Epidemic HI2 Plasmids Mobilising the Carbapenemase Gene blaIMP-4 in Australian Clinical Samples Identified in Multiple Sublineages of Escherichia coli ST216 Colonising Silver Gulls
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. E. coli ST216 Collection from Gulls
Whole Genome Sequencing
2.2. E. coli ST216 Metadata
2.2.1. WGS Analysis
2.2.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing of Gull Isolates
2.2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of Complete and Closed Plasmids
2.2.5. Transferability of HI2 Plasmids
3. Results
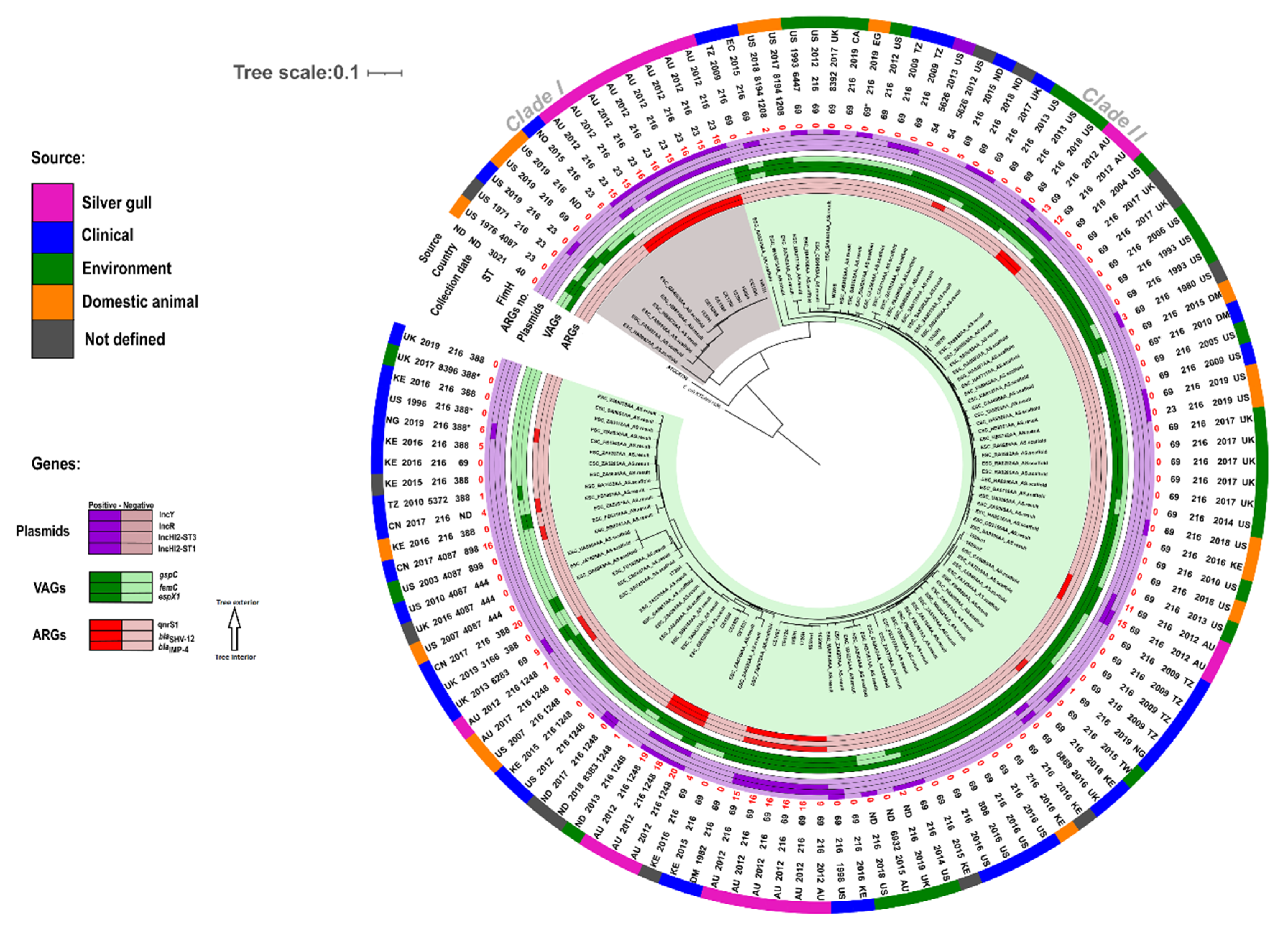
3.1. Population Structure of Gull E. coli ST216
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of E. coli ST216
3.3. Virulence Associated Genes (VAGs) of Gull Isolates
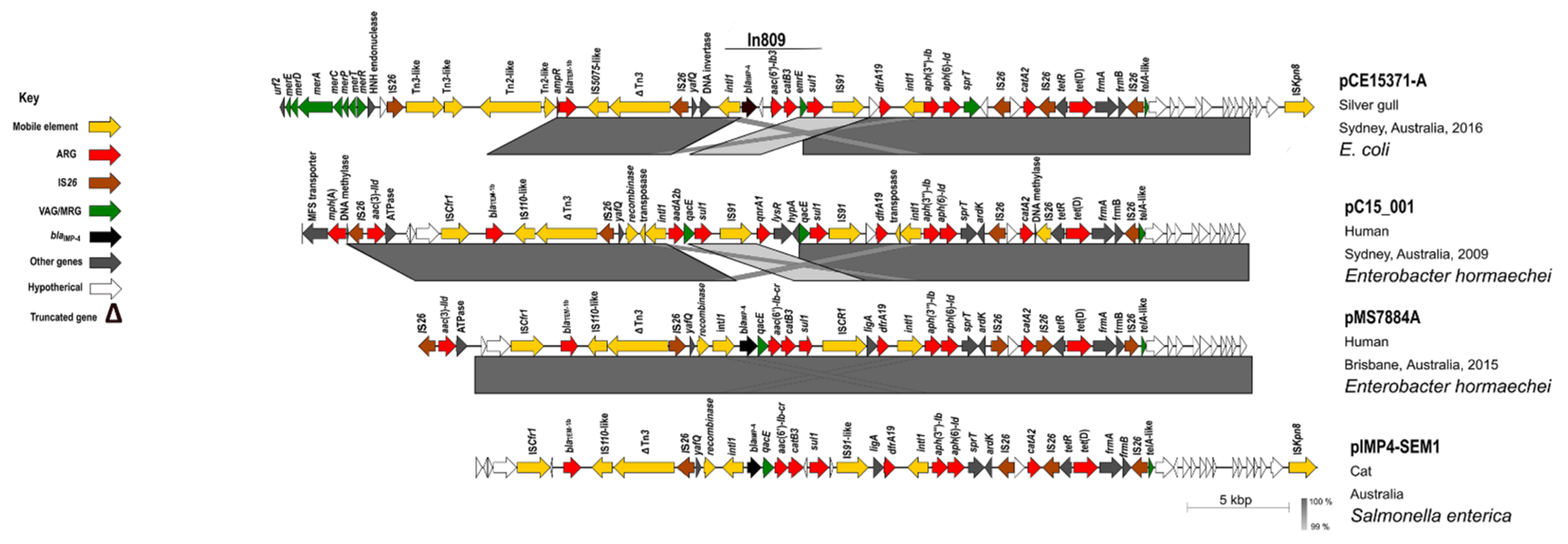
3.4. Antibiotic Resistance Phenotypes and Genes of Gull Isolates
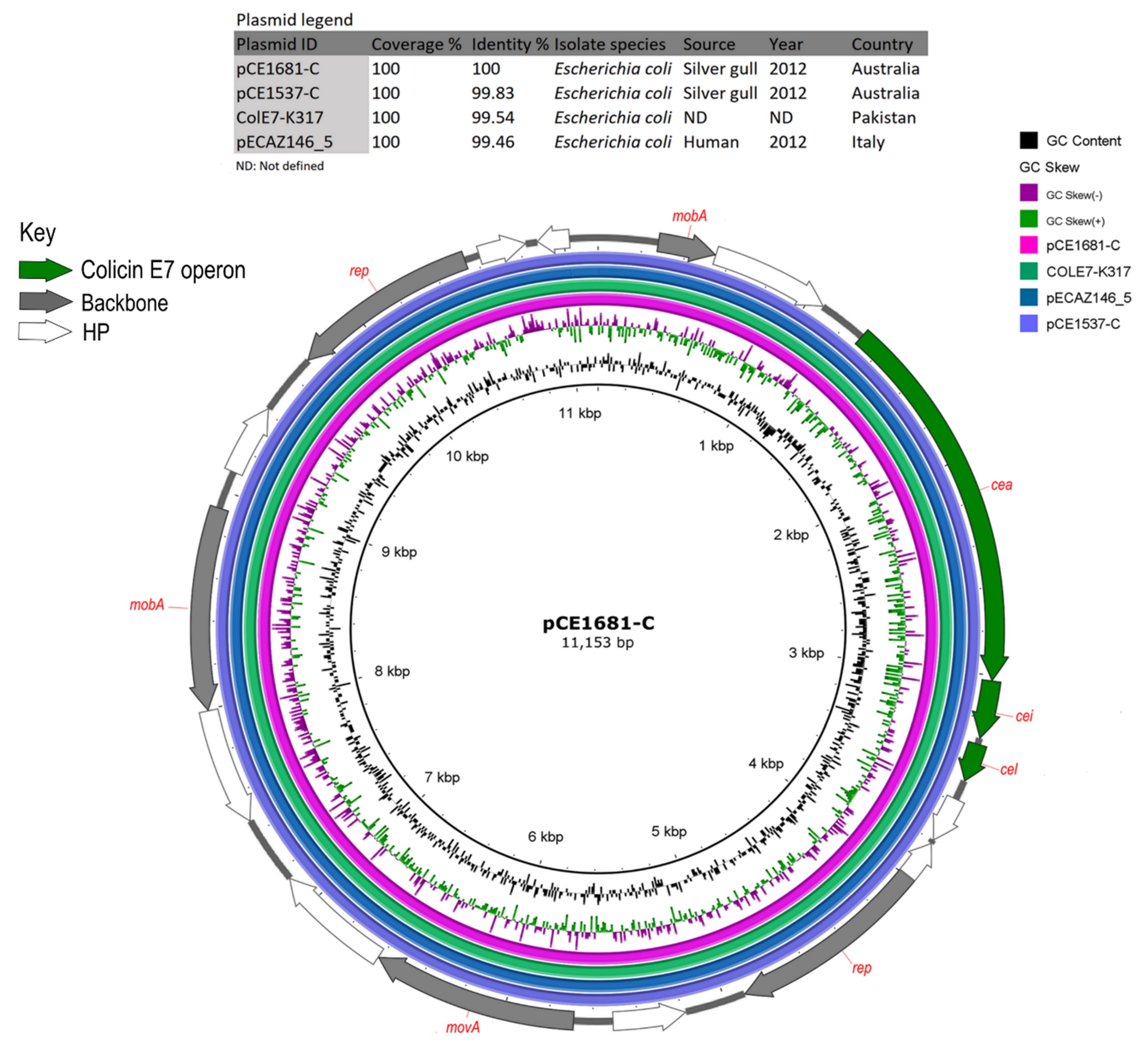
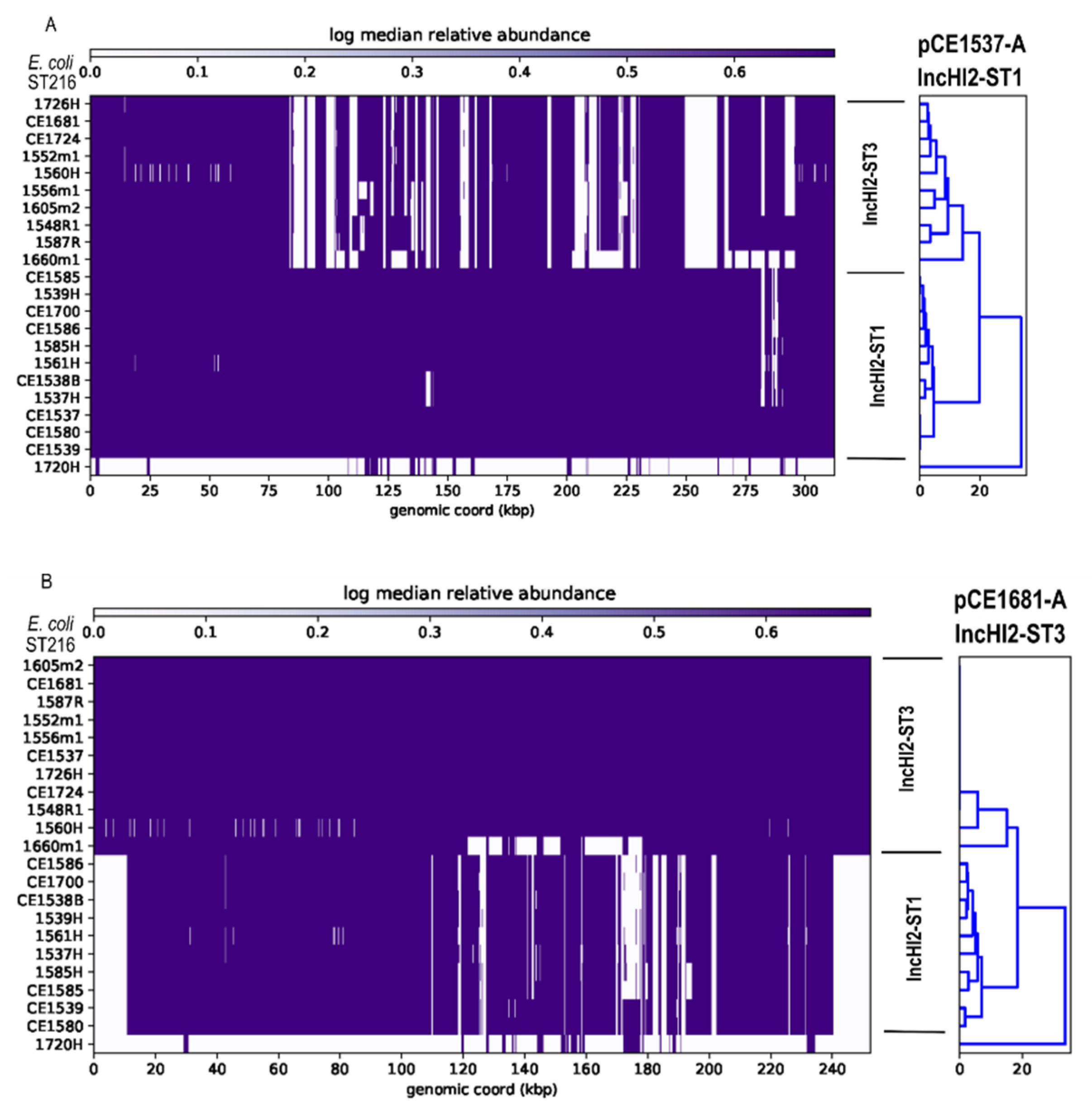
3.5. Plasmids Identified in ST216 Isolates
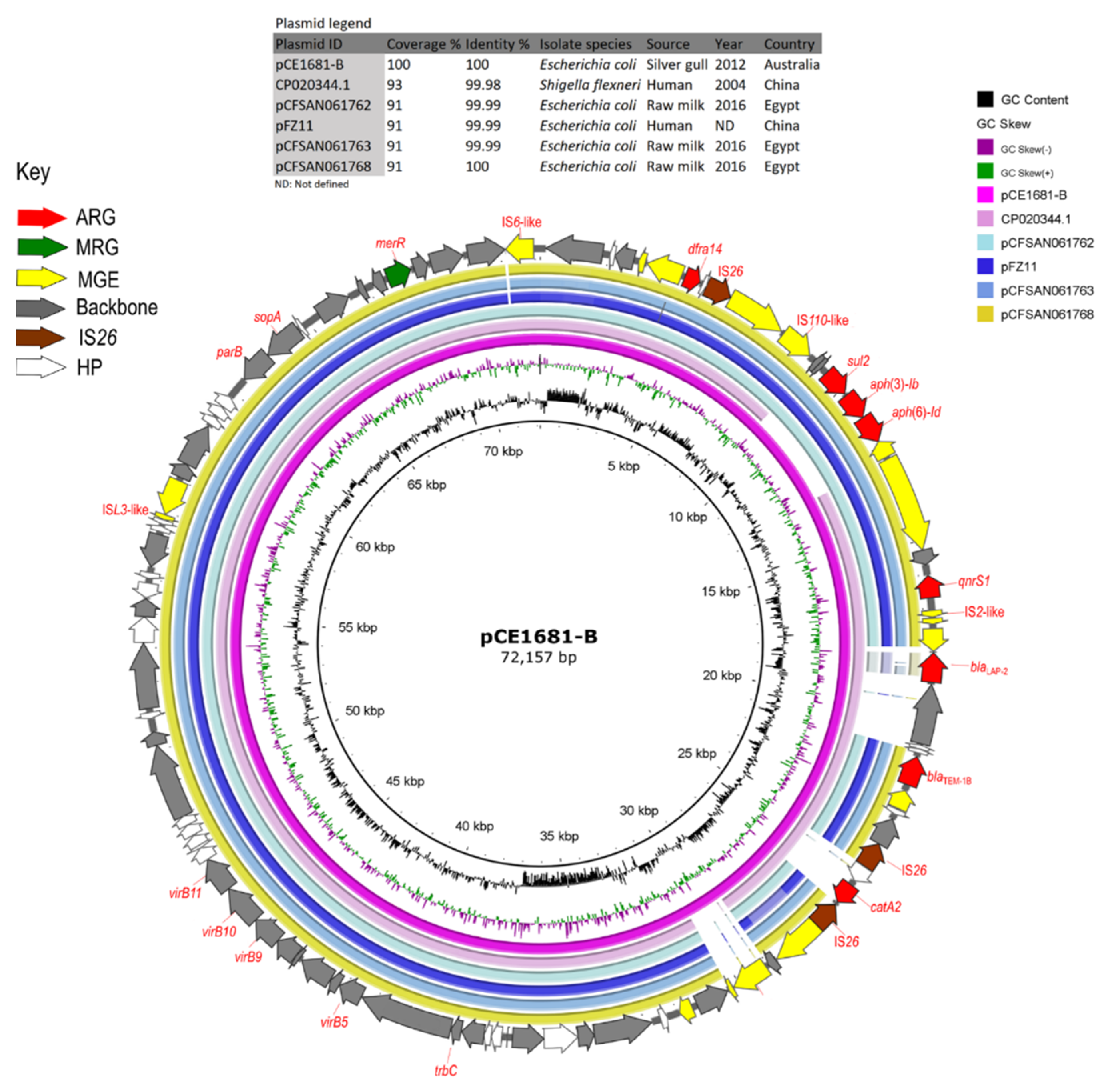
3.6. Analysis of HI-ST1, HI2-ST3, FIA, FIB(K), X5, R and Col156 Plasmids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vittecoq, M.; Godreuil, S.; Prugnolle, F.; Durand, P.; Brazier, L.; Renaud, N.; Arnal, A.; Aberkane, S.; Jean-Pierre, H.; Gauthier-Clerc, M.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance in wildlife. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eradhouani, H.; Esilva, N.; Epoeta, P.; Etorres, C.; Ecorreia, S.; Eigrejas, G. Potential impact of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife, environment and human health. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolejska, M.; Literak, I. Wildlife Is Overlooked in the Epidemiology of Medically Important Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01167-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelino, V.R.; Wille, M.; Hurt, A.C.; González-Acuña, D.; Klaassen, M.; Schlub, T.E.; Eden, J.-S.; Shi, M.; Iredell, J.R.; Sorrell, T.C.; et al. Meta-transcriptomics reveals a diverse antibiotic resistance gene pool in avian microbiomes. BMC Biol. 2019, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, B.M.; Bennett, M.; Waller, K.; Dodd, C.; Murray, A.; Gomes, R.L.; Humphreys, B.; Hobman, J.L.; Jones, M.A.; Whitlock, S.E.; et al. Anthropogenic environmental drivers of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolejska, M.; Papagiannitsis, C.C. Plasmid-mediated resistance is going wild. Plasmid 2018, 99, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwich, L.; Vidal, A.; Seminati, C.; Albamonte, A.; Casado, A.; López, F.; Molina-López, R.A.; Migura-Garcia, L. High prevalence and diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamase and emergence of OXA-48 producing Enterobacterales in wildlife in Catalonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oteo, J.; Mencía, A.; Bautista, V.; Pastor, N.; Lara, N.; González-González, F.; García-Peña, F.J.; Campos, J. Colonization with Enterobacteriaceae-Producing ESBLs, AmpCs, and OXA-48 in Wild Avian Species, Spain 2015–2016. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, A.; Loucif, L.; Ayachi, A.; Guehaz, K.; Bendjama, E.; Rolain, J.-M. Migratory White Stork (Ciconia ciconia): A Potential Vector of the OXA-48-Producing Escherichia coli ST38 Clone in Algeria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabai, H.; Valcek, A.; Jamborova, I.; Vazhov, S.V.; Karyakin, I.V.; Raab, R.; Literak, I.; Dolejska, M. Plasmid-Mediated mcr-1 Colistin Resistance in Escherichia coli from a Black Kite in Russia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01266-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellera, F.P.; Fernandes, M.R.; Sartori, L.; Carvalho, M.P.N.; Esposito, F.; Nascimento, C.L.; Dutra, G.H.P.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Pérez-Chaparro, P.J.; McCulloch, J.A.; et al. Escherichia colicarrying IncX4 plasmid-mediatedmcr-1andblaCTX-Mgenes in infected migratory Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 72, 1255–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakopoulos, A.; Mevius, D.J.; Olsen, B.; Bonnedahl, J. The colistin resistancemcr-1gene is going wild: Table 1. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2335–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahlstrom, C.A.; Ramey, A.M.; Woksepp, H.; Bonnedahl, J. Early emergence of mcr- 1-positive Enterobacteriaceae in gulls from Spain and Portugal. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, E.J.; Wong, V.K.; Dougan, G. Emergence of dominant multidrug-resistant bacterial clades: Lessons from history and whole-genome sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018, 115, 12872–12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, C.; Hassan, K.A.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Paulsen, I.T.; Walker, M.J.; Djordjevic, S.P. Sequences of Two Related Multiple Antibiotic Resistance Virulence Plasmids Sharing a Unique IS26-Related Molecular Signature Isolated from Different Escherichia coli Pathotypes from Different Hosts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangat, C.S.; Bekal, S.; Irwin, R.J.; Mulvey, M.R. A Novel Hybrid Plasmid Carrying Multiple Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Genes in Salmonella enterica Serovar Dublin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02601-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinnon, J.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Djordjevic, S.P. Genomic analysis of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli ST58 causing urosepsis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrsch, E.R.; Hawkey, J.; Judd, L.M.; Haites, R.; Holt, K.E.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Billman-Jacobe, H. Z/I1 Hybrid Virulence Plasmids Carrying Antimicrobial Resistance genes in S. Typhimurium from Australian Food Animal Production. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Thorsness, J.L.; Anderson, C.P.; Lynne, A.M.; Foley, S.L.; Han, J.; Fricke, W.F.; McDermott, P.F.; White, D.G.; Khatri, M.; et al. Horizontal Gene Transfer of a ColV Plasmid Has Resulted in a Dominant Avian Clonal Type of Salmonella enterica Serovar Kentucky. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, C.; Beatson, S.A.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Walker, M.J. Multiple antibiotic resistance gene recruitment onto the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli virulence plasmid. FASEB J. 2009, 24, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.-Y.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Chen, S. IS26-mediated formation of a virulence and resistance plasmid in Salmonella Enteritidis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2750–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.C.; Santos, F.F.; Silva, R.M.; Gomes, T.A.T. Diversity of Hybrid- and Hetero-Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Their Potential Implication in More Severe Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croucher, N.J.; Klugman, K.P. The Emergence of Bacterial “Hopeful Monsters”. mBio 2014, 5, e01355-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decraene, V.; Phan, H.T.T.; George, R.; Wyllie, D.H.; Akinremi, O.; Aiken, Z.; Cleary, P.; Dodgson, A.; Pankhurst, L.; Crook, D.W.; et al. A Large, Refractory Nosocomial Outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli Demonstrates Carbapenemase Gene Outbreaks Involving Sink Sites Require Novel Approaches to Infection Control. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01689-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniak, A.; Izdebski, R.; Fiett, J.; Herda, M.; Derde, L.P.G.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Adler, A.; Carmeli, Y.; Goossens, H.; Hryniewicz, W.; et al. KPC-Like Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Colonizing Patients in Europe and Israel. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazen, T.H.; Zhao, L.; Boutin, M.A.; Stancil, A.; Robinson, G.; Harris, A.D.; Rasko, D.A.; Johnson, J.K. Comparative Genomics of an IncA/C Multidrug Resistance Plasmid from Escherichia coli and Klebsiella Isolates from Intensive Care Unit Patients and the Utility of Whole-Genome Sequencing in Health Care Settings. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4814–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manges, A.R.; Geum, H.M.; Guo, A.; Edens, T.J.; Fibke, C.D.; Pitout, J.D.D. Global Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) Lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00135-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roer, L.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Hansen, F.; Schønning, K.; Wang, M.; Røder, B.L.; Hansen, D.S.; Justesen, U.S.; Andersen, L.P.; Fulgsang-Damgaard, D.; et al. Escherichia coliSequence Type 410 Is Causing New International High-Risk Clones. mSphere 2018, 3, e00337-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingali, T.; Chapman, T.A.; Webster, J.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Djordjevic, S.P. Genomic Characterisation of a Multiple Drug Resistant IncHI2 ST4 Plasmid in Escherichia coli ST744 in Australia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Baraniak, A.; Izdebski, R.; Fiett, J.; Salvia, A.; Samso, J.; Lawrence, C.; Solomon, J.; Paul, M.; Lerman, Y.; et al. A multinational study of colonization with extended spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in healthcare personnel and family members of carrier patients hospitalized in rehabilitation centres. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O516–O523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bianco, F.; Morotti, M.; Pedna, M.; Farabegoli, P.; Sambri, V. Microbiological surveillance of plasmid mediated colistin resistance in human Enterobacteriaceae isolates in Romagna (Northern Italy): August 2016–July 2017. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 69, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheruvanky, A.; Stoesser, N.; Sheppard, A.E.; Crook, D.W.; Hoffman, P.S.; Weddle, E.; Carroll, J.; Sifri, C.D.; Chai, W.; Barry, K.; et al. Enhanced Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase Expression from a Novel Tn4401 Deletion. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00025-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedra-Carrasco, N.; Fàbrega, A.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Cornejo-Sánchez, T.; Brown-Jaque, M.; Mir-Cros, A.; Muniesa, M.; González-López, J.J. Carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae recovered from a Spanish river ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolejska, M.; Masarikova, M.; Dobiasova, H.; Jamborova, I.; Karpiskova, R.; Havlicek, M.; Carlile, N.; Priddel, D.; Cizek, A.; Literak, I. High prevalence ofSalmonellaand IMP-4-producing Enterobacteriaceae in the silver gull on Five Islands, Australia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nesporova, K.; Wyrsch, E.R.; Valcek, A.; Bitar, I.; Chaw, K.; Harris, P.; Hrabak, J.; Literak, I.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Dolejska, M. Escherichia coli Sequence Type 457 Is an Emerging Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactam-Resistant Lineage with Reservoirs in Wildlife and Food-Producing Animals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e01118-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, M.L.; Sanderson-Smith, M.; Newton, P.; Carlile, N.; Phalen, D.N.; Maute, K.; Monahan, L.G.; Hoye, B.J.; Djordjevic, S.P. Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis of an Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Agona Isolate from an Australian Silver Gull (Chroicocephalus novaehollandiae) Reveals the Acquisition of Multidrug Resistance Plasmids. mSphere 2020, 5, e00743-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolejska, M.; Cizek, A.; Literak, I. High prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant genes and integrons in Escherichia coli isolates from Black-headed Gulls in the Czech Republic. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, D.; Drum, D.J.; Stallknecht, D.E.; White, D.G.; Lee, M.D.; Ayers, S.; Sobsey, M.; Maurer, J.J. Free-living Canada Geese and Antimicrobial Resistance. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, T. Shovill: Faster SPAdes Assembly of Illumina Reads (v0.9.0). Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/shovill (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Chin, C.-S.; Alexander, D.H.; Marks, P.; Klammer, A.A.; Drake, J.; Heiner, C.; Clum, A.; Copeland, A.; Huddleston, J.; Eichler, E.E.; et al. Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; Achtman, M.; the Agama Study Group; Brown, D.; Chattaway, M.; Dallman, T.; Delahay, R.; et al. The EnteroBase user’s guide, with case studies on Salmonella transmissions, Yersinia pestis phylogeny, and Escherichia core genomic diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.-L.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis—10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.J.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, srep08365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siguier, P. ISfinder: The reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34 (Suppl. 1), D32–D36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.; Grant, J.R.; Marcu, A.; Sajed, T.; Pon, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHASTER: A better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W16–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. EUCAST Disk Diffusion Method. Available online: http://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Disk_test_documents/2019_manuals/Manual_v_7.0_EUCAST_Disk_Test_2019.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2019).
- EUCAST. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Available online: http://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_9.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. In CLSI Supplement M100, 27th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017; Available online: http://file.qums.ac.ir/repository/mmrc/clsi%202017.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Jouy, E.; Haenni, M.; Le Devendec, L.; Le Roux, A.; Châtre, P.; Madec, J.-Y.; Kempf, I. Improvement in routine detection of colistin resistance in E. coli isolated in veterinary diagnostic laboratories. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 132, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotova, V.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Skalova, A.; Chudejova, K.; Hrabak, J. Comparison of imipenem and meropenem antibiotics for the MALDI-TOF MS detection of carbapenemase activity. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 137, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the Problem of Comparing Whole Bacterial Genomes across Different Sequencing Platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W256–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. progressiveMauve: Multiple Genome Alignment with Gene Gain, Loss and Rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, M.L.; Reid, C.J.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Bushell, R.N.; Esbert, N.; Tivendale, K.A.; Noormohammadi, A.H.; Islam, S.; Marenda, M.S.; Browning, G.F.; et al. Whole genome sequence analysis of Australian avian pathogenic Escherichia coli that carry the class 1 integrase gene. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.-F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Bertini, A.; Villa, L.; Falbo, V.; Hopkins, K.L.; Threlfall, E.J. Identification of plasmids by PCR-based replicon typing. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 63, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcek, A.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Hansen, F.; Dolejska, M.; Hasman, H. Complete Genome Sequence of Escherichia coli MT102, a Plasmid-Free Recipient Resistant to Rifampin, Azide, and Streptomycin, Used in Conjugation Experiments. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00383-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, M.J.; Jin, Y.F.; Ricci, V.; Piddock, L.J. Contributions of individual mechanisms to fluoroquinolone resistance in 36 Escherichia coli strains isolated from humans and animals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pong, C.H.; Harmer, C.J.; Ataide, S.F.; Hall, R.M. An IS26variant with enhanced activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.J.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Djordjevic, S.P. Tn6026 and Tn6029 are found in complex resistance regions mobilised by diverse plasmids and chromosomal islands in multiple antibiotic resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Plasmid 2015, 80, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrsch, E.R.; Reid, C.J.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Liu, M.Y.; Chapman, T.A.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Djordjevic, S.P. Complete Sequences of Multiple-Drug Resistant IncHI2 ST3 Plasmids in Escherichia coli of Porcine Origin in Australia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascales, E.; Buchanan, S.K.; Duché, D.; Kleanthous, C.; Lloubès, R.; Postle, K.; Riley, M.; Slatin, S.; Cavard, D. Colicin Biology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 158–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.K.; Phan, H.T.T.; Lipworth, S.I.; Cheong, E.; Gottlieb, T.; George, S.; Peto, T.E.A.; Mathers, A.J.; Walker, A.S.; Crook, D.W.; et al. Genomic dynamics of species and mobile genetic elements in a prolonged blaIMP-4-associated carbapenemase outbreak in an Australian hospital. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.W.; Harris, P.N.A.; Forde, B.M.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Catchpoole, E.; Stanton-Cook, M.; Phan, M.-D.; Sidjabat, H.E.; Bergh, H.; Heney, C.; et al. Integrating multiple genomic technologies to investigate an outbreak of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacter hormaechei. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, S.; O’Dea, M.; Trott, D.J.; Abraham, R.J.; Hughes, D.; Pang, S.; McKew, G.; Cheong, E.Y.L.; Merlino, J.; Saputra, S.; et al. Isolation and plasmid characterization of carbapenemase (IMP-4) producing Salmonella enterica Typhimurium from cats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolejska, M.; Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Medvecky, M.; Davidova-Gerzova, L.; Valcek, A. Characterization of the Complete Nucleotide Sequences of IMP-4-Encoding Plasmids, Belonging to Diverse Inc Families, Recovered from Enterobacteriaceae Isolates of Wildlife Origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02434-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Z.-B.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Yang, X.-W.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.-H. The role of wildlife (wild birds) in the global transmission of antimicrobial resistance genes. Zool. Res. 2017, 38, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Rao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K. Evidence for Environmental Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance Mediated by Wild Birds. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukerji, S.; Stegger, M.; Truswell, A.V.; Laird, T.; Jordan, D.; Abraham, R.J.; Harb, A.; Barton, M.; O’Dea, M.; Abraham, S. Resistance to critically important antimicrobials in Australian silver gulls (Chroicocephalus novaehollandiae) and evidence of anthropogenic origins. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2566–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, C.J.; Moran, R.A.; Hall, R.M. Movement of IS26-Associated Antibiotic Resistance Genes Occurs via a Translocatable Unit That Includes a Single IS26 and Preferentially Inserts Adjacent to Another IS26. mBio 2014, 5, e01801-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Gao, X.; Lv, L.; Cai, Z.; Liu, J.H. IS26 mediate the acquisition of tigecycline resistance gene cluster tmexCD1-toprJ1 by IncHI1B-FIB plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsie lla quasipneumoniae from food market sewage. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e02178-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, A.K.; Liu, X.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Hall, R.M. Transposons Related to Tn1696in IncHI2 Plasmids in Multiply Antibiotic ResistantSalmonella entericaSerovar Typhimurium from Australian Animals. Microb. Drug Resist. 2010, 16, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastak, P.; Cummins, M.L.; Gottlieb, T.; Cheong, E.; Merlino, J.; Myers, G.S.A.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Chowdhury, P.R. Genomic profiling of Escherichia coli isolates from bacteraemia patients: A 3-year cohort study of isolates collected at a Sydney teaching hospital. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, e000371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.J.; Wyrsch, E.R.; Chowdhury, P.R.; Zingali, T.; Liu, M.; Darling, A.E.; Chapman, T.A.; Djordjevic, S.P. Porcine commensal Escherichia coli: A reservoir for Class 1 Integrons Associated with IS26. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, F.E.; Kuzevski, A.; Bettelheim, K.A.; Hornitzky, M.A.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Walker, M.J. Distribution of Class 1 Integrons with IS26-Mediated Deletions in Their 3′-Conserved Segments in Escherichia coli of Human and Animal Origin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Reid, C.J.; Kudinha, T.; Jarocki, V.M.; Djordjevic, S.P. Genomic analysis of trimethoprim-resistant extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli and recurrent urinary tract infections. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, mgen000475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, V.; García, P.; Rodríguez, I.; Rodicio, R.; Rodicio, M.D.R.R. The role of IS 26 in evolution of a derivative of the virulence plasmid of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis which confers multiple drug resistance. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 45, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porse, A.; Schønning, K.; Munck, C.; Sommer, M.O. Survival and Evolution of a Large Multidrug Resistance Plasmid in New Clinical Bacterial Hosts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2860–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ye, L.; Li, Y.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Identification of a Chromosomal Integrated DNA Fragment Containing the rmpA2 and iucABCDiutA Virulence Genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. mSphere 2020, 5, e01179-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A. Plasmids in Gram negatives: Molecular typing of resistance plasmids. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, A.; Valdés-Varela, L.; Gueimonde, M.; Rudi, K. Transmission and persistence of IncF conjugative plasmids in the gut microbiota of full-term infants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girón, J.A.; Torres, A.G.; Freer, E.; Kaper, J.B. The flagella of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli mediate adherence to epithelial cells. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, S.N.; Badea, L.; Bennett-Wood, V.; Robins-Browne, R.; Hartland, E.L. Contribution of FliC to Epithelial Cell Invasion by Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O113:H21. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6999–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Xu, T.; Fossheim, L.E.; Zhang, X.-H. FliC, a Flagellin Protein, Is Essential for the Growth and Virulence of Fish Pathogen Edwardsiella tarda. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eporcheron, G.; Egarenaux, A.; Eproulx, J.; Esabri, M.; Dozois, C.M. Iron, copper, zinc, and manganese transport and regulation in pathogenic Enterobacteria: Correlations between strains, site of infection and the relative importance of the different metal transport systems for virulence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.; Asiani, K.; Arya, S.; Rensing, C.; Stekel, D.J.; Larsson, D.J.; Hobman, J.L. Metal Resistance and Its Association With Antibiotic Resistance. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2017, 70, 261–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.C.; Carlile, N. Food and Feeding Ecology of Breeding Silver Gulls (Larus novaehollandiae) in Urban Australia. Colon. Waterbirds 1993, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.W.; Johnson, L.J.; Clarke, S.R.; Arnold, D.L. Bacterial pathogen evolution: Breaking news. Trends Genet. 2011, 27, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sequence ID | Sequence Type | Enterobase Barcode No. | GenBank Accession No. | Coverage | Total Sequences | Poor Quality Sequences | Sequence Length (bp) | GC% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1556m1 | SR | ESC_QA8784AA | JAEUYL000000000 | 95× | 1,226,163 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| CE1586 | SR | ESC_QA8782AA | JAEUYK000000000 | 72× | 1,588,914 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1548R1 | SR | ESC_QA8786AA | JAEUXR000000000 | 79× | 1,386,478 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1552m1 | SR | ESC_QA8785AA | JAEUXS000000000 | 83× | 1,425,868 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| CE1585 | SR | ESC_RA0975AA | JAEUXT000000000 | 143× | 2,366,204 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1587R | SR | ESC_RA0998AA | JAEUXU000000000 | 84× | 1,440,780 | 0 | 151 | 50 |
| CE1724 | SR | ESC_RA0997AA | JAEUXV000000000 | 76× | 1,286,453 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| CE1681 | SR | ESC_RA0995AA | JAEUXW000000000 | 73× | 1,367,751 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1605m2 | SR | ESC_RA0996AA | JAEUXX000000000 | 81× | 1,354,070 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1660m1 | SR | ESC_QA8910A | JAEUXY000000000 | 77× | 1,298,542 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| CE1700 | SR | ESC_QA8911AA | JAEUXZ000000000 | 74× | 1,254,843 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1537H | SR | ESC_QA8912AA | JAEUYA000000000 | 127× | 2,206,779 | 0 | 151 | 52 |
| 1720H | SR | ESC_QA8787AA | JAEUYJ000000000 | 16× | 221,227 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1726H | SR | ESC_QA8788AA | JAEUYI000000000 | 58× | 974,309 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1560H | SR | ESC_QA8790AA | JAEUYH000000000 | 61× | 1,042,416 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1561H | SR | ESC_QA8789AA | JAEUYG000000000 | 43× | 729,472 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1539H | SR | ESC_QA8791AA | JAEUYF000000000 | 106× | 1,912,588 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| 1585H | SR | ESC_QA8795AA | JAEUYE000000000 | 499× | 9,553,397 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| CE1539 | SR | ESC_QA8792AA | JAEUYD000000000 | 161× | 2,911,482 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| CE1580 | SR | ESC_QA8794AA | JAEUYC000000000 | 358× | 7,231,680 | 0 | 151 | 52 |
| CE1538B | SR | ESC_QA8793AA | JAEUYB000000000 | 123× | 2,115,704 | 0 | 151 | 51 |
| CE1537 | GLR | ND | JABBCF000000000 | 203× | 462,216 | 0 | 51-197802 | 50 |
| CE1537 | PLR | ND | ND | 317× | 98,607 | 0 | 50-103991 | 46 |
| Plasmid ID | Comparison Plasmid | GenBank Accession no. | Coverage (%) | Identity (%) | Replicon | Species | Source | Country | Region | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pCE1537-A | pAUSMDU8141-1 | CP022696.1 | 100 | 99.77 | IncHI2-ST1 | Citrobacter farmeri | Human | Australia | Victoria | 2015 |
| pC15_001 | CP042489.1 | 99 | 99.31 | IncHI2-ST1 | Enterobacter hormaechei | Human | Australia | Sydney | 2009 | |
| pIMP4-SEM1 | KX810825.1 | 96 | 99.73 | IncHI2-ST1 | Salmonella enterica | Cat | Australia | ND | ND | |
| pMS7884A | CP022533.1 | 91 | 99.71 | IncHI2-ST1 | Enterobacter hormaechei | Human | Australia | Brisbane | 2015 | |
| pCE1681-B | CP020344.1 | CP020344.1 | 93 | 99.98 | IncFIB(K) | Shigella flexneri | Human | China | Hangzhou | 2004 |
| pCFSAN061762 | CP042902.1 | 91 | 99.99 | IncFIB(K) | Escherichia coli | Raw milk | Egypt | ND | 2016 | |
| pFZ11 | KY051550.1 | 91 | 99.99 | IncFIB(K) | Escherichia coli | Human | China | Fujian | ND | |
| pCFSAN061763 | CP042900.1 | 91 | 99.99 | IncFIB(K) | Escherichia coli | Raw milk | Egypt | ND | 2016 | |
| pCFSAN061768 | CP042974.1 | 91 | 100 | IncFIB(K) | Escherichia coli | Raw milk | Egypt | ND | 2016 | |
| pCE1681-C | pCE1537-C | MT162141.1 | 100 | 99.83 | Col156 | Escherichia coli | Silver gull | Australia | Sydney | 2012 |
| ColE7-K317 | KJ470776.1 | 100 | 99.54 | Col156 | Escherichia coli | ND | Pakistan | ND | ND | |
| pECAZ146_5 | CP018986.1 | 100 | 99.46 | Col156 | Escherichia coli | Human | Italy | Pisa | 2012 | |
| pCE1681-E | pCE1537-C | MT162141.1 | 100 | 99.83 | Col156 | Escherichia coli | Silver gull | Australia | Sydney | 2012 |
| pEc1677 | MG516910.1 | 86 | 100 | IncX5 | Escherichia coli | Silver gull | Australia | Sydney | 2012 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarabai, H.; Wyrsch, E.R.; Bitar, I.; Dolejska, M.; Djordjevic, S.P. Epidemic HI2 Plasmids Mobilising the Carbapenemase Gene blaIMP-4 in Australian Clinical Samples Identified in Multiple Sublineages of Escherichia coli ST216 Colonising Silver Gulls. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030567
Tarabai H, Wyrsch ER, Bitar I, Dolejska M, Djordjevic SP. Epidemic HI2 Plasmids Mobilising the Carbapenemase Gene blaIMP-4 in Australian Clinical Samples Identified in Multiple Sublineages of Escherichia coli ST216 Colonising Silver Gulls. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarabai, Hassan, Ethan R. Wyrsch, Ibrahim Bitar, Monika Dolejska, and Steven P. Djordjevic. 2021. "Epidemic HI2 Plasmids Mobilising the Carbapenemase Gene blaIMP-4 in Australian Clinical Samples Identified in Multiple Sublineages of Escherichia coli ST216 Colonising Silver Gulls" Microorganisms 9, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030567
APA StyleTarabai, H., Wyrsch, E. R., Bitar, I., Dolejska, M., & Djordjevic, S. P. (2021). Epidemic HI2 Plasmids Mobilising the Carbapenemase Gene blaIMP-4 in Australian Clinical Samples Identified in Multiple Sublineages of Escherichia coli ST216 Colonising Silver Gulls. Microorganisms, 9(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030567







