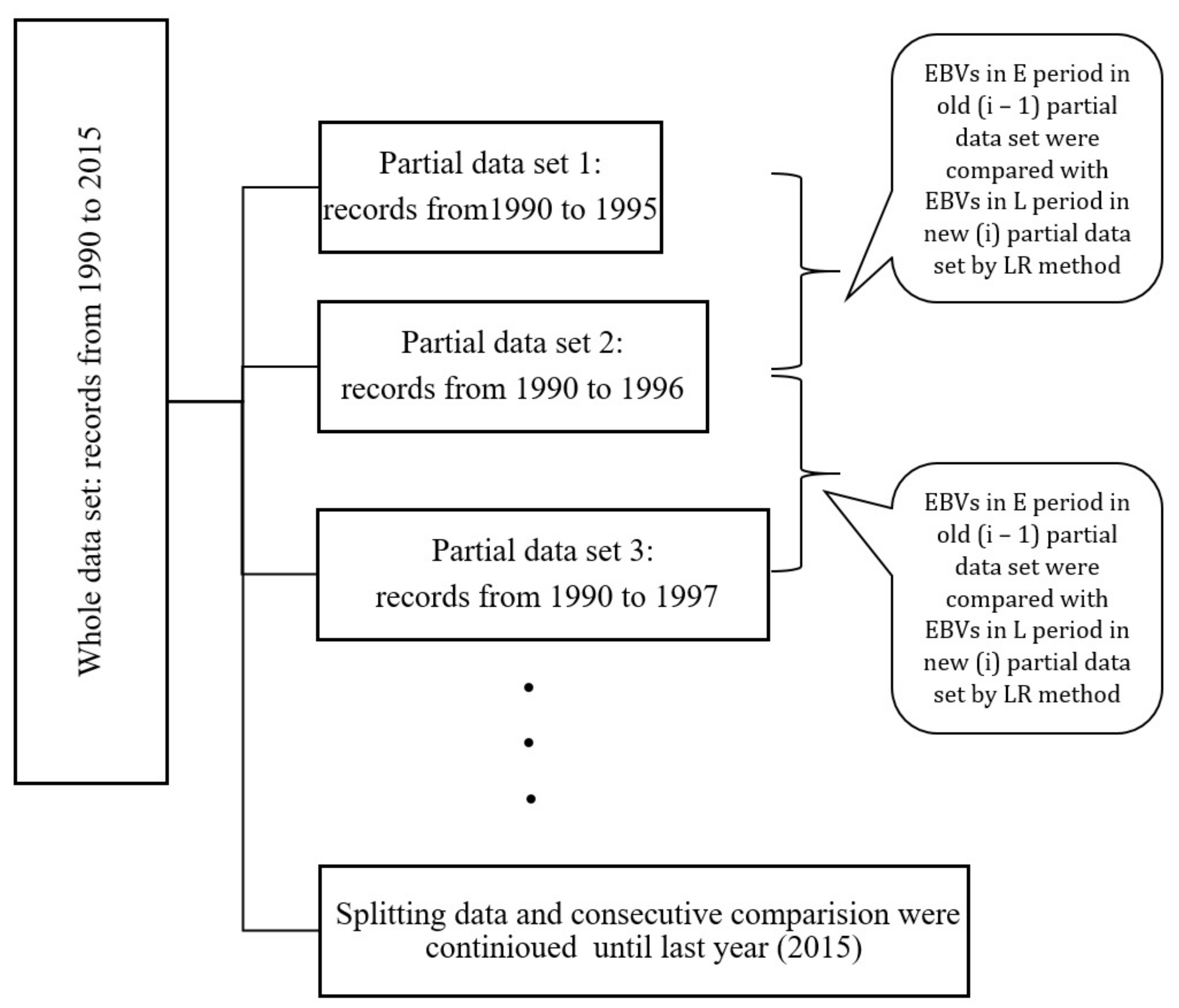
2.5. Cross-Validation
3. Results
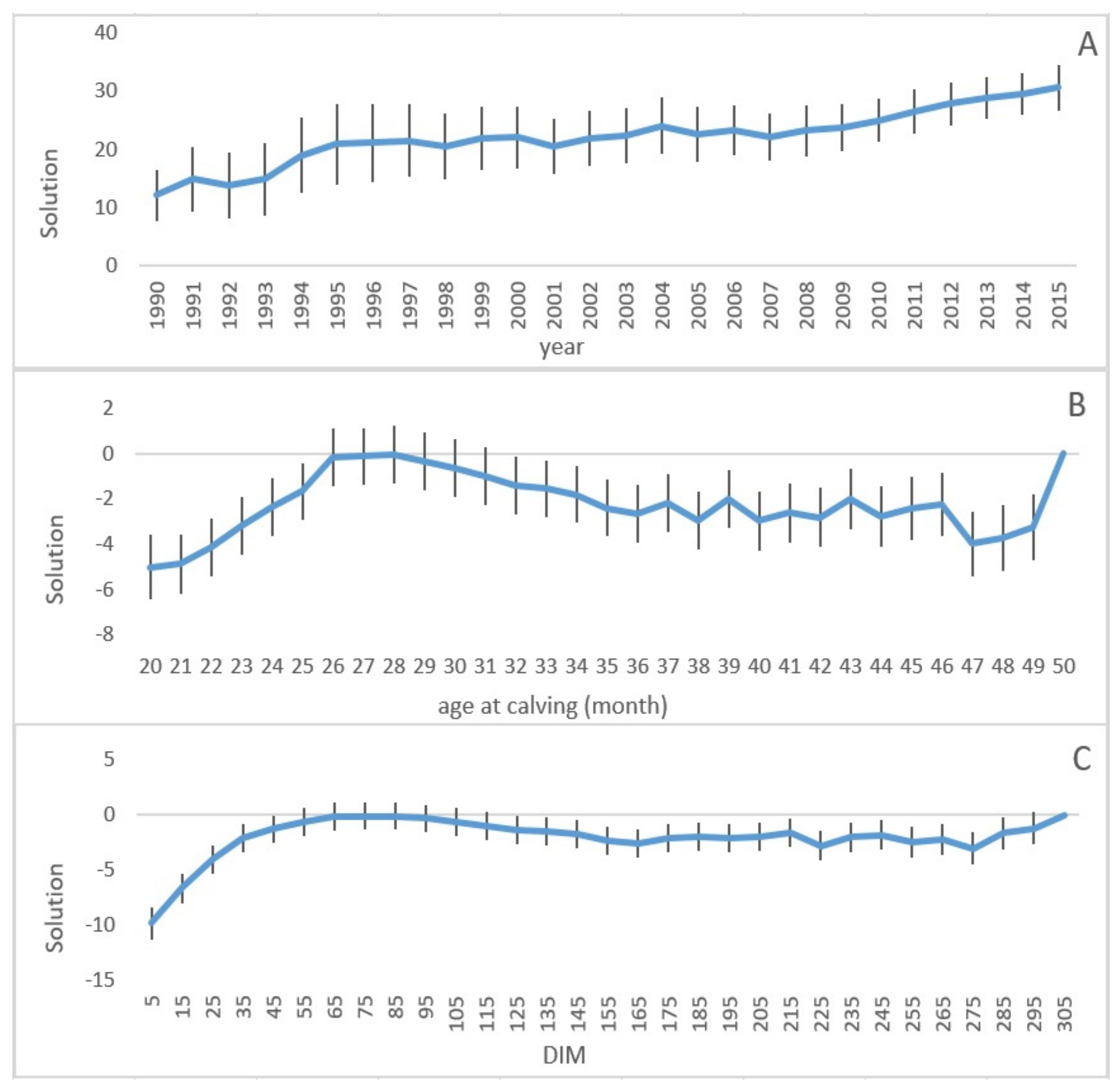
3.1. Fixed Effects
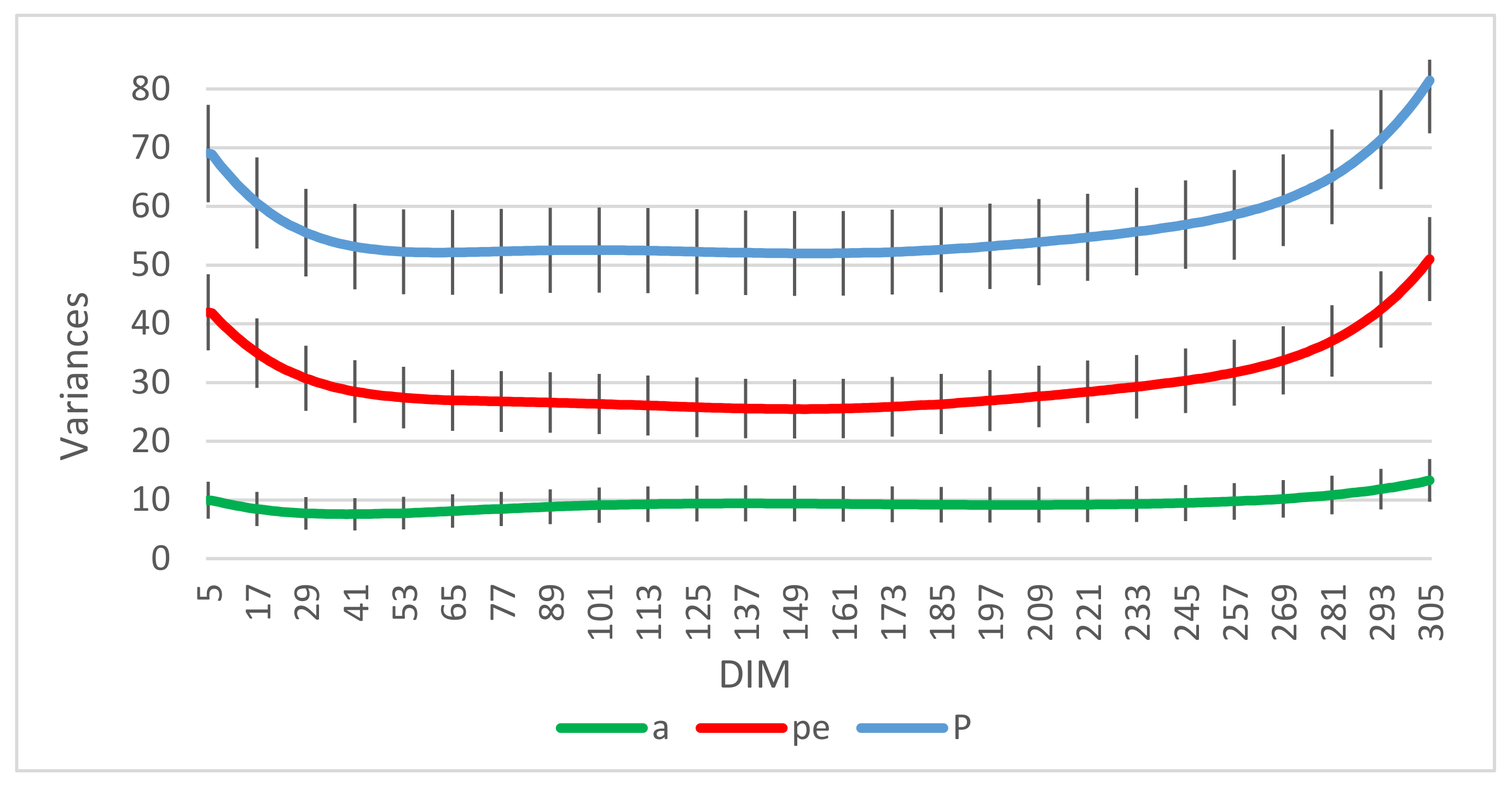
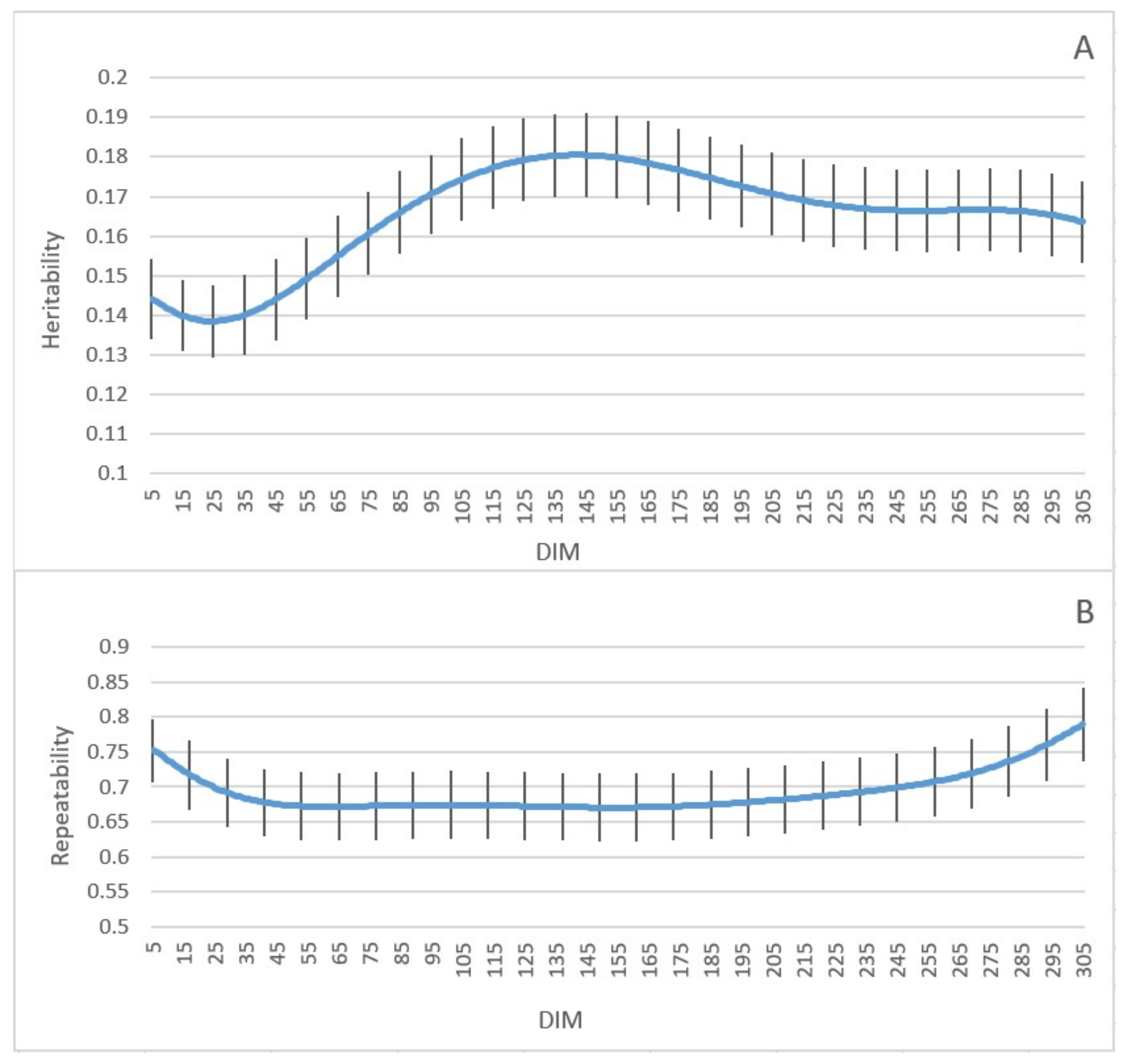
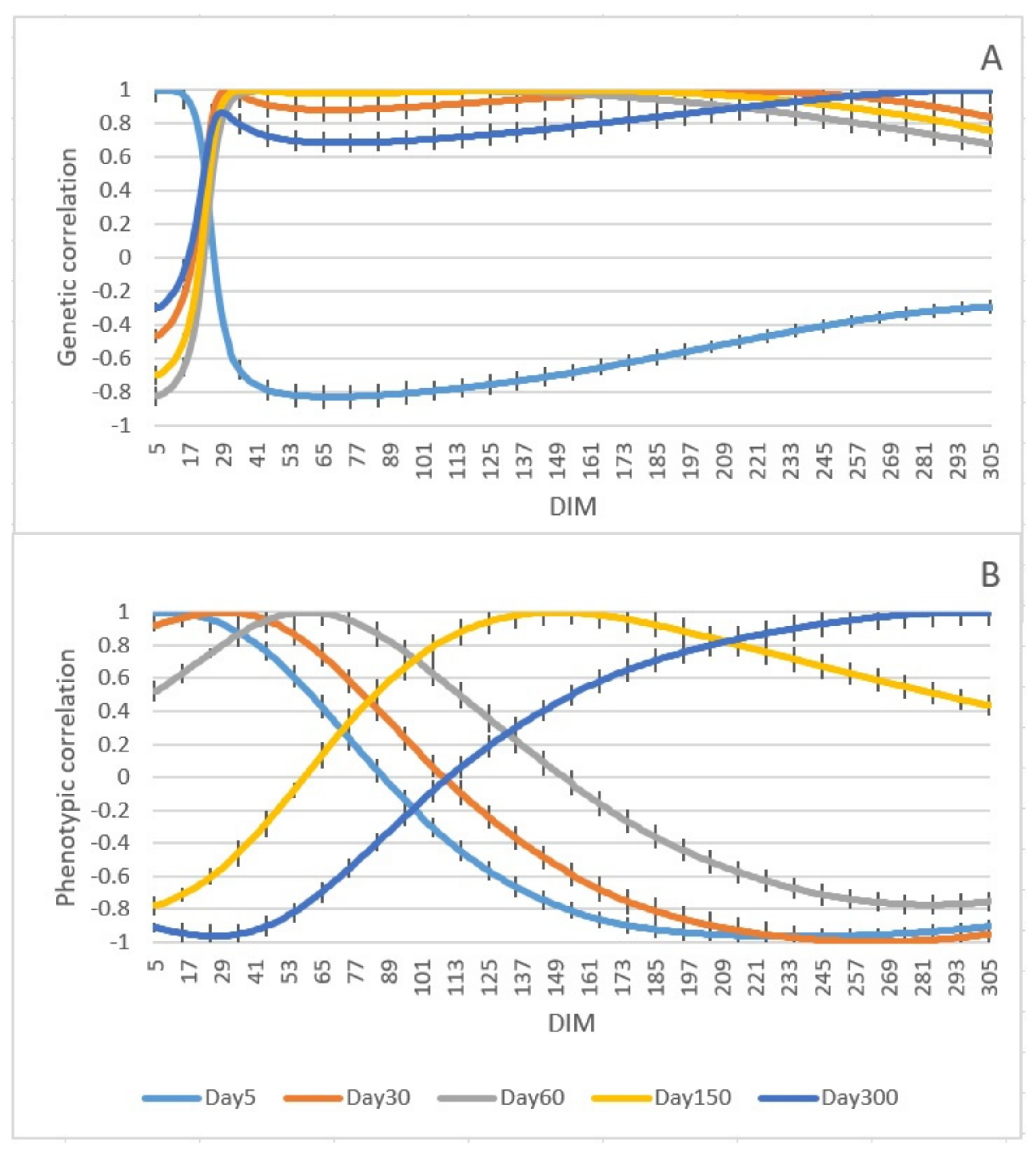
3.2. Estimation of Genetic Parameters
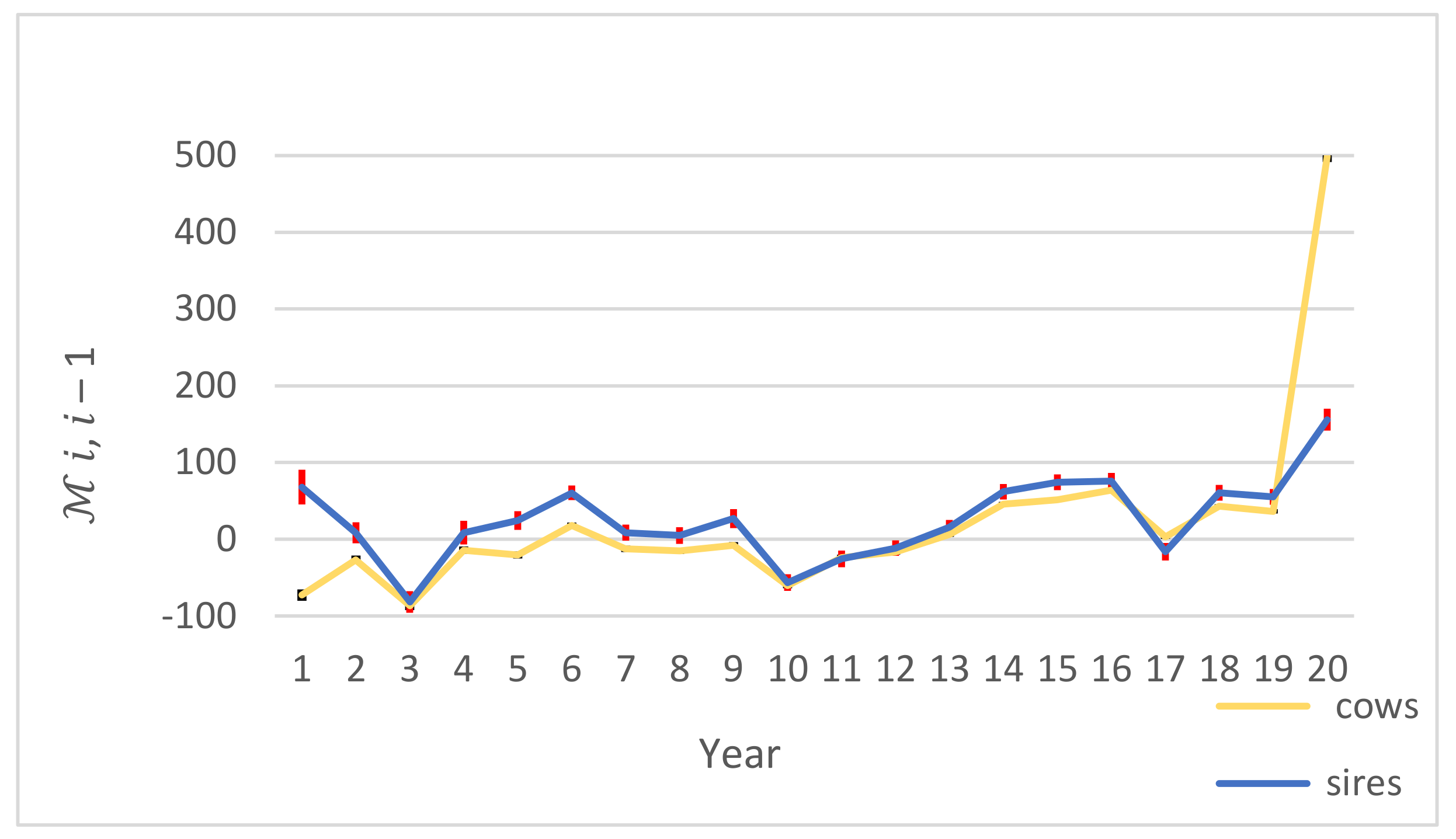
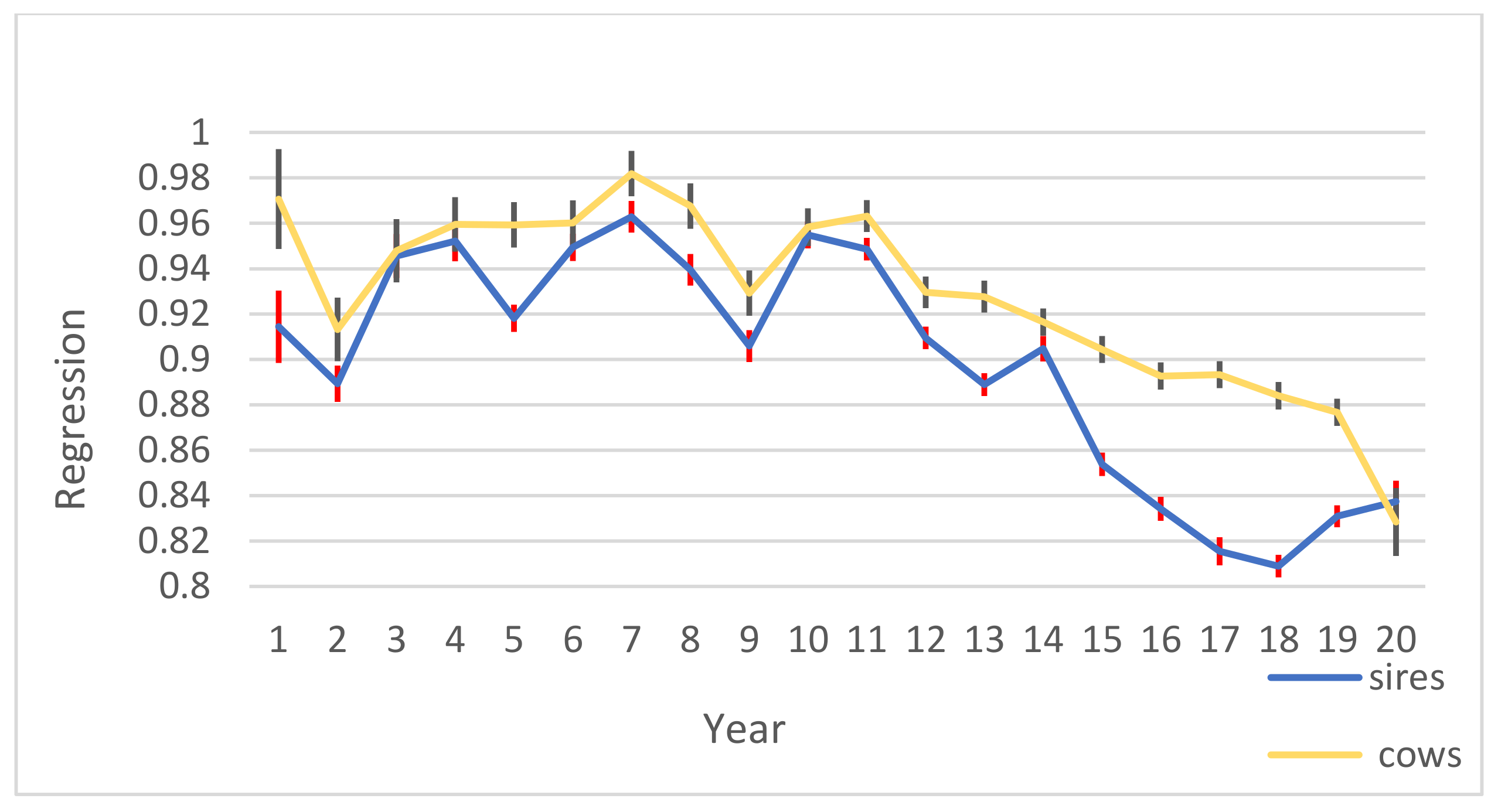
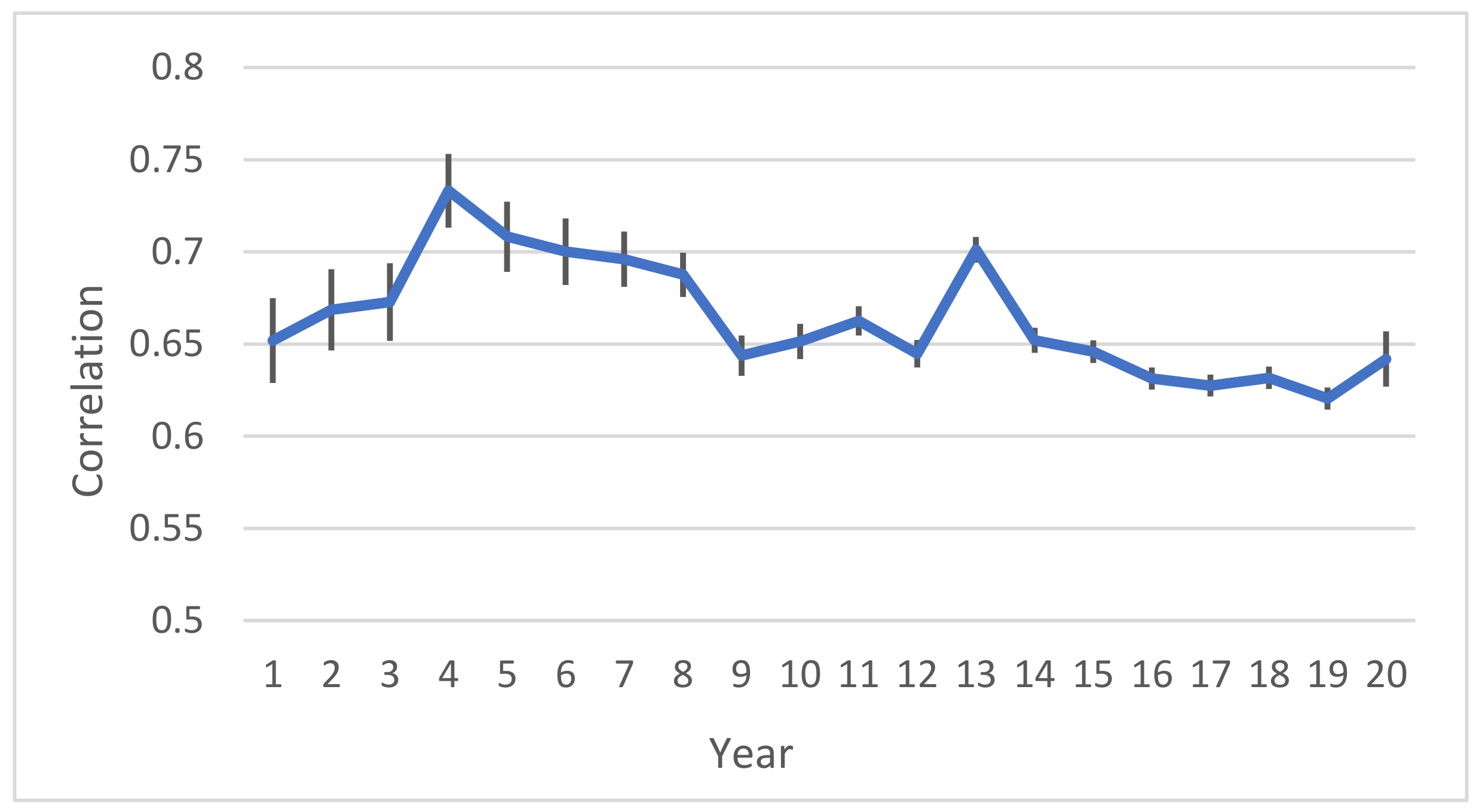
3.3. Cross-Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Model
4.2. Genetic Parameters
4.3. Cross Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrabi, S.; Moran, C. Selection of dairy cow bulls for artificial insemination. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2007, 9, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, R.; Norman, H.; Sanders, A. Progeny testing and selection intensity for Holstein bulls in different countries. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3386–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRaden, P.; Van Tassell, C.; Wiggans, G.; Sonstegard, T.; Schnabel, R.; Taylor, J.; Schenkel, F. Invited review: Reliability of genomic predictions for North American Holstein bulls. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, K.; VanRaden, P.; Norman, H.; Grosu, H. A 100-Year Review: Methods and impact of genetic selection in dairy cattle—from daughter–dam comparisons to deep learning algorithms. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10234–10250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, J.; McDaniel, B.T. Prediction of most recent evaluations of Holstein bulls from first available pedigree information. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, H.; Powell, R.; Wright, J.; Sattler, C. Timeliness and effectiveness of progeny testing through artificial insemination. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, B. Efficient parentage assignment and pedigree reconstruction with dense single nucleotide polymorphism data. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 2114–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarani, A.; Hidalgo, J.; Garcia, A.; Degano, L.; Vicario, D.; Masuda, Y.; Misztal, I.; Lourenco, D. Beef trait genetic parameters based on old and recent data and its implications for genomic predictions in Italian Simmental cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patry, C.; Ducrocq, V. Evidence of biases in genetic evaluations due to genomic preselection in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedet, A.; Costa, A.; De Marchi, M.; Penasa, M. Heritability estimates of predicted blood beta-hydroxybutyrate and nonesterified fatty acids and relationships with milk traits in early-lactation Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 6354–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, K.; Tiezzi, F.J.; Clay, S.; Maltecca, C. Causal relationships between clinical mastitis events, milk yields and lactation persistency in US Holsteins. Livest. Sci. 2016, 189, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendiville, R.; Pierce, K.; Delaby, L.; Buckley, F. Animal performance and production efficiencies of Holstein-Friesian, Jersey and Jersey× Holstein-Friesian cows throughout lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 138, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadparvar, A.; Yazdanshenas, M. Genetic parameters of milk yield and milk fat percentage test day records of Iranian Holstein cows. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, J.; Tsuruta, S.; Lourenco, D.; Masuda, Y.; Huang, Y.; Gray, K.A.; Misztal, I. Changes in genetic parameters for fitness and growth traits in pigs under genomic selection. JAS 2020, 98, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsen, J.H.; Madsen, P.; Jensen, J.; Pedersen, J.; Christensen, L.; Sorensen, D. Genetic parameters for milk production and persistency for Danish Holsteins estimated in random regression models using REML. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, L.R. Application of random regression models in animal breeding. Livest. Sci. 2004, 86, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legarra, A.; Reverter, A. Semi-parametric estimates of population accuracy and bias of predictions of breeding values and future phenotypes using the LR method. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijma, P. Accuracies of estimated breeding values from ordinary genetic evaluations do not reflect the correlation between true and estimated breeding values in selected populations. J. Anim. Breed. Genet 2012, 129, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen, M.; Campbell, M.T.; Walia, H.; Morota, G. Predicting longitudinal traits derived from high-throughput phenomics in contrasting environments using genomic Legendre polynomials and B-splines. G3 Bethesda 2019, 9, 3369–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legarra, A.; Reverter, A. Can we frame and understand cross-validation results in animal breeding. In Proceedings of the 22nd Conference Association for the Advancement of Animal Breeding and Genetics 2017, Townsville, Australia, 2–5 July 2017; pp. 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. JCGS 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.; Madsen, P. DMU: A package for the analysis if multivariate mixed models 1994. In Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, Guelph, ON, Canada, 7–12 August 1994; pp. 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Novomestky, F. Collection of functions for orthogonal and orthonormal polynomials Package. CRAN 2013, 02-04 07:42:24. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/orthopolynom/ (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Pool, M.; Janss, L.; Meuwissen, T. Genetic parameters of Legendre polynomials for first parity lactation curves. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2640–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, J.; Goddard, M.; Meyer, K. The use of covariance functions and random regressions for genetic evaluation of milk production based on test day records. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 3300–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olori, V.; Hill, W.; McGuirk, B.; Brotherstone, S. Estimating variance components for test day milk records by restricted maximum likelihood with a random regression animal model. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1999, 61, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Romero, P.; Rekaya, R.; Carabaño, M. Assessment of homogeneity vs. heterogeneity of residual variance in random regression test-day models in a Bayesian analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3374–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirlo, G.; Miglior, F.; Speroni, M. Effect of age at first calving on production traits and on difference between milk yield returns and rearing costs in Italian Holsteins. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, J.; Palmer, R.W.; Jackson-Smith, D.B. Modeling Milk Production and Labor Efficiencyin Modernized Wisconsin Dairy Herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilforooshan, M.; Edriss, M. Effect of age at first calving on some productive and longevity traits in Iranian Holsteins of the Isfahan province. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 2130–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, S.; France, J.; Odongo, N.; McBride, R.; Kebreab, E.; AlZahal, O.; McBride, B.; Dijkstra, J. On the analysis of Canadian Holstein dairy cow lactation curves using standard growth functions. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2701–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollott, G. A biological approach to lactation curve analysis for milk yield. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2448–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidie, R.; Shadparvar, A.; Hossein-Zadeh, N.G.; Shakalgurabi, S. Genetic trends for 305-day milk yield and persistency in Iranian Holsteins. Livest. Sci. 2012, 144, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Hagiya, K.; Takeda, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Osawa, T.; Nagamine, Y. Genetic correlations among female fertility, 305-day milk yield and persistency during the first three lactations of Japanese Holstein cows. Livest. Sci 2014, 168, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.K.; Gupta, A.; Singh, A.; Chakravarty, A.; Valsalan, J.; Shivahre, P.; Panmei, A.; Divya, P. Analysis of genetic trend in fertility and production traits of Karan Fries (Holstein Friesian crossbred) cattle using BLUP estimation of breeding values. Indian J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 69, 186–189. [Google Scholar]
- Gara, A.B.; Rekik, B.; Bouallègue, M. Genetic parameters and evaluation of the Tunisian dairy cattle population for milk yield by Bayesian and BLUP analyses. Livest. Sci. 2006, 100, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekaya, R.; Carabano, M.; Toro, M. Bayesian analysis of lactation curves of Holstein-Friesian cattle using a nonlinear model. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2691–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, Y. Estimation of genetic parameters for milk yield, somatic cell score, and fertility traits in Iranian Holstein dairy cattle. IIOAB J. 2016, 7, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Cilek, S.; Sahin, E. Estimation of some genetic parameters (heritability and repeatability) for milk yield in the Anatolian population of Holstein cows. Arch. Zootech. 2009, 12, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Erfani-Asl, Z.; Hashemi, A.; Farhadian, M. Estimates of repeatability and heritability of productive trait in Holstein dairy cattle. IJAAS 2015, 5, 827–832. [Google Scholar]
- Breider, I.S.; Wall, E.; Garnsworthy, P.C. Short communication: Heritability of methane production and genetic correlations with milk yield and body weight in Holstein-Friesian dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7277–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biassus, I.D.O.; Cobuci, J.A.; Costa, C.N.; Rorato, P.R.N.; Braccini Neto, J.; Cardoso, L.L. Genetic parameters for production traits in primiparous Holstein cows estimated by random regression models. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2011, 40, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cobuci, J.A.; Costa, C.N.; Braccini Neto, J.; Freitas, A.F. Genetic parameters for milk production by using random regression models with different alternatives of fixed regression modeling. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2011, 40, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.N.; de Melo, C.M.R.; Packer, I.U.; de Freitas, A.F.; Teixeira, N.M.; Cobuci, J.A. Genetic parameters for test day milk yield of first lactation Holstein cows estimated by random regression using Legendre polynomials. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2008, 37, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salimiyekta, Y.; Vaez-Torshizi, R.; Abbasi, M.A.; Emmamjome-Kashan, N.; Amin-Afshar, M.; Guo, X.; Jensen, J. Random Regression Model for Genetic Evaluation and Early Selection in the Iranian Holstein Population. Animals 2021, 11, 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123492
Salimiyekta Y, Vaez-Torshizi R, Abbasi MA, Emmamjome-Kashan N, Amin-Afshar M, Guo X, Jensen J. Random Regression Model for Genetic Evaluation and Early Selection in the Iranian Holstein Population. Animals. 2021; 11(12):3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123492
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalimiyekta, Yasamin, Rasoul Vaez-Torshizi, Mokhtar Ali Abbasi, Nasser Emmamjome-Kashan, Mehdi Amin-Afshar, Xiangyu Guo, and Just Jensen. 2021. "Random Regression Model for Genetic Evaluation and Early Selection in the Iranian Holstein Population" Animals 11, no. 12: 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123492
APA StyleSalimiyekta, Y., Vaez-Torshizi, R., Abbasi, M. A., Emmamjome-Kashan, N., Amin-Afshar, M., Guo, X., & Jensen, J. (2021). Random Regression Model for Genetic Evaluation and Early Selection in the Iranian Holstein Population. Animals, 11(12), 3492. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123492





