Epidemic Alphaviruses: Ecology, Emergence and Outbreaks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Overview of Genus Alphavirus
1.2. Alphavirus Genome Organization and Replication
1.3. Alphavirus Structure and Protein Functions
2. Specific Alphaviruses
2.1. Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus (VEEV)
2.1.1. Disease
2.1.2. Ecology and Transmission Cycles of VEEV
2.1.3. Outbreaks
2.1.4. Potential for Future Outbreaks
2.2. Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus/Madariaga Virus (EEEV/MADV)
2.2.1. Disease
2.2.2. Ecology and Transmission Cycles of EEEV and MADV
2.2.3. History of Outbreaks
2.2.4. Potential for Future Outbreaks
2.3. Western Equine Encephalitis Virus (WEEV)
2.3.1. Disease
2.3.2. Ecology and Transmission Cycles of WEEV
2.3.3. History of Outbreaks
2.3.4. Potential for Future Outbreaks
2.4. Chikungunya Virus (CHIKV)
2.4.1. Disease
2.4.2. Ecology and Transmission Cycles of CHIKV
2.4.3. History of Outbreaks
2.4.4. Potential for Future Outbreaks
2.5. Mayaro Virus (MAYV)
2.5.1. Disease
2.5.2. Ecology and Transmission Cycles of MAYV
2.5.3. History of Outbreaks
2.5.4. Potential Future Outbreaks
2.6. Sindbis Virus (SINV)
2.6.1. Disease
2.6.2. Ecology and Transmission Cycles of SINV
2.6.3. History of Outbreaks
2.6.4. Potential for Future Outbreaks
2.7. Ross River Virus (RRV)
2.7.1. Disease
2.7.2. Ecology and Transmission Cycles of RRV
2.7.3. History of Outbreaks
2.7.4. Potential for Future Outbreaks
3. Future Threats and Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffin, D.E. Alphaviruses. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 652–686. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Merits, A.; Bolling, B.; Nasar, F.; Coffey, L.L.; Powers, A.; Weaver, S.C.; Ictv Report, C. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Togaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 761–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, J.H.; Strauss, E.G. The Alphaviruses: Gene Expression, Replication, and Evolution. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1994, 58, 491–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.Y.; Ng, M.M.; Chu, J.J. Replication of alphaviruses: A review on the entry process of alphaviruses into cells. Adv. Virol. 2011, 2011, 249640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, C.E.; Wyckoff, R.W. Venezuelan Equine Encephalomyelitis. Science 1938, 88, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.; Mills, J.W. Fatal Encephalitis in Man Due to the Venezuelan Virus of Equine Encephalomyelitis in Trinidad. Science 1944, 99, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubes, V.; Gallia, F. Neutralization of Encephalomyelitis Virus by Human Sera. Can. J. Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 1944, 8, 296–298. [Google Scholar]
- Franck, P.T.; Johnson, K.M. An Outbreak of Venezuelan Encephalitis in Man in the Panamá Canal Zone. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, K.E.; Twenhafel, N.A. Pathology of animal models of alphavirus encephalitis. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 790–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.M.; Callahan, J.; Rossi, C.; Oberste, M.S.; Roehrig, J.T.; Wooster, M.T.; Smith, J.F.; Cropp, C.B.; Gentrau, E.M.; Karabatsos, N.; et al. Venezuelan equine encephalitis febrile cases among humans in the Peruvian Amazon River region. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1998, 58, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehrenkranz, N.J.; Ventura, A.K. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infection in man. Annu. Rev. Med. 1974, 25, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, L.; Carey, B.; Kehn-Hall, K. Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus Capsid-The Clever Caper. Viruses 2017, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilcarromero, S.; Aguilar, P.V.; Halsey, E.S.; Laguna-Torres, V.A.; Razuri, H.; Perez, J.; Valderrama, Y.; Gotuzzo, E.; Suarez, L.; Cespedes, M.; et al. Venezuelan equine encephalitis and 2 human deaths, Peru. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Knollmann-Ritschel, B. Current Understanding of the Molecular Basis of Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus Pathogenesis and Vaccine Development. Viruses 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivas, F.; Diaz, L.A.; Cardenas, V.M.; Daza, E.; Bruzon, L.; Alcala, A.; De la Hoz, O.; Caceres, F.M.; Aristizabal, G.; Martinez, J.W.; et al. Epidemic Venezuelan equine encephalitis in La Guajira, Colombia, 1995. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Estrada-Franco, J.G.; Navarro-Lopez, R.; Ferro, C.; Haddow, A.D.; Weaver, S.C. Endemic Venezuelan equine encephalitis in the Americas: Hidden under the dengue umbrella. Future Virol. 2011, 6, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zacks, M.A.; Paessler, S. Encephalitic alphaviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charlier, C.; Beaudoin, M.-C.; Couderc, T.; Lortholary, O.; Lecuit, M. Arboviruses and pregnancy: Maternal, fetal, and neonatal effects. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2017, 1, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.S.; Fashinell, T.R.; Dean, P.B.; Gregg, M.B. Clinical aspects of human Venezuelan equine encephalitis in Texas. Bull. Pan Am. Health Organ. 1976, 10, 46–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ronca, S.E.; Dineley, K.T.; Paessler, S. Neurological Sequelae Resulting from Encephalitic Alphavirus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, I.P.; Paessler, S.; Austgen, L.; Anishchenko, M.; Brault, A.C.; Bowen, R.A.; Weaver, S.C. Envelope Glycoprotein Mutations Mediate Equine Amplification and Virulence of Epizootic Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9128–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.C.; Ferro, C.; Barrera, R.; Boshell, J.; Navarro, J.C. Venezuelan equine encephalitis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2004, 49, 141–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin-Cohen, R.A.; Porter, A.I.; Pittman, P.R.; Rossi, C.A.; DaSilva, L. Human transcriptome response to immunization with live-attenuated Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus vaccine (TC-83): Analysis of whole blood. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittman, P.R.; Makuch, R.S.; Mangiafico, J.A.; Cannon, T.L.; Gibbs, P.H.; Peters, C.J. Long-term duration of detectable neutralizing antibodies after administration of live-attenuated VEE vaccine and following booster vaccination with inactivated VEE vaccine. Vaccine 1996, 14, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, L.L.; Crawford, C.; Dee, J.; Miller, R.; Freier, J.; Weaver, S.C. Serologic Evidence of Widespread Everglades Virus Activity in Dogs, Florida. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, P.; Grayson, M.A. Culex (Melanoconion) aikenii: Natural vector in Panama of endemic Venezuelan encephalitis. Science 1971, 172, 594–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.; Adams, A.P.; Kenney, J.L.; Wang, E.; Weaver, S.C. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus in the mosquito vector Aedes taeniorhynchus: Infection initiated by a small number of susceptible epithelial cells and a population bottleneck. Virology 2008, 372, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherer, W.F.; Dickerman, R.W.; Diaz-Najera, A.; Ward, B.A.; Miller, M.H.; Schaffer, P.A. Ecologic studies of Venezuelan encephalitis virus in southeastern Mexico. 3. Infection of mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1971, 20, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonzo, D.; Grillet, M.E.; Liria, J.; Navarro, J.; Weaver, S.C.; Barrera, R. Ecological Characterization of the Aquatic Habitats of Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in Enzootic Foci of Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus in Western Venezuela. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, C.; Boshell, J.; Moncayo, A.C.; Gonzalez, M.; Ahumada, M.L.; Kang, W.; Weaver, S.C. Natural enzootic vectors of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus, Magdalena Valley, Colombia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncayo, A.C.; Lanzaro, G.; Kang, W.; Orozco, A.; Ulloa, A.; Arredondo-Jimenez, J.; Weaver, S.C. Vector competence of eastern and western forms of Psorophora columbiae (Diptera: Culicidae) mosquitoes for enzootic and epizootic Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.I.; Anishchenko, M.; Weaver, S.C. Susceptibility of Psorophora confinnis (Diptera: Culicidae) to infection with epizootic (subtype IC) and enzootic (subtype ID) Venezuelan Equine encephalitis viruses. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrom, J.O.; Turell, M.J.; Niklasson, B. Antibodies to Ockelbo Virus in Three Orders of Birds (Anseriformes, Galliformes and Passeriformes) in Sweden. J. Wildl. Dis. 1992, 28, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilder-Smith, A.; Gubler, D.J.; Weaver, S.C.; Monath, T.P.; Heymann, D.L.; Scott, T.W. Epidemic arboviral diseases: Priorities for research and public health. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e101–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deardorff, E.R.; Forrester, N.L.; Travassos-da-Rosa, A.P.; Estrada-Franco, J.G.; Navarro-Lopez, R.; Tesh, R.B.; Weaver, S.C. Experimental infection of potential reservoir hosts with Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus, Mexico. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrara, A.S.; Coffey, L.L.; Aguilar, P.V.; Moncayo, A.C.; Da Rosa, A.P.; Nunes, M.R.; Tesh, R.B.; Weaver, S.C. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infection of cotton rats. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, A.S.; Gonzales, G.; Ferro, C.; Tamayo, M.; Aronson, J.; Paessler, S.; Anishchenko, M.; Boshell, J.; Weaver, S.C. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infection of spiny rats. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor-Bonilla, J.; Abella-Medrano, C.A.; Chaves, A.; Alvarez-Mendizabal, P.; Rico-Chavez, O.; Ibanez-Bernal, S.; Rostal, M.K.; Ojeda-Flores, R.; Barbachano-Guerrero, A.; Gutierrez-Espeleta, G.; et al. Potential Sympatric Vectors and Mammalian Hosts of Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus in Southern Mexico. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittor, A.Y.; Armien, B.; Gonzalez, P.; Carrera, J.P.; Dominguez, C.; Valderrama, A.; Glass, G.E.; Beltran, D.; Cisneros, J.; Wang, E.; et al. Epidemiology of Emergent Madariaga Encephalitis in a Region with Endemic Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis: Initial Host Studies and Human Cross-Sectional Study in Darien, Panama. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, C.; Calderon, A.; Oviedo, T.; Mattar, S.; Castaneda, J.; Rodriguez, V.; Moraes Figueiredo, L.T. Molecular and cellular evidence of natural Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infection in frugivorous bats in Colombia. Vet. World 2020, 13, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, S.J.; Pearce, J.M.; Ramey, A.M. Vectors, Hosts, and Control Measures for Zika Virus in the Americas. Ecohealth 2017, 14, 821–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Franco, J.G.; Navarro-Lopez, R.; Freier, J.E.; Cordova, D.; Clements, T.; Moncayo, A.; Kang, W.; Gomez-Hernandez, C.; Rodriguez-Dominguez, G.; Ludwig, G.V.; et al. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus, southern Mexico. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, D.L.; Trainer, D.O. Serologic evidence of Venezuelan equine encephalitis in some wild and domestic populations of southern Texas. J. Wildl. Dis. 1975, 11, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudia, W.D.; McLean, R.G.; Newhouse, V.F.; Johnston, J.G.; Miller, D.L.; Trevino, H.; Bowen, G.S.; Sather, G. Epidemic Venezuelan equine encephalitis in North America in 1971: Vertebrate field studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1975, 101, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudia, W.D.; Newhouse, V.F.; Henderson, B.E. Experimental infection of horses with three strains of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. II. Experimental vector studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1971, 93, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brault, A.C.; Powers, A.M.; Holmes, E.C.; Woelk, C.H.; Weaver, S.C. Positively charged amino acid substitutions in the e2 envelope glycoprotein are associated with the emergence of venezuelan equine encephalitis virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1718–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinney, R.M.; Tsuchiya, K.R.; Sneider, J.M.; Trent, D.W. Molecular evidence for the origin of the widespread Venezuelan equine encephalitis epizootic of 1969 to 1972. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 3301–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubes, V.; Rios, F.A. The Causative Agent of Infectious Equine Encephalomyelitis in Venezuela. Science 1939, 90, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerman, R.W.; Cupp, E.W.; Groot, H.; Alarcon, A.M.; Cura, E.; Dickerman, A.W.; Ibagos, A.L.; Ricco-Hesse, R.; Taylor, C.A.; Weaver, S.C. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus activity in northern Colombia during April and May 1983. Bull. Pan Am. Health Organ. 1986, 20, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Rico-Hesse, R.; Weaver, S.C.; de Siger, J.; Medina, G.; Salas, R.A. Emergence of a new epidemic/epizootic Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus in South America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5278–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberste, M.S.; Fraire, M.; Navarro, R.; Zepeda, C.; Zarate, M.L.; Ludwig, G.V.; Kondig, J.F.; Weaver, S.C.; Smith, J.F.; Rico-Hesse, R. Association of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus subtype IE with two equine epizootics in Mexico. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1998, 59, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.C.; Forshey, B.M.; Notyce, D.; Astete, H.; Lopez, V.; Rocha, C.; Carrion, R.; Carey, C.; Eza, D.; Montgomery, J.M.; et al. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus in Iquitos, Peru: Urban transmission of a sylvatic strain. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burgueno, A.; Frabasile, S.; Diaz, L.A.; Cabrera, A.; Pisano, M.B.; Rivarola, M.E.; Contigiani, M.; Delfraro, A. Genomic Characterization and Seroprevalence Studies on Alphaviruses in Uruguay. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrera, J.P.; Bagamian, K.H.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.; Wang, E.; Beltran, D.; Gundaker, N.D.; Armien, B.; Arroyo, G.; Sosa, N.; Pascale, J.M.; et al. Human and Equine Infection with Alphaviruses and Flaviviruses in Panama during 2010: A Cross-Sectional Study of Household Contacts during an Encephalitis Outbreak. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardozo, F.; Konigheim, B.; Albrieu-Llinas, G.; Rivarola, M.E.; Aguilar, J.; Rojas, A.; Quaglia, A.I.; Paez, M.; Guillen, Y.; Diaz, A.; et al. Alphaviruses: Serological Evidence of Human Infection in Paraguay (2012–2013). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudia, W.D.; Lord, R.D.; Newhouse, V.F.; Miller, D.L.; Kissling, R.E. Vector-host studies of an epizootic of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis in Guatemala, 1969. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1971, 93, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinman, A.R.; McGowan, J.E.; Henderson, B.E. Venezuelan Equine Encephalomyelitis: Surveys of Human Illness During an Epizootic in Guatemala and El Salvador. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1971, 93, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudia, W.D.; Newhouse, V.F.; Beadle, L.D.; Miller, D.L.; Johnston, J.G.; Young, R.; Calisher, C.H.; Maness, K. Epidemic Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis in North America in 1971: Vector Studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1975, 101, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, T.O.; Banks, I.S.; Tigertt, W.D. Attenuation of Venezuelan Equine Encephalomyelitis Virus by in vitro cultivation in guinea-pig heart cells. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1961, 73, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, G.A.; MArtin, D.H.; Reeves, W.C.; Johnson, K.M. Field Studies of an Attenuated Venezuelan Equine Encephalomyelitis Vaccine (Strain TC-83). Infect. Immun. 1972, 5, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.C.; Salas, R.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Ludwig, G.V.; Oberste, M.S.; Boshell, J.; Tesh, R.B. Re-emergence of epidemic Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis in South America. VEE Study Group. Lancet 1996, 348, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, A.M.; Oberste, M.S.; Brault, A.C.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Schmura, S.M.; Smith, J.F.; Kang, W.; Sweeney, W.P.; Weaver, S.C. Repeated emergence of epidemic/epizootic Venezuelan equine encephalitis from a single genotype of enzootic subtype ID virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 6697–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.C.; Bellew, L.A.; Rico-Hesse, R. Phylogenetic analysis of alphaviruses in the Venezuelan equine encephalitis complex and identification of the source of epizootic viruses. Virology 1992, 191, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.W.; Weaver, S.C. Eastern Equine Encephalomyelitis Virus: Epidemiology and Evolution of Mosquito Transmission. In Advances in Virus Research; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1989; Volume 37, pp. 277–328. [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo, N.C.; Adams, A.P.; Weaver, S.C. Evolutionary patterns of eastern equine encephalitis virus in North versus South America suggest ecological differences and taxonomic revision. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrigo, N.C.; Weaver, S.C. Proposal 2012.007aV. In the Genus Alphavirus, Create a Species Named Madariaga Virus Comprising Some of the Virus Strains Currently Classified in the Species Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv/proposals/2012.007aV.A.v1.Alphavirus-sp.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Kumar, B.; Manuja, A.; Gulati, B.R.; Virmani, N.; Tripathi, B.N. Zoonotic Viral Diseases of Equines and Their Impact on Human and Animal Health. Open Virol. J. 2018, 12, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindsey, N.P.; Staples, J.E.; Fischer, M. Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus in the United States, 2003–2016. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morens, D.M.; Folkers, G.K.; Fauci, A.S. Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus-Another Emergent Arbovirus in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfield, M.; Welsh, J.N.; Taylor, B.F. The 1959 Outbreak of Eastern Encephalitis in New Jersey 5. The Inapparent Infection: Disease Ratio. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1968, 87, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.E.; Beckham, J.D.; Tyler, K.L. North American encephalitic arboviruses. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 727–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.C.; Winegar, R.; Manger, I.D.; Forrester, N.L. Alphaviruses: Population genetics and determinants of emergence. Antivir. Res. 2012, 94, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldfield, M.; Sussman, O. The 1959 Outbreak of Eastern Encephalitis in New Jersey 1. Introduction and Description of Outbreak. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1968, 87, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, J.C.; Feemster, R.F. The Sequelae of Eastern Equine Encephalomyelitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1949, 240, 960–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feemster, R.F. Outbreak of Encephalitis in Man Due to the Eastern Virus of Equine Encephalomyelitis. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1938, 28, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsey, N.P.; Martin, S.W.; Staples, J.E.; Fischer, M. Multistate Outbreak if Eastern Equine Encephalitis-United States, 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villari, P.; Spielman, A.; Komar, N.; McDowell, M.; Timperi, R.J. The economic burden imposed by a residual case of eastern encephalitis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 52, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilliam, D.N.; Gosciminski, M.; Bandy, U. Eastern Equine Encephalitis Surveillance and Response, Rhode Island, 2019. R I Med. J. 2020, 103, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Deresiewicz, R.L.; Thaler, S.J.; Hsu, L.; Zamani, A.A. Clinical and Neuroradiographic Manifestations of Eastern Equine Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feemster, R.F. Equine Encephalitis in Massachusetts. N. Engl. J. Med. 1957, 257, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monath, T.P. Arthropod-borne encephalitides in the Americas. Bull. World Health Organ. 1979, 57, 513–533. [Google Scholar]
- Alice, F.J. Infecção humana pelo vírus “Leste” da encefalite eqüina. Bol. Inst. Biol. Bahia (Braz.) 1956, 3, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Corniou, B.; Ardoin, P.; Bartholomew, C.; Ince, W.; Massiah, V. First isolation of a South American strain of Eastern Equine virus from a case of encephalitis in Trinidad. Trop. Geogr. Med. 1972, 24, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, P.V.; Robich, R.M.; Turell, M.J.; O’Guinn, M.L.; Klein, T.A.; Huaman, A.; Guevara, C.; Rios, Z.; Tesh, R.B.; Watts, D.M.; et al. Endemic eastern equine encephalitis in the Amazon region of Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrera, J.P.; Forrester, N.; Wang, E.; Vittor, A.Y.; Haddow, A.D.; Lopez-Verges, S.; Abadia, I.; Castano, E.; Sosa, N.; Baez, C.; et al. Eastern equine encephalitis in Latin America. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franklin, R.P.; Kinde, H.; Jay, M.T.; Kramer, L.D.; Emily-Gene, N.G.; Chiles, R.E.; Ostlund, E.; Husted, S.; Smith, J.; Parker, M.D. Eastern Equine Encephalomyelitis Virus Infection in a Horse from California. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.L.C.R.; Auguste, A.J.; Terzian, A.C.B.; Vedovello, D.; Riet-Correa, F.; Macario, V.M.K.; Mourao, M.P.G.; Ullmann, L.S.; Araujo, J.P., Jr.; Weaver, S.C.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Madariaga Virus from a Horse in Paraiba State, Brazil. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenier, S.; Cote, G.; Vanderstock, J.; Macieira, S.; Laperle, A.; Helie, P. An eastern equine encephalomyelitis (EEE) outbreak in Quebec in the fall of 2008. Can. Vet. J. 2010, 51, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.L.; Galiza, G.J.; Dantas, A.F.; Oliveira, R.N.; Iamamoto, K.; Achkar, S.M.; Riet-Correa, F. Outbreaks of Eastern equine encephalitis in northeastern Brazil. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanson, R.P. An epizootic of equine encephalomyelitis that occurred in Massachusetts in 1831. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1957, 6, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.N. Arboviruses—Case studies of transmission. In The Biology of Mosquitoes: Transmission of Viruses and Interactions with Bacteria; Cutts, R., Ed.; CABI: Cambridge, UK, 2012; Volume 3, pp. 175–194. [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein-Larson, L.A.; Tan, Y.; Stark, L.M.; Cannons, A.C.; Shilts, M.H.; Unnasch, T.R.; Das, S.R. Complex Epidemiological Dynamics of Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus in Florida. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.G.; Mathias, D.K.; Day, J.F.; Acevedo, C.; Unnasch, T.R.; Burkett-Cadena, N.D. Seasonal Changes of Host Use by Culiseta melanura (Diptera: Culicidae) in Central Florida. J. Med. Entomol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estep, L.K.; McClure, C.J.; Burkett-Cadena, N.D.; Hassan, H.K.; Hicks, T.L.; Unnasch, T.R.; Hill, G.E. A multi-year study of mosquito feeding patterns on avian hosts in a southeastern focus of eastern equine encephalitis virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, F.; Crans, W.J. Effect of Temperature on the Development of Culiseta melanura (Diptera: Culicidae) and its Impact on the Amplification of Eastern Equine Encephalomyelitis Virus in Birds. J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaff, N.K.; Armstrong, P.M.; Andreadis, T.G.; Cheruvelil, K.S. Wetland characteristics linked to broad-scale patterns in Culiseta melanura abundance and eastern equine encephalitis virus infection. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edman, J.D.; Webber, L.A.; Kale, H.W., II. Host-Feeding Patterns of Florida Mosquitoes II. Culiseta. J. Med. Entomol. 1972, 9, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaei, G.; Oliver, J.; Andreadis, T.G.; Armstrong, P.M.; Howard, J.J. Molecular Identification of Blood-Meal Sources in Culiseta Melanura and Culiseta Morsitans From an Endemic Focus of Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus in New York. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, G.; Andreadis, T.G. Identification of Avian- and Mammalian-Derived Bloodmeals in Aedes vexans and Culiseta melanura (Diptera: Culicidae) and Its Implication for West Nile Virus Transmission in Connecticut, USA. J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molaei, G.; Armstrong, P.M.; Abadam, C.F.; Akaratovic, K.I.; Kiser, J.P.; Andreadis, T.G. Vector-Host Interactions of Culiseta melanura in a Focus of Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus Activity in Southeastern Virginia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, G.; Andreadis, T.G.; Armstrong, P.M.; Thomas, M.C.; Deschamps, T.; Cuebas-Incle, E.; Montgomery, W.; Osborne, M.; Smole, S.; Matton, P.; et al. Vector-host interactions and epizootiology of eastern equine encephalitis virus in Massachusetts. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burkett-Cadena, N.D.; Bingham, A.M.; Hunt, B.; Morse, G.; Unnasch, T.R. Ecology of Culiseta Melanura and Other Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) from Walton County, FL, During Winter Period 2013–2014. J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kissling, E.E.; Chamberlain, R.W.; Sikes, B.K.; Eidson, M.E. Studies on the North American Arthopod-Borne Encephalitedes: III. Eastern Equine Encephaltiis in Wild Birds. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1954, 60, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.A. A Study of Birds and Mosquitoes as Hosts for the virus of Eastern Equine Encephalomyelitis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1940, 32, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, N.; Dohm, D.J.; Turell, M.J.; Spielman, A. Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus in Birds: Relative Competence of European Starlings (Sturnus Vulgaris). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crans, W.J.; Caccamise, D.F.; McNelly, J.R. Eastern Equine Encephalomyelitis Virus in Relation to the Avian Community of a Coastal Cedar Swamp. J. Med. Entomol. 1994, 31, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Main, A.J.; Anderson, K.S.; Maxfield, H.K.; Rosenau, B.; Oliver, C. Duration of Alphavirus Neutralizing Antibody in Naturally Infected Birds. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1988, 38, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satriano, S.F.; Luginbuhl, R.E.; Robert, C.W.; Jungherr, E.L.; Williamson, L.A. Investigation of Eastern Equine Encephalotmyelitis: IV. Susceptibility and Transmission Studies with Virus of Pheasant Origin. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1958, 67, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, J.S.; Barnes, H.J.; Smith, L.G. Experimental Infection of Young Broiler Chickens with Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus and Highlands J Virus. Avian Dis. 1994, 38, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, J.S.; Ficken, M.D.; Barnes, H.J.; Wages, D.P.; Smith, L.G. Experimental Infection of Young Turkeys With Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus and Highlands J Virus. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.G.; Crans, W.J.; Caccamise, D.F.; McNelly, J.; Kirk, L.J.; Mitchell, C.J.; Calisher, C.H. Experimental Infection of wading birds with Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus. J. Wildl. Dis. 1995, 31, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguirre, A.A.; McLean, R.G.; Cook, R.A. Experimental Inoculation of Three Arboviruses in Black-Bellied Whistling Ducks (Dendrocygna autumnalis). J. Wildl. Dis. 1992, 28, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, P.M.; Andreadis, T.G. Eastern equine encephalitis virus in mosquitoes and their role as bridge vectors. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1869–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turell, M.J.; O’Guinn, M.L.; Dohm, D.; Zyzak, M.; Watts, D.; Fernandez, R.; Calampa, C.; Klein, T.A.; Jones, J.W. Susceptibility of Peruvian Mosquitoes to Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondig, J.P.; Turell, M.J.; Lee, J.S.; O’Guinn, M.L.; Wasieloski, L.P. Genetic Analysis of South American Eastern Equine Encephalomyeletis Viruses isolated from Mosquitoes collected in the Amazon basin region of Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Guinn, M.L.; Lee, J.S.; Kondig, J.P.; Fernandez, R.; Carbajal, F. Field Detection of Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus in the Amazon Basin Region of Peru using Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction adapted for field identification of arthropod-borne pathogens. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 70, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walder, R.; Suarez, O.M.; Calisher, C.H. Arbovirus Studies in the Guajira Region of Venezuela: Activities of Eastern Equine Encephalitis and Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Viruses during an Interepizootic Period. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1984, 33, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, W.; Liria, J.; Navarro, J.; Garcia, C.Z.; Freier, J.E.; Salas, R.; Weaver, S.C.; Barrera, R. Spatial Dispersion of Adult Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) in a Sylvatic Focus of Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cupp, E.W.; Scherer, W.F.; Lok, J.B.; Brenner, R.J.; Dziem, G.M.; Ordonez, J.V. Entomological Studies at an Enzootic Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus Focus in Guatemala, 1977–1980. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 35, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigo, N.C.; Adams, A.P.; Watts, D.M.; Newman, P.C.; Weaver, S.C. Cotton rats and house sparrows as hosts for North and South American strains of eastern equine encephalitis virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.D. Eastern Equine Encephalomyelitis In The Arboviruses: Epidemiology and Ecology; Monath, T.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986; Volume 3, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Broeck, C. Birds as possible carriers of the virus of equine encephalomyelitis. Arch. Pathol. 1938, 25, 759. [Google Scholar]
- Kissling, R.E.; Rubin, H.; Chamberlain, R.W.; Eidson, M.E. Recovery of virus of Eastern equine encephalomyelitis from blood of a purple grackle. In Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine; Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine: New York, NY, USA, 1951; Volume 77, pp. 398–399. [Google Scholar]
- Hubalek, Z.; Rudolf, I.; Nowotny, N. Arboviruses pathogenic for domestic and wild animals. Adv. Virus Res. 2014, 89, 201–275. [Google Scholar]
- Fothergill, L.D.; Dingle, J.H.; Farber, S.; Connerley, M.D. Human Encephalitis Caused by the Virus of the Eastern Variety of Equine Encephalomyelitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1938, 219, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Easten Equine Encephalitis: Statistics & Maps. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/easternequineencephalitis/tech/epi.html (accessed on 23 May 2020).
- CDC. ArboNET Disease Maps. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/arbonet/maps/ADB_Diseases_Map/index.html (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Sabattini, M.S.; Monath, T.P.; Mitchell, C.J.; Daffner, J.F.; Bowen, G.S.; Pauli, R.; Contigiani, M.S. Arbovirus investigations in Argentina, 1977–1980. I. Historical aspects and description of study sites. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 34, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabattini, M.S.; Daffner, J.F.; Monath, T.P.; Bianchi, T.I.; Cropp, C.B.; Mitchell, C.J.; Aviles, G. Localized eastern equine encephalitis in Santiago del Estero Province, Argentina, without human infection. Medicina 1991, 51, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lednicky, J.; De Rochars, V.M.; Elbadry, M.; Loeb, J.; Telisma, T.; Chavannes, S.; Anilis, G.; Cella, E.; Ciccozzi, M.; Okech, B.; et al. Mayaro Virus in Child with Acute Febrile Illness, Haiti, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 2000–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lednicky, J.A.; White, S.K.; Mavian, C.N.; El Badry, M.A.; Telisma, T.; Salemi, M.; BA, O.K.; Beau De Rochars, V.M.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Emergence of Madariaga virus as a cause of acute febrile illness in children, Haiti, 2015–2016. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0006972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blohm, G.M.; Lednicky, J.A.; White, S.K.; Mavian, C.N.; Marquez, M.C.; Gonzalez-Garcia, K.P.; Salemi, M.; Morris, J.G., Jr.; Paniz-Mondolfi, A.E. Madariaga Virus: Identification of a Lineage III Strain in a Venezuelan Child With Acute Undifferentiated Febrile Illness, in the Setting of a Possible Equine Epizootic. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, J.G.; Carrera, J.P.; Serrano, E.; Pitti, Y.; Maguina, J.L.; Mentaberre, G.; Lescano, A.G.; Valderrama, A.; Mayor, P. Serologic Evidence of Zoonotic Alphaviruses in Humans from an Indigenous Community in the Peruvian Amazon. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.O.; Hess, A.D. Climatological Conditions associated with Outbreaks of Eastern Encephalitis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, S.R.; Weaver, S.C. Vector Competence: What Has Zika Virus Taught Us? Viruses 2019, 11, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavicchioli, R.; Ripple, W.J.; Timmis, K.N.; Azam, F.; Bakken, L.R.; Baylis, M.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boetius, A.; Boyd, P.W.; Classen, A.T.; et al. Scientists’ warning to humanity: Microorganisms and climate change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gould, E.; Pettersson, J.; Higgs, S.; Charrel, R.; de Lamballerie, X. Emerging arboviruses: Why today? One Health 2017, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Reisen, W.K. Present and future arboviral threats. Antivir. Res. 2010, 85, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reisen, W.K.; Monath, T.P. Western equine encephalomyelitis. In The Arboviruses: Epidemiology and Ecology; Monath, T.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; Volume 5, pp. 89–137. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, W.C.; Hammon, W.M. Epidemiology of the Arthropod-Borne Viral Encephalitides in Kern County, California 1943–1952; University of California at Berkeley: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Kokernot, R.H.; Shinefield, H.R.; Longshore, W.A. The 1952 outbreak of encephalitis in California. Differential diagnosis. Calif. Med. 1953, 79, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medovy, H. Western equine encephalomyelitis in infants. J. Pediatr. 1943, 22, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, J.E.; Bryan, J.S.; Gregg, M.B. Surveillance of arboviral encephalitis in the United States, 1955–1971. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1973, 97, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnest, M.P.; Goolishian, H.A.; Calverley, J.R.; Hayes, R.O.; Hill, H.R. Neurologic, intellectual, and psychologic sequelae following western encephalitis: A follow-up study of 35 cases. Neurology 1971, 21, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzon, H.; Shelton, J.T.; Bruyn, H.E. Sequelae of Western Equine and Other Arthropod-Borne Encephalitides. Neurology 1957, 7, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monath, T.P.; Trent, D.W. Togaviral diseases of domestic animals. In Comparative Diagnosis of Viral Diseases; Kurstack, E., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 6, p. 331. [Google Scholar]
- Minke, J.M.; Audonnet, J.-C.; Fischer, L. Equine viral vaccines: The past, present and future. Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chamberlain, R.W. Vector relationships of the arthropod-borne encephalitides in North America. Annu. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 70, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.D.; Hayes, R.O. Seasonal dynamics of western encephalitis virus. Am. J. Med Sci. 1967, 253, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.O. Section B: Viral Zoonoses. In CRC Handbook Series in Zoonoses; Beran, G.W., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1981; Volume 1, p. 37. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, W.C.; Bellamy, R.E.; Scrivani, R.P. Relationships of mosquito vectors to winter survival of encephalitis viurses under natural conditions. Am. J. Hyg. 1958, 67, 78–98. [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn, T.A.; Sooter, C.A.; Langmuir, A.D. Ecology of western equine and St. Louis encephalitis viruses. A summary of feild investigations in Weld County, Colorado, 1949 to 1953. Am. J. Hyg. 1957, 65, 130–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, R.O.; LaMotte, L.C.; Holden, P. Ecology of arboviruses from Hale County, Texas, during 1965. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1967, 16, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuill, T.M.; Hanson, R.P. Serological evidence of California encephalitis virus and western equine encephalitis virus in snowshoe hares. Zoonoses Res. 1964, 3, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iversen, J.O.; Seawright, G.; Hanson, R.P. Serologic survey for arboviruses in central Alberta. Can. J. Public Health 1971, 62, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burton, A.N.; McLintock, J.R.; Spalatin, J.; Rempel, J.G. Western equine encephalitis in Saskatchewan birds and mammals. Can. J. Microbiol. 1966, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.K.; Burton, A.N.; Iversen, J.O.; McLintock, J.R. Natural infections of Richardson’s grownd squirrels with western equine encephalomyelitis virus, Saskatchewan, Canada. Can. J. Microbiol. 1975, 21, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLintock, J.R.; Burton, A.N.; McKiel, J.A.; Hall, R.R.; Rempel, J.G. Known mosquito hosts of western encephalitis virus in Saskatchewan. J. Med. Entomol. 1970, 7, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammon, W.D.; Reeves, W.C.; Benner, S.R.; Brookman, B. Human encephalitis in the Yakima Valley, Washington, 1942: With forty-nine virus isolations (western equine and st. louis types) from mosquitoes. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1945, 128, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekla, L.H.; Stackiw, W.; Burst, R.A. Arbovirus isolations from mosquitoes in Manitoba. Mosq. News 1980, 40, 377–380. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, W.C. Overwintering of arthropod-borne viruses. Prog. Med. Virol. 1961, 3, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, W.C. Overwintering of arboviruses. Prog. Med. Virol. 1974, 17, 193–220. [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt, L.P.; Hill, D.W. Overwintering of Western Equine Encephalitis Virus. Exp. Biol. Med. 1960, 104, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhardt, L.P.; Stanton, G.J.; Hill, D.W.; Collett, G.C. Natural overwintering hosts of the virus of western equine encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1964, 217, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.A.; Eklund, C.M. Overwintering of western equine encephalomyelitis virus in experimentally infected garter snakes and transmission to mosquitos. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1960, 105, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulhorst, C.; Hardy, J.; Eldridge, B.; Presser, S.; Reeves, W. Natural vertical transmission of western equine encephalomyelitis virus in mosquitoes. Science 1994, 263, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giltner, L.T.; Shahan, M.S. The present Status of infectious Equine Encephalomyelitis in the United States. J. Am. Vet. Med Assoc. 1936, 88, 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Sponseller, M.L.; Binn, L.N.; Wooding, W.L.; Yager, R.H. Field Strains of Western Encephalitis Virus in Ponies: Virologic, Clinical, and Pathologic Observations. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1966, 27, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, R.J.; French, G.R.; Yancey, F.S.; Gochenour, W.S.; Russell, P.K.; Ramsburg, H.H.; Brand, O.A.; Scheider, F.G.; Buescher, E.L. Clinical and Immunological interrelationships among Venezuelan, eastern, and western encephalomyelitis in burros. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1964, 25, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson, L. Bird Positive for WEEV Found in Summer of 2015 in Harris County; Bergren, N., Ed.; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Disease Maps. Available online: http://diseasemaps.usgs.gov/mapviewer/ (accessed on 15 May 2016).
- Robb, L.L.; Hartman, D.A.; Rice, L.; deMaria, J.; Bergren, N.A.; Borland, E.M.; Kading, R.C. Continued Evidence of Decline in the Enzootic Activity of Western Equine Encephalitis Virus in Colorado. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 56, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.F.; Haring, C.M.; Howitt, B. The etiology of epizootic encephalomyelitis of horses in the San Joaquin Valley, 1930. Science 1931, 74, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, W.C.; Howitt, B.F. Human Equine Encephalomyelitis in Kern County, California, 1938, 1939, and 1940. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1941, 31, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, R.O. Encephalomyelitis in Saskatchewan, 1941. Can. J. Public Health 1942, 33, 388. [Google Scholar]
- Eklund, C.M. Human Encephalitis of the Western Equine Type in Minnesota in 1941: Clinical and Epidemiological Study of Serologically Positive Cases. Am. J. Hyg. 1946, 43, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hollister, A.C.; Longshore, W.A.; Dean, B.H.; Stevens, I.M. The 1952 outbreak of encephalitis in California. Epidemiologic Aspects. Calif. Med. 1953, 79, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.; Currier, R.; Pearson, J.; Harris, J.; Parker, R. Western equine encephalomyelitis in horses in the Northern Red River Valley, 1975. J. Am. Vet. Med Assoc. 1977, 170, 1396–1399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eadie, J.A.; Friesen, B. Epidemiological study of western equine encephalitis—Manitoba 1981. In Western Equine Encephalitis in Manitoba; Sekla, L., Ed.; Manitoba Ministry of Health: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Delfraro, A.; Bugueno, A.; Morel, N.; Gonzalez, G.; Garcia, A.; Morelli, J.; Perez, W.; Chiparelli, H.; Arbiza, J. Fatal human case of Western equine encephalitis, Uraguay. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergren, N.A.; Auguste, A.J.; Forrester, N.L.; Negi, S.S.; Braun, W.A.; Weaver, S.C. Western Equine Encephalitis Virus: Evolutionary Analysis of a Declining Alphavirus Based on Complete Genome Sequences. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 9260–9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forrester, N.L.; Kenney, J.L.; Deardorff, E.; Wang, E.; Weaver, S.C. Western Equine Encephalitis submergence: Lack of evidence for a decline in virus virulence. Virology 2008, 380, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logue, C.H.; Bosio, C.F.; Welte, T.; Keene, K.M.; Ledermann, J.P.; Phillips, A.; Sheahan, B.J.; Pierro, D.J.; Marlenee, N.; Brault, A.C.; et al. Virulence variation among isolates of western equine encephalitis virus in an outbred mouse model. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1848–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisen, W.K.; Fang, Y.; Brault, A.C. Limited Interdecadal Variation in Mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) and Avian Host Competence for Western Equine Encephalomyelitis Virus (Togaviridae: Alphavirus). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, Y.; Brault, A.C.; Reisen, W.K. Variation in Western Equine Encephalomyelitis Viral Strain Growth in Mammalian, Avian, and Mosquito Cells Fails to Explain Temporal Changes in Enzootic and Epidemic Activity in California. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.C.; Kang, W.; Shirako, Y.; Rumenapf, T.; Strauss, E.G.; Strauss, J.H. Recombinational history and molecular evolution of western equine encephalomyelitis complex alphaviruses. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mossel, E.C.; Ledermann, J.P.; Phillips, A.T.; Borland, E.M.; Powers, A.M.; Olson, K.E. Molecular determinants of mouse neurovirulence and mosquito infection for Western equine encephalitis virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergren, N.A.; Haller, S.; Rossi, S.L.; Seymour, R.L.; Huang, J.; Miller, A.L.; Bowen, R.A.; Hartman, D.A.; Brault, A.C.; Weaver, S.C. “Submergence” of Western equine encephalitis virus: Evidence of positive selection argues against genetic drift and fitness reductions. PLOS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brouard, C.; Bernillon, P.; Quatresous, I.; Pillonel, J.; Assal, A.; De Valk, H.; Desenclos, J.C.; Workgroup Quantitative Estimation of the Risk of Blood Donation Contamination by Infectious, A. Estimated risk of Chikungunya viremic blood donation during an epidemic on Reunion Island in the Indian Ocean, 2005 to 2007. Transfusion 2008, 48, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhrbier, A.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Gasque, P. Arthritogenic alphaviruses-an overview. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Lecuit, M. Chikungunya virus and the global spread of a mosquito-borne disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Organization, P.A.H. Chikungunya: Data, Maps, and Statistics. Available online: https://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_topics&view=rdmore&cid=5927&Itemid=40931&lang=en (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Tandale, B.V.; Sathe, P.S.; Arankalle, V.A.; Wadia, R.S.; Kulkarni, R.; Shah, S.V.; Shah, S.K.; Sheth, J.K.; Sudeep, A.B.; Tripathy, A.S.; et al. Systemic involvements and fatalities during Chikungunya epidemic in India, 2006. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economopoulou, A.; Dominguez, M.; Helynck, B.; Sissoko, D.; Wichmann, O.; Quenel, P.; Germonneau, P.; Quatresous, I. Atypical Chikungunya virus infections: Clinical manifestations, mortality and risk factors for severe disease during the 2005–2006 outbreak on Reunion. Epidemiol. Infect. 2009, 137, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerbino-Neto, J.; Mesquita, E.C.; Amancio, R.T.; Brasil, P. Events preceding death among chikungunya virus infected patients: A systematic review. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e04312019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérardin, P.; Couderc, T.; Bintner, M.; Tournebize, P.; Renouil, M.; Lémant, J.; Boisson, V.; Borgherini, G.; Staikowsky, F.; Schramm, F.; et al. Chikungunya virus–associated encephalitis. Neurology 2016, 86, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Gerardin, P.; de Brito, C.A.A.; Soares, C.N.; Ferreira, M.L.B.; Solomon, T. The neurological complications of chikungunya virus: A systematic review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2018, 28, e1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renault, P.; Solet, J.; Sissoko, D.; Balleydier, E.; Larrieu, S.; Filleul, L.; Lassalle, C.; Thiria, J.; Rachou, E.; De Valk, H.; et al. A Major Epidemic of Chikungunya Virus Infection on Réunion Island, France, 2005–2006. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aalst, M.; Nelen, C.M.; Goorhuis, A.; Stijnis, C.; Grobusch, M.P. Long-term sequelae of chikungunya virus disease: A systematic review. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 15, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmakumar, B.; Jayan, J.B.; Menon, R.; Kottarathara, A.J. Clinical profile of chikungunya sequelae, association with obesity and rest during acute phase. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2010, 41, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moro, M.L.; Grilli, E.; Corvetta, A.; Silvi, G.; Angelini, R.; Mascella, F.; Miserocchi, F.; Sambo, P.; Finarelli, A.C.; Sambri, V.; et al. Long-term chikungunya infection clinical manifestations after an outbreak in Italy: A prognostic cohort study. J. Infect. 2012, 65, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, D. The Cost and Burden of Chikungunya in the Americas Yale. Master’s Thesis, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA, 1 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Langsjoen, R.M.; Haller, S.L.; Roy, C.J.; Vinet-Oliphant, H.; Bergren, N.A.; Erasmus, J.H.; Livengood, J.A.; Powell, T.D.; Weaver, S.C.; Rossi, S.L. Chikungunya Virus Strains Show Lineage-Specific Variations in Virulence and Cross-Protective Ability in Murine and Nonhuman Primate Models. mBio 2018, 9, e02449-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Althouse, B.M.; Guerbois, M.; Cummings, D.A.T.; Diop, O.M.; Faye, O.; Faye, A.; Diallo, D.; Sadio, B.D.; Sow, A.; Faye, O.; et al. Role of monkeys in the sylvatic cycle of chikungunya virus in Senegal. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coffey, L.L.; Failloux, A.B.; Weaver, S.C. Chikungunya virus-vector interactions. Viruses 2014, 6, 4628–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, M.; Thonnon, J.; Traore-Lamizana, M.; Fontenille, D. Vectors of Chikungunya virus in Senegal: Current data and transmission cycles. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jupp, P.G.; McIntosh, B.M. Aedes furcifer and other mosquitoes as vectors of chikungunya virus at Mica, northeastern Transvaal, South Africa. J. Am. Mosq. Control. Assoc. 1990, 6, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Weinbren, M.P.; Haddow, A.J.; Williams, M.C. The Occurrence of Chikungunya Virus in Uganda. I. Isolation From Mosquitoes. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1958, 52, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, H.; Van Bortel, W.; Sudre, B. Chikungunya: Its History in Africa and Asia and Its Spread to New Regions in 2013–2014. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, S436–S440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, A.M.; Logue, C.H. Changing patterns of chikungunya virus: Re-emergence of a zoonotic arbovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammon, W.D.; Rundnick, A.; Sather, G.E. Viruses Associated with Epidemic Hemorrhagic Fevers of the Philippines and Thailand. Science 1960, 131, 1102–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmannitya, S.; Halstead, S.B.; Cohen, S.N.; Margiotta, M.R. Dengue and Chikungunya Virus Infection in Man in Thailand, 1962–1964 I. Observations on Hospitalized Patients with Hemorrhagic Fever. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 19699, 18, 954–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Goeta, C.; Mousson, L.; Rougeon, F.; Failloux, A.B. Dissemination and transmission of the E1-226V variant of chikungunya virus in Aedes albopictus are controlled at the midgut barrier level. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetsarkin, K.A.; Vanlandingham, D.L.; McGee, C.E.; Higgs, S. A single mutation in chikungunya virus affects vector specificity and epidemic potential. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezza, G.; Nicoletti, L.; Angelini, R.; Romi, R.; Finarelli, A.C.; Panning, M.; Cordioli, P.; Fortuna, C.; Boros, S.; Magurano, F.; et al. Infection With Chikungunya Virus in Italy: An Outbreak in a Temperate Region. Lancet 2007, 370, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, I.C.; Chan, Y.F.; Chan, S.Y.; Loong, S.K.; Chin, H.K.; Hooi, P.S.; Ganeswrie, R.; Abubakar, S. Chikungunya virus of Asian and Central/East African genotypes in Malaysia. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.C.; Tan, L.K.; Tan, C.H.; Tan, S.S.; Hapuarachchi, H.C.; Pok, K.Y.; Lai, Y.L.; Lam-Phua, S.G.; Bucht, G.; Lin, R.T.; et al. Entomologic and virologic investigation of Chikungunya, Singapore. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theamboonlers, A.; Rianthavorn, P.; Praianantathavorn, K.; Wuttirattanakowit, N.; Poovorawan, Y. Clinical and molecular characterization of chikungunya virus in South Thailand. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 62, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, H.; Ke, C.; Deng, X.; Guan, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Chikungunya outbreak in Guangdong Province, China, 2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, T.M.L.; Vieira, Y.R.; Delatorre, E.; Barbosa-Lima, G.; Luiz, R.L.F.; Vizzoni, A.; Jain, K.; Miranda, M.M.; Bhuva, N.; Gogarten, J.F.; et al. Emergence of the East-Central-South-African genotype of Chikungunya virus in Brazil and the city of Rio de Janeiro may have occurred years before surveillance detection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, J.; Giovanetti, M.; Fonseca, V.; Theze, J.; Graf, T.; Fabri, A.; Goes de Jesus, J.; Lima de Mendonca, M.C.; Damasceno Dos Santos Rodrigues, C.; Mares-Guia, M.A.; et al. Circulation of chikungunya virus East/Central/South African lineage in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjos, R.O.; Mugabe, V.A.; Moreira, P.S.S.; Carvalho, C.X.; Portilho, M.M.; Khouri, R.; Sacramento, G.A.; Nery, N.R.R., Jr.; Reis, M.G.; Kitron, U.D.; et al. Transmission of Chikungunya Virus in an Urban Slum, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saude, M.D. Monitoramento dos casos de dengue, febre de chikungunya e febre pelo vírus Zika até a Semana Epidemiológica 35, 2017. Bol. Epidemiol. 2017, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. First Chikungunya Case Acquired in the United States Reported in Florida. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2014/p0717-chikungunya.html (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Services, T.D.o.S.H. DSHS Announces First Texas-Acquired Chikungunya Case. News Release. Available online: https://www.dshs.state.tx.us/news/releases/2016/20160531.aspx (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Figueiredo, L.T.M. Human Urban Arboviruses Can Infect Wild Animals and Jump to Sylvatic Maintenance Cycles in South America. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lourenco-de-Oliveira, R.; Failloux, A.B. High risk for chikungunya virus to initiate an enzootic sylvatic cycle in the tropical Americas. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slosek, J. Aedes aegypti mosquitoes in the Americas: A review of their interactions with the human population. Soc. Sci. Med. 1986, 23, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Rodriguez, Y.; Pacheco, Y.; Anaya, J.M.; Ramirez-Santana, C. Mayaro: An emerging viral threat? Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.P.; Freitas, R.B.; Travassos da Rosa, J.F.; Gabbay, Y.B.; Mello, W.A.; LeDuc, J.W. An Outbreak of Mayaro Virus Disease in Belterra, Brazil. I. Clinical and Virological Findings. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Luis, M.A.; Del Valle-Mendoza, J.; Silva-Caso, W.; Gil-Ramirez, T.; Levy-Blitchtein, S.; Bazan-Mayra, J.; Zavaleta-Gavidia, V.; Cornejo-Pacherres, D.; Palomares-Reyes, C.; Del Valle, L.J. An emerging public health threat: Mayaro virus increases its distribution in Peru. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tesh, R.B.; Watts, D.M.; Russell, K.L.; Damodaran, C.; Calampa, C.; Cabezas, C.; Ramirez, G.; Vasquez, B.; Hayes, C.G.; Rossi, C.A.; et al. Mayaro Virus Disease: An Emerging Mosquito-Borne Zoonosis in Tropical South America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mota, M.T.O.; Costa, V.V.; Sugimoto, M.A.; Guimaraes, G.F.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; Moreira, T.P.; de Sousa, C.D.; Santos, F.M.; Queiroz, V.F.; Passos, I.; et al. In-depth characterization of a novel live-attenuated Mayaro virus vaccine candidate using an immunocompetent mouse model of Mayaro disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, D.M.; Cole, F.E., Jr.; McManus, A.T.; Pedersen, C.E., Jr. Inactivated Mayaro vaccine produced in human diploid cell cultures. Mil. Med. 1976, 141, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, W.J.; Hermance, M.E.; Forrester, N.; Adams, A.P.; Langsjoen, R.; Gorchakov, R.; Wang, E.; Alcorn, M.D.; Tsetsarkin, K.; Weaver, S.C. A novel live-attenuated vaccine candidate for mayaro Fever. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoisy, B.; Gardon, J.; Salas, R.A.; Morvan, J.; Kazanji, M. Mayaro Virus in Wild Mammals, French Guiana. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, A.L.; Peterson, N.E.; LeDuc, J.W.; Pinheiro, F.P. An Outbreak of Mayaro Virus Disease in Belterra, Brazil. III. Entomological and Ecological Studies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, F.; Alout, H.; Diagne, C.T.; Bengue, M.; Baronti, C.; Hamel, R.; Talignani, L.; Liegeois, F.; Pompon, J.; Morales Vargas, R.E.; et al. Differential Susceptibility and Innate Immune Response of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus to the Haitian Strain of the Mayaro Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, K.C.; Ziegler, S.A.; Thangamani, S.; Hausser, N.L.; Kochel, T.J.; Higgs, S.; Tesh, R.B. Experimental transmission of Mayaro virus by Aedes aegypti. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 85, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serra, O.P.; Cardoso, B.F.; Ribeiro, A.L.; Santos, F.A.; Slhessarenko, R.D. Mayaro virus and dengue virus 1 and 4 natural infection in culicids from Cuiaba, state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2016, 111, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzi, L.; LaBeaud, A.D.; Reusken, C.B.; Drexler, J.F.; Vasilakis, N.; Diallo, M.; Simon, F.; Jaenisch, T.; Gallian, P.; Sall, A.; et al. GloPID-R report on chikungunya, o’nyong-nyong and Mayaro virus, part 2: Epidemiological distribution of o’nyong-nyong virus. Antivir. Res. 2019, 172, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.R.; Downs, W.G.; Wattley, G.H.; Ahin, N.W.; Reese, A.A. Mayaro Virus: A New Human Disease Agent. II. Isolation From Blood of Patients in Trinidad, B.W.I. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1957, 6, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Causey, O.R.; Maroja, O.M. Mayaro Virus: A New Human Disease Agent. III. Investigation of an Epidemic of Acute Febrile Illness on the River Guama in Pará, Brazil, and Isolation of Mayaro Virus as Causative Agent. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1957, 6, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, M.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Lema, A.B.; Eichenwald, H. Epidemic Jungle Fevers Among Okinawan Colonists in the Bolivian Rain Forest. I. Epidemiology. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1959, 8, 372–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDuc, J.W.; Pinheiro, F.P.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P. An Outbreak of Mayaro Virus Disease in Belterra, Brazil. II. Epidemiology. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, R.S.; Silva, E.V.; Carvalho, V.L.; Rodrigues, S.G.; Nunes-Neto, J.P.; Monteiro, H.; Peixoto, V.S.; Chiang, J.O.; Nunes, M.R.; Vasconcelos, P.F. Mayaro fever virus, Brazilian Amazon. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1830–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguste, A.J.; Liria, J.; Forrester, N.L.; Giambalvo, D.; Moncada, M.; Long, K.C.; Moron, D.; de Manzione, N.; Tesh, R.B.; Halsey, E.S.; et al. Evolutionary and Ecological Characterization of Mayaro Virus Strains Isolated during an Outbreak, Venezuela, 2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, D.L.A.; Fonseca, B. Will Mayaro virus be responsible for the next outbreak of an arthropod-borne virus in Brazil? Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 21, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.T.O.; Avilla, C.M.S.; Mogueira, M.L. Mayaro virus: A neglected threat could cause the next worldwide viral epidemic. Future Virol. 2019, 14, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Wu, D. Mayaro virus, a regional or global threat? Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 101462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izurieta, R.O.; Macaluso, M.; Watts, D.M.; Tesh, R.B.; Guerra, B.; Cruz, L.M.; Galwankar, S.; Vermund, S.H. Hunting in the Rainforest and Mayaro Virus Infection: An emerging Alphavirus in Ecuador. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2011, 3, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeiro, M.F.; Fumagalli, M.J.; Dos Anjos, A.B.; Figueiredo, L.T.M. Serological evidence of Mayaro virus infection in blood donors from Sao Carlos, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjian, N.; Riviere-Cinnamond, A. Mayaro virus in Latin America and the Caribbean. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2020, 44, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarrete-Espinosa, J.; Gómez-Dantés, H. [Arbovirus causing hemorrhagic fever at IMSS]. Rev. Med. Inst. Mex. Seguro Soc. 2006, 44, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, C.; Freitas Ribeiro, A.; Chiaravalloti-Neto, F. Mayaro virus distribution in South America. Acta Trop. 2019, 198, 105093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.M.; Azar, S.R.; Haller, S.L.; Langsjoen, R.M.; Cuthbert, C.E.; Ramjag, A.T.; Luo, H.; Plante, K.; Wang, T.; Simmons, G.; et al. Effects of Chikungunya virus immunity on Mayaro virus disease and epidemic potential. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adouchief, S.; Smura, T.; Sane, J.; Vapalahti, O.; Kurkela, S. Sindbis virus as a human pathogen-epidemiology, clinical picture and pathogenesis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2016, 26, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrom, J.O.; Pfeffer, M. Phylogeographic Structure and Evolutionary History of Sindbis Virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 889–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Smura, T.; Lundstrom, J.O.; Pettersson, J.H.; Sironen, T.; Vapalahti, O.; Lundkvist, A.; Hesson, J.C. Introduction and Dispersal of Sindbis Virus from Central Africa to Europe. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundstrom, J.O.; Hesson, J.C.; Schafer, M.L.; Ostman, O.; Semmler, T.; Bekaert, M.; Weidmann, M.; Lundkvist, A.; Pfeffer, M. Sindbis virus polyarthritis outbreak signalled by virus prevalence in the mosquito vectors. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lundstrom, J.O.; Vene, S.; Espmark, A.; Engvall, M.; Niklasson, B. Geographical and temporal distribution of Ockelbo disease in Sweden. Epidemiol. Infect. 1991, 106, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, N.; Weyer, J.; Markotter, W.; Kemp, A.; Leman, P.A.; Dermaux-Msimang, V.; Nel, L.H.; Paweska, J.T. Human cases of Sindbis fever in South Africa, 2006-2010. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, M.; Luukkainen, R.; Toivanen, A. Sindbis Viruses and Other Alphaviruses as a Cause of Human Arthritic Disease. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummer-Korvenkontio, M.; Vapalahti, O.; Kuusisto, P.; Saikku, P.; Manni, T.; Koskela, P.; Nygren, T.; Brummer-Korvenkontio, H.; Vaheri, A. Epidemiology of Sindbis virus infections in Finland 1981-96: Possible factors explaining a peculiar disease pattern. Epidemiol. Infect. 2002, 129, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sane, J.; Guedes, S.; Ollgren, J.; Kurkela, S.; Klemets, P.; Vapalahti, O.; Kela, E.; Lyytikainen, O.; Nuorti, J.P. Epidemic sindbis virus infection in Finland: A population-based case-control study of risk factors. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horling, J.; Vene, S.; Franzen, C.; Niklasson, B. Detection of Ockelbo Virus RNA in Skin Biopsies by Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2004–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurkela, S.; Manni, T.; Myllynen, J.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Clinical and Laboratory Manifestations of Sindbis Virus Infection Prospective Study, Finland, 2002–2003. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 1820–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkela, S.; Helve, T.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Arthritis and arthralgia three years after Sindbis virus infection: Clinical follow-up of a cohort of 49 patients. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 40, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklasson, B.; Espmark, A. Ockelbo Disease: Arthralgia 3-4 Years After Infection With a Sindbis Virus Related Agent. Lancet 1986, 327, 1039–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklasson, B.; Espmark, A.; Lundstrom, J. Occurrence of Arthralgia and Specific IgM Antibodies Three to Four Years after Ockelbo Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 157, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.M.; Hurlbut, H.S.; Work, T.H.; Kingston, J.R.; Frothingham, T.E. Sindbis Virus: A Newly Recognized Arthropodtransmitted Virus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1955, 4, 844–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundström, J.O. Mosquito-borne viruses in western Europe: A review. J. Vector Ecol. J. Soc. Vector Ecol. 1999, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Go, Y.Y.; Balasuriya, U.B.; Lee, C.K. Zoonotic encephalitides caused by arboviruses: Transmission and epidemiology of alphaviruses and flaviviruses. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2014, 3, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storm, N.; Weyer, J.; Markotter, W.; Leman, P.A.; Kemp, A.; Nel, L.H.; Paweska, J.T. Phylogeny of Sindbis virus isolates from South Africa. South. Afr. J. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 28, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergqvist, J.; Forsman, O.; Larsson, P.; Naslund, J.; Lilja, T.; Engdahl, C.; Lindstrom, A.; Gylfe, A.; Ahlm, C.; Evander, M.; et al. Detection and isolation of Sindbis virus from mosquitoes captured during an outbreak in Sweden, 2013. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015, 15, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francy, D.B.; Jaenson, T.G.; Lundstrom, J.O.; Schildt, E.B.; Espmark, A.; Henriksson, B.; Niklasson, B. Ecologic Studies of Mosquitoes and Birds as Hosts of Ockelbo Virus in Sweden and Isolation of Inkoo and Batai Viruses From Mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1989, 41, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sane, J.; Kurkela, S.; Putkuri, N.; Huhtamo, E.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Complete coding sequence and molecular epidemiological analysis of Sindbis virus isolates from mosquitoes and humans, Finland. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, D.K.; Skvortsova, T.M.; Berezina, L.K.; Gromashevsky, V.L.; Yakovlev, B.I.; Gushchin, B.V.; Aristova, V.A.; Sidorava, G.A.; Gushchina, E.L.; Klimenko, S.M.; et al. Isolation of Karelian Fever Agent From Aedes communis Mosquitoes. Lancet 1984, 324, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turell, M.J.; Lundstrom, J.O.; Niklasson, B. Transmission of Ockelbo Virus by Aedes cinereus, Ae, communis, and Ae. excrucians (Diptera Culicidae) Collected in an Enzootic Area in Central Sweden. J. Med. Entomol. 1990, 27, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammels, L.M.; Lindsay, M.D.; Poidinger, M.; Coelen, R.J.; MacKenzie, J.S. Geographic distribution and evolution of Sindbis virus in Australia. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eiden, M.; Ziegler, U.; Keller, M.; Muller, K.; Granzow, H.; Jost, H.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Groschup, M.H. Isolation of sindbis virus from a hooded crow in Germany. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstrom, J.O.; Turell, M.J.; Niklasson, B. Viremia in Three Orders of Birds (Anseriformes, Galliformes and Passeriformes) Inoculated With Ockelbo Virus. J. Wildl. Dis. 1993, 29, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundstrom, J.O.; Lindstrom, K.M.; Olsen, B.; Dufva, R.; Krakower, D.S. Prevalence of sindbis virus neutralizing antibodies among Swedish passerines indicates that thrushes are the main amplifying hosts. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesson, J.C.; Lundstrom, J.O.; Tok, A.; Ostman, O.; Lundkvist, A. Temporal Variation in Sindbis Virus Antibody Prevalence in Bird Hosts in an Endemic Area in Sweden. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, U.; Fischer, D.; Eiden, M.; Reuschel, M.; Rinder, M.; Muller, K.; Schwehn, R.; Schmidt, V.; Groschup, M.H.; Keller, M. Sindbis virus- a wild bird associated zoonotic arbovirus circulates in Germany. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 239, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malherbe, H.; Strickland-Cholmley, M.; Jackson, A.L. Sinbis Virus Infection in Man. Report of a Case With Recovery of Virus From Skin Lesions. S. Afr. Med. J. 1963, 37, 547–552. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, B.M.; McGillivray, G.M.; Dickinson, D.B.; Malherbe, H. Illness caused by Sindbis and West Nile viruses in South Africa. S. Afr. Med. J. 1964, 38, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porath, E.; Fattal, B.; Goldblum, N.; Yofe, J. Occurrence of antibodies to sindbis virus in children from a west nile endemic area. Isr. J. Med Sci. 1965, 1, 88–90. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, V.; Hanna, A.T.; Wahdan, M.H.; Mohamed, J.S.; el-Dawla, K. Prevalence of Sindbis virus antibodies in an Egyptian rural community. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1967, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, R.L.; Bodey, A.S.; Carew, J.S. Sindbis virus infection in Australia. Med. J. Aust. 1969, 2, 1016–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlatos, M.; Smith, C.E. Antibodies to arthropod-borne viruses in greece. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 58, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, M.; Verani, P.; Lopes, M.C.; Gregorig, B. Survey for antibodies against arthropod-borne viruses in man and animals in Italy. II. Serologic status of human beings in a northern Italian region (Gorizia province). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1967, 16, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skogh, M.; Espmark, A. Ockelbo Disease: Epidemic Arthritis-Exanthema Syndrome in Sweden Caused by a Sindbis-virus Like Agent. Lancet 1982, 319, 795–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turunen, M.; Kuusisto, P.; Uggeldahl, P.-E.; Toivanen, A. Pogosta Disease: Clinical Observations During an Outbreak in the Province of North Karelia, Finland. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 37, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroneld, R.; Meurman, O.; Forsen, K.; Lassenius, R. The Prevalence of Antibodies against Viruses Causing Kumlinge and Pogosta Diseases on the Islands of Iniö on the Southwest Coast of Finland. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 21, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, M.; Vainionpaa, R.; Oksi, J.; Luukkainen, R.; Toivanen, A. The prevalence of antibodies against Sindbis-related (Pogosta) virus in different parts of Finland. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkela, S.; Manni, T.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Causative Agent of Pogosta Disease Isolated from Blood and Skin Lesions. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sane, J.; Guedes, S.; Kurkela, S.; Lyytikainen, O.; Vapalahti, O. Epidemiological analysis of mosquito-borne Pogosta disease in Finland, 2009. Euro Surveill. 2010, 15, 19462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espmark, A.; Niklasson, B. Ockelbo disease in Sweden: Epidemiological, clinical, and virological data from the 1982 outbreak. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1984, 33, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, B.M.; Jupp, P.G.; Dos Santos, I.; Meenehan, G.M. Epidemics of West Nile and Sindbis viruses in South Africa with Culex (Culex) univittatus Theobald as vector. S. Afr. J. Sci 1976, 72, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, P.G.; Blackburn, N.K.; Thompson, D.L.; Meenehan, G.M. Sindbis and West Nile virus infections in the Witwatersrand-Pretoria region. S. Afr. Med. J. 1986, 70, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sigei, F.; Nindo, F.; Mukunzi, S.; Ng’ang’a, Z.; Sang, R. Evolutionary analyses of Sindbis virus strains isolated from mosquitoes in Kenya. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2465–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guard, R.W.; McAuliffe, M.J.; Stallman, N.D.; Bramston, B.A. Haemorrhagic manifestations with Sindbis infection. Case report. Pathology 1982, 14, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avizov, N.; Zuckerman, N.; Orshan, L.; Shalom, U.; Yeger, T.; Vapalahti, O.; Israely, T.; Paran, N.; Melamed, S.; Mendelson, E.; et al. High Endemicity and Distinct Phylogenetic Characteristics of Sindbis Virus in Israel. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, R.; Bassal, R.; Shohat, T.; Cohen, D.; Mor, O.; Mendelson, E.; Lustig, Y. Presence of Antibodies against Sindbis Virus in the Israeli Population: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. Viruses 2019, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jost, H.; Bialonski, A.; Storch, V.; Gunther, S.; Becker, N.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J. Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of Sindbis viruses from mosquitoes in Germany. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1900–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jost, H.; Burck-Kammerer, S.; Hutter, G.; Lattwein, E.; Lederer, S.; Litzba, N.; Bock-Hensley, O.; Emmerich, P.; Gunther, S.; Becker, N.; et al. Medical importance of Sindbis virus in south-west Germany. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flexman, J.P.; Smith, D.W.; MacKenzie, J.S.; Fraser, J.R.E.; Bass, S.P.; Hueston, L.; Lindsay, M.D.A.; Cunningham, A.L. A comparison of the diseases caused by Ross River virus and Barmah Forest virus. Med. J. Aust. 1998, 169, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, D.; Sleigh, A.; Ritchie, S. Ross River virus transmission, infection, and disease: A cross-disciplinary review. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 909–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, C.; Aubry, M.; Musso, D.; Teissier, A.; Paulous, S.; Despres, P.; de-Lamballerie, X.; Pastorino, B.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Weinstein, P. New evidence for endemic circulation of Ross River virus in the Pacific Islands and the potential for emergence. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 57, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Tharmarajah, K.; Taylor, A. Ross River virus disease clinical presentation, pathogenesis and current therapeutic strategies. Microbes Infect. 2017, 19, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Lindsay, M.D.; Coelen, R.J.; Broom, A.K.; Hall, R.A.; Smith, D.W. Arboviruses causing human disease in the Australasian zoogeographic region. Arch. Virol. 1994, 136, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, J.R.; Cunningham, A.L.; Mathews, J.D.; Riglar, A. Immune Complexes and Ross River Virus Disease (Epidemic Polyarthritis). Rheumatol. Int. 1988, 8, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanks, G.D. Could Ross River Virus be the next Zika? J. Travel Med. 2019, 26, taz003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, A.D.; Brown, A.M.; Carthew, T.L.; McGrath, B.; Purdie, D.M.; Pandeya, N.; Vecchio, P.C.; Collin, L.C.; Gardner, I.D.; de Looze, F.J.; et al. Natural History of Ross River Virus-Induced Epidemic Polyarthritis. Med. J. Aust. 2002, 177, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harley, D.; Bossingham, D.; Purdie, D.M.; Pandeya, N.; Sleigh, A.C. Ross River Virus Disease in Tropical Queensland: Evolution of Rheumatic Manifestations in an Inception Cohort Followed for Six Months. Med. J. Aust. 2002, 177, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claflin, S.B.; Webb, C.E. Ross River Virus: Many Vectors and Unusual Hosts Make for an Unpredictable Pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, R.C. Ross River Virus: Ecology and Distribution. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesh, R.B.; McLean, R.G.; Shroyer, D.A.; Calisher, C.H.; Rosen, L. Ross River virus (Togaviridae: Alphavirus) infection (epidemic polyarthritis) in American Samoa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 75, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, S.A.; Fanning, I.D.; Phillips, D.A.; Standfast, H.A.; Mcginn, D.; Kay, B.H. Ross River Virus in Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) During the 1994 Epidemic Around Brisbane, Australia. J. Med. Entomol. 1997, 34, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, R.L.; Whitehead, R.H.; Gorman, B.M.; O’gower, A.K. The Isolation of a Third Group A Arbovirus in Australia, with Preliminary Observations on its Relationship to Epidemic Polyarthritis. Aust. J. Sci. 1963, 26, 183–184. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, R.C. Mosquito-borne Arboviruses in Australia: The Current Scene and Implications of Climate Change for Human Health. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, D.; Ritchie, S.; Phillips, D.; van den Hurk, A. Mosquito Isolates of Ross River Virus From Cairns, Queensland, Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 62, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shope, R.E.; Anderson, S.G. The virus aetiology of epidemic exanthem and polyarthritis. Med. J. Aust. 1960, 47, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, R.L.; Carley, J.G.; Best, J.C. Isolation of Ross River virus from man. Med. J. Aust. 1972, 1, 1083–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaskov, J.G.; Mataika, J.U.; Lawrence, G.W.; Rabukawaqa, V.; Tucker, M.M.; Miles, J.A.; Dalglish, D.A. An Epidemic of Ross River Virus Infection in Fiji, 1979. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, L.; Gubler, D.J.; Bennett, P.H. Epidemic Polyarthritis (Ross River) Virus Infection in the Cook Islands. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly-Hope, L.A.; Purdie, D.M.; Kay, B.H. Ross River Virus Disease in Australia, 1886–1998, with Analysis of Risk Factors Associated with Outbreaks. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.C.; Kay, B.H. Medical entomology: Changes in the spectrum of mosquito-borne disease in Australia and other vector threats and risks, 1972–2004. Aust. J. Entomol. 2004, 43, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.C.; Shivas, M.A.; May, F.J.; Pyke, A.T.; Onn, M.B.; Lodo, K.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; McMahon, J.L.; Montgomery, B.L.; Darbro, J.M.; et al. Epidemiologic, Entomologic, and Virologic Factors of the 2014-15 Ross River Virus Outbreak, Queensland, Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knope, K.; Doggett, S.L.; Jansen, C.C.; Johansen, C.A.; Kurucz, N.; Feldman, R.; Lynch, S.E.; Hobby, M.P.; Sly, A.; Jardine, A.; et al. Arboviral diseases and malaria in Australia, 2014–15: Annual report of the National Arbovirus and Malaria Advisory Committee. Commun. Dis. Intell. 2019, 43, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, E.B.; Peel, A.J.; Reid, S.A.; Jansen, C.C.; McCallum, H. The non-human reservoirs of Ross River virus: A systematic review of the evidence. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fauci, A.S.; Morens, D.M. Zika Virus in the Americas—Yet Another Arbovirus Threat. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetsarkin, K.A.; Chen, R.; Weaver, S.C. Interspecies transmission and chikungunya virus emergence. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 16, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsetsarkin, K.A.; Chen, R.; Yun, R.; Rossi, S.L.; Plante, K.S.; Guerbois, M.; Forrester, N.; Perng, G.C.; Sreekumar, E.; Leal, G.; et al. Multi-peaked adaptive landscape for chikungunya virus evolution predicts continued fitness optimization in Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C. Arrival of chikungunya virus in the new world: Prospects for spread and impact on public health. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahid, B.; Ali, A.; Rafique, S.; Idrees, M. Global expansion of chikungunya virus: Mapping the 64-year history. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 58, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yactayo, S.; Staples, J.E.; Millot, V.; Cibrelus, L.; Ramon-Pardo, P. Epidemiology of Chikungunya in the Americas. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, S441–S445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.S.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D.L. Emergence and re-emergence of mosquito-borne arboviruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
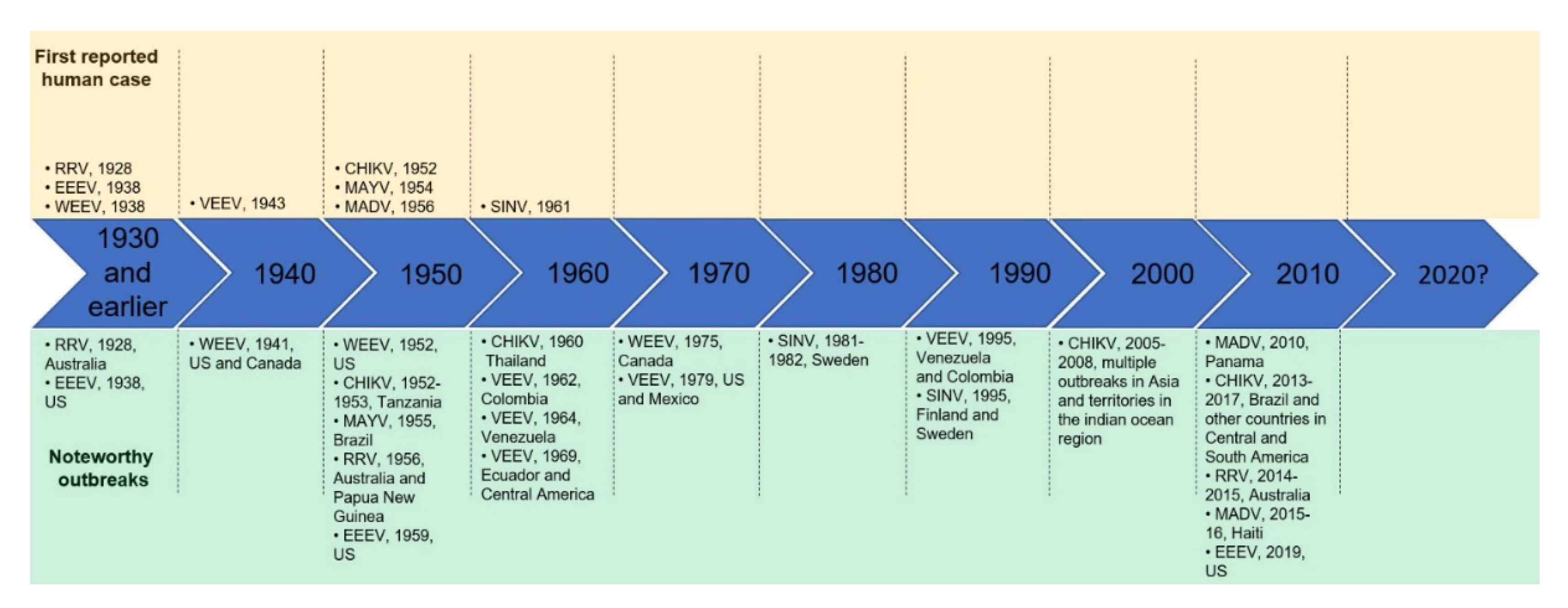
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azar, S.R.; Campos, R.K.; Bergren, N.A.; Camargos, V.N.; Rossi, S.L. Epidemic Alphaviruses: Ecology, Emergence and Outbreaks. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081167
Azar SR, Campos RK, Bergren NA, Camargos VN, Rossi SL. Epidemic Alphaviruses: Ecology, Emergence and Outbreaks. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(8):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081167
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzar, Sasha R., Rafael K. Campos, Nicholas A. Bergren, Vidyleison N. Camargos, and Shannan L. Rossi. 2020. "Epidemic Alphaviruses: Ecology, Emergence and Outbreaks" Microorganisms 8, no. 8: 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081167
APA StyleAzar, S. R., Campos, R. K., Bergren, N. A., Camargos, V. N., & Rossi, S. L. (2020). Epidemic Alphaviruses: Ecology, Emergence and Outbreaks. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081167





