Evaluation of the Morphometry of Sperm from the Epididymides of Dogs Using Different Staining Methods
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Semen Collection
2.2. Staining Methods
2.2.1. DiffQuick Staining
2.2.2. SpermBlue Staining
2.2.3. Eosin-Nigrosin Staining
2.2.4. Eosin-Gentian Staining
2.3. Morphometric Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brito, L.F.; Greene, L.M.; Kelleman, A.; Knobbe, M.; Turner, R. Effect of method and clinician on stallion sperm morphology evaluation. Theriogenology 2011, 76, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, F.; Saravia, F.; Garcia-Herreros, M.; Núñezmartínez, I.; A Tapia, J.; Wallgren, M.; Rodríguez-Martinez, H.; Johannisson, A. Identification of Sperm Morphometric Subpopulations in Two Different Portions of the Boar Ejaculate and Its Relation to Postthaw Quality. J. Androl. 2005, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravia, F.; Núñez-Martínez, I.; Morán, J.; Soler, C.; Muriel, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, H.; Peña, F. Differences in boar sperm head shape and dimensions recorded by computer-assisted sperm morphometry are not related to chromatin integrity. Theriogenology 2007, 68, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, M.; Rodríguez, I.; Dorado, J.; Soler, C. Morphometric classification of Spanish thoroughbred stallion sperm heads. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2008, 103, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroto-Morales, A.; García-Álvarez, O.; Ramón, M.; Martínez-Pastor, F.; Fernández-Santos, M.R.; Soler, A.J.; Garde, J.J. Current status and potential of morphometric sperm analysis. Asian J. Androl. 2016, 18, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Van Der Horst, G.; Maree, L.; Du Plessis, S.S. Current perspectives of CASA applications in diverse mammalian spermatozoa. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2018, 30, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago, C.; Pérez-Sánchez, F.; Yeung, C.-H.; Tablado, L.; Cooper, T.G.; Soler, C. Standardization of sampling and staining methods for the morphometric evaluation of sperm heads in the Cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis) using computer-assisted image analysis. Int. J. Androl. 1998, 21, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yániz, J.; Soler, C.; Santolaria, P. Computer assisted sperm morphometry in mammals: A review. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 156, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, M.M.; Ghoneim, I.; Abdou, M.S. Morphometric Characteristics of Spermatozoa in the Arabian Horse With Regard to Season, Age, Sperm Concentration, and Fertility. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2015, 35, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubaszek, M.; Andraszek, K.; Banaszewska, D.; Walczak-Jedrzejowska, R. The effect of the staining technique on morphological and morphometric parameters of boar sperm. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokińska, A.; Kondracki, S. Heterosis for morphometric characteristics of sperm cells from Duroc x Pietrain crossbred boars. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 211, 106217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijsselaere, T.; Van Soom, A.; Hoflack, G.; Maes, D.; De Kruif, A. Automated sperm morphometry and morphology analysis of canine semen by the Hamilton-Thorne analyser. Theriogenology 2004, 62, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvoni, G.C.; Morselli, M.G. Canine epididymal spermatozoa: A hidden treasure with great potential. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasler, J.M.; Hermo, L.; Robaire, B. Morphological Changes in the Testis and Epididymis of Rats Treated with Cyclophosphamide: A Quantitative Approach1. Biol. Reprod. 1988, 38, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunkitti, P.; Bergqvist, A.-S.; Sjunnesson, Y.; Axnér, E. The ability of feline spermatozoa in different epididymal regions to undergo capacitation and acrosome reaction. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 161, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, C.; Alambiaga, A.; A Martí, M.; García-Molina, A.; Valverde, A.; Contell, J.; Campos, M. Dog sperm head morphometry: Its diversity and evolution. Asian J. Androl. 2017, 19, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Horst, G.; Maree, L. SpermBlue®: A new universal stain for human and animal sperm which is also amenable to automated sperm morphology analysis. Biotech. Histochem. 2010, 84, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange-Consiglio, A.; Antonucci, N.; Manes, S.; Corradetti, B.; Cremonesi, F.; Bizzaro, D. Morphometric characteristics and chromatin integrity of spermatozoa in three Italian dog breeds. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 51, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chłopik, A.; Wysokińska, A. Canine spermatozoa—What do we know about their morphology and physiology? An overview. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2019, 55, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sringam, S.; Kitiyanant, Y.; Lewin, L.M.; Saikhun, K. Semen quality and chromatin condensation in domestic cat sperm during passage through the epididymis. Kasetsart J. Nat. Sci. 2011, 45, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Martinez, I.; Moran, J.M.; Peña, F. Identification of sperm morphometric subpopulations in the canine ejaculate: Do they reflect different subpopulations in sperm chromatin integrity? Zygote 2007, 15, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbano, M.; Ortiz, I.; Dorado, J.; Hidalgo, M. Identification of sperm morphometric subpopulations in cooled-stored canine sperm and its relation with sperm DNA integrity. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, I.P.; Cancelli, C.H.B.; Grassi, T.L.M.; Oliveira, P.R.H.; Franciscato, D.A.; Carreira, J.; Koivisto, M.B. Evaluation of sperm head dimensions and chromatin integrity of epididymal sperm from domestic cats using the toluidine blue technique. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 197, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijsselaere, T.; Van Soom, A.; Maes, D.; Niżański, W. Computer-Assisted Sperm Analysis in Dogs and Cats: An Update after 20 Years. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2012, 47, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Vázquez, F.A.; Gadea, J.; Matás, C.; Holt, W.V. Importance of sperm morphology during their transport and fertilization in mammals. Asian J. Androl. 2016, 18, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrimani, D.; Losano, J.D.D.A.; Lucio, C.; Veiga, G.; Landim, F.; Nichi, M.; Vannucchi, C. Cytoplasmic droplet acting as a mitochondrial modulator during sperm maturation in dogs. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 181, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, R.R.; Angrimani, D.S.R.; Brito, M.M.; Nichi, M.; Vannucchi, C.; Lucio, C.F. Susceptibility of epididymal sperm against reactive oxygen species in dogs. Anim. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomendio, M.; Roldan, E.R.S. Sperm competition influences sperm size in mammals. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 1991, 243, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björndahl, L.; Söderlund, I.; Kvist, U. Evaluation of the one-step eosin-nigrosin staining technique for human sperm vitality assessment. Hum. Reprod. 2003, 18, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokińska, A.; Kondracki, S. Assessment of changes in sperm cell membrane integrity occurring during the storage of semen from genetically different males using two diagnostic methods. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 94, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondracki, S.; Wysokińska, A.; Kania, M.; Górski, K. Application of two staining methods for sperm morphometric evaluation in domestic pigs. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 61, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaszewska, D.; Andraszek, K.; Czubaszek, M.; Biesiada–Drzazga, B. The effect of selected staining techniques on bull sperm morphometry. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 159, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łacka, K.; Kondracki, S.; Iwanina, M.; Wysokińska, A. Assessment of stallion semen morphology using two different staining methods, microscopic techniques, and sample sizes. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 60, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraszek, K.; Banaszewska, D.; Biesiada-Drzazga, B. The use of two staining methods for identification of spermatozoon structure in roosters. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2575–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.P.M.; Tavares, R.S.; De La Calle, J.F.V.; Figueiredo, H.; Almeida, V.; Santos, T.A.; Ramalho-Santos, J. Dual use of Diff-Quik-like stains for the simultaneous evaluation of human sperm morphology and chromatin status. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 24, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maree, L.; Du Plessis, S.S.; Menkveld, R.; Van Der Horst, G. Morphometric dimensions of the human sperm head depend on the staining method used. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, C.C.; Gadea, B.; Soler, A.; Fernández-Santos, M.; Esteso, M.; Nunez, J.; Moreira, P.N.; Núñez, M.; Gutierrez, R.G.; Sancho, M.; et al. Comparison of three different staining methods for the assessment of epididymal red deer sperm morphometry by computerized analysis with ISAS®. Theriogenology 2005, 64, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, A.F.; Gomendio, M.; Garde, J.J.; Lang-Lenton, B.; Soler, A.J.; Roldan, E.R.S. Sperm design and sperm function. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
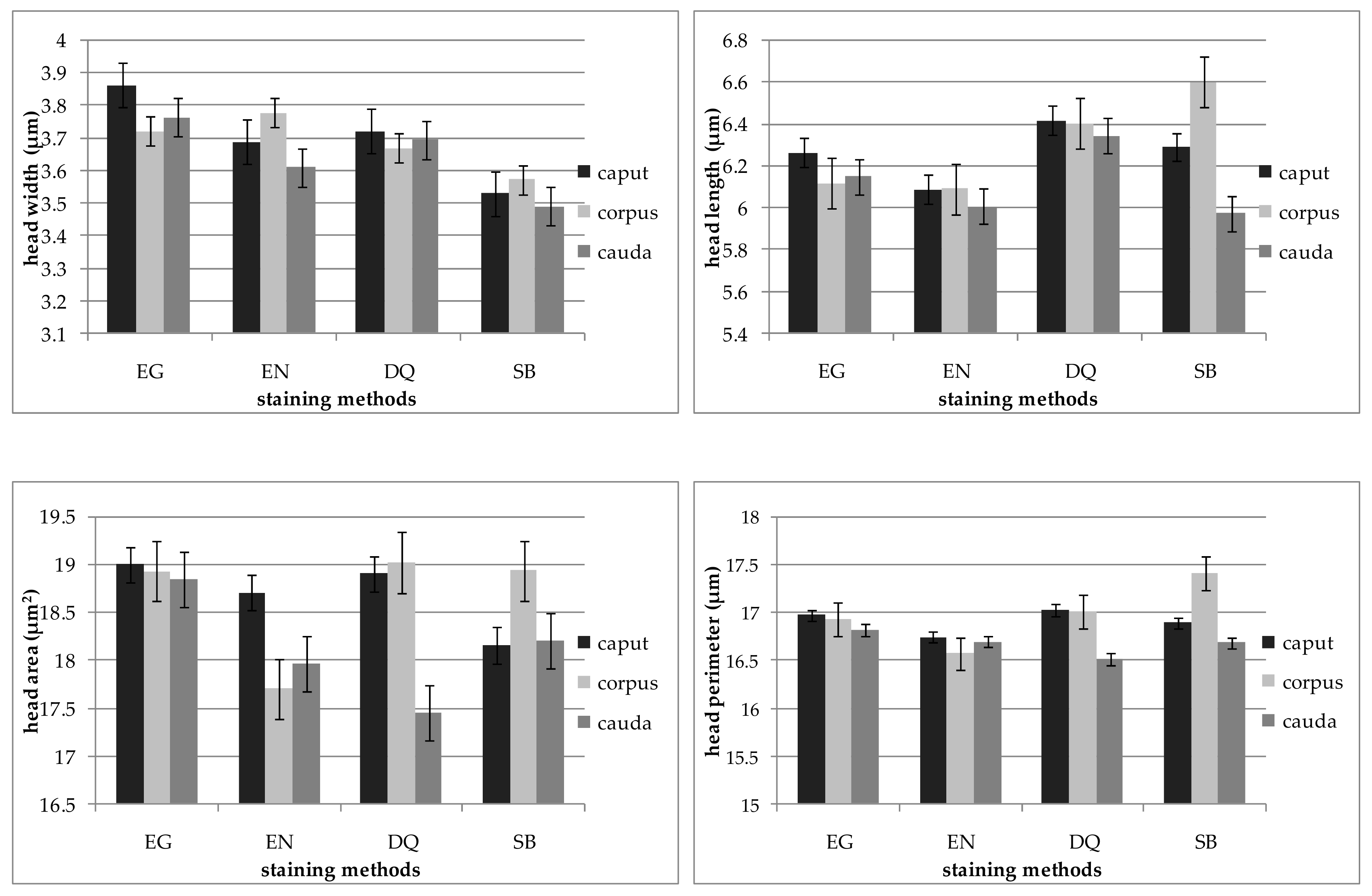
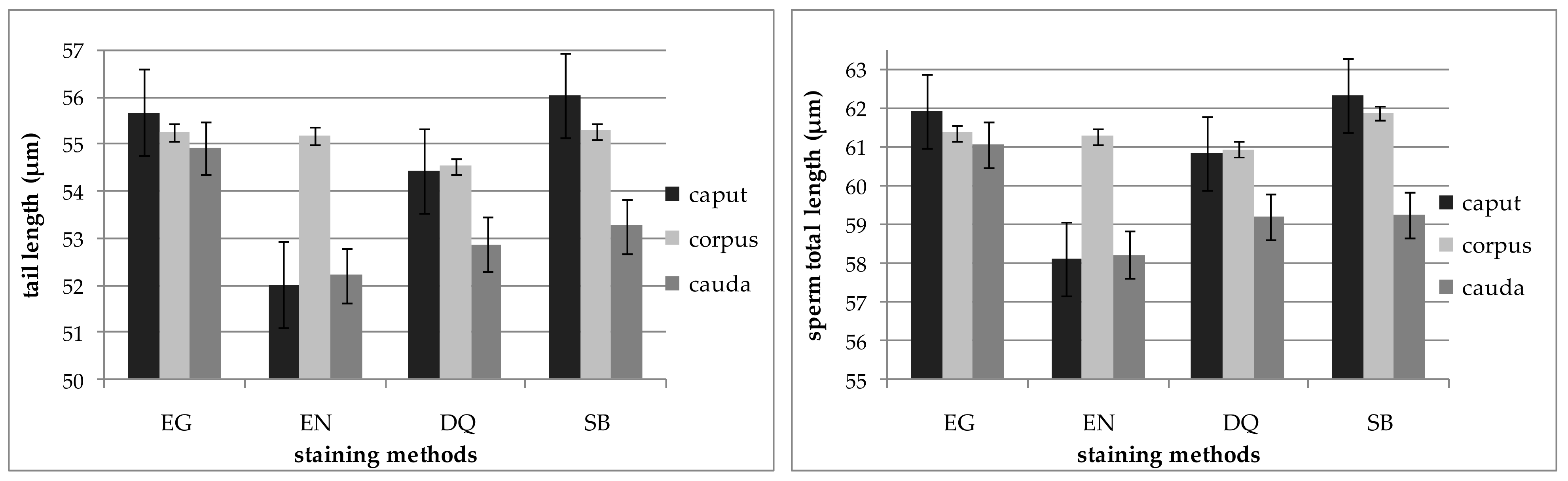
| Item. | Epididymal Segment | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caput | Corpus | Cauda | ||
| Number of Analyzed Cells | 800 | 800 | 800 | |
| Head | ||||
| Length (µm) | 6.28 ± 0.05 a | 6.32 ± 0.05 a | 6.11 ± 0.05 b | 0.01 |
| Width (µm) | 3.70 ± 0.03 a | 3.67 ± 0.02 a | 3.63 ± 0.02 a | 0.56 |
| Area (µm2) | 18.67 ± 0.18 a | 18.69 ± 0.13 a | 18.12 ± 0.13 b | 0.02 |
| Perimeter (µm) | 16.90 ± 0.08 ab | 17.01 ± 0.08 a | 16.70 ± 0.07 b | 0.04 |
| Tail | ||||
| Length (µm) | 54.62 ± 0.34 a | 55.04 ± 0.35 a | 53.31 ± 0.30 b | 0.01 |
| Sperm total length (µm) | 60.89 ± 0.35 a | 61.36 ± 0.35 a | 59.42 ± 0.31 b | 0.00 |
| Shape indices | ||||
| Ellipticity | 1.72 ± 0.02 a | 1.73 ± 0.02 a | 1.69 ± 0.02 a | 0.44 |
| Elongation | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 0.26 ± 0.00 a | 0.25 ± 0.00 a | 0.33 |
| Rugosity | 0.82 ± 0.01 a | 0.81 ± 0.00 a | 0.82 ± 0.00 a | 0.46 |
| Regularity | 0.99 ± 0.01 a | 0.98 ± 0.01 a | 0.96 ± 0.01 a | 0.68 |
| Item | Staining Method | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | EN | DQ | SB | ||
| Number of Analyzed Cells | 600 | 600 | 600 | 600 | |
| Head | |||||
| Length (µm) | 6.17 ± 0.06 a | 6.06 ± 0.06 a | 6.39 ± 0.06 b | 6.27 ± 0.06 b | 0.00 |
| Width (µm) | 3.78 ± 0.03 a | 3.69 ± 0.03 b | 3.70 ± 0.03 ab | 3.53 ± 0.02 c | 0.00 |
| Area (µm2) | 18.92 ± 0.18 a | 18.11 ± 0.18 b | 18.46 ± 0.17 ab | 18.42 ± 0.15 ab | 0.02 |
| Perimeter (µm) | 16.93 ± 0.10 a | 16.67 ± 0.09 a | 16.85 ± 0.09 a | 16.97 ± 0.08 a | 0.11 |
| Tail | |||||
| Length (µm) | 55.25 ± 0.27 a | 53.06 ± 0.53 b | 53.94 ± 0.32 b | 54.75 ± 0.37 a | 0.00 |
| Sperm total length (µm) | 61.43 ± 0.28 a | 59.12 ± 0.53 b | 60.33 ± 0.34 ab | 61.02 ± 0.38 a | 0.00 |
| Shape indices | |||||
| Ellipticity | 1.64 ± 0.02 a | 1.66 ± 0.02 a | 1.74 ± 0.02 b | 1.79 ± 0.02 b | 0.00 |
| Elongation | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 b | 0.28 ± 0.01 b | 0.00 |
| Rugosity | 0.83 ± 0.00 a | 0.82 ± 0.01 ab | 0.82 ± 0.00 ab | 0.80 ± 0.01 b | 0.00 |
| Regularity | 0.97 ± 0.01 a | 0.97 ± 0.01 a | 1.01 ± 0.01 b | 0.95 ± 0.01 a | 0.00 |
| Item | Epididymal Segment | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caput | Corpus | Cauda | ||||||||
| DQ | EG | EN | DQ | EG | EN | DQ | EG | EN | ||
| Head | ||||||||||
| Length (µm) | EG | 0.56 * | - | 0.30 | 0.41 * | - | 0.45 * | 0.71 * | - | 0.72 * |
| EN | 0.33 * | 0.30 | - | 0.62 * | 0.45 * | - | 0.57 * | 0.72 * | - | |
| SB | 0.31 * | 0.31 * | 0.02 | 0.46 * | 0.22 | 0.29 | −0.16 | −0.10 | −0.24 | |
| Width (µm) | EG | 0.24 | - | −0.21 | 0.06 | - | −0.13 | −0.12 | - | −0.07 |
| EN | 0.21 | −0.21 | - | −0.03 | −0.13 | - | −0.01 | −0.07 | - | |
| SB | −0.01 | −0.09 | 0.11 | −0.30 | −0.11 | 0.10 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −0.07 | |
| Area (µm2) | EG | 0.44 * | - | −0.02 | 0.16 | - | 0.07 | −0.02 | - | 0.01 |
| EN | −0.03 | −0.02 | - | 0.05 | 0.07 | - | 0.02 | 0.01 | - | |
| SB | 0.07 | 0.23 | −0.09 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.13 | |
| Perimeter (µm) | EG | 0.41 * | - | -0.03 | −0.09 | - | 0.08 | 0.29 | - | 0.18 |
| EN | 0.04 | −0.03 | - | 0.26 | 0.08 | - | 0.24 | 0.18 | - | |
| SB | 0.18 | 0.35 * | 0.08 | 0.34 * | 0.28 | 0.01 | −0.09 | 0.15 | 0.29 | |
| Tail | ||||||||||
| Length (µm) | EG | −0.24 | - | −0.41 * | 0.39 * | - | 0.27 | 0.26 | - | 0.06 |
| EN | 0.30 | −0.41 * | - | 0.06 | 0.27 | - | −0.12 | 0.06 | - | |
| SB | 0.18 | −0.25 | −0.01 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.34 * | 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.07 | |
| Sperm total length (µm) | EG | −0.09 | - | −0.28 | 0.45 * | - | 0.21 | 0.32 * | - | 0.10 |
| EN | 0.38 * | −0.28 | - | 0.06 | 0.21 | - | −0.06 | 0.10 | - | |
| SB | 0.19 | −0.27 | 0.02 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.40* | 0.06 | 0.30 | 0.11 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wysokińska, A.; Wójcik, E.; Chłopik, A. Evaluation of the Morphometry of Sperm from the Epididymides of Dogs Using Different Staining Methods. Animals 2021, 11, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010227
Wysokińska A, Wójcik E, Chłopik A. Evaluation of the Morphometry of Sperm from the Epididymides of Dogs Using Different Staining Methods. Animals. 2021; 11(1):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010227
Chicago/Turabian StyleWysokińska, Anna, Ewa Wójcik, and Angelika Chłopik. 2021. "Evaluation of the Morphometry of Sperm from the Epididymides of Dogs Using Different Staining Methods" Animals 11, no. 1: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010227
APA StyleWysokińska, A., Wójcik, E., & Chłopik, A. (2021). Evaluation of the Morphometry of Sperm from the Epididymides of Dogs Using Different Staining Methods. Animals, 11(1), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010227





