Unveiling the Immunomodulatory Characteristics of Haemonchus contortus Ephrin Domain Containing Protein in the Parasite–Host Interactions
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Parasites
2.2. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of H. Contortus EPH Gene
2.3. Expression of Recombined Proteins
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Localization Assay
2.6. Preparation of Goat PBMCs
2.7. PBMCs Binding Assay
2.8. Cell Activity Assay
2.9. Cell Migration Assay
2.10. Annexin V-FITC/Propidium Iodide Staining Assay
2.11. Detection of Cytokine Transcripts by FQ-PCR
2.12. Determination of Goat PBMCs-Derived T helper-9 Cells
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Cloning, Expression, Purification, and Western Blot Anaylsis of HcEPH
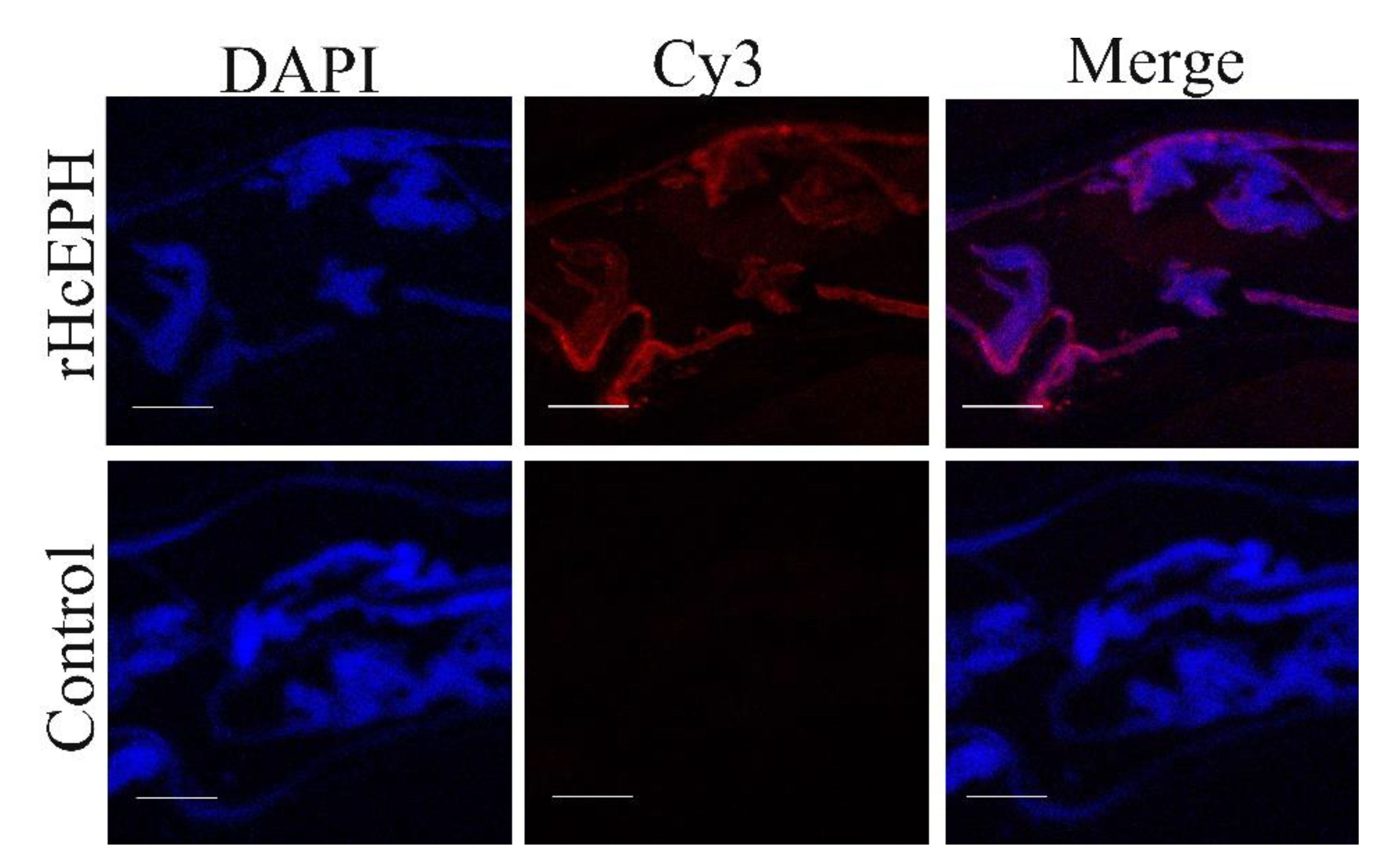
3.2. HcEPH Localized of H. contortus Adult Worm Sections
3.3. Validation of rHcEPH Binding with PBMCs
3.4. rHcEPH Reduced Cell Activity of Goat PMBCs
3.5. rHcEPH Increased Cell Migration of Goat PMBCs
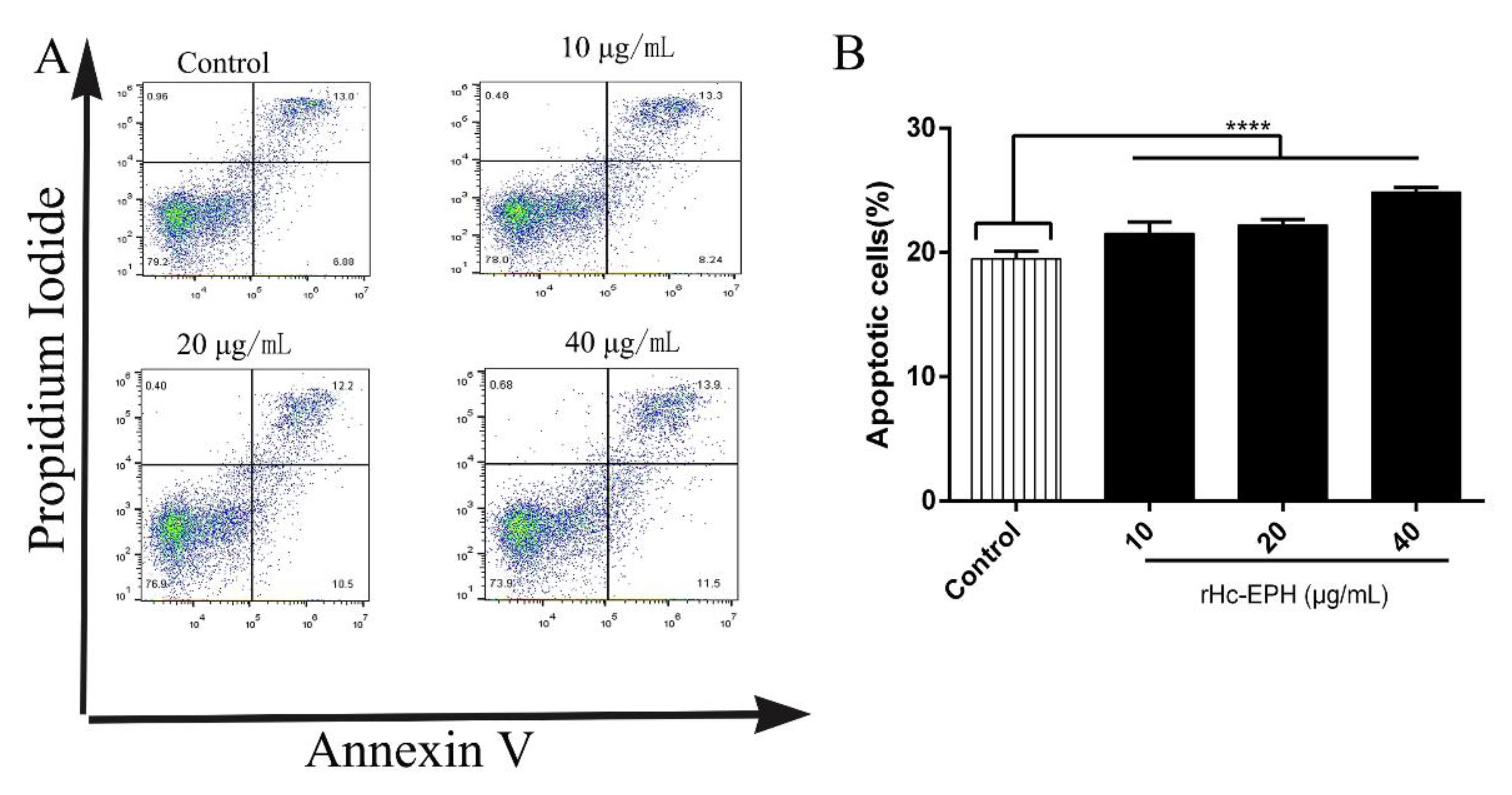
3.6. rHcEPH Dramatically Modulated Apoptosis of Goat PBMCs
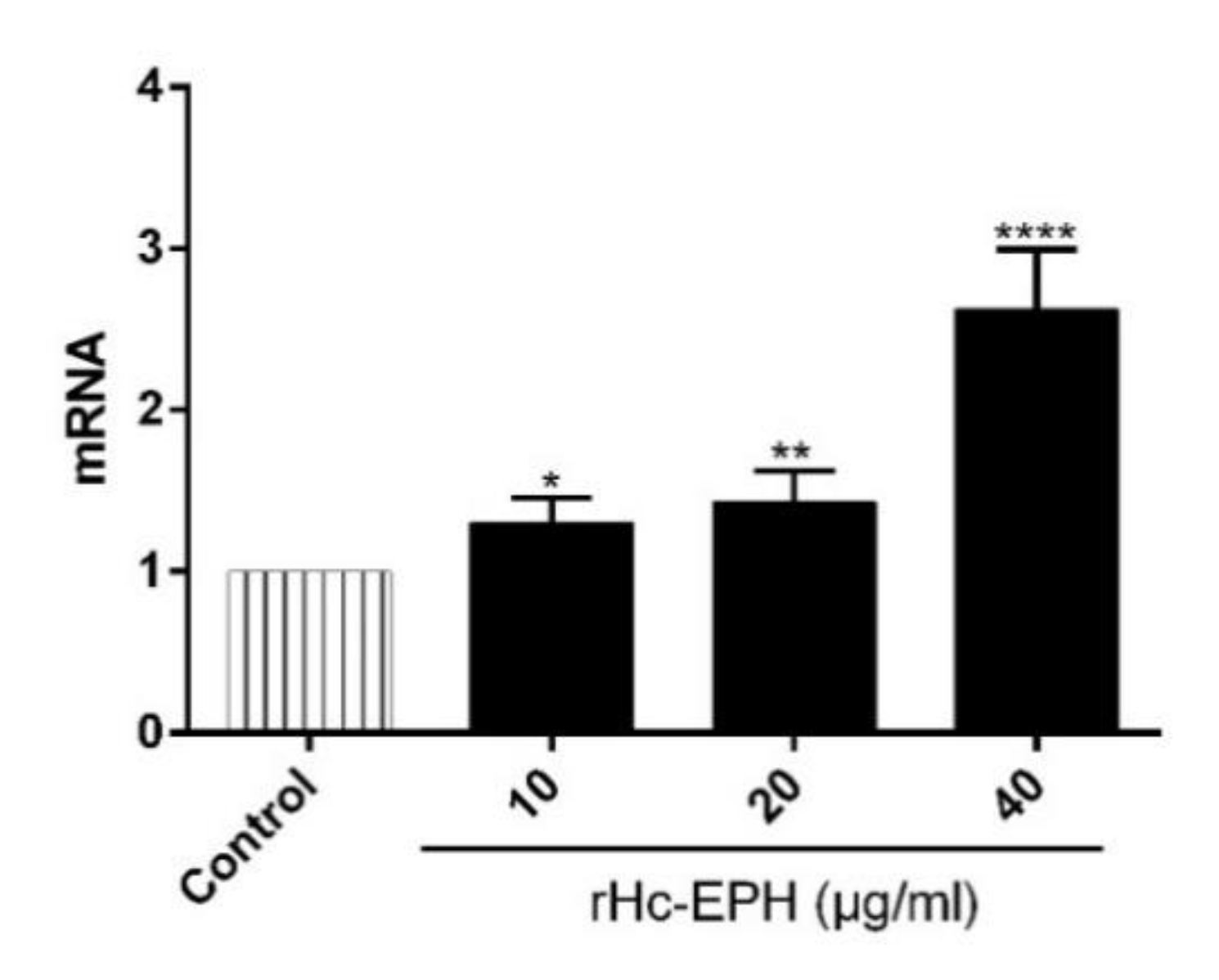
3.7. rHcEPH Modulated IL-9 Secretion by PBMCs
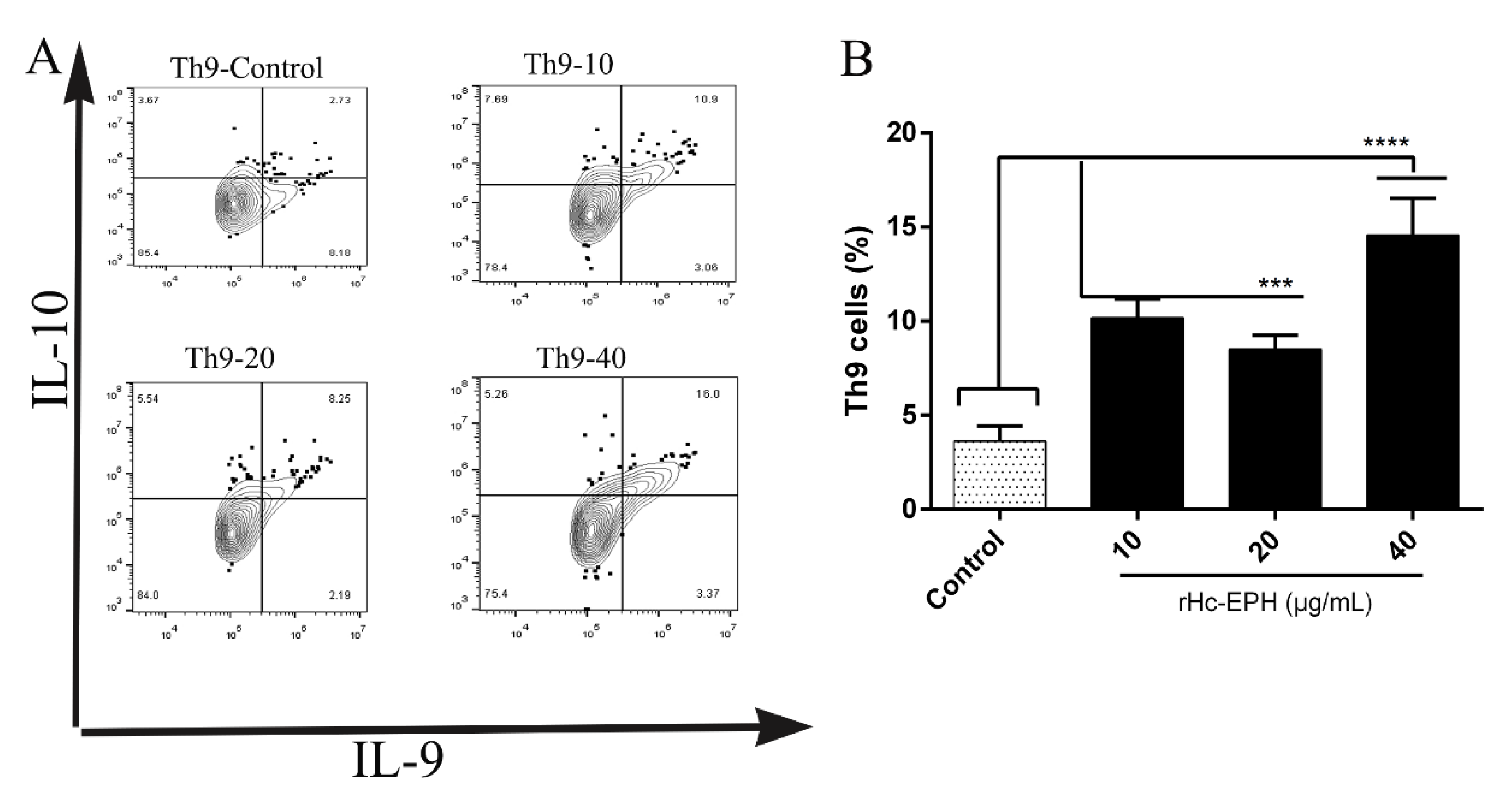
3.8. Effect of rHcEPH on Th9 Cells Differentiation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, X.; Lu, M.; Jia, C.; Bu, Y.; Aimulajiang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, R.-F.; Xu, L.-X.; Song, X.; et al. Haemonchus contortus transthyretin domain—Containing protein (HcTTR): A promising vaccine candidate against Haemonchus contortus infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 279, 109045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimulajiang, K.; Yan, R.; Chu, W.; Lu, M.; Tian, X.; Bu, Y.; Memon, M.A.; Li, X.; Xu, L.-X.; Song, X.; et al. Adhesion-regulating molecule from Haemonchus contortus: Potential antigen for diagnosis of early infection in goats. Pathogens 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimulajiang, K.; Cao, M.; Liao, S.; Yan, R.; Tian, X.; Li, Z.; Lu, M.; Lakho, S.A.; Li, X.; Xu, L.-X.; et al. Development and potential application of ras domain containing protein from Haemonchus contortus for diagnosis of goat infection. Animals 2020, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Jia, C.; Tian, X.; Aimulajiang, K.; Memon, M.A.; Yan, R.-F.; Song, X.; Xu, L.-X.; Li, X. Immunization of goats with recombinant protein 14-3-3 isoform 2(rhcftt-2) induced moderate protection against Haemonchus contortus challenge. Pathogens 2020, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Xu, L.-X.; Yan, R.-F.; Song, X.; Li, X. Vaccination of goats with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase DNA vaccine induced partial protection against Haemonchus contortus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 149, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djafsia, B.; Ndjonka, D.; Dikti, J.; Van Hoorn, S.; Manchang, K.; Brattig, N.; Liebau, E. Immune recognition of excretory and secretory products of the filarial nematode Onchocerca ochengi in cattle and human sera. J. Helminthol. 2015, 94, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.A.; Yan, R.; Xin, H.; Meng, L.; Hasan, M.W.; Haseeb, M.; Lakho, S.A.; Aimulajiang, K.; Bu, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Immunomodulatory dynamics of excretory and secretory products on th9 immune response during Haemonchus contortus infection in goat. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadahi, J.A.; Wang, S.; Bo, G.; Ehsan, M.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Xu, L.; Li, X. Proteomic analysis of the excretory and secretory proteins of Haemonchus contortus (HcESP) binding to goat PBMCs in vivo revealed stage-specific binding profiles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosato, G. Ephrin ligands and Eph receptors contribution to hematopoiesis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3377–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.G. Regulation of cell differentiation by Eph receptor and ephrin signaling. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 8, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, T.K.; Lamb, T.J. Emerging roles for Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Memon, M.A.; Jamil, T.; Naqvi, S.Z.; Aimulajiang, K.; Gadahi, J.A.; Xu, L.-X.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Yan, R.-F.; et al. Galectin Domain Containing Protein from Haemonchus contortus Modulates the Immune Functions of Goat PBMCs and Regulates CD4+ T-Helper Cells In Vitro. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angkasekwinai, P.; Srimanote, P.; Wang, Y.-H.; Pootong, A.; Sakolvaree, Y.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; Chaicumpa, W.; Chaiyaroj, S.; Dong, C. Interleukin-25 (IL-25) promotes efficient protective immunity against Trichinella spiralis infection by enhancing the antigen-specific IL-9 response. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3731–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.H.; Hufford, M.M.; Olson, M.R. The development and in vivo function of T helper 9 cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guan, L.; Tang, L.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, C.; He, Z.; Xu, L. T helper 9 cells: A new player in immune-related diseases. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.I.; Richard, M.; Akiho, H.; Blennerhasset, P.A.; Humphreys, N.E.; Grencis, R.K.; Van Snick, J.; Collins, S.M. Modulation of intestinal muscle contraction by Interleukin-9 (IL-9) or IL-9 neutralization: Correlation with worm expulsion in murine nematode infections. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2430–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, H.; Renauld, J.-C.; Van Snick, J.; Grencis, R.K. Interleukin-9 enhances resistance to the intestinal nematode Trichuris muris. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 3832–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licona-Limón, P.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Temann, A.U.; Gagliani, N.; Licona-Limón, I.; Ishigame, H.; Hao, L.; Herbert, D.R.; Flavell, R.A. Th9 cells drive host immunity against gastrointestinal worm infection. Immunity 2013, 39, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wu, C.-Y. Differentiation, regulation and function of Th9 cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 841, 181–207. [Google Scholar]
- Gadahi, J.A.; Li, B.; Ehsan, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hasan, M.W.; Yan, R.; Song, X.; Xu, L.; et al. Recombinant Haemonchus contortus 24 kda excretory/secretory protein (rHcES-24) modulate the immune functions of goat PBMCs in vitro. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83926–83937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, I.; Mavrangelos, C.; Fung, K.Y.C.; Ayhan, M.; Levichkin, I.; Johnston, A.J.; Zola, H.; Hoogenraad, N.J. Characterisation of the protein composition of peripheral blood mononuclear cell microsomes by SDS-PAGE and mass spectrometry. J. Immunol. Methods 2005, 305, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsan, M.; Wang, W.; Gadahi, J.A.; Hasan, M.W.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Haseeb, M.; Yan, R.; Xu, L.; et al. The serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 1 from Haemonchus contortus is actively involved in suppressive regulatory roles on immune functions of goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadahi, J.A.; Yongqian, B.; Ehsan, M.; Zhang, Z.C.; Wang, S.; Yan, R.F.; Song, X.K.; Xu, L.X.; Li, X. Haemonchus contortus excretory and secretory proteins (HcESPs) suppress functions of goat PBMCs in vitro. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35670–35679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, L.; Hasan, M.W.; Lu, M.; Wang, W.; Yan, R.-F.; Xu, L.-X.; Song, X.; Li, X. Hepatocellular carcinoma-associated antigen 59 of Haemonchus contortus modulates the functions of PBMCs and the differentiation and maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells of goats in vitro. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.-J.; Yuan, M.-L.; Zhou, Q.; Du, R.-H.; Yang, W.-B.; Xiong, X.-Z.; Zhang, J.-C.; Wu, C.; Qin, S.-M.; Shi, H.-Z. Differentiation and recruitment of Th9 cells stimulated by pleural mesothelial cells in human mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Manzo, A.; Vitolo, B.; La Manna, M.P.; Giardina, G.; Sireci, G.; Dieli, F.; Montecucco, C.M.; et al. Potential involvement of IL-9 and Th9 cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 2264–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitson, J.P.; Grainger, J.R.; Maizels, R.M. Helminth immunoregulation: The role of parasite secreted proteins in modulating host immunity. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2009, 167, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, A.J.; Meeusen, E.; González, J.; Piedrafita, D. Immunity to Haemonchus contortus and vaccine development. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 353–396. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsan, M.; Hu, R.-S.; Liang, Q.-L.; Hou, J.-L.; Song, X.; Yan, R.-F.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Li, X. Advances in the Development of Anti-Haemonchus contortus Vaccines: Challenges, Opportunities, and Perspectives. Vaccines 2020, 8, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, R.; Muleke, C.I.; Zhao, G.; Xu, L.; Li, X. Recombinant galectins of Haemonchus contortus parasite induces apoptosis in the peripheral blood lymphocytes of goat. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2006, 13, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, P.; Macdonald, A.S.; Robb, A.; Maizels, R.M.; Allen, J.E. Alternatively activated macrophages induced by nematode infection inhibit proliferation via cell-to-cell contact. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.-L.; Lu, M.; Calderón-Mantilla, G.; Petsalaki, E.; Dottorini, T.; Tian, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Hou, J.-L.; Li, X.; et al. A recombinant Fasciola gigantica 14-3-3 epsilon protein (rFg14-3-3e) modulates various functions of goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, K.E.; Wilson, E.H. Role of chemokines and trafficking of immune cells in parasitic infections. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 9, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licona-Limon, P.; Arias-Rojas, A.; Olguín-Martínez, E. IL-9 and Th9 in parasite immunity. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 39, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Lu, L. Ex vivo induced regulatory t cells regulate inflammatory response of Kupffer cells by TGF-beta and attenuate liver ischemia reperfusion injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, A.M.; Shirley, J.E.; Stoner, G. Regulation of proliferation and differentiation of respiratory tract epithelial cells by TGFβ. Exp. Cell Res. 1986, 167, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angkasekwinai, P. Th9 cells in allergic disease. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Kaplan, M.H. Th9 cells in immunity and immunopathological diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 39, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, H.; Humphreys, N.; Renauld, J.-C.; Van Snick, J.; Grencis, R. Interleukin-9 is involved in host protective immunity to intestinal nematode infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 2536–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuradha, R.; Munisankar, S.; Bhootra, Y.; Jagannathan, J.; Dolla, C.; Kumaran, P.; Nutman, T.B.; Babu, S. IL-10- and TGFβ-mediated Th9 responses in a human helminth infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claerebout, E.; Geldhof, P. Helminth vaccines in ruminants. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. 2020, 36, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.B.; Geldhof, P.; Tzelos, T.; Claerebout, E. Progress in the development of subunit vaccines for gastrointestinal nematodes of ruminants. Parasite Immunol. 2016, 38, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aimulajiang, K.; Wen, Z.; Tian, X.; Lakho, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Naqvi, M.A.-u.-H.; Liang, M.; Song, X.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; et al. Unveiling the Immunomodulatory Characteristics of Haemonchus contortus Ephrin Domain Containing Protein in the Parasite–Host Interactions. Animals 2020, 10, 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112137
Aimulajiang K, Wen Z, Tian X, Lakho SA, Zhang Y, Naqvi MA-u-H, Liang M, Song X, Xu L, Li X, et al. Unveiling the Immunomodulatory Characteristics of Haemonchus contortus Ephrin Domain Containing Protein in the Parasite–Host Interactions. Animals. 2020; 10(11):2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112137
Chicago/Turabian StyleAimulajiang, Kalibixiati, Zhaohai Wen, Xiaowei Tian, Shakeel Ahmed Lakho, Yang Zhang, Muhammad Ali-ul-Husnain Naqvi, Meng Liang, Xiaokai Song, Lixin Xu, Xiangrui Li, and et al. 2020. "Unveiling the Immunomodulatory Characteristics of Haemonchus contortus Ephrin Domain Containing Protein in the Parasite–Host Interactions" Animals 10, no. 11: 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112137
APA StyleAimulajiang, K., Wen, Z., Tian, X., Lakho, S. A., Zhang, Y., Naqvi, M. A.-u.-H., Liang, M., Song, X., Xu, L., Li, X., & Yan, R. (2020). Unveiling the Immunomodulatory Characteristics of Haemonchus contortus Ephrin Domain Containing Protein in the Parasite–Host Interactions. Animals, 10(11), 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10112137







