Italian Consumers’ Readiness to Adopt Eggs from Insect-Fed Hens
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Questionnaire
Conjoint Analyses
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Total Distribution
3.2. Willingness to Consume IFH Eggs
3.3. Eating Habits
3.4. Sustainable Food Choice
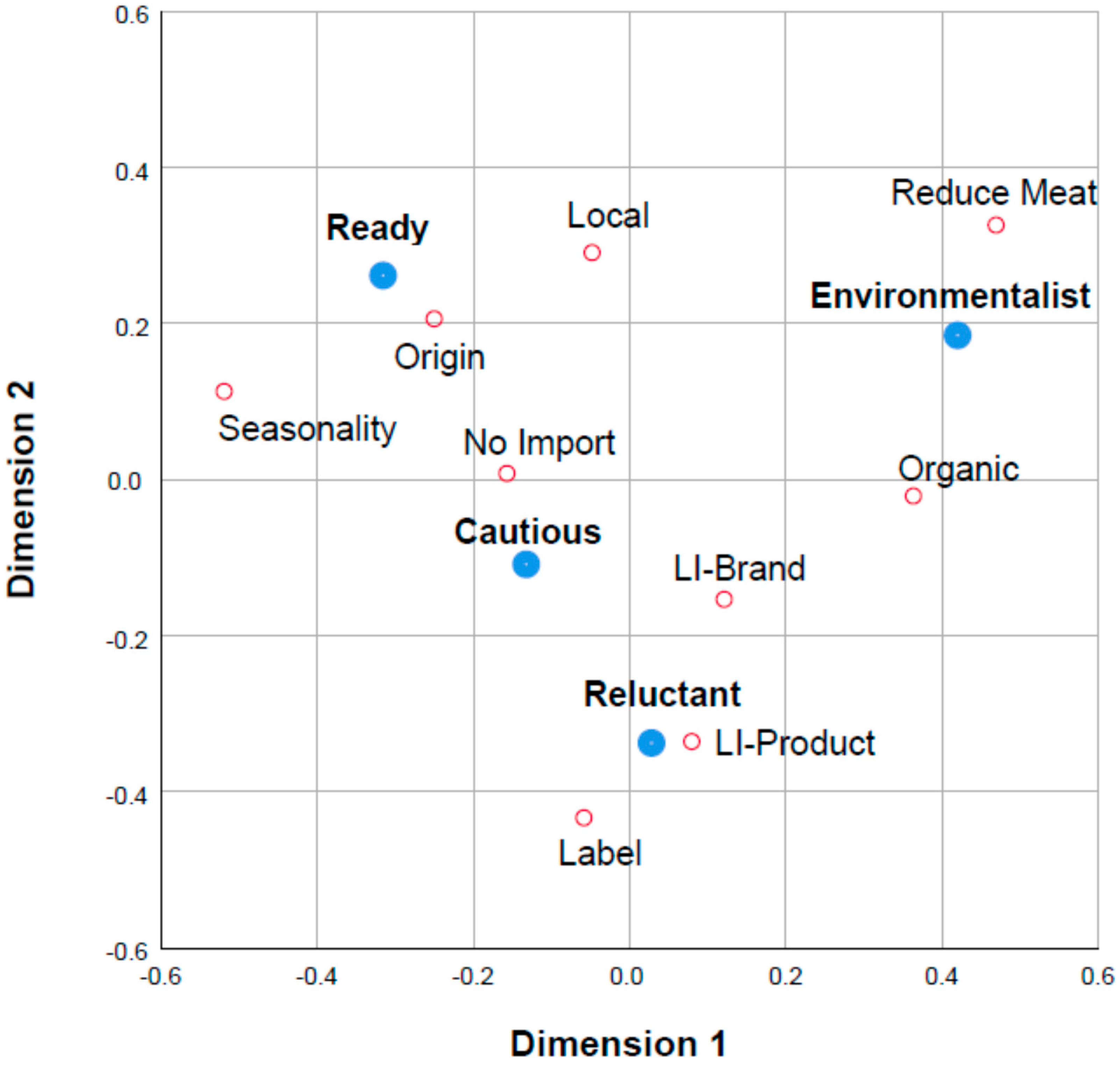
3.5. Egg Attributes That Guide Consumers’ Choices
3.6. Relative Importance of the Commercial Attributes and Part-Worth Utilities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guiné, R.P.F.; Correia, P.; Coelho, C.; Costa, C.A. The role of edible insects to mitigate challenges for sustainability. Open Agric. 2021, 6, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Visser, C.L.M.; Schreuder, R.; Stoddard, R. The EU’s dependency on soya bean import for the animal feed industry and potential for EU produced alternatives. OCL Oilseeds Fats Crop. Lipids 2014, 21, D407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spring, P. The challenge of cost effective poultry and animal nutrition: Optimizing existing and applying novel concepts. Lohmann Inf. 2013, 48, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsson, J.; Cederberg, C.; Sonesson, U.; Van Otterdijk, R.; Meybeck, A. Global Food Losses and Food Waste—Extent, Causes and Prevention; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011; ISBN 9789251072059. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, J.R.; Newton, R.W.; Tlusty, M.; Little, D.C. The rise of aquaculture by-products: Increasing food production, value, and sustainability through strategic utilisation. Mar. Policy 2018, 90, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieco, C.; Morrone, L.; Bertazza, G.; Cappellozza, S.; Saviane, A.; Gai, F.; Di Virgilio, N.; Rossi, F. The effect of strain and rearing medium on the chemical composition, fatty acid profile and carotenoid content in silkworm (Bombyx mori) pupae. Animals 2019, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch, G.; van Zanten, H.H.E.; Zamprogna, A.; Veenenbos, M.; Meijer, N.P.; van der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; van Loon, J. Conversion of organic resources by black soldier fly larvae: Legislation, efficiency and environmental impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinotti, L.; Giromini, C.; Ottoboni, M.; Tretola, M.; Marchis, D. Review: Insects and former foodstuffs for upgrading food waste biomasses/streams to feed ingredients for farm animals. Animal 2019, 13, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbi, S.; Macavei, L.I.; Fuso, A.; Luparelli, A.V.; Caligiani, A.; Ferrari, A.M.; Maistrello, L.; Montorsi, M. Valorization of seasonal agri-food leftovers through insects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, D.; Swift, J.A.; Field, L.M. Opportunities and hurdles of edible insects for food and feed. BNF Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Huis, A.; Oonincx, D.G. The environmental sustainability of insects as food and feed. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, E.; de Vries, W. Potential benefits of using Hermetia illucens frass as a soil amendment on food production and for environmental impact reduction. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 25, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, L.; Francia, E.; Pulvirenti, A.; Gigliano, S.; Zaccardelli, M.; Pane, C.; Caradonia, F.; Bortolini, S.; Maistrello, L.; Ronga, D. Use of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens (L.), Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae processing residue in peat-based growing media. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolini, S.; Macavei, L.I.; Saadoun, J.H.; Foca, G.; Ulrici, A.; Bernini, F.; Malferrari, D.; Setti, L.; Ronga, D.; Maistrello, L. Hermetia illucens (L.) larvae as chicken manure management tool for circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisinger, R. Innovative layer genetics to handle global challenges in egg production. Br. Poult. Sci. 2018, 59, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerema, A.; Peeters, A.; Swolfs, S.; Vandevenne, F.; Jacobs, S.; Staes, J.; Meire, P. Soybean Trade: Balancing Environmental and Socio-Economic Impacts of an Intercontinental Market. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Baek, Y.C.; Ryu, C.H.; Ji, S.Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, M.; Jung, H.; Kim, B. Effects of Dietary Inclusion Level of Microwave-Dried and Press-Defatted Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal on Productive Performance, Cecal Volatile Fatty Acid Profile, and Egg Quality in Laying Hens. Animals 2021, 11, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuel, M.; Sandrock, C.; Leiber, F.; Mathys, A.; Gold, M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Gangnat, I.D.M.; Kreuzer, M.; Terranova, M. Black soldier fly larvae meal and fat can completely replace soybean cake and oil in diets for laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhnke, I.; Normant, C.; Campbel, D.L.M.; Iqbal, Z.; Lee, C.; Hinch, G.N.; Roberts, J. Impact of on-range choice feeding with black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) on flock performance, egg quality, and range use of free-range laying hens. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejaei, M.; Cheng, K.M. The effect of including full-fat dried black soldier fly larvae in laying hen diet on egg quality and sensory characteristics. J. Insects Food Feed 2020, 6, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerini, F.; Alfnes, F.; Schjøll, A. Organic- and Animal Welfare-labelled Eggs: Competing for the Same Consumers. J. Agric. Econ. 2016, 67, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngo, H.M.; Moritaka, M. Consumer Attitudes and Acceptance of Insects as Food and Feed: A Review. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2021, 66, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Wassmann, B.; Siegrist, M.; Hartmann, C. Correlates of the willingness to consume insects: A meta-analysis. J. Insects Food Feed 2021, 7, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moruzzo, R.; Mancini, S.; Boncinelli, F.; Riccioli, F. Exploring the Acceptance of Entomophagy: A Survey of Italian Consumers. Insects 2021, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossey, A.T.; Tatum, J.T.; McGill, W.L. Modern insect-based food industry: Current status, insect processing technology, and recommendations moving forward. In Insects as Sustainable Food Ingredients Production, Processing and Food Applications; Dossey, A.T., Morales-Ramos, J.A., Rojas, M.G., Eds.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 113–152. ISBN 9780128028926. [Google Scholar]
- Culliford, A.; Bradbury, J. A cross-sectional survey of the readiness of consumers to adopt an environmentally sustainable diet. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, W.; Spranghers, T.; De Clercq, P.; De Smet, S.; Sas, B.; Eeckhout, M. Insects in animal feed: Acceptance and its determinants among farmers, agriculture sector stakeholders and citizens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 204, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliner, P.; Hobden, K. Development of a scale to measure neophobia in humans the trait of food. Appetite 1992, 19, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureati, M.; Spinelli, S.; Monteleone, E.; Dinnella, C.; Prescott, J.; Cattaneo, C.; Proserpio, C.; de Toffoli, A.; Gasperi, F.; Endrizzi, I.; et al. Associations between food neophobia and responsiveness to “warning” chemosensory sensations in food products in a large population sample. Food Qual. Prefer. 2018, 68, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISMEA. Il Comparto Delle Uova Da Consumo 2018; ISMEA (Italian Institute of Services for the Agricultural and Food Market), Direzione Servizi per lo Sviluppo Rurale, Unità Operativa Studi e Analisi: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EEC) No 1274/91 of 15 May 1991 introducing detailed rules for implementing Regulation (EEC) No 1907/90 on certain marketing standards for eggs. Off. J. L 1991, 121, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Council Regulation (EEC) No 2092/91 of 24 June 1991 on organic production of agricultural products and indications referring thereto on agricultural products and foodstuffs. Off. J. L 1991, 198, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mesıas, F.J.; Martınez-Carrasco, F.; Martınezb, J.; Gaspara, P. Functional and organic eggs as an alternative to conventional production: A conjoint analysis of consumers’ preferences. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoukian, E.B. Mathematical Nonparametric Statistics; Gordon & Breach: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso, T.; Baldi, L.; Gasco, L. An empirical study on consumer acceptance of farmed fish fed on insect meals: The Italian case. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 1489–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menozzi, D.; Sogari, G.; Mora, C.; Gariglio, M.; Gasco, L.; Schiavone, A. Insects as Feed for Farmed Poultry: Are Italian Consumers Ready to Embrace This Innovation? Insects 2021, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazoche, P.; Poret, S. What do trout eat: Acceptance of insects in animal feed? In Proceedings of the 11èmes Journées de Recherche en Sciences Sociales (JRRS), Lyon, France, 14–15 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Orsi, L.; Voege, L.L.; Stranieri, S. Eating edible insects as sustainable food? Exploring the determinants of consumer acceptance in Germany. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Predieri, S.; Sinesio, F.; Monteleone, E.; Spinelli, S.; Cianciabella, M.; Daniele, G.M.; Dinella, C.; Gasperi, F.; Endrizzi, I.; Torri, L.; et al. Gender, Age, Geographical Area, Food Neophobia and Their Relationships with the Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet: New Insights from a Large Population Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, K.; Muhlhausler, B.; Motley, C.; Crump, A.; Bray, H.; Ankeny, R. Australian consumers’ awareness and acceptance of insects as food. Insects 2018, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szendro, K.; Nagy, M.Z.; Toth, K. Consumer Acceptance of Meat from Animals Reared on Insect Meal as Feed. Animals 2020, 10, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Levels | Attributes |
|---|---|
| Price | |
| 1 | 1.55 € |
| 2 | 1.85 € |
| 3 | 2.50 € |
| Rearing system | |
| 1 | Free-range |
| 2 | Barn |
| 3 | Organic |
| Insects | |
| 1 | Yes |
| 2 | No |
| Description | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Total respondents | 510 | 100% |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 245 | 48% |
| Male | 259 | 51% |
| Undisclosed | 6 | 1% |
| Education Background | ||
| None/Primary/Lower secondary/Upper secondary school | 108 | 21% |
| Degree | 233 | 46% |
| Post degree (MSc; PhD) | 165 | 32% |
| Undisclosed | 4 | 1% |
| Place of residence | ||
| Urban area | 284 | 56% |
| Suburban area | 106 | 20% |
| Rural area | 115 | 23% |
| Undisclosed | 5 | 1% |
| Income Level (€/year) | ||
| <10,000 | 55 | 11% |
| Between 10,000 and 20,000 | 100 | 20% |
| >20,000 | 136 | 26% |
| >30,000 | 151 | 30% |
| >50,000 | 52 | 10% |
| Undisclosed | 16 | 3% |
| Place of residence | ||
| Cluster | Number of Respondents | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Ready | 205 | 40.1 |
| Environmentalist | 123 | 24.3 |
| Cautious | 111 | 21.4 |
| Reluctant | 71 | 13.9 |
| Total sample | 510 | 100 |
| Attributes | Total Sample | Ready | Environmentalist | Cautious | Reluctant | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | |
| FNS | 29.51 | 0.45 | 27.91 b | 0.70 | 28.01 b | 0.87 | 29.49 b | 0.89 | 36.73 a | 1.13 |
| Acc. Score | 5.48 | 0.07 | 6.00 a | 0.09 | 6.01 a | 0.10 | 5.47 b | 0.12 | 3.10 c | 0.19 |
| Parameters | Total Sample | Ready | Environmentalist | Cautious | Reluctant | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | |
| Meat | 2.23 | 0.03 | 2.31 a | 0.06 | 2.04 b | 0.07 | 2.25 a | 0.06 | 2.26 a | 0.09 |
| Eggs | 2.43 | 0.04 | 2.52 ns | 0.06 | 2.34 ns | 0.08 | 2.36 ns | 0.08 | 2.42 ns | 0.10 |
| Legumes | 2.51 | 0.05 | 2.66 a | 0.08 | 2.60 a | 0.10 | 2.20 b | 0.10 | 2.41 b | 0.14 |
| Vegetables | 4.57 | 0.03 | 4.65 a | 0.04 | 4.58 ab | 0.07 | 4.52 ab | 0.07 | 4.39 b | 0.12 |
| Fresh Fruit | 2.57 | 0.07 | 2.64 ns | 0.11 | 2.66 ns | 0.13 | 2.41 ns | 0.14 | 2.49 ns | 0.17 |
| Milk Products | 3.46 | 0.05 | 3.46 ns | 0.09 | 3.37 ns | 0.12 | 3.60 ns | 0.11 | 3.38 ns | 0.14 |
| Fish | 2.22 | 0.04 | 2.34 ns | 0.06 | 2.12 ns | 0.08 | 2.15 ns | 0.08 | 2.14 ns | 0.10 |
| Shell fruit | 4.39 | 0.05 | 4.37 ns | 0.070 | 4.48 ns | 0.08 | 4.47 ns | 0.09 | 4.20 ns | 0.15 |
| Cereals | 3.65 | 0.07 | 3.77 ns | 0.10 | 3.74 ns | 0.14 | 3.51 ns | 0.15 | 3.35 ns | 0.19 |
| Cluster | Label * | LI-Brand ns | LI-Product ns | Local ns | No Import ns | Reduce Meat ** | Organic * | Origin * | Seasonality ns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ready | 39.0 | 28.8 | 0.1 | 53.7 | 28.8 | 40.5 | 19.0 | 71.2 | 83.9 |
| Environmentalist | 43.9 | 34.1 | 10.6 | 60.2 | 26.8 | 58.5 | 30.9 | 74.8 | 82.1 |
| Cautious | 51.3 | 32.4 | 0.1 | 55.0 | 22.5 | 41.4 | 20.7 | 73.9 | 87.4 |
| Reluctant | 52.1 | 43.7 | 14.1 | 47.9 | 33.8 | 38.0 | 25.3 | 67.6 | 81.7 |
| Total consumers | 44.7 | 32.9 | 9.0 | 54.7 | 27.6 | 44.7 | 23.1 | 72.2 | 83.9 |
| Attributes | Total Sample | Ready | Environmentalist | Cautious | Reluctant | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | |
| Size | 3.26 | 0.076 | 3.18 a | 0.116 | 3.11 a | 0.166 | 3.41 a | 0.153 | 3.54 a | 0.218 |
| Shell Color | 2.77 | 0.074 | 2.65 ab | 0.117 | 2.56 b | 0.150 | 3.02 ab | 0.149 | 3.08 a | 0.211 |
| Breeding | 5.97 | 0.065 | 5.83 a | 0.110 | 6.04 a | 0.127 | 6.14 a | 0.122 | 5.96 a | 0.185 |
| Yolk Color | 4.06 | 0.086 | 3.95 bc | 0.134 | 3.59 c | 0.175 | 4.29 b | 0.176 | 4.83 a | 0.231 |
| Feeding | 5.01 | 0.088 | 4.73 b | 0.146 | 5.02 ab | 0.176 | 5.21 ab | 0.166 | 5.46 a | 0.232 |
| Brand | 3.88 | 0.085 | 3.72 b | 0.134 | 3.66 b | 0.175 | 3.96 b | 0.166 | 4.59 a | 0.234 |
| Origin | 5.64 | 0.072 | 5.45 b | 0.121 | 5.47 b | 0.153 | 5.91 a | 0.128 | 6.08 a | 0.168 |
| Label | 3.97 | 0.091 | 3.42 b | 0.145 | 4.12 a | 0.175 | 4.55 a | 0.178 | 4.39 a | 0.253 |
| Attribute | Attribute Level | Total | Ready | Environmentalist | Cautious | Reluctant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Relative importance (%) | 41.2 | 43.4 | 43.0 | 45.0 | 21.0 |
| 1.55 € | 0.380 | 0.407 | 0.461 | 0.407 | 0.389 | |
| 1.85 € | 0.156 | 0.141 | 0.196 | 0.191 | −0.611 | |
| 2.50 € | −0.536 | −0.548 | −0.657 | −0.598 | 0.222 | |
| Rearing system | Relative importance (%) | 33.4 | 34.2 | 34.0 | 34.0 | 31.0 |
| Free-range | −0.319 | −0.307 | −0.445 | −0.296 | 0.722 | |
| Barn | 0.051 | 0.086 | 0.024 | 0.021 | 0.056 | |
| Organic | 0.268 | 0.220 | 0.422 | 0.275 | −0.778 | |
| Insects | Relative importance (%) | 25.4 | 22.4 | 23.0 | 21.0 | 48.0 |
| Yes | 0.020 | 0.195 | 0.219 | 0.122 | −1.167 | |
| No | −0.020 | −0.195 | −0.219 | −0.122 | 1.167 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lippi, N.; Predieri, S.; Chieco, C.; Daniele, G.M.; Cianciabella, M.; Magli, M.; Maistrello, L.; Gatti, E. Italian Consumers’ Readiness to Adopt Eggs from Insect-Fed Hens. Animals 2021, 11, 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113278
Lippi N, Predieri S, Chieco C, Daniele GM, Cianciabella M, Magli M, Maistrello L, Gatti E. Italian Consumers’ Readiness to Adopt Eggs from Insect-Fed Hens. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113278
Chicago/Turabian StyleLippi, Nico, Stefano Predieri, Camilla Chieco, Giulia Maria Daniele, Marta Cianciabella, Massimiliano Magli, Lara Maistrello, and Edoardo Gatti. 2021. "Italian Consumers’ Readiness to Adopt Eggs from Insect-Fed Hens" Animals 11, no. 11: 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113278
APA StyleLippi, N., Predieri, S., Chieco, C., Daniele, G. M., Cianciabella, M., Magli, M., Maistrello, L., & Gatti, E. (2021). Italian Consumers’ Readiness to Adopt Eggs from Insect-Fed Hens. Animals, 11(11), 3278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113278








