Vibrio Colonization Is Highly Dynamic in Early Microplastic-Associated Biofilms as Well as on Field-Collected Microplastics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. In Situ Incubation Experiment
2.2. Field-Collected Plastic Particles

2.3. DNA Extraction, Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. Sequence Processing and Downstream Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
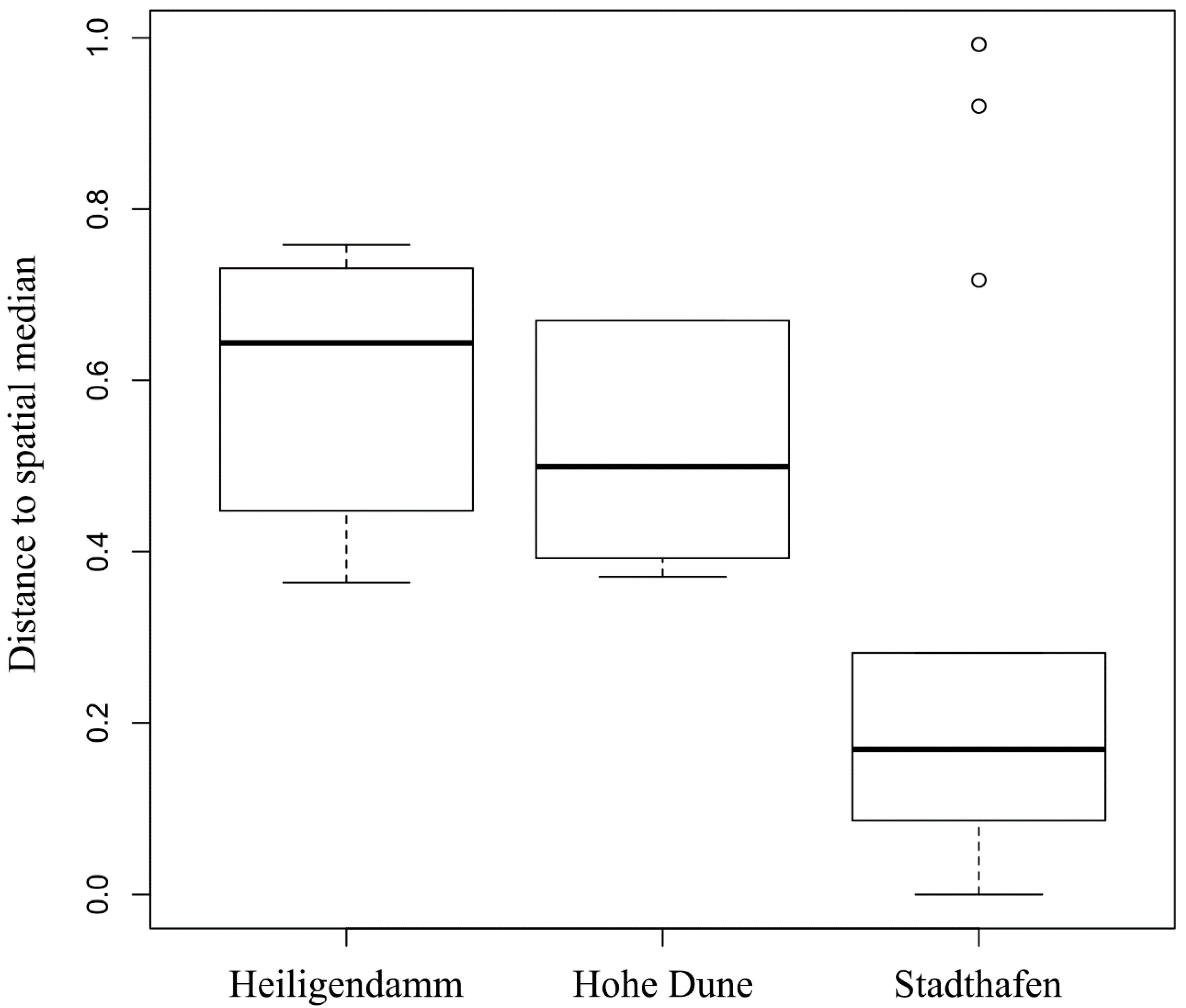
3.1. Vibrio Abundances and Composition Are Highly Variable during the First Hours of Colonization
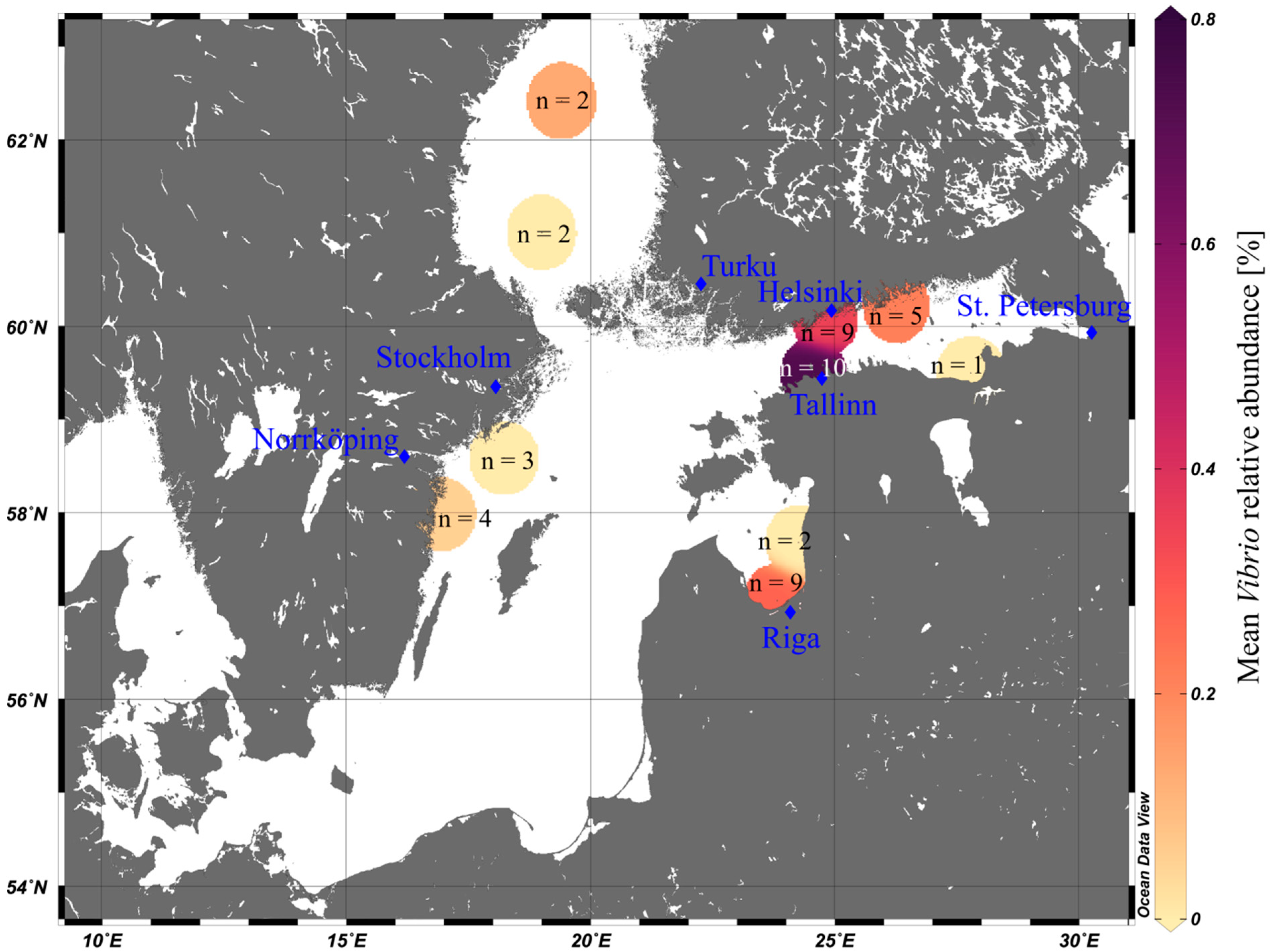
3.2. Vibrio Abundances on Field-Collected Particles Correspond with Proximity to Major Cities
3.3. Vibrio Bacteria Are not Well Connected in Biofilm Networks
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takemura, A.F.; Chien, D.M.; Polz, M.F. Associations and dynamics of Vibrionaceae in the environment, from the genus to the population level. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Wichels, A.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Gerdts, G. Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus in the German Bight over a seasonal cycle. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2011, 100, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Fuchs, B.M.; Meiners, M.; Wichels, A.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Gerdts, G. Seasonal dynamics and modeling of a Vibrio community in coastal waters of the North Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzulli, L.; Grande, C.; Reid, P.C.; Hélaouët, P.; Edwards, M.; Höfle, M.G.; Brettar, I.; Colwell, R.R.; Pruzzo, C. Climate influence on Vibrio and associated human diseases during the past half-century in the coastal North Atlantic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5062–E5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Kirmizi, S.; Wichels, A.; Garin-Fernandez, A.; Erler, R.; Löder, M.; Gerdts, G. Dangerous hitchhikers? Evidence for potentially pathogenic Vibrio spp. on microplastic particles. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 120, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.M.; Maldonado, G.C.; Castro, R.O.; Felizardo, J.P.; Cardoso, R.P.; Anjos, R.M.; Araújo, F.V. de Dispersal of potentially pathogenic bacteria by plastic debris in Guanabara Bay, RJ, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverty, A.L.; Primpke, S.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G.; Dobbs, F.C. Bacterial biofilms colonizing plastics in estuarine waters, with an emphasis on Vibrio spp. and their antibacterial resistance. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frère, L.; Maignien, L.; Chalopin, M.; Huvet, A.; Rinnert, E.; Morrison, H.; Kerninon, S.; Cassone, A.-L.; Lambert, C.; Reveillaud, J.; et al. Microplastic bacterial communities in the Bay of Brest: Influence of polymer type and size. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J.A.; Clemente, T.M.; Viviani, D.A.; Fong, A.A.; Thomas, K.A.; Kemp, P.; Karl, D.M.; White, A.E.; DeLong, E.F. Diversity and activity of communities inhabiting plastic debris in the North Pacific Gyre. mSystems 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curren, E.; Leong, S.C.Y. Profiles of bacterial assemblages from microplastics of tropical coastal environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Labrenz, M. Marine microbial assemblages on microplastics: Diversity, adaptation, and role in degradation. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulon, V.; Le Roux, F.; Lambert, C.; Huvet, A.; Soudant, P.; Paul-Pont, I. Colonization of polystyrene microparticles by Vibrio crassostreae: Light and electron microscopic investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10988–10996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesy, K.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Labrenz, M. Spatial environmental heterogeneity determines young biofilm assemblages on microplastics in Baltic Sea mesocosms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.; Ma, Y.; Niu, Z. Colonization characteristics of bacterial communities on plastic debris influenced by environmental factors and polymer types in the Haihe Estuary of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10763–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseler, M.; Weder, C.; Buschbeck, L.; Wesnigk, S.; Schernewski, G. Cost-effective monitoring of large micro- and meso-litter in tidal and flood accumulation zones at south-western Baltic Sea beaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schernewski, G.; Radtke, H.; Hauk, R.; Baresel, C.; Olshammar, M.; Osinski, R.; Oberbeckmann, S. Transport and behavior of microplastics emissions from urban sources in the Baltic Sea. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Trinanes, J.A.; Taylor, N.G.H.; Hartnell, R.; Siitonen, A.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Emerging Vibrio risk at high latitudes in response to ocean warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Labrenz, M. Environmental factors support the formation of specific bacterial assemblages on microplastics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasshoff, K.; Kremling, K.; Ehrhardt, M. (Eds.) Methods of Seawater Analysis, 3rd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- IOC. SCOR Protocols for the Joint Global Ocean Flux Study (JGOFS) core measurements. In IOC. Manuals and Guides; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1994; Volume 29, p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- ICES. Chemical measurements in the Baltic Sea: Guidelines on quality assurance. In ICES Techniques in Marine Environmental Sciences; Lysiak-Pastuszak, E., Krysell, M., Eds.; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004; p. 149. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, C.; Roscher, L.; Meyer, M.S.; Hildebrandt, L.; Prume, J.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments and surface waters of the southern North Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View; Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.G.; McKay, L.L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of Bacteria and Archaea using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D. MiSeq SOP; Mothur: Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Available online: https://www.mothur.org/wiki/MiSeq_SOP (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, P.; Parfrey, L.W.; Yarza, P.; Gerken, J.; Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Ludwig, W.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA and “All-species Living Tree Project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Reshaping data with the reshape package. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.M.; Proctor, D.M.; Holmes, S.P.; Relman, D.A.; Callahan, B.J. Simple statistical identification and removal of contaminant sequences in marker-gene and metagenomics data. Microbiome 2018, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, M. Mikemc/Speedyseq: Speedyseq v0.2.0; Zenodo: Geneve, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, W.; Strunk, O.; Westram, R.; Richter, L.; Meier, H.; Kumar, Y.; Buchner, A.; Lai, T.; Steppi, S.; Jobb, G.; et al. ARB: A software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinno, A. Conover. Test: Conover-Iman Test of Multiple Comparisons Using Rank Sums; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Distance-based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 2006, 62, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Ellingsen, K.E.; McArdle, B.H. Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körösi, M.J. Pour arriver a une comparabilité internationale des ouvrages de recensement. Bull. L’Inst. Intern. Stat. 1887, 200–215. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, P. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. CoNet app: Inference of biological association networks using Cytoscape. F1000 Res. 2016, 5, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawabe, T.; Ogura, Y.; Matsumura, Y.; Feng, G.; Amin, A.R.; Mino, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Sawabe, T.; Kumar, R.; Fukui, Y.; et al. Updating the Vibrio clades defined by multilocus sequence phylogeny: Proposal of eight new clades, and the description of Vibrio tritonius sp. nov. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Gil, B.; Thompson, C.C.; Matsumura, Y.; Sawabe, T.; Iida, T.; Christen, R.; Thompson, F.; Sawabe, T. The Family Vibrionaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Gammaproteobacteria; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, C.C.; Vicente, A.C.P.; Souza, R.C.; Vasconcelos, A.T.R.; Vesth, T.; Alves, N.; Ussery, D.W.; Iida, T.; Thompson, F.L. Genomic taxonomy of vibrios. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakib, S.N.; Reddi, G.; Almagro-Moreno, S. Environmental role of pathogenic traits in Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.K.; Oliver, J.D. Vibrio vulnificus: Disease and pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederdorfer, R.; Peter, H.; Battin, T.J. Attached biofilms and suspended aggregates are distinct microbial lifestyles emanating from differing hydraulics. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, B.; Xia, B.; Li, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Qu, K. Impact of mariculture-derived microplastics on bacterial biofilm formation and their potential threat to mariculture: A case in situ study on the Sungo Bay, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastaraud, A.; Cecchi, P.; Handschumacher, P.; Altmann, M.; Jambou, R. Urbanization and waterborne pathogen emergence in low-income countries: Where and how to conduct surveys? Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2020, 17, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacuvellerie, A.; Cyriaque, V.; Gobert, S.; Benali, S.; Wattiez, R. The plastisphere in marine ecosystem hosts potential specific microbial degraders including Alcanivorax borkumensis as a key player for the low-density polyethylene degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; He, L.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, C.; Qian, Z.-J.; Hong, P.; Sun, S.; Li, C. Investigating the composition and distribution of microplastics surface biofilms in coral areas. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidelberg, J.F.; Eisen, J.A.; Nelson, W.C.; Clayton, R.A.; Gwinn, M.L.; Dodson, R.J.; Haft, D.H.; Hickey, E.K.; Peterson, J.D.; Umayam, L.; et al. DNA sequence of both chromosomes of the cholera pathogen Vibrio cholerae. Nature 2000, 406, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Steele, J.A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Steinbrück, L.; Reeder, J.; Temperton, B.; Huse, S.; McHardy, A.C.; Knight, R.; Joint, I.; et al. Defining seasonal marine microbial community dynamics. ISME J. 2012, 6, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westrich, J.R.; Ebling, A.M.; Landing, W.M.; Joyner, J.L.; Kemp, K.M.; Griffin, D.W.; Lipp, E.K. Saharan dust nutrients promote Vibrio bloom formation in marine surface waters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5964–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, M.S.; Sliwerska, E.; Gore, J.; Polz, M.F.; Cordero, O.X. Microbial interactions lead to rapid micro-scale successions on model marine particles. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampadarath, S.; Bandhoa, K.; Puchooa, D.; Jeewon, R.; Bal, S. Early bacterial biofilm colonizers in the coastal waters of Mauritius. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 29, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.J.; Erni-Cassola, G.; Zadjelovic, V.; Latva, M.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Marine plastic debris: A new surface for microbial colonization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11657–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kesy, K.; Labrenz, M.; Scales, B.S.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Oberbeckmann, S. Vibrio Colonization Is Highly Dynamic in Early Microplastic-Associated Biofilms as Well as on Field-Collected Microplastics. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010076
Kesy K, Labrenz M, Scales BS, Kreikemeyer B, Oberbeckmann S. Vibrio Colonization Is Highly Dynamic in Early Microplastic-Associated Biofilms as Well as on Field-Collected Microplastics. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(1):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010076
Chicago/Turabian StyleKesy, Katharina, Matthias Labrenz, Brittan S. Scales, Bernd Kreikemeyer, and Sonja Oberbeckmann. 2021. "Vibrio Colonization Is Highly Dynamic in Early Microplastic-Associated Biofilms as Well as on Field-Collected Microplastics" Microorganisms 9, no. 1: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010076
APA StyleKesy, K., Labrenz, M., Scales, B. S., Kreikemeyer, B., & Oberbeckmann, S. (2021). Vibrio Colonization Is Highly Dynamic in Early Microplastic-Associated Biofilms as Well as on Field-Collected Microplastics. Microorganisms, 9(1), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010076