An Update on Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Genotypes in Humans
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Genotypes
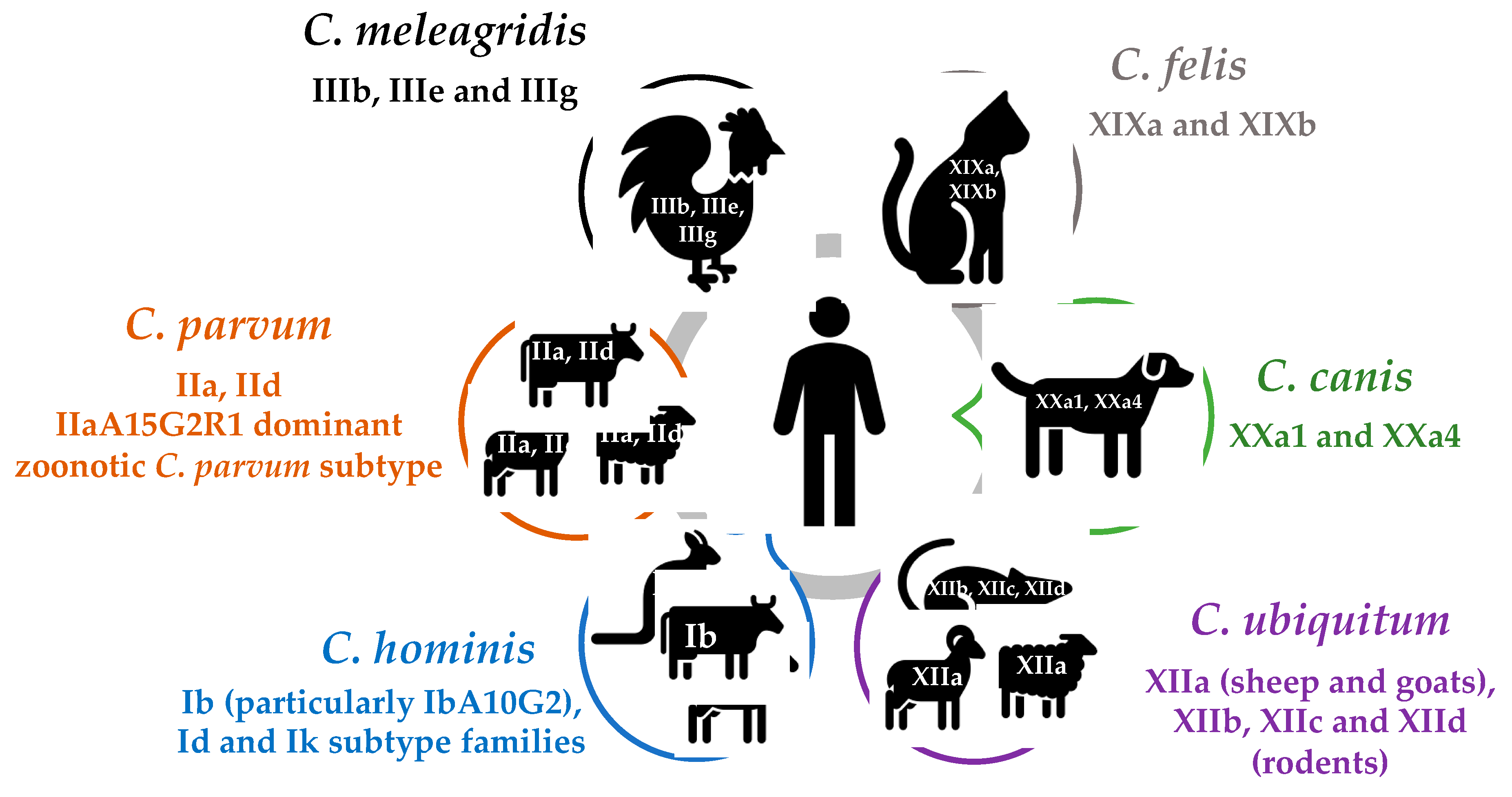
2.1. Cryptosporidium hominis
2.2. Cryptosporidium parvum and Other Livestock-Associated Species
2.3. C. meleagridis
2.4. Companion Animal-Associated Species (C. canis and C. felis)
2.5. Wildlife-Associated Species and Genotypes
| Species Name | gp60 Subtypes | References |
|---|---|---|
| C. hominis | IbA9G3, IbA13G3, IbA14G2, IbA10G2, IdA15G1, IbA10G2R2 and Ik subtype family | [22,125,127,131,132,133,134,139,221] |
| C. parvum | Many subtypes but mainly the IIa (particularly IIaA15G2R1) and IId subtype families | [11,22,23,31,117,140] |
| C. meleagridis | IIIbA21G1R1b, IIIbA22G1R1cIIIbA23G1R1b, IIIbA23G1R1c, IIIbA24G1R1, IIIbA26G1R1b, IIIeA17G2R1, IIIeA19G2R1, IIIeA21G2R1, IIIeA21G2R1 and IIIgA31G3R1 | [51,52,79,181,182,183,184] |
| C. felis | XIXa and XIXb | [40,46,186,192] |
| C. canis | XXa1 and XXa4 | [40,49] |
| C. ubiquitum | XIIa, XIIb, XIIc and XIId | [23,44,51,52] |
| C. cuniculus | VaA18, VbA19, VbA22 to Vb26, Vb28, VbA29 and VbA31 to VbA33 | [51,52,53,54,55,56,58,210,211] |
| C. viatorum | XVaA3g, XVaA3h and XVcA2G1 | [65,66,114,207,209] |
| Chipmunk genotype I | XIVaA18G2T2 | [37,45,51,60,71,72,75,76,77] |
| C. muris | Gastric Cryptosporidium species do not appear to have the gp60 gene | |
| C. andersoni | ||
| C. suis | A gp60 typing tool has not yet been developed | |
| Horse genotype | VIbA13 and VIcA16 | [51,58,82,104,105] |
| C. erinacei | XIIIaA20R10, XIIIaA23R12, XIIIaA24R9, XIIIaA24R10, XIIIaA25R10 XIIIaA25R11, XIIIaA26R9 and XIIIaA26R10 (humans only) | [53,54] |
| C. bovis | No gp60 sequences available from humans | |
| Skunk genotype | XVIbA16G2b and XVIcA22 (humans only but XVIbA16G2a in wildlife) | [111,224] |
| C. tyzzeri | IXaA8 and IXbA6 | [43,113] |
| C. occultus | A gp60 typing tool has not yet been developed | |
| C. ditrichi | A gp60 typing tool has not yet been developed | |
| Mink genotype | No gp60 sequences available from humans | |
| C. fayeri | IVaA9G4T1R1, IVgA10G1T1R1 | [119,120] |
| C. xiaoi | No gp60 sequences available from humans | |
| C. scrofarum | A gp60 typing tool has not yet been developed |
3. Knowledge Gaps and Future Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y. Molecular epidemiology of human cryptosporidiosis in low- and middle-income countries. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00087-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyzzer, E.E. A sporozoan found in the peptic glands of the common mouse. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1907, 5, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control. Cryptosporidiosis: Assessment of chemotherapy of males with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 1982, 31, 589–592. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, A.; Kumar, S.; Smith, W.A.; Sahu, P.S. Revisiting the global problem of cryptosporidiosis and recommendations. Trop. Parasitol. 2017, 7, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-J.; Li, J.-Q.; Chen, Y.-C.; Zhang, L.-X.; Xiao, L.-H. Widespread occurrence of Cryptosporidium infections in patients with HIV/AIDS: Epidemiology, clinical feature, diagnosis, and therapy. Acta Trop. 2018, 187, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotloff, K.L.; Nataro, J.P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Nasrin, D.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Wu, Y.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013, 382, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.M.; Nasrin, D.; Ac’acio, S.; Bassat, Q.; Powell, H.; Tennant, S.M.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Zaidi, A.K.; Faruque, A.S.G.; et al. Diarrhoeal disease and subsequent risk of death in infants and children residing in low-income and middle-income countries: Analysis of the GEMS case-control study and 12-month GEMS-1A follow-on study. Lancet Glob. Health. 2020, 8, e204–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mac Kenzie, W.R.; Schell, W.L.; Blair, K.A.; Addiss, D.G.; Peterson, D.E.; Hoxie, N.J.; Kazmierczak, J.J.; Davis, J.P. Massive Outbreak of Waterborne Cryptosporidium Infection in Milwaukee, Wisconsin: Recurrence of Illness and Risk of Secondary Transmission. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 21, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstratiou, A.; Ongerth, J.E.; Karanis, P. Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: Review of worldwide outbreaks—An update 2011–2016. Water Res. 2017, 114, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, U.; Hijjawi, N.; Xiao, L. Foodborne cryptosporidiosis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zahedi, A.; Ryan, U. Cryptosporidium—An update with an emphasis on foodborne and waterborne transmission. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 132, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, B.; Monis, P.T. Critical processes affecting Cryptosporidium oocyst survival in the environment. Parasitology 2007, 134 Pt 3, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharpure, R.; Perez, A.; Miller, A.D.; Wikswo, M.E.; Silver, R.; Hlavsa, M.C. Cryptosporidiosis outbreaks—United States, 2009–2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunasekera, S.; Zahedi, A.; O’Dea, M.; King, B.; Monis, P.; Thierry, B.; Carr, J.M.; Ryan, U. Organoids and bioengineered intestinal models: Potential solutions to the Cryptosporidium culturing dilemma. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrant, D.I.; Lima, A.; Patrick, P.D.; Schorling, J.B.; Moore, S.; Guerrant, R.L. Association of early childhood diarrhea and cryptosporidiosis with impaired physical fitness and cognitive function four-seven years later in a poor urban community in northeast Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 61, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, D.; Sack, R.B.; Haque, R.; Jr, W.A.P.; Kirkpatrick, B.D. Attribution of malnutrition to cause-specific diarrheal illness: Evidence from a prospective study of preschool children in Mirpur, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, B.L.; Chalmers, R.M.; Davies, A.P. Health sequelae of human cryptosporidiosis in industrialised countries: A systematic review. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, N.; Gorgani-Firouzjaee, T.; Ghaffari, S.; Bayani, M.; Ghaffari, T.; Chehrazi, M. Association between Cryptosporidium infection and cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 74, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.J.; Vinayak, S. Cryptosporidium: Host-Parasite Interactions and Pathogenesis. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2021, 8, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, M.; Baydoun, M.; Creusy, C.; Chabé, M.; Viscogliosi, E.; Certad, G.; Benamrouz-Vanneste, S. Cryptosporidium and colon cancer: Cause or consequence? Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.; Hamilton, C.A.; Hope, J.C.; Katzer, F.; Mabbott, N.A.; Morrison, L.J.; Innes, E.A. Bovine cryptosporidiosis: Impact, host-parasite interaction and control strategies. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santin, M. Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Ruminants. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Ryan, U.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Small ruminants and zoonotic cryptosporidiosis. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, C.; Williams, A.; Yang, R.; Ryan, U.; Carmichael, I.; Campbell, A.J.; Gardner, G. Greater intensity and frequency of Cryptosporidium and Giardia oocyst shedding beyond the neonatal period is associated with reductions in growth, carcase weight and dressing efficiency in sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 228, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, C.; Al-Habsi, K.; Ryan, U.; Williams, A.; Anderson, F.; Yang, R.; Abraham, S.; Miller, D. Cryptosporidium infection is associated with reduced growth and diarrhoea in goats beyond weaning. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 260, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaw, H.J.; Innes, E.A.; Morrison, L.J.; Katzer, F.; Wells, B. Long-term production effects of clinical cryptosporidiosis in neonatal calves. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, C.L.; Kirkpatrick, B.D. Is nitazoxanide an effective treatment for patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome-related cryptosporidiosis? Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 4, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadi, B.; Mwiya, M.; Sianongo, S.; Payne, L.; Watuka, A.; Katubulushi, M.; Kelly, P. High dose prolonged treatment with nitazoxanide is not effective for cryptosporidiosis in HIV positive Zambian children: A randomised controlled trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashigbie, P.G.; Shepherd, S.; Steiner, K.L.; Amadi, B.; Aziz, N.; Manjunatha, U.H.; Spector, J.M.; Diagana, T.T.; Kelly, P. Use-case scenarios for an anti-Cryptosporidium therapeutic. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, C.K.; Kol, A. The Mucosal Innate Immune Response to Cryptosporidium parvum, a Global one health issue. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Feng, Y. Molecular epidemiologic tools for waterborne pathogens Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2017, 8-9, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roellig, D.M.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium Genotyping for epidemiology tracking. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2052, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, U.M.; Feng, Y.; Fayer, R.; Xiao, L. Taxonomy and molecular epidemiology of Cryptosporidium and Giardia—A 50 year perspective (1971–2021). Int. J. Parasitol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamu, H.; Petros, B.; Zhang, G.; Kassa, H.; Amer, S.; Ye, J.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Distribution and clinical manifestations of Cryptosporidium species and subtypes in HIV/AIDS patients in Ethiopia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouzid, M.; Kintz, E.; Hunter, P. Risk factors for Cryptosporidium infection in low and middle income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Shams, S.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, S.; Ali, A. Evaluation of prevalence and risk factors associated with Cryptosporidium infection in rural population of district Buner, Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeck, B.K.; Pedati, C.; Iwen, P.C.; McCutchen, E.; Roellig, D.M.; Hlavsa, M.C.; Fullerton, K.; Safranek, T.; Carlson, A.V. Genotyping and subtyping Cryptosporidium to identify risk factors and transmission patterns—Nebraska, 2015–2017. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, R.M.; Robinson, G.; Elwin, K.; Elson, R. Analysis of the Cryptosporidium spp. and gp60 subtypes linked to human outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis in England and Wales, 2009 to 2017. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Lopez, D.; Müller, L.; Vestergaard, L.S.; Christoffersen, M.; Andersen, A.-M.; Jokelainen, P.; Agerholm, J.S.; Stensvold, C.R. Veterinary students have a higher risk of contracting cryptosporidiosis when calves with high fecal Cryptosporidium loads are used for fetotomy exercises. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01250-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ryan, U.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Advances in molecular epidemiology of cryptosporidiosis in dogs and cats. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.P.; Newton, K.; Rimdap, E.; Wight, A.; Robinson, G.; Chalmers, R.M. Review of investigations of premises housing animals that were linked to human outbreaks of cryptosporidiosis in England and Wales between 2009 and 2019. Vet. Rec. 2021, 189, e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, W.B.; Gut, J.; Nelson, R.G. Cloning and sequence analysis of a highly polymorphic Cryptosporidium parvum gene encoding a 60-kilodalton glycoprotein and characterization of Its 15- and 45-kilodalton zoite surface antigen products. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 4117–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Hira, P.R.; Zhou, L.; Al-Ali, F.M.; Al-Shelahi, F.A.; Shweiki, H.M.; Iqbal, J.; Khalid, N.; Xiao, L. Unique endemicity of cryptosporidiosis in children in Kuwait. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2805–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Xiao, L.; Alderisio, K.; Elwin, K.; Cebelinski, E.; Chalmers, R.; Santín, M.; Fayer, R.; Kvac, M.; Ryan, U.; et al. Subtyping Cryptosporidium ubiquitum, A zoonotic pathogen emerging in humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cebelinski, E.; Matusevich, C.; Alderisio, K.A.; Lebbad, M.; McEvoy, J.; Roellig, D.M.; Yang, C.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Subtyping novel zoonotic pathogen Cryptosporidium chipmunk genotype I. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas-López, L.; Elwin, K.; Chalmers, R.M.; Enemark, H.L.; Beser, J.; Troell, K. Development of a gp60-subtyping method for Cryptosporidium felis. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, N.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Kváč, M.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Subtyping Cryptosporidium ryanae: A Common pathogen in bovine animals. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, X.; Guo, S.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L.; Li, N. Subtyping Cryptosporidium xiaoi, a common pathogen in sheep and goats. Pathogens 2021, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Roellig, D.M.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Development of a subtyping tool for zoonotic pathogen Cryptosporidium canis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wan, M.; Yang, F.; Li, N.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Y. Development and Application of a gp60-Based Subtyping Tool for Cryptosporidium bovis. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebbad, M.; Winiecka-Krusnell, J.; Stensvold, C.; Beser, J. High Diversity of Cryptosporidium Species and subtypes identified in cryptosporidiosis acquired in sweden and abroad. Pathogens 2021, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, R.A.; Yanta, C.A.; Muchaal, P.K.; Rankin, M.A.; Thivierge, K.; Lau, R.; Boggild, A.K. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium isolates from humans in Ontario, Canada. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia–R, J.C.; French, N.; Pita, A.; Velathanthiri, N.; Shrestha, R.; Hayman, D. Local and global genetic diversity of protozoan parasites: Spatial distribution of Cryptosporidium and Giardia genotypes. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia–R, J.C.; Pita, A.B.; Velathanthiri, N.; French, N.P.; Hayman, D.T.S. Species and genotypes causing human cryptosporidiosis in New Zealand. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, A.V.; Whipp, M.J.; Haydon, S.R.; Gasser, R.B. Cryptosporidium cuniculus—New records in human and kangaroo in Australia. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puleston, R.L.; Mallaghan, C.M.; Modha, D.E.; Hunter, P.; Nguyen-Van-Tam, J.; Regan, C.M.; Nichols, G.L.; Chalmers, R.M. The first recorded outbreak of cryptosporidiosis due to Cryptosporidium cuniculus (formerly rabbit genotype), following a water quality incident. J. Water Health 2014, 12, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Ruiz, R.; de Lucio, A.; Fuentes, I.; Carmena, D. Autochthonous Cryptosporidium cuniculus infection in Spain: First report in a symptomatic paediatric patient from Madrid. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2016, 34, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, R.M.; Elwin, K.; Hadfield, S.J.; Robinson, G. Sporadic human cryptosporidiosis caused by Cryptosporidium cuniculus, United Kingdom, 2007–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, S.F.; Kirwan, P.; Asaolu, S.O.; Holland, C.V.; Nichols, R.A.B.; Connelly, L.; Smith, H.V. Identification of a High Diversity of Cryptosporidium Species Genotypes and Subtypes in a Pediatric Population in Nigeria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anofel Cryptosporidium National Network. Laboratory-based surveillance for Cryptosporidium in France, 2006–2009. Eurosurveilliance 2010, 15, 19642. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, R.M.; Robinson, G.; Elwin, K.; Hadfield, S.J.; Xiao, L.; Ryan, U.; Modha, D.; Mallaghan, C. Cryptosporidium sp. Rabbit genotype, a newly identified human pathogen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 829–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muadica, A.S.; Köster, P.C.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; Hernández-de-Mingo, M.; Balasegaram, S.; Carmena, D. Molecular diversity of Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis sp. in symptomatic and asymptomatic school children in Zambezia province (Mozambique). Pathogens 2021, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, S.K.; Ghosal, A.; Saito-Nakano, Y.; Dutta, S.; Nozaki, T.; Ganguly, S. Molecular Identification of Cryptosporidium viatorum infection in a patient suffering from unusual cryptosporidiosis in West Bengal, India. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarekegn, Z.S.; Tigabu, Y.; Dejene, H. Cryptosporidium infection in cattle and humans in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2021, 14, e00219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Gong, B.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, J.; Yao, L.; Li, H.; Liu, A.; Shen, Y. Identification of uncommon Cryptosporidium viatorum (a novel subtype XVcA2G1c) and Cryptosporidium andersoni as well as common Giardia duodenalis assemblages A and B in humans in Myanmar. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braima, K.; Zahedi, A.; Oskam, C.; Reid, S.; Pingault, N.; Xiao, L.; Ryan, U. Retrospective analysis of Cryptosporidium species in Western Australian human populations (2015–2018), and emergence of the C. hominis IfA12G1R5 subtype. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 73, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdha, B.R.; Khalil, S.; Paul, J.; Panda, A.; Singh, Y. Molecular Detection and Identification of Cryptosporidium viatorum in a Human Immunodeficiency Virus-seropositive Patient. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2018, 10, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, A.; Munoz, M.; Gómez, N.; Tabares, J.; Segura, L.; Salazar, Á.; Restrepo, C.; Ruíz, M.; Reyes, P.; Qian, Y.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Giardia, Blastocystis and Cryptosporidium among Indigenous Children from the Colombian Amazon Basin. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwah, B.N.; Ezeonu, I.M.; Ezeonu, C.T.; Roellig, D.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium species and subtypes in diarrheal children and HIV-infected persons in Ebonyi and Nsukka, Nigeria. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2017, 11, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayinmode, A.B.; Zhang, H.; Dada-Adegbola, H.O.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium hominis Subtypes and Enterocytozoon bieneusi Genotypes in HIV-Infected Persons in Ibadan, Nigeria. Zoonoses Public Health 2014, 61, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebbad, M.; Beser, J.; Insulander, M.; Karlsson, L.; Mattsson, J.G.; Svenungsson, B.; Axen, C. Unusual cryptosporidiosis cases in Swedish patients: Extended molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium viatorum and Cryptosporidium chipmunk genotype I. J. Parasitol. 2013, 140, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Insulander, M.; Silverlås, C.; Lebbad, M.; Karlsson, L.; Mattsson, J.G.; Svenungsson, B. Molecular epidemiology and clinical manifestations of human cryptosporidiosis in Sweden. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elwin, K.; Hadfield, S.J.; Robinson, G.; Crouch, N.D.; Chalmers, R.M. Cryptosporidium viatorum n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) among travellers returning to Great Britain from the Indian subcontinent, 2007–2011. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lucio, A.; Amor-Aramendía, A.; Bailo, B.; Saugar, J.M.; Anegagrie, M.; Arroyo, A.; López-Quintana, B.; Zewdie, D.; Ayehubizu, Z.; Yizengaw, E.; et al. Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. among School Children in a Rural Area of the Amhara Region, North-West Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bujila, I.; Troell, K.; Fischerström, K.; Nordahl, M.; Killander, G.; Hansen, A.; Söderlund, R.; Lebbad, M.; Beser, J. Cryptosporidium chipmunk genotype I—An emerging cause of human cryptosporidiosis in Sweden. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 92, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Roellig, D.M.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Comparative analysis reveals conservation in genome organization among intestinal Cryptosporidium species and sequence divergence in potential secreted pathogenesis determinants among major human-infecting species. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feltus, D.C.; Giddings, C.W.; Schneck, B.L.; Monson, T.; Warshauer, D.; McEvoy, J.M. Evidence supporting zoonotic transmission of Cryptosporidium spp. in Wisconsin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4303–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higuera, A.; Villamizar, X.; Herrera, G.; Giraldo, J.C.; Vasquez-A., L.R.; Urbano, P.; Villalobos, O.; Tovar, C.; Ramírez, J.D. Molecular detection and genotyping of intestinal protozoa from different biogeographical regions of Colombia. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sannella, A.R.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Wongsawat, E.; Cacciò, S.M. A retrospective molecular study of Cryptosporidium species and genotypes in HIV-infected patients from Thailand. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayinmode, A.B.; Oliveira, B.C.M.; Obebe, O.O.; Dada-Adgebola, H.O.; Ayede, A.I.; Widmer, G.; Dada-Adegbola, H. Genotypic Characterization of Cryptosporidium Species in Humans and Peri-Domestic Animals in Ekiti and Oyo States, Nigeria. J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattula, D.; Jeyavelu, N.; Prabhakaran, A.D.; Premkumar, P.S.; Velusamy, V.; Venugopal, S.; Geetha, J.C.; Lazarus, R.P.; Das, P.; Nithyanandhan, K.; et al. Natural History of Cryptosporidiosis in a Birth Cohort in Southern India. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elwin, K.; Hadfield, S.J.; Robinson, G.; Chalmers, R.M. The epidemiology of sporadic human infections with unusual cryptosporidia detected during routine typing in England and Wales, 2000–2008. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 140, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Brikan, F.A.; Salem, H.S.; Beeching, N.; Hilal, N. Multilocus genetic analysis of Cryptosporidium isolates from Saudi Arabia. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gatei, W.; Kamwati, S.K.; Mbae, C.; Waruru, A.; Hart, C.A.; Wamae, C.N.; Revathi, G.; Mulinge, E.; Gatika, S.M.; Waithera, T. Cryptosporidiosis: Prevalence, genotype analysis, and symptoms associated with infections in children in Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muthusamy, D.; Rao, S.S.; Ramani, S.; Monica, B.; Banerjee, I.; Abraham, O.C.; Mathai, D.C.; Primrose, B.; Muliyil, J.; Wanke, C.A.; et al. Multilocus Genotyping of Cryptosporidium sp. Isolates from Human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals in South India. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmer, C.J.; Xiao, L.; Terashima, A.; Guerra, H.; Gotuzzo, E.; Saldias, G.; Bonilla, J.A.; Zhou, L.; Lindquist, A.; Upton, S.J. Cryptosporidium muris, a rodent pathogen, recovered from a human in Peru. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1174–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatei, W.; Ashford, R.W.; Beeching, N.J.; Kamwati, S.K.; Greensill, J.; Hart, C.A. Cryptosporidium muris infection in an HIV-infected adult, Kenya. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiangtip, R.; Jongwutiwes, S. Molecular analysis of Cryptosporidium species isolated from HIV-infected patients in Thailand. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2002, 7, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsumata, T.; Hosea, D.; Uga, S.; Kohno, S.; Ranuh, I.G.; Yanagi, T. Short report: Possible Cryptosporidium muris infection in humans. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, G.; Roychoudhury, S.; Singha, B.; Paul, J. Incidence of Cryptosporidium andersoni in diarrheal patients from southern Assam, India: A molecular approach. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Ren, J.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, A.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Chu, L.; Pan, W.; Cao, J.; Lin, Y.; et al. Cryptosporidium andersoni as a novel predominant Cryptosporidium species in outpatients with diarrhea in Jiangsu Province, China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Shen, Y.; Yin, J.; Yuan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pan, W.; Hu, Y.; Cao, J. Prevalence and genetic characterization of Cryptosporidium, Enterocytozoon, Giardia and Cyclospora in diarrheal outpatients in china. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agholi, M.; Hatam, G.M.; Motazedian, M.H. HIV/AIDS-associated opportunistic protozoal diarrhoea. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2013, 29, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldron, L.S.; Dimeski, B.; Beggs, P.; Ferrari, B.; Power, M.L. Molecular Epidemiology, Spatiotemporal Analysis, and Ecology of Sporadic Human Cryptosporidiosis in Australia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7757–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morse, T.D.; Nichols, R.A.B.; Grimason, A.M.; Campbell, B.M.; Tembo, K.C.; Smith, H.V. Incidence of cryptosporidiosis species in paediatric patients in Malawi. Epidemiol. Infect. 2007, 135, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, F.; Amar, C.; Nichols, G.; Pedraza-Díaz, S.; McLauchlin, J. Genetic analysis of Cryptosporidium from 2414 humans with diarrhoea in England between 1985 and 2000. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyot, K.; Follet-Dumoulin, A.; Lelièvre, E.; Sarfati, C.; Rabodonirina, M.; Nevez, G.; Cailliez, J.C.; Camus, D.; Dei-Cas, E. Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium Isolates Obtained from Humans in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3472–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Gong, B.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cao, J. A retrospective epidemiological analysis of human Cryptosporidium infection in China during the past three decades (1987–2018). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.E.; Elwin, K.; Phot, N.; Seng, C.; Mao, S.; Suy, K.; Kumar, V.; Nader, J.; Bousfield, R.; Perera, S.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium Species and Giardia duodenalis from Symptomatic Cambodian Children. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodager, J.R.; Parsons, M.B.; Wright, P.C.; Rasambainarivo, F.; Roellig, D.; Xiao, L.; Gillespie, T.R. Complex epidemiology and zoonotic potential for Cryptosporidium suis in rural Madagascar. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.-W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Guo, M.; Liu, L.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Enterocytozoon bieneusi Genotypes in HIV-positive patients on antiretroviral therapy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 51, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cama, V.A.; Ross, J.; Crawford, S.; Kawai, V.; Chavez-Valdez, R.; Vargas-Pacherrez, D.; Vivar, A.; Ticona, E.; Ñavincopa, M.; Williamson, J.; et al. Differences in Clinical Manifestations among Cryptosporidium Species and Subtypes in HIV-Infected Persons. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Bern, C.; Arrowood, M.; Sulaiman, I.; Zhou, L.; Kawai, V.; Vivar, A.; Lal, A.A.; Gilman, R.H. Identification of the Cryptosporidium Pig genotype in a human patient. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1846–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Hlavsa, M.C.; Yoder, J.; Ewers, C.; Dearen, T.; Yang, W.; Nett, R.; Harris, S.; Brend, S.M.; Harris, M.; et al. Subtype analysis of Cryptosporidium specimens from sporadic cases in Colorado, Idaho, New Mexico, and Iowa in 2007: Widespread Occurrence of One Cryptosporidium hominis subtype and case history of an infection with the Cryptosporidium Horse Genotype. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 3017–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, G.; Elwin, K.; Chalmers, R.M. Unusual Cryptosporidium genotypes in human cases of diarrhea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1800–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.; Razakandrainibe, R.; Sautour, M.; Valot, S.; Basmaciyan, L.; Gargala, G.; Lemeteil, D.; Favennec, L.; Dalle, F.; Debourgogne, A.; et al. Human cryptosporidiosis in immunodeficient patients in France (2015–2017). Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 192, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvac, M.; Saková, K.; Květoňová, D.; Kicia, M.; Wesołowska, M.; McEvoy, J.; Sak, B. Gastroenteritis Caused by the Cryptosporidium Hedgehog Genotype in an Immunocompetent Man. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.M.; Debnath, C.; Pramanik, A.K.; Xiao, L.; Nozaki, T.; Ganguly, S. Molecular characterization and assessment of zoonotic transmission of Cryptosporidium from dairy cattle in West Bengal, India. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 171, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, J.S.Y.; Eastwood, K.; Walker, B.; Durrheim, D.N.; Massey, P.D.; Porigneaux, P.; Kemp, R.; McKinnon, B.; Laurie, K.; Miller, D.; et al. Evidence of Cryptosporidium transmission between cattle and humans in northern New South Wales. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 130, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helmy, Y.A.; Krücken, J.; Nöckler, K.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Zessin, K.-H. Molecular epidemiology of Cryptosporidium in livestock animals and humans in the Ismailia province of Egypt. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 193, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Alderisio, K.; Roellig, D.M.; Elwin, K.; Chalmers, R.M.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Subtype analysis of zoonotic pathogen Cryptosporidium skunk genotype. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, A.P.; Campbell, B.; Evans, M.R.; Bone, A.; Roche, A.; Chalmers, R.M. Asymptomatic carriage of protozoan parasites in children in day care centers in the United Kingdom. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2009, 28, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasková, V.; Kvetonová, D.; Sak, B.; McEvoy, J.; Edwinson, A.; Stenger, B.; Kvác, M. Human cryptosporidiosis is caused by Cryptosporidium tyzzeri and C. parvum isolates presumably transmitted from wild mice. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, N.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yin, J.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, Y.; Cao, J. First report of Cryptosporidium viatorum and Cryptosporidium occultus in humans in China, and of the unique novel C. viatorum subtype XVaA3h. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ong, C.S.L.; Eisler, D.L.; Alikhani, A.; Fung, V.W.K.; Tomblin, J.; Bowie, W.R.; Isaac-Renton, J.L. Novel Cryptosporidium genotypes in sporadic cryptosporidiosis cases: First report of human infections with a cervine genotype. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beser, J.; Bujila, I.; Wittesjö, B.; Lebbad, M. From mice to men: Three cases of human infection with Cryptosporidium ditrichi. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 78, 104120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng-Hublin, J.S.Y.; Combs, B.; MacKenzie, B.; Ryan, U. Human Cryptosporidiosis Diagnosed in Western Australia: A Mixed Infection with Cryptosporidium meleagridis, the Cryptosporidium Mink Genotype, and an Unknown Cryptosporidium Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2463–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebner, J.; Koehler, A.; Robertson, G.; Bradbury, R.; Jex, A.; Haydon, S.; Stevens, M.A.; Norton, R.; Joachim, A.; Gasser, R.B. Genetic analysis of Giardia and Cryptosporidium from people in Northern Australia using PCR-based tools. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldron, L.S.; Cheung-Kwok-Sang, C.; Power, M.L. Wildlife-associated Cryptosporidium fayeri in human, Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 2006–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braima, K.; Zahedi, A.; Oskam, C.; Austen, J.; Egan, S.; Reid, S.; Ryan, U. Zoonotic infection by Cryptosporidium fayeri IVgA10G1T1R1 in a Western Australian human. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kváč, M.; Květoňová, D.; Sak, B.; Ditrich, O. Cryptosporidium Pig genotype II in immunocompetent man. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 982–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.J.; Johansen, H.; Kifleyohannes, T.; Efunshile, A.M.; Terefe, G. Cryptosporidium Infections in Africa—How important is zoonotic transmission? A review of the evidence. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 575881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, J.P.; Carmena, D.; Rodríguez, E.; Checa, R.; López, A.M.; Fidalgo, L.E.; Gálvez, R.; Marino, V.; Fuentes, I.; Miró, G.; et al. The red fox (Vulpes vulpes) as a potential natural reservoir of human cryptosporidiosis by Cryptosporidium hominis in Northwest Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golomazou, E.; Malandrakis, E.E.; Panagiotaki, P.; Karanis, P. Cryptosporidium in fish: Implications for aquaculture and beyond. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, G.; Köster, P.C.; Carmena, D. Cryptosporidium hominis infections in non-human animal species: Revisiting the concept of host specificity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, C.L.; Tzipori, S.; Akiyoshi, D.E.; Okhuysen, P.; Tanriverdi, S.; Langer-Curry, R.; Widmer, G. Cryptosporidium hominis: Experimental challenge of healthy adults. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeywardena, H.; Jex, A.R.; Nolan, M.J.; Haydon, S.R.; Stevens, M.A.; McAnulty, R.W.; Gasser, R.B. Genetic characterisation of Cryptosporidium and Giardia from dairy calves: Discovery of species/genotypes consistent with those found in humans. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1984–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Guk, S.-M.; Han, E.-T.; Shin, E.-H.; Kim, J.-L.; Chai, J.-Y. Genotype analysis of Cryptosporidium spp. prevalent in a rural village in Hwasun-gun, Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2006, 44, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, J.; Yang, R.; Whiffin, V.; Cox, P.; Ryan, U. Identification of zoonotic Cryptosporidium and Giardia genotypes infecting animals in Sydney’s water catchments. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 128, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koehler, A.V.; Haydon, S.; Jex, A.R.; Gasser, R.B. Cryptosporidium and Giardia taxa in faecal samples from animals in catchments supplying the city of Melbourne with drinking water (2011 to 2015). Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahedi, A.; Monis, P.; Gofton, A.; Oskam, C.L.; Ball, A.; Bath, A.; Bartkow, M.; Robertson, I.; Ryan, U. Cryptosporidium species and subtypes in animals inhabiting drinking water catchments in three states across Australia. Water Res. 2018, 134, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krawczyk, A.I.; Van Leeuwen, A.D.; Jacobs-Reitsma, W.; Wijnands, L.M.; Bouw, E.; Jahfari, S.; Hoek, A.H.A.M.V.; Van Der Giessen, J.W.B.; Roelfsema, J.H.; Kroes, M.; et al. Presence of zoonotic agents in engorged ticks and hedgehog faeces from Erinaceus europaeus in (sub) urban areas. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danišová, O.; Valenčáková, A.; Stanko, M.; Luptáková, L.; Hatalová, E.; Canády, A. Rodents as a reservoir of infection caused by multiple zoonotic species genotypes of C. parvum, C. hominis, C. suis, C. scrofarum, and the first evidence of C. muskrat genotypes I and II of rodents in Europe. Acta Trop. 2017, 172, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condlová, Š.; Horčičková, M.; Sak, B.; Květoňová, D.; Hlásková, L.; Konecny, R.; Stanko, M.; McEvoy, J.; Kváč, M. Cryptosporidium apodemi sp. n. and Cryptosporidium ditrichi sp. n. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) in Apodemus spp. Eur. J. Protistol. 2018, 63, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, F.; Liu, A.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Qi, M.; Zhao, W.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Common occurrence of Cryptosporidium hominis in horses and donkeys. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 43, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inácio, S.V.; Widmer, G.; De Brito, R.L.L.; Zucatto, A.S.; De Aquino, M.C.C.; Oliveira, B.C.M.; Nakamura, A.A.; Neto, L.D.S.; Carvalho, J.G.B.; Gomes, J.F.; et al. First description of Cryptosporidium hominis GP60 genotype IkA20G1 and Cryptosporidium parvum GP60 genotypes IIaA18G3R1 and IIaA15G2R1 in foals in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 233, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Su, J.; Chahan, B.; Guo, Q.; Wang, T.; Yu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Different distribution of Cryptosporidium species between horses and donkeys. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Jing, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Qi, M.; Zhao, W. Prevalence and genotypic identification of Cryptosporidium in free-ranging and farm-raised donkeys (Equus asinus asinus) in Xinjiang, China. Parasite 2020, 27, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.; Monis, P.; Aucote, S.; King, B.; Paparini, A.; Jian, F.; Yang, R.; Oskam, C.; Ball, A.; Robertson, I.; et al. Zoonotic Cryptosporidium species in animals inhabiting sydney water catchments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahedi, A.; Gofton, A.W.; Jian, F.; Paparini, A.; Oskam, C.; Ball, A.; Robertson, I.; Ryan, U. Next Generation Sequencing uncovers within-host differences in the genetic diversity of Cryptosporidium gp60 subtypes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahedi, A.; Paparini, A.; Jian, F.; Robertson, I.; Ryan, U. Public health significance of zoonotic Cryptosporidium species in wildlife: Critical insights into better drinking water management. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2016, 5, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Ryan, U.M.; Xiao, L. Genetic diversity and population structure of Cryptosporidium. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam-Nahavandi, K.; Ahmadpour, E.; Carmena, D.; Spotin, A.; Bangoura, B.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium infections in terrestrial ungulates with focus on livestock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Molecular Epidemiology of Cryptosporidiosis in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, P.; Tyler, K.M.; Hunter, P.R. Anthroponotic transmission of Cryptosporidium parvum predominates in countries with poorer sanitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, J.L.; Mathers, T.; Ward, B.J.; Pachebat, J.; Swain, M.T.; Robinson, G.; Chalmers, R.M.; Hunter, P.R.; Van Oosterhout, C.; Tyler, K.M. Evolutionary genomics of anthroponosis in Cryptosporidium. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, H.; Johansen, O.H.; Vold, L.; Robertson, L.J.; Anthonisen, I.L.; Nygard, K. Second outbreak of infection with a rare Cryptosporidium parvum genotype in schoolchildren associated with contact with lambs/goat kids at a holiday farm in Norway. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 2105–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Torres, E.; Li, N.; Wang, L.; Bowman, D.; Xiao, L. Population genetic characterisation of dominant Cryptosporidium parvum subtype IIaA15G2R1. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayer, R.; Santín, M.; Macarisin, D. Cryptosporidium ubiquitum n. sp. in animals and humans. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 172, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, N.; Song, M.; Roellig, D.M.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Development of a multilocus sequence typing tool for high-resolution subtyping and genetic structure characterization of Cryptosporidium ubiquitum. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 45, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindsay, D.S.; Upton, S.J.; Owens, D.S.; Morgan, U.M.; Mead, J.R.; Blagburn, B.L. Cryptosporidium andersoni n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporiidae) from Cattle, Bos taurus. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2000, 47, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, R.; Jian, F.; Ning, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in deer in Henan and Jilin, China. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Chai, Y.; Deng, L.; Liu, H.; Zhong, Z.; Fu, H.; Hu, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Geng, Y.; et al. Cryptosporidium spp. in Pet Dwarf Winter White Russian Hamsters (Phodopus sungoris sungoris) in China. J. Parasitol. 2021, 107, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Lin, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Kvac, M.; Ryan, U.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Genetic characterizations of Cryptosporidium spp. from pet rodents indicate high zoonotic potential of pathogens from chinchillas. One Health 2021, 13, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ježková, J.; Prediger, J.; Holubová, N.; Sak, B.; Konečný, R.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L.; Rost, M.; McEvoy, J.; Kváč, M. Cryptosporidium ratti n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) and genetic diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. in brown rats (Rattus norvegicus) in the Czech Republic. Parasitology 2021, 148, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Jian, F.; Zhang, S.; Ning, C.; Wang, H.; Feng, C.; Wang, X.; Ren, X.; et al. Cryptosporidium spp. in Wild, Laboratory, and Pet Rodents in China: Prevalence and molecular characterization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7692–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Ryan, U.; Zhang, L.; Kváč, M.; Koudela, B.; Modrý, D.; Li, N.; Fayer, R.; Xiao, L. Development of a Multilocus Sequence Tool for Typing Cryptosporidium muris and Cryptosporidium andersoni. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Jian, F.; Zhang, L.; Ning, C.; Liu, A.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Qi, M.; Wang, H.; Lv, C.; et al. Multilocus sequence subtyping and genetic structure of Cryptosporidium muris and Cryptosporidium andersoni. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, A.; Cao, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L. MLST Subtypes and Population Genetic Structure of Cryptosporidium andersoni from dairy cattle and beef cattle in northeastern china’s heilongjiang province. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kváč, M.; Hanzlíková, D.; Sak, B.; Květoňová, D. Prevalence and age-related infection of Cryptosporidium suis, C. muris and Cryptosporidium pig genotype II in pigs on a farm complex in the Czech Republic. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 160, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Presedo, I.; Pedraza-Díaz, S.; González-Warleta, M.; Mezo, M.; Gómez-Bautista, M.; Ortega-Mora, L.-M.; Castro-Hermida, J.A. Presence of Cryptosporidium scrofarum, C. suis and C. parvum subtypes IIaA16G2R1 and IIaA13G1R1 in Eurasian wild boars (Sus scrofa). Vet Parasitol. 2013, 196, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, U.; Fayer, R.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium species in humans and animals: Current understanding and research needs. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1667–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyzzer, E.E. Coccidiosis in gallinaceous birds. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1929, 10, 269–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, D. Cryptosporidium Meleagridis (Sp. Nov.). J. Comp. Pathol. Ther. 1955, 65, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroudi, D.; Khelef, D.; Goucem, R.; Adjou, K.T.; Adamu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, L. Common occurrence of zoonotic pathogen Cryptosporidium meleagridis in broiler chickens and turkeys in Algeria. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Cryptosporidium and cryptosporidiosis in wild birds: A One Health perspective. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 3035–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdušek, O.; Ditrich, O.; Šlapeta, J. Molecular identification of Cryptosporidium spp. in animal and human hosts from the Czech Republic. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 122, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, B.; Petrželková, K.J.; Květoňová, D.; Mynářová, A.; Pomajbíková, K.J.; Modrý, D.; Cranfield, M.R.; Mudakikwa, A.; Kváč, M. Diversity of Microsporidia, Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Mountain Gorillas (Gorilla beringei beringei) in Volcanoes National Park, Rwanda. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeulen, E.T.; Ashworth, D.L.; Eldridge, M.; Power, M. Diversity of Cryptosporidium in brush-tailed rock-wallabies (Petrogale penicillata) managed within a species recovery programme. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2015, 4, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Ling, H.; Liu, A.; Shen, Y. Distribution and genetic characterizations of Cryptosporidium spp. in pre-weaned dairy calves in northeastern China’s Heilongjiang Province. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tao, W.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wan, Q.; Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, W. First report of Cryptosporidium canis in foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and identification of several novel subtype families for Cryptosporidium mink genotype in minks (Mustela vison) in China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 41, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Ren, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, A. Molecular detection and genetic characterizations of Cryptosporidium spp. in farmed foxes, minks, and raccoon dogs in northeastern China. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, D.E.; Dilo, J.; Pearson, C.; Chapman, S.; Tumwine, J.; Tzipori, S. Characterization of Cryptosporidium meleagridis of Human Origin Passaged through Different Host Species. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chappell, C.L.; Okhuysen, P.; Tzipori, S.; Widmer, G.; Akiyoshi, D.E.; Langer-Curry, R.C. Cryptosporidium meleagridis: Infectivity in Healthy Adult Volunteers. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 85, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omolabi, K.F.; Odeniran, P.O.; Soliman, M.E. A meta-analysis of Cryptosporidium species in humans from southern Africa (2000–2020). J. Parasit. Dis. 2021, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopacz, Ż.; Kváč, M.; Karpiński, P.; Hendrich, A.B.; Sąsiadek, M.M.; Leszczyński, P.; Sak, B.; McEvoy, J.; Kicia, M. The first evidence of Cryptosporidium meleagridis infection in a colon adenocarcinoma from an immunocompetent patient. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Sulaiman, I.M.; Ryan, U.; Zhou, L.; Atwill, E.R.; Tischler, M.L.; Zhang, X.; Fayer, R.; Lal, A.A. Host adaptation and host–parasite co-evolution in Cryptosporidium: Implications for taxonomy and public health. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpe, P.S.; Gilchrist, C.; Burkey, C.; Taniuchi, M.; Ahmed, E.; Madan, V.; Castillo, R.; Ahmed, S.; Arju, T.; Alam, M.; et al. Case-Control Study of Cryptosporidium Transmission in Bangladeshi Households. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng-Hublin, J.S.; Combs, B.; Reid, S.; Ryan, U. Differences in the occurrence and epidemiology of cryptosporidiosis in Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal people in Western Australia (2002–2012). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silverlås, C.; Mattsson, J.G.; Insulander, M.; Lebbad, M. Zoonotic transmission of Cryptosporidium meleagridis on an organic Swedish farm. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Beser, J.; Axén, C.; Lebbad, M. High Applicability of a Novel Method for gp60-Based Subtyping of Cryptosporidium meleagridis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Cama, V.; Wang, L.; Cabrera, L.; Ortega, Y.; Bern, C.; Feng, Y.; Gilman, R.; Xiao, L. Population genetics of Cryptosporidium meleagridis in humans and birds: Evidence for cross-species transmission. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fan, Y.; Koehler, A.; Ma, G.; Li, T.; Hu, M.; Gasser, R.B. First survey of Cryptosporidium, Giardia and Enterocytozoon in diarrhoeic children from Wuhan, China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 51, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Wang, T.; Koehler, A.V.; Fan, Y.; Hu, M.; Gasser, R.B. Molecular investigation of Cryptosporidium in farmed chickens in Hubei Province, China, identifies ‘zoonotic’ subtypes of C. meleagridis. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, K.J.; Petersen, C.A. Transmission and epidemiology of zoonotic protozoal diseases of companion animals. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 58–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yang, F.; Liang, R.; Guo, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Subtype Characterization and Zoonotic Potential of Cryptosporidium felis in Cats in Guangdong and Shanghai, China. Pathogens 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucio-Forster, A.; Griffiths, J.K.; Cama, V.A.; Xiao, L.; Bowman, D.D. Minimal zoonotic risk of cryptosporidiosis from pet dogs and cats. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghipour, A.; Olfatifar, M.; Bahadory, S.; Godfrey, S.S.; Abdoli, A.; Khatami, A.; Javanmard, E.; Shahrivar, F. The global prevalence of Cryptosporidium infection in dogs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 281, 109093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Cama, V.A.; Cabrera, L.; Ortega, Y.; Pearson, J.; Gilman, R.H. Possible Transmission of Cryptosporidium canis among Children and a Dog in a Household. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2014–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beser, J.; Toresson, L.; Eitrem, R.; Troell, K.; Winiecka-Krusnell, J.; Lebbad, M. Possible zoonotic transmission of Cryptosporidium felis in a household. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 28463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glaser, C.A.; Safrin, S.; Reingold, A.; Newman, T.B. Association between Cryptosporidium infection and animal exposure in HIV-infected individuals. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1998, 17, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Roellig, D.M.; Lebbad, M.; Beser, J.; Troell, K.; Guo, Y.; Li, N.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y. Subtype distribution of zoonotic pathogen Cryptosporidium felis in humans and animals in several countries. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghipour, A.; Olfatifar, M.; Foroutan, M.; Bahadory, S.; Malih, N.; Norouzi, M. Global prevalence of Cryptosporidium infection in rodents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 182, 105119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Huang, L.; Wang, R.; Xiao, L.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, L. Natural infection of Cryptosporidium muris in ostriches (Struthio camelus). Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagnerová, P.; Sak, B.; McEvoy, J.; Rost, M.; Matysiak, A.P.; Ježková, J.; Kváč, M. Genetic diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. including novel identification of the Cryptosporidium muris and Cryptosporidium tyzzeri in horses in the Czech Republic and Poland. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, S.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Liao, C.; Han, Q.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium hominis subtypes in crab-eating macaques. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Livia, K.; Martín-Alonso, A.; Foronda, P. Diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. in wild rodents from the Canary Islands, Spain. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Zheng, S.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L. Molecular identification and biological characterization of Cryptosporidium muris from camels (Camelus bactrianus) in China. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, C.L.; Okhuysen, P.; Tzipori, S.; Widmer, G.; Lupo, P.; Langer-Curry, R.C. Cryptosporidium muris: Infectivity and Illness in Healthy Adult Volunteers. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Čondlová, Š.; Horčičková, M.; Havrdová, N.; Sak, B.; Hlásková, L.; Perec-Matysiak, A.; Kicia, M.; McEvoy, J.; Kváč, M. Diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. in Apodemus spp. in Europe. Eur. J. Protistol. 2019, 69, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Ning, C.; Jian, F.; Wang, R.; Lv, C.; Wang, Q.; Arrowood, M.J.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium tyzzeri n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) in domestic mice (Mus musculus). Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 130, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kváč, M.; Vlnatá, G.; Ježková, J.; Horčičková, M.; Konečný, R.; Hlásková, L.; McEvoy, J.; Sak, B. Cryptosporidium occultus sp. n. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) in rats. Eur. J. Protistol. 2018, 63, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, C.; Hou, M.; Qi, M. Molecular identification of Cryptosporidium spp. in alpacas (Vicugna pacos) in China. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 12, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Environmental Transport of Emerging Human-Pathogenic Cryptosporidium Species and Subtypes through Combined Sewer Overflow and Wastewater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00682-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koehler, A.V.; Wang, T.; Haydon, S.R.; Gasser, R.B. Cryptosporidium viatorum from the native Australian swamp rat Rattus lutreolus-An emerging zoonotic pathogen? Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2018, 7, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Zheng, W.-B.; Zhang, N.-Z.; Gui, B.-Z.; Lv, Q.-Y.; Yan, J.-Q.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, G.-H. Identification of Cryptosporidium viatorum XVa subtype family in two wild rat species in China. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Rao, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Yi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Cryptosporidium spp. in wild rats (Rattus spp.) from the Hainan Province, China: Molecular detection, species/genotype identification and implications for public health. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Elwin, K.; Winiecka-Krusnell, J.; Chalmers, R.M.; Xiao, L.; Lebbad, M. Development and Application of a gp60-Based Typing Assay for Cryptosporidium viatorum. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Alderisio, K.A.; Xiao, L. Distribution of Cryptosporidium Genotypes in storm event water samples from three watersheds in New York. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4446–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Alderisio, K.A.; Yang, W.; Blancero, L.A.; Kuhne, W.G.; Nadareski, C.A.; Reid, M.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium Genotypes in Wildlife from a New York Watershed. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6475–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, G.; Wright, S.; Elwin, K.; Hadfield, S.J.; Katzer, F.; Bartley, P.M.; Hunter, P.R.; Nath, M.; Innes, E.A.; Chalmers, R.M. Redescription of Cryptosporidium cuniculus Inman and Takeuchi, 1979 (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae): Morphology, biology and phylogeny. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, S.J.; Chalmers, R.M. Detection and characterization of Cryptosporidium cuniculus by real-time PCR. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, D.; Roellig, D.; Arafat, N.; Xiao, L. Genetic Characterization of Cryptosporidium cuniculus from Rabbits in Egypt. Pathogens 2021, 10, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, A.V.; Rashid, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Vaughan, J.L.; Gasser, R.B.; Jabbar, A. First cross-sectional, molecular epidemiological survey of Cryptosporidium, Giardia and Enterocytozoon in alpaca (Vicugna pacos) in Australia. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaupke, A.; Kwit, E.; Chalmers, R.; Michalski, M.; Rzeżutka, A. An outbreak of massive mortality among farm rabbits associated with Cryptosporidium infection. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, W.; Deng, J.; Niu, L.; Wang, Q.; Peng, G. New Subtype of Cryptosporidium cuniculus Isolated from Rabbits by Sequencing the Gp60 Gene. J. Parasitol. 2014, 100, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, M.; Jing, B.; Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Wei, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L. Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis, and Enterocytozoon bieneusi in Rabbits in Xinjiang, China. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, A.; Ling, H.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Shu, J.; Zhang, L. Cryptosporidium cuniculus and Giardia duodenalis in Rabbits: Genetic Diversity and Possible Zoonotic Transmission. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Cao, J.; Zhao, W.; Gong, B.; Yan, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, A.; Shen, Y. Multilocus sequence typing and population genetic structure of Cryptosporidium cuniculus in rabbits in Heilongjiang Province, China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 64, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kváč, M.; Hofmannová, L.; Hlásková, L.; Květoňová, D.; Vítovec, J.; McEvoy, J.; Sak, B. Cryptosporidium erinacei n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) in hedgehogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 201, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laatamna, A.E.; Wagnerová, P.; Sak, B.; Květoňová, D.; Aissi, M.; Rost, M.; Kváč, M. Equine cryptosporidial infection associated with Cryptosporidium hedgehog genotype in Algeria. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 197, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyachenko, V.; Kuhnert, Y.; Schmaeschke, R.; Etzold, M.; Pantchev, N.; Daugschies, A. Occurrence and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. genotypes in European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus L.) in Germany. Parasitology 2010, 137, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmannová, L.; Hauptman, K.; Huclová, K.; Květoňová, D.; Sak, B.; Kváč, M. Cryptosporidium erinacei and C. parvum in a group of overwintering hedgehogs. Eur. J. Protistol. 2016, 56, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prediger, J.; Horčičková, M.; Hofmannová, L.; Sak, B.; Ferrari, N.; Mazzamuto, M.V.; Romeo, C.; Wauters, L.A.; McEvoy, J.; Kváč, M. Native and introduced squirrels in Italy host different Cryptosporidium spp. Eur. J. Protistol. 2017, 61 Pt A, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, M.L.; Cheung-Kwok-Sang, C.; Slade, M.; Williamson, S. Cryptosporidium fayeri: Diversity within the GP60 locus of isolates from different marsupial hosts. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 121, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, Y.; Takami, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Nakaya, T.; Murakoshi, F. Molecular identification of Cryptosporidium isolates from ill exotic pet animals in Japan including a new subtype in Cryptosporidium fayeri. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 21, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Lv, C.; Qi, M. Molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. in minks (Neovison vison), blue foxes (Vulpes lagopus), and raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) in farms from Xinjiang, Northwest China. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3923–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Lal, A.A.; Li, N.; Xiao, L. Subtypes of Cryptosporidium spp. in mice and other small mammals. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettwiler, I.; Troell, K.; Robinson, G.; Chalmers, R.M.; Basso, W.; Rentería-Solís, Z.M.; Daugschies, A.; Mühlethaler, K.; Dale, M.I.; Raghavendra, J.B.; et al. TIDE Analysis of Cryptosporidium Infections by gp60 Typing Reveals Obscured Mixed Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanta, C.A.; Bessonov, K.; Robinson, G.; Troell, K.; Guy, R.A. CryptoGenotyper: A new bioinformatics tool for rapid Cryptosporidium identification. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2021, 23, e00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braima, K.; Zahedi, A.; Egan, S.; Austen, J.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y.; Witham, B.; Pingault, N.; Perera, S.; Oskam, C.; et al. Molecular analysis of cryptosporidiosis cases in Western Australia in 2019 and 2020 supports the occurrence of two swimming pool associated outbreaks and reveals the emergence of a rare C. hominis IbA12G3 subtype. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 92, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayak, S.; Pawlowic, M.C.; Sateriale, A.; Brooks, C.F.; Studstill, C.J.; Bar-Peled, Y.; Cipriano, M.J.; Striepen, B. Genetic modification of the diarrhoeal pathogen Cryptosporidium parvum. Nature 2015, 523, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangah, S.J.; Katalani, C.; Booneh, H.A.; Hajizade, A.; Sijercic, A.; Ahmadian, G. CRISPR-Based Diagnosis of Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases. Biol. Proced. Online 2020, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. CRISPR/Cas12a-based on-site diagnostics of Cryptosporidium parvum IId-subtype-family from human and cattle fecal samples. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Comparative genomics: How has it advanced our knowledge of cryptosporidiosis epidemiology? Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 3195–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, R.; Cooper, G.; Kissinger, J. Challenges for Cryptosporidium Population Studies. Genes 2021, 12, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Comparative genomic analysis of three intestinal species reveals reductions in secreted pathogenesis determinants in bovine-specific and non-pathogenic Cryptosporidium species. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, e000379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Jin, C.; Wu, H.; Fei, J.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Differential expression of three Cryptosporidium species-specific MEDLE Proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, K.; Rowe, L.A.; Li, N.; Roellig, D.M.; Knipe, K.; Frace, M.; Yang, C.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Comparative genomic analysis reveals occurrence of genetic recombination in virulent Cryptosporidium hominis subtypes and telomeric gene duplications in Cryptosporidium parvum. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pallen, M.J. Diagnostic metagenomics: Potential applications to bacterial, viral and parasitic infections. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, R.J.; Merida, A.M.; Carneiro, M. Unleashing the potential of public genomic resources to find parasite genetic data. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beghini, F.; Pasolli, E.; Truong, T.D.; Putignani, L.; Cacciò, S.M.; Segata, N. Large-scale comparative metagenomics of Blastocystis, a common member of the human gut microbiome. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2848–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franssen, F.F.J.; Janse, I.; Janssen, D.; Caccio, S.M.; Vatta, P.; van der Giessen, J.W.B.; van Passel, M.W.J. Mining public metagenomes for environmental surveillance of parasites: A proof of principle. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Species Name | Main Reservoir Hosts | Reports in Humans |
|---|---|---|
| C. hominis | Non-human primates, donkeys | Most common species in humans |
| C. parvum | Ruminants, wildlife | Second most common species in humans |
| C. meleagridis | Birds | Third most commonly reported species in humans |
| C. felis | Cats | Commonly reported [40] |
| C. canis (previously canine genotype) | Dog | Commonly reported [40] |
| C. ubiquitum (previously cervine genotype) | Ruminants, rodents, carnivores, non-human primates | Commonly reported [31,44,51,52] |
| C. cuniculus (previously rabbit genotype) | Rabbits | Many reports in humans [51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] |
| C. viatorum | Rodents | [34,51,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74] |
| Chipmunk genotype I | Rodents | [37,45,51,60,71,72,75,76,77] |
| C. muris | Rodents | [52,60,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89] |
| C. andersoni (previously C. muris-like genotype) | Cattle | [65,81,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97] |
| C. suis (previously pig genotype I) | Pigs, wild boars | [79,96,98,99,100,101,102,103] |
| Horse genotype | Horses | [51,58,82,104,105] |
| C. erinacei (previously hedgehog genotype) | Hedgehogs, horses | [51,53,54,106,107] |
| C. bovis (previously bovine B genotype) | Cattle | [78,108,109,110] |
| Skunk genotype | Skunk | [37,82,105,111,112] |
| C. tyzzeri (previously mouse genotype I) | Rodents | [43,54,113] |
| C. occultus (previously C. suis-like genotype and C. parvum VF383) | Rodents | Refs. [114,115] Unpublished report in a human in GenBank (HQ822146) |
| C. ditrichi | Rodents (mainly mice) | [51,116] |
| Mink genotype | Mink | [117,118] |
| C. fayeri (previously marsupial genotype I) | Marsupials | [119,120] |
| C. xiaoi (previously C. bovis-like genotype) | Sheep, goats | [34] |
| C. scrofarum (previously pig genotype II) | Pigs, wild boar | [121] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryan, U.; Zahedi, A.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. An Update on Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Genotypes in Humans. Animals 2021, 11, 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113307
Ryan U, Zahedi A, Feng Y, Xiao L. An Update on Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Genotypes in Humans. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113307
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyan, Una, Alireza Zahedi, Yaoyu Feng, and Lihua Xiao. 2021. "An Update on Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Genotypes in Humans" Animals 11, no. 11: 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113307
APA StyleRyan, U., Zahedi, A., Feng, Y., & Xiao, L. (2021). An Update on Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species and Genotypes in Humans. Animals, 11(11), 3307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113307








