Evaluating Different Storage Media for Identification of Taenia saginata Proglottids Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Study Design and Experimental Set-Up
2.4. Molecular Diagnosis Using PCR and Partial Sequencing
2.5. Differential Sample Storage Conditions
2.6. MALDI-TOF Analysis
2.6.1. Protein Extraction
2.6.2. MALDI-TOF Target Plate Preparation and Measurements
2.6.3. MALDI-TOF MS Parameters
2.6.4. Spectral Analysis, MSP Creation, and Clustering Analysis
2.6.5. MALDI-TOF Identification Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Identification of Taenia Proglottids
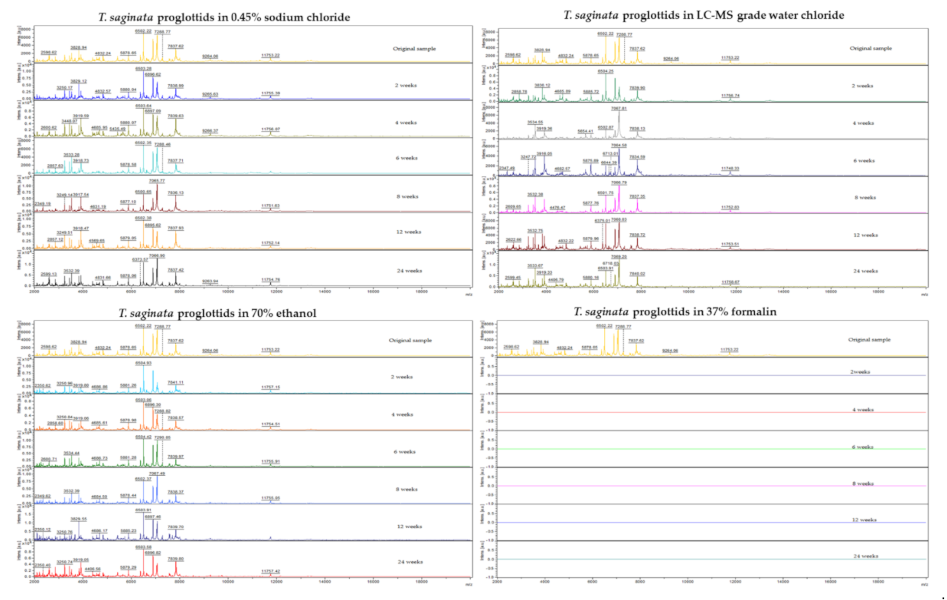
3.2. Comparative MALDI-TOF MS Analysis after Different Storage Periods
3.2.1. Protein Spectra and LSV Analysis
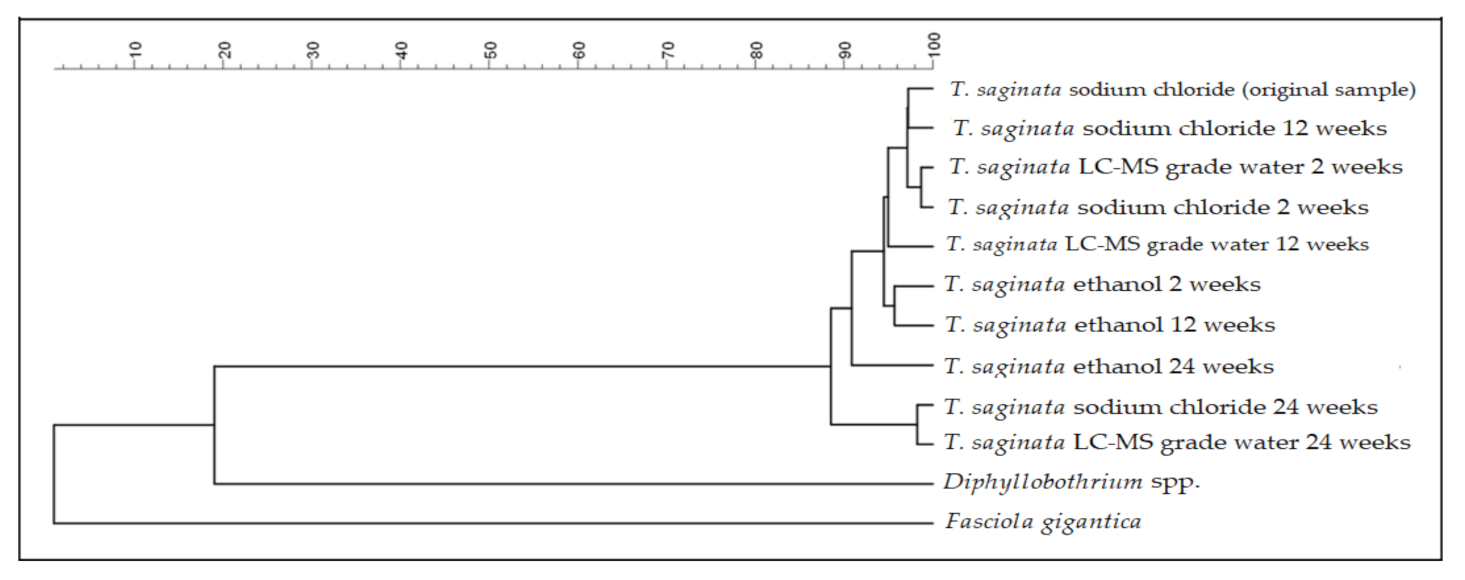
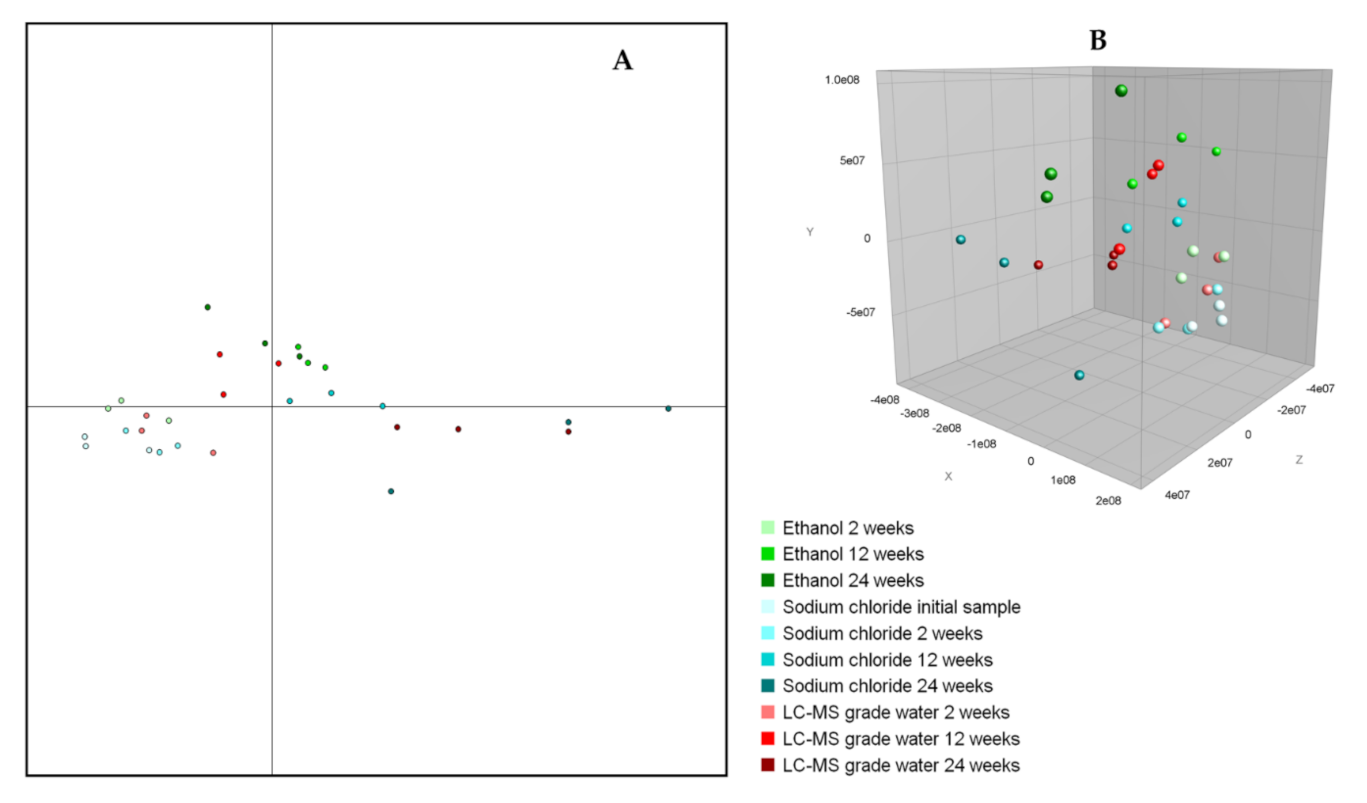
3.2.2. Cluster Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laranjo-González, M.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Trevisan, C.; Allepuz, A.; Sotiraki, S.; Abraham, A.; Afonso, M.B.; Blocher, J.; Cardoso, L.; Correia da Costa, J.M.; et al. Epidemiology of taeniosis/cysticercosis in Europe, a systematic review: Western Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, H.H.; Gonzalez, A.E.; Gilman, R.H. Taenia solium cysticercosis and its impact in neurological disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00085-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krecek, R.C. WHO/FAO/OIE Guidelines for the Surveillance, Prevention and Control of Taeniosis/Cysticercosis; Murrell, K.D., Dorny, P., Flisser, A., Geerts, S., Kyvsgaard, N.C., McManus, D.P., Nash, T.E., Pawlowski, Z.S., Eds.; Book Review; WHO/FAO/OIE: Paris, France, 2006; Volume 77, pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okello, A.L.; Thomas, L.F. Human taeniasis: Current insights into prevention and management strategies in endemic countries. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2017, 10, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeonidou, I.; Arsenopoulos, K.; Tzilves, D.; Soba, B.; Gabriël, S.; Papadopoulos, E. Human taeniasis/cysticercosis: A potentially emerging parasitic disease in Europe. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzinger, J.; Becker, S.L.; Knopp, S.; Blum, J.; Neumayr, A.L.; Keiser, J.; Hatz, C.F. Neglected tropical diseases: Diagnosis, clinical management, treatment and control. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2012, 142, w13727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenberger, R.M.; Thomas, L.F.; Gabriël, S.; Bobić, B.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Robertson, L.J.; Saratsis, A.; Torgerson, P.R.; Braae, U.C.; Dermauw, V.; et al. Epidemiology of Taenia saginata taeniosis/cysticercosis: A systematic review of the distribution in East, Southeast and South Asia. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratsis, A.; Sotiraki, S.; Braae, U.C.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Dermauw, V.; Eichenberger, R.M.; Thomas, L.F.; Bobić, B.; Dorny, P.; Gabriël, S.; et al. Epidemiology of Taenia saginata taeniosis/cysticercosis: A systematic review of the distribution in the Middle East and North Africa. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braae, U.C.; Thomas, L.F.; Robertson, L.J.; Dermauw, V.; Dorny, P.; Willingham, A.L.; Saratsis, A.; Devleesschauwer, B. Epidemiology of Taenia saginata taeniosis/cysticercosis: A systematic review of the distribution in the Americas. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermauw, V.; Dorny, P.; Braae, U.C.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Robertson, L.J.; Saratsis, A.; Thomas, L.F. Epidemiology of Taenia saginata taeniosis/cysticercosis: A systematic review of the distribution in Southern and Eastern Africa. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, P.; Ito, A. Intestinal cestodes. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 30, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2017 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 359 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1859–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feucherolles, M.; Poppert, S.; Utzinger, J.; Becker, S.L. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry as a diagnostic tool in human and veterinary helminthology: A systematic review. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, N.; Nakamura, S.; Inoue, T.; Oku, Y.; Katakura, K.; Matsumoto, J.; Mathis, A.; Chembesofu, M.; Phiri, I.G.K. Coprological survey of alimentary tract parasites in dogs from Zambia and evaluation of a coproantigen assay for canine echinococcosis. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2011, 105, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, L.M.; Montero, E.; Harrison, L.J.S.; Parkhouse, R.M.E.; Garate, T. Differential diagnosis of Taenia saginata and Taenia solium infection by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxatto, A.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G. Applications of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical diagnostic microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 380–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, I.; Margardt, L.; Ngbede, E.O.; Adah, M.I.; Yusuf, S.T.; Keiser, J.; Rehner, J.; Utzinger, J.; Poppert, S.; Becker, S.L. Identification of adult Fasciola spp. using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadjian, G.; Bilska-Zając, E.; Bahn, P.; Py, J.-S.; Johne, A.; Gassilloud, B.; Różycki, M.; Cencek, T.; Mayer-Scholl, A.; Vallée, I. Species identification of Trichinella originated from various host and different geographical location by MALDI-TOF. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 213, 107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, V.; Pane, S.; Foglietta, G.; Mortera, S.L.; Vernocchi, P.; Muda, A.O.; Putignani, L. Mass spectrometry based-proteomic analysis of Anisakis spp.: A preliminary study towards a new diagnostic tool. Genes 2020, 11, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng-Nguyen, D.; Stevenson, M.A.; Dorny, P.; Gabriël, S.; Vo, T.V.; Nguyen, V.A.T.; Phan, T.V.; Hii, S.F.; Traub, R.J. Comparison of a new multiplex real-time PCR with the Kato Katz thick smear and copro-antigen ELISA for the detection and differentiation of Taenia spp. in human stools. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, M. Proteomics for routine identification of microorganisms. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3143–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, S.; Kostrzewa, M. MALDI-TOF MS in microbiology laboratory: Current trends. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2017, 23, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoy, S.; Diarra, A.Z.; Laudisoit, A.; Gembu, G.-C.; Verheyen, E.; Mubenga, O.; Mbalitini, S.G.; Baelo, P.; Laroche, M.; Parola, P. Using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry to identify ticks collected on domestic and wild animals from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2021, 84, 637–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebbak, A.; El Hamzaoui, B.; Berenger, J.M.; Bitam, I.; Raoult, D.; Almeras, L.; Parola, P. Comparative analysis of storage conditions and homogenization methods for tick and flea species for identification by MALDI-TOF MS. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2017, 31, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebbak, A.; Almeras, L. Identification of Aedes mosquitoes by MALDI-TOF MS biotyping using protein signatures from larval and pupal exuviae. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouarti, B.; Laroche, M.; Righi, S.; Meguini, M.N.; Benakhla, A.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Development of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the identification of lice isolated from farm animals. Parasite 2020, 27, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredtmann, C.M.; Krücken, J.; Murugaiyan, J.; Balard, A.; Hofer, H.; Kuzmina, T.A.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G. Concurrent proteomic fingerprinting and molecular analysis of cyathostomins. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1800290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagorny, S.A.; Aleshukina, A.V.; Aleshukina, I.S.; Ermakova, L.A.; Pshenichnaya, N.Y. The application of proteomic methods (MALDI-TOF MS) for studying protein profiles of some nematodes (Dirofilaria and Ascaris) for differentiating species. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 82, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Scholl, A.; Murugaiyan, J.; Neumann, J.; Bahn, P.; Reckinger, S.; Nöckler, K. Rapid identification of the foodborne pathogen Trichinella spp. by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0152062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Ye, W.; Zhou, L.; Collins, L.B.; Chen, X.; Gold, A.; Ball, L.M.; Swenberg, J.A. Structural characterization of formaldehyde-induced cross-links between amino acids and deoxynucleosides and their oligomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3388–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, J.; Haslam, C.; Hardy, N.; Leveridge, M.; Marshall, P. A systematic investigation of the best buffers for use in screening by MALDI-mass spectrometry. SLAS Discov. 2017, 22, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]

| (A) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Preservation Medium | Number of Samples | Number of Spectra | Bruker Taxonomy Database | ||
| Correct Identification | Average LSV | Most Frequently Suggested Result | |||
| 0.45% sodium chloride | 6 | 560 | 0% | 1.38 | Arthrobacter monumenti |
| 70% ethanol | 6 | 574 | 0% | 1.39 | Arthrobacter monumenti |
| LC–MS grade water | 6 | 570 | 0% | 1.38 | Arthrobacter monumenti |
| 37% formalin | 6 | 0 | 0% | 0 | None |
| (B) | |||||
| Sample Preservation Medium | Number of Spectra | Combination of Bruker Taxonomy and In-House Helminth Database | |||
| Number of Samples | Correct Identification | Average LSV | Most Frequently Suggested Result | ||
| 0.45% sodium chloride | 6 | 560 | 97.2% (560/576) | 2.54 | T. saginata proglottid |
| 70% ethanol | 6 | 574 | 99.7% (574/576) | 2.53 | T. saginata proglottid |
| LC–MS grade water | 6 | 570 | 99.0% (570/576) | 2.57 | T. saginata proglottid |
| 37% formalin | 6 | 0 | 0% | 0 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wendel, T.P.; Feucherolles, M.; Rehner, J.; Poppert, S.; Utzinger, J.; Becker, S.L.; Sy, I. Evaluating Different Storage Media for Identification of Taenia saginata Proglottids Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102006
Wendel TP, Feucherolles M, Rehner J, Poppert S, Utzinger J, Becker SL, Sy I. Evaluating Different Storage Media for Identification of Taenia saginata Proglottids Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(10):2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102006
Chicago/Turabian StyleWendel, Tabea P., Maureen Feucherolles, Jacqueline Rehner, Sven Poppert, Jürg Utzinger, Sören L. Becker, and Issa Sy. 2021. "Evaluating Different Storage Media for Identification of Taenia saginata Proglottids Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry" Microorganisms 9, no. 10: 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102006
APA StyleWendel, T. P., Feucherolles, M., Rehner, J., Poppert, S., Utzinger, J., Becker, S. L., & Sy, I. (2021). Evaluating Different Storage Media for Identification of Taenia saginata Proglottids Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Microorganisms, 9(10), 2006. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9102006








