Molecular Identification and Characterization of Probiotic Bacillus Species with the Ability to Control Vibrio spp. in Wild Fish Intestines and Sponges from the Vietnam Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
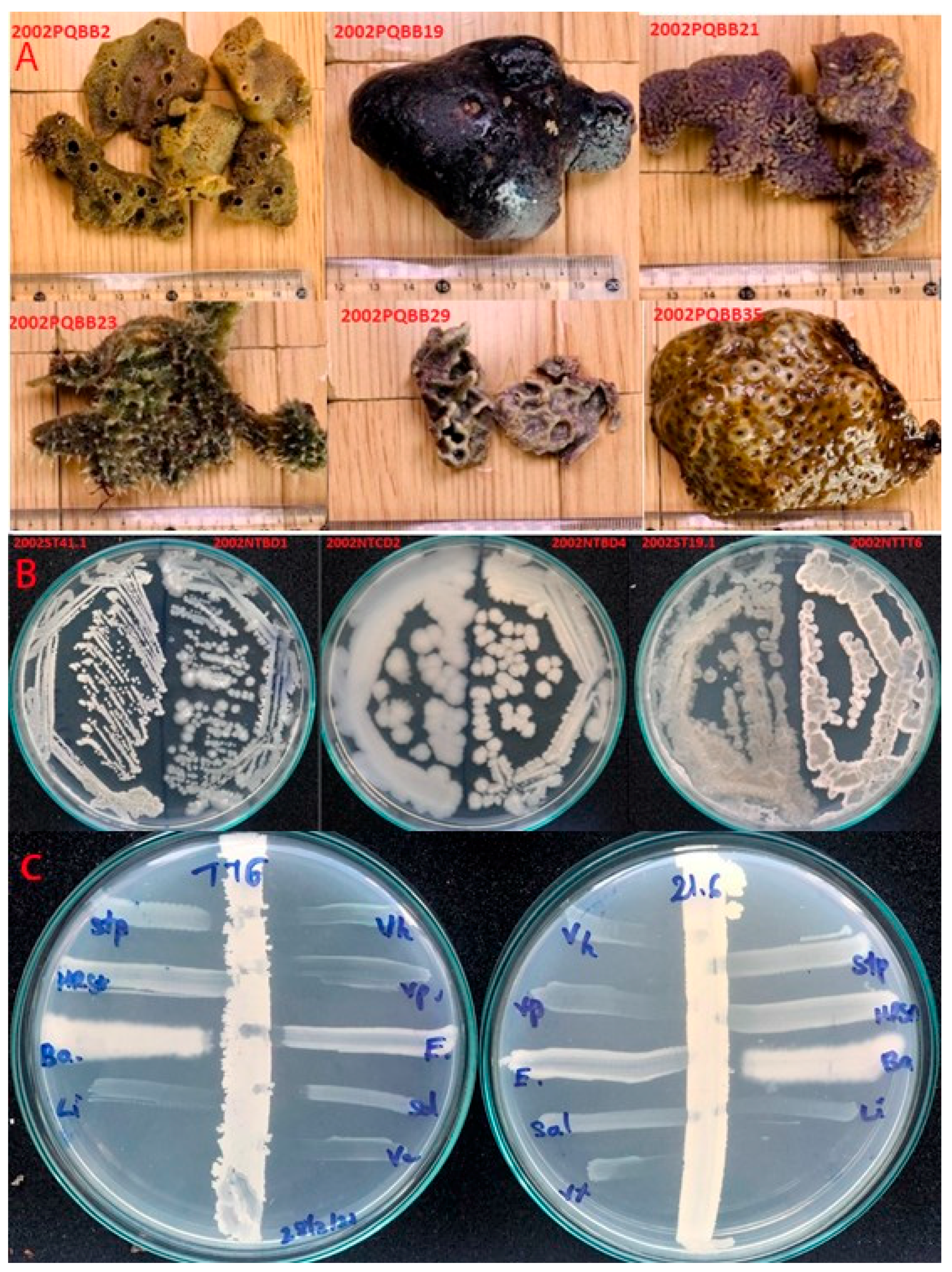
2.1. Strain Collection
2.2. Screening of Vi+ Strains for Antimicrobial Activity toward Foodborne and Clinically Relevant Pathogens
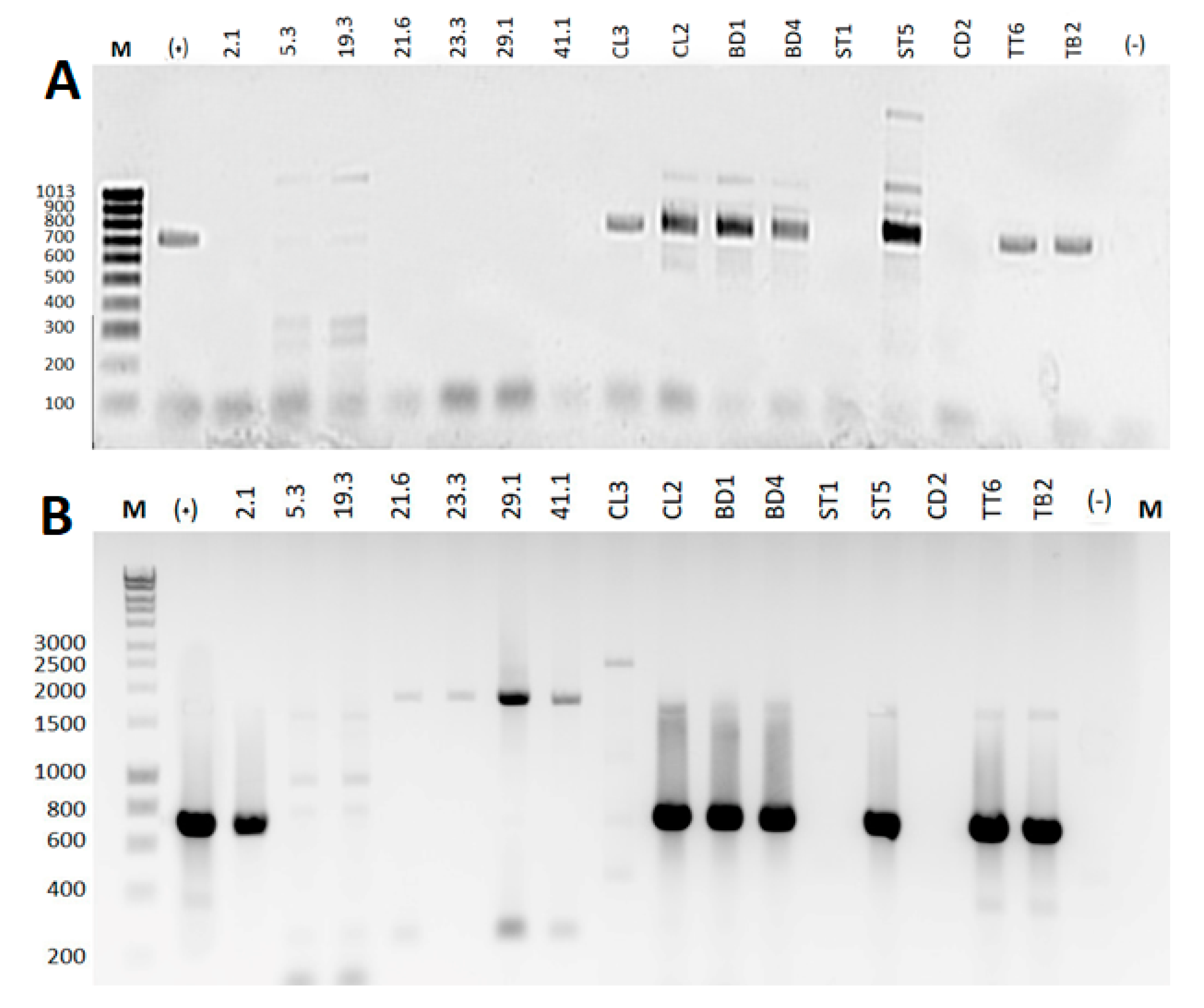
2.3. Extraction of Genomic DNA and Amplification of 16S rRNA Sequence
2.4. Amplification of Nonribosomal Peptide and Polyketide Biosynthetic Gene Clusters
2.5. Sequencing of 16S rRNA Products and Antimicrobial Gene Products
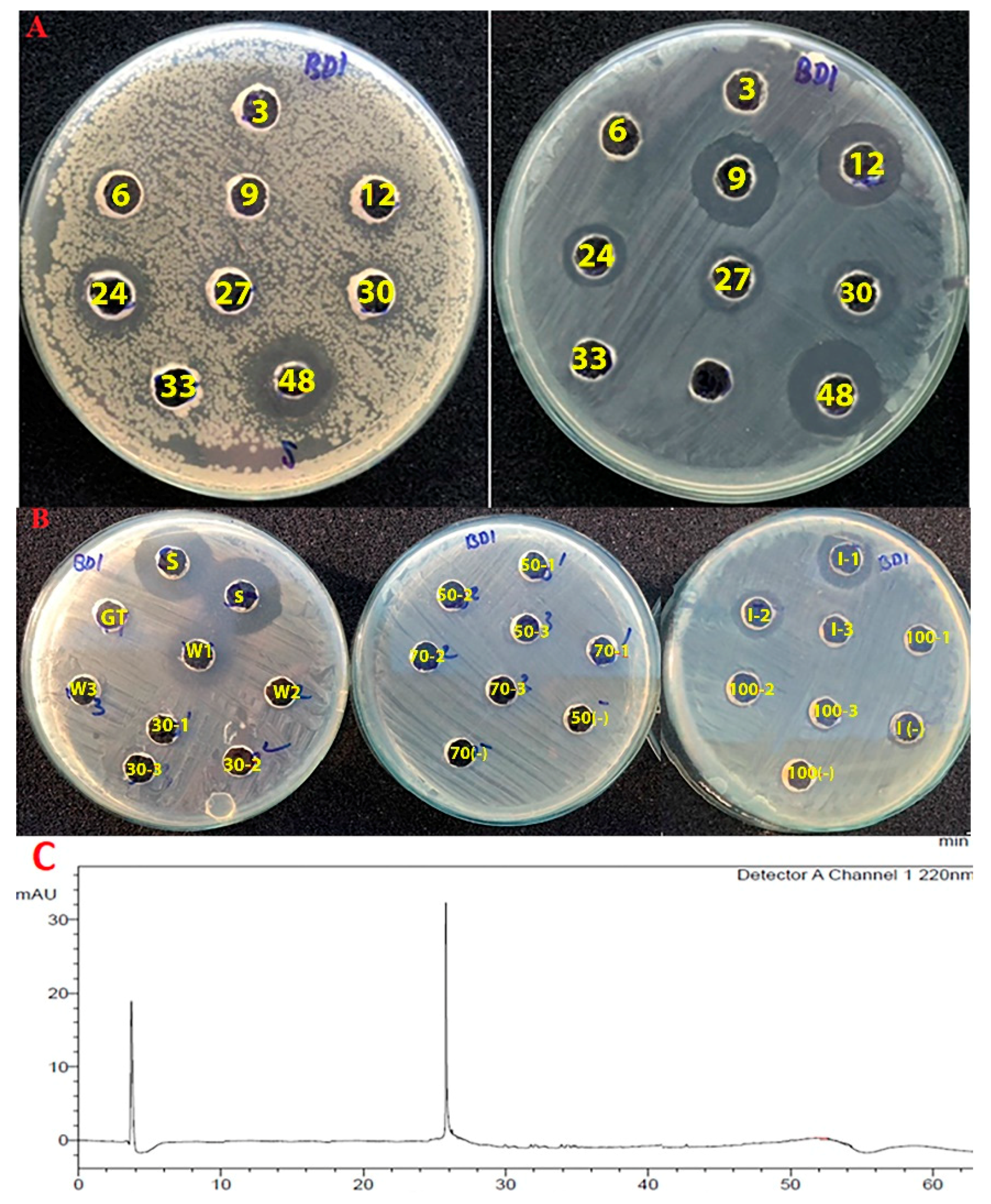
2.6. Effect of Cultivation Time on Anti-Vibrio Bacteriocin Production
2.7. Purification of Bacteriocin Produced by B. methylotrophicus NTBD01
2.8. Estimation of Bacteriocin’s Molecular Mass by TRICINE Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Zymogram
2.9. Effects of Enzymes and Heat Treatment on Bacteriocin’s Activity
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Effect of Vi+
3.2. 16S rRNA Gene Analysis
3.3. PCR Amplification of PKS and NRPS Biosynthetic Genes
3.4. Sequencing and Sequencing Analysis of (PKS-I) Gene Products
3.5. A Three-Step Procedure for the Rapid Purification of Bacteriocin-Like Substance from Bacterial Cells
3.6. The Thermal and Antimicrobial Properties of the Bacteriocin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, F.L.; Iida, T.; Swings, J. Biodiversity of vibrios. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 403–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong To, T.T.; Yanagawa, H.; Khanh Thuan, N.; Hiep, D.M.; Cuong, D.V.; Khai, L.T.L.; Taniguchi, T.; Kubo, R.; Hayashidani, H. Prevalence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus causing acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease of shrimp in shrimp, molluscan shellfish and water samples in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. Biology 2020, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewcharoen, W.; Srisapoome, P. Probiotic effects of Bacillus spp. from Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) on water quality and shrimp growth, immune responses, and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus (AHPND strains). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 94, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, H.; Hirose, Y.; Matsuo, N.; Deguchi, Y. Production of the antibacterial substance by Bacillus sp. strain NM 12, an intestinal bacterium of Japanese coastal fish. Aquaculture 1998, 165, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Pham, T.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Hoj, L. Screening of marine bacteria with bacteriocin-like activities and probiotic potential for ornate spiny lobster (Panulirus ornatus) juveniles. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 40, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.M.; Rong, Y.J.; Zhao, M.X.; Song, B.; Chi, Z.M. Antibacterial activity of the lipopetides produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens M1 against multidrug-resistant Vibrio spp. isolated from diseased marine animals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindiya, E.S.; Tina, K.J.; Sasidharan, R.S.; Bhat, S.G. BaCf3: Highly thermostable bacteriocin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BTSS3 antagonistic on food-borne pathogens. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraturo, A.; Raieta, K.; Ottaviani, D.; Russo, G.L. Inhibition of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by a bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance (BLIS) produced by Vibrio mediterranei 1. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, C.D.; Yang, B.W.; Yeo, I.C.; Hahm, Y.T. Antimicrobial peptides of the genus Bacillus: A new era for antibiotics. Can. J. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahyudi, A.T.; Priyanto, J.A.; Maharsiwi, W.; Astuti, R.I. Screening and characterization of sponge-associated bacteria producing bioactive compounds anti-Vibrio sp. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lertcanawanichakul, M.; Sawangnop, S. A comparison of two methods used for measuring the antagonistic activity of Bacillus species. Walailak. J. Sci. Tech. 2008, 5, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Karaoz, U.; Volegova, M.; MacKichan, J.; Kato-Maeda, M.; Miller, S.; Nadarajan, R.; Brodie, E.L.; Lynch, S.V. Use of 16S rRNA gene for identification of a broad range of clinically relevant bacterial pathogens. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, F.; Kim, E.L.; Li, J.L.; Hong, J.; Bae, K.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, J.H. Antibacterial polyketides from the jellyfish-derived fungus Paecilomyces variotii. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiaji, J.; Feliatra, F.; Teruna, H.Y.; Lukistyowati, I.; Suharman, I.; Muchlisin, Z.A.; Johan, T.I. Antibacterial activity in secondary metabolite extracts of heterotrophic bacteria against Vibrio alginolyticus, Aeromonas hydrophila, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Samak, M.; Solyman, S.M.; Hanora, A. Antimicrobial activity of bacteria isolated from Red Sea marine invertebrates. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 19, e00275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busarcevic, M.; Dalgalarrondo, M. Purification and genetic characterisation of the novel bacteriocin LS2 produced by the human oral strain Lactobacillus salivarius BGHO1. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2012, 40, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, N.; Hashim, R.; Pham, H.Q.; Choi, S.D.; Lee, D.W.; Shin, J.H.; Rajagopal, K. Lactobacillus acidophilus antimicrobial peptide Is antagonistic to Aeromonas hydrophila. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 570851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schägger, H. Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Blom, J.; Klenk, H.P.; Borriss, R. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus velezensis, and Bacillus siamensis form an “operational group B. amyloliquefaciens” within the B. subtilis species complex. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, Q.; Dong, C.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Li, G.; Shao, Z. Phylogenetic diversity of the Bacillus pumilus group and the marine ecotype revealed by multilocus sequence analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thankappan, B.; Ramesh, D.; Ramkumar, S.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Anbarasu, K. Characterization of Bacillus spp. from the gastrointestinal tract of Labeo rohita-towards to identify novel probiotics against fish pathogens. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; André, C.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Saavedra, M.; Enes, P.; Serra, C. Fish gut sporeformers to control fish pathogens. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, M.; Raja, M.; Perumal, P. Evaluation of probiotic potential of Bacillus spp. isolated from the digestive tract of freshwater fish Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822). Aquac. Rep. 2018, 11, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, P.; Zhu, W.; Mo, Z. The ability of marine Bacillus spp. isolated from fish gastrointestinal tract and culture pond sediment to inhibit growth of aquatic pathogenic bacteria. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2016, 15, 701–714. [Google Scholar]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Lu, Y.; Abarike, E.D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Sakyi, M.E. In vitro assessment of the probiotic characteristics of three Bacillus species from the gut of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Probiotics. Antimicrob. Proteins. 2020, 12, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-O.; Park, I.; Kim, D.J.; Nam, B.; Kim, D.-G.; Jee, Y.; An, C. Identification and characterization of a bacteriocin produced by an isolated Bacillus sp. SW1-1 that exhibits antibacterial activity against fish pathogens. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2014, 57, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.M.; Van Quyen, D.; Fraser, J.M.; Smith, A.T.; Van, T.T.H.; Moore, R.J. Broad spectrum antimicrobial activities from spore-forming bacteria isolated from the Vietnam Sea. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Soran, H.; Beyatli, Y. Antimicrobial activities of some Bacillus spp. strains isolated from the soil. Microbiol. Res. 2006, 161, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omardien, S.; Brul, S.; Zaat, S.A. antimicrobial activity of cationic antimicrobial peptides against Gram-positives: Current progress made in understanding the mode of action and the response of bacteria. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fewer, D.P.; Holm, L.; Rouhiainen, L.; Sivonen, K. Atlas of nonribosomal peptide and polyketide biosynthetic pathways reveals common occurrence of nonmodular enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9259–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mien, P.T.; Ha, D.V.; Ben, H.X.; Chen, B.; Liu, L.; Minh-Thu, P. Antimicrobial activities of sponge-derived microorganisms from coastal waters of central Vietnam. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvin, J.; Sathiyanarayanan, G.; Lipton, A.N.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Valan Arasu, M.; Kiran, G.S. Ketide synthase (KS) domain prediction and analysis of iterative type II PKS gene in marine sponge-associated Actinobacteria producing biosurfactants and antimicrobial agents. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abriouel, H.; Franz, C.M.; Ben Omar, N.; Gálvez, A. Diversity and applications of Bacillus bacteriocins. FEMS. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 201–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Wang, C.; Song, X.; Ding, X.; Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Gao, X.; Borriss, R. Bacillus velezensis FZB42 in 2018: The gram-positive model strain for plant growth promotion and biocontrol. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No | Isolates | Reference Strains | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vh | Vp | Sa | Ec | Bc | Stp | Li | Ca | MRSA | ||
| Sponge-associated isolated Vi+ | ||||||||||
| 1 | PQBB2.1 | - | ++ | - | - | + | - | ++ | - | - |
| 2 | PQBB5.3 | +++ | +++ | + | - | + | - | ++ | - | - |
| 3 | PQBB19.3 | + | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | - |
| 4 | PQBB21.6 | ++ | ++ | - | - | ++ | - | ++ | - | - |
| 5 | PQBB23.3 | +++ | ++ | - | - | + | - | ++ | - | - |
| 6 | PQBB29.1 | +++ | ++ | - | - | + | - | ++ | - | - |
| 7 | PQBB41.1 | +++ | +++ | + | + | + | - | ++ | - | - |
| Killing percent (%) | 85.7 | 100 | 28.5 | 14.2 | 100 | 14.2 | 85.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| Intestinal isolated Vi+ | ||||||||||
| 8 | NTCL2 | +++ | +++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | - |
| 9 | NTCL3 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | NTBD1 | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | + | - |
| 11 | NTBD4 | +++ | +++ | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | - |
| 12 | NTST1 | +++ | +++ | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | - | - |
| 13 | NTST5 | +++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | ++ | + | - |
| 14 | NTCD2 | ++ | ++ | - | - | + | + | ++ | + | - |
| 15 | NTTB2 | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | + | ++ | - | - |
| 16 | NTTT6 | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | ++ | ++ | - |
| Killing percent (%) | 100 | 100 | 77.7 | 77.7 | 88.9 | 88.9 | 88.9 | 66.7 | 0 | |
| Killing percent by all Vi+ (%) | 93.8 | 100 | 62.5 | 50.0 | 93.8 | 50.0 | 87.5 | 37.5 | 0 | |
| Code | Accession Number | Name of the Most Closely Related Strains | Maximum Score | Identity (%) | Accession Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sponge-associated Vi+ isolates | ||||||
| 1 | PQBB2.1 | MZ489228 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MPA | 2128 | 97.4 | NR_117946.1 |
| 2 | PQBB5.3 | MZ489229 | Bacillus licheniformis DSM 13 | 1842 | 99.0 | NR_118996.1 |
| 3 | PQBB19.3 | MZ489230 | Bacillus licheniformis 302-2 | 1869 | 98.5 | MT795776.1 |
| 4 | PQBB21.6 | MZ489231 | Bacillus pumilus TBMAX76 | 1618 | 99.2 | MK834714.1 |
| 5 | PQBB23.3 | MZ489232 | Bacillus pumilus ChST1.7 | 1663 | 98.4 | JF935095.1 |
| 6 | PQBB29.1 | MZ489233 | Bacillus pumilus CBS-i1 | 2121 | 99.4 | GQ220330.1 |
| 7 | PQBB41.1 | MZ489234 | Bacillus altitudinis NPB34b | 2015 | 98.4 | MT598007.1 |
| Intestinal Vi+ isolates | ||||||
| 8 | NTCL2 | MZ489235 | Bacillus velezensis InAD-161 | 1941 | 97.7 | KY859772.1 |
| 9 | NTCL3 | MZ489236 | Bacillus flexus strain LE9 | 1917 | 99.3 | MT279468.1 |
| 10 | NTBD1 | MZ489237 | Bacillus methylotrophicus S611Ba-40 | 1386 | 98.2 | HQ238543.1 |
| 11 | NTBD4 | MZ489238 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DH8030 | 2228 | 99.1 | CP041770.1 |
| 12 | NTST1 | MZ489239 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens P1 | 2176 | 98.2 | MT416658.1 |
| 13 | NTST5 | MZ489240 | Bacillus velezensis BRM 046306 | 2156 | 98.1 | MK461867.1 |
| 14 | NTCD2 | MZ489241 | Bacillus cereus LA333 | 1816 | 98.2 | KY622412.1 |
| 15 | NTTT6 | MZ489242 | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens W36 | 2115 | 99.1 | MN922613.1 |
| 16 | NTTB2 | MZ489243 | Bacillus. velezensis InAD-161 | 1941 | 97.8 | KY859772.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chau, K.M.; Van, T.T.H.; Quyen, D.V.; Le, H.D.; Phan, T.H.T.; Ngo, N.D.T.; Vo, T.D.T.; Dinh, T.T.; Le, H.T.; Khanh, H.H.N. Molecular Identification and Characterization of Probiotic Bacillus Species with the Ability to Control Vibrio spp. in Wild Fish Intestines and Sponges from the Vietnam Sea. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091927
Chau KM, Van TTH, Quyen DV, Le HD, Phan THT, Ngo NDT, Vo TDT, Dinh TT, Le HT, Khanh HHN. Molecular Identification and Characterization of Probiotic Bacillus Species with the Ability to Control Vibrio spp. in Wild Fish Intestines and Sponges from the Vietnam Sea. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(9):1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091927
Chicago/Turabian StyleChau, Khanh Minh, Thi Thu Hao Van, Dong Van Quyen, Hung Dinh Le, Trinh Hoai Thi Phan, Ngoc Duy Thi Ngo, Trang Dieu Thi Vo, Trung Thanh Dinh, Hoa Thi Le, and Huynh Hoang Nhu Khanh. 2021. "Molecular Identification and Characterization of Probiotic Bacillus Species with the Ability to Control Vibrio spp. in Wild Fish Intestines and Sponges from the Vietnam Sea" Microorganisms 9, no. 9: 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091927
APA StyleChau, K. M., Van, T. T. H., Quyen, D. V., Le, H. D., Phan, T. H. T., Ngo, N. D. T., Vo, T. D. T., Dinh, T. T., Le, H. T., & Khanh, H. H. N. (2021). Molecular Identification and Characterization of Probiotic Bacillus Species with the Ability to Control Vibrio spp. in Wild Fish Intestines and Sponges from the Vietnam Sea. Microorganisms, 9(9), 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9091927







