Relative Importance of Deterministic and Stochastic Processes on Soil Microbial Community Assembly in Temperate Grasslands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Samples and Data Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, High-Throughput Amplicon Sequencing and Sequence Processing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Estimation of Soil Microbial β-Diversity
2.3.2. The Relationship between Microbial β-Diversity and Distance
2.3.3. Variation Partitioning and Null Model Analysis
2.3.4. Random Forest Analysis
2.3.5. Estimation of Habitat Niche Breadth
2.4. Accession Numbers
3. Results
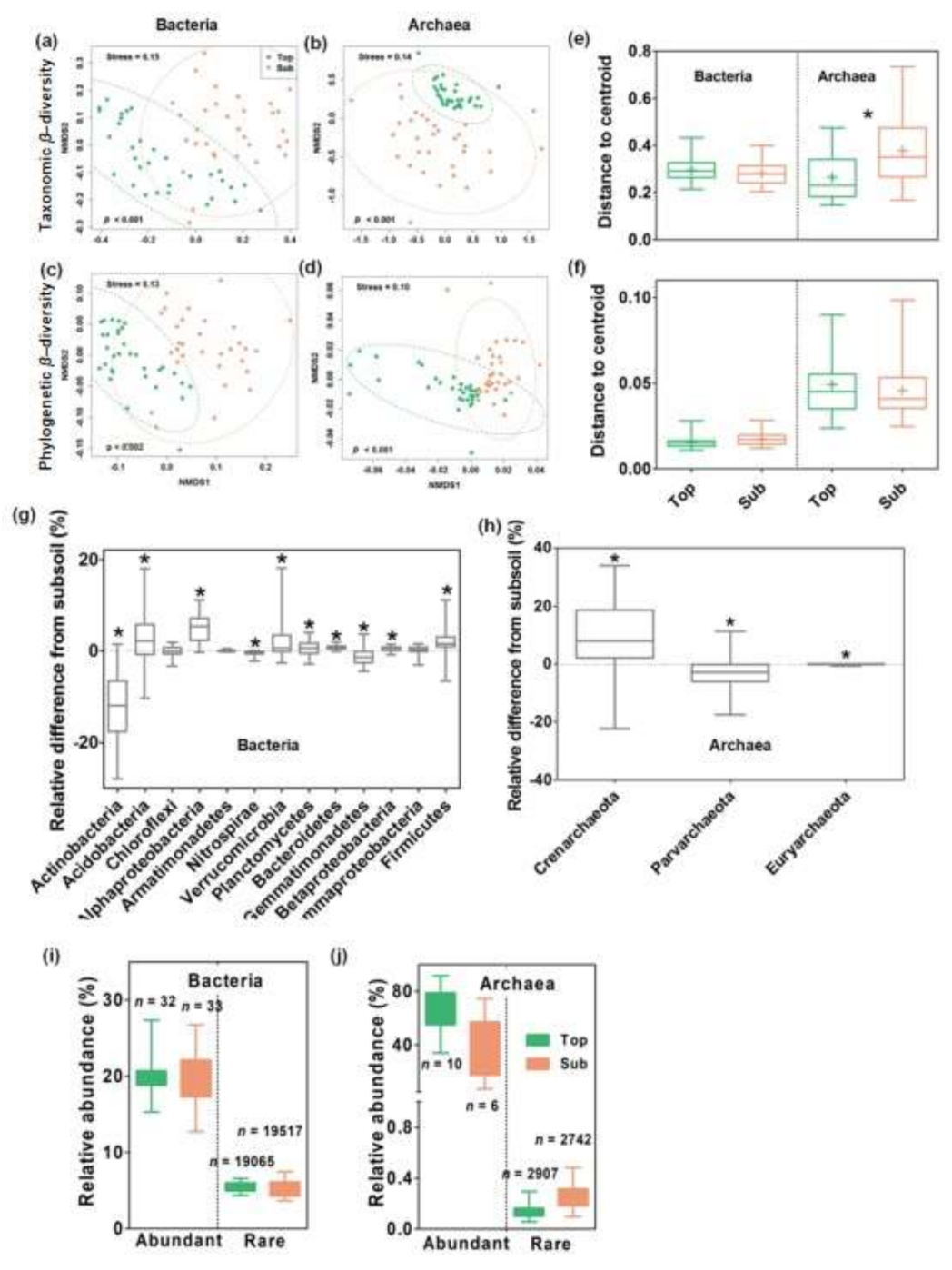
3.1. Microbial Communities in Top- and Subsoils
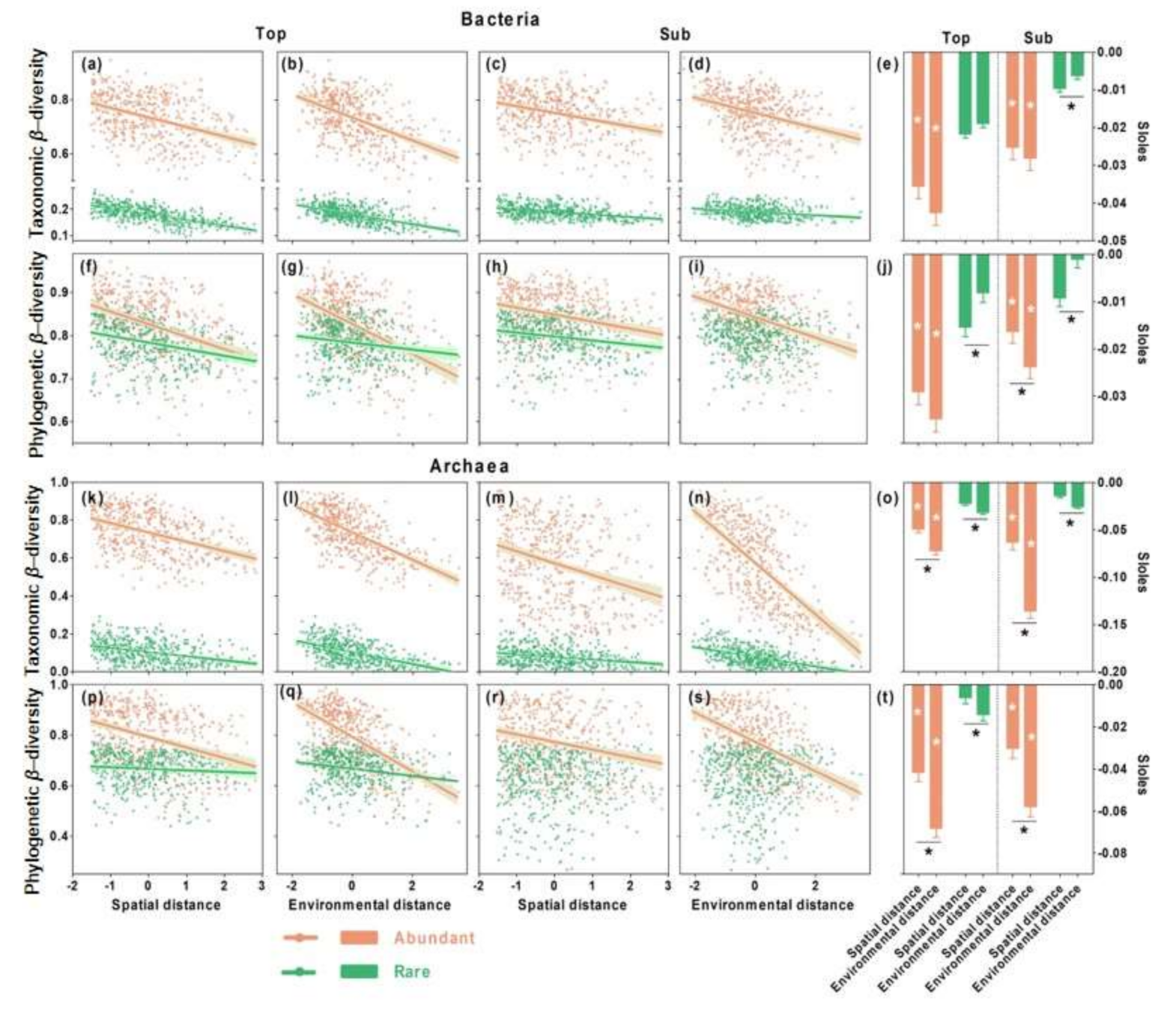
3.2. Distance–Decay Relationships in Top- and Subsoils
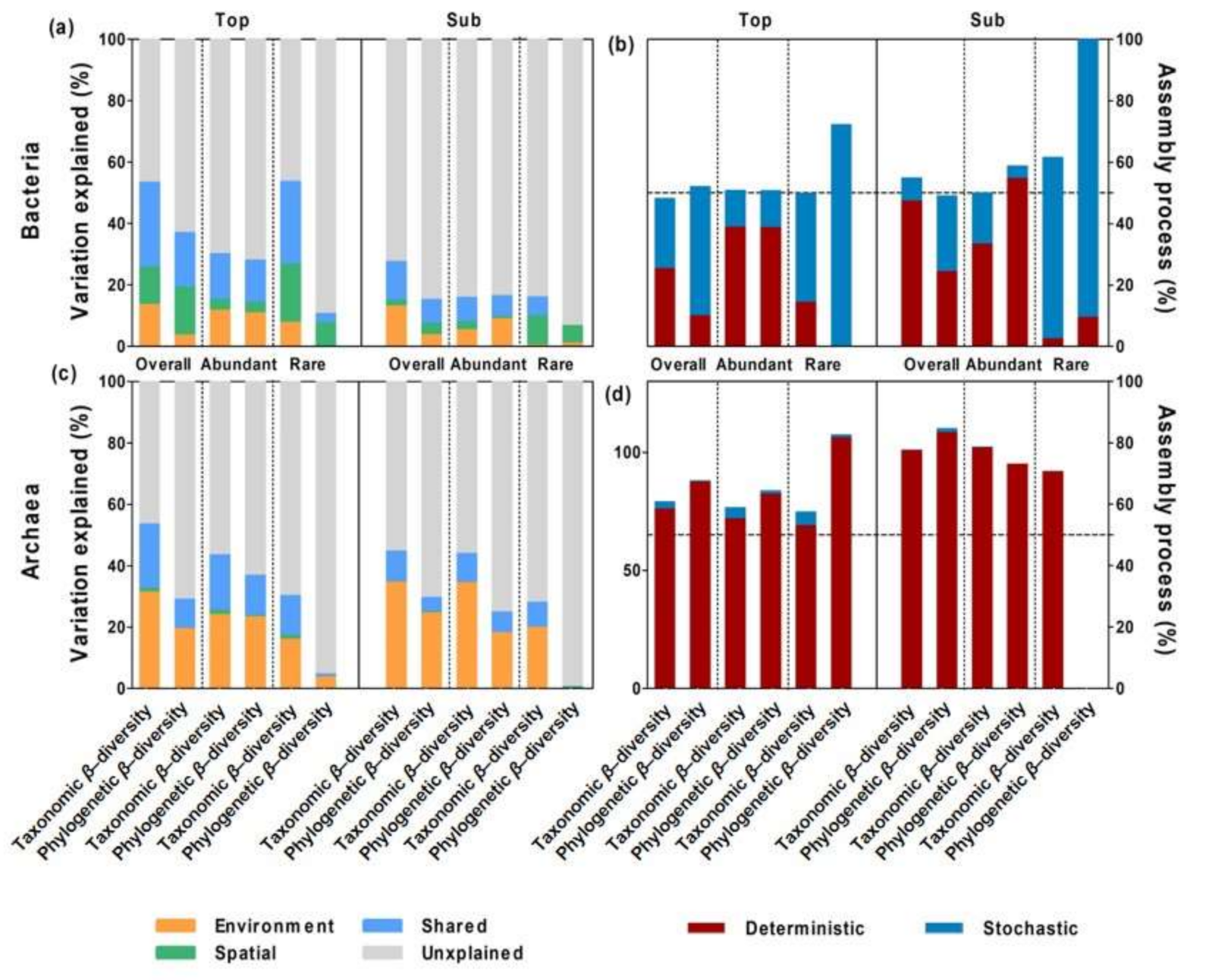
3.3. Relative Importance of Spatial versus Environmental Distances on Microbial β-Diversity
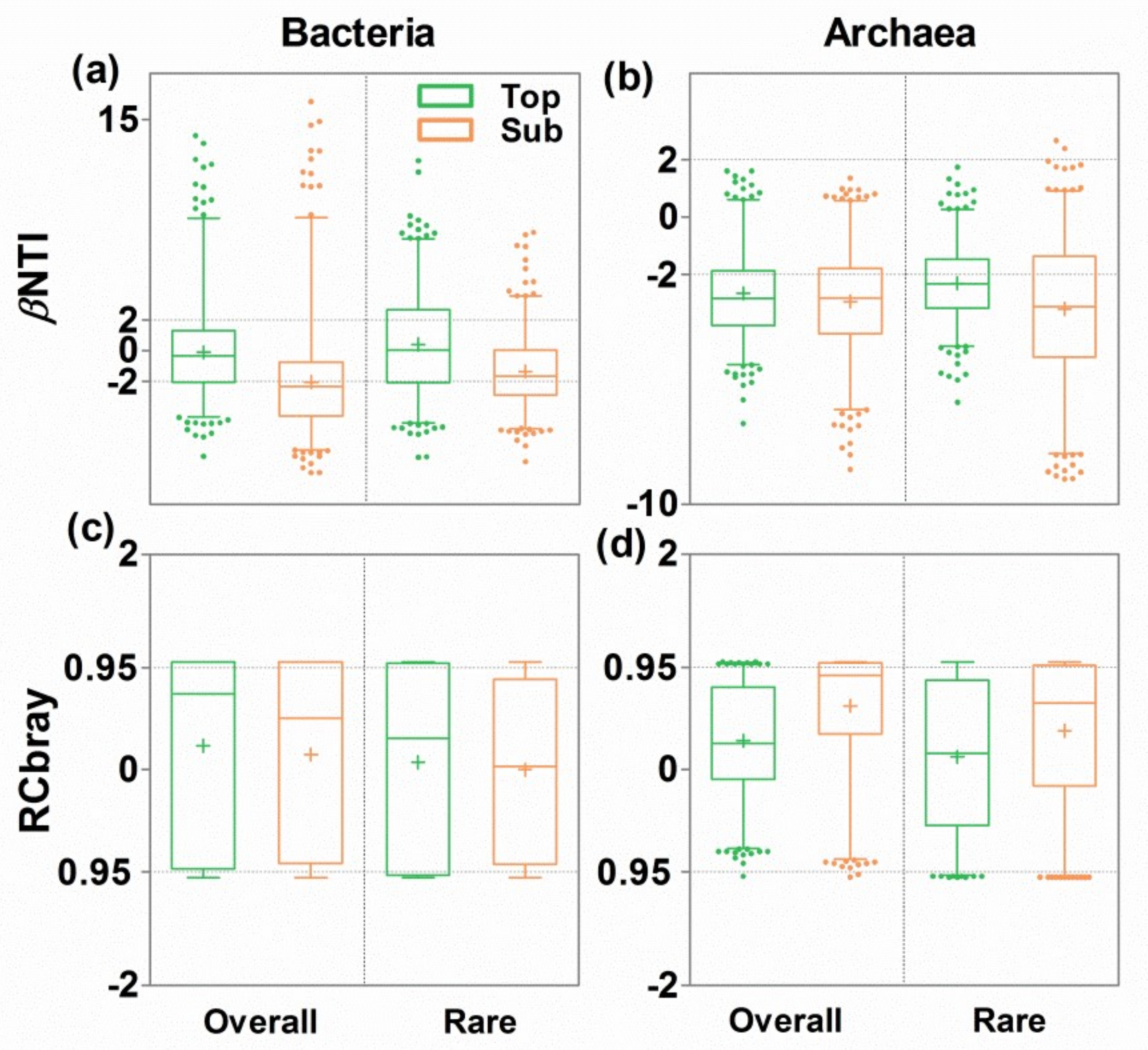
3.4. Ecological Mechanisms Underlying Microbial β-diversity
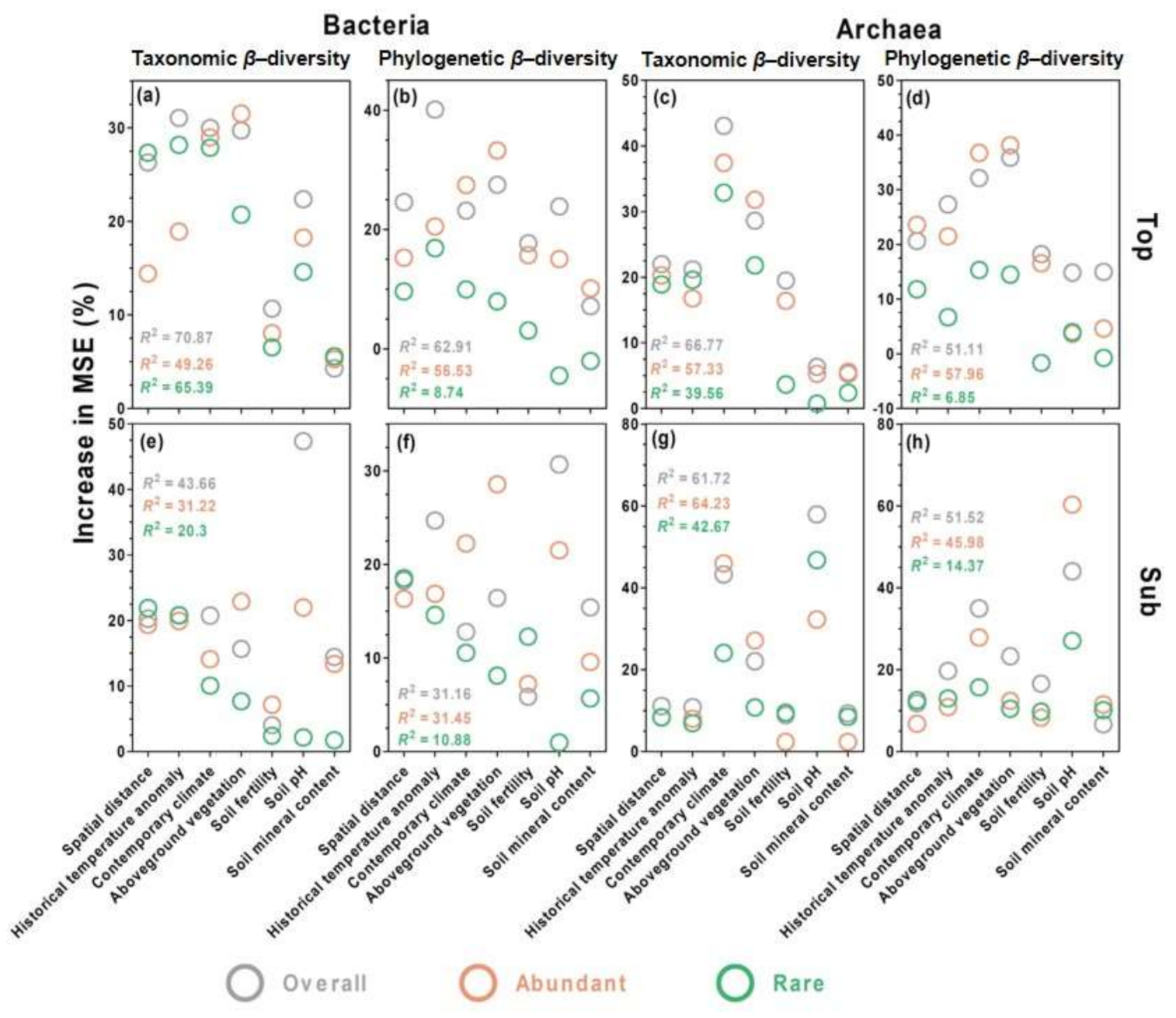
3.5. Environmental Drivers of Microbial Community Composition
3.6. Niche Breadth
4. Discussion
4.1. Consistent Community Assembly Processes across Soil Depths
4.2. Distinct Community Assembly Processes for Abundant and Rare Bacterial Microbes
4.3. Distinct Environmental Drivers of β-Diversity across Soil Depths and Microbial Groups
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.Z.; Ning, D.L. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanson, C.A.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Martiny, J.B. Beyond biogeographic patterns: Processes shaping the microbial landscape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Fang, J.Y.; Tang, Z.Y.; Shi, L. Geographical patterns in the beta diversity of China’s woody plants: The influence of space, environment and range size. Ecography 2012, 35, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, K.; Svenning, J.C.; Jeppesen, E. Environmental species sorting dominates forest-bird community assembly across scales. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.J.; Shen, J.; Wu, Y.C.; Tu, C.; Soininen, J.; Stegen, J.C.; He, J.Z.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, E.L. Phylogenetic beta diversity in bacterial assemblages across ecosystems: Deterministic versus stochastic processes. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.K.; Chai, L.W.; Jiang, D.L.; Zhang, M.J.; Zhao, Y.R.; Huang, Y. Increasing aridity affects soil archaeal communities by mediating soil niches in semi-arid regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.B.; Lu, X.T.; Yao, J.; Wang, Z.W.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, W.X.; Zhou, J.Z.; Han, X.G. Habitat-specific patterns and drivers of bacterial beta-diversity in China’s drylands. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.Y.; Sun, H.B.; Tripathi, B.M.; Adams, J.M.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Shi, Y. Bacterial community dissimilarity between the surface and subsurface soils equals horizontal differences over several kilometers in the western Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumpel, C.; Chabbi, A.; Marschner, B. Carbon storage and sequestration in subsoil horizons: Knowledge, gaps and potentials. p. 445–464. In Recarbonization of the Biosphere: Ecosystems and the Global Carbon Cycle; Lal, R., Lorenz, K., Hüttl, R., Uwe Schneider, B., von Braun, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Adams, J.M.; Shi, Y.; He, J.-S.; Jing, X.; Chen, L.T.; Tedersoo, L.; Chu, H.Y. Soil fungal diversity in natural grasslands of the Tibetan Plateau: Associations with plant diversity and productivity. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.F.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.Z.; Escalas, A.; Feng, K.; He, Q.; Wang, Z.J.; Wu, Y.N.; Wang, D.; Peng, X.; et al. Steeper spatial scaling patterns of subsoil microbiota are shaped by deterministic assembly process. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 30, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, R.; Bouvier, T. ‘Everything is everywhere, but the environment selects’; what did baas becking and beijerinck really say? Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M.; Myers, J.A. Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 2351–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, J.L.; Holmes, A.J.; Westoby, M.; Oliver, I.; Briscoe, D.; Dangerfield, M.; Gillings, M.; Beattie, A.J. Spatial scaling of microbial eukaryote diversity. Nature 2004, 432, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M.; Kraft, N.J.B.; Smith, K.G.; Vellend, M.; Inouye, B.D. Using null models to disentangle variation in community dissimilarity from variation in α-diversity. Ecosphere 2011, 2, art24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Stegen, J.C.; Kim, M.; Dong, K.; Adams, J.M.; Lee, Y.K. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbrell, A.J.; Nelson, M.; Helgason, T.; Dytham, C.; Fitter, A.H. Relative roles of niche and neutral processes in structuring a soil microbial community. ISME J. 2010, 4, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caruso, T.; Chan, Y.K.; Lacap, D.C.; Lau, M.C.; McKay, C.P.; Pointing, S.B. Stochastic and deterministic processes interact in the assembly of desert microbial communities on a global scale. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, J.R.; Karunaratne, S.; Campbell, C.D.; Yao, H.Y.; Robinson, L.; Singh, B.K. Deterministic processes vary during community assembly for ecologically dissimilar taxa. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Y.T.; Xiang, X.J.; Sun, R.B.; Yang, T.; He, D.; Zhang, K.P.; Ni, Y.Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Adams, J.M.; et al. Spatial scale affects the relative role of stochasticity versus determinism in soil bacterial communities in wheat fields across the north China plain. Microbiome 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, T.; Bini, L.M.; Roque, F.O.; Marques Couceiro, S.R.; Trivinho-Strixino, S.; Cottenie, K. Common and rare species respond to similar niche processes in macroinvertebrate metacommunities. Ecography 2012, 35, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, W.K.; Ackerly, D. A link between plant traits and abundance: Evidence from coastal California woody plants. J. Ecol. 2010, 98, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Lu, Y.H. Soil pH and temperature regulate assembly processes of abundant and rare bacterial communities in agricultural ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.K.; Kong, W.D.; Stegen, J.; Yue, L.Y.; Wang, F.; Dong, X.B.; Cowan, D.A.; Ferrari, B.C. Distinct assembly mechanisms underlie similar biogeographical patterns of rare and abundant bacteria in Tibetan Plateau grassland soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.M.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wilkinson, D.M. The biogeography of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in the lakes and reservoirs of China. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.N.; Hu, H.F.; Ma, W.H.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Hao, B.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Dimitrov, D.; Feng, X.J.; Wang, Z.H. Contrasting biogeographic patterns of bacterial and archaeal diversity in the top- and subsoils of temperate grasslands. mSystems 2019, 4, e00566-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Xu, S.; Zhao, M.Y.; Li, H.; Kou, D.; Fang, J.Y.; Hu, H.F. Allocation of mass and stability of soil aggregate in different types of Nei Mongol grasslands. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.F.; Wu, J.G.; Xing, Q.; Pan, Q.M.; Huang, J.H.; Yang, D.L.; Han, X.G. Primary production and rain use efficiency across a precipitation gradient on the Mongolia Plateau. Ecology 2008, 89, 2140–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Hajima, T.; Sudo, K.; Nagashima, T.; Takemura, T.; Okajima, H.; Nozawa, T.; Kawase, H.; Abe, M.; Yokohata, T.; et al. MIROC-ESM: Model description and basic results of CMIP5-20c3m experiments. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2011, 4, 1063–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Clim. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, J.W.; Jones, S.E.; Prober, S.M.; Barberan, A.; Borer, E.T.; Firn, J.L.; Harpole, W.S.; Hobbie, S.E.; Hofmockel, K.S.; Knops, J.M.; et al. Consistent responses of soil microbial communities to elevated nutrient inputs in grasslands across the globe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10967–10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.W.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhu, J.G.; Lin, X.G.; Feng, Y.Z. Divergent responses of methanogenic archaeal communities in two rice cultivars to elevated ground-level O3. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Zhang, Z.J.; Cai, W.W.; Liu, W.Z.; Xu, M.Y.; Yin, H.Q.; Wang, A.J.; He, Z.L.; Deng, Y. Biodiversity and species competition regulate the resilience of microbial biofilm community. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6170–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.S.; Bai, Y.H.; Tao, Y.L.; Huang, B.; Wen, D.H. Identifying the key taxonomic categories that characterize microbial community diversity using full-scale classification: A case study of microbial communities in the sediments of Hangzhou Bay. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, M.J.; Ellingsen, K.E.; McArdle, B.H. Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.A.; Somers, K.M. Are probability estimates from the permutation model of mantel’s test stable? Can. J. Zool. 1989, 67, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.V. Least-squares means: The r package lsmeans. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 69, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borcard, D.; Legendre, P.; Drapeau, P. Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation. Ecology 1992, 73, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R. News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.X.; Lu, H.P.; Sastri, A.; Yeh, Y.C.; Gong, G.C.; Chou, W.C.; Hsieh, C.H. Contrasting the relative importance of species sorting and dispersal limitation in shaping marine bacterial versus protist communities. ISME J. 2018, 12, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.L. Spaa: Species Association Analysis; R Package Version 0.2.1.; The R Project for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cottenie, K. Integrating environmental and spatial processes in ecological community dynamics. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Carroll, C.; Wilkins, B.; Johnson, P.; Gabhainn, S.N.; Smith, L.P. The effect of wind speed and direction on the distribution of sewage-associated bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 28, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberan, A.; Ladau, J.; Leff, J.W.; Pollard, K.S.; Menninger, H.L.; Dunn, R.R.; Fierer, N. Continental-scale distributions of dust-associated bacteria and fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5756–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.J.; Liu, J.F.; Tonkin, J.D.; Shen, J.; Xiao, N.W.; Wang, J.J. The effects of abiotic and biotic factors on taxonomic and phylogenetic diversity of stream epilithic bacteria around Qiandao Lake. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morlon, H.; Chuyong, G.; Condit, R.; Hubbell, S.; Kenfack, D.; Thomas, D.; Valencia, R.; Green, J.L. A general framework for the distance-decay of similarity in ecological communities. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, W.M.; Wei, G.H. Biogeography and ecological diversity patterns of rare and abundant bacteria in oil-contaminated soils. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5305–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Bissett, A.; Eldridge, D.J.; Maestre, F.T.; He, J.Z.; Wang, J.T.; Hamonts, K.; Liu, Y.R.; Singh, B.K.; Fierer, N. Palaeoclimate explains a unique proportion of the global variation in soil bacterial communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averill, C.; Waring, B.G.; Hawkes, C.V. Historical precipitation predictably alters the shape and magnitude of microbial functional response to soil moisture. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.T.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Caporaso, J.G.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J. 2011, 5, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.W.; Rensing, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.Q.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.W.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.R. Deciphering the associations between soil microbial diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality driven by long-term fertilization management. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Hu, H.; Ma, W.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, A.; Meng, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, Z. Relative Importance of Deterministic and Stochastic Processes on Soil Microbial Community Assembly in Temperate Grasslands. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091929
Liu N, Hu H, Ma W, Deng Y, Wang Q, Luo A, Meng J, Feng X, Wang Z. Relative Importance of Deterministic and Stochastic Processes on Soil Microbial Community Assembly in Temperate Grasslands. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(9):1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091929
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Nana, Huifeng Hu, Wenhong Ma, Ye Deng, Qinggang Wang, Ao Luo, Jiahui Meng, Xiaojuan Feng, and Zhiheng Wang. 2021. "Relative Importance of Deterministic and Stochastic Processes on Soil Microbial Community Assembly in Temperate Grasslands" Microorganisms 9, no. 9: 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091929
APA StyleLiu, N., Hu, H., Ma, W., Deng, Y., Wang, Q., Luo, A., Meng, J., Feng, X., & Wang, Z. (2021). Relative Importance of Deterministic and Stochastic Processes on Soil Microbial Community Assembly in Temperate Grasslands. Microorganisms, 9(9), 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091929





