I Wanna Draw Like You: Inter- and Intra-Individual Differences in Orang-Utan Drawings
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Collection of Drawings
2.2. Ethics Note
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Quantitative Variables
2.3.2. Qualitative Variables
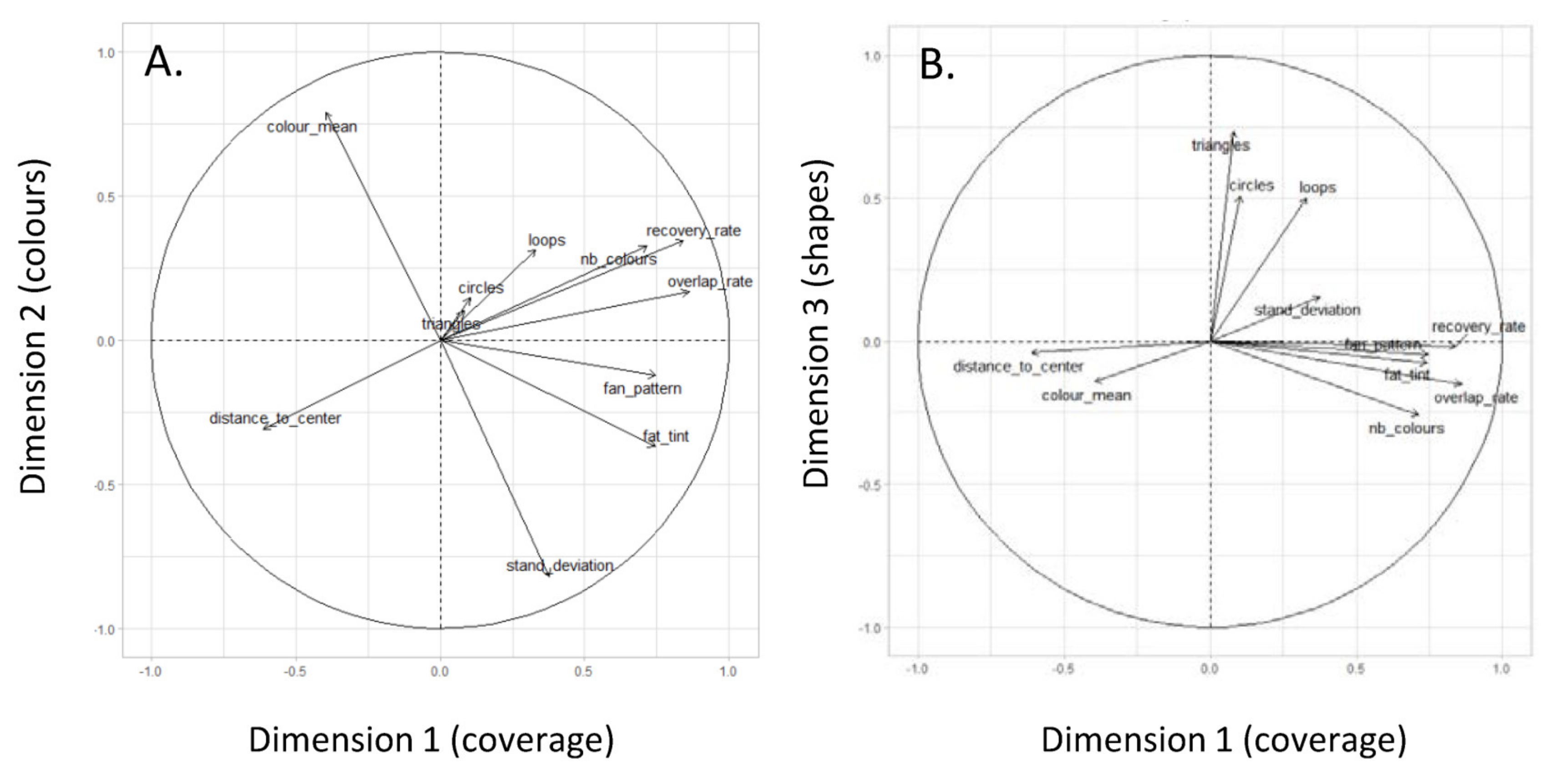
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
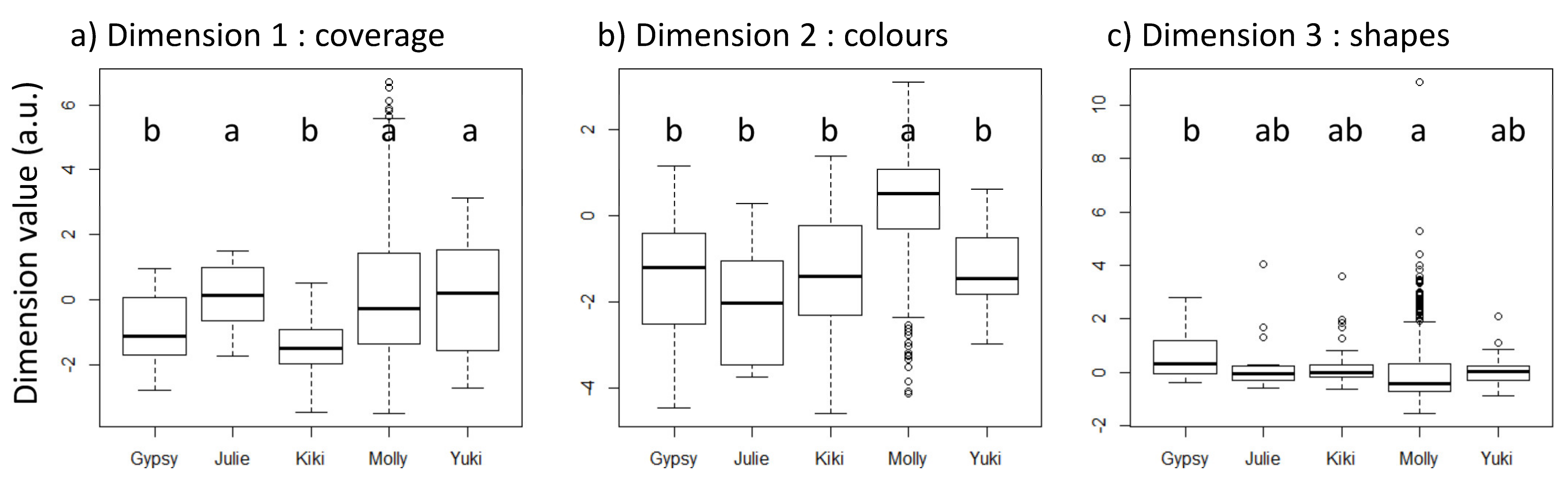
3.1. Comparative Analyses between Individuals
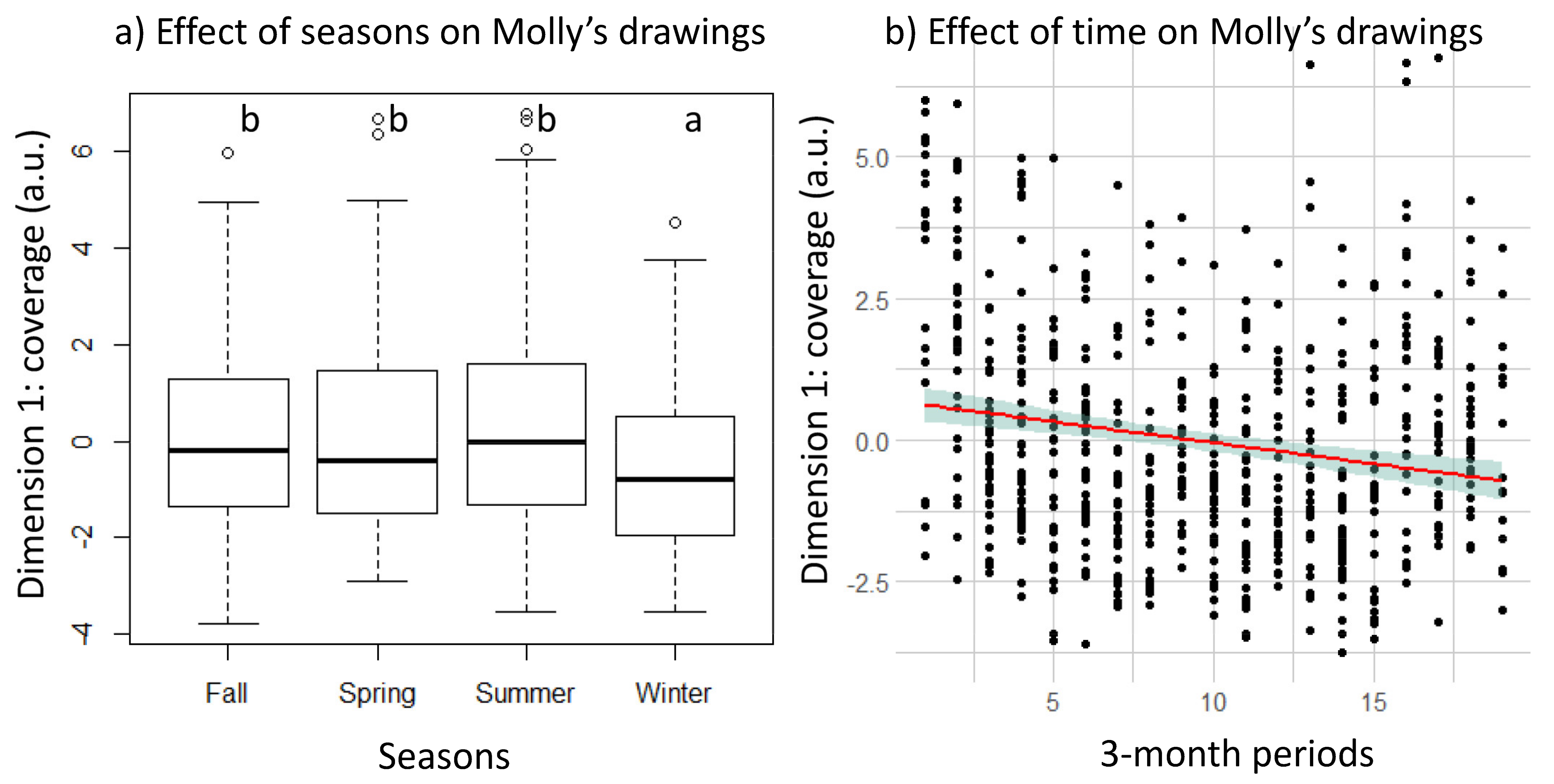
3.2. Longitudinal Changes in Molly’s Drawing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinet, L.; Pelé, M. Drawing in Nonhuman Primates: What We Know and What Remains to Be Investigated. J. Comp. Psychol. 2020, 135, 176–184. [Google Scholar]
- Martinet, L.; Sueur, C.; Hirata, S.; Hosselet, J.; Matsuzawa, T.; Pelé, M. New Indices to Characterize Drawing Behavior in Humans (Homo Sapiens) and Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, D.P.; Hillier, L.W.; Warren, W.C.; Worley, K.C.; Nazareth, L.V.; Muzny, D.M.; Yang, S.-P.; Wang, Z.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Minx, P.; et al. Comparative and Demographic Analysis of Orang-Utan Genomes. Nature 2011, 469, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dufour, V.; Pelé, M.; Neumann, M.; Thierry, B.; Call, J. Calculated Reciprocity after All: Computation behind Token Transfers in Orang-Utans. Biol. Lett. 2009, 5, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lethmate, J. Tool-Using Skills of Orang-Utans. J. Hum. Evol. 1982, 11, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardo, A.; Cornette, R.; Borel, A.; Pouydebat, E. Manual Function and Performance in Humans, Gorillas, and Orangutans during the Same Tool Use Task. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2017, 164, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, N.; Steinbeis, N.; Bueno-Guerra, N.; Call, J.; Singer, T. Preschool Children and Chimpanzees Incur Costs to Watch Punishment of Antisocial Others. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2018, 2, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damerius, L.A.; Burkart, J.M.; van Noordwijk, M.A.; Haun, D.B.; Kosonen, Z.K.; Galdikas, B.M.; Saraswati, Y.; Kurniawan, D.; van Schaik, C.P. General Cognitive Abilities in Orangutans (Pongo Abelii and Pongo pygmaeus). Intelligence 2019, 74, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, J. The Behaviour and Ecology of Wild Orang-Utans (Pongo pygmaeus). Anim. Behav. 1974, 22, 3–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanazuka, Y.; Kurotori, H.; Shimizu, M.; Midorikawa, A. The Effects of the Environment on the Drawings of an Extraordinarily Productive Orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus) Artist. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysen, S.T.; Berntson, G.G.; Prentice, J. Simian Scribbles: A Reappraisal of Drawing in the Chimpanzee (Pan Troglodytes). J. Comp. Psychol. 1987, 101, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Tomonaga, M.; Matsuzawa, T. Finger Drawing by Infant Chimpanzees (Pan yroglodytes). Anim. Cogn. 2003, 6, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoache, J.S.; Pickard, M.B.; LoBue, V. How very young children think about animals. In How Animals Affect Us: Examining the Influences of Human–Animal Interaction on Child Development and Human Health; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 85–99. ISBN 978-1-4338-0865-4. [Google Scholar]
- Casti, A.B. Reaction to Stimulus Figures in Chimpanzee Drawings. Master Thesis, Central Washington University, Ellensburg, WA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schiller, P.H. Figural Preferences in the Drawings of a Chimpanzee. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1951, 44, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D. The Biology of Art: A Study of the Picture-Making Behaviour of the Great Apes and Its Relationship to Human Art; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.A. Systematic Study of Chimpanzee Drawing. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1973, 82, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adi-Japha, E.; Levin, I.; Solomon, S. Emergence of Representation in Drawing: The Relation between Kinematic and Referential Aspects. Cogn. Dev. 1998, 13, 25–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, A. ‘What’s in a Picture?’ A Comparison of Drawings by Apes and Children. Semiotica 2007, 2007, 181–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, E.; Gross, J.; Patterson, T.; Hayne, H. Does Children’s Colour Use Reflect the Emotional Content of Their Drawings? Infant Child Dev. 2012, 21, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, T. SAGA and GAIN for Great Apes. Primates 2016, 57, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sueur, C.; Pelé, M. Importance of living environment for the welfare of captive animals: Behaviours and enrichment. In Animal Welfare: From Science to Law; La Fondation Droit Animal, Éthique et Sciences: Paris, France, 2019; pp. 175–188. Available online: https://www.fondation-droit-animal.org/proceedings-aw/importance-of-living-environment-for-the-welfare-of-captive-animals/ (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Kellogg, R. Analyzing Children’s Art; National Press Books: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.G.; Carl, P. PerformanceAnalytics: Econometric Tools for Performance and Risk Analysis. 2020. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/PerformanceAnalytics/man/PerformanceAnalytics-package.html (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: A Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaiser, H.F. The Varimax Criterion for Analytic Rotation in Factor Analysis. Psychometrika 1958, 23, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, T.; Hornik, K.; van de Wiel, M.A.; Zeileis, A. Implementing a Class of Permutation Tests: The Coin Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Giraudoux, P. Pgirmess: Spatial Analysis and Data Mining for Field Ecologists. R Package Version 2018, 1, 678. [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi, M.; Uno, H. On Permutation Tests for Comparing Restricted Mean Survival Time with Small Sample from Randomized Trials. Stat. Med. 2020, 39, 2655–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, P. Permutation, Parametric and Bootstrap Tests of Hypotheses, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mangiafico, S. Rcompanion: Functions to Support Extension Education Program Evaluation. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/307608990_rcompanion_Functions_to_support_extension_education_program_evaluation_R_statistical_package (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelé, M.; Thierry, B.; Call, J.; Dufour, V. Monkeys Fail to Reciprocate in an Exchange Task. Anim. Cogn. 2010, 13, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupenye, C.; Kano, F.; Hirata, S.; Call, J.; Tomasello, M. Great Apes Anticipate That Other Individuals Will Act According to False Beliefs. Science 2016, 354, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinet, L.; Sueur, C.; Beltzung, B.; Pelé, M. Understanding the Emergence of Drawing Behaviour with Age: A Multi-Metric Analysis. Available online: https://osf.io/aybz6 (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Sueur, C.; Martinet, L.; Beltzung, B.; Pelé, M. Making Drawings Speak through Mathematical Metrics. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.02276. [Google Scholar]
- Tigges, J. On Color Vision in Gibbon and Orang-Utan. Folia Primatol. 1963, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikellides, B. Colour psychology: The emotional effects of colour perception. In Colour Design; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 105–128. [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, H.M.; Burriss, R.P. Human Colour in Mate Choice and Competition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vancatova, M. Creativity and Innovative Behaviour in Primates on the Example of Picture-Making Activity of Apes. Available online: https://nsu.ru/xmlui/bitstream/handle/nsu/3372/05.pdf;sequence=1 (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Saito, A.; Hayashi, M.; Takeshita, H.; Matsuzawa, T. The Origin of Representational Drawing: A Comparison of Human Children and Chimpanzees. Child Dev. 2014, 85, 2232–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willats, J. Making Sense of Children’s Drawings; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-1-135-62498-9. [Google Scholar]
- Almeling, L.; Hammerschmidt, K.; Sennhenn-Reulen, H.; Freund, A.M.; Fischer, J. Motivational Shifts in Aging Monkeys and the Origins of Social Selectivity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1744–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sueur, C.; Quque, M.; Naud, A.; Bergouignan, A.; Criscuolo, F. Social Capital: An Independent Dimension of Healthy Ageing. 2021. Available online: https://ecoevorxiv.org/bg94n/ (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Gardner, H.; Wolf, D. The Symbolic Products of Early Childhood; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa, T. The 40th Anniversary of the Ai Project: The Commemorative Gift Is a Silk Scarf Painted by Ai the Chimpanzee. Primates 2017, 58, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iversen, I.H.; Matsuzawa, T. Visually Guided Drawing in the Chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes)1. Jpn. Psychol. Res. 1996, 38, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiten, A.; Goodall, J.; McGrew, W.C.; Nishida, T.; Reynolds, V.; Sugiyama, Y.; Tutin, C.E.; Wrangham, R.W.; Boesch, C. Cultures in Chimpanzees. Nature 1999, 399, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schaik, C.P.; Ancrenaz, M.; Borgen, G.; Galdikas, B.; Knott, C.D.; Singleton, I.; Suzuki, A.; Utami, S.S.; Merrill, M. Orangutan Cultures and the Evolution of Material Culture. Science 2003, 299, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Name | Date of Birth | Birthplace | Number of Drawings | Percentage of Drawings | Stay at Tama Zoo | Drawing Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molly | 1 January 1952 | Wild | 1299 | 91% | 2005–2011 | 2006–2011 |
| Gypsy | 1 January 1955 | Wild | 26 | 2% | 1958–2017 | 2007–2014 |
| Julie | 6 May 1965 | Captivity | 16 | 1% | 2005–Today | 2009–2014 |
| Yuki | 1 January 1970 | Wild | 32 | 2% | 2008–2015 | 2008–2010 |
| Kiki | 21 October 2000 | Wild | 60 | 4% | 2007–Today | 2010–2016 |
| Dim.1 | Dim.2 | Dim.3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage rate | 0.84 | 0.34 | −0.02 |
| Overlap rate | 0.86 | 0.17 | −0.15 |
| Number of colours | 0.72 | 0.32 | −0.26 |
| Fan patterns | 0.76 | −0.12 | −0.05 |
| Circles | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.50 |
| Triangles | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.73 |
| Loops | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.50 |
| Colour mean | −0.39 | 0.79 | −0.14 |
| Std. deviation of colour mean | 0.38 | −0.82 | 0.15 |
| Distance to centre | −0.61 | −0.31 | −0.02 |
| Solid colour rate | 0.74 | −0.37 | −0.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelé, M.; Thomas, G.; Liénard, A.; Eguchi, N.; Shimada, M.; Sueur, C. I Wanna Draw Like You: Inter- and Intra-Individual Differences in Orang-Utan Drawings. Animals 2021, 11, 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113202
Pelé M, Thomas G, Liénard A, Eguchi N, Shimada M, Sueur C. I Wanna Draw Like You: Inter- and Intra-Individual Differences in Orang-Utan Drawings. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113202
Chicago/Turabian StylePelé, Marie, Gwendoline Thomas, Alaïs Liénard, Nagi Eguchi, Masaki Shimada, and Cédric Sueur. 2021. "I Wanna Draw Like You: Inter- and Intra-Individual Differences in Orang-Utan Drawings" Animals 11, no. 11: 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113202
APA StylePelé, M., Thomas, G., Liénard, A., Eguchi, N., Shimada, M., & Sueur, C. (2021). I Wanna Draw Like You: Inter- and Intra-Individual Differences in Orang-Utan Drawings. Animals, 11(11), 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113202









