Nearly Identical Plasmids Encoding VIM-1 and Mercury Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from North-Eastern Germany
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
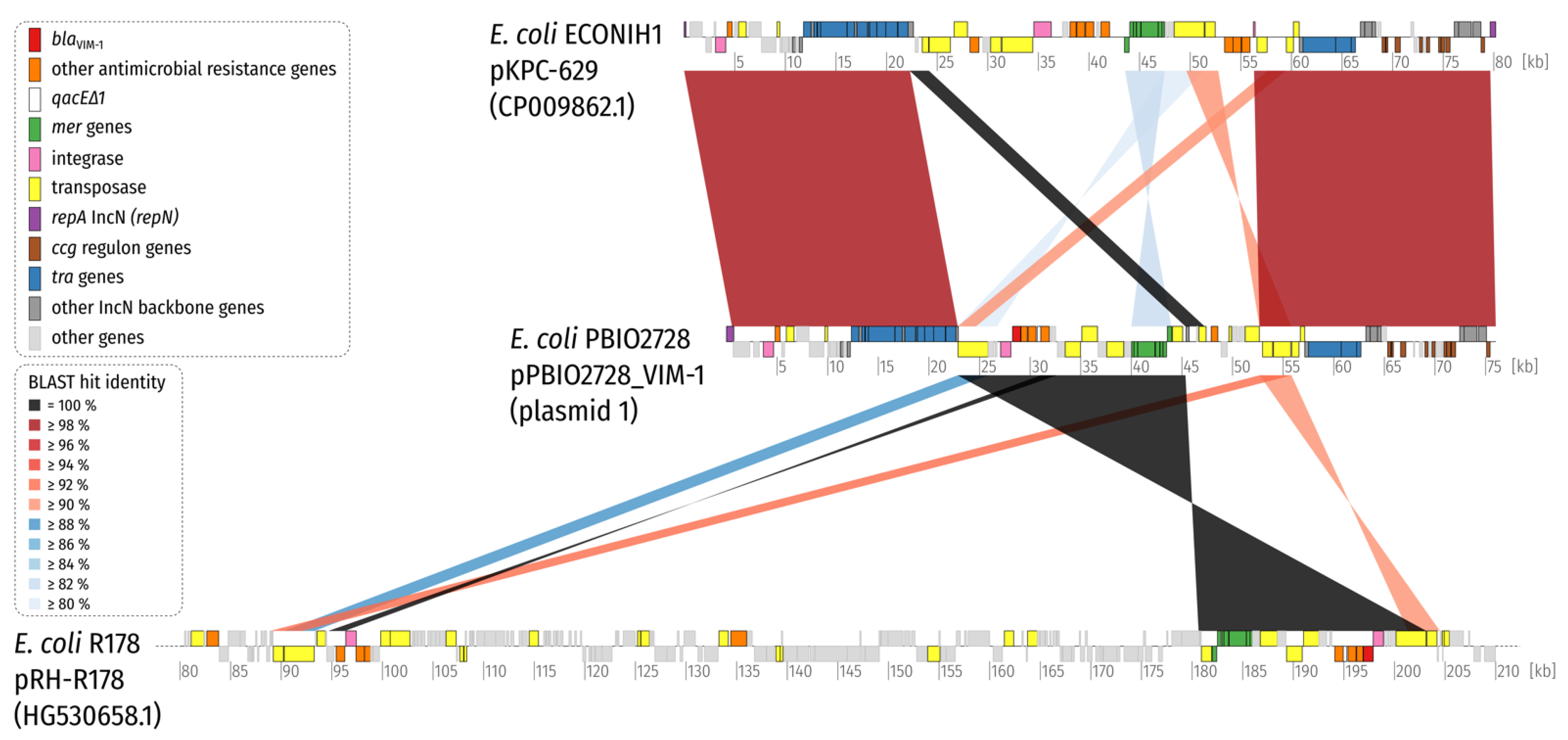
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, G.T. Continuous Evolution: Perspective on the Epidemiology of Carbapenemase Resistance among Enterobacterales and Other Gram-Negative Bacteria. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roschanski, N.; Guenther, S.; Vu, T.T.T.; Fischer, J.; Semmler, T.; Huehn, S.; Alter, T.; Roesler, U. VIM-1 carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli isolated from retail seafood, Germany 2016. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irrgang, A.; Tenhagen, B.A.; Pauly, N.; Schmoger, S.; Kaesbohrer, A.; Hammerl, J.A. Characterization of VIM-1-Producing E. coli Isolated From a German Fattening Pig Farm by an Improved Isolation Procedure. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauretti, L.; Riccio, M.L.; Mazzariol, A.; Cornaglia, G.; Amicosante, G.; Fontana, R.; Rossolini, G.M. Cloning and characterization of blaVIM, a new integron-borne metallo-beta-lactamase gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bush, K. Metallo-beta-lactamases: A class apart. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27 (Suppl. S1), S48–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, T.R.; Toleman, M.A.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Metallo-beta-lactamases: The quiet before the storm? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumura, Y.; Peirano, G.; Devinney, R.; Bradford, P.A.; Motyl, M.R.; Adams, M.D.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.; Pitout, J.D.D. Genomic epidemiology of global VIM-producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordmann, P.; Naas, T.; Poirel, L. Global spread of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance plasmid families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psichogiou, M.; Tassios, P.T.; Avlamis, A.; Stefanou, I.; Kosmidis, C.; Platsouka, E.; Paniara, O.; Xanthaki, A.; Toutouza, M.; Daikos, G.L.; et al. Ongoing epidemic of blaVIM-1-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae in Athens, Greece: A prospective survey. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozwandowicz, M.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Fischer, J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B.; Guerra, B.; Mevius, D.J.; Hordijk, J. Plasmids carrying antimicrobial resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1121–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peirano, G.; Lascols, C.; Hackel, M.; Hoban, D.J.; Pitout, J.D. Molecular epidemiology of Enterobacteriaceae that produce VIMs and IMPs from the SMART surveillance program. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 78, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Moller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Villa, L.; Moodley, A.; Hasman, H.; Miriagou, V.; Guardabassi, L.; Carattoli, A. Multilocus sequence typing of IncN plasmids. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1987–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guy, L.; Kultima, J.R.; Andersson, S.G. genoPlotR: Comparative gene and genome visualization in R. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2334–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaufler, K.; Wieler, L.H.; Semmler, T.; Ewers, C.; Guenther, S. ESBL-plasmids carrying toxin-antitoxin systems can be "cured" of wild-type Escherichia coli using a heat technique. Gut Pathog. 2013, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heiden, S.E.; Hübner, N.O.; Bohnert, J.A.; Heidecke, C.D.; Kramer, A.; Balau, V.; Gierer, W.; Schaefer, S.; Eckmanns, T.; Gatermann, S.; et al. A Klebsiella pneumoniae ST307 outbreak clone from Germany demonstrates features of extensive drug resistance, hypermucoviscosity and enhanced iron acquisition. Eur. Nucleotide Arch. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.M.; Gaballa, A.; Guldimann, C.; Sullivan, G.; Henderson, L.O.; Wiedmann, M. Identification of Novel Mobilized Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-9 in a Multidrug-Resistant, Colistin-Susceptible Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium Isolate. Mbio 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tyson, G.H.; Li, C.; Hsu, C.H.; Ayers, S.; Borenstein, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Tran, T.T.; McDermott, P.F.; Zhao, S. The mcr-9 Gene of Salmonella and Escherichia coli Is Not Associated with Colistin Resistance in the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolejska, M.; Villa, L.; Hasman, H.; Hansen, L.; Carattoli, A. Characterization of IncN plasmids carrying bla CTX-M-1 and qnr genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella from animals, the environment and humans. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falgenhauer, L.; Ghosh, H.; Guerra, B.; Yao, Y.; Fritzenwanker, M.; Fischer, J.; Helmuth, R.; Imirzalioglu, C.; Chakraborty, T. Comparative genome analysis of IncHI2 VIM-1 carbapenemase-encoding plasmids of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica isolated from a livestock farm in Germany. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, E.S.; Barkay, T. The mercury resistance operon: From an origin in a geothermal environment to an efficient detoxification machine. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mindlin, S.; Kholodii, G.; Gorlenko, Z.; Minakhina, S.; Minakhin, L.; Kalyaeva, E.; Kopteva, A.; Petrova, M.; Yurieva, O.; Nikiforov, V. Mercury resistance transposons of gram-negative environmental bacteria and their classification. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, C.A.; Hall, R.M.; Summers, A.O. Transposon Tn21, flagship of the floating genome. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Strain | Species | ST | Patient | Source | Date | Lab | MDR | Antimicrobial Resistance Phenotype (mg/L) | Antimicrobial Resistance Genotype | Incompatibility Types | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAZ | CIP | GEN | IPM | MEM | TZP | SXT | ||||||||||
| PBIO2726 | C. freundii | 396 | 1 | rectal swab | 21 June 2020 | MVZ | yes | >64 (R) | 4 (R) | 4 (R) | >16 (R) | >16 (R) | >128 (R) | >320 (R) | aac(6’)-Ib-G, aadA1, blaCMY-78, blaVIM-1, dfrA14, fosA7.2, qnrS1, sul1, sul2, tet(34) | IncN (ST7), IncFII(S), IncFII(SARC14) |
| PBIO2728 | E. coli | 10 | 2 | rectal swab | 26 July 2020 | MVZ | yes | >64 (R) | 0.5 (I) | 4 (R) | >16 (R) | >16 (R) | >128 (R) | >320 (R) | aac(6’)-Ib-G, aadA1, blaVIM-1, dfrA14, qnrS1, sul1, tet(34) | IncN (ST7), IncFIA(HI1), IncFIB(K), IncFII(p96A), IncFII |
| PBIO2729 | K. oxytoca | 168 | 2 | rectal swab | 26 July 2020 | MVZ | yes | >64 (R) | 2 (R) | 8 (R) | >16 (R) | >16 (R) | >128 (R) | >320 (R) | aac(6’)-Ib-G, aadA1, blaOXY-6-1, blaVIM-1, dfrA14, fosA_gen, oqxA10, oqxB20, qnrS1, sul1, tet(34) | IncN (ST7), IncFIB(K) |
| PBIO2730 | K. oxytoca | 172 | 3 | sternal wound | 5 August 2020 | IMD | yes | >64 (R) | 4 (R) | 2 (R) | >16 (R) | >16 (R) | >128 (R) | >320 (R) | aac(6’)-Ib-G, aph(3’’)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, blaOXA-10, blaOXY-6-2, blaVIM-1, catA1, cmlA5, dfrA14, fosA_gen, mcr-9.1, oqxA10, oqxB20, qnrS1, sul1, tet(34) | IncHI2, IncHI2A, IncFII(pCRY) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heiden, S.E.; Sydow, K.; Schaefer, S.; Klempien, I.; Balau, V.; Bauer, P.; Hübner, N.-O.; Schaufler, K. Nearly Identical Plasmids Encoding VIM-1 and Mercury Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from North-Eastern Germany. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071345
Heiden SE, Sydow K, Schaefer S, Klempien I, Balau V, Bauer P, Hübner N-O, Schaufler K. Nearly Identical Plasmids Encoding VIM-1 and Mercury Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from North-Eastern Germany. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(7):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071345
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeiden, Stefan E., Katharina Sydow, Stephan Schaefer, Ingo Klempien, Veronika Balau, Peter Bauer, Nils-Olaf Hübner, and Katharina Schaufler. 2021. "Nearly Identical Plasmids Encoding VIM-1 and Mercury Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from North-Eastern Germany" Microorganisms 9, no. 7: 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071345
APA StyleHeiden, S. E., Sydow, K., Schaefer, S., Klempien, I., Balau, V., Bauer, P., Hübner, N.-O., & Schaufler, K. (2021). Nearly Identical Plasmids Encoding VIM-1 and Mercury Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae from North-Eastern Germany. Microorganisms, 9(7), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9071345






