Lung Ultrasound for Imaging of B-Lines in Dogs and Cats—A Prospective Study Investigating Agreement between Three Types of Transducers and the Accuracy in Diagnosing Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema, Pneumonia and Lung Neoplasia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Ultrasound Examination and Classification of Patients
- -
- left ventricular M-mode systolic or diastolic dimensions exceeding reference values for the given body weight,
- -
- LA/Ao > 2.1,
- -
- fractional shortening (FS) < 20%,
- -
- left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Animals
3.2. Agreement between Results Obtained by Different USG Transducers
3.2.1. B-Lines
3.2.2. A-Lines
3.3. Accuracy of LUSscore in 3 Main Conditions Causing Dyspnea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buda, N.; Kosiak, W.; Radzikowska, E.; Olszewski, R.; Jassem, E.; Grabczak, E.M.; Pomiecko, A.; Piotrkowski, J.; Piskunowicz, M.; Sołtysiak, M.; et al. Polish Recommendations for Lung Ultrasound in Internal Medicine (POLLUS-IM). J. Ultrason. 2018, 18, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Lisciandro, G.R.; Ware, W.A.; Miles, K.G.; Viall, A.K.; DeFrancesco, T.C. Lung Ultrasonography Findings in Dogs with Various Underlying Causes of Cough. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2019, 255, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, S.R.; Lisciandro, G.R. The Use of Ultrasound for Dogs and Cats in the Emergency Room. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pracr. 2013, 43, 773–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touw, H.R.; Parlevliet, K.L.; Beerepoot, M.; Schober, P.; Vonk, A.; Twisk, J.W.; Elbers, P.W.; Boer, C.; Tuinman, P.R. Lung Ultrasound Compared with Chest X-Ray in Diagnosing Postoperative Pulmonary Complications Following Cardiothoracic Surgery: A Prospective Observational Study. Anaesthesia 2018, 73, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzosi, T.; Mannucci, T.; Pistoresi, A.; Toma, F.; Tognetti, R.; Zini, E.; Domenech, O.; Auriemma, E.; Citi, S. Assessment of Lung Ultrasound B-Lines in Dogs with Different Stages of Chronic Valvular Heart Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisciandro, G.R.; Fulton, R.M.; Fosgate, G.T.; Mann, K.A. Frequency and Number of B-Lines Using a Regionally Based Lung Ultrasound Examination in Cats with Radiographically Normal Lungs Compared to Cats with Left-Sided Congestive Heart Failure: Assessment of B-Lines in Lung Ultrasound Examinations in Cats. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2017, 27, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademacher, N.; Pariaut, R.; Pate, J.; Saelinger, C.; Kearney, M.T.; Gaschen, L. Transthoracic Lung Ultrasound In Normal Dogs And Dogs With Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema: A Pilot Study: Transthoracic Ultrasound of the Lungs in Dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2014, 55, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Lisciandro, G.R.; DeFrancesco, T.C. Distribution of Alveolar-Interstitial Syndrome in Dogs and Cats with Respiratory Distress as Assessed by Lung Ultrasound versus Thoracic Radiographs: Distribution of Pathology Using Lung Ultrasound. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2018, 28, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivetta, E.; Goffi, A.; Lupia, E.; Tizzani, M.; Porrino, G.; Ferreri, E.; Volpicelli, G.; Balzaretti, P.; Banderali, A.; Iacobucci, A.; et al. Lung Ultrasound-Implemented Diagnosis of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure in the ED. Chest 2015, 148, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichtenstein, D. Fluid Administration Limited by Lung Sonography: The Place of Lung Ultrasound in Assessment of Acute Circulatory Failure (the FALLS-Protocol). Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2012, 6, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, O.; Hatipoglu, O.N.; Cagli, B.; Ermis, V. Sonography of the Chest Using Linear-Array versus Sector Transducers: Correlation with Auscultation, Chest Radiography, and Computed Tomography: US of the Chest. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2016, 44, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, D.A. Ultrasound in the Management of Thoracic Disease. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, S250–S261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisciandro, G.R.; Fosgate, G.T.; Fulton, R.M. Frequency and number of ultrasound lung rockets (B-lines) using a regionally based lung ultrasound examination named vet BLUE (veterinary bedside lung ultrasound exam) in dogs with radiographically normal lung findings Vet Radiol Ultrasound. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2014, 55, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciandro, G.R. Point-of-Care Ultrasound Techniques for the Small Animal Practitioner, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-119-46102-9. [Google Scholar]
- Baron Toaldo, M.; Romito, G.; Guglielmini, C.; Diana, A.; Pelle, N.G.; Contiero, B.; Cipone, M. Prognostic Value of Echocardiographic Indices of Left Atrial Morphology and Function in Dogs with Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Madron, E.; Domenech, O. Clinical Echocardiography of the Dog and Cat; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-323-31651-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kittleson, M.D.; Kienle, R.D. Small Animal Cardiovascular Medicine; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-8151-5140-1. [Google Scholar]
- Szaluś-Jordanow, O.; Stabińska-Smolarz, M.; Czopowicz, M.; Moroz, A.; Mickiewicz, M.; Łobaczewski, A.; Chrobak-Chmiel, D.; Kizerwetter-Świda, M.; Rzewuska, M.; Sapierzyński, R.; et al. Focused Cardiac Ultrasound Examination as a Tool for Diagnosis of Infective Endocarditis and Myocarditis in Dogs and Cats. Animals 2021, 11, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hew, M.; Tay, T.R. The Efficacy of Bedside Chest Ultrasound: From Accuracy to Outcomes. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2016, 25, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleiss, J.L.; Cohen, J.; Everitt, B.S. Large Sample Standard Errors of Kappa and Weighted Kappa. Psychol. Bull. 1969, 72, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greiner, M.; Pfeiffer, D.; Smith, R.D. Principles and Practical Application of the Receiver-Operating Characteristic Analysis for Diagnostic Tests. Prev. Vet. Med. 2000, 45, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.V.; Pan, J.; Rai, S.N.; Galandiuk, S. ROC-Ing along: Evaluation and Interpretation of Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves. Surgery 2016, 159, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, T.P.; Trigiani, M.; Zanforlin, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Zanobetti, M.; Sammicheli, L.; Conte, E.G.; Buggio, G.; Villari, L.; Corbetta, L.; et al. Competence in Thoracic Ultrasound. Panminerva Med. 2019, 61, 344–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gargani, L. Lung Ultrasound: A New Tool for the Cardiologist. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2011, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Goldstein, I.; Mourgeon, E.; Cluzel, P.; Grenier, P.; Rouby, J.-J. Comparative Diagnostic Performances of Auscultation, Chest Radiography, and Lung Ultrasonography in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Anesthesiology 2004, 100, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
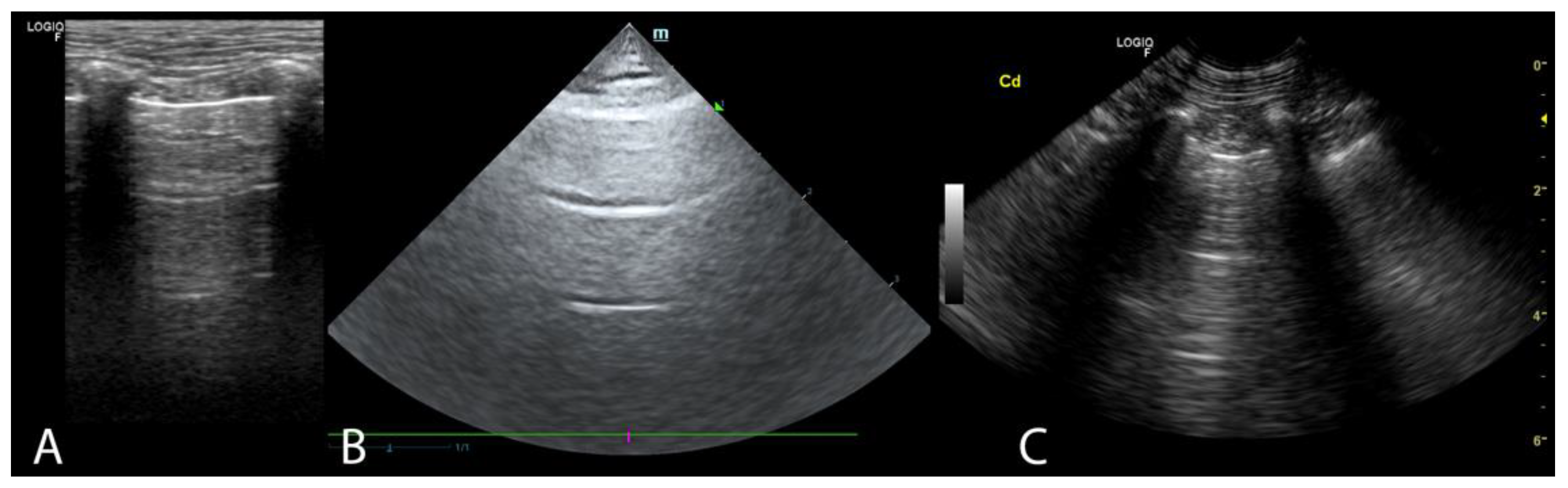


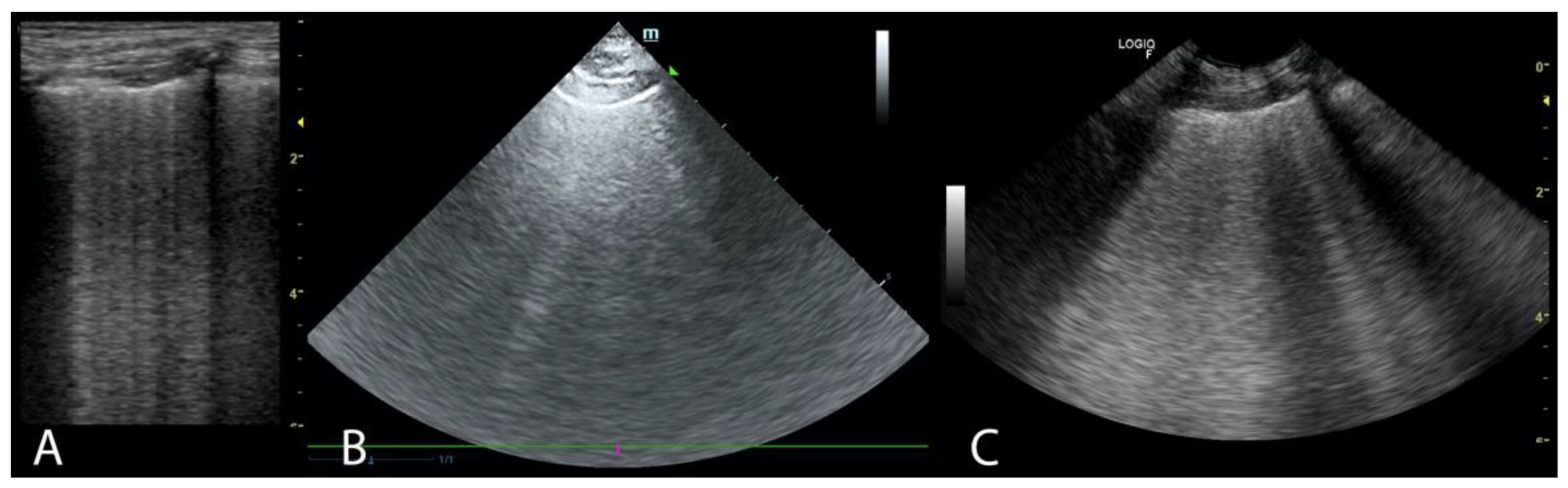


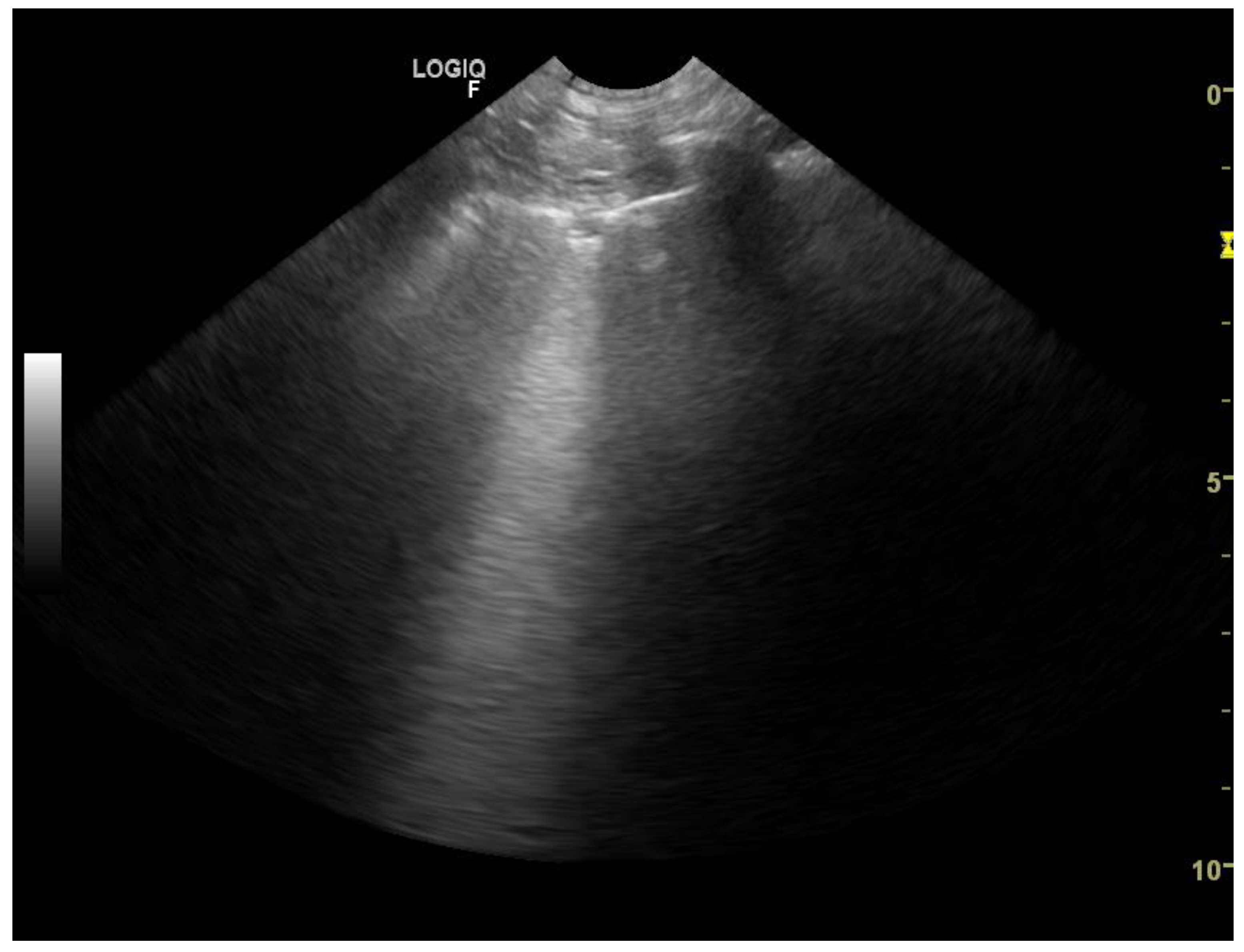



| 5-Point Classification of the Occurrence of B-Lines | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.9 |
| 4 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1 |
| Pair of Transducers Compared | Microconvex vs. Linear (n = 150) | Microconvex vs. Phased Array (n = 55) | Linear vs. Phased Array (n = 74) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized location of the transducers | Right side | Left side | Right side | Left side | Right side | Left side |
| caudodorsal | 1.00 (1.00, 1.00) | 0.993 (0.984, 1.00) | 0.930 (0.876, 0.983) | 0.947 (0.909, 0.986) | 0.942 (0.900, 0.984) | 0.941 (0.895, 0.986) |
| perihilar | 0.991 (0.980, 1.00) | 0.973 (0.951, 0.995) | 0.798 (0.666, 0.930) | 0.771 (0.636, 0.906) | 0.854 (0.757, 0.952) | 0.830 (0.723, 0.937) |
| middle | 0.972 (0.954, 0.990) | 0.988 (0.975, 1.00) | 0.771 (0.630, 0.911) | 0.828 (0.715, 0.940) | 0.770 (0.654, 0.886) | 0.844 (0.753, 0.935) |
| cranial | 0.981 (0.963, 0.999) | 0.991 (0.981, 1.00) | 0.895 (0.814, 0.975) | 0.915 (0.851, 0.979) | 0.886 (0.799, 0.973) | 0.929 (0.878, 0.979) |
| Pair of Transducers Compared | Microconvex vs. Linear (n = 76) | Microconvex vs. Phased Array (n = 33) | Linear vs. Phased Array (n = 48) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized location of the transducers | Right side | Left side | Right side | Left side | Right side | Left side |
| caudodorsal | 1.00 (1.00, 1.00) | 0.993 (0.978, 1.00) | 0.904 (0.815, 0.994) | 0.953 (0.903, 1.00) | 0.924 (0.859, 0.989) | 0.932 (0.860, 1.00) |
| perihilar | 0.994 (0.981, 1.00) | 0.967 (0.938, 0.995) | 0.828 (0.654, 1.00) | 0.767 (0.584, 0.949) | 0.886 (0.767, 1.00) | 0.846 (0.707, 0.986) |
| middle | 0.969 (0.943, 0.996) | 0.988 (0.971, 1.00) | 0.815 (0.619, 1.00) | 0.904 (0.786, 1.00) | 0.786 (0.630, 0.943) | 0.899 (0.802, 0.995) |
| cranial | 0.983 (0.964, 1.00) | 0.989 (0.973, 1.00) | 0.875 (0.751, 999) | 0.961 (0.916, 1.00) | 0.857 (0.727, 0.988) | 0.963 (0.927, 0.999) |
| Pair of Transducers Compared | Microconvex vs. Linear (n = 74) | Microconvex vs. Phased Array (n = 22) | Linear vs. Phased Array (n = 26) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardized location of the transducers | Right side | Left side | Right side | Left side | Right side | Left side |
| caudodorsal | 1.00 (1.00, 1.00) | 0.994 (0.981, 1.00) | 0.962 (0.914, 1.00) | 0.939 (0.878, 1.00) | 0.968 (0.927, 1.00) | 0.950 (0.899, 1.00) |
| perihilar | 0.987 (0.970, 1.00) | 0.978 (0.946, 1.00) | 0.756 (0.553, 0.959) | 0.774 (0.571, 0.977) | 0.799 (0.629, 0.970) | 0.796 (0.622, 0.970) |
| middle | 0.974 (0.948, 0.999) | 0.987 (0.969, 1.00) | 0.687 (0.483, 0.891) | 0.708 (0.497, 0.918) | 0.736 (0.569, 0.903) | 0.739 (0.557, 0.922) |
| cranial | 0.979 (0.947, 1.00) | 0.994 (0.981, 1.00) | 0.922 (0.849, 0.995) | 0.831 (0.690, 0.972) | 0.935 (0.871, 0.998) | 0.868 (0.745, 0.990) |
| Pair of Transducers. | No. of Pairs | Mean (±SD) Difference (CI 95%) | p-Value | Limits of Agreement (CI 95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Microconvex and linear | 150 | −0.09 ± 0.64 (−0.19, 0.02) | 0.102 | −1.3 (−1.5, −1.2) | 1.2 (1.0, 1.4) |
| Microconvex and phased array | 55 | 0.71 ± 2.92 (−0.08, 1.50) | 0.078 | −5.0 (−6.4, −3.7) | 6.4 (5.1, 7.8) |
| Linear and phased array | 74 | 0.73 ± 2.71 (0.10, 1.36) | 0.023 | −4.6 (−5.7, −3.5) | 6.0 (5.0, 7.1) |
| Pair of Transducers | No. of Pairs | Mean (SD) Difference | p-Value | Limits of Agreement (CI 95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Patients with cardiogenic pulmonary edema (n = 69) | |||||
| Microconvex and linear | 43 | −0.07 ± 0.86 (−0.33, 0.19) | 0.596 | −1.7 (−2.2, −1.3) | 1.6 (1.2, 2.1) |
| Microconvex and phased array | 17 | 0.29 ± 3.58 (−1.55, 2.14) | 0.739 | −6.7 (−9.9, −3.5) | 7.3 (4.1, 10.5) |
| Linear and phased array | 33 | 0.58 ± 2.93 (−0.46, 1.61) | 0.267 | −5.2 (−7.0, −5.2) | 6.3 (4.5, 8.1) |
| Patients with pneumonia (n = 63) | |||||
| Microconvex and linear | 59 | −0.14 ± 0.66 (−0.31, 0.04) | 0.117 | −1.4 (−1.7, −1.1) | 1.1 (0.9, 1.4) |
| Microconvex and phased array | 24 | 1.33 ± 3.10 (0.02, 2.64) | 0.046 | −4.8 (−7.0, −2.5) | 7.4 (5.2, 9.7) |
| Linear and phased array | 27 | 1.19 ± 3.06 (−0.03, 2.40) | 0.055 | −4.8 (−6.9, −2.7) | 7.2 (5.1, 9.3) |
| Patients with lung neoplasm (n = 53) | |||||
| Microconvex and linear | 36 | −0.06 ± 0.41 (−0.19, 0.08) | 0.422 | −0.9 (−1.1, −0.6) | 0.7 (0.5, 1.0) |
| Microconvex and phased array | 12 | 0.00 ± 1.13 (−0.72, 0.72) | 0.999 | −2.2 (−3.5, −1.0) | 2.2 (1.0, 3.5) |
| Linear and phased array | 12 | 0.08 ± 0.67 (−0.34, 0.51) | 0.674 | −1.2 (−2.0, −0.5) | 1.4 (0.7, 2.1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łobaczewski, A.; Czopowicz, M.; Moroz, A.; Mickiewicz, M.; Stabińska, M.; Petelicka, H.; Frymus, T.; Szaluś-Jordanow, O. Lung Ultrasound for Imaging of B-Lines in Dogs and Cats—A Prospective Study Investigating Agreement between Three Types of Transducers and the Accuracy in Diagnosing Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema, Pneumonia and Lung Neoplasia. Animals 2021, 11, 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113279
Łobaczewski A, Czopowicz M, Moroz A, Mickiewicz M, Stabińska M, Petelicka H, Frymus T, Szaluś-Jordanow O. Lung Ultrasound for Imaging of B-Lines in Dogs and Cats—A Prospective Study Investigating Agreement between Three Types of Transducers and the Accuracy in Diagnosing Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema, Pneumonia and Lung Neoplasia. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113279
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁobaczewski, Andrzej, Michał Czopowicz, Agata Moroz, Marcin Mickiewicz, Marta Stabińska, Hanna Petelicka, Tadeusz Frymus, and Olga Szaluś-Jordanow. 2021. "Lung Ultrasound for Imaging of B-Lines in Dogs and Cats—A Prospective Study Investigating Agreement between Three Types of Transducers and the Accuracy in Diagnosing Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema, Pneumonia and Lung Neoplasia" Animals 11, no. 11: 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113279
APA StyleŁobaczewski, A., Czopowicz, M., Moroz, A., Mickiewicz, M., Stabińska, M., Petelicka, H., Frymus, T., & Szaluś-Jordanow, O. (2021). Lung Ultrasound for Imaging of B-Lines in Dogs and Cats—A Prospective Study Investigating Agreement between Three Types of Transducers and the Accuracy in Diagnosing Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema, Pneumonia and Lung Neoplasia. Animals, 11(11), 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113279






