Developing Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Identification of Cod Products by RAD-Seq
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cod Samples and DNA Isolation
2.2. Species Identification by COI
2.3. RAD-Seq and Data Analysis
2.4. Primer Design and SNPs Validation
3. Results
3.1. DNA Barcoding of Cod Samples
3.2. SNPs Identification Based on RAD Sequencing Data
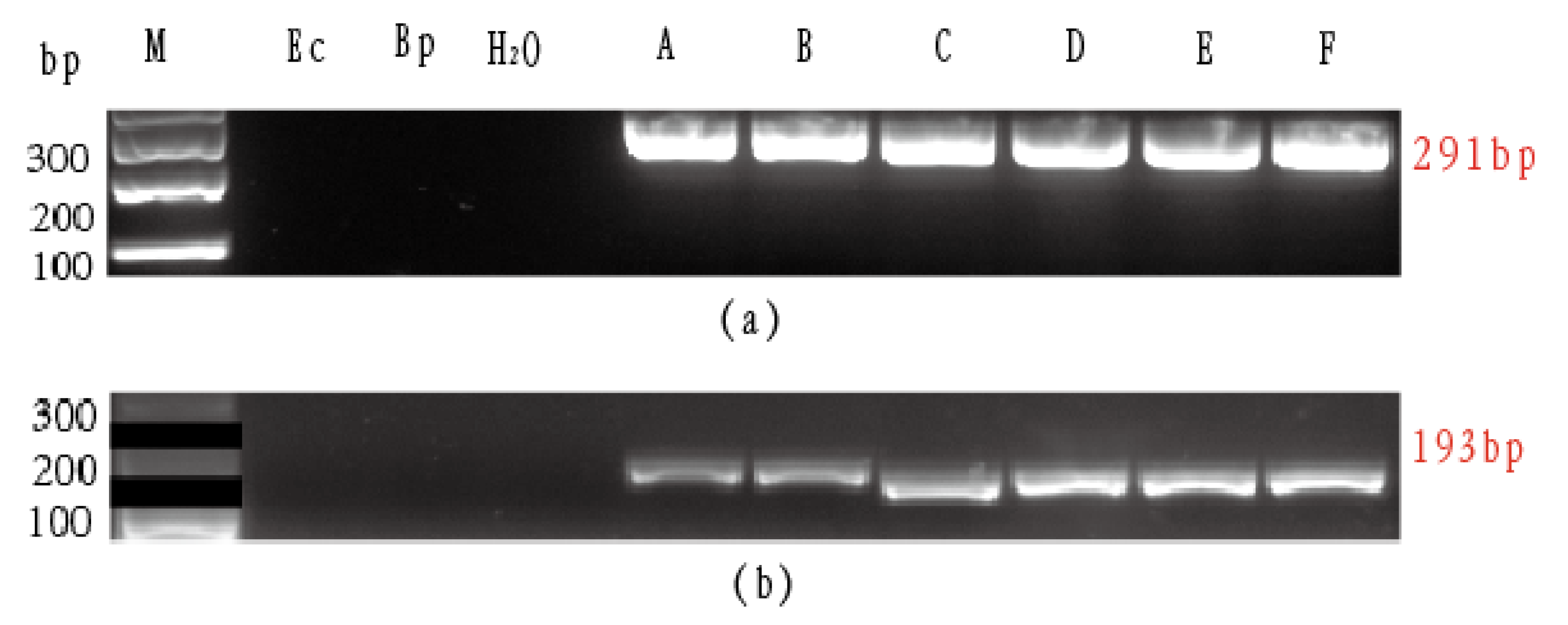
3.3. Primer Design and SNPs Verification
4. Discussion
4.1. The Confusion of Commercial Cod Species
4.2. COI Gene and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. RAD-seq Identification of Cod Species
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sumathi, G.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Shakila, R.J.; Sivaraman, B.; Arunkumar, G.; Manimaran, U.; Sukumar, D. Molecular identification of grouper species using PCR-RFLP technique. Food Control 2015, 51, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossier, P. Authentication of seafood products by DNA patterns. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.S.; Morrissey, M.T. DNA-based methods for the identification of commercial fish and seafood species. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food 2008, 7, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Yu, K.; Qu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Kimura, I. An online survey study of consumer preferences on aquatic products in China: Current seafood consumption patterns and trends. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, J.; Ross, T. A semi-quantitative seafood safety risk assessment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 77, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armani, A.; Tinacci, L.; Lorenzetti, R.; Benvenuti, A.; Susini, F.; Gasperetti, L.; Ricci, E.; Guarducci, M.; Guidi, A. Is raw better? A multiple DNA barcoding approach (full and mini) based on mitochondrial and nuclear markers reveals low rates of misdescription in sushi products sold on the Italian market. Food Control 2017, 79, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.; Timme, W.; Lowell, B.; Hirschfield, M. Oceana Study Reveals Seafood Fraud Nationwide; Oceana: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Guardone, L.; Giusti, A.; Castigliego, L.; Gianfaldoni, D.; Guidi, A.; Andrea, A. DNA barcoding reveals chaotic labeling and misrepresentation of cod (鳕, Xue) products sold on the Chinese market. Food Control 2016, 60, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.-M.; Remais, J.; Fung, M.-C.; Xu, L.; Sun, S.S.-M. Food supply and food safety issues in China. Lancet 2013, 381, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etienne, M.; Jérôme, M.; Fleurence, J.; Rehbein, H.; Kündiger, R.; Mendes, R.; Costa, H.; Martínez, I. Species identification of formed fishery products and high pressure-treated fish by electrophoresis: A collaborative study. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, C.; Ferrando, S.; Gatti, A.M.; Cataldi, E.; Ramoino, P.; Aluigi, M.G.; Faimali, M.; Diaspro, A.; Falugi, C. Morphofunctional and biochemical markers of stress in sea urchin life stages exposed to engineered nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, A.; Hilger, C.; Graf, T.; Hentges, F. Protein and DNA-based assays as complementary tools for fish allergen detection. Allergologie 2017, 1, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás, C.; Ferreira, I.; Faria, M. Codfish authentication by a fast short amplicon high resolution melting analysis (SA-HRMA) method. Food Control 2017, 71, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, J.L.; Ram, M.L.; Baidoun, F.F. Authentication of canned tuna and bonito by sequence and restriction site analysis of polymerase chain reaction products of mitochondrial DNA. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wen, J.; Fan, S.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhao, J. Species identification of fish maw (Porcupinefish) products sold on the market using DNA sequencing of 16S rRNA and COI genes. Food Control 2018, 86, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devassy, A.; Kumar, R.; Shajitha, P.; John, R.; Padmakumar, K.; Basheer, V.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Mathew, L. Genetic identification and phylogenetic relationships of Indian clariids based on mitochondrial COI sequences. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 3777–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cutarelli, A.; Galiero, G.; Capuano, F.; Corrado, F. Species identification by means of mitochondrial cytochrome b DNA sequencing in processed anchovy, sardine and tuna products. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2018, 9, 369. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazali, S.N.; Ahmad, A.; Quraishia, S.F.; Panneerchelvam, S.; Rashid, N.H.A. Molecular characterization of ornamental fish (Poeciliidae) using mitochondrial DNA 12s rRNA and 16s rRNA genes. Ann. Biol. Res. 2016, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Akasaki, T.; Yanagimoto, T.; Yamakami, K.; Tomonaga, H.; Sato, S. Species identification and PCR-RFLP analysis of cytochrome b gene in cod fish (order Gadiformes) products. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C190–C195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comi, G.; Iacumin, L.; Rantsiou, K.; Cantoni, C.; Cocolin, L. Molecular methods for the differentiation of species used in production of cod-fish can detect commercial frauds. Food Control 2005, 16, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubalkova, Z.; Kralik, P.; Tremlova, B.; Rencova, E. Methods of gadoid fish species identification in food and their economic impact in the Czech Republic: A review. Vet. Med. Czech. 2007, 52, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Cheng, L.; Tong, J.; Yu, X. Development and characterization of new single nucleotide polymorphism markers from expressed sequence tags in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 7343–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davey, J.W.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Etter, P.D.; Boone, J.Q.; Catchen, J.M.; Blaxter, M.L. Genome-wide genetic marker discovery and genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, C.; Appleby, N.; Edwards, D.; Batley, J. Molecular genetic markers: Discovery, applications, data storage and visualisation. Curr. Bioinform. 2009, 4, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvin, M.; Gharrett, A. DEco-TILLING: An inexpensive method for single nucleotide polymorphism discovery that reduces ascertainment bias. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, L.; Simmons, M.; Li, P.; Kim, S.; Liu, Z. Putative SNP discovery in interspecific hybrids of catfish by comparative EST analysis. Anim. Genet. 2003, 34, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenke, P.L.; Rhydderch, J.G.; Ford, M.J.; Marshall, A.R.; Park, L.K. Forensic identification of endangered Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) using a multilocus SNP assay. Conserv. Genet. 2006, 7, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, T.; Hayes, B.; Nilsen, F.; Delghandi, M.; Fjalestad, K.T.; Fevolden, S.-E.; Berg, P.R.; Lien, S. Identification and characterisation of novel SNP markers in Atlantic cod: Evidence for directional selection. BMC Genet. 2008, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robledo, D.; Palaiokostas, C.; Bargelloni, L.; Martínez, P.; Houston, R. Applications of genotyping by sequencing in aquaculture breeding and genetics. Rev. Aquacult. 2018, 10, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Dunham, J.P.; Amores, A.; Cresko, W.A.; Johnson, E.A. Rapid and cost-effective polymorphism identification and genotyping using restriction site associated DNA (RAD) markers. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etienne, M.; Jérôme, M.; Fleurence, J.; Rehbein, H.; Kündiger, R.; Mendes, R.; Costa, H.; Pérez-Martín, R.; Piñeiro-González, C.; Craig, A. Identification of fish species after cooking by SDS- PAGE and urea IEF: A collaborative study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2653–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, A.; Lara, T.; Xiong, X.; Evgeniya, T.; Alessandra, G.; Lorenzo, C. Development of a simple and cost-effective bead-milling method for DNA extraction from fish muscles. Food Anal. Method 2014, 7, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baird, N.A.; Etter, P.D.; Atwood, T.S.; Currey, M.C.; Shiver, A.L.; Lewis, Z.A.; Selker, E.U.; Cresko, W.A.; Johnson, E.A. Rapid SNP discovery and genetic mapping using sequenced RAD markers. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z. SOAPnuke: A MapReduce acceleration-supported software for integrated quality control and preprocessing of high-throughput sequencing data. Gigascience 2017, 7, gix120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Star, B.; Nederbragt, A.J.; Jentoft, S.; Grimholt, U.; Malmstrøm, M.; Gregers, T.F.; Rounge, T.B.; Paulsen, J.; Solbakken, M.H.; Sharma, A. The genome sequence of Atlantic cod reveals a unique immune system. Nature 2011, 477, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kofanova, O.; Bellora, C.; Frasquilho, S.G.; Antunes, L.; Hamot, G.; Mathay, C.; Mommaerts, K.; Muller, A.; DeWitt, B.; Betsou, F. Standardization of the preanalytical phase of DNA extraction from fixed tissue for next-generation sequencing analyses. New Biotechnol. 2019, 54, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, J.L.; Pauly, D. Trade secrets: Renaming and mislabeling of seafood. Mar. Policy 2008, 32, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.E.; Cariani, A.; Mac Aoidh, E.; Maes, G.E.; Milano, I.; Ogden, R.; Taylor, M.; Hemmer-Hansen, J.; Babbucci, M.; Bargelloni, L. Gene-associated markers provide tools for tackling illegal fishing and false eco-certification. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardo, M.Á.; Jiménez, E.; Pérez-Villarreal, B. Misdescription incidents in seafood sector. Food Control 2016, 62, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero, B.; Madrinan, M.; Vieites, J.M.; ESPINeira, M. Authentication of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) using real time PCR. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4794–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Finizio, A.; Guerriero, G.; Russo, G.L.; Ciarcia, G. Identification of gadoid species (Pisces, Gadidae) by sequencing and PCR–RFLP analysis of mitochondrial 12S and 16S rRNA gene fragments. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 225, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, V.; Sengar, S. DNA Barcoding: Current status application and future perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 6, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinoff, D.; Cameron, S.; Will, K. A genomic perspective on the shortcomings of mitochondrial DNA for “barcoding” identification. J. Hered. 2006, 97, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Recknagel, H.; Elmer, K.R.; Meyer, A. A hybrid genetic linkage map of two ecologically and morphologically divergent Midas cichlid fishes (Amphilophus spp.) obtained by massively parallel DNA sequencing (ddRADSeq). G3 Genes Genom Genet. 2013, 3, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews, K.R.; Good, J.M.; Miller, M.R.; Luikart, G.; Hohenlohe, P.A. Harnessing the power of RADseq for ecological and evolutionary genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devine, J.; Watling, L.; Cailliet, G.; Drazen, J.; Muñoz, P.D.; Orlov, A.; Bezaury, J. Evaluation of potential sustainability of deep-sea fisheries for grenadiers (Macrouridae). J. Paleolimnol. 2012, 52, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, C.; Stasko, A.; Walkusz, W.; Majewski, A.; Rosenberg, B.; Power, M.; Swanson, H.; Reist, J.D. Feeding of Greenland halibut (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides) in the Canadian Beaufort Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2018, 183, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datsky, A.; Yarzhombek, A.; Andronov, P.Y. Arrow-toothed halibuts Atheresthes spp. (Pleuronectiformes, Pleuronectidae) and their role in the fish community of Olyutorsky-Navarin region and adjacent areas of the Bering Sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2014, 54, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evseenko, S.; Kock, K.-H.; Nevinsky, M. Early life history of the Patagonian toothfish, Dissostichus eleginoides Smitt, 1898 in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean. Antarct. Sci. 1995, 7, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
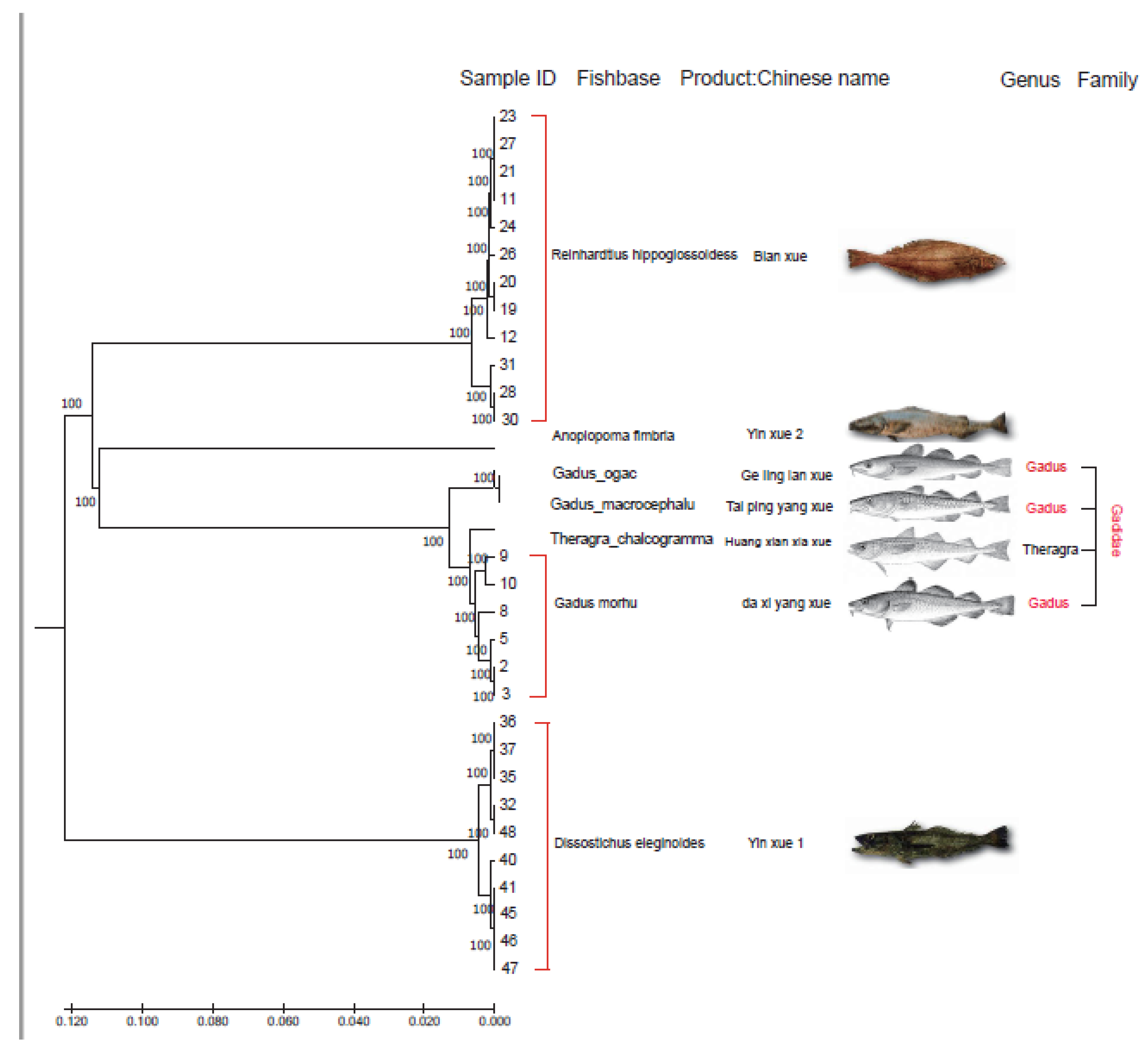
| Selected Products | Label of the Received Products | COI Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample ID | Species in Label | Product Status | Matched Accession Number | ID GenBank (% Similarity) | |
| Da xi yang xue | NO2 | Iceland Atlantic cod | In bulk | LS999407.1 | G. morhua 99.41% |
| NO3 | Iceland Atlantic cod | In bulk | LS999407.1 | G. morhua 99.56% | |
| NO5 | Wild cod | Prepackaged | LS999106.1 | G. morhua 99.26% | |
| NO8 | Wild cod | Prepackaged | LS999106.1 | G. morhua 99.56% | |
| NO9 | Norwegian Atlantic cod | Prepackaged | MK011280.1 | G. morhua 99.55% | |
| NO10 | Norwegian Atlantic cod | Prepackaged | LS999407.1 | G. morhua 99.41% | |
| Bian xue | NO11 | Greenland cod | Prepackaged | AM749133.1 | R. hippoglossoides 99.12% |
| NO12 | Greenland cod | Prepackaged | AM749133.1 | R. hippoglossoides 99.12% | |
| NO19 | Greenland cod | Prepackaged | MH032539.1 | R. hippoglossoides 99.85% | |
| NO20 | Greenland flat cod | In bulk | AM749132.1 | R. hippoglossoides 98.38% | |
| NO21 | Greenland flat cod | In bulk | MH032539.1 | R. hippoglossoides 98.96% | |
| NO23 | Greenland flat cod | In bulk | AM749130.1 | R. hippoglossoides 98.96% | |
| NO24 | Greenland flat cod | In bulk | HM421730.1 | R. hippoglossoides 100% | |
| NO26 | Greenland halibut | Prepackaged | KC015874.1 | R. hippoglossoides 99.85% | |
| NO27 | Greenland halibut | Prepackaged | KF386352.1 | R. hippoglossoides 100% | |
| NO28 | Greenland halibut | Prepackaged | MH032539.1 | R. hippoglossoides 98.96% | |
| NO30 | Greenland halibut | Prepackaged | KF386350.1 | R. hippoglossoides 98.96% | |
| NO31 | Greenland halibut | Prepackaged | MH032539.1 | R. hippoglossoides 98.96% | |
| Yin Xue | NO32 | French cod | In bulk | AB723627.1 | D. eleginoides 98.97% |
| NO35 | French cod | In bulk | JN640625.1 | D. eleginoides 99.54% | |
| NO36 | French toothfish | In bulk | AB723627.1 | D. eleginoides 98.97% | |
| NO37 | French toothfish | Prepackaged | AB723627.1 | D. eleginoides 99.56% | |
| NO40 | French toothfish | Prepackaged | AB723627.1 | D. eleginoides 98.37% | |
| NO41 | French toothfish | Prepackaged | EU752077.1 | D. eleginoides 98.61% | |
| NO45 | French toothfish | Prepackaged | EF609344.1 | D. eleginoides 98.47% | |
| NO46 | French toothfish | Prepackaged | AB723627.1 | D. eleginoides 98.97% | |
| NO47 | French toothfish | Prepackaged | EU074416.1 | D. eleginoides 98.61% | |
| NO48 | French toothfish | Prepackaged | AB723627.1 | D. eleginoides 98.97% | |
| Primer | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F12014 | CAGATACCCTCGAATA | 64 | 291 |
| R12014 | CAAACAAATAGAGGGGTTTGGTA | ||
| F42229 | ATTCGGGCAGAACTAAGCCAACCTG | 63 | 193 |
| R42229 | CTCATGTTATTTATTCGAGGGAAAGC |
| Sequence ID | F12014 | F42229 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | 82th Base | 112th Base | 220th Base | 127th Base | 163th Base |
| G. morhua | G | T | A | G | A |
| R. hippoglossoides | T | A | G | A | C |
| D. eleginoides | A | G | T | T | G |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Ma, X.; Li, T.; Zhu, C.; You, X. Developing Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Identification of Cod Products by RAD-Seq. Animals 2020, 10, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030423
Jiang S, Ma X, Li T, Zhu C, You X. Developing Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Identification of Cod Products by RAD-Seq. Animals. 2020; 10(3):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030423
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shoujia, Xingyu Ma, Tao Li, Changqing Zhu, and Xinxin You. 2020. "Developing Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Identification of Cod Products by RAD-Seq" Animals 10, no. 3: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030423
APA StyleJiang, S., Ma, X., Li, T., Zhu, C., & You, X. (2020). Developing Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Identification of Cod Products by RAD-Seq. Animals, 10(3), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030423





