Compositional and Functional Characteristics of Swine Slurry Microbes through 16S rRNA Metagenomic Sequencing Approach
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation, Demultiplexing and Quality Filtering
2.2. Operational Taxonomic Unit (OTU) Clustering and Taxonomy Assignment
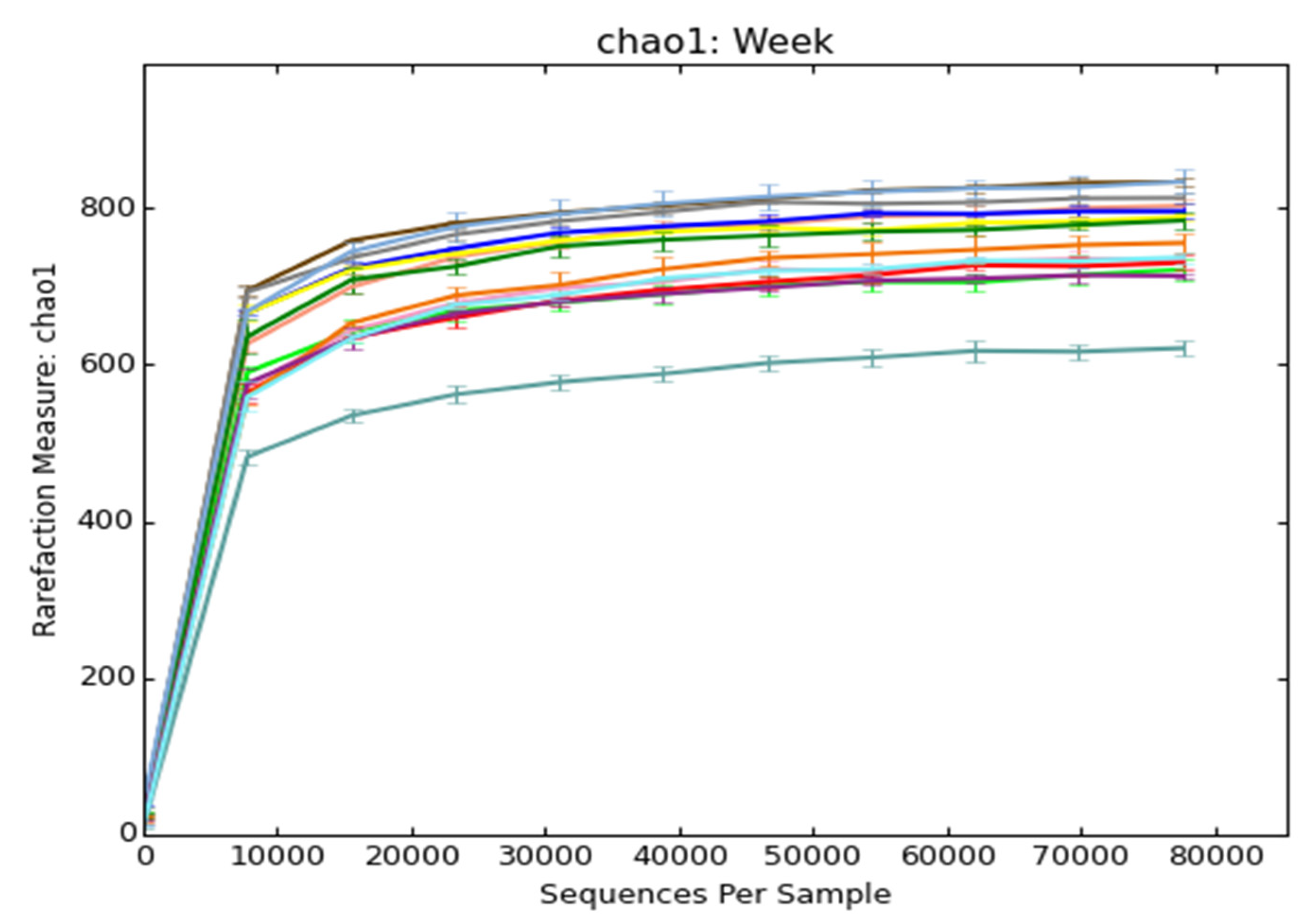
2.3. Microbial Diversity Analysis
2.4. Feature Selection through Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) Effect Size (LEfSe)
2.5. Investigation of Co-Occurring and Mutually Exclusive Microbes
2.6. Microbial Functional Profiling
2.7. Data Availability
3. Results
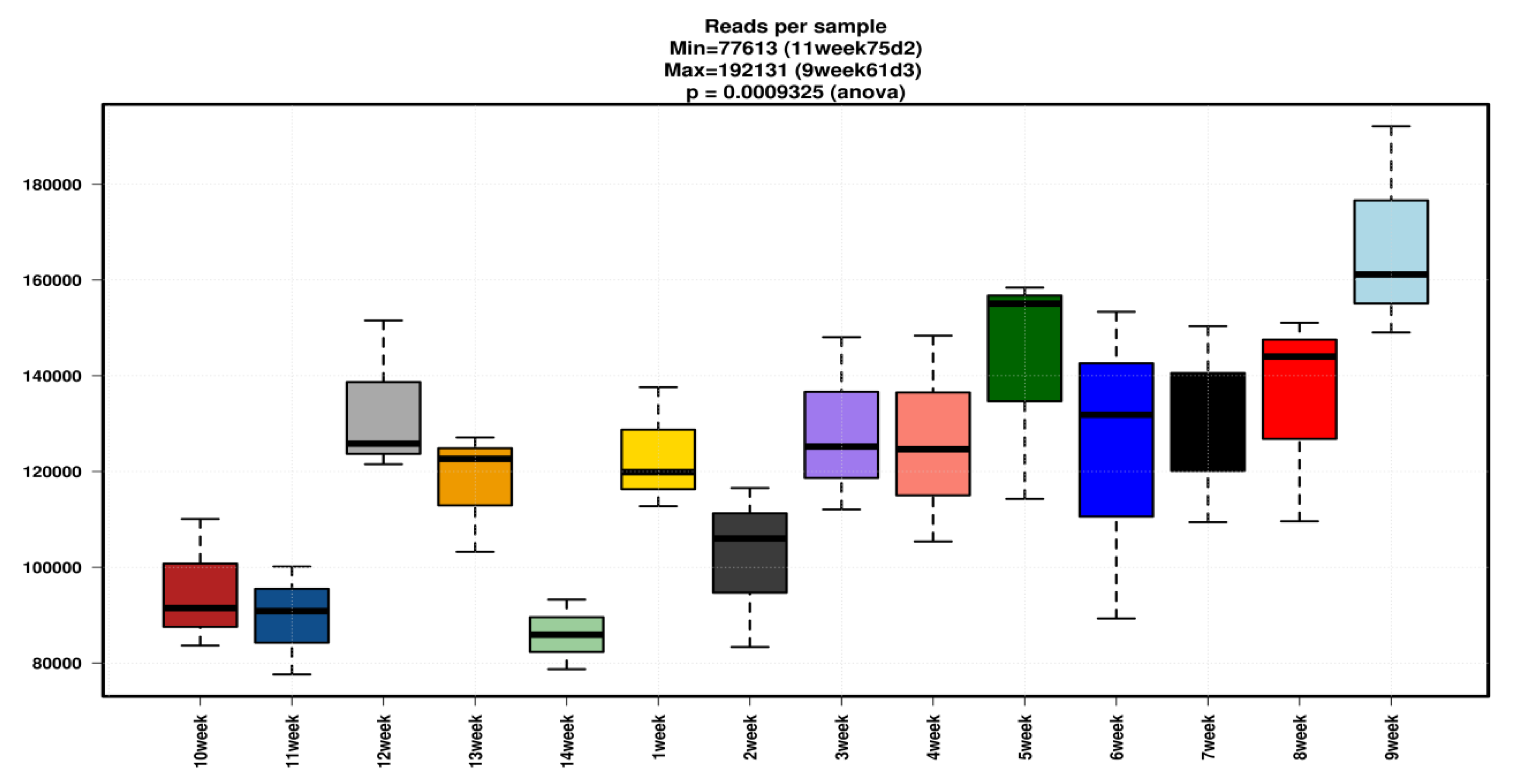
3.1. Sample Information and Read Statistics
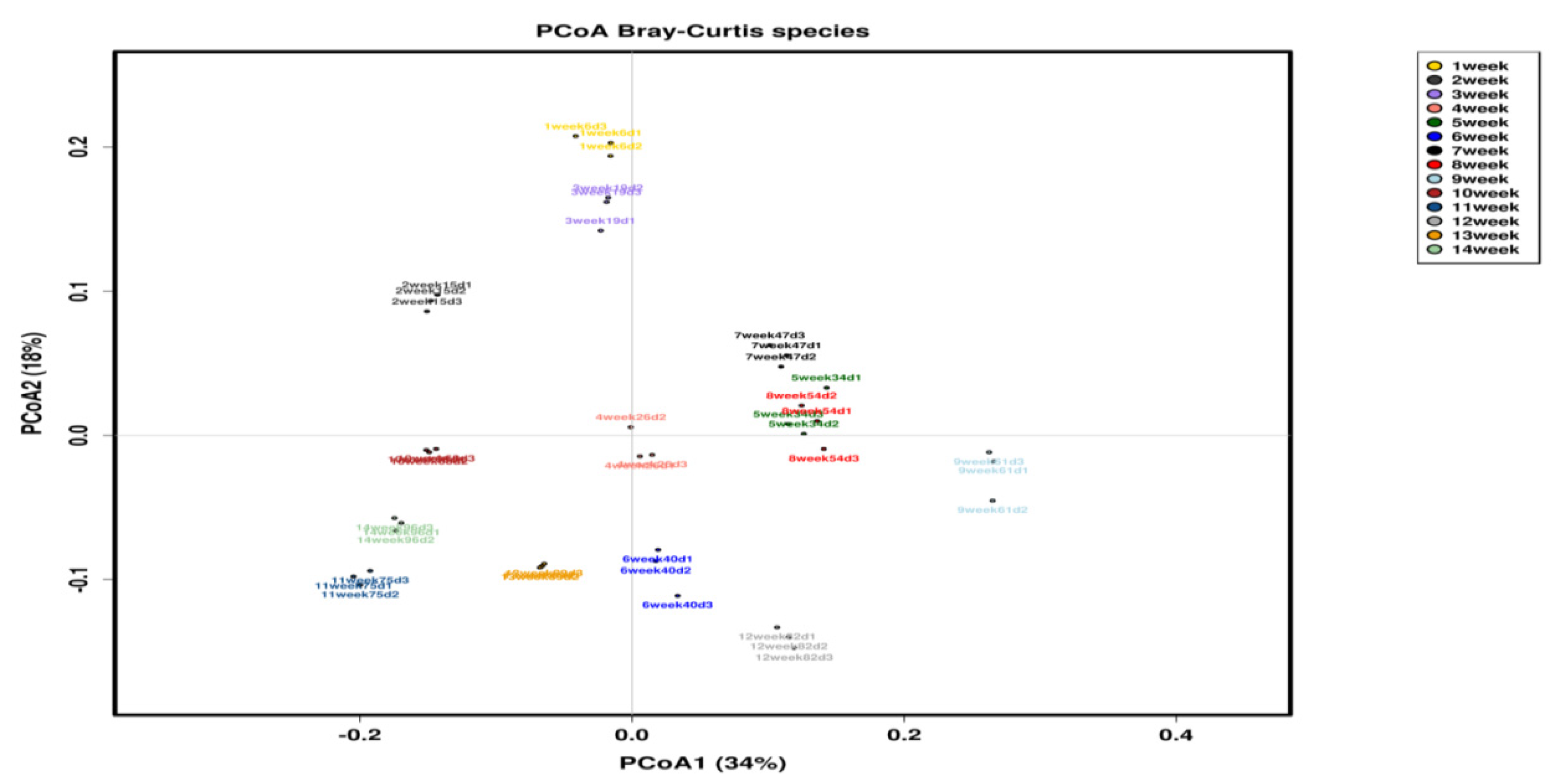
3.2. Multivariate Analysis
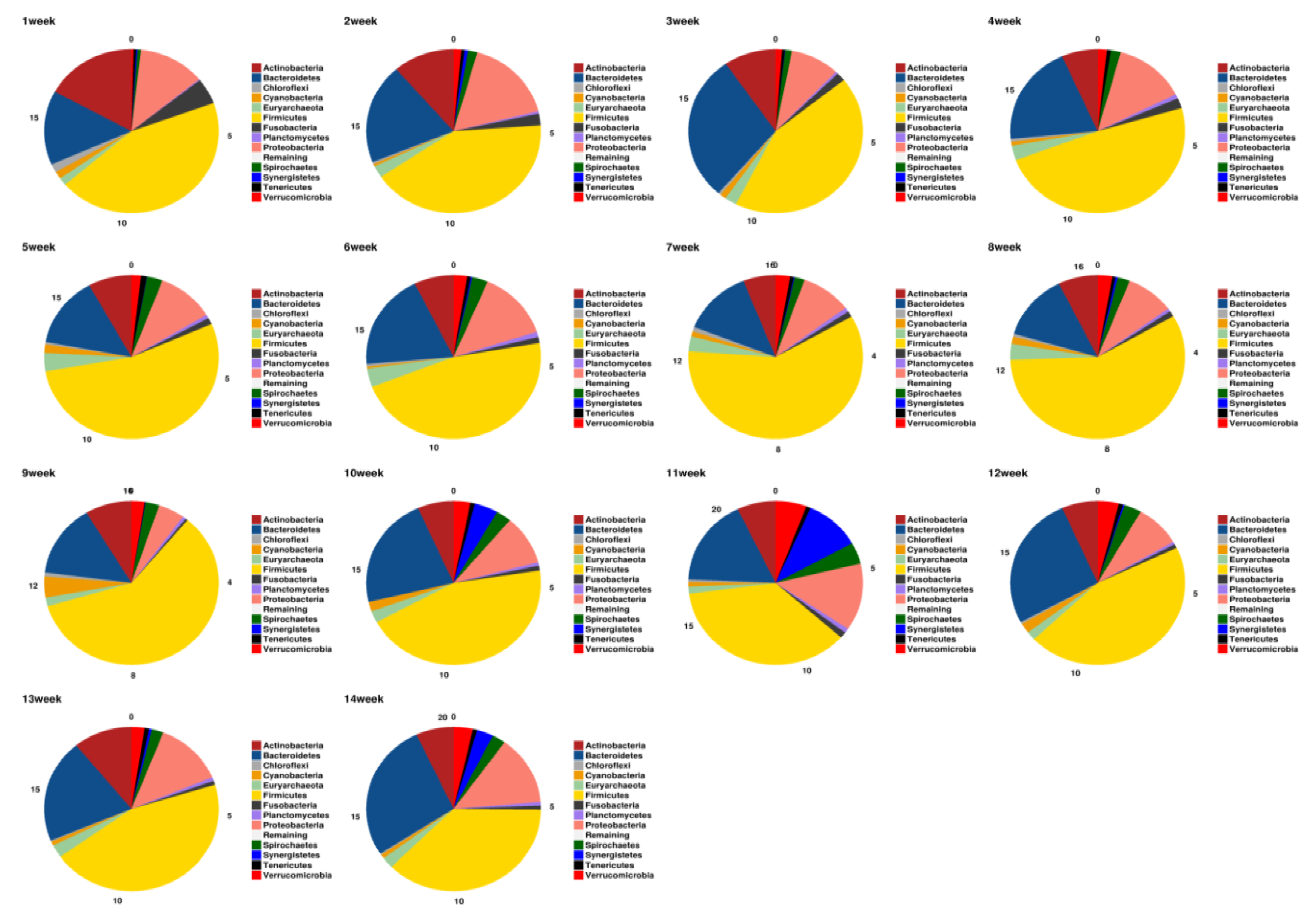
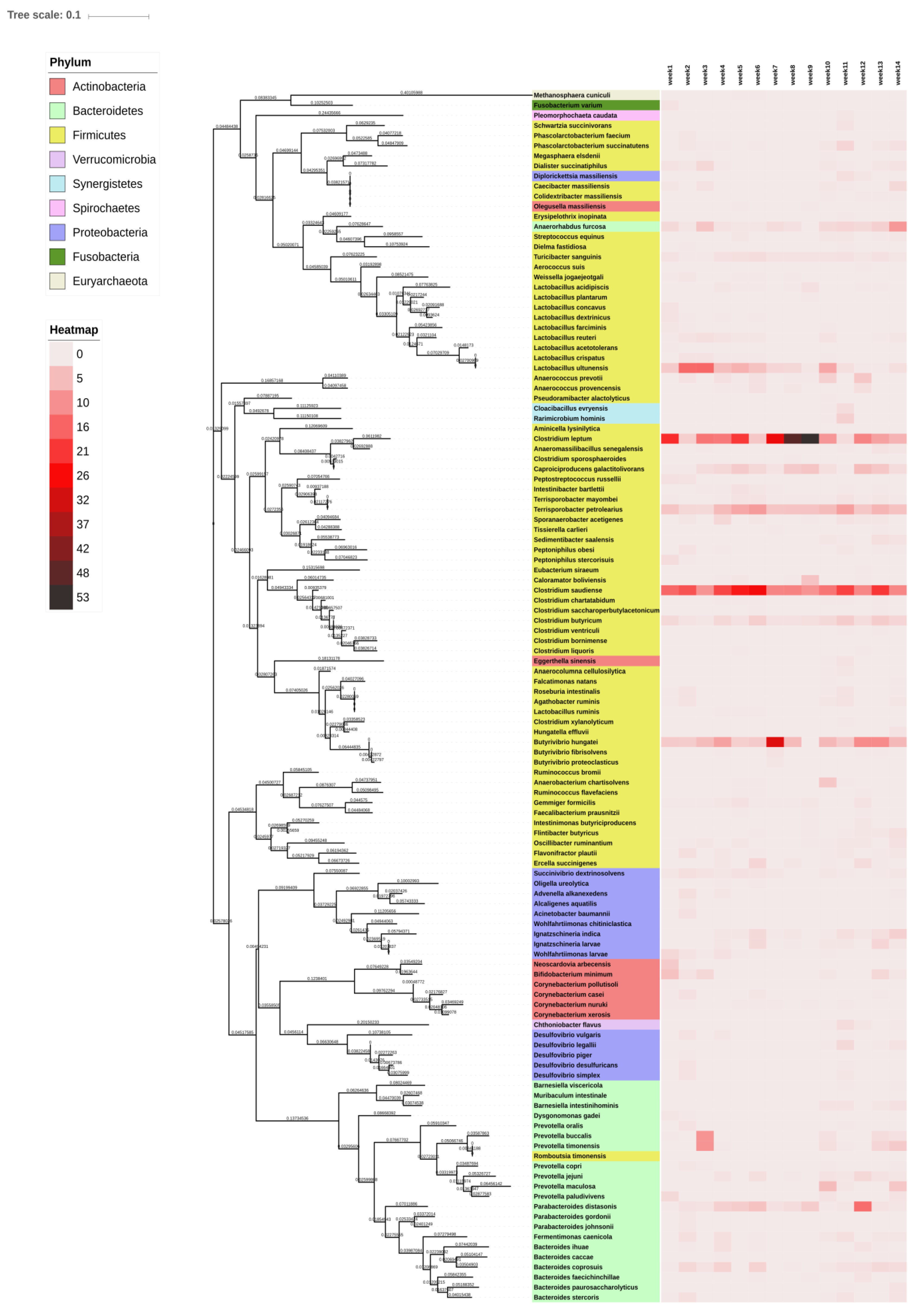
3.3. Microbial Taxonomy Annotation
3.4. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
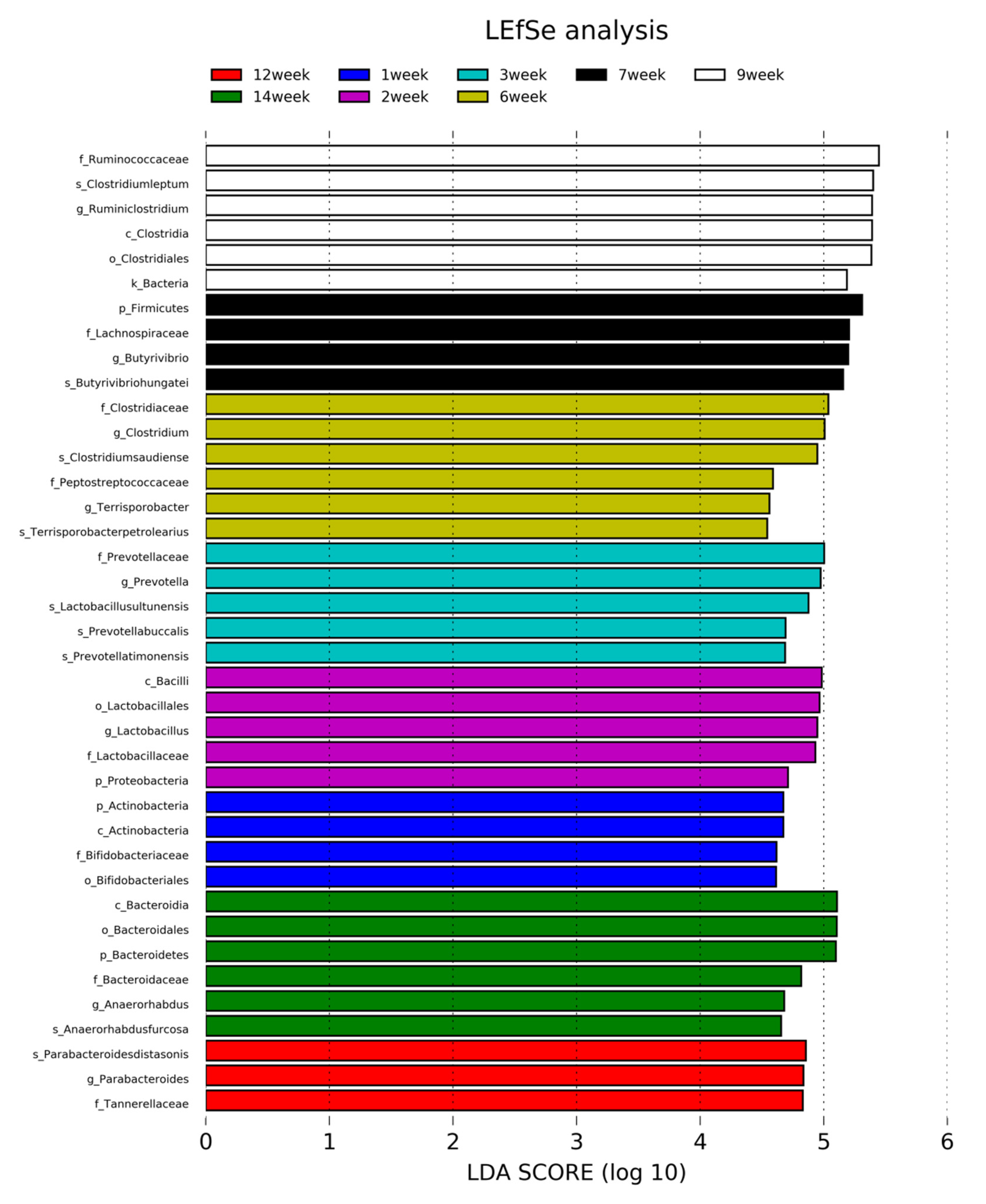
3.5. Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size Method
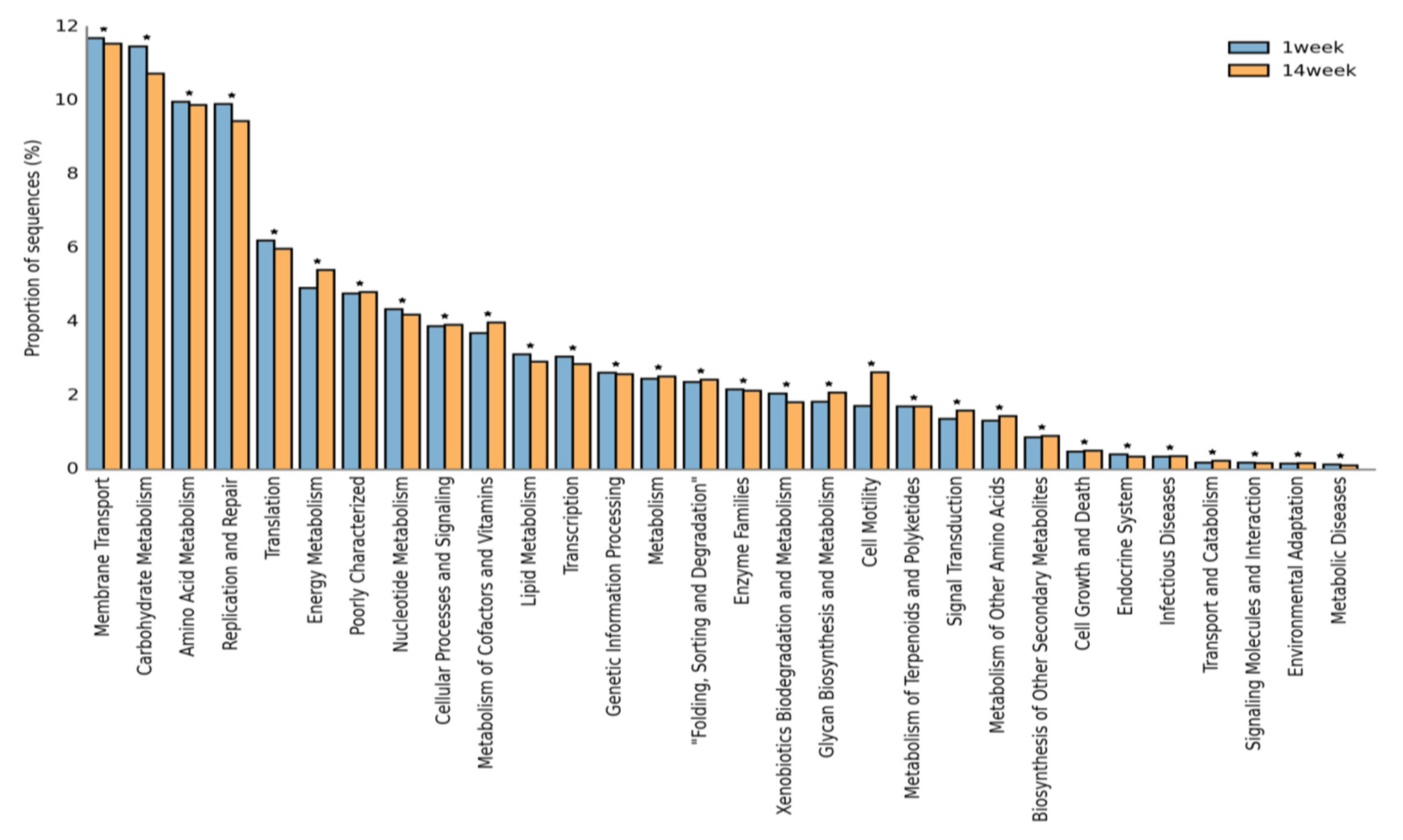
3.6. Functional Annotations of Microbes
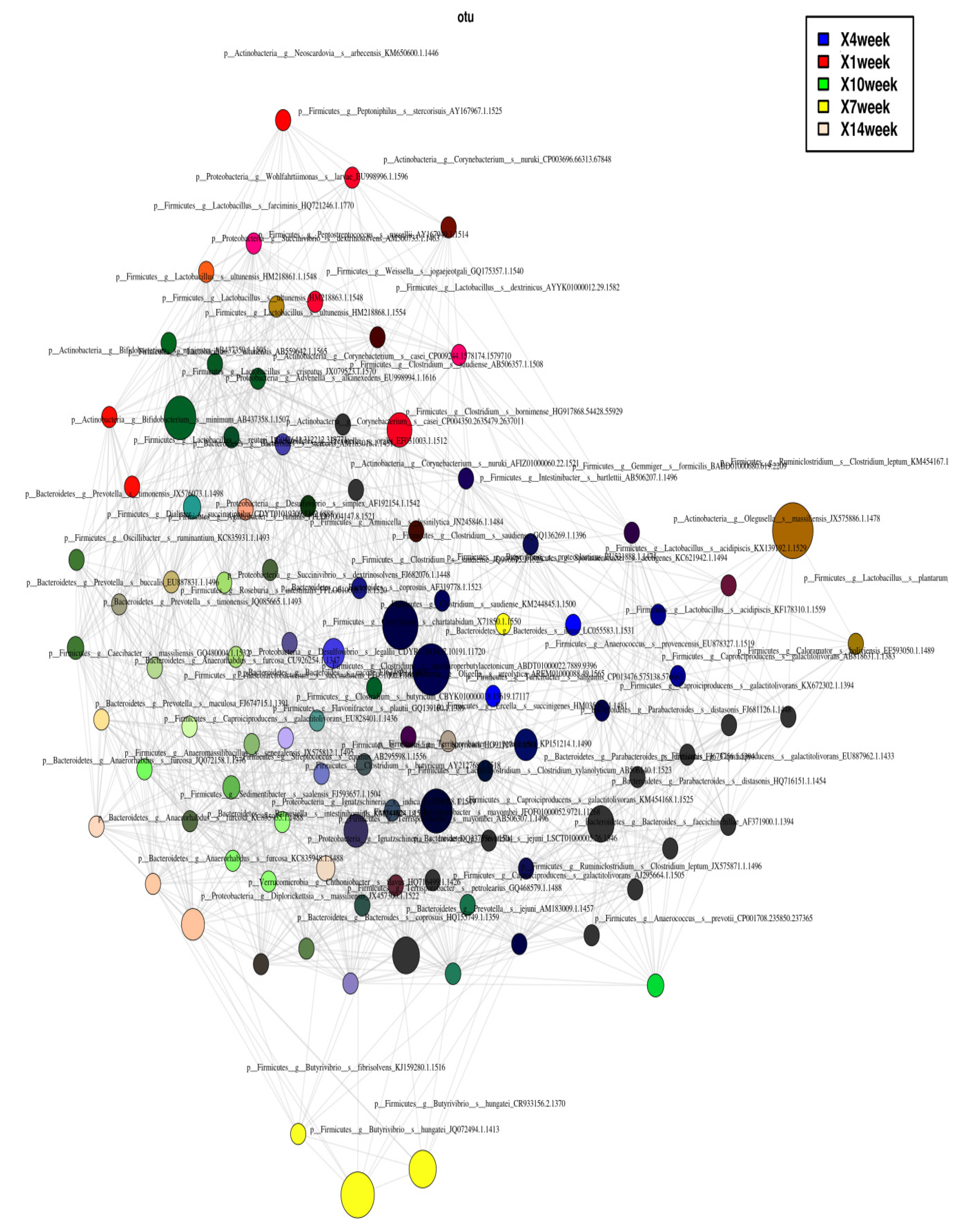
3.7. Identification of Co-Occurring and Mutually Exclusive Microbes through Network Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gjedrem, T.; Robinson, N.; Rye, M. The importance of selective breeding in aquaculture to meet future demands for animal protein: A review. Aquaculture 2012, 350, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; Whitley, N.C. Pork Production in China, Japan and South Korea. Asian-Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 24, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makara, A.; Kowalski, Z. Pig manure treatment and purification by filtration. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 161, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, B.D.; Hengemuehle, S.M.; Person, H.L.; Yokoyama, M.T.; Masten, S.J. Ozonation of swine manure wastes to control odors and reduce the concentrations of pathogens and toxic fermentation metabolites. Ozone Sci. Eng. 1997, 19, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susaya, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Chang, Y.-S. Characterization of major offensive odorants released from lake sediment. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder, J.; Libra, B.; Weyer, P.; Heathcote, S.; Kolpin, D.; Thorne, P.S.; Wichman, M. Impacts of waste from concentrated animal feeding operations on water quality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 115, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Gupta, S.C.; Baidoo, S.; Chander, Y.; Rosen, C.J. Antibiotic uptake by plants from soil fertilized with animal manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 2082–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicudo, J.R.; Goyal, S.M. Pathogens and manure management systems: A review. Environ. Technol. 2003, 24, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, S.G.; Christensen, M.L.; Jensen, L.S.; Schmidt, T. Animal Manure Recycling: Treatment and Management; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, S.O.; Sommer, S.; Béline, F.; Burton, C.; Dach, J.; Dourmad, J.; Leip, A.; Misselbrook, T.; Nicholson, F.; Poulsen, H.D. Recycling of livestock manure in a whole-farm perspective. Livest. Sci. 2007, 112, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.; Tran, M.; Dang, T. A survey of manure management on pig farms in Northern Vietnam. Livest. Sci. 2007, 112, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibañez, T.R.; Laukkanen-Ninios, R.; Hakkinen, M.; Johansson, T.; Vilar, M.; Korkeala, H. Prevalence of pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica in finnish slaughter pigs. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, P.S.; Slutsker, L.; Dietz, V.; McCaig, L.F.; Bresee, J.S.; Shapiro, C.; Griffin, P.M.; Tauxe, R.V. Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montville, T.J.; Matthews, K.R. Principles which influence microbial growth, survival, and death in foods. In Food Microbiology Fundamentals and Frontiers; ASM: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, T.; Gong, Y. Long-term manure and fertilizer effects on soil organic matter fractions and microbes under a wheat–maize cropping system in northern China. Geoderma 2009, 149, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzerke, A.; Sharma, S.; Schauss, K.; Heuer, H.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Smalla, K.; Wilke, B.-M.; Schloter, M. Alterations in soil microbial activity and N-transformation processes due to sulfadiazine loads in pig-manure. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.N.; Jung, M.W. Biochemical Changes and Biological Origin of Key Odor Compound Generations in Pig Slurry during Indoor Storage Periods: A Pyrosequencing Approach. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.; Lindgreen, S.; Orlando, L. AdapterRemoval v2: Rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.T.; Jedlicka, J.A. Protocols for metagenomic DNA extraction and Illumina amplicon library preparation for faecal and swab samples. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majaneva, M.; Hyytiäinen, K.; Varvio, S.L.; Nagai, S.; Blomster, J. Bioinformatic amplicon read processing strategies strongly affect eukaryotic diversity and the taxonomic composition of communities. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cole, J.R.; Rosen, G.L. Using the RDP classifier to predict taxonomic novelty and reduce the search space for finding novel organisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D. Secondary structure improves OTU assignments of 16S rRNA gene sequences. ISME J. 2013, 7, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balvočiūtė, M.; Huson, D.H. SILVA, RDP, Greengenes, NCBI and OTT—How do these taxonomies compare? BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Casaburi, G.; Precone, V.; Salvatore, F. Comparative metagenomic analysis of human gut microbiome composition using two different bioinformatic pipelines. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancabelli, L.; Ferrario, C.; Milani, C.; Mangifesta, M.; Turroni, F.; Duranti, S.; Lugli, G.A.; Viappiani, A.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; van Sinderen, D. Insights into the biodiversity of the gut microbiota of broiler chickens. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4727–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solonenko, S.A.; Ignacio-Espinoza, J.C.; Alberti, A.; Cruaud, C.; Hallam, S.; Konstantinidis, K.; Tyson, G.; Wincker, P.; Sullivan, M.B. Sequencing platform and library preparation choices impact viral metagenomes. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dethlefsen, L.; Huse, S.; Sogin, M.L.; Relman, D.A. The pervasive effects of an antibiotic on the human gut microbiota, as revealed by deep 16S rRNA sequencing. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahinas, D.; Silverman, M.; Sittler, T.; Chiu, C.; Kim, P.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Weese, S.; Wong, A.; Low, D.E.; Pillai, D.R. Toward an understanding of changes in diversity associated with fecal microbiome transplantation based on 16S rRNA gene deep sequencing. MBio 2012, 3, e00338-00312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaufi, M.A.M.; Sieo, C.C.; Chong, C.W.; Gan, H.M.; Ho, Y.W. Deciphering chicken gut microbial dynamics based on high-throughput 16S rRNA metagenomics analyses. Gut Pathog. 2015, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Choi, H.L. Manure removal system influences the abundance and composition of airborne biotic contaminants in swine confinement buildings. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, C.; Rigottier-Gois, L.; Holmstrøm, K.; Rajilic, M.; Vaughan, E.E.; de Vos, W.M.; Collins, M.D.; Thiel, R.; Namsolleck, P.; Blaut, M. Colonic microbiota signatures across five northern European countries. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4153–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghir, A.; Gramet, G.; Suau, A.; Rochet, V.; Pochart, P.; Dore, J. Quantification of bacterial groups within human fecal flora by oligonucleotide probe hybridization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2263–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagier, J.-C.; Dubourg, G.; Million, M.; Cadoret, F.; Bilen, M.; Fenollar, F.; Levasseur, A.; Rolain, J.-M.; Fournier, P.-E.; Raoult, D. Culturing the human microbiota and culturomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Kim, N.; Nam, R.H.; Park, J.H.; Choi, S.I.; Park, Y.-T.; Kim, Y.-R.; Seok, Y.-J.; Shin, C.M.; Lee, D.H. Gut microbiota and butyrate level changes associated with the long-term administration of proton pump inhibitors to old rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, M.P.; Small, N. The anaerobic monotrichous butyric acid-producing curved rod-shaped bacteria of the rumen. J. Bacteriol. 1956, 72, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmokoff, M.; Teather, R. Isolation and characterization of a bacteriocin (Butyrivibriocin AR10) from the ruminal anaerobe Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens AR10: Evidence in support of the widespread occurrence of bacteriocin-like activity among ruminal isolates of B. fibrisolvens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepler, C.R.; Hirons, K.P.; McNeill, J.; Tove, S. Intermediates and products of the biohydrogenation of linoleic acid by Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.A.; Jayaraman, T.; Daly, P.; Canchaya, C.; Curran, S.; Fang, F.; Quigley, E.M.; O’Toole, P.W. Isolation of lactobacilli with probiotic properties from the human stomach. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 47, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilig, H.G.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Vaughan, E.E.; Marteau, P.; Akkermans, A.D.; de Vos, W.M. Molecular diversity of Lactobacillus spp. and other lactic acid bacteria in the human intestine as determined by specific amplification of 16S ribosomal DNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.G.W.; Claesson, M.H.; Jensen, S.S.; Ravn, P.; Kristensen, N.N. Antigen-presenting cells exposed to Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM, Bifidobacterium bifidum BI-98, and BI-504 reduce regulatory T cell activity. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 16, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavasani, S.; Dzhambazov, B.; Nouri, M.; Fåk, F.; Buske, S.; Molin, G.; Thorlacius, H.; Alenfall, J.; Jeppsson, B.; Weström, B. A novel probiotic mixture exerts a therapeutic effect on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mediated by IL-10 producing regulatory T cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedamallu, C.S.; Bhatt, A.S.; Bullman, S.; Fowler, S.; Freeman, S.S.; Durand, J.; Jung, J.; Duke, F.; Manzo, V.; Cai, D. Metagenomic characterization of microbial communities in situ within the deeper layers of the ileum in Crohn’s disease. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 563–566.e565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Park, W.; Srikanth, K.; Choi, B.-H.; Cho, E.-S.; Lee, K.-T.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, K.; Park, J.; Lim, D. Comparison of Bacterial Populations in the Ceca of Swine at Two Different Stages and Their Functional Annotations. Genes 2019, 10, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Park, W.; Lim, D.; Srikanth, K.; Kim, J.-M.; Jia, X.-Z.; Han, J.-L.; Hanotte, O.; Park, J.-E.; Oyola, S.O. Whole metagenome sequencing of cecum microbiomes in Ethiopian indigenous chickens from two different altitudes reveals antibiotic resistance genes. Genomics 2020, 112, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Wilkins, D.; Chen, J.; Ng, S.-K.; Lu, H.; Jia, Y.; Lee, P.K. Metagenomic reconstruction of key anaerobic digestion pathways in municipal sludge and industrial wastewater biogas-producing systems. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Ng, S.-K.; Lim, C.K.; Lu, H.; Jia, Y.; Lee, P.K. Physiological and metagenomic characterizations of the synergistic relationships between ammonia-and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in freshwater nitrification. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, H.; Jang, Y.N.; Kim, K.; Park, J.; Jung, M.W.; Park, J.-E. Compositional and Functional Characteristics of Swine Slurry Microbes through 16S rRNA Metagenomic Sequencing Approach. Animals 2020, 10, 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081372
Kumar H, Jang YN, Kim K, Park J, Jung MW, Park J-E. Compositional and Functional Characteristics of Swine Slurry Microbes through 16S rRNA Metagenomic Sequencing Approach. Animals. 2020; 10(8):1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081372
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Himansu, Yu Na Jang, Kwangmin Kim, Junhyung Park, Min Woong Jung, and Jong-Eun Park. 2020. "Compositional and Functional Characteristics of Swine Slurry Microbes through 16S rRNA Metagenomic Sequencing Approach" Animals 10, no. 8: 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081372
APA StyleKumar, H., Jang, Y. N., Kim, K., Park, J., Jung, M. W., & Park, J.-E. (2020). Compositional and Functional Characteristics of Swine Slurry Microbes through 16S rRNA Metagenomic Sequencing Approach. Animals, 10(8), 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081372




