Experimental Evidence Reveals Both Cross-Infection and Cross-Contamination Risk of Embryo Storage in Liquid Nitrogen Biobanks
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
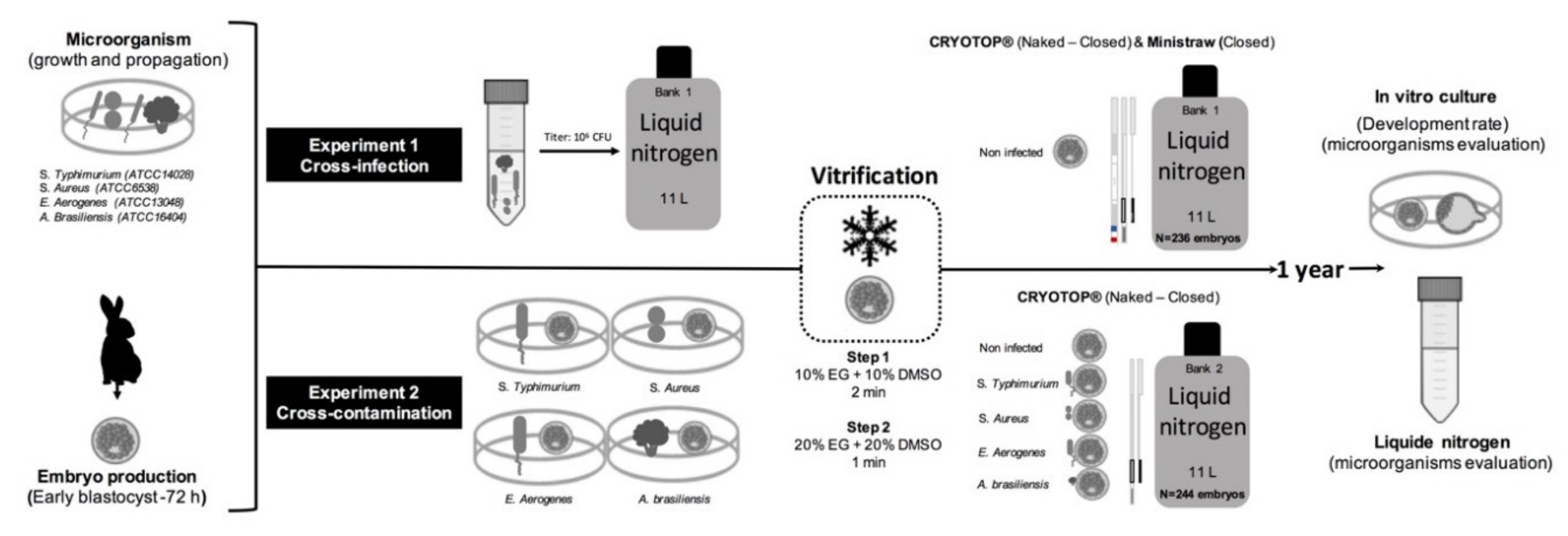
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Experiment 1. Cross-Infection: From Artificially Contaminated Liquid Nitrogen to Embryos
2.3. Embryo Recovery and Vitrification
2.4. Experiment 2. Cross-Contamination: From Artificially Infected Embryos to Liquid Nitrogen
2.5. Detection of Infectious Agents
2.5.1. Sample Collection (Experiment 1 and Experiment 2)
2.5.2. Microbiological Procedures
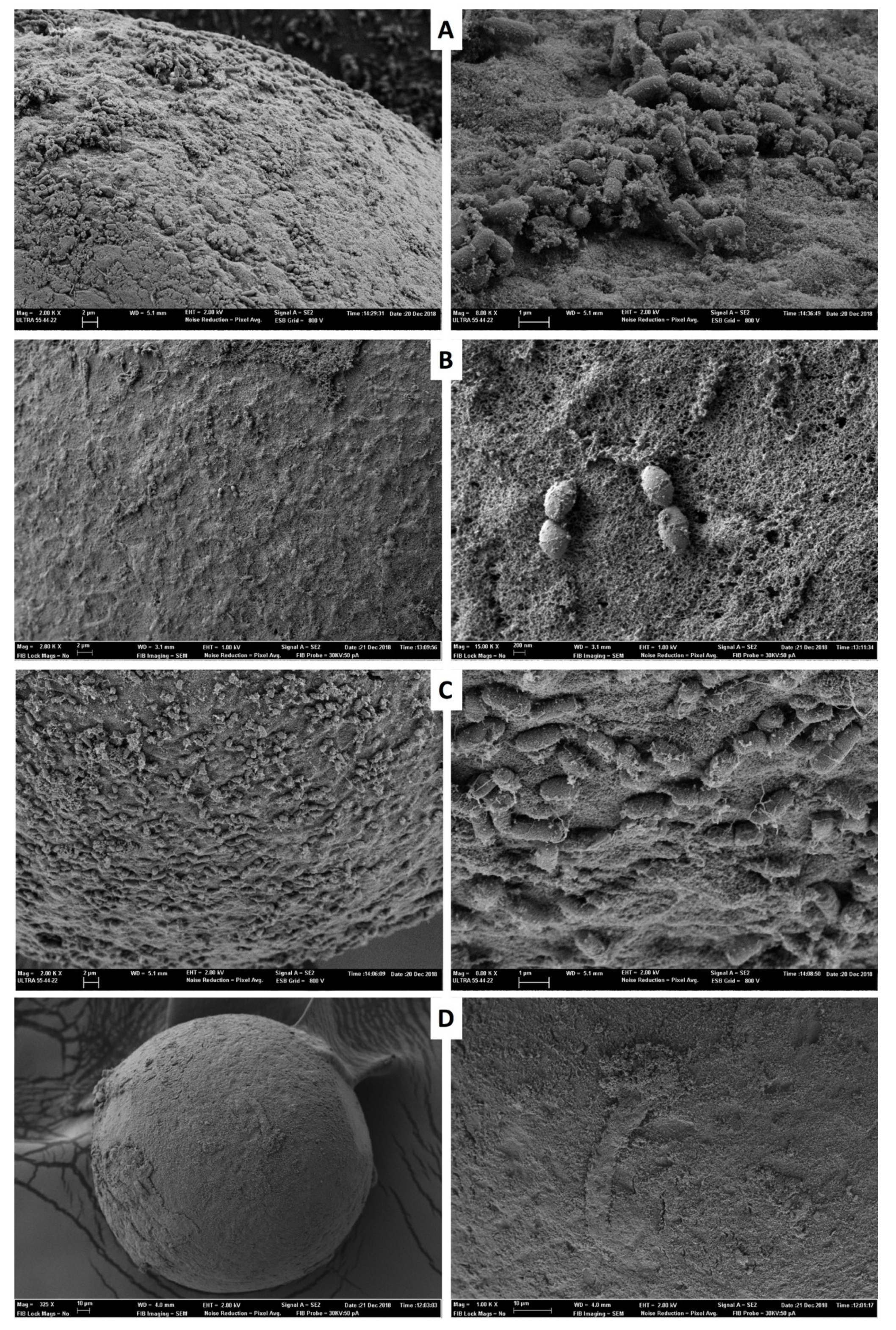
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Experiment 1. Cross-Infection: From Contaminated Liquid Nitrogen to Embryos
3.2. Experiment 2. Cross-Contamination: From Infected Embryos to Liquid Nitrogen
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| FSH | follicle stimulating hormone |
| hCG | human chorionic gonadotropin |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| BM | base medium |
| API | analytical profile index |
References
- Kushnir, V.A.; Barad, D.H.; Albertini, D.F.; Darmon, S.K.; Gleicher, N. Systematic review of worldwide trends in assisted reproductive technology 2004–2013. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2017, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geyter, C.; Calhaz-Jorge, C.; Kupka, M.S.; Wyns, C.; Mocanu, E.; Motrenko, T.; Scaravelli, G.; Smeenk, J.; Vidakovic, S.; Goossens, V. European IVF-monitoring Consortium (EIM) for the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE). ART in Europe, 2014: Results generated from European registries by ESHRE: The European IVF-monitoring Consortium (EIM) for the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE). Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1586–1601. [Google Scholar]
- Viana, J. 2017 Statistics of embryo production and transfer in domestic farm animals. Embryo Transf. Newsl. 2018, 36, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bielanski, A.; Bergeron, H.; Lau, P.C.; Devenish, J. Microbial contamination of embryos and semen during long term banking in liquid nitrogen. Cryobiology 2003, 46, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielanski, A.; Vajta, G. Risk of contamination of germplasm during cryopreservation and cryobanking in IVF units. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, I.; Mari, M.; Martinez, J.V.; Novella-Maestre, E.; Pellicer, N.; Peman, J. Bacterial and fungal contamination risks in human oocyte and embryo cryopreservation: Naked versus closed vitrification systems. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielanski, A. Biosafety in embryos and semen cryopreservation, storage, management and transport. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 753, 429–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bielanski, A.; Nadin-Davis, S.; Sapp, T.; Lutze-Wallace, C. Viral contamination of embryos cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen. Cryobiology 2000, 40, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, R.; De Paoli, P. Collection and preservation of frozen microorganisms. Methods. Mol. Biol. 2011, 675, 313–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwayama, M.; Vajta, G.; Ieda, S.; Kato, O. Comparison of naked and closed methods for vitrification of human embryos and the elimination of potential contamination. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2005, 11, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielanski, A. Disinfection procedures for controlling microorganisms in the semen and embryos of human and farm animals. Theriogenology 2007, 68, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikani, M. Cryostorage of human gametes and embryos: A reckoning. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2018, 37, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielanski, A. A review of the risk of contamination of semen and embryos during cryopreservation and measures to limit crosscontamination during banking to prevent disease transmission in ET practices. Theriogenology 2012, 77, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joaquim, D.C.; Borges, E.D.; Viana, I.G.R.; Navarro, P.A.; Vireque, A.A. Risk of Contamination of Gametes and Embryos during Cryopreservation and Measures to Prevent Cross-Contamination. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1840417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubálek, Z. Protectants used in the cryopreservation of microorganisms. Cryobiology 2003, 46, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, K.O.; Harris, S.; Conaghan, J.; Papadakis, M.; Centola, G.; Basuray, R.; Battaglia, D. Storage of cryopreserved reproductive tissues: Evidence that cross-contamination of infectious agents is a negligible risk. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrop, P.M.; de Graaf-Miltenburg, L.A.; Gutknecht, D.R.; Weima, S.M. Microbial contamination of embryo cultures in an ART laboratory: Sources and management. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 2243–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibier, M. Embryo transfer: A comparative biosecurity advantage in international movements of germplasm. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2011, 30, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.M.; Amaranath, K.A.; Perera, R.R.; Wijesinghe, P.S. Antibiotics supplemented culture media can eliminate non-specific bacteria from human semen during sperm preparation for intra uterine insemination. J. Hum. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 7, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magli, M.C.; Gianaroli, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Ferraretti, A.P.; Fortini, D.; Panzella, S. Improved cleavage rate of human embryos cultured in antibiotic-free medium. Hum. Reprod. 1996, 11, 1520–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; McKiernan, S.H.; Ji, W.; Bavister, B.D. Effect of antibiotics on development in vitro of hamster pronucleate ova. Theriogenology 2000, 54, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larman, M.G.; Hashimoto, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Gardner, D.K. Cryopreservation in ART and concerns with contamination during cryobanking. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2014, 13, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Embryo Transfer Society. Manual of the International Embryo Transfer Society. In IETS Manual; Stringfellow, D.A., Seidel, S.M., Eds.; Savoy: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Marco-Jiménez, F.; Jiménez-Trigos, E.; Almela-Miralles, V.; Vicente, J.S. Development of Cheaper Embryo Vitrification Device Using the Minimum Volume Method. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, A.C.; Romero, J.L.; Pérez, S.; de los Santos, M.J.; Meseguer, M.; Remohí, J. Storage of human oocytes in the vapor phase of nitrogen. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecka-Serafin, M. The effect of the sediment accumulated in containers under experimental conditions on the infection of semen stored directly in liquid nitrogen (−196 degree °C). Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci. Biol. 1972, 20, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, A.; Ino, N.; Kusumi, M.; Ohgi, S.; Ito, M.; Horikawa, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Saito, T.; Kamura, T.; Saito, H. Optimization of a novel nylon mesh container for human embryo ultrarapid vitrification. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 93, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen., Y.; Zheng, X.; Yan, J.; Qiao, J.; Liu, P. Neonatal outcomes after the transfer of vitrified blastocysts: Closed versus naked vitrification system. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2013, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotidis, Y.; Vanderzwalmen, P.; Prapas, Y.; Kasapi, E.; Goudakou, M.; Papatheodorou, A.; Passadaki, T.; Petousis, S.; Nikolettos, N.; Veletza, S.; et al. Open versus closed vitrification of blastocysts from an oocyte-donation programme: A prospective randomized study. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2013, 26, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Niringiyumukiza, J.D.; Li, Y.; Lai, Q.; Jia, Y.; Su, P.; Xiang, W. Naked versus closed with a closed system of human oocytes and embryos: A systematic review and meta-analysis of embryologic and clinical outcomes. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paffoni, A.; Guarneri, C.; Ferrari, S.; Restelli, L.; Nicolosi, A.E.; Scarduelli, C.; Ragni, G. Effects of two vitrification protocols on the developmental potential of human mature oocytes. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2011, 22, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Dominguez, X.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Puigcerver-Barber, M.; Mas-Pellicer, A.; Vicente, J.S. The harmful effect of removing the extracellular vitrification medium during embryo cryopreservation using a nylon mesh device in rabbit. Cryobiology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehaisen, G.M.; Saeed, A.M. In vitro development rate of preimplantation rabbit embryos cultured with different levels of melatonin. Zygote 2015, 23, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmegiani, L.; Accorsi, A.; Bernardi, S.; Arnone, A.; Cognigni, G.E.; Filicori, M. A reliable procedure for decontamination before thawing of human specimens cryostored in liquid nitrogen: Three washes with sterile liquid nitrogen (SLLN2). Fertil. Steril. 2012, 98, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arav, A.; Natan, Y. The Near Future of Vitrification of Oocytes and Embryos: Looking into Past Experience and Planning into the Future. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2019, 46, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedder, R.S.; Zuckerman, M.A.; Goldstone, A.H.; Hawkins, A.E.; Fielding, A.; Briggs, E.M.; Irwin, D.; Blair, S.; Gorman, A.M.; Patterson, K.G.; et al. Hepatitis B transmission from contaminated cryopreservation tank. Lancet 1995, 346, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaffaldano, N.; Reale, A.; Sorrentino, E.; Coppola, R.; Di Iorio, M.; Rosato, M.P. Risk of Salmonella transmission via cryopreserved semen in turkey flocks. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayatollahi, A.A.; Amini, A.; Rahimi, S.; Takrami, S.R.; Darsanaki, R.K.; Nezhad, M.S. Prevalence of Gram-Negative Bacilli Isolated from the Equipment and Surfaces in Hospital Wards of Golestan Province, North of Iran. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. (Bp) 2017, 7, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancraeynest, D.; Haesebrouck, F.; Deplano, A.; Denis, O.; Godard, C.; Wildemauwe, C.; Hermans, K. International dissemination of a high virulence rabbit Staphylococcus aureus clone. J. Vet. Med. B. Infect. Dis. Vet. Public. Health. 2006, 53, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, G.K.; Harrison, E.M.; Holmes, M.A. The emergence of mecC methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Trends. Microbiol. 2014, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.F.; Lassala, A.L.; Spencer, T.E. Staphylococcus-associated Abortions in Ewes with Long-term Central Venous Catheterization. Vet. Pathol. 2018, 45, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardigò, P.; D’Incau, M.; Pongolini, S. Abortion in cattle due to infection with Staphylococcus lugdunensis. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2014, 26, 818–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z. Staphylococcal infection and infertility. In Genital Infections and Infertility; Darwish, A.M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 159–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, R.; Choudhury, D.R. Effect of liquid nitrogen freezing and subsequent storage on survival of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes in treated prawn meat. Fish. Technol. 1988, 25, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kest, S.E.; Marth, E.H. Freezing of Listeria monocytogenes and Other Microorganisms: A Review. J. Food. Prot. 1992, 55, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolami, A.; Williams, N.J.; McGowan, C.M.; Kelly, P.G.; Archer, D.C.; Corrò, M.; Pinchbeck, G.; Saunders, C.J.; Timofte, D. Environmental surveillance identifies multiple introductions of MRSA CC398 in an Equine Veterinary Hospital in the UK, 2011–2016. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, N.D.; Temkin, E.; Carmeli, Y. The negative impact of antibiotic resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemeire, K.; Van Merris, V.; Cortvrindt, R. The antibiotic streptomycin assessed in a battery of in vitro tests for reproductive toxicology. Toxicol. In Vitro 2007, 21, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.N.; Khan, A.U. Breaking the Spell: Combating Multidrug Resistant ‘Superbugs’. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, G.V.; Ramadhan, T.; Ahmed, E.; Sanad, H. WHO Global Priority Pathogens List: A Bibliometric Analysis of Medline-PubMed for Knowledge Mobilization to Infection Prevention and Control Practices in Bahrain. Oman Med. J. 2019, 34, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, M.F.; Marco-Jimenez, F.; Duncan, D.; Marín, C.; Smith, R.P.; Evans, S.J. Livestock-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus From Animals and Animal Products in the UK. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M.; SchaÈfer, J.; Simmet, C.; Jung, M.; Gabler, C. Detection and characterization of Lactobacillus spp. in the porcine seminal plasma and their influence on boar semen quality. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, I.; Bordeau, V.; Bondon, A.; BaudyFloc’h, M.; Felden, B. Novel antibiotics effective against gram-positive and -negative multiresistant bacteria with limited resistance. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Device | n | Hatching/Hatched Blastocyst Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Cryotop-naked | 57 | 71.0 ± 5.10 |
| Cryotop-closed | 67 | 76.0 ± 4.50 |
| Mini-straw | 87 | 82.0 ± 3.70 |
| Device | Pathogen | n | Hatching/Hatched Blastocyst Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cryotop-naked | Salmonella Typhimurium | 23 | 78.0 ± 8.6 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 24 | 71.0 ± 9.3 | |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | 22 | 77.0 ± 8.9 | |
| Aspergillus brasiliensis | 24 | 79.0 ± 8.3 | |
| Control | 14 | 86.0 ± 9.4 | |
| Cryotop-closed | Salmonella Typhimurium | 19 | 73.0 ± 11.1 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 24 | 79.0 ± 8.3 | |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | 25 | 82.0 ± 5.4 | |
| Aspergillus brasiliensis | 25 | 74.0 ± 9.6 | |
| Control | 24 | 79.0 ± 8.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marin, C.; Garcia-Dominguez, X.; Montoro-Dasi, L.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; Vicente, J.S.; Marco-Jimenez, F. Experimental Evidence Reveals Both Cross-Infection and Cross-Contamination Risk of Embryo Storage in Liquid Nitrogen Biobanks. Animals 2020, 10, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040598
Marin C, Garcia-Dominguez X, Montoro-Dasi L, Lorenzo-Rebenaque L, Vicente JS, Marco-Jimenez F. Experimental Evidence Reveals Both Cross-Infection and Cross-Contamination Risk of Embryo Storage in Liquid Nitrogen Biobanks. Animals. 2020; 10(4):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040598
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarin, Clara, Ximo Garcia-Dominguez, Laura Montoro-Dasi, Laura Lorenzo-Rebenaque, José S. Vicente, and Francisco Marco-Jimenez. 2020. "Experimental Evidence Reveals Both Cross-Infection and Cross-Contamination Risk of Embryo Storage in Liquid Nitrogen Biobanks" Animals 10, no. 4: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040598
APA StyleMarin, C., Garcia-Dominguez, X., Montoro-Dasi, L., Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L., Vicente, J. S., & Marco-Jimenez, F. (2020). Experimental Evidence Reveals Both Cross-Infection and Cross-Contamination Risk of Embryo Storage in Liquid Nitrogen Biobanks. Animals, 10(4), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040598






