Cultivable Bacterial Communities in Brines from Perennially Ice-Covered and Pristine Antarctic Lakes: Ecological and Biotechnological Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
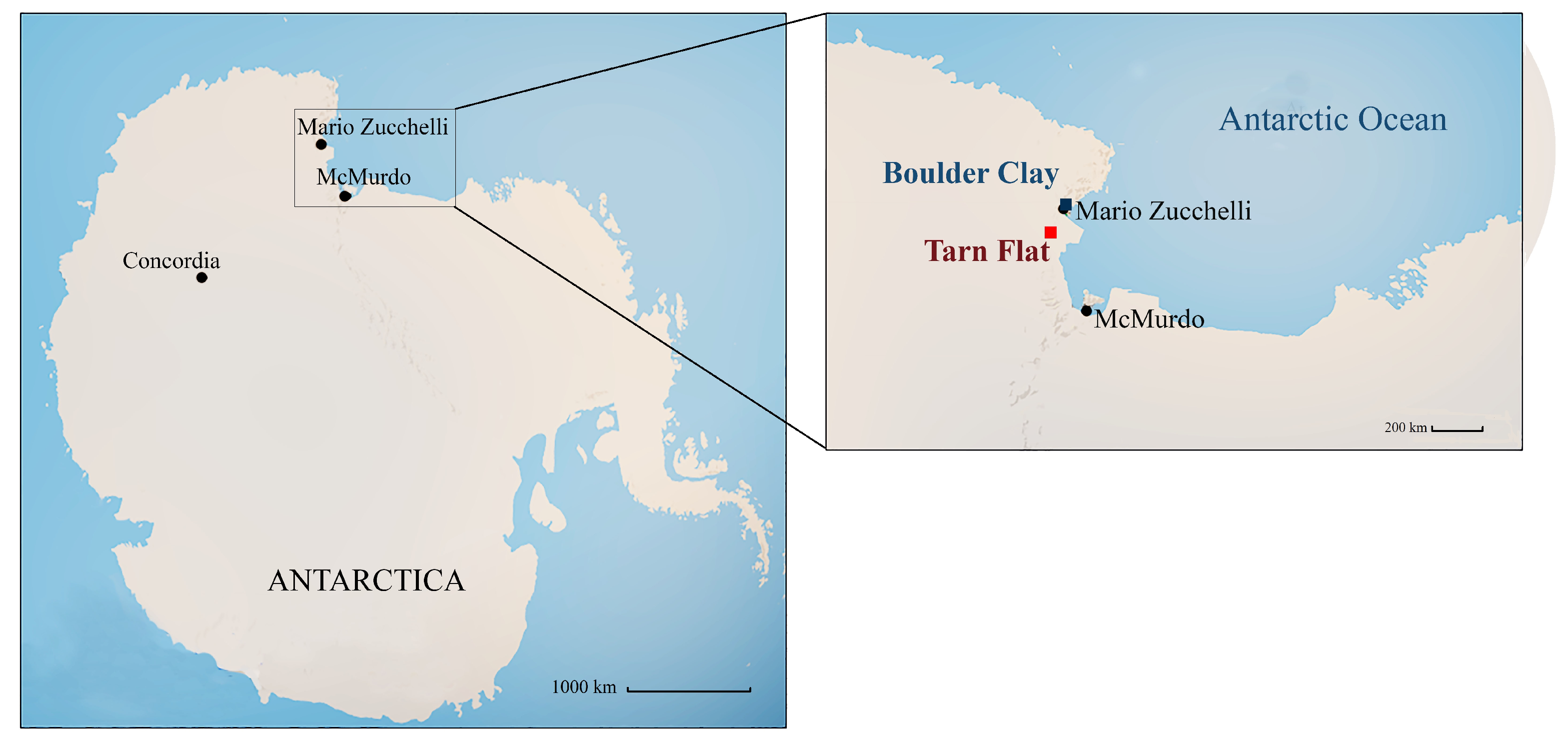
2.1. Study Areas and Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Analyses
2.3. Cultivable Bacterial Community
2.3.1. Isolation of Heterotrophic Bacteria
2.3.2. PCR-Amplification of 16S rRNA Genes
2.3.3. Sequencing and Analysis of the 16S rRNA Genes
2.3.4. Culture Conditions for Bacterial Growth
2.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Heavy Metal Tolerance
2.4.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility
2.4.2. Heavy Metal Tolerance
2.5. Biotechnological Potential of Bacterial Isolates
2.5.1. Oxidation of Hydrocarbons
2.5.2. Oxidation of Polychlorobiphenyls
2.5.3. Extracellular Enzymes and Hydrolysis of Complex Substrata
2.5.4. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth
2.5.5. Other Enzymes
2.5.6. Production of Extracellular Polymeric Substances
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
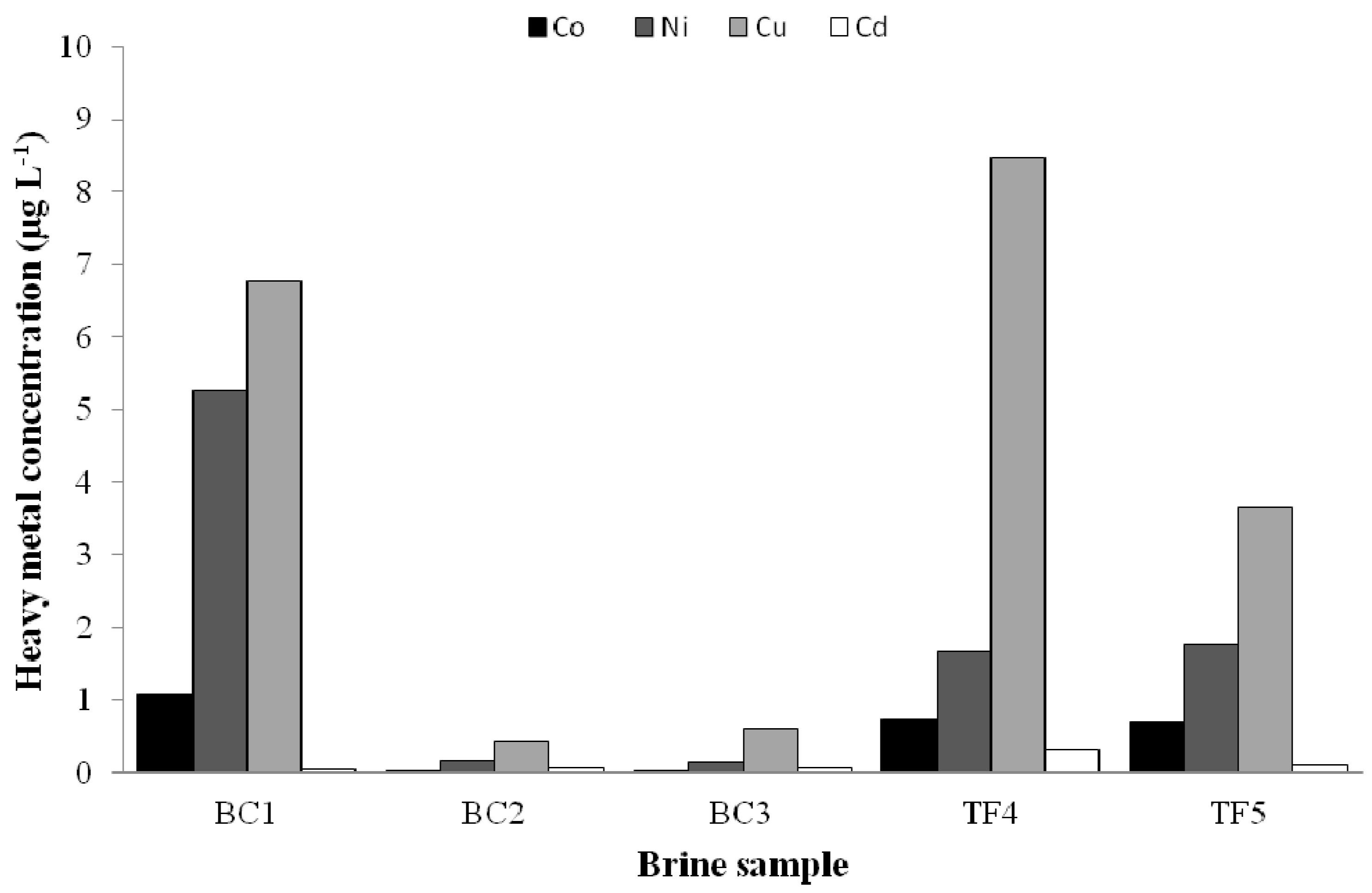
3.1. Chemical Analyses
3.2. Cultivable Bacteria Community
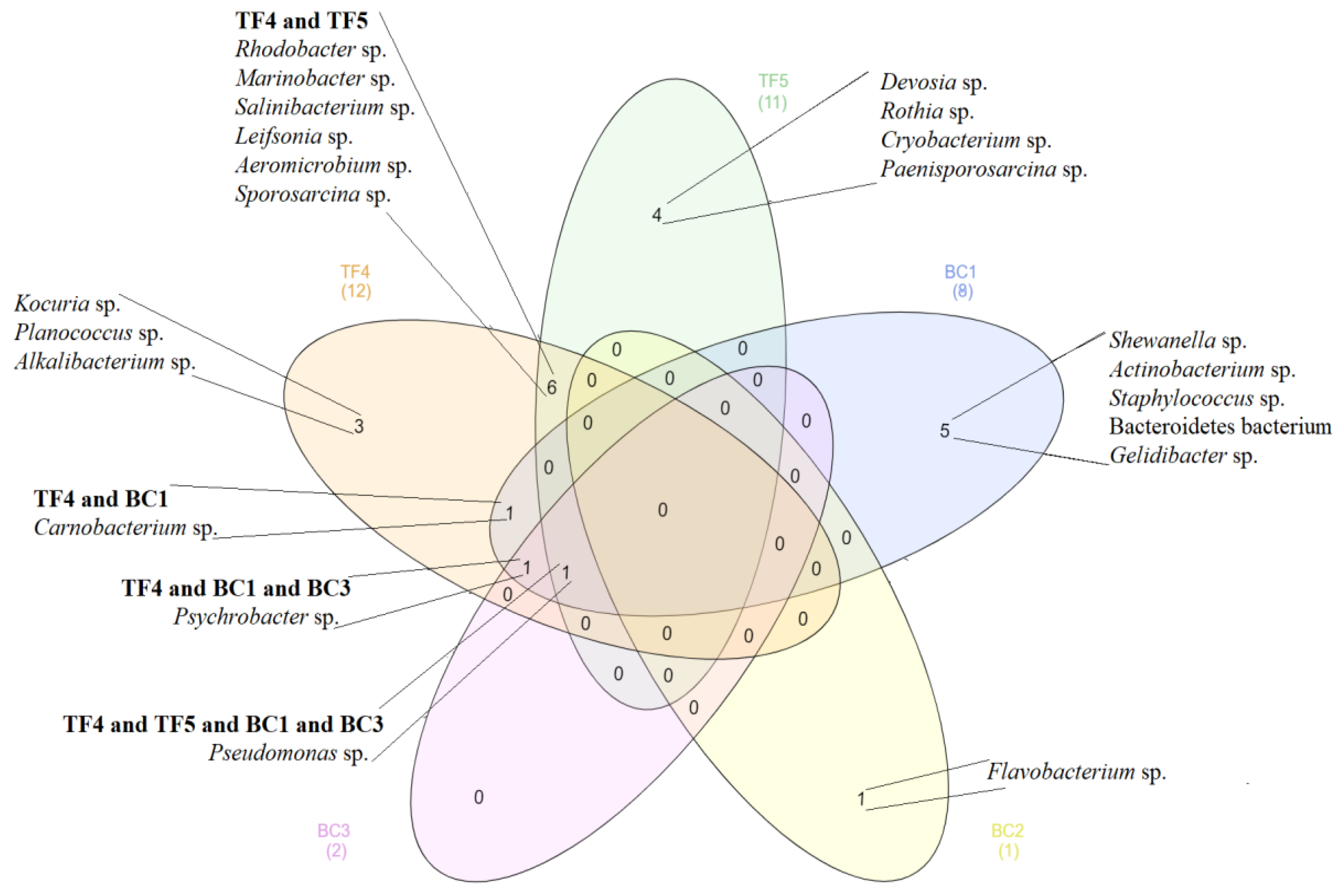
3.2.1. Bacterial Isolation
3.2.2. Bacterial Identification
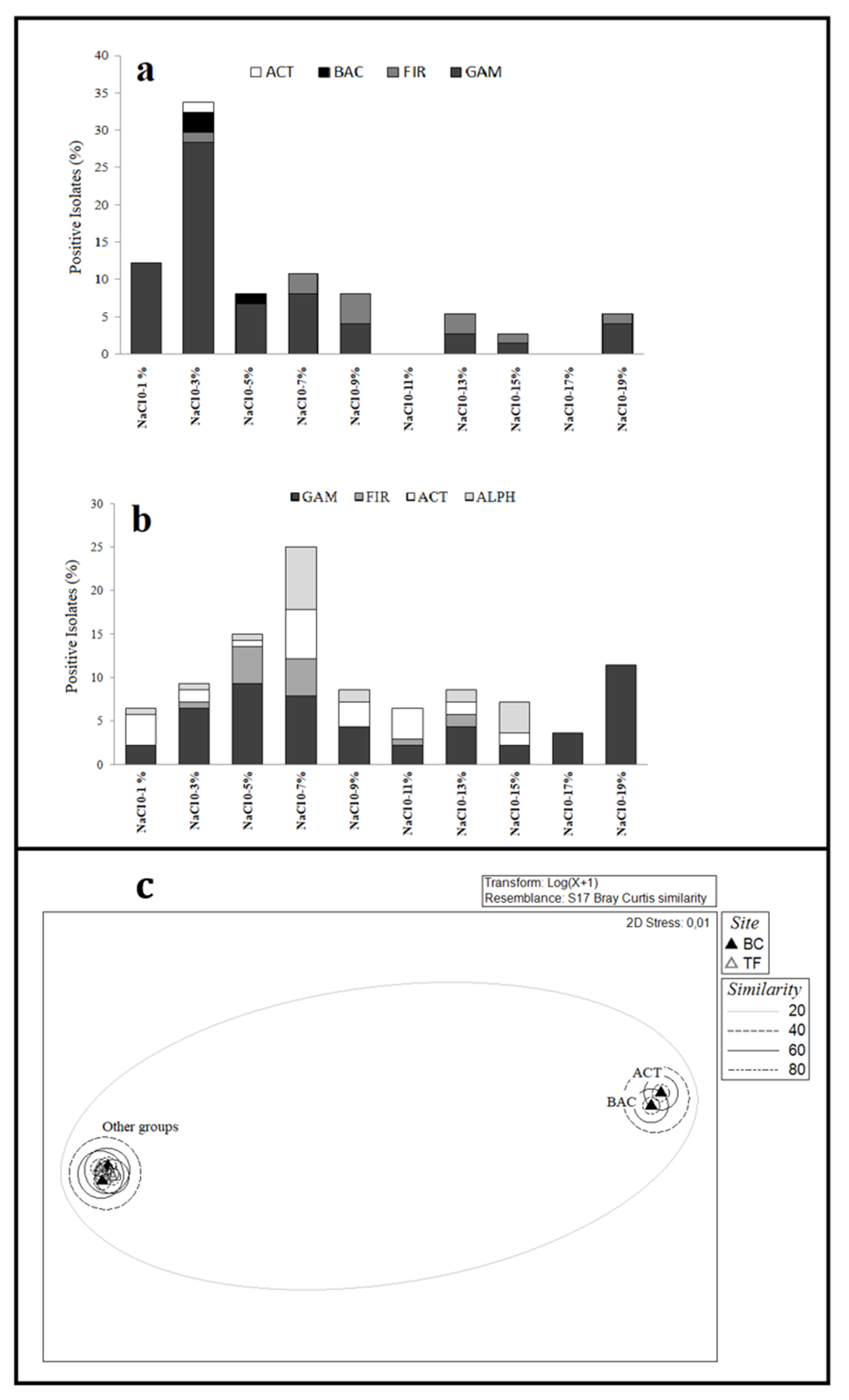
3.2.3. Growth Conditions of Bacterial Isolates
3.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility and Heavy Metal Tolerance
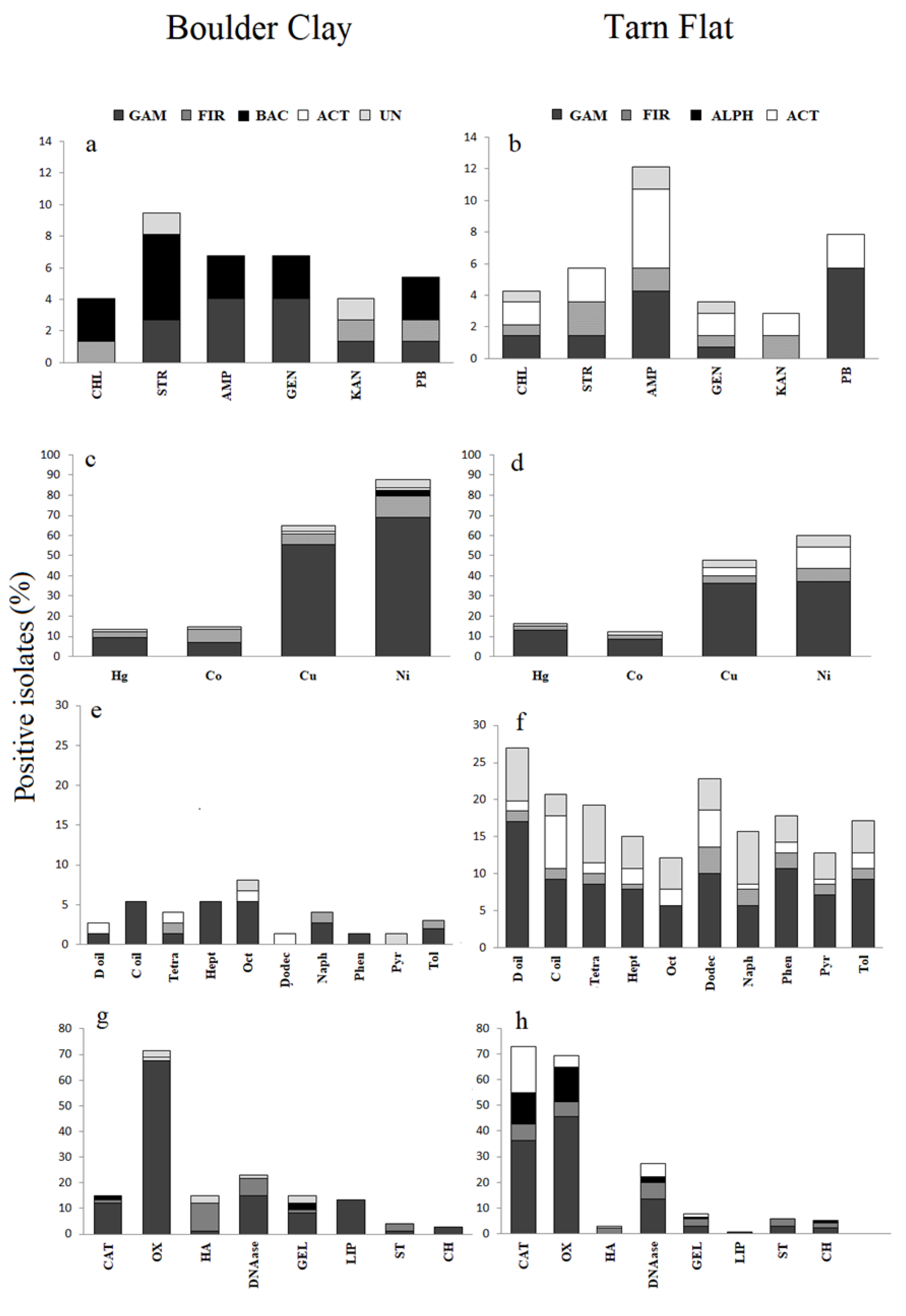
3.3.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility
3.3.2. Heavy Metal Tolerance
3.4. Biotechnological Potential of Bacterial Isolates
3.4.1. Oxidation of Hydrocarbons
3.4.2. Oxidation of Polychlorobiphenyls
3.4.3. Extracellular Enzymes and Hydrolysis of Complex Substrata
3.4.4. Other Enzymes
3.4.5. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth
3.4.6. Production of Extracellular Polymeric Substances
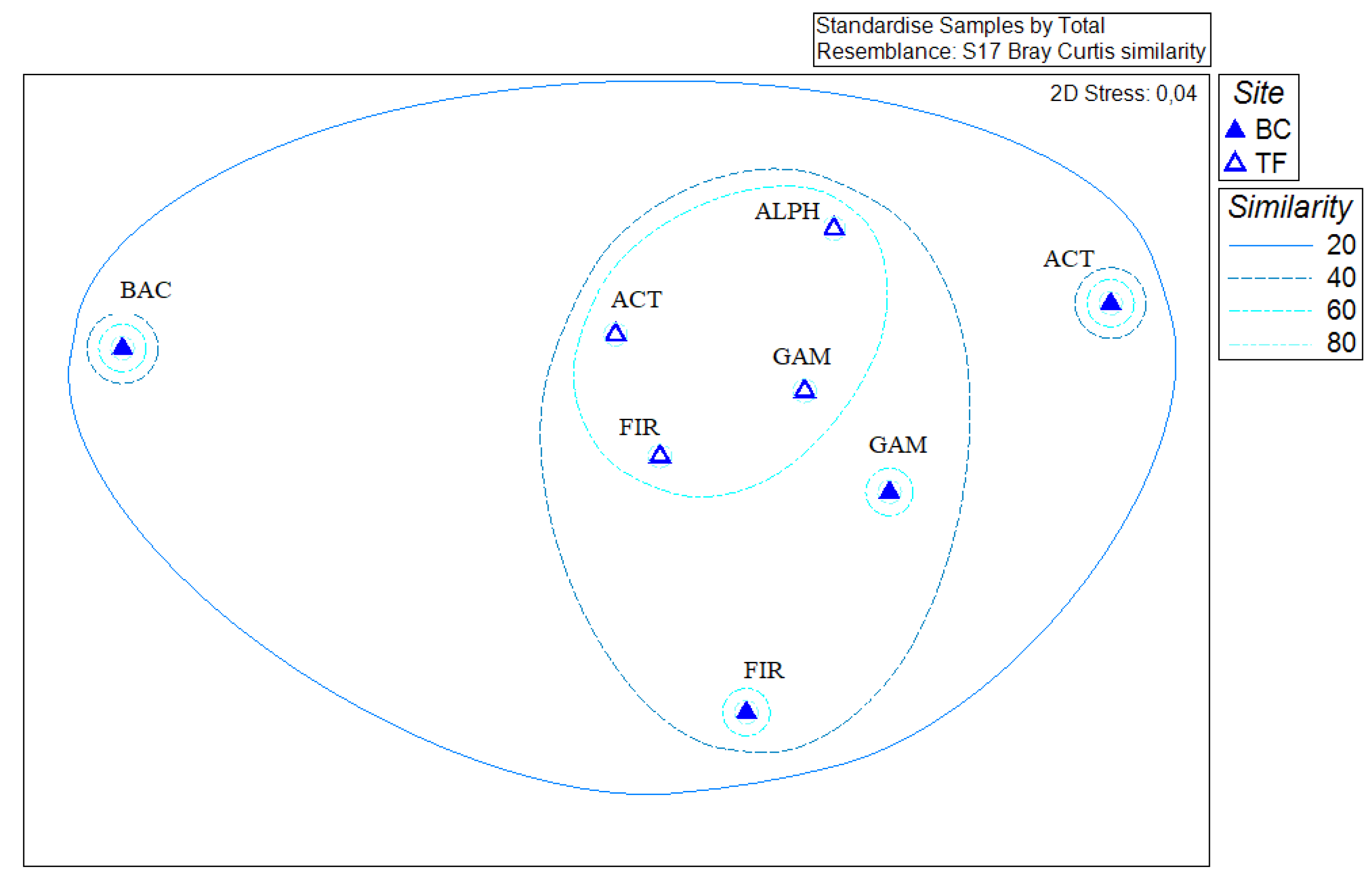
3.5. Statistical Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, A.E.; Kenig, F.; Fritsen, C.H.; McKay, C.P.; Cawley, K.M.; Edwards, R.; Kuhn, E.; McKnight, D.M.; Ostrom, N.E.; Peng, V.; et al. Microbial life at −13°C in the brine of an ice-sealed Antarctic lake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20626–20631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, J.; Head, J.; Levy, J.S.; Marchant, D.R. Don Juan Pond, Antarctica: Near-surface CaCl2-brine feeding Earth’s most saline lake and implications for Mars. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, J.D.; Sletten, R.S.; Prentice, M.L. Soluble salt accumulations in Taylor Valley, Antarctica: Implications for paleolakes and Ross Sea Ice Sheet dynamics. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2013, 118, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, H.A.; Doran, P.T.; Wagner, B.; Kenig, F.; Fritsen, C.H.; Arcone, S.A.; Kuhn, E.; Ostrom, N.E.; Warnock, J.P.; Murray, A.E. Stratigraphy of Lake Vida, Antarctica: Hydrologic implications of 27 m of ice. Cryosphere 2015, 9, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikucki, J.; Auken, E.; Tulaczyk, S.R.; Virginia, A.; Schamper, C.; Sørensen, K.I.; Doran, P.T.; Dugan, H.; Foley, N. Deep groundwater and potential subsurface habitats beneath an Antarctic dry valley. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, E.; Dalle Fratte, M.; Azzaro, M.; Guglielmin, M. Pressurized brines in continental Antarctica as a possible analogue of Mars. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgeley, J.A.; Pettit, E.C.; Carr, C.G.; Tulaczyk, S.; Mikucki, J.A.; Lyons, W.B.; MIDGE Science Team. An englacial hydrologic system of brine within a cold glacier: Blood Falls, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.; Siegert, M. A fourth inventory of Antarctic subglacial lakes. Antarc. Sci. 2012, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, M.J.; Ross, N.; Le Brocq, A.M. Recent advances in understanding Antarctic subglacial lakes and hydrology. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, W.B.; Mikucki, J.A.; German, L.A.; Welch, K.A.; Welch, S.A.; Gardner, C.B.; Tulaczyk, S.M.; Pettit, E.C.; Kowalski, J.; Dachwald, B. The geochemistry of englacial brine from Taylor Glacier, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, S.J.; Gibson, E.K.; Velbel, M.A.; McKay, D.S. Antarctic Dry Valleys and indigenous weathering in Mars meteorites: Implications for water and life on Mars. Icarus 2005, 174, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, D.R.; Head, J.W. Antarctic Dry Valleys: Microclimate zonation, variable geomorphic processes and implications for assessing climate change on Mars. Icarus 2009, 192, 187–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, M.; Lo Giudice, A.; Conte, A.; Rizzo, C.; Rappazzo, A.C.; Maimone, G.; Caruso, G.; La Ferla, R.; Azzaro, M.; Gugliandolo, C.; et al. Microbial assemblages in pressurized Antarctic brine pockets (Tarn Flat, Northern Victoria Land): A hotspot of biodiversity and activity. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchiato, M.; Zambon, S.; Argiriadis, E.; Barbante, C.; Gambaro, A.; Piazza, R. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Antarctic ice-free areas: Influence of local sources on lakes and soils. Microchem. J. 2015, 120, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Caruso, G.; Rizzo, C.; Papale, M.; Azzaro, M. Bacterial communities versus anthropogenic disturbances in the Antarctic coastal marine environment. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 2, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchon, F.A.M.; Boutron, C.F.; Barbante, C.; Cozzi, G.; Gaspari, V.; Wolf, E.W.; Ferrari, C.P.; Cescon, P. Changes in heavy metals in Antarctic snow from Coats Land since the mid-19th to the late20th century. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2002, 200, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez, S.; Motas, M.; Palacios, M.J.; Valera, F.; Cuervo, J.J.; Barbosa, A. Concentration of trace elements in feathers of three Antarctic penguins: Geographical and interspecifc differences. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2412–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klánová, J.; Matykiewiczová, N.; Mácka, Z.; Prošek, P.; Láska, K.; Klán, P. Persistent organic pollutants in soils and sediments from James Ross Island, Antarctica. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukučka, P.; Lammel, G.; Dvorská, A.; Klánová, J.; Moeller, A.; Fries, E. Contamination of Antarctic snow by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons dominated by combustion sources in the polar region. Environ. Chem. 2010, 7, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.A.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Martins, C.C.; Silva, C.R.A.; França, E.J.; Bícego, M.C.; Mahique, M.M.; Montone, R.C. Arsenic and trace metal contents in sediment profiles from the Admiralty Bay, King George Island, Antarctica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmin, M.; Biasini, A.; Smiraglia, C. The contribution of geoelectrical investigations in the analysis of periglacial and glacial landforms in ice free areas of the Northern Foothills (Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica). Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys. Geogr. 1997, 79, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, H.M.; Guglielmin, M. Observations on the icemarginal periglacial geomorphology of Terra Nova Bay, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Permafr. Perigl. Proc. 1999, 10, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, H.M.; Guglielmin, M. Frozen ground phenomena in the vicinity of Terra Nova Bay, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica: A preliminary report. Geogr. Ann. 2000, 82, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcino, N.; Cosenza, A.; Azzaro, M. A review on the geochemistry of lakes in Victoria Land (Antarctica). Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioli, R.; Della Vedova, A.M.; Gragnani, R.; Grigioni, P.; Maggi, V.; Serra, F.; Stenni, B.; Torcini, S. Stratigraphic, isotopic and chemical profiles of a firn core from Drygalski ice tongue and a snow pit from Aviator Glacier (Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica). Terra Antarctica Rep. 1997, 1, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmin, M.; French, H.M. Ground ice in the Northern Foothills, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 2004, 39, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cannone, N.; Wagner, D.; Hubberten, H.W.; Guglielmin, M. Biotic and abiotic factors influencing soil properties across a latitudinal gradient in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Geoderma 2008, 144, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orombelli, G.; Baroni, C.; Denton, G.H. Late Cenozoic glacial history of the Terra Nova Bay region, Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Geogr. Fis. Dinam. Quat. 1991, 13, 139–163. [Google Scholar]
- Borruso, L.; Sannino, C.; Selbmann, L.; Battistel, D.; Zucconi, L.; Azzaro, M.; Turchetti, B.; Buzzini, P.; Guglielmin, M. A thin ice layer segregates two distinct fungal communities in Antarctic brines from Tarn Flat (Northern Victoria Land). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaro, M.; Maimone, G.; La Ferla, R.; Cosenza, A.; Rappazzo, A.C.; Caruso, G.; Paranhos, R.; Cabral, A.S.; Forte, E.; Guglielmin, M. The prokaryotic community in an extreme Antarctic environment: The brines of Boulder Clay lakes (Northern Victoria Land). Hydrobiologia. under review.
- Lo Giudice, A.; Conte, A.; Papale, M.; Rizzo, C.; Azzaro, M.; Guglielmin, M. Prokaryotic diversity and metabolically active communities in brines from two perennially ice-covered Antarctic lakes. Astrobiology. under review.
- Lorenzo-Parodi, N.; Kaziur, W.; Stojanovi, N.; Jochmann, M.A.; Schmidt, T.C. Solventless microextraction techniques for water analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, L.; Di Cello, F.; Brilli, M.; Fani, R.; Lo Giudice, A.; Bruni, V. Biodiversity of cultivable psychrotrophic marine bacteria isolated from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 230, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, M.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, M.J.; Nair, S.; Bharathi, P.A.L.; Chandramohan, D. Metal and antibiotic-resistance in psychrotrophic bacteria from Antarctic marine waters. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Casella, P.; Bruni, V.; Michaud, L. Response of bacterial isolates from Antarctic shallow sediments towards heavy metals, antibiotics and polychlorinated biphenyls. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, S.; Michaud, L.; Caruso, C.; Lo Giudice, A. Metal and antibiotic resistance in psychrotrophic bacteria associated with the Antarctic sponge Hemigellius pilosus (Kirkpatrick, 1907). Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, S.; Papale, M.; Rizzo, C.; Giannarelli, S.; Conte, A.; Moscheo, F.; Graziano, M.; Aspholm, P.E.; Onor, M.; De Domenico, E.; et al. Metal resistance in bacteria from contaminated Arctic sediment is driven by metal local inputs. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 77, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappazzo, A.C.; Papale, M.; Rizzo, C.; Conte, A.; Giannarelli, S.; Onor, M.; Abete, C.; Cefali, P.; De Domenico, E.; Michaud, L.; et al. Heavy metal tolerance and polychlorinated biphenyl oxidation in bacterial communities inhabiting the Pasvik River and the Varanger Fjord area (Arctic Norway). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Bruni, V.; De Domenico, M.; Michaud, L. Psychrophiles- Cold-adapted hydrocarbon-degrading microorganisms. In Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology; Timmis, K.N., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 3, pp. 1897–1922. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Casella, P.; Caruso, C.; Mangano, S.; Bruni, V.; De Domenico, M.; Michaud, L. Occurrence and characterization of psychrotolerant hydrocarbon–oxidizing bacteria from surface seawater along the Victoria Land coast (Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2010, 33, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, C.; Michaud, L.; Hörmann, B.; Gerçe, B.; Syldatk, C.; Hausmann, R.; De Domenico, E.; Lo Giudice, A. Bacteria associated with Sabellids (Polychaeta: Annelida) as a novel source of surface active compounds. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2013, 70, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frame, G.M.; Cochran, J.W.; Boewadt, S.S. Complete PCB congener distributions for 17 Aroclor mixtures determined by 3 HRGC systems optimized for comprehensive, quantitative, congener-specific analysis. J. High Resol. Chromatogr. 1996, 19, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, L.; Di Marco, G.; Bruni, V.; Lo Giudice, A. Biodegradative potential and characterization of psychrotolerant polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading bacteria isolated from a coastal station in Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, M.; Giannarelli, S.; Francesconi, S.; Di Marco, G.; Mikkonen, A.; Conte, A.; Rizzo, C.; De Domenico, E.; Michaud, L.; Lo Giudice, A. Enrichment, isolation and biodegradation potential of psychrotolerantm polychlorinated-biphenyl degrading bacteria from the Kongsfjorden (Svalbard Islands, High Arctic Norway). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Michaud, L.; De Pascale, D.; De Domenico, M.; Di Prisco, G.; Fani, R.; Bruni, V. Lipolytic activity of Antarctic cold-adapted marine bacteria (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Caruso, C.; Mangano, S.; Bruni, V.; De Domenico, M.; Michaud, L. Marine bacterioplankton diversity and community composition in an Antarctic coastal environment. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Brilli, M.; Bruni, V.; De Domenico, M.; Fani, R.; Michaud, L. Bacterium-bacterium inhibitory interactions among psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from Antarctic seawater (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Bruni, V.; Michaud, L. Characterization of Antarctic psychrotrophic bacteria with antibacterial activities against terrestrial microorganisms. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, G.D.; Simpson, W.A.; Younger, J.J.; Baddour, L.M.; Barrett, F.F.; Melton, D.M.; Beachey, E.H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: A quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 22, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, C.; Rizzo, C.; Mangano, S.; Poli, A.; Di Donato, P.; Nicolaus, B.; Di Marco, G.; Michaud, L.; Lo Giudice, A. Extracellular polymeric substances with metal adsorption capacity produced by Pseudoalteromonas sp. MER144 from Antarctic seawater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4667–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamilla, C.; Pavez, M.; Santos, A.; Hermosilla, A.; Llanquinao, V.; Barrientos, L. Bioprospecting for extracellular enzymes from culturable Actinobacteria from the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2017, 40, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, E.; Ichimura, A.S.; Peng, V.; Fritsen, C.H.; Trubl, G.; Doran, P.T.; Murray, A.E. Brine assemblages of ultrasmall microbial cells within the ice cover of Lake Vida, Antarctica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3687–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skidmore, M.L.; Foght, J.M.; Sharp, M.J. Microbial life beneath a high Arctic glacier. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miteva, V.I.; Sheridan, P.P.; Brenchley, J.E. Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of microorganisms isolated from a deep Greenland glacier ice core. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christner, B.C.; Kvitko, I.B.H.; Reeve, J.N. Molecular identification of bacteria and eukarya inhabiting an Antarctic cryoconite hole. Extremophiles 2003, 7, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christner, B.C. Recovery of Bacteria from Glacial and Subglacial Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, B. Bacterial diversity and bioprospecting for cold-active hydrolytic enzymes from culturable bacteria associated with sediment from Nella Fjord, Eastern Antarctica. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Yao, T.; An, L.; Xu, B.; Wang, J. 16S rRNA sequences and differences in bacteria isolated from the Muztag Ata glacier at increasing depths. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4619–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilichinsky, D.; Rivkina, E.; Bakermans, C.; Shcherbakova, V.; Petrovskaya, L.; Ozerskaya, S.; Ivanushkina, N.; Kochkina, G.; Laurinavichuis, K.; Pecheritsina, S.; et al. Biodiversity of cryopegs in permafrost. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 53, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-C.; Li, H.-R.; Xin, Y.-H.; Chi, Z.-M.; Zhou, P.-J.; Yu, Y. Marinobacter psychrophilus sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium isolated from the Arctic. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-del-Río, H.L.; Chain, P.S.; Grzymski, J.J.; Ponder, M.; Ivanova, N.; Bergholz, P.W.; Di Bartolo, G.; Hauser, L.; Land, M.; Bakermans, C.; et al. The genome sequence of Psychrobacter arcticus 273-4, a psychroactive Siberian permafrost bacterium, reveals mechanisms for adaptation to low-temperature growth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 76, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.M.; Vander Schaaf, N.A.; Cunningham, A.M.G.; Hang, A.C.; Reeves, C.L.; Huffman, E.R.; Riester, C.L.; Madigan, M.T.; Sattley, W.M. Chemoorganotrophic bacteria from Lake Fryxell, Antarctica, including Pseudomonas strain LFY10, a cold-adapted, halotolerant bacterium useful in teaching labs. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.P.; McCammon, S.A.; Brown, M.V.; Nichols, D.S.; McMeekin, T.A. Diversity and association of psychrophilic bacteria in Antarctic sea-ice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3068–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.P.; Nichols, D.S.; McMeekin, T.A. Psychrobacter glacincola sp. nov, a halotolerant, psychrophilic bacterium isolated from Antarctic sea ice. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 20, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, K.; Imhoff, F.; Staley, T.; Deming, J.W. Phylogenetic diversity of numerically important Arctic sea-ice bacteria at subzero temperature. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 43, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmeyer, R.; Knittel, K.; Jürgens, J.; Weyland, H.; Amann, R.; Helmke, E. Diversity and structure of bacterial communities in Arctic versus Antarctic pack ice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6610–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatz, R.E.; Lepp, P.W.; Ward, B.B.; Francis, C.A. Planktonic microbial community composition across steep physical/chemical gradients in permanently ice-covered Lake Bonney, Antarctica. Geobiology 2006, 4, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikucki, J.A.; Priscu, J.C. Bacterial diversity associated with Blood Falls, a subglacial outflow from the Taylor Glacier, Antarctica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4029–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozal, N.; Montes, M.J.; Tudela, E.; Guinea, J. Characterization of several Psychrobacter strains isolated from Antarctic environments and description of Psychrobacter luti sp. nov. and Psychrobacter fozii sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evolut. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumoto, I.; Hirota, K.; Sogabe, Y.; Nodasaka, Y.; Yokota, Y.; Hoshino, T. Psychrobacter okhotskensis sp. nov., a lipase-producing facultative psychrophile isolated from the coast of the Okhotsk Sea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnivetskaya, T.; Kathariou, S.; McGrath, J.; Gilichinsky, D.; Tiedje, J.M. Low-temperature recovery strategies for the isolation of bacteria from ancient permafrost sediments. Extremophiles 2000, 4, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilichinsky, D.A.; Rivkina, E.; Shcherbakova, V.; Laurinavichuis, K.; Tiedje, J.M. Supercooled water brines within permafrost—An unknown ecological niche for microorganisms: A model for astrobiology. Astrobiology 2003, 3, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondino, L.J.; Asao, M.; Madigan, M.T. Cold-active halophilic bacteria from the ice-sealed Lake Vida, Antarctica. Arch. Microbiol. 2009, 191, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, K.; Hodgson, D.A.; Convey, P.; Willems, A. Culturable diversity of heterotrophic bacteria in Forlidas Pond (Pensacola Mountains) and Lundström Lake (Shackleton Range), Antarctica. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzmann, P.D.; Hopfl, P.; Weiss, N.; Tindall, B.J. Psychrotrophic, lactic acid producing bacteria from anoxic waters in Ace Lake, Antarctica: Carnobacterium funditum sp. nov. and Carnobacterium aherfunditum sp. nov. Arch. Microbiol. 1991, 156, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratina, B.J.; Stevenson, B.S.; Green, W.J.; Schmidt, T.M. Manganese reduction by microbes from oxic regions of the Lake Vanda (Antarctica) water column. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3791–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.S.; Matsumoto, G.I.; Shivaji, S. Sporosarcina macmurdoensis sp. nov., from a cyanobacterial mat sample from a pond in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikuta, E.V.; Marsic, D.; Bej, A.; Tang, J.; Krader, P.; Hoover, R.B. Carnobacterium pleistocenium sp. nov., a novel psychrotolerant, facultative anaerobe isolated from permafrost of the Fox tunnel in Alaska. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomova, I.; Stoilova-Disheva, M.; Lazarkevich, I.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E. Antimicrobial activity and resistance to heavy metals and antibiotics of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from sediment and soil samples collected from two Antarctic islands. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goethem, M.W.; Pierneef, R.; Bezuidt, O.K.I.; Van De Peer, Y.; Cowan, D.A.; Makhalanyane, T.P. A reservoir of ‘historical’ antibiotic resistance genes in remote pristine Antarctic soils. Microbiome 2018, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara, D.; Bello-Toledo, H.; Domínguez, M.; Cigarroa, C.; Fernández, P.; Vergara, L.; Quezada-Aguiluz, M.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Lima, C.A.; González-Rocha, G. Antibiotic resistance in bacterial isolates from freshwater samples in Fildes Peninsula, King George Island, Antarctica. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, T.; Takeuchi, N.; Rivera, A.; Yamada, A.; Yoshimura, Y.; Barcaza, G.; Shinbori, K.; Motoyama, H.; Kohshima, S.; Ushida, K. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in glacier environments. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2012, 5, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjolund, M.; Bonnedahl, J.; Hernandez, J.; Bengtsson, S.; Cederbrant, G.; Pinhassi, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsen, B. Dissemination of multidrug-resistant bacteria into the Arctic. Emerg. Inf. Dis. J. 2008, 14, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camenzuli, D.; Freidman, B.L. On-site and in situ remediation technologies applicable to petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated sites in the Antarctic and Arctic. Polar Res. 2015, 34, 24492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Meng, X.Z.; Wu, C.-C.; Bao, L.-J.; Wang, F.; Wu, F.-C.; Zeng, E.Y. Tracking human footprints in Antarctica through passive sampling of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in inland lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavenda, R.; Rizzo, C.; Michaud, L.; Gerçe, B.; Bruni, V.; Syldatk, C.; Hausmann, R.; Lo Giudice, A. Biosurfactant production by Arctic and Antarctic bacteria growing on hydrocarbons. Polar Biol. 2015, 38, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabagaran, S.R.; Manorama, R.; Delille, D.; Shivaji, S. Predominance of Roseobacter, Sulfitobacter, Glaciecola and Psychrobacter in seawater collected off Ushuaia, Argentina, Sub-Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Giuliano, L.; Gentile, G.; Crisafi, E.; Chernikova, T.N.; Abraham, W.R.; Lunsdorf, H.; Timmis, K.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Oleispira antarctica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterium isolated from Antarctic coastal sea water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, S.S.-A.; Al-Mailem, D.M. Microbial hydrocarbon-removal under halostress. Halophiles 2015, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaro, A.; Manodori, L.; Zangrando, R.; Cincinelli, A.; Capodaglio, G.; Cescon, P. Atmospheric PCB concentrations at Terra Nova Bay, Antarctica. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 9406–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combi, T.; Martins, C.C.; Taniguchi, S.; Leonel, J.; Lourenço, R.A.; Montone, R.C. Depositional history and inventories of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediment cores from an Antarctic Specially Managed Area (Admiralty Bay, King George Island). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, L.; Chauhan, A.; Ranjan, A.; Jindal, T. Persistent organic pollutants in biotic and abiotic components of Antarctic pristine environment. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Giuliano, L.; Bruni, V.; Scarfì, S.; Golyshin, P.N. Characterization of Antarctic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria capable of producing bioemulsifiers. New Microbiol. 1999, 22, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Domenico, M.; Lo Giudice, A.; Michaud, L.; Saitta, M.; Bruni, V. Diesel oil and PCB-degrading bacteria isolated from Antarctic seawaters (Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea). Polar Res. 2004, 23, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.; Sharp, R.; Russell, N.J.; Roller, S. Antarctic bacteria inhibit growth of food-borne microorganisms at low temperatures. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 48, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesheva, V.; Negoita, T. Psychrotrophic microorganism communities in soils of Haswell Island, Antarctica and their biosynthetic potential. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.Y.; Tan, G.Y.A.; Convey, P.; Pearce, D.A.; Tan, I.K.P. Diversity and bioactivity of actinomycetes from Signy Island terrestrial soils, maritime Antarctic. Adv. Polar Sci. 2013, 24, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Papaleo, M.C.; Fondi, M.; Maida, I.; Perrin, E.; Lo Giudice, A.; Michaud, L.; Mangano, S.; Bartolucci, G.; Romoli, R.; Fani, R. Sponge-associated microbial Antarctic communities exhibiting antimicrobial activity against Burkholderia cepacia complex bacteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 272–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimenko, T.A.; Efremenkova, O.V.; Demkina, E.V.; Demkina, E.V.; Petrova, M.A.; Sumarukova, I.G.; Vasilyeva, B.F.; El-Registan, G.I. Bacteria isolated from Antarctic permafrost are efficient antibiotic producers. Microbiology 2018, 87, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli, R.; Charlton, T.; Ertan, H.; Mohd, O.S.; Siddiqui, K.S.; Williams, T.J. Biotechnological uses of enzymes from psychrophiles. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Giudice, A.; Poli, A.; Finore, I.; Rizzo, C. Peculiarities of extracellular polymeric substances produced by Antarctic bacteria and their possible applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2923–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Viable Counts (Number of Isolates) on Different Culture Media 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSA1 | TSA50 | TSA100 | DSMZ97 | R2A10 | Isolates (n.) | |
| Boulder Clay | ||||||
| BC1 | 15.5 ± 0.7 (38) | 4.3 ± 0.9 (15) | 5.3 ± 0.8 (11) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 64 |
| BC2 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.3 (1) | 0.1 ± 0.8 (1) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 2 |
| BC3 | 0.0 ± 0.0 (2) | 0.9 ± 0.3 (5) | 2.3 ± 0.8 (1) | 0.1 ± 0.7 (0) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 8 |
| Tarn Flat | ||||||
| TF4 | 3.1 ± 0.8 (14) | 4.7 ± 0.9 (16) | 3.3 ± 0.1 (31) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 (5) | 66 |
| TF5 | 7.2 ± 0.6 (41) | 5.5 ± 0.0 (14) | 5.5 ± 0.8 (16) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.1 ± 0.0 (4) | 75 |
| Isolates (n.) | 93 | 51 | 62 | 0 | 9 | 215 |
| Next Relative by Gen Bank Alignment (AN a, Organisms) | RI b | AN a | OUT c | Hom (%) d | Isolates (n.) | Isolation Medium e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC1 | BC2 | BC3 | BC1 | BC2 | BC3 | |||||
| Boulder Clay | ||||||||||
| Gammaproteobacteria | ||||||||||
| JQ229609, Pseudomonas sp. ALI-cc18 | BC1-5 | MT350301 | 24 | 99 | 42 | 1 | B (10), C (32) | A | ||
| DQ677864, Psychrobacter sp. BF01 S5 | BC3-33 | MT350302 | 27 | 99 | 1 | 5 | B | B | ||
| KU179857, Shewanella arctica RKAT059 | BC1-22B | MT350303 | 28 | 99 | 3 | A | ||||
| CF group of Bacteroidetes | ||||||||||
| HQ538744, Gelidibacter gilvus strain Z20 | BC1-72A | MT350304 | na | 96 | 1 | A | ||||
| AF001367, Gelidibacter algens | BC1-118A | MT350305 | 30 | 98 | 2 | A | ||||
| FR772078, Flavobacterium sp. R-40832 | BC2-39 | MT350306 | 31 | 99 | 2 | A (1), B (1) | ||||
| Actinobacteria | ||||||||||
| KT965169, Leifsonia sp. N10 | BC1bis-11 | MT350307 | na | 98 | 1 | C | ||||
| Firmicutes | ||||||||||
| LC145583, Carnobacterium JCM 12498 | BC1-54 | MT350308 | 22 | 99 | 9 | A (6), B (3) | ||||
| LT221233, Staphylococcus LK1HaP1 | BC1bis-71 | MT350309 | na | 99 | 1 | A | ||||
| Tarn Flat | RI b | AN a | OTU c | Hom (%) d | TF4 | TF5 | TF4 | TF5 | ||
| Alphaproteobacteria | ||||||||||
| KR140230, Devosia psychrophila strain NJES-30 16S | TF5-10A | KY437988 | 3 | 99 | 4 | C | ||||
| AF513400, Rhodobacter sp. 1-5 | TF5-149 | KY437996 | 13 | 99 | 2 | 15 | A, B | C (1), B (8), A (6) | ||
| EU369117, Uncultured clone MBIOS-01 | TF5-35A | KY438003 | na | 96 | 1 | C | ||||
| Gammaproteobacteria | ||||||||||
| KF384120, Marinobacter sp. LV10R510-5 | TF4-237 | KY437991 | 6 | 99 | 7 | 8 | D (5), B (2) | D (4), B (1), A (3) | ||
| KU749990, Pseudomonas stutzeri strain 1005 | TF4-100 | KY437993 | 8 | 99 | 4 | B | ||||
| DQ677869, Pseudomonas sp. BF02_S14 | TF4-182 | KY437992 | 9 | 99 | 2 | 19 | A, C | C (16), B (1), A (2) | ||
| KX417186, Psychrobacter fozii strain 9.22 | TF4-146 | KY437994 | 10 | 100 | 33 | A (22), B (7), C (4) | ||||
| DQ677864, Psychrobacter sp. BF02_S5 | TF4-164 | KY437995 | na | 96 | 1 | A | ||||
| Actinobacteria | ||||||||||
| FJ196003, Aeromicrobium sp. ZS1-19 | TF4-24 | KY437986 | 1 | 99 | 1 | 4 | C | C | ||
| KM507649, Kocuria sp. FXJ8.237 | TF4-15 | KY438002 | na | 99 | 1 | C | ||||
| KC478079, Leifsonia sp. FO17 | TF5-105B | KY437990 | 4 | 99 | 6 | 14 | C | A (3), C (11) | ||
| KF295312, Rhodoglobus sp. Y4_509_3 | TF5-20A | KY437989 | na | 96 | 1 | C | ||||
| AM183255, Rothia sp. BBH4 | TF5-35B | KY438000 | na | 99 | 1 | C | ||||
| DQ521554, uncultured bacterium ANTLV9_C09 | TF5-151 | KY437999 | na | 99 | 1 | A | ||||
| Next Relative by Gen Bank Alignment (AN a, Organisms) | RI b | AN a | OUT c | Hom (%) d | Isolates (n.) | Isolation Medium e | ||||
| TF4 | TF5 | TF4 | TF5 | |||||||
| Firmicutes | ||||||||||
| KF151857, Alkalibacterium kapii strain MGR70 | TF4-239 | KY438001 | na | 97 | 1 | B | ||||
| LC145583, Carnobacterium alterfunditum JCM 12498 | TF4-156 | KY437987 | 2 | 99 | 3 | A | ||||
| FR691465, Planococcus antarcticus strain R-36948 | TF4-125 | KY437998 | na | 99 | 1 | A | ||||
| HM224487, Sporosarcina sp. TPD39 | TF4-168 | KY437997 | 15 | 99 | 4 | 7 | A (2), B (1), C (1) | A (1), B (4), C (2) | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzo, C.; Conte, A.; Azzaro, M.; Papale, M.; Rappazzo, A.C.; Battistel, D.; Roman, M.; Lo Giudice, A.; Guglielmin, M. Cultivable Bacterial Communities in Brines from Perennially Ice-Covered and Pristine Antarctic Lakes: Ecological and Biotechnological Implications. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060819
Rizzo C, Conte A, Azzaro M, Papale M, Rappazzo AC, Battistel D, Roman M, Lo Giudice A, Guglielmin M. Cultivable Bacterial Communities in Brines from Perennially Ice-Covered and Pristine Antarctic Lakes: Ecological and Biotechnological Implications. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(6):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060819
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzo, Carmen, Antonella Conte, Maurizio Azzaro, Maria Papale, Alessandro C. Rappazzo, Dario Battistel, Marco Roman, Angelina Lo Giudice, and Mauro Guglielmin. 2020. "Cultivable Bacterial Communities in Brines from Perennially Ice-Covered and Pristine Antarctic Lakes: Ecological and Biotechnological Implications" Microorganisms 8, no. 6: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060819
APA StyleRizzo, C., Conte, A., Azzaro, M., Papale, M., Rappazzo, A. C., Battistel, D., Roman, M., Lo Giudice, A., & Guglielmin, M. (2020). Cultivable Bacterial Communities in Brines from Perennially Ice-Covered and Pristine Antarctic Lakes: Ecological and Biotechnological Implications. Microorganisms, 8(6), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060819









