Babesia pisicii n. sp. and Babesia canis Infect European Wild Cats, Felis silvestris, in Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
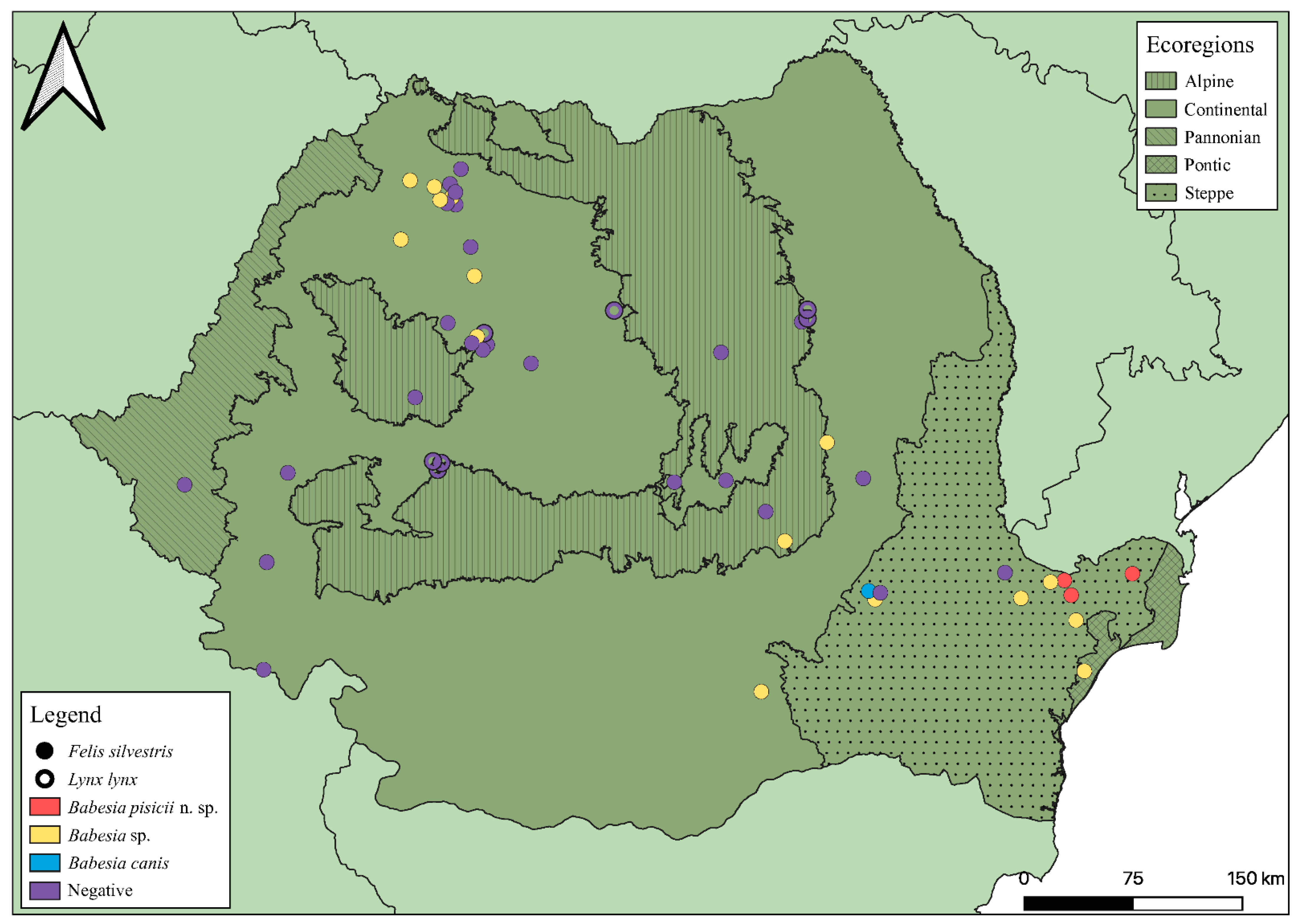
2.1. Samples
2.2. DNA Isolation, PCR Amplification, and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.3. Sensitivity of the Assay Targeting 18S rDNA Fragment of 376 bp
3. Results
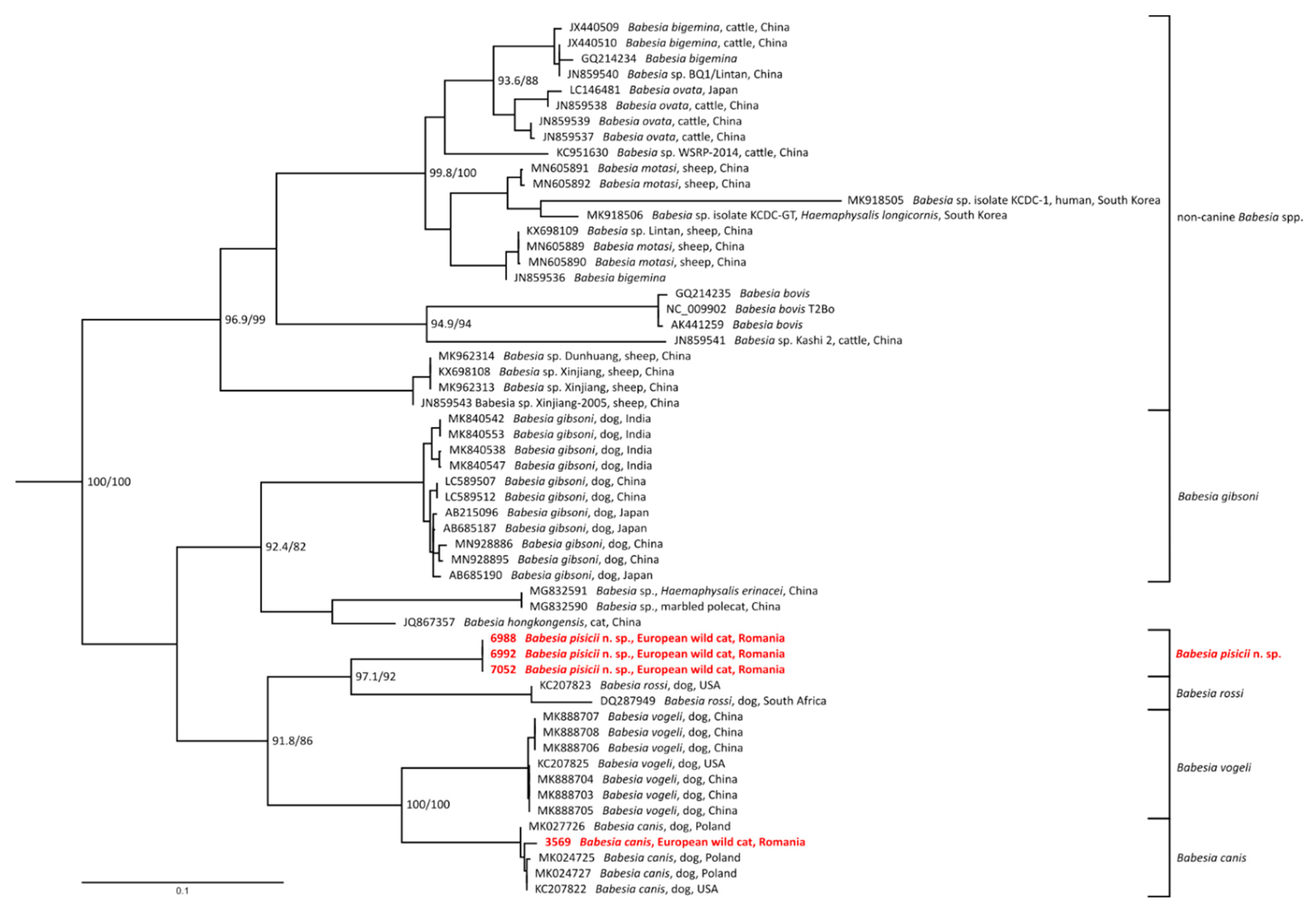
3.1. 18S rDNA Sequence Analyses
3.2. Evaluation of Assay Sensitivity Targeting the 376 bp Fragment of the 18S rDNA
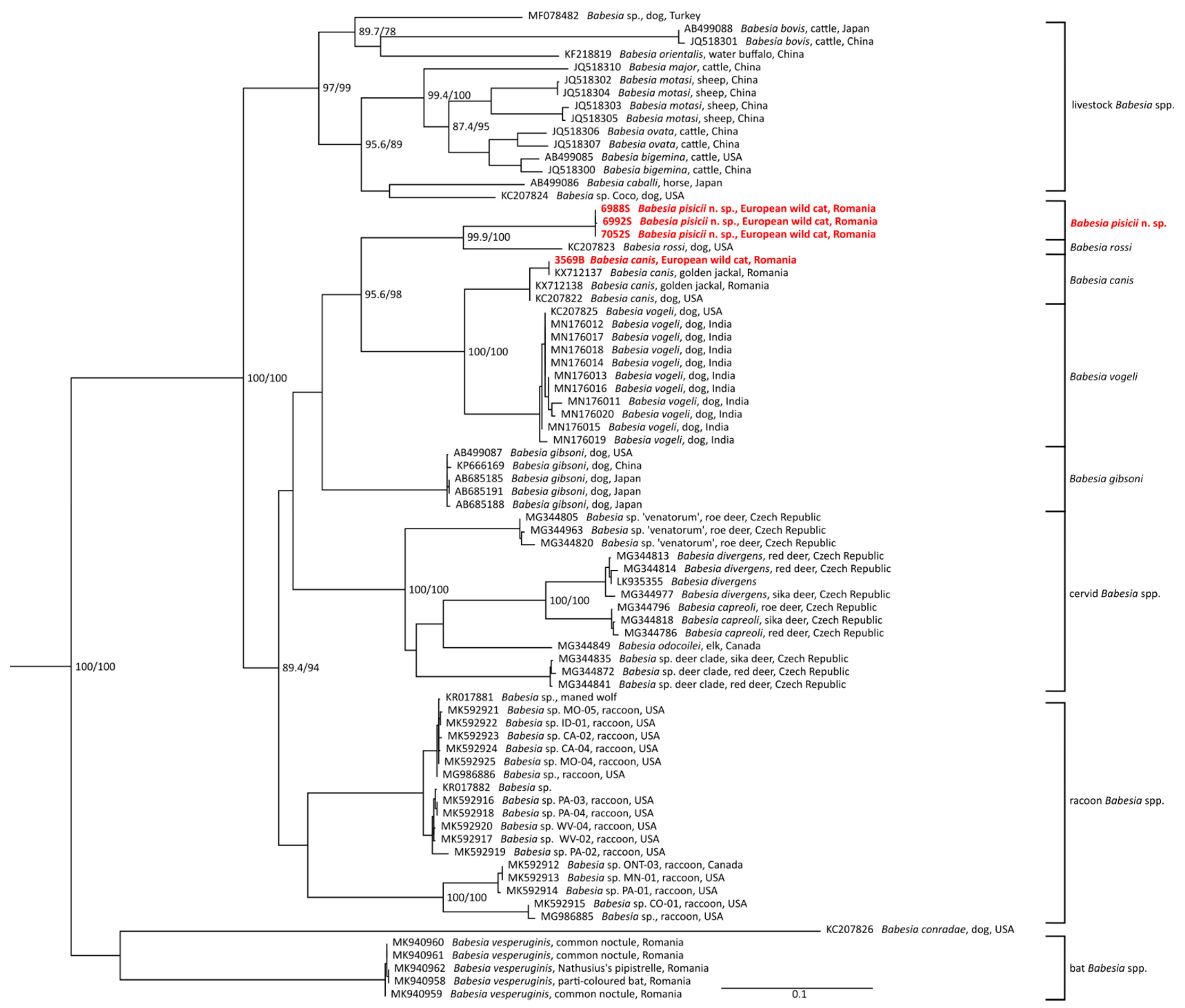
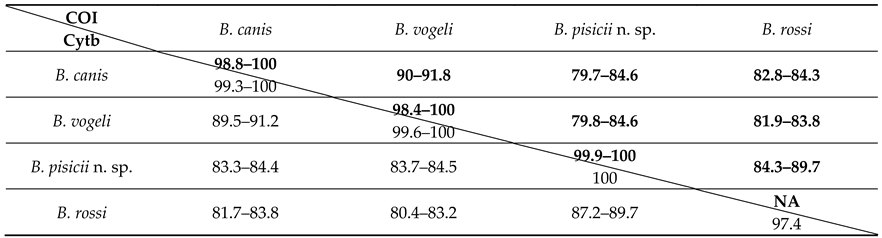
3.3. Mitochondrial Genes Analyses
3.4. Taxonomic Summary and Species Description
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarado-Rybak, M.; Solano-Gallego, L.; Millán, J. A review of piroplasmid infections in wild carnivores worldwide: Importance for domestic animal health and wildlife conservation. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittger, L.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Morrison, D.A. Babesia: A world emerging. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1788–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabsley, M.J.; Shock, B.C. Natural history of zoonotic Babesia: Role of wildlife reservoirs. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2013, 2, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannier, E.; Gewurz, B.E.; Krause, P.J. Human babesiosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 22, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.M.; Corrin, T.; Wilhelm, B.; Uhland, C.; Greig, J.; Mascarenhas, M.; Waddell, L.A. Zoonotic Babesia: A scoping review of the global evidence. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babeş, V. Sur l’hemoglobinurie bacterienne du boeuf (On the bacterian hemoglobinuria of cattle) (in French). C. R. Hebd. Acad. Sci. 1888, 107, 692–694. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalca, A.D.; Cozma, V.; Şuteu, E.; Marinculic, A.; Boireau, P. The quest for piroplasms: From Babeş and Smith to molecules. Sci. Parasitol. 2010, 11, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hrazdilová, K.; Rybářová, M.; Široký, P.; Votypka, J.; Zintl, A.; Burgess, H.; Steinbauer, V.; Žákovčík, V.; Modrý, D. Diversity of Babesia spp. in cervid ungulates based on the 18S rDNA and cytochrome c oxidase subunit I phylogenies. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 77, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panait, L.C.; Mihalca, A.D.; Modrý, D.; Juránková, J.; Ionică, A.M.; Deak, G.; Gherman, C.M.; Heddergott, M.; Hodžić, A.; Veronesi, F.; et al. Three new species of Cytauxzoon in European wild felids. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 290, 109344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoob, A.L.; Prittie, J.; Hackner, S.G. Feline babesiosis. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2010, 20, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L. On a piroplasm of the Sudanese wild cat (Felis ocreata). Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1929, 22, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudaliar, S.V.; Achary, G.R.; Alwar, V.S. On a species of Babesia in an Indian wild cat (Felis catus). Indian Vet. J. 1950, 26, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dennig, H.K. Babesia infections in exotic cats and the significance of these blood parasites for veterinary research. Acta Zool. Pathol. Antverp. 1969, 48, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dennig, H.K.; Brocklesby, D.W. Babesia pantherae sp. nov., a piroplasm of the leopard (Panthera pardus). Parasitology 1972, 64, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzhorn, B.L.; Kjemtrup, A.M.; Lopez-Rebollar, L.M.; Conrad, P.A. Babesia leo n. sp. from lions in the Kruger National Park, South Africa, and its relation to other small piroplasms. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, A.-M.; Oosthuizen, M.C.; Peirce, M.A.; Venter, E.H.; Penzhorn, B.L. Babesia lengau sp. nov., a novel Babesia species in cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus, Schreber, 1775) populations in South Africa. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2703–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, A.-M.; Penzhorn, B.L.; Brayton, K.A.; Schoeman, T.; Oosthuizen, M.C. A novel Babesia sp. associated with clinical signs of babesiosis in domestic cats in South Africa. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baneth, G.; Kenny, M.J.; Tasker, S.; Anug, Y.; Shkap, V.; Levy, A.; Shaw, S.E. Infection with a proposed new subspecies of Babesia canis, Babesia canis subsp. presentii, in domestic cats. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.S.Y.; Poon, R.W.S.; Hui, J.J.Y.; Yuen, K.-Y. Detection of Babesia hongkongensis sp. nov. in a free-roaming Felis catus cat in Hong Kong. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2799–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado-Fornelio, A.; Martinez-Marcos, A.; Buling-Saraña, A.; Barba-Carretero, J. Presence of Mycoplasma haemofelis, Mycoplasma haemominutum and piroplasmids in cats from southern Europe: A molecular study. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 93, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.R.; Denardi, N.C.B.; de Sousa, K.C.M.; Gonçalves, L.R.; Henrique, P.C.; Ontivero, C.R.G.R.; Gonzalez, I.; Nery, C.V.C.; Chagas, C.R.F.; Monticelli, C.; et al. Arthropod-borne pathogens circulating in free-roaming domestic cats in a zoo environment in Brazil. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, E.; Proverbio, D.; Galluzzo, P.; Perego, R.; De Giorgi, G.B.; Roggero, N.; Caracappa, S. Frequency of piroplasms Babesia microti and Cytauxzoon felis in stray cats from northern Italy. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 943754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Köster, L.; Liza, K.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Branford, G.C.; Marchi, S.; Vandenplas, M.; Wang, C. Survey of vector-borne agents in feral cats and first report of Babesia gibsoni in cats on St Kitts, West Indies. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodžić, A.; Alić, A.; Duscher, G.G. High diversity of blood-associated parasites and bacteria in European wild cats in Bosnia and Herzegovina: A molecular study. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakou, A.; Dimzas, D.; Astaras, C.; Savvas, I.; Di Cesare, A.; Morelli, S.; Neofitos, Κ.; Migli, D.; Traversa, D. Clinical investigations and treatment outcome in a European wildcat (Felis silvestris silvestris) infected by cardio-pulmonary nematodes. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 19, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilhena, H.; Martinez-Díaz, V.L.; Cardoso, L.; Vieira, L.; Altet, L.; Francino, O.; Pastor, J.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.C. Feline vector-borne pathogens in the north and centre of Portugal. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, C.; Ramos, C.; Coimbra, M.; Bastos, F.; Martins, Â.; Pinto, P.; Nunes, M.; Vieira, M.L.; Cardoso, L.; Campino, L. Bacterial and protozoal agents of feline vector-borne diseases in domestic and stray cats from southern Portugal. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Sainz, Á.; Roura, X.; Peña, A.E.; Miró, G. A review of canine babesiosis: The European perspective. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallusovã¡, M.; Jirsovã¡, D.; Mihalca, A.D.; Gherman, C.M.; D’Amico, G.; Qablan, M.A.; Modrý, D. Cytauxzoon infections in wild felids from Carpathian-Danubian-Pontic space: Further evidence for a different Cytauxzoon species in European felids. J. Parasitol. 2016, 102, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchener, A.C.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ward, J.M.; Macdonald, D.W. A diagnosis for the Scottish wildcat (Felis silvestris): A tool for conservation action for a critically-endangered felid. Anim. Conserv. 2005, 8, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrisor, A.-I.; Ianos, I.; Tălângă, C. Land cover and use changes focused on the urbanization processes in Romania. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2010, 9, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgroi, G.; Iatta, R.; Veneziano, V.; Bezerra-Santos, M.A.; Lesiczka, P.; Hrazdilová, K.; Annoscia, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Golovchenko, M.; Rudenko, N.; et al. Molecular survey on tick-borne pathogens and Leishmania infantum in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from southern Italy. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrazdilová, K.; Myśliwy, I.; Hildebrand, J.; Buńkowska-Gawlik, K.; Janaczyk, B.; Perec-Matysiak, A.; Modrý, D. Paralogs vs. genotypes? Variability of Babesia canis assessed by 18S rDNA and two mitochondrial markers. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 266, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalovecka, M.; Sojka, D.; Ascencio, M.; Schnittger, L. Babesia life cycle—When phylogeny meets biology. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B. Q IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICZN. International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature. Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bull. Zool. Nomencl. 2012, 69, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreeg, M.E.; Marr, H.S.; Tarigo, J.L.; Cohn, L.A.; Bird, D.M.; Scholl, E.H.; Levy, M.G.; Wiegmann, B.M.; Birkenheuer, A. Mitochondrial genome sequences and structures aid in the resolution of Piroplasmida phylogeny. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzhorn, B.L.; Oosthuizen, M.C. Babesia species of domestic cats: Molecular characterization has opened Pandora’s box. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaro, N.; Larocca, V.; Parisi, A.; Losurdo, M.; Lia, R.P.; Greco, M.F.; Miccolis, A.; Ventrella, G.; Otranto, D.; Buonavoglia, C. Clinical bovine piroplasmosis caused by Babesia occultans in Italy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2432–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma-Naic, A.; Györk, A.; Nedișan, M.E.; Borșan, S.D.; Berar, C.; Bojan, A.; Cozma, V. Babesiosis in a 7-week-old calf: Case report. Sci. Parasitol. 2018, 19, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Criado-Fornelio, A.; Martinez-Marcos, A.; Buling-Saraña, A.; Barba-Carretero, J. Molecular studies on Babesia, Theileria and Hepatozoon in southern Europe: Part II. Phylogenetic analysis and evolutionary history. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 113, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Capewell, P.; Loney, C.; Katzer, F.; Shiels, B.R.; Weir, W. Sheep as host species for zoonotic Babesia venatorum, United Kingdom. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2257–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, G.; Cersini, A.; Nardini, R.; Del Pino, L.E.B.; Antognetti, V.; Zini, M.; Conti, R.; Lorenzetti, R.; Veneziano, V.; Autorino, G.L.; et al. Genetic diversity of Theileria equi and Babesia caballi infecting horses of Central-Southern Italy and preliminary results of its correlation with clinical and serological status. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobba, R.; Parpaglia, M.L.P.; Spezzigu, A.; Pittau, M.; Alberti, A. First molecular identification and phylogeny of a Babesia sp. from a symptomatic sow (Sus scrofa Linnaeus 1758). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2321–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiegala, A.; Pfeffer, M.; Pfister, K.; Karnath, C.; Silaghi, C. Molecular examinations of Babesia microti in rodents and rodent-attached ticks from urban and sylvatic habitats in Germany. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2015, 6, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchigiani, G.; Ebani, V.V.; Nardoni, S.; Bertelloni, F.; Bascherini, A.; Leoni, A.; Mancianti, F.; Poli, A. Molecular survey on the occurrence of arthropod-borne pathogens in wild brown hares (Lepus europaeus) from Central Italy. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 59, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silaghi, C.; Woll, D.; Hamel, D.; Pfister, K.; Mahling, M.; Pfeffer, M. Babesia spp. and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in questing ticks, ticks parasitizing rodents and the parasitized rodents—Analyzing the host-pathogen-vector interface in a metropolitan area. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corduneanu, A.; Hrazdilová, K.; Sándor, A.D.; Matei, I.A.; Ionică, A.M.; Barti, L.; Ciocănău, M.-A.; Măntoiu, D.Ș.; Coroiu, I.; Hornok, S.; et al. Babesia vesperuginis, a neglected piroplasmid: New host and geographical records, and phylogenetic relations. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciò, S.M.; Antunovic, B.; Moretti, A.; Mangili, V.; Marinculic, A.; Baric, R.R.; Slemenda, S.B.; Pieniazek, N.J. Molecular characterisation of Babesia canis canis and Babesia canis vogeli from naturally infected European dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdélyi, K.; Mezősi, L.; Vladov, S.; Földvári, G. Fatal acute babesiosis in captive grey wolves (Canis lupus) due to Babesia canis. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitková, B.; Hrazdilová, K.; D’Amico, G.; Duscher, G.G.; Suchentrunk, F.; Forejtek, P.; Gherman, C.M.; Matei, I.A.; Ionică, A.M.; Daskalaki, A.A.; et al. Eurasian golden jackal as host of canine vector-borne protists. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodžić, A.; Mrowietz, N.; Cézanne, R.; Bruckschwaiger, P.; Punz, S.; Habler, V.E.; Tomsik, V.; Lazar, J.; Duscher, G.G.; Glawischnig, W.; et al. Occurrence and diversity of arthropod-transmitted pathogens in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in western Austria, and possible vertical (transplacental) transmission of Hepatozoon canis. Parasitology 2018, 145, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, M.; Auriemma, C.; Lucibelli, M.G.; Borriello, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Sgroi, G.; Veneziano, V.; Galiero, G.; Fusco, G. Molecular detection of Babesia spp. (Apicomplexa: Piroplasma) in free-ranging canids and mustelids from Southern Italy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, E.; Trotta, M.; Chinelli, R.; Drigo, M.; Sinigoi, L.; Tosolini, P.; Furlanello, T.; Millotti, A.; Caldin, M.; Solano-Gallego, L. Cytauxzoon sp. infection in the first endemic focus described in domestic cats in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 183, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, F.; Ravagnan, S.; Cerquetella, M.; Carli, E.; Olivieri, E.; Santoro, A.; Pesaro, S.; Berardi, S.; Rossi, G.; Ragni, B.; et al. First detection of Cytauxzoon spp. infection in European wildcats (Felis silvestris silvestris) of Italy. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Regañón, D.; Villaescusa, A.; Ayllón, T.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Baneth, G.; Calleja-Bueno, L.; García-Sancho, M.; Agulla, B.; Sainz, Á. Molecular detection of Hepatozoon spp. and Cytauxzoon sp. in domestic and stray cats from Madrid, Spain. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, M.L.; Cattori, V.; Martínez, F.; López, G.; Vargas, A.; Simón, M.A.; Zorrilla, I.; Muñoz, A.; Palomares, F.; López-Bao, J.V.; et al. Feline leukemia virus and other pathogens as important threats to the survival of the critically endangered Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus). PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodžić, A.; Alić, A.; PraŠović, S.; Otranto, D.; Baneth, G.; Duscher, G.G. Hepatozoon silvestris sp. nov.: Morphological and molecular characterization of a new species of Hepatozoon (Adeleorina: Hepatozoidae) from the European wild cat (Felis silvestris silvestris). Parasitology 2017, 144, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corduneanu, A.; Sándor, A.D.; Mihalca, A.D.; Hrazdilová, K.; Modrý, D.; Hornok, S. Molecular evidence of canine pathogens in tissues of European bats. In Proceedings of the 17th International Bat Research Conference, Durban, South Africa, 31 July–5 August 2016; pp. 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zanet, S.; Bassano, M.; Trisciuoglio, A.; Taricco, I.; Ferroglio, E. Horses infected by Piroplasms different from Babesia caballi and Theileria equi: Species identification and risk factors analysis in Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 236, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uilenberg, G.; Gray, J.; Kahl, O. Research on Piroplasmorida and other tick-borne agents: Are we going the right way? Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corduneanu, A.; Ursache, T.D.; Taulescu, M.; Sevastre, B.; Modrý, D.; Mihalca, A.D. Detection of DNA of Babesia canis in tissues of laboratory rodents following oral inoculation with infected ticks. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörger, K.M.; Schrödl, M. How to describe a cryptic species? Practical challenges of molecular taxonomy. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greay, T.L.; Zahedi, A.; Krige, A.-S.; Owens, J.M.; Rees, R.L.; Ryan, U.M.; Oskam, C.L.; Irwin, P.J. Endemic, exotic and novel apicomplexan parasites detected during a national study of ticks from companion animals in Australia. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; Dumitrache, M.O.; Matei, I.A.; Ionică, A.M.; Gherman, C.M.; Sándor, A.D.; Modrý, D.; Mihalca, A.D. Ixodid ticks parasitizing wild carnivores in Romania. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 71, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Genetic Marker | Primers (Forward, Reverse) | Nucleotide Sequence (5′–3′) | Annealing Temperature | Product Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18S rDNA | Bc_F1 | CGTAGTTGTATTTTTGCGT | 50 °C | ≈430 bp | [33] |
| GR2 | CCAAAGACTTTGATTTCTCTC | ||||
| Bc_F2 | CATTTGGTTGGTTATTTCGTTTT | 53 °C | 376 bp | ||
| Bc_R1 | GTTCCTGAAGGGGTCAAAAA | ||||
| 18S rDNA | BT1F | GGTTGATCCTGCCAGTAGT | 65 °C–55 °C | ≈1730 bp | Modified after [8] |
| BT outer R | GGAAACCTTGTTACGACTTCTC | ||||
| Piro0F2 | GCCAGTAGTCATATGCTTGTCTTA | 65 °C–55 °C | ≈1670 bp | ||
| BT inner R | TTCTCCTTCCTTTAAGTGATAAG | ||||
| Cytb | Bc_cytb_F1 | TGGTCWTGGTATTCWGGAATG | 50 °C | ≈700 bp | [34] |
| Bc_cytb_R1 | AAGMYARTCTYCCTAAACATCC | ||||
| Bc_cytb_F2 | RATKAGYTAYTGGGGAGC | 48 °C | ≈580 bp | ||
| Bc_cytb_R2 | GCTGGWATCATWGGTATAC | ||||
| COI | Bab_For1 | ATWGGATTYTATATGAGTAT | 45 °C | 1250 bp | [34] |
| Bab_Rev1 | ATAATCWGGWATYCTCCTTGG | ||||
| Bab_For2 | TCTCTWCATGGWTTAATTATGATAT | 49 °C | 980 bp | ||
| Bab_Rev2 | TAGCTCCAATTGAHARWACAAAGTG |
 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panait, L.C.; Hrazdilová, K.; Ionică, A.M.; Deak, G.; Chişamera, G.B.; Adam, C.; Gherman, C.M.; Mihalca, A.D. Babesia pisicii n. sp. and Babesia canis Infect European Wild Cats, Felis silvestris, in Romania. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071474
Panait LC, Hrazdilová K, Ionică AM, Deak G, Chişamera GB, Adam C, Gherman CM, Mihalca AD. Babesia pisicii n. sp. and Babesia canis Infect European Wild Cats, Felis silvestris, in Romania. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(7):1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071474
Chicago/Turabian StylePanait, Luciana Cătălina, Kristýna Hrazdilová, Angela Monica Ionică, Georgiana Deak, Gabriel Bogdan Chişamera, Costică Adam, Călin Mircea Gherman, and Andrei Daniel Mihalca. 2021. "Babesia pisicii n. sp. and Babesia canis Infect European Wild Cats, Felis silvestris, in Romania" Microorganisms 9, no. 7: 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071474
APA StylePanait, L. C., Hrazdilová, K., Ionică, A. M., Deak, G., Chişamera, G. B., Adam, C., Gherman, C. M., & Mihalca, A. D. (2021). Babesia pisicii n. sp. and Babesia canis Infect European Wild Cats, Felis silvestris, in Romania. Microorganisms, 9(7), 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071474











