Interferon Lambda Delays the Emergence of Influenza Virus Resistance to Oseltamivir
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Tissues, Viruses, and Compounds
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Infectivity of A(H1N1)pdm09 Influenza Viruses Measured by Plaque Assay in MDCK
2.4. Virus Yield Reduction Assay in Calu-3 Cells
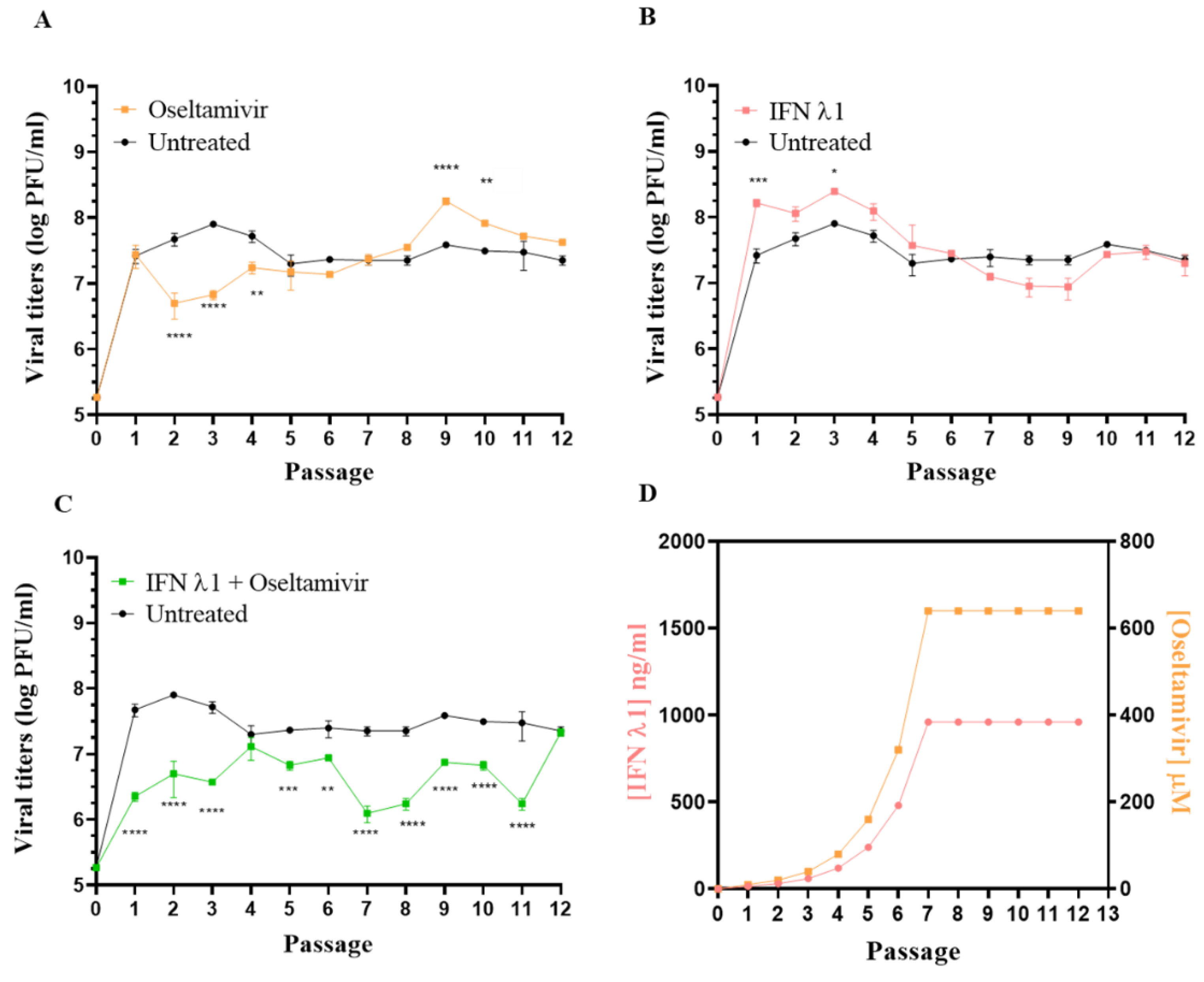
2.5. Selection of Resistant Variants
2.6. Assessment of Viral Fitness in Calu-3 and in Respiratory Tissues
2.7. RT-qPCR Analysis and Viral RNA Copies Quantification
2.8. Virus Sequencing
2.9. C11-6′ Inhibition Assay
3. Results
3.1. Determination of IFN λ1 and Oseltamivir Non-Toxic Doses
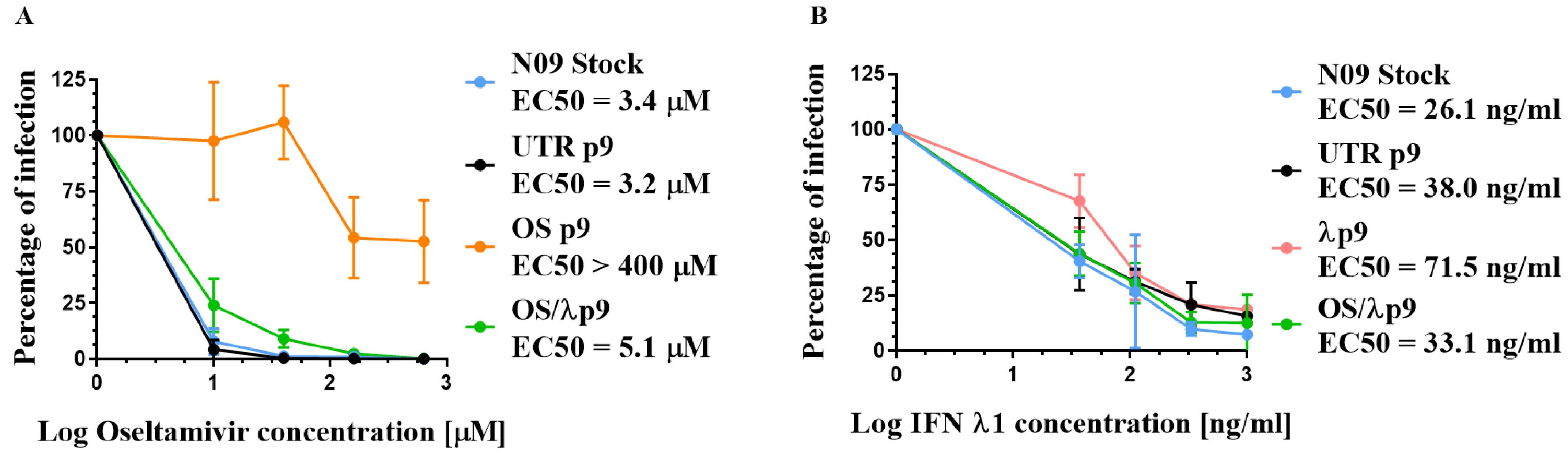
3.2. Susceptibility of A(H1N1)pdm09 Virus to Oseltamivir and IFN λ1
3.3. Selection of Resistant Variants against Oseltamivir Administered Alone or in Combination with IFN λ1
3.4. Viral Fitness Assessment of the A(H1N1)pdm09 Variants In Vitro and Ex Vivo
3.5. Sequence Analysis of Selected A(H1N1)pdm09 Variants
3.6. Effect of HA Changes on Receptor Specificity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDCK | Mardin-Darby Canine Kidney cells |
| Calu-3 | Human sub-mucosal cell line derived from lung adenocarcinoma |
| DMEM | Dulbecco′s Modified Eagle′s—Medium |
| MEM | Minimum Essential Medium Eagle |
| A(H1N1)pdm09 | Influenza A/Netherlands/602/2009 virus |
| NA | Neuraminidase |
| HA | Hemagglutinin |
| PFU | Plaque forming unit |
| IV | Influenza virus |
| IAV | Influenza A virus |
| IBV | Influenza B virus |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| IFN | Interferon |
| OS | Oseltamivir |
| N09 Stock | A/Netherlands/602/2009 stock virus produced in MDCK cells |
| UTR p9 | Variant passaged 9 times without drug in Calu-3 cells |
| UTR p3 | Variant passaged 3 times without drug in Calu-3 cells |
| UTR p4 | Variant passaged 4 times without drug in Calu-3 cells |
| OS p9 | Variant passaged 9 times with increasing doses of OS in Calu-3 cells |
| OS p8 | Variant passaged 8 times with increasing doses of OS in Calu-3 cells |
| Λ p9 | Variant passaged 9 times with increasing doses of IFN λ1 in Calu-3 cells |
| λ/OS | p9 Variant passaged 9 times with increasing doses of OS plus IFN λ1 in Calu-3 cells |
| λ p9 | Variant passaged 9 times with increasing doses of IFN λ1 in Calu-3 cells |
| 6′SLN | 6′sialyl-N-acetyllactosamine |
| C11-6′ | Virucidal nanomaterial based on a β-cyclodextrin core, exposing 6′SLN |
| Hpi | Hours post infection |
| Hbi | Hours before infection |
| EC50 | Maximal effective concentration |
| RdRp | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| p | p value |
References
- Paget, J.; Spreeuwenberg, P.; Charu, V.; Taylor, R.J.; Iuliano, A.D.; Bresee, J.; Lone, S.; Cecile, V. Global mortality associated with seasonal influenza epidemics: New burden estimates and predictors from the GLaMOR Project. J. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 020421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.S.; Mistry, B.; Haslam, S.M.; Barclay, W.S. Host and viral determinants of influenza A virus species specificity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders-Hastings, P.R.; Krewski, D. Reviewing the History of Pandemic Influenza: Understanding Patterns of Emergence and Transmission. Pathogens 2016, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampejo, T. Influenza and antiviral resistance: An overview. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, F.G.; de Jong, M.D. Emerging influenza antiviral resistance threats. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, A.J.; Wolstenholme, A.J.; Skehel, J.J.; Smith, M.H. The molecular basis of the specific anti-influenza action of amantadine. EMBO J. 1985, 4, 3021–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bright, R.A.; Medina, M.J.; Xu, X.; Perez-Oronoz, G.; Wallis, T.R.; Davis, X.M.; Povinelli, L.; Cox, N.I.; Klimov, A.I. Incidence of adamantane resistance among influenza A (H3N2) viruses isolated worldwide from 1994 to 2005: A cause for concern. Lancet 2005, 366, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, A.C.; Holien, J.K.; Parker, M.; Kelso, A.; Barr, I.G. Zanamivir-resistant influenza viruses with a novel neuraminidase mutation. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10366–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Huillier, A.G.; Abed, Y.; Petty, T.J.; Cordey, S.; Thomas, Y.; Bouhy, X.; Schibler, M.; Simon, A.; Chalandon, Y.; van Delden, C.; et al. E119D Neuraminidase Mutation Conferring Pan-Resistance to Neuraminidase Inhibitors in an A(H1N1)pdm09 Isolate From a Stem-Cell Transplant Recipient. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1726–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborda, P.; Wang, S.Y.; Voglmeir, J. Influenza Neuraminidase Inhibitors: Synthetic Approaches, Derivatives and Biological Activity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, Y.; Pizzorno, A.; Bouhy, X.; Boivin, G. Role of permissive neuraminidase mutations in influenza A/Brisbane/59/2007-like (H1N1) viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, J.D.; Gong, L.I.; Baltimore, D. Permissive secondary mutations enable the evolution of influenza oseltamivir resistance. Science 2010, 328, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranovich, T.; Saito, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Zaraket, H.; Dapat, C.; Caperig-Dapat, I.; Oguma, T.; Ibrahim Shabana, I.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, T. Emergence of H274Y oseltamivir-resistant A(H1N1) influenza viruses in Japan during the 2008–2009 season. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossyvakis, A.; Mentis, A.A.; Tryfinopoulou, K.; Pogka, V.; Kalliaropoulos, A.; Antalis, E.; Lytras, T.; Meijer, A.; Tsiodras, S.; Karakitsos, P.; et al. Antiviral susceptibility profile of influenza A viruses; keep an eye on immunocompromised patients under prolonged treatment. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leang, S.K.; Deng, Y.M.; Shaw, R.; Caldwell, N.; Iannello, P.; Komadina, N.; Buchy, F.; Chittaganpitch, M.; Dwyer, D.E.; Fagan, P.; et al. Influenza antiviral resistance in the Asia-Pacific region during 2011. Antivir. Res. 2013, 97, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okomo-Adhiambo, M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Abd Elal, A.; Sleeman, K.; Fry, A.M.; Gubareva, L.V. Drug susceptibility surveillance of influenza viruses circulating in the United States in 2011–2012: Application of the WHO antiviral working group criteria. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2014, 8, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragstad, K.; Hungnes, O.; Litleskare, I.; Nyrerod, H.C.; Dorenberg, D.H.; Hauge, S.H. Community spread and late season increased incidence of oseltamivir-resistant influenza A(H1N1) viruses in Norway 2016. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2019, 13, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.M.; Azhar, E.I.; Shalhoub, S.; Abujamel, T.S.; Othman, N.A.; Al Zahrani, A.B.; Abdullah, H.M.; Al-Alawi, M.M.; A Sindi, A.A. Genetic characterization and diversity of circulating influenza A/H1N1pdm09 viruses isolated in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia between 2014 and 2015. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashita, E.; Meijer, A.; Lackenby, A.; Gubareva, L.; Rebelo-de-Andrade, H.; Besselaar, T.; Fry, A.; Gregory, V.; Leang, S.-K.; Huang, W.; et al. Global update on the susceptibility of human influenza viruses to neuraminidase inhibitors, 2013–2014. Antivir. Res. 2015, 117, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Hurt, A.C. Neuraminidase inhibitor resistance in influenza: A clinical perspective. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhill, D.H.; Te Velthuis, A.J.W.; Fletcher, R.A.; Langat, P.; Zambon, M.; Lackenby, A.; S Barclay, W.S. The mechanism of resistance to favipiravir in influenza. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelson, A.S.; Rong, L.; Hayden, F.G. Combination antiviral therapy for influenza: Predictions from modeling of human infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 1642–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.T.; Smee, D.F.; Barnard, D.L.; Julander, J.G.; Gross, M.; de Jong, M.D.; Went, G.T. Efficacy of combined therapy with amantadine, oseltamivir, and ribavirin in vivo against susceptible and amantadine-resistant influenza A viruses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoggins, J.W. Interferon-Stimulated Genes: What Do They All Do? Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.; Cohen, M.H.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA drug approval summary: Bevacizumab plus interferon for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Oncologist 2010, 15, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murira, A.; Lamarre, A. Type-I Interferon Responses: From Friend to Foe in the Battle against Chronic Viral Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Schnepf, D.; Staeheli, P. Interferon-lambda orchestrates innate and adaptive mucosal immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreakos, E.; Salagianni, M.; Galani, I.E.; Koltsida, O. Interferon-lambdas: Front-Line Guardians of Immunity and Homeostasis in the Respiratory. Tract. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.; McCabe, T.M.; Crotta, S.; Gad, H.H.; Hessel, E.M.; Beinke, S.; Hartmann, R.; Wack, A. IFNlambda is a potent anti-influenza therapeutic without the inflammatory side effects of IFNalpha treatment. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermant, P.; Michiels, T. Interferon-lambda in the context of viral infections: Production, response and therapeutic implications. J. Innate. Immun. 2014, 6, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.A.; Nice, T.J. You Can Breathe Easy: IFNlambda Handles Flu without Triggering a Damaging Inflammatory Response. Immunity 2017, 46, 768–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galani, I.E.; Triantafyllia, V.; Eleminiadou, E.E.; Koltsida, O.; Stavropoulos, A.; Manioudaki, M.; Thanos, D.; Doyle, S.E.; Kotenko, S.V.; Thanopoulou, K.; et al. Interferon-lambda Mediates Non-redundant Front-Line Antiviral Protection against Influenza Virus Infection without Compromising Host Fitness. Immunity 2017, 46, 875–890e876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordstein, M.; Kochs, G.; Dumoutier, L.; Renauld, J.C.; Paludan, S.R.; Klucher, K.; Staeheli, P. Interferon-lambda contributes to innate immunity of mice against influenza A virus but not against hepatotropic viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, E.L. Preclinical and clinical development of pegylated interferon-lambda 1 in chronic hepatitis C. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasfar, A.; Zloza, A.; Cohen-Solal, K.A. IFN-lambda therapy: Current status and future perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordstein, M.; Neugebauer, E.; Ditt, V.; Jessen, B.; Rieger, T.; Falcone, V.; Sorgeloos, F.; Ehl, S.; Mayer, D.; Kochs, G.; et al. Lambda interferon renders epithelial cells of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts resistant to viral infections. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5670–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommereyns, C.; Paul, S.; Staeheli, P.; Michiels, T. IFN-lambda (IFN-lambda) is expressed in a tissue-dependent fashion and primarily acts on epithelial cells in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushina, N.A.; Donnelly, R.P. In vitro anti-influenza A activity of interferon (IFN)-lambda1 combined with IFN-beta or oseltamivir carboxylate. Antivir. Res. 2014, 111, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chidekel, A.; Shaffer, T.H. Cultured human airway epithelial cells (calu-3): A model of human respiratory function, structure, and inflammatory responses. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BeruBe, K.; Aufderheide, M.; Breheny, D.; Clothier, R.; Combes, R.; Duffin, R.; Forbes, B.; Gaça, M.; Gray, A.; Hall, I.; et al. In vitro models of inhalation toxicity and disease. The report of a FRAME workshop. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2009, 37, 89–141. [Google Scholar]
- Essaidi-Laziosi, M.; Brito, F.; Benaoudia, S.; Royston, L.; Cagno, V.; Fernandes-Rocha, M.; Piuz, I.; Zdobnov, E.; Huang, S.; Constant, S.; et al. Propagation of respiratory viruses in human airway epithelia reveals persistent virus-specific signatures. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaidi-Laziosi, M.; Geiser, J.; Huang, S.; Constant, S.; Kaiser, L.; Tapparel, C. Author Correction: Interferon-Dependent and Respiratory Virus-Specific Interference in Dual Infections of Airway Epithelia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseligka, E.D.; Sobo, K.; Stoppini, L.; Cagno, V.; Abdul, F.; Piuz, I.; Meylan, P.; Huang, S.; Constant, S.; Tapparel, C. A VP1 mutation acquired during an enterovirus 71 disseminated infection confers heparan sulfate binding ability and modulates ex vivo tropism. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocabiyik, O.; Cagno, V.; Silva, P.J.; Zhu, Y.; Sedano, L.; Bhide, Y.; Mettier, J.; Medaglia, C.; Da Costa, B.; Constant, S.; et al. Non-Toxic Virucidal Macromolecules Show High Efficacy Against Influenza Virus Ex Vivo and In Vivo. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.X.; Traini, D.; Young, P.M. Pharmaceutical applications of the Calu-3 lung epithelia cell line. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Goldsmith, C.; Thawatsupha, P.; Chittaganpitch, M.; Waicharoen, S.; Zaki, S.; Tumpey, T.M.; Katz, J.M. Highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 viruses elicit an attenuated type i interferon response in polarized human bronchial epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12439–12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottcher-Friebertshauser, E.; Stein, D.A.; Klenk, H.D.; Garten, W. Inhibition of influenza virus infection in human airway cell cultures by an antisense peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomer targeting the hemagglutinin-activating protease TMPRSS2. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1554–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushina, N.A.; Lugovtsev, V.Y.; Samsonova, A.P.; Sheikh, F.G.; Bovin, N.V.; Donnelly, R.P. Generation and characterization of interferon-lambda 1-resistant H1N1 influenza A viruses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, S.E.; Lugovtsev, V.Y.; Kan, A.; Bovin, N.V.; Donnelly, R.P.; Ilyushina, N.A. Laninamivir-Interferon Lambda 1 Combination Treatment Promotes Resistance by Influenza A Virus More Rapidly than Laninamivir Alone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Kati, W.; Carrick, R.; Steffy, K.; Shi, Y.; Montgomery, D.; Gusick, N.; Stoll, V.S.; Stewart, K.D.; Ng, T.I.; et al. In vitro selection and characterization of influenza A (A/N9) virus variants resistant to a novel neuraminidase inhibitor, A-315675. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5380–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Domingo, E.; de Avila, A.I.; Gallego, I.; Sheldon, J.; Perales, C. Viral fitness: History and relevance for viral pathogenesis and antiviral interventions. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boda, B.; Benaoudia, S.; Huang, S.; Bonfante, R.; Wiszniewski, L.; Tseligka, E.D.; Tapparel, C.; Constant, S. Antiviral drug screening by assessing epithelial functions and innate immune responses in human 3D airway epithelium model. Antivir. Res. 2018, 156, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, I.; Uboldi, C.; Bernard, E.; Sobrido, M.S.; Dine, S.; Hagege, A.; Dominique Vrel, D.; Herlin, N.; Rose, J.; Orsière, T.; et al. Toxicological Assessment of ITER-Like Tungsten Nanoparticles Using an In Vitro 3D Human Airway Epithelium Model. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brookes, D.W.; Miah, S.; Lackenby, A.; Hartgroves, L.; Barclay, W.S. Pandemic H1N1 2009 influenza virus with the H275Y oseltamivir resistance neuraminidase mutation shows a small compromise in enzyme activity and viral fitness. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Govorkova, E.A.; Bahl, J.; Zaraket, H.; Baranovich, T.; Seiler, P.; Prevost, K.; Webster, R.G.; Webby, R.J. Epistatic interactions between neuraminidase mutations facilitated the emergence of the oseltamivir-resistant H1N1 influenza viruses. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla, L.T.; Holder, B.P.; Abed, Y.; Boivin, G.; Beauchemin, C.A. The H275Y neuraminidase mutation of the pandemic A/H1N1 influenza virus lengthens the eclipse phase and reduces viral output of infected cells, potentially compromising fitness in ferrets. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10651–10660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinola, E.E.; Amarilla, A.A.; Martinez, M.; Aquino, V.H.; Russomando, G. Influenza A H1N1pdm 2009 Virus in Paraguay: Nucleotide Point Mutations in Hemagglutinin and Neuraminidase Genes are not Associated with Drug Resistance. Open Virol. J. 2014, 8, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseko, C.A.; Heidari, A.; Odaibo, G.N.; Olaleye, D.O. Complete genome sequencing of H1N1pdm09 swine influenza isolates from Nigeria reveals likely reverse zoonotic transmission at the human-animal interface in intensive piggery. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2019, 9, 1696632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekosz, A.; Newby, C.; Bose, P.S.; Lutz, A. Sialic acid recognition is a key determinant of influenza A virus tropism in murine trachea epithelial cell cultures. Virology 2009, 386, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.F.; Smith, D.J. A recommended numbering scheme for influenza A HA subtypes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, P.M. Influenza virus neuraminidase: Structure, antibodies, and inhibitors. Protein Sci. 1994, 3, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, N.M.; Cummings, D.A.; Fraser, C.; Cajka, J.C.; Cooley, P.C.; Burke, D.S. Strategies for mitigating an influenza pandemic. Nature 2006, 442, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, T.; Murray, M.; Levin, B.R. Antiviral resistance and the control of pandemic influenza. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameix-Welti, M.A.; Munier, S.; Le Gal, S.; Cuvelier, F.; Agou, F.; Enouf, V.; Naffakh, N.; van der Werf, S. Neuraminidase of 2007–2008 influenza A(H1N1) viruses shows increased affinity for sialic acids due to the D344N substitution. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorna, J.; Pachl, P.; Karlukova, E.; Hejdanek, J.; Rezacova, P.; Machara, A.; Hudlický, J.; Konvalinka, J.; Kožíšek, M. Kinetic, Thermodynamic, and Structural Analysis of Drug Resistance Mutations in Neuraminidase from the 2009 Pandemic Influenza Virus. Viruses 2018, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.G.; Pinilla, L.T.; Holder, B.P.; Abed, Y.; Boivin, G.; Beauchemin, C.A. Impact of the H275Y and I223V Mutations in the Neuraminidase of the 2009 Pandemic Influenza Virus In Vitro and Evaluating Experimental Reproducibility. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S. Treating Influenza Infection, From Now and Into the Future. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubareva, L.V.; Fry, A.M. Baloxavir and Treatment-Emergent Resistance: Public Health Insights and Next Steps. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Primer | Binding Position | Sequence * |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA | Forward 1 | 1–22 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT ATGAAGGCAATACTAGTAGTTCTG |
| HA | Reverse 1 | 901–921 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC GAGGCTGGTGTTTATAGCACC |
| HA | Forward 2 | 802–822 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT CCGAGATATGCATTCGCAATG |
| HA | Reverse 2 | 1676–end | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC TTAAATACATATTCTACACTGTAGAG |
| NA | Forward 1 | 1–26 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT ATGAATCCAAACCAAAAGATAATAAC |
| NA | Reverse 1 | 823–842 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CAGGAGCATTCCTCATAGTG |
| NA | Forward 2 | 706–729 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT GGTTCTTGCTTTACTGTAATGACC |
| NA | Reverse 2 | 1386–1410 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC TTACTTGTCAATGGTAAATGGCAAC |
| NA ● | Forward | 727–748 | CTGTAATGACCGATGGACCAAG |
| NA ● | Reverse | 913–935 | CAGATTCTGGTTGAAAGACACCC |
| PB1 | Forward 1 | 1–22 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT ATGGATGTCAATCCGACTCTAC |
| PB1 | Reverse 1 | 996–1017 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CATGCTCAGGATGTTTCTGAAC |
| PB1 | Forward 2 | 597–618 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT GGTCACGCAAAGAACAATAGG |
| PB1 | Reverse 2 | 1521–1542 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CACTCCAAAGCTGGGTAGCT |
| PB1 | Forward 3 | 1301–1321 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT CAATATACTGGTGGGATGGGC |
| PB1 | Reverse 3 | 2251–end | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC TTATTTTTGCCGTCTGAGTTCTTC |
| PB2 | Forward 1 | 1–23 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT ATGGAGAGAATAAAAGAACTGAGAG |
| PB2 | Reverse 1 | 998–021 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CTTTCTTGACTGATGATCCGC |
| PB2 | Forward 2 | 603–626 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT GGTGGCGTACATGCTAGAAAG |
| PB2 | Reverse 2 | 1552–1573 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CAGTTCCTTGCGTTTCACTGAC |
| PB2 | Forward 3 | 1230–1248 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT GATCAAGGCAGTTAGGGGC |
| PB2 | Reverse 3 | 2258–end | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CTAATTGATGGCCATCCGAATTC |
| PA | Forward 1 | 1–23 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT ATGGAAGACTTTGTGCGACAATG |
| PA | Reverse 1 | 996–1017 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CTTCCAAGCCATGAGGTAATTG |
| PA | Forward 2 | 616–36 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT GAGATTACAGGAACTATGCGC |
| PA | Reverse 2 | 1519–1540 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CATTTCTCAAATGAGACCTTCC |
| PA | Forward 3 | 1162–1184 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT GGAGACCTTAAACAGTATGACAG |
| PA | Reverse 3 | 2130–end | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC CTACTTCAGTGCATGTGTGAGG |
| M | Forward | 1–21 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT ATGAGTCTTCTAACCGAGGTC |
| M | Reverse | 959–982 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC TTACTCTAGCTCTATGTTGACAAA |
| NP | Forward 1 | 1–20 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT ATGGCGTCTCAAGGCACC |
| NP | Reverse 1 | 801–821 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC GATTTATGTGCAACTGATCCC |
| NP | Forward 2 | 702–721 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT CCAGAGGGCAATGATGGATC |
| NP | Reverse 2 | 1477–end | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC TCAACTGTCATACTCCTCTGC |
| NS | Forward | 1–20 | TGT AAA ACG ACG GCC AGT ATGGACTCCAACACCATGTC |
| NS | Reverse | 840–863 | CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG ACC GTAGAAACAAGGGTGTTTTTTATC |
| Virus | Passage No. | Oseltamivir (μM) | IFN λ1 (ng/mL) | HA * | NA ** | PA | PB1 | PB2 | NP | M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N09 Stock | - | - | - | - | D344N, D354G | - | - | - | - | - |
| UTR p3 | 3 | - | - | - | D344N, D354G | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| UTR p4 | 4 | - | - | K62R, G239D, Q240R | D344N, D354G | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| UTR p9 | 9 | - | - | K62R, G239D, Q240R | D344N, D354G | V100L ■ | A1920T ° | T303S ■ | - | K57R ■ |
| OS p7 | 7 | 640 | - | ns | H275Y ■, D344N, D354G | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| OS p8 | 8 | 640 | - | ns | H275Y ■, D344N, D354G | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| OS p9 | 9 | 640 | - | - | H275Y, D344N, D354G | N65K ■ | - | - | - | K57R ■ |
| λ p9 | 9 | - | 960 | K62R, G239D, Q240R | D344N, D354G | - | - | I57M ■ | P318Q ■ | K57R ■ |
| OS/λ p9 | 9 | 640 | 960 | - | D344N, D354G | - | - | - | - | K57R ■ |
| OS/λ p10 | 10 | 640 | 960 | ns | H275Y ■, D344N, D354G | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| OS/λ p11 | 11 | 640 | 960 | ns | H275Y ■, D344N, D354G | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| OS/λ p12 | 12 | 640 | 960 | ns | H275Y ■, D344N, D354G | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medaglia, C.; Zwygart, A.C.-A.; Silva, P.J.; Constant, S.; Huang, S.; Stellacci, F.; Tapparel, C. Interferon Lambda Delays the Emergence of Influenza Virus Resistance to Oseltamivir. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061196
Medaglia C, Zwygart AC-A, Silva PJ, Constant S, Huang S, Stellacci F, Tapparel C. Interferon Lambda Delays the Emergence of Influenza Virus Resistance to Oseltamivir. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(6):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061196
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedaglia, Chiara, Arnaud Charles-Antoine Zwygart, Paulo Jacob Silva, Samuel Constant, Song Huang, Francesco Stellacci, and Caroline Tapparel. 2021. "Interferon Lambda Delays the Emergence of Influenza Virus Resistance to Oseltamivir" Microorganisms 9, no. 6: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061196
APA StyleMedaglia, C., Zwygart, A. C.-A., Silva, P. J., Constant, S., Huang, S., Stellacci, F., & Tapparel, C. (2021). Interferon Lambda Delays the Emergence of Influenza Virus Resistance to Oseltamivir. Microorganisms, 9(6), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9061196






