Phytophthora Diversity in Pennsylvania Nurseries and Greenhouses Inferred from Clinical Samples Collected over Four Decades
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation, Morphological Characterization, and Culture Storage
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
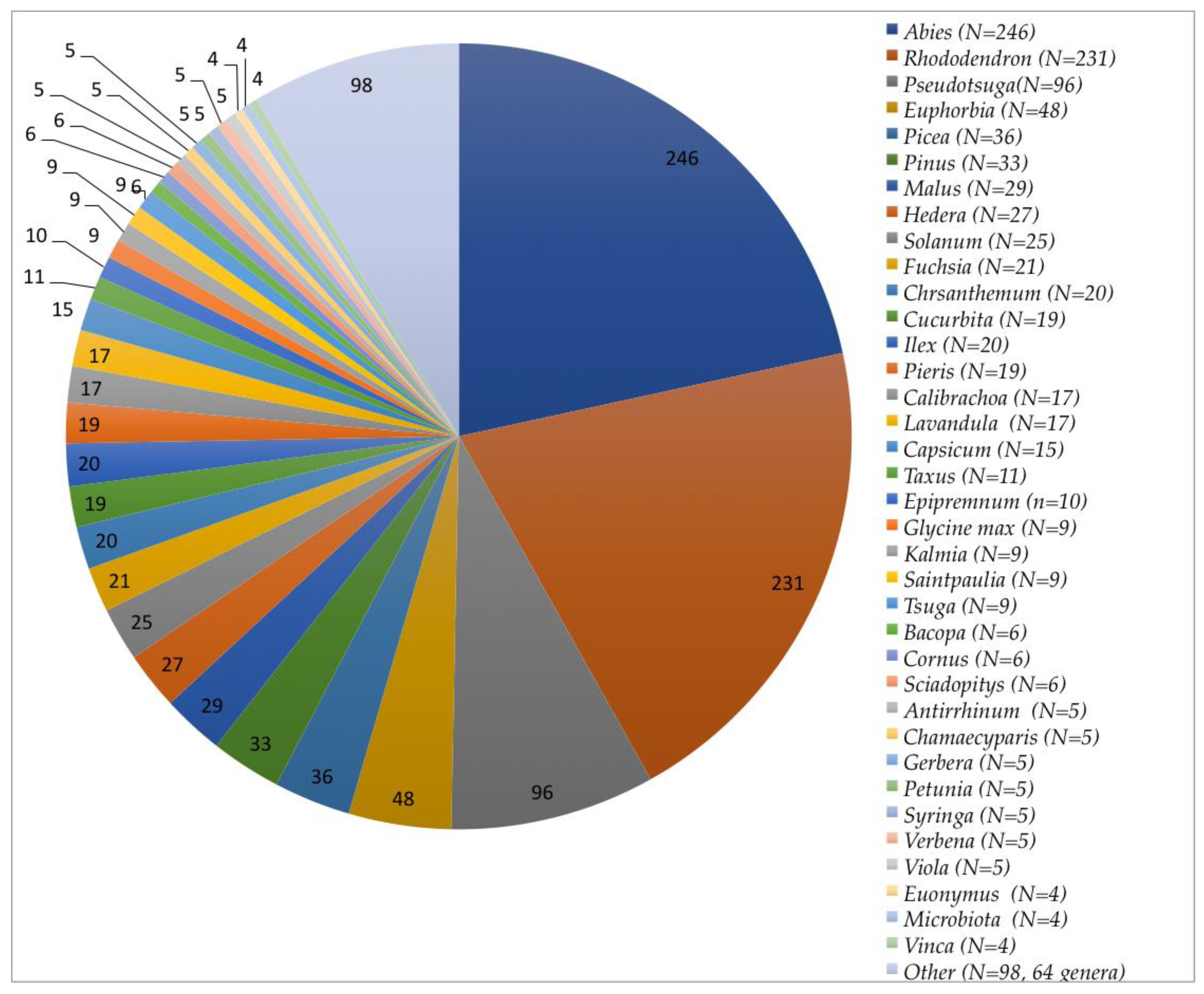
3. Results
3.1. Collection and Identification of Isolates
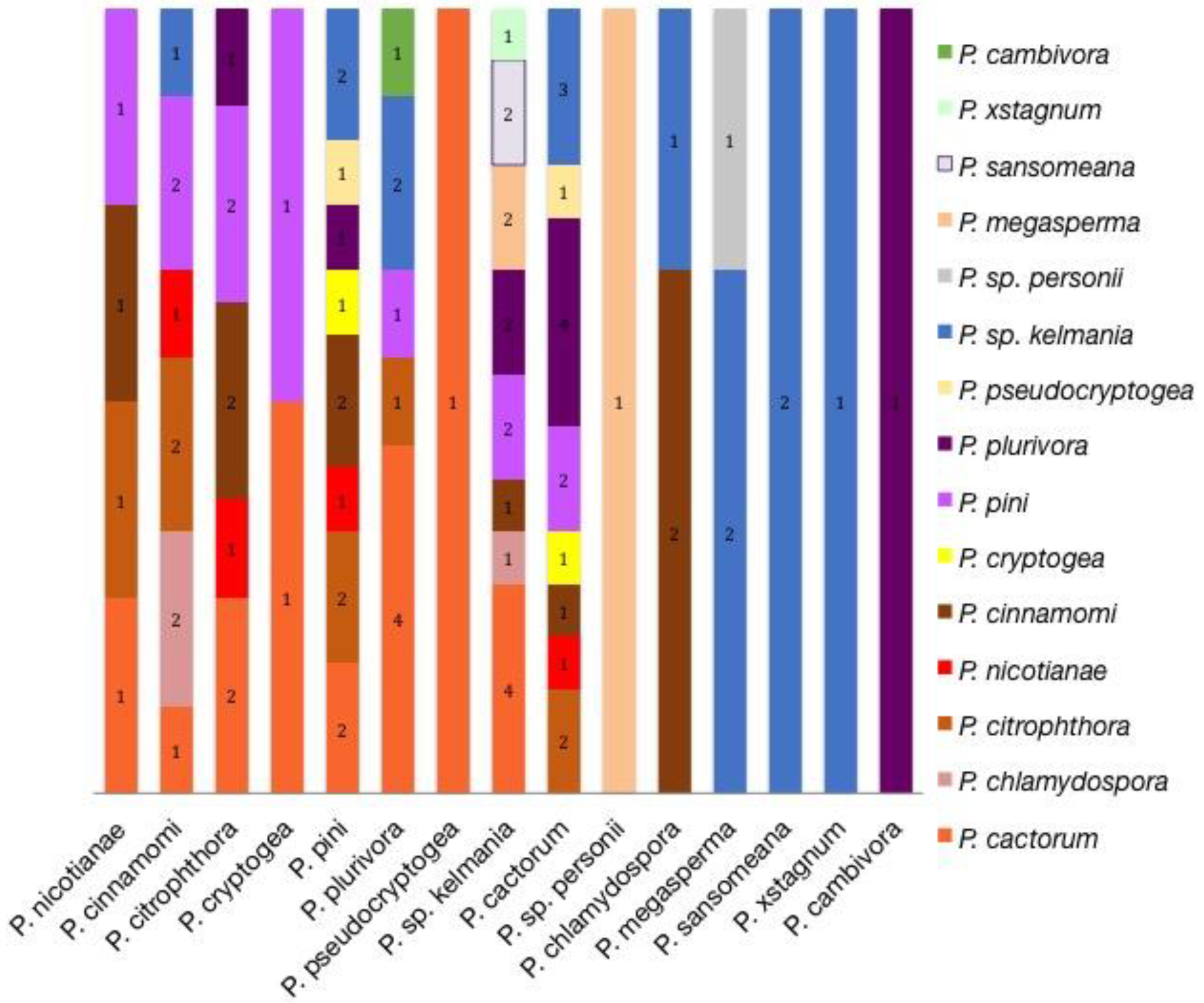
3.2. Patterns within Clades
3.2.1. Patterns Associated with Clade 1 Species
3.2.2. Patterns Associated with Clade 2 Species
3.2.3. Patterns Associated with Clade 4 Species
3.2.4. Patterns Associated with Clade 5 Species
3.2.5. Patterns Associated with Clade 6 Species
3.2.6. Patterns Associated with Clade 7 Species
3.2.7. Patterns Associated with Clade 8 Species
3.2.8. Patterns Associated with Clade 9 Species
3.2.9. A Potential New Species Originated from Juniperus horizontalis Roots
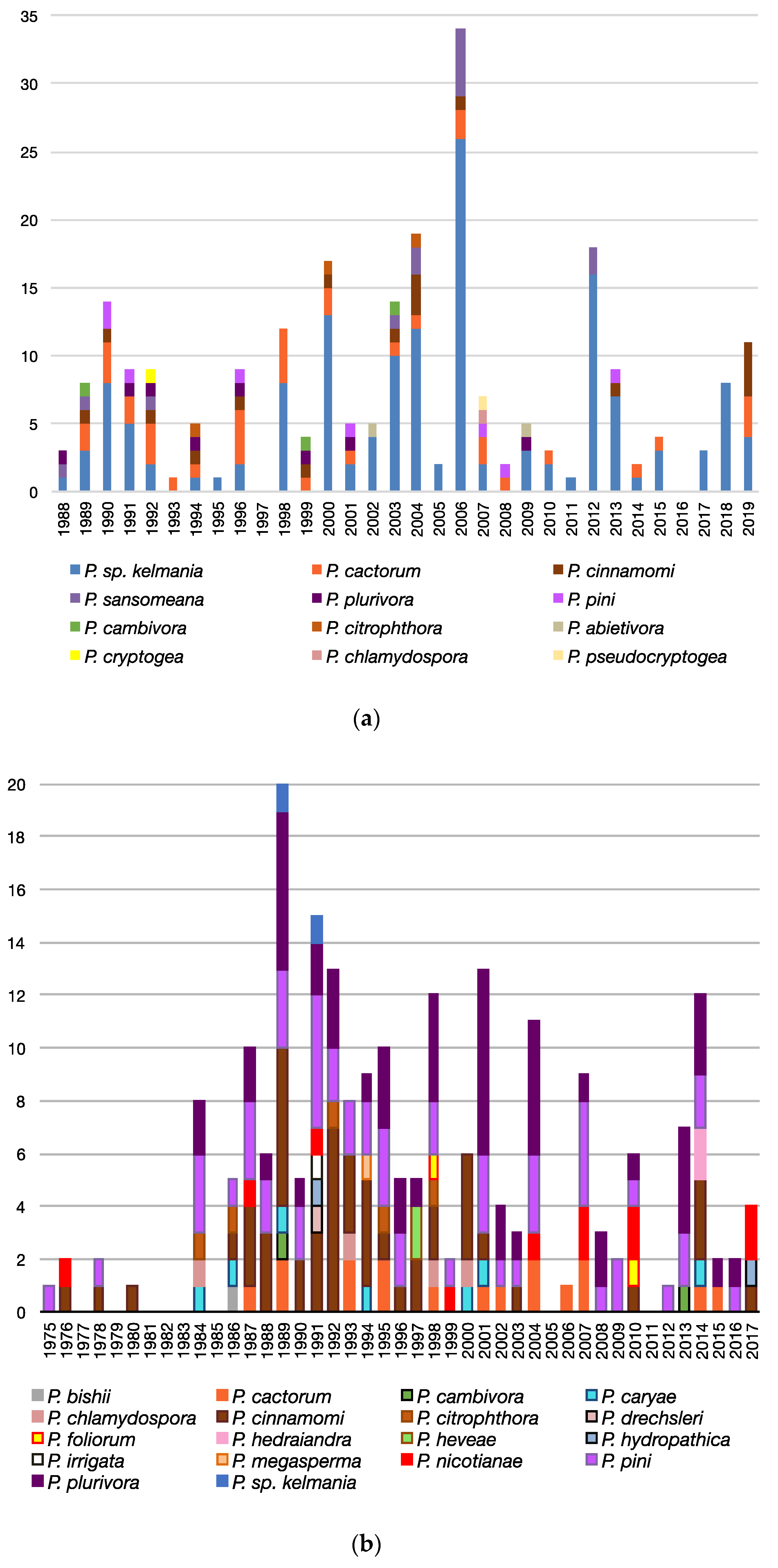
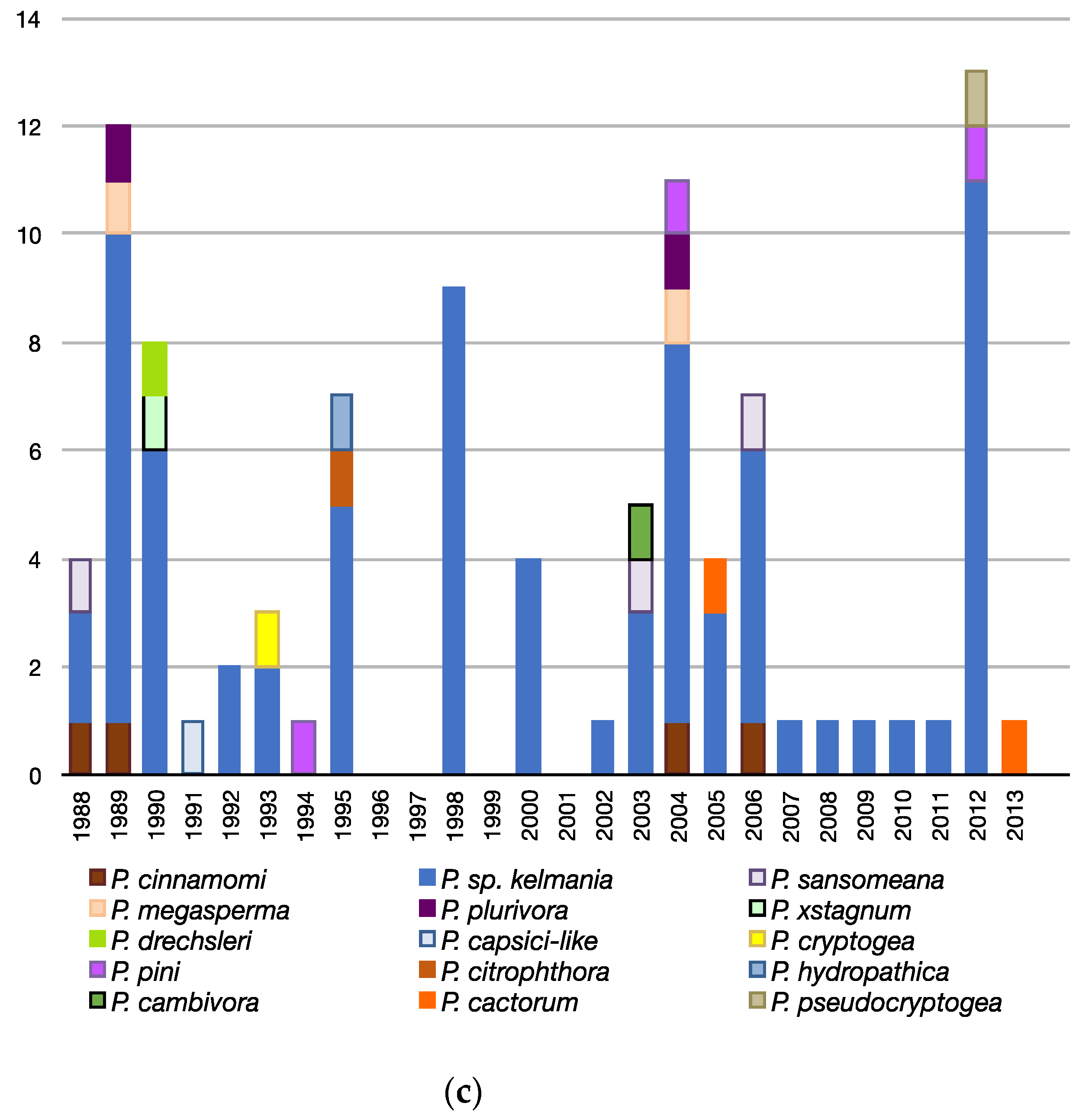
3.3. Patterns Observed Over Time
3.3.1. Geographic Occurrence of Species and Samples
3.3.2. Co-Isolations
3.3.3. Trends Associated with Abies, Rhododendron, and Pseudotsuga
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibbs, J.N. Intercontinental Epidemiology of Dutch Elm Disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1978, 16, 287–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhold, A.M.; Macdonald, W.L.; Bergdahl, D.; Mastro, V.C. Invasion by Exotic Forest Pests: A Threat to Forest Ecosystems. For. Sci. 1995, 41, a0001–z0001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, D.M.; Garbelotto, M.; Davidson, J.M.; Slaughter, G.W.; Koike, S.T. Phytophthora ramorum as the Cause of Extensive Mortality of Quercus spp. and Lithocarpus densiflorus in California. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werres, S.; Marwitz, R.; Man In‘t veld, W.A.; De Cock, A.W.; Bonants, P.J.; De Weerdt, M.; Themann, K.; Ilieva, E.; Baayen, R.P. Phytophthora ramorum sp. nov., a new pathogen on Rhododendron and Viburnum. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Goheen, E.M.; Frankel, S.J. Phytophthora biodiversity: How many Phytophthora species are there? Presented at the 4th Meeting of IUFRO Working Party, Monterey, CA, USA, 9 February 2007; pp. 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M.; Mizubuti, E.S.G.; Goodwin, S.B.; Fry, W.E. Sensitivity to Protectant Fungicides and Pathogenic Fitness of Clonal Lineages of Phytophthora infestans in the United States. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, D.E.L.; Drenth, A.; Duncan, J.M.; Wagels, G.M.; Brasier, C.M. A Molecular Phylogeny of Phytophthora and Related Oomycetes. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2000, 30, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tyler, B.M.; Hong, C. An expanded phylogeny for the genus Phytophthora. IMA Fungus 2017, 8, 355–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, S.N. Comparison of Two Media Selective for Phytophthora and Pythium Species. Plant Dis. 1986, 70, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, A.J.; Jeffers, S.N. Detecting Multiple Species of Phytophthora in Container Mixes from Ornamental Crop Nurseries. Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, S.N. Enhancing Detection of Phytophthora cactorum in Naturally Infested Soil. Phytopathology 1987, 77, 1475–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.N.; Blair, J.E.; Coffey, D. A combined mitochondrial and nuclear multilocus phylogeny of the genus Phytophthora. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 66, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünwald, N.J.; Martin, F.N.; Larsen, M.M.; Sullivan, C.M.; Press, C.M.; Coffey, M.D.; Hansen, E.M.; Parke, J.L. Phytophthora-ID.org: A Sequence-Based Phytophthora Identification Tool. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroon, L.; Bakker, F.; Bosch, G.V.D.; Bonants, P.; Flier, W. Phylogenetic analysis of Phytophthora species based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2004, 41, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, Z.G.; Burgess, T.I.; Bienapfl, J.C.; Redford, A.J.; Coffey, M.; Knight, L. IDphy: Molecular and Morphological Identification of Phytophthora Based on the Types. Available online: https://idtools.org/id/phytophthora/index.php (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Blair, J.E.; Coffey, D.; Park, S.-Y.; Geiser, D.M.; Kang, S. A multi-locus phylogeny for Phytophthora utilizing markers derived from complete genome sequences. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, T.D.; Martin, F.N.; Coffey, D. Development of Rapid Isothermal Amplification Assays for Detection of Phytophthora spp. in Plant Tissue. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hong, C. Differential Usefulness of Nine Commonly Used Genetic Markers for Identifying Phytophthora Species. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O.; Dufayard, J.F. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Schultes, N.P.; Lamondia, J.; Cowles, R.S. Phytophthora abietivora, A New Species Isolated from Diseased Christmas Trees in Connecticut, U.S.A. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaiefarahani, B.; Mostowfizadeh-Ghalamfarsa, R.; Hardy, G.E.S.J.; Burgess, T.I. Species from within the Phytophthora cryptogea complex and related species, P. erythroseptica and P. sansomeana, readily hybridize. Fungal Biol. 2016, 120, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.Z.; Uematsu, S.; Kimishima, E.; Kanto, T.; Kusunoki, M.; Motohashi, K.; Ishiguro, Y.; Suga, H.; Kageyama, K. Two plant pathogenic species of Phytophthora associated with stem blight of Easter lily and crown rot of lettuce in Japan. Mycoscience 2015, 56, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienapfl, J.C.; Balci, Y. Movement of Phytophthora spp. in Maryland’s Nursery Trade. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakabe, L.E.; Blomquist, C.L.; Thomas, S.L.; Macdonald, J.D. Identification and Frequency of Phytophthora Species Associated with Foliar Diseases in California Ornamental Nurseries. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeever, K.M.; Chastagner, G.A. A Survey of Phytophthora spp. Associated with Abiesin U.S. Christmas Tree Farms. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.M.; Goheen, D.J.; Jules, E.S.; Ullian, B. Managing Port-Orford-Cedar and the Introduced Pathogen Phytophthora lateralis. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabima, J.; Coffey, D.; Zazada, I.A.; Grünwald, N.J.; Zasada, I.A. Populations of Phytophthora rubi Show Little Differentiation and High Rates of Migration Among States in the Western United States. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanu, B.; Hunter, G.C.; Linaldeddu, B.T.; Franceschini, A.; Maddau, L.; Jung, T.; Denman, S. A taxonomic re-evaluation reveals that Phytophthora cinnamomiandP. cinnamomivar.parvisporaare separate species. For. Pathol. 2013, 44, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzburg, K.; Hartzog, H.; Landry, C.; Rogers, J.; Randall-Schadel, B. Prioritization of Phytophthora of concern to the United States; USDA PERAL APHIS PPQ CPHST: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, M.J.; Gerdemann, J.W. Root and stem rot soybean caused by Phytophthora sojae n. sp. Phytopathology 1958, 48, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Naher, M.; Motohash, K.; Watanabe, H.; Chikuo, Y.; Senda, M.; Suga, H.; Brasier, C.; Kageyama, K. Phytophthora chrysanthemi sp. nov., a new species causing root rot of chrysanthemum in Japan. Mycol. Prog. 2010, 10, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Martin, D.E.; Taylor, N.J.; Gabriel, C.K.; Hand, F.P. Occurrence of Phytophthora chrysanthemi Causing Root and Stem Rot on Garden Mums in the United States. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney-Latham, S.; Blomquist, C.; Kosta, K.L.; Gou, Y.Y.; Woods, P.W.; Guo, Y.Y.; Soriano, M.C. Phytophthora Species Are Common on Nursery Stock Grown for Restoration and Revegetation Purposes in California. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahoo, R.S.; Lamour, K. Interspecific hybridization and apomixis between Phytophthora capsiciand Phytophthora tropicalis. Mycologia 2008, 100, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.; Burgess, T.I. Re-evaluation of Phytophthora citricola isolates from multiple woody hosts in Europe and North America reveals a new species, Phytophthora plurivora sp. nov. Persoonia 2009, 22, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, P.; Burgess, T.I.; Barber, P.; Shearer, B.; Stukely, M.; Hardy, G.E.S.J.; Jung, T. Phytophthora multivora sp. nov., a new species recovered from declining Eucalyptus, Banksia, Agonis and other plant species in Western Australia. Persoonia 2009, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazee, N.J.; Wick, R.L.; Hulvey, J.P. Phytophthora species recovered from the Connecticut River Valley in Massachusetts, USA. Mycologia 2016, 108, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delshad, D.; Mostowfizadeh-Ghalamfarsa, R.; Safaiefarahani, B. Potential host range and the effect of temperature on the pathogenicity of Phytophthora pseudocryptogea and its close relatives. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, L.; Tjosvold, S.; Chambers, D.; Garbelotto, M. Control of Phytophthora species in plant stock for habitat restoration through best management practices. Plant Pathol. 2018, 68, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, S.J.; Alexander, J.; Benner, D.; Hillman, J.; Shor, A. Phytophthora pathogens threaten rare habitats and conservation plants. Sibbaldia 2020, 18, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bourret, T.B.; Choudhury, R.A.; Mehl, H.K.; Blomquist, C.L.; McRoberts, N.; Rizzo, D.M. Multiple origins of downy mildews and mito-nuclear discordance within the paraphyletic genus Phytophthora. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Richardson, P.A.; Hong, C. Phytophthora ×stagnum nothosp. nov., a New Hybrid from Irrigation Reservoirs at Ornamental Plant Nurseries in Virginia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Gallegly, M.E.; Kong, P.; Richardson, P.A. Phytophthora pini Leonian resurrected to distinct species status. Mycologia 2011, 103, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaiefarahani, B.; Mostowfizadeh-Ghalamfarsa, R.; Hardy, G.E.S.J.; Burgess, T.I. Re-evaluation of the Phytophthora cryptogea species complex and the description of a new species, Phytophthora pseudocryptogea sp. nov. Mycol. Prog. 2015, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, C.M.; Cooke, D.; Duncan, J.M.; Hansen, E.M. Multiple new phenotypic taxa from trees and riparian ecosystems in Phytophthora gonapodyides-P. megasperma ITS Clade 6, which tend to be high-temperature tolerant and either inbreeding or sterile. Mycol. Res. 2003, 107, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moralejo, E.; Pérez-Sierra, A.M.; Alvarez, L.A.; Belbahri, L.; Lefort, F.; Descals, E. Multiple alien Phytophthora taxa discovered on diseased ornamental plants in Spain. Plant Pathol. 2009, 58, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwingle, B.W.; Smith, J.A.; Blanchette, R.A. Phytophthora Species Associated with Diseased Woody Ornamentals in Minnesota Nurseries. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamour, K.; Daughtrey, M.L.; Benson, D.M.; Hwang, J.; Hausbeck, M.K. Etiology of Phytophthora drechsleri and P. nicotianae (=P. parasitica) Diseases Affecting Floriculture Crops. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Burgess, T.I.; Webster, J.L.; Ciampini, J.A.; White, D.; Hardy, G.E.S.; Stukely, M.J.C. Re-evaluation of Phytophthora Species Isolated During 30 Years of Vegetation Health Surveys in Western Australia Using Molecular Techniques. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bertier, L.; Leus, L.; D’Hondt, L.; De Cock, A.W.A.M.; Höfte, M. Host Adaptation and Speciation through Hybridization and Polyploidy in Phytophthora. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, T.I. Molecular Characterization of Natural Hybrids Formed between Five Related Indigenous Clade 6 Phytophthora Species. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molnar, C.; Nikolaeva, E.; Kim, S.; Olson, T.; Bily, D.; Kim, J.-E.; Kang, S. Phytophthora Diversity in Pennsylvania Nurseries and Greenhouses Inferred from Clinical Samples Collected over Four Decades. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071056
Molnar C, Nikolaeva E, Kim S, Olson T, Bily D, Kim J-E, Kang S. Phytophthora Diversity in Pennsylvania Nurseries and Greenhouses Inferred from Clinical Samples Collected over Four Decades. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(7):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071056
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolnar, Cody, Ekaterina Nikolaeva, Seonghwan Kim, Tracey Olson, Devin Bily, Jung-Eun Kim, and Seogchan Kang. 2020. "Phytophthora Diversity in Pennsylvania Nurseries and Greenhouses Inferred from Clinical Samples Collected over Four Decades" Microorganisms 8, no. 7: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071056
APA StyleMolnar, C., Nikolaeva, E., Kim, S., Olson, T., Bily, D., Kim, J.-E., & Kang, S. (2020). Phytophthora Diversity in Pennsylvania Nurseries and Greenhouses Inferred from Clinical Samples Collected over Four Decades. Microorganisms, 8(7), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8071056




