Microbial Biogeography along the Gastrointestinal Tract Segments of Sympatric Subterranean Rodents (Eospalax baileyi and Eospalax cansus)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Habitat Suitability Analysis of the Plateau Zokor and the Gansu Zokor
2.1.1. Data Collection on the Geographical Distribution of the Two Species
2.1.2. Climate Data
2.1.3. Habitat Suitability Analysis of the Two Species Based on the MaxEnt Model
2.2. Samples Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.4. Amplicon Sequence Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Habitat Suitability Analysis of the Plateau Zokor and the Gansu Zokor
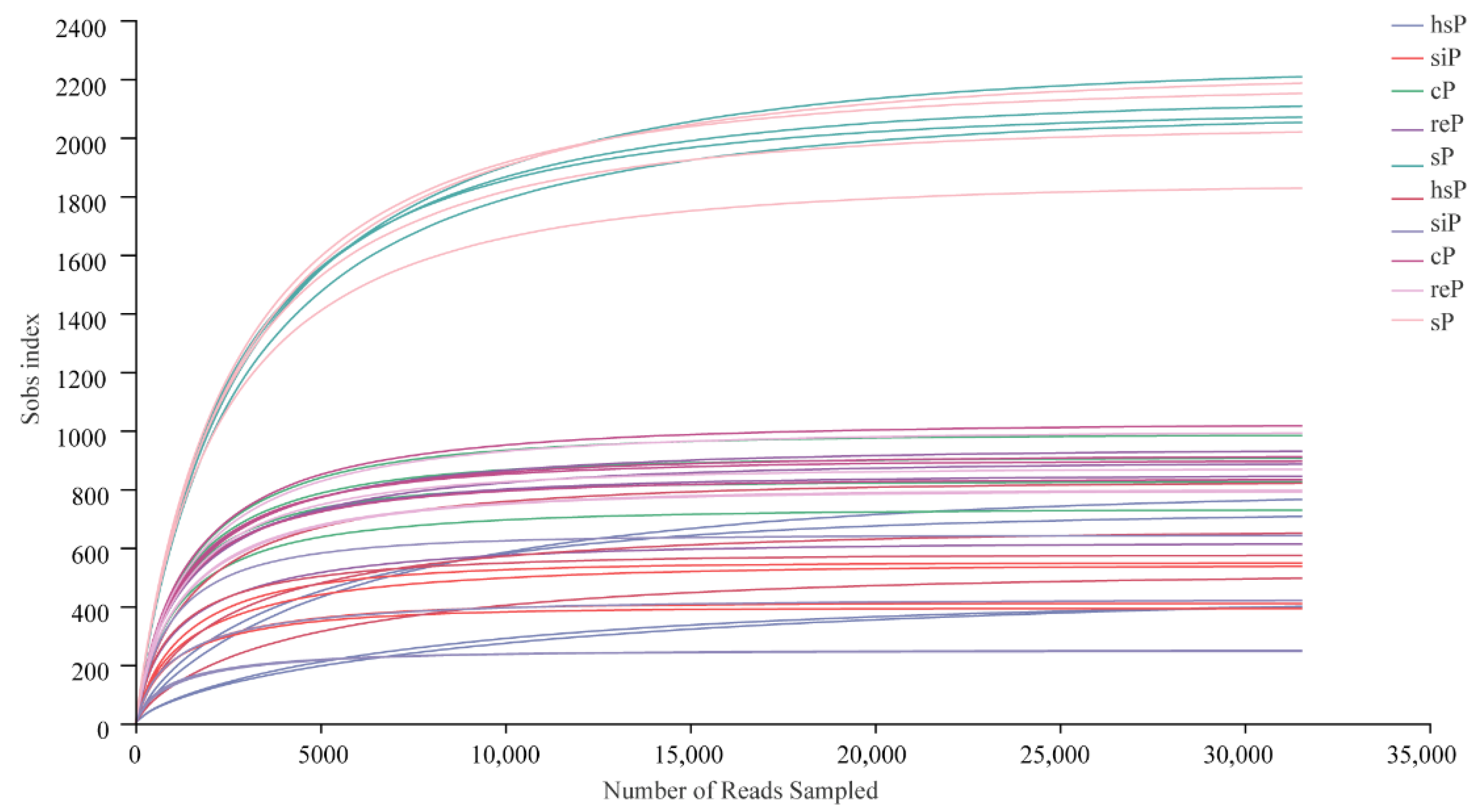
3.2. Sequencing Metrics
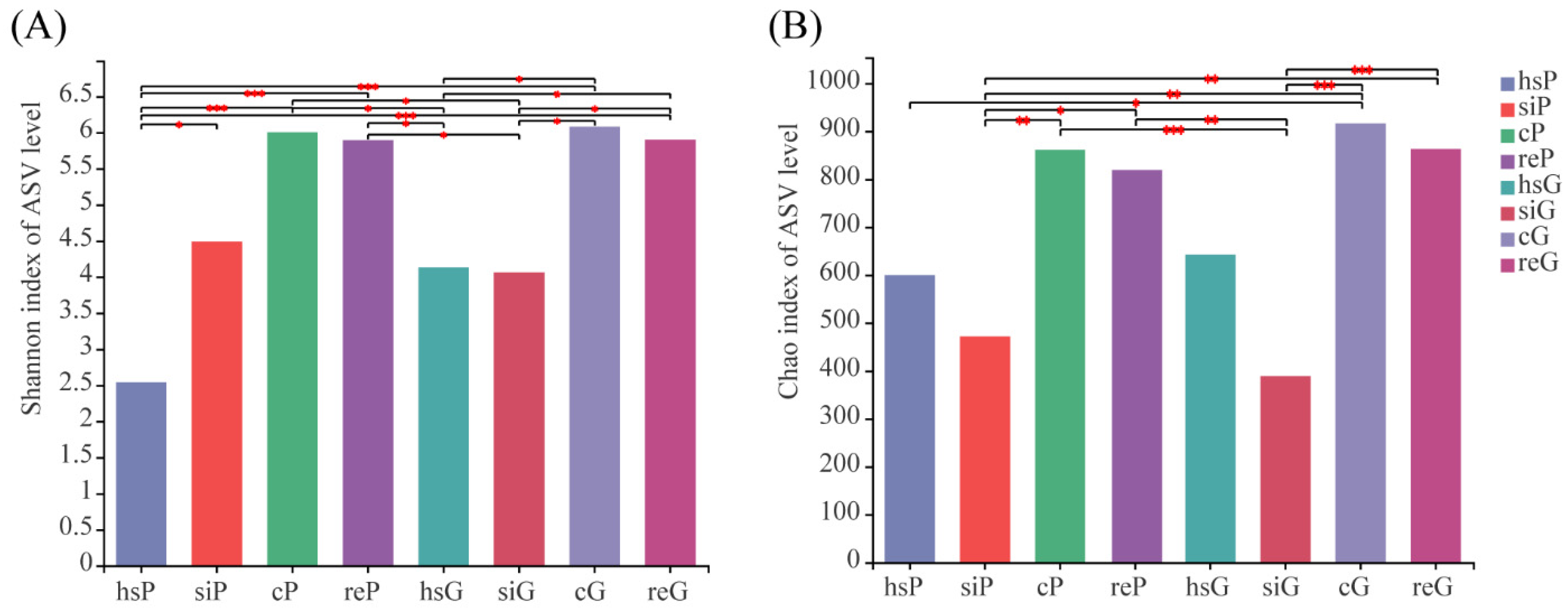
3.3. Alpha Diversity of the Bacterial Community in the Two Zokor Species’ GITs
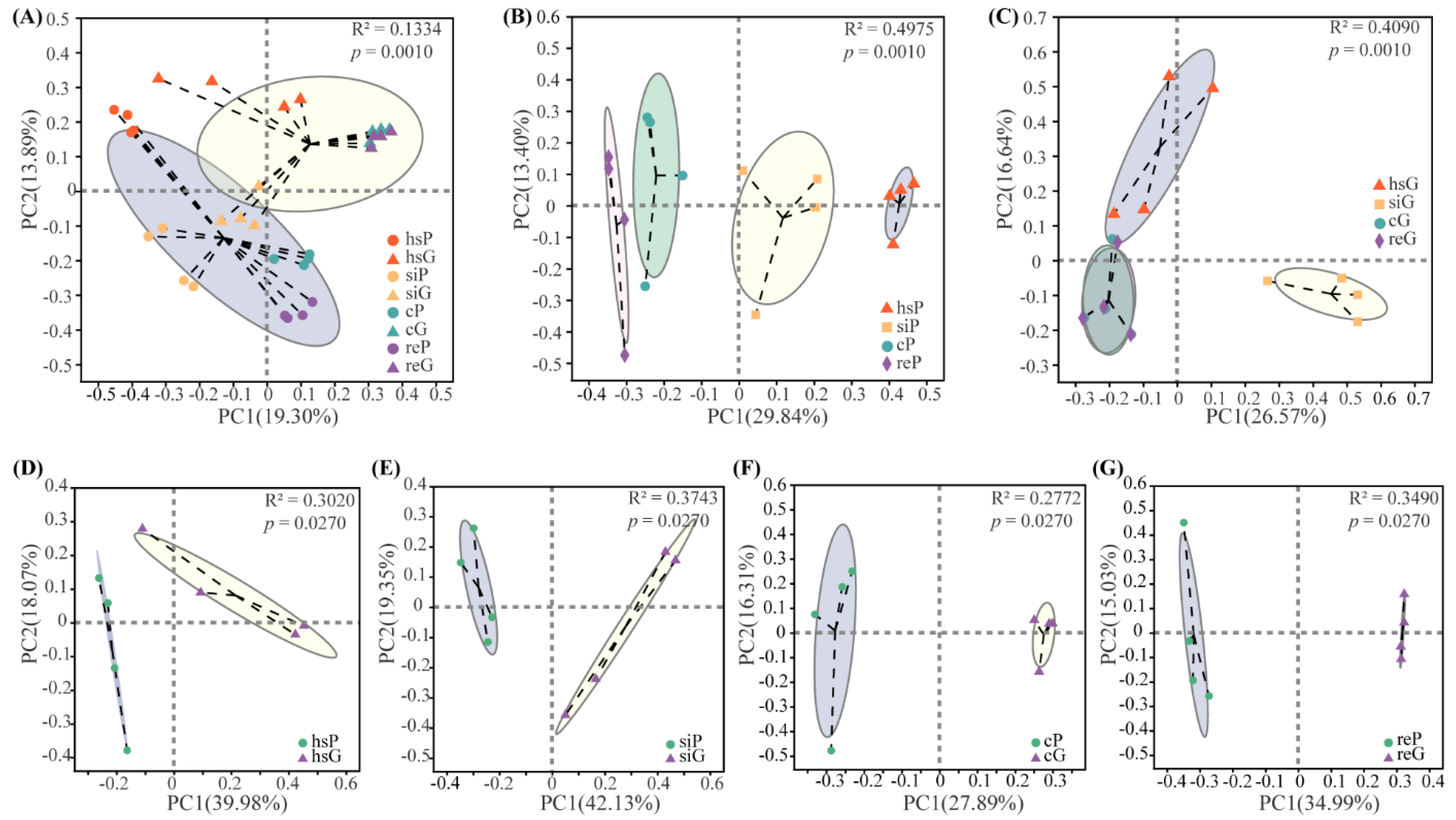
3.4. Beta Diversity of the Bacterial Community in the Two Zokor Species’ GITs
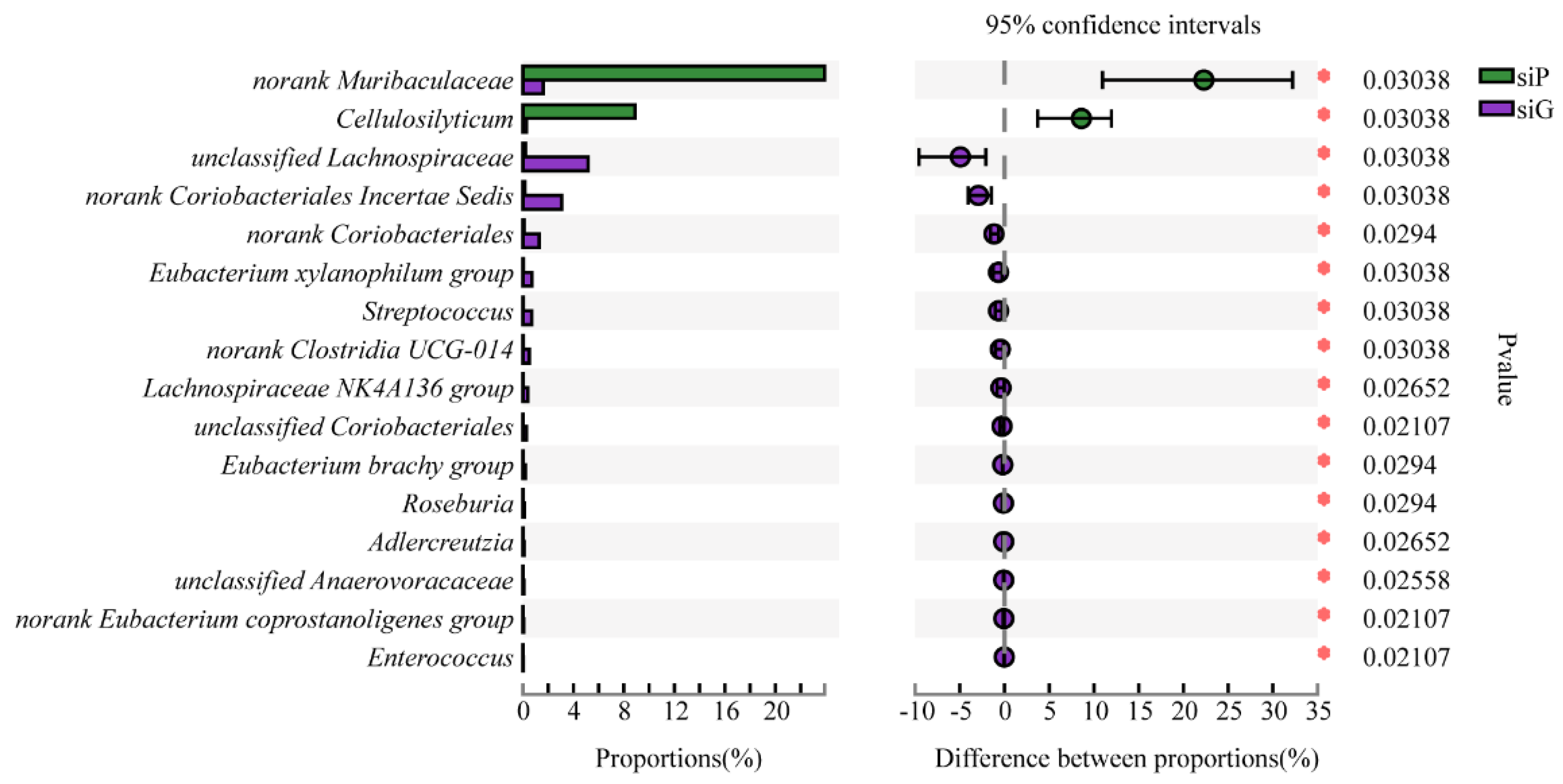
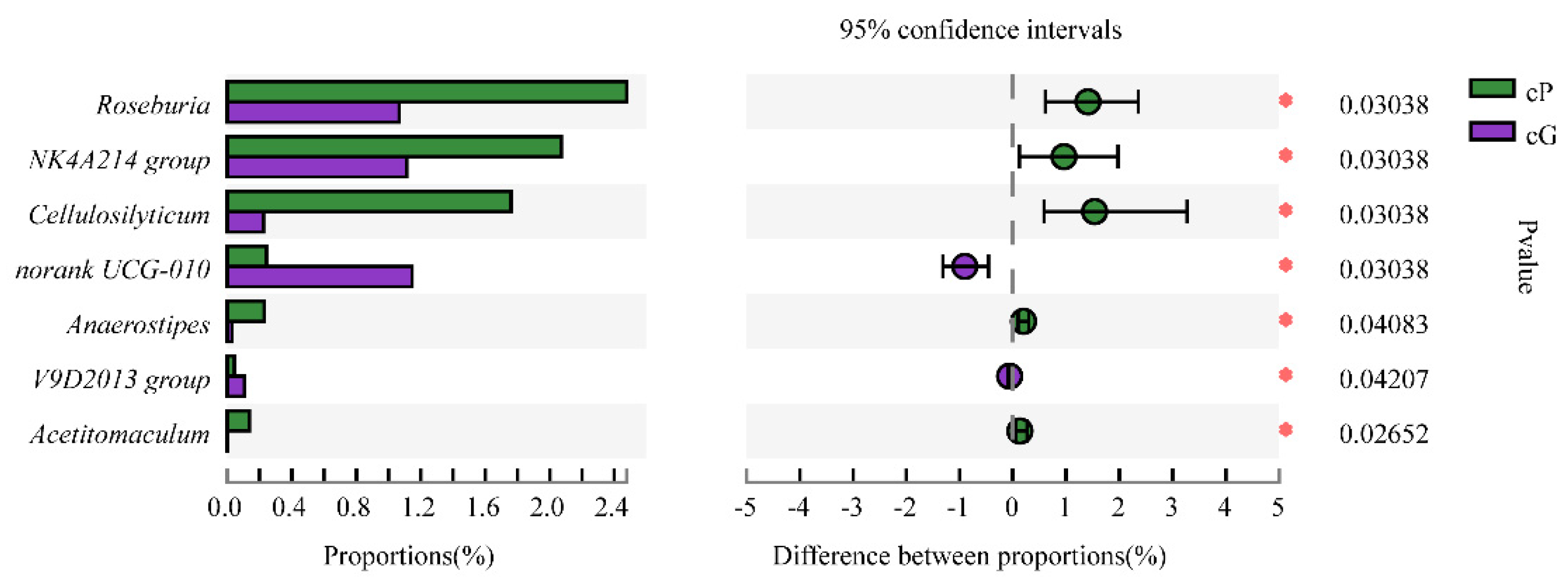
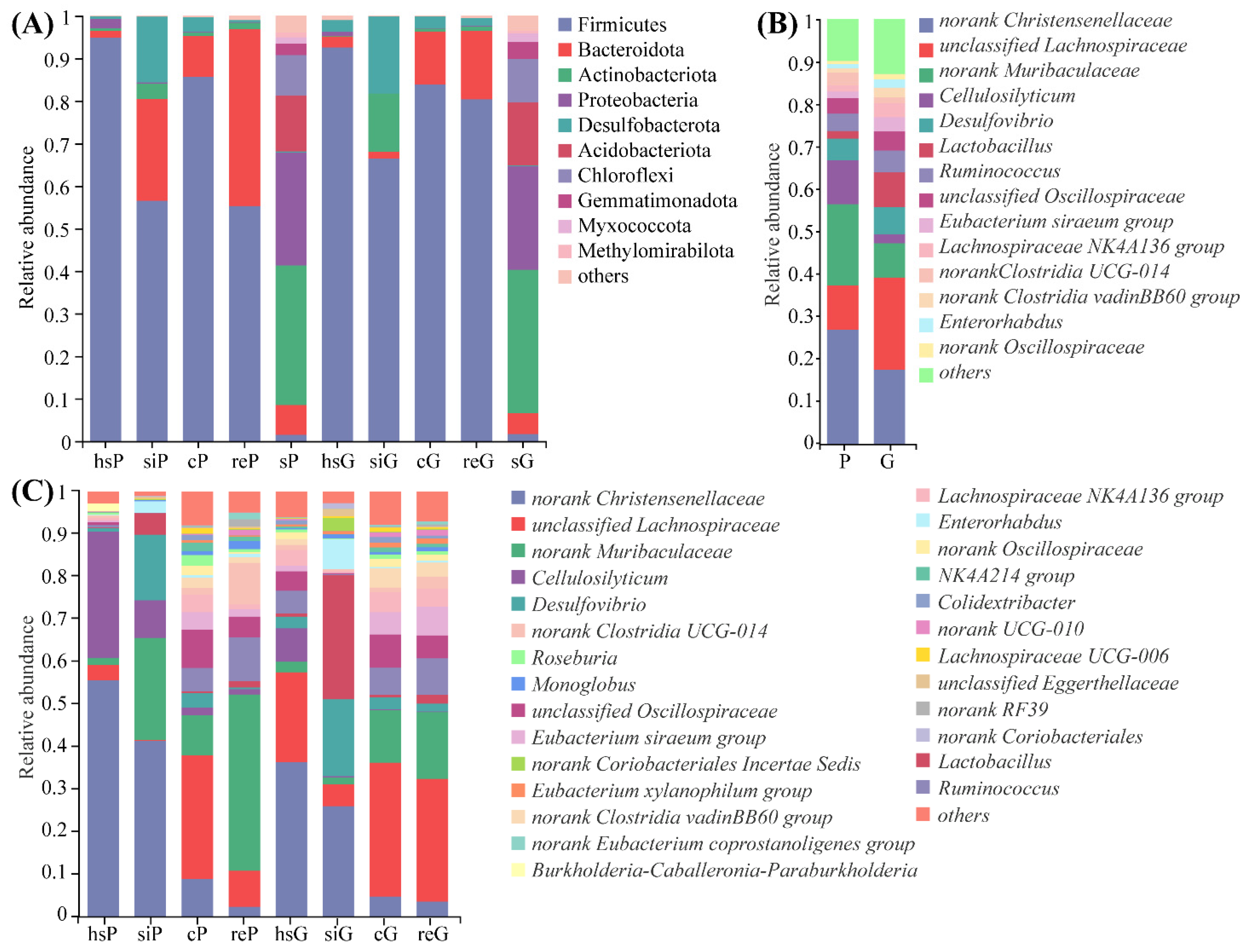
3.5. Microbiome Composition from the GITs of Zokors and Soil
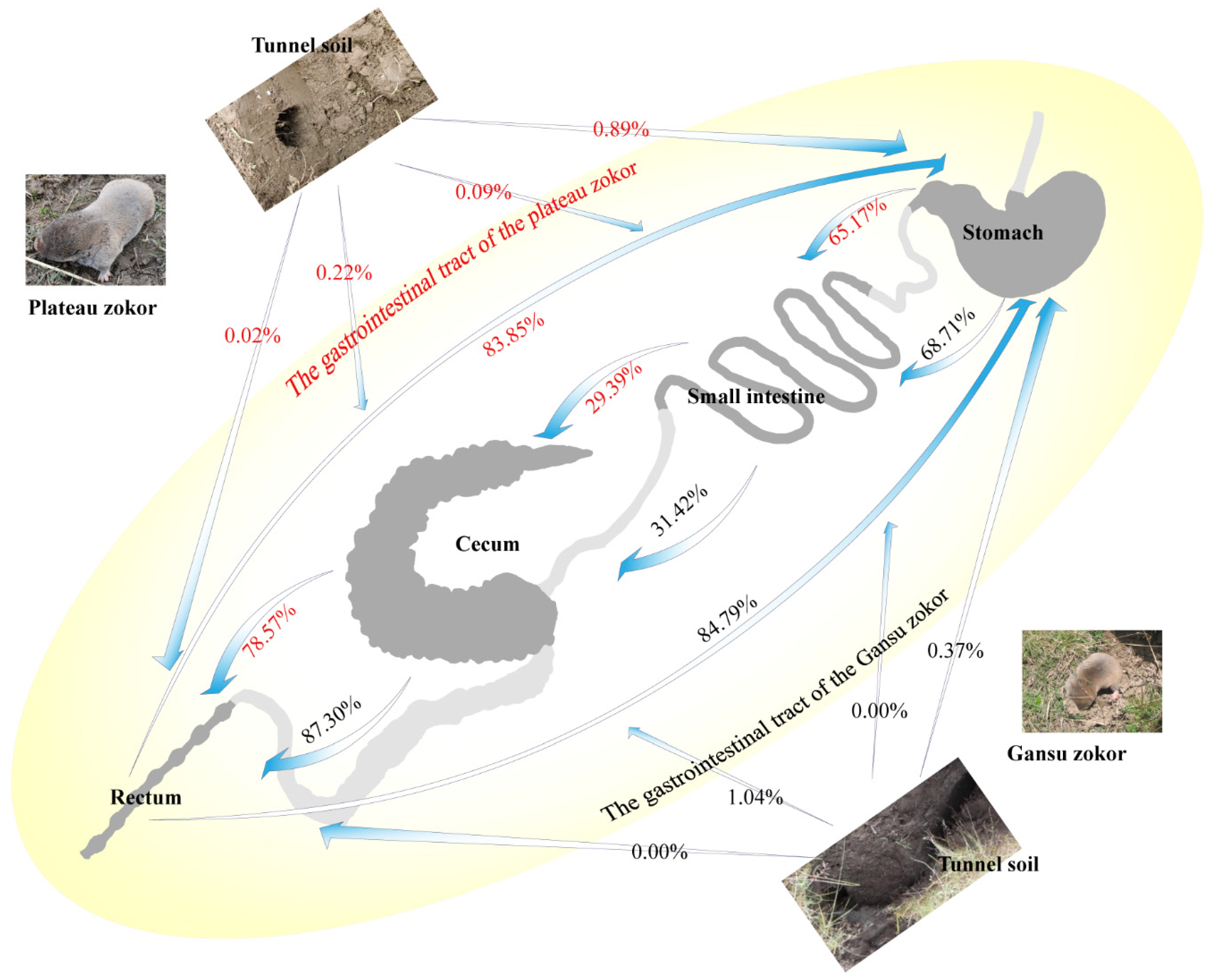
3.6. Microbial Source Tracking of the Different Segments in the Two Zokor Species’ GITs
4. Discussion
4.1. The Suitable Habitat of the Two Zokor Species
4.2. The Difference of the Microbial Communities between Zokor Species and among Segments of the GIT
4.3. Indications of Source Tracking Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Shapira, M. Gut microbiotas and host evolution: Scaling up symbiosis. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wei, C.; et al. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bo, T.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Kohl, K.D.; Wen, J.; Tian, S.J.; Wang, D.H. Coprophagy prevention alters microbiome, metabolism, neurochemistry, and cognitive behavior in a small mammal. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2625–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucker, R.M.; Bordenstein, S.R. The Hologenomic Basis of Speciation: Gut Bacteria Cause Hybrid Lethality in the Genus Nasonia. Science 2013, 341, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieneisen, L.E.; Charpentier, M.J.; Alberts, S.C.; Blekhman, R.; Bradburd, G.; Tung, J.; Archie, E.A. Genes, geology and germs: Gut microbiota across a primate hybrid zone are explained by site soil properties, not host species. Proc. R. Soc. B 2019, 286, 20190431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amato, K.R.; Sanders, J.G.; Song, S.J.; Nute, M.; Metcalf, J.L.; Thompson, L.R.; Morton, J.T.; Amir, A.; McKenzie, V.J.; Humphrey, G.; et al. Evolutionary trends in host physiology outweigh dietary niche in structuring primate gut microbiomes. ISME J. 2019, 13, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, V.L.; Tan, C.L.; Niu, K.; Yang, Y.; Knight, R.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, D.; Amato, K.R. Diet Versus Phylogeny: A Comparison of Gut Microbiota in Captive Colobine Monkey Species. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieneisen, L.; Muehlbauer, A.L.; Blekhman, R. Microbial control of host gene regulation and the evolution of host-microbiome interactions in primates. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, S.C.; Eccles, R.M.; Baltrunaite, L. Species identity dominates over environment in shaping the microbiota of small mammals. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Ley, R. Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Nelson, C.D.; Driver, J.D.; Elzo, M.A.; Penagaricano, F.; Jeong, K.C. Host genetics exerts lifelong effects upon hindgut microbiota and its association with bovine growth and immunity. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2306–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, A.T.; Dunn, R.R. Drivers of microbiome biodiversity: A review of general rules, feces, and ignorance. mBio 2018, 9, e01294-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anslan, S.; Li, H.; Kuenzel, S.; Vences, M. Microbiomes from feces vs. gut in tadpoles: Distinct community compositions between substrates and preservation methods. Salamandra 2021, 57, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Song, P.; Lin, G.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, T. Gut Microbiota plasticity influences the adaptability of wild and domestic animals in co-inhabited areas. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.X.; Song, P.F.; Yan, J.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Cai, Z.Y.; Xie, J.X.; Zhang, T.Z. Gut Microbiome Changes in Captive Plateau Zokors (Eospalax baileyi). Evol. Bioinform. 2021, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Characterization and Comparison of Microbiota in the Gastrointestinal Tracts of the Goat (Capra hircus) During Preweaning Development. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Li, T.; Berasategui, A.; Rui, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Xiao, Z.; Li, X. Gut region influences the diversity and interactions of bacterial communities in pikas (Ochotona curzoniae and Ochotona daurica). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, N.; Shi, Y. A revision of the zokors of subgenus Eospalax. Acta Theriol. Sin. 1982, 2, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Ji, W.; Howitt, R.; Hua, L.; Gleeson, D.; Duan, H. Novel microsatellite markers obtained from Gansu zokor (Eospalax cansus) and cross-species amplification in Plateau zokor (Eospalax baileyi). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 57, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Su, J.; Yao, B.; Ji, W.; Hegab, I.M.; Hanafy, A.M.; Zhang, D. Geometric morphometric analysis of the plateau zokor (Eospalax baileyi) revealed significant effects of environmental factors on skull variations. Zoology 2020, 140, 125779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Hao, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, W.; Lu, X.; Shi, P.; Wang, Y. ZokorDB: Tissue specific regulatory network annotation for non-coding elements of plateau zokor. Quant. Biol. 2020, 8, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, F.; Li, G.; Qin, W.; Wu, T.; Xu, F.; Hou, Y.; Song, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T. The four antelope species on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau face habitat loss and redistribution to higher latitudes under climate change. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, R.A. Use of Maximum Entropy Modeling in Wildlife Research. Entropy 2009, 11, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yi, L.; Hai, L.; Ming, L.; Gao, W.; Ji, R. Characterizing the bacterial microbiota in different gastrointestinal tract segments of the Bactrian camel. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, A.; Waqas, M.; Gao, X.; Li, K.; Xie, G.; Zhang, J.; Mehmood, K.; Zhao, S.; et al. Characterization of the microbial community structure in intestinal segments of yak (Bos grunniens). Anaerobe 2020, 61, 102115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Luo, R.; Gong, G.; Wang, Y.; Gesang, Z.; Wang, K.; Xu, Z.; Suolang, S. Characterization of Metagenome-Assembled Genomes and Carbohydrate-Degrading Genes in the Gut Microbiota of Tibetan Pig. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 595066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenhav, L.; Thompson, M.; Joseph, T.A.; Briscoe, L.; Furman, O.; Bogumil, D.; Mizrahi, I.; Pe’er, I.; Halperin, E. FEAST: Fast expectation-maximization for microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huws, S.A.; Edwards, J.E.; Kim, E.J.; Scollan, N.D. Specificity and sensitivity of eubacterial primers utilized for molecular profiling of bacteria within complex microbial ecosystems. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 70, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Rubio, V. ggplot2-elegant graphics for data analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 77, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Du, Y.; Lin, G.; Su, J.; Zhang, T. Histological structure comparison of the small intestine between Gansu zokor (Myospalax cansus) and plateau zokor (Myospalax baileyi). Acta Theriol. Sin. 2013, 33, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Deng, X.; Zhang, T.; Su, J.; Lin, G. Molecular authentication of Sailonggu and its resource distribution in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2015, 40, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.P.; Lai, Y.C.; Huang, S.W.; Chen, H.C.; Hsieh, C.H.; Yu, H.T. Spatial heterogeneity of gut microbiota reveals multiple bacterial communities with distinct characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiorka, A.; Dahlke, F.; Morgulis, M.S. Broiler adaptation to post-hatching period. Ciência Rural 2006, 36, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohl, K.D.; Miller, A.W.; Marvin, J.E.; Mackie, R.; Dearing, M.D. Herbivorous rodents (Neotoma spp.) harbour abundant and active foregut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2869–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Liang, N.; Zhang, X.; Han, C.; Nan, X. Functional differentiation related to decomposing complex carbohydrates of intestinal microbes between two wild zokor species based on 16SrRNA sequences. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Chi, X.; Qin, W.; Wang, L.; Song, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Comparison of the gut microbiota composition between the wild and captive Tibetan wild ass (Equus kiang). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z. Variations in the gut microbiota of sympatric Francois’ langurs and rhesus macaques living in limestone forests in southwest Guangxi, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasov, W.H.; Martinez del Rio, C.; Caviedes-Vidal, E. Ecological physiology of diet and digestive systems. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011, 73, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Du, Y.; Xie, J.; Cui, X.; Su, J.; Zhang, T. Morphological differences of internal organs in two species of zokor and their significance in classification. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2012, 32, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbán, A.; Abellán, J.J.; Jiménez-Hernández, N.; Ponce, M.; Ponce, J.; Sala, T.; D’Auria, G.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A.J. Assessing gut microbial diversity from feces and rectal mucosa. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 61, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingala, M.R.; Simmons, N.B.; Wultsch, C.; Krampis, K.; Speer, K.A.; Perkins, S.L. Comparing microbiome sampling methods in a wild mammal: Fecal and intestinal samples record different signals of host ecology, evolution. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, T.W.; Baer, J.G.; Ward, J.E. Direct Comparison of Fecal and Gut Microbiota in the Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Discourages Fecal Sampling as a Proxy for Resident Gut Community. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 81, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, T.; Yao, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wirth, S.; Cao, W.; Lin, Q.; Li, X. Pika Gut May Select for Rare but Diverse Environmental Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Li, W.; Nevo, E.; Su, J.; Zhang, T. Adaptive evolution of flaky thumb claw and elongated compulsory arousal duration in the subterranean rodent plateau zokor. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2011, 23, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, N.M.; Niehus, R.; Foster, K.R. Evolutionary limits to cooperation in microbial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17941–17946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuzawa, T.; Nakata, M.; Tsushima, M. Feeding and excretion in the Afghan pika (Ochotona rufescens rufescens), a new laboratory animal. Lab. Anim. 1981, 15, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Taxonomic Units | Plateau Zokor | Gansu Zokor | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIT (Gastrointestinal Tract) | Tunnel Soil | Share | GIT | Tunnel Soil | Share | ||
| Phylum | 15 | 36 | 12 | 11 | 34 | 10 | 39 |
| Class | 29 | 104 | 21 | 21 | 96 | 15 | 117 |
| Order | 75 | 224 | 49 | 53 | 207 | 28 | 271 |
| Family | 123 | 332 | 72 | 81 | 320 | 35 | 429 |
| Genus | 255 | 582 | 101 | 159 | 584 | 39 | 872 |
| ASV(amplicon sequence variant) | 4319 | 4774 | 101 | 3646 | 4568 | 28 | 15,046 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Yan, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, F.; Song, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T. Microbial Biogeography along the Gastrointestinal Tract Segments of Sympatric Subterranean Rodents (Eospalax baileyi and Eospalax cansus). Animals 2021, 11, 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113297
Liu D, Yan J, Wang H, Jiang F, Song P, Cai Z, Zhang T. Microbial Biogeography along the Gastrointestinal Tract Segments of Sympatric Subterranean Rodents (Eospalax baileyi and Eospalax cansus). Animals. 2021; 11(11):3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113297
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Daoxin, Jingyan Yan, Haijing Wang, Feng Jiang, Pengfei Song, Zhenyuan Cai, and Tongzuo Zhang. 2021. "Microbial Biogeography along the Gastrointestinal Tract Segments of Sympatric Subterranean Rodents (Eospalax baileyi and Eospalax cansus)" Animals 11, no. 11: 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113297
APA StyleLiu, D., Yan, J., Wang, H., Jiang, F., Song, P., Cai, Z., & Zhang, T. (2021). Microbial Biogeography along the Gastrointestinal Tract Segments of Sympatric Subterranean Rodents (Eospalax baileyi and Eospalax cansus). Animals, 11(11), 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113297






