Diversity, Transmission, and Cophylogeny of Ledanteviruses (Rhabdoviridae: Ledantevirus) and Nycteribiid Bat Flies Parasitizing Angolan Soft-Furred Fruit Bats in Bundibugyo District, Uganda
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. Metagenomics for Virus Identification
2.3. Ledantevirus Phylogenetics
2.4. Bat Fly Mitogenome Sequencing
2.5. Identifying Patterns of Selection Across Viral Genomes
2.6. Cophylogenetic Analyses
2.7. Episodic Diversifying Selection on Virus Diversity
3. Results
3.1. Bat Flies and Bat Oral Swabs
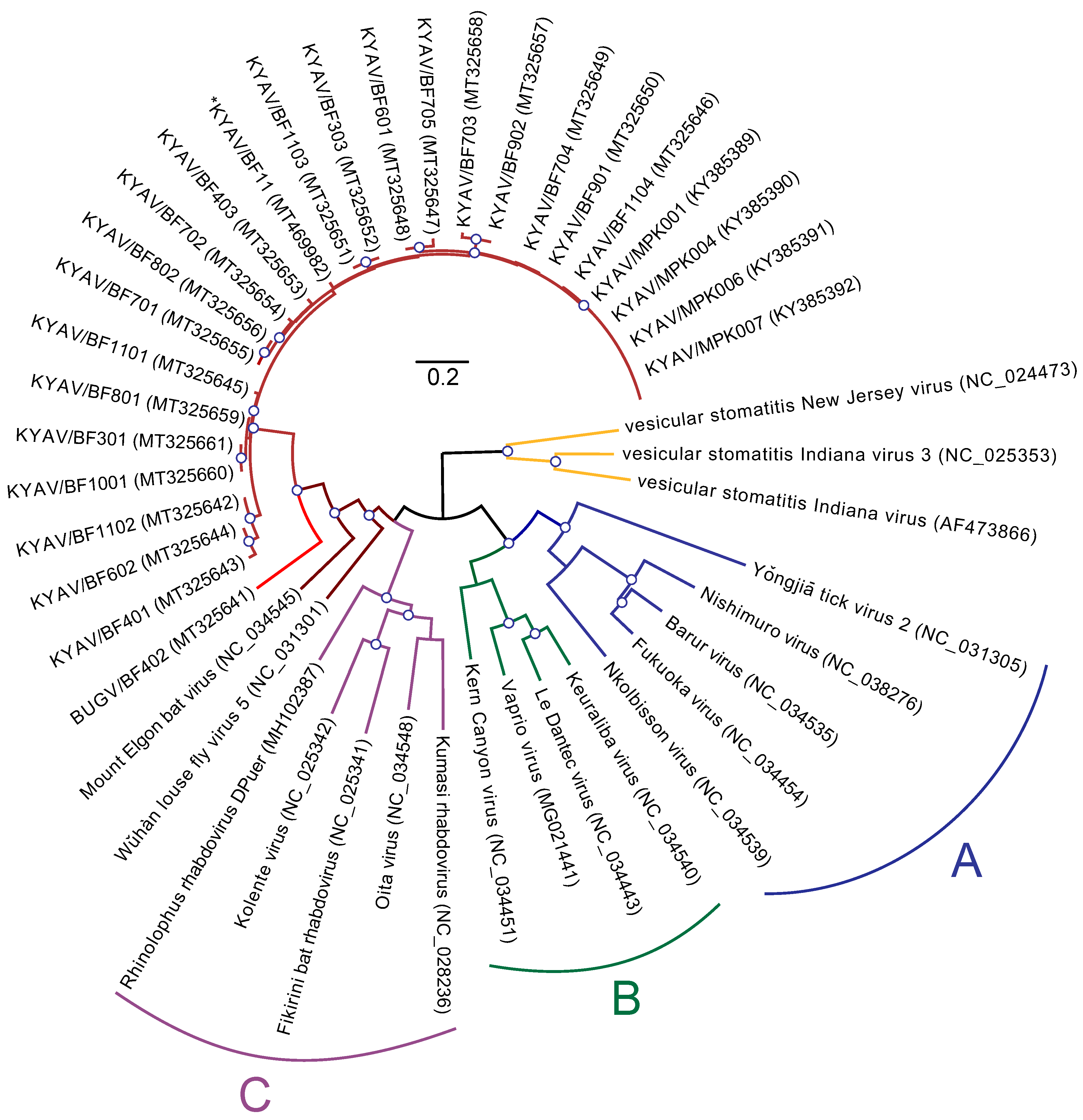
3.2. Phylogeny of Ledanteviruses
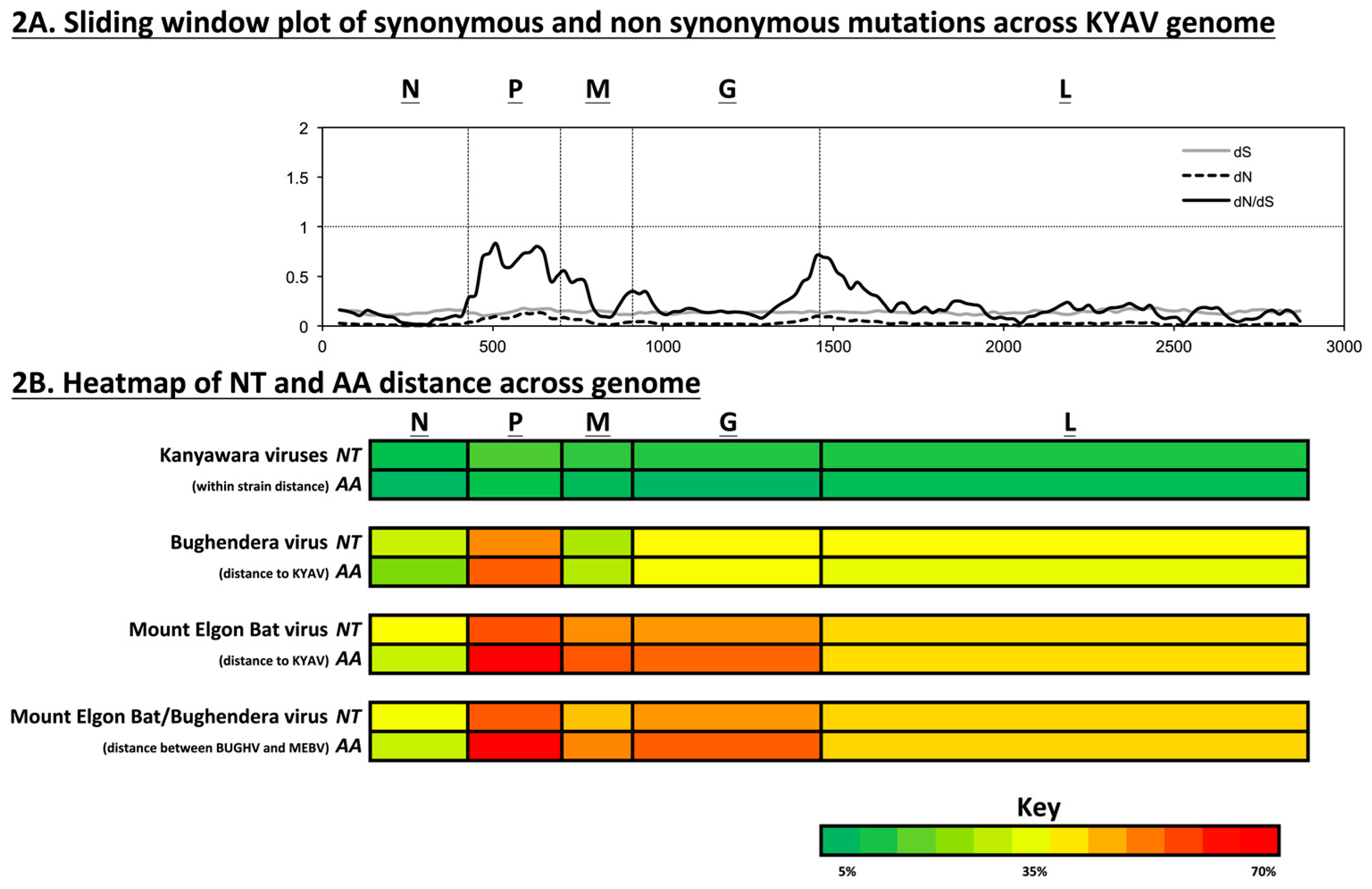
3.3. Viral Diversity and Selection
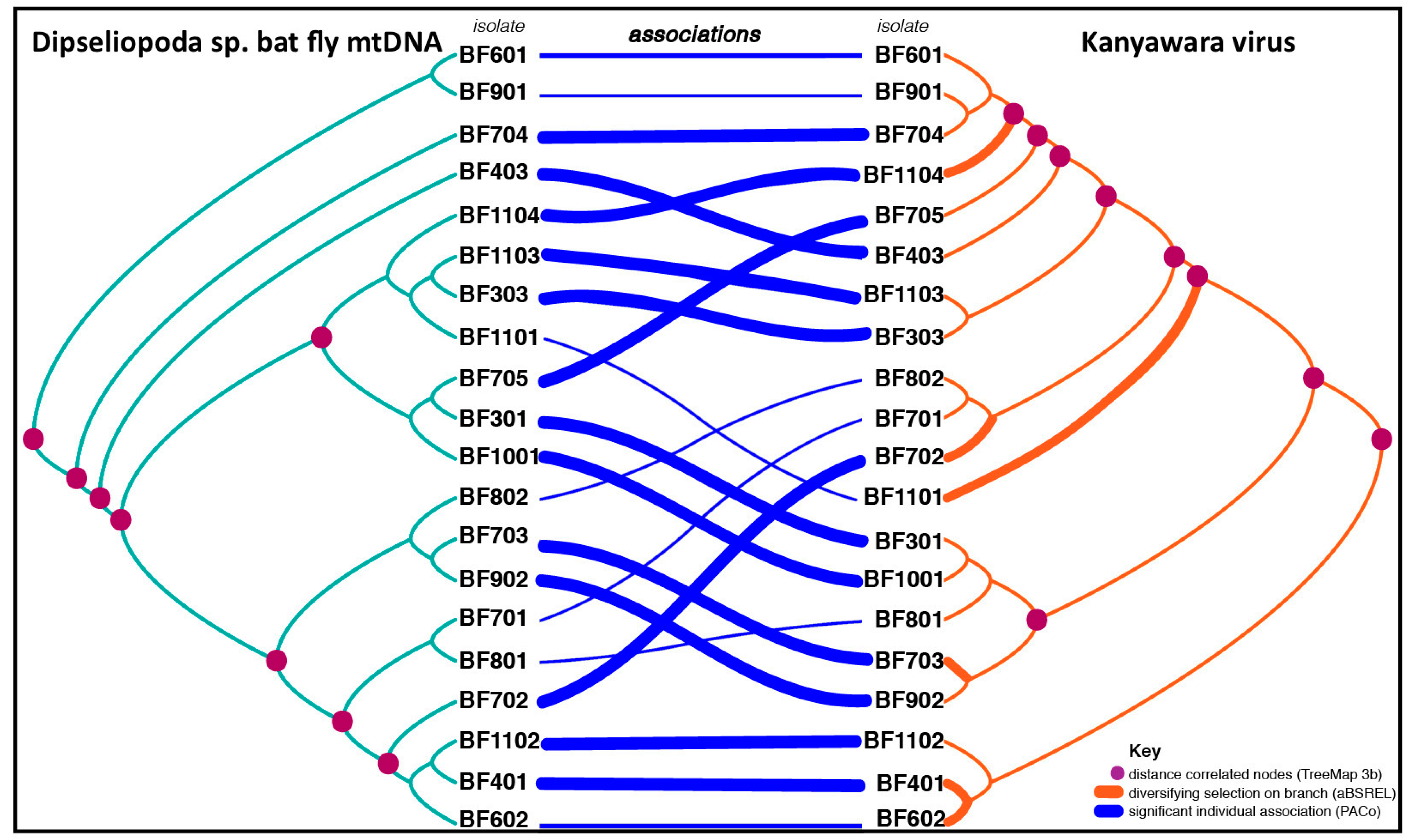
3.4. Cophylogenetic Analyses
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dick, C.W.; Patterson, B.D. 11 Bat Flies-Obligate Ectoparasites of Bats; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen van Vuren, P.; Wiley, M.; Palacios, G.; Storm, N.; McCulloch, S.; Markotter, W.; Birkhead, M.; Kemp, A.; Paweska, J.T. Isolation of a novel fusogenic orthoreovirus from Eucampsipoda africana bat flies in South Africa. Viruses 2016, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen van Vuren, P.; Wiley, M.R.; Palacios, G.; Storm, N.; Markotter, W.; Birkhead, M.; Kemp, A.; Paweska, J.T. Isolation of a novel orthobunyavirus from bat flies (Eucampsipoda africana). J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, S.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, H.; Liang, G. Isolation of Kaeng Khoi virus (KKV) from Eucampsipoda sundaica bat flies in China. Virus Res. 2017, 238, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, W.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, S.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.J.; et al. Isolation and Identification of a highly divergent Kaeng Khoi virus from bat flies (Eucampsipoda sundaica) in China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, T.L.; Bennett, A.J.; Kityo, R.; Kuhn, J.H.; Chapman, C.A. Kanyawara virus: A novel rhabdovirus infecting newly discovered nycteribiid bat flies infesting previously unknown pteropodid bats in Uganda. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasdell, K.R.; Guzman, H.; Widen, S.G.; Firth, C.; Wood, T.G.; Holmes, E.C.; Tesh, R.B.; Vasilakis, N.; Walker, P.J. Ledantevirus: A proposed new genus in the Rhabdoviridae has a strong ecological association with bats. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.-H.; Lin, X.-D.; Kang, Y.-J.; Chen, L.-J.; Qin, X.-C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. eLife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, A.D.; Hayman, D.T.S.; O’Shea, T.J.; Cryan, P.M.; Gilbert, A.T.; Pulliam, J.R.C.; Mills, J.N.; Timonin, M.E.; Willis, C.K.R.; Cunningham, A.A.; et al. A comparison of bats and rodents as reservoirs of zoonotic viruses: Are bats special? Proc. R. Soc. 2013, 280, 20122753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olival, K.J.; Hosseini, P.R.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Ross, N.; Bogich, T.L.; Daszak, P. Host and viral traits predict zoonotic spillover from mammals. Nature 2017, 546, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moratelli, R.; Calisher, C.H. Bats and zoonotic viruses: Can we confidently link bats with emerging deadly viruses? Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2015, 110, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisher, C.H.; Childs, J.E.; Field, H.E.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szentiványi, T.; Christe, P.; Glaizot, O. Bat Flies and their microparasites: Current knowledge and distribution. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binetruy, F.; Dupraz, M.; Buysse, M.; Duron, O. Surface sterilization methods impact measures of internal microbial diversity in ticks. Parasite Vector 2019, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, G.; Lim, E.S.; Droit, L.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Barouch, D.H.; Virgin, H.W.; Wang, D. VirusSeeker, a computational pipeline for virus discovery and virome composition analysis. Virology 2017, 503, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Meleshko, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; Pevzner, P.A. metaSPAdes: A new versatile metagenomic assembler. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löytynoja, A.; Goldman, N. An algorithm for progressive multiple alignment of sequences with insertions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10557–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.; Zardoya, R.; Telford, M.J. TranslatorX: Multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences guided by amino acid translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W7–W13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, V.; Longueville, J.-E.; Gascuel, O. SMS: Smart Model Selection in PhyML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2422–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korber, B. HIV signature and sequence variation analysis. In Computational Analysis of HIV Molecular Sequences; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sibley, S.D.; Lauck, M.; Bailey, A.L.; Hyeroba, D.; Tumukunde, A.; Weny, G.; Chapman, C.A.; O’Connor, D.H.; Goldberg, T.L.; Friedrich, T.C. Discovery and characterization of distinct simian pegiviruses in three wild African Old World monkey species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Sato, K. Maternal inheritance of mitochondrial DNA by diverse mechanisms to eliminate paternal mitochondrial DNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 1979–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.P.; Charleston, M.A. A cophylogenetic perspective of RNA-virus evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balbuena, J.A.; Míguez-Lozano, R.; Blasco-Costa, I. PACo: A novel procrustes application to cophylogenetic analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.C.; Cagua, E.F.; Balbuena, J.A.; Stouffer, D.B.; Poisot, T. paco: Implementing procrustean approach to cophylogeny in R. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D.; Wertheim, J.O.; Weaver, S.; Murrell, B.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Less is more: An adaptive branch-site random effects model for efficient detection of episodic diversifying selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucl. Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Blasdell, K.R.; Calisher, C.H.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Kondo, H.; Kurath, G.; Longdon, B.; Stone, D.M.; Tesh, R.B.; Tordo, N.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Rhabdoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropp, C.B.; Prange, W.C.; Monath, T.P. Le Dantec virus: Identification as a rhabdovirus associated with human infection and formation of a new serogroup. J. Gen. Virol. 1985, 66, 2749–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, A.W.; Ansdell, V.E.; Bowen, E.T. Le Dantec virus infection in a patient who had not been to West Africa. Br. Med. J. 1977, 2, 1632–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhy, H.; Cowley, J.A.; Larrous, F.; Holmes, E.C.; Walker, P.J. Phylogenetic relationships among rhabdoviruses inferred using the L polymerase gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butenko, A.M.; Gromashevsky, V.L.; L’vov, D.K.; Popov, V.F. First isolations of Barur virus (Rhabdoviridae) from ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Africa. J. Med. Entomol. 1981, 18, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghedin, E.; Rogers, M.B.; Widen, S.G.; Guzman, H.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Wood, T.G.; Fitch, A.; Popov, V.; Holmes, E.C.; Walker, P.J.; et al. Kolente virus, a rhabdovirus species isolated from ticks and bats in the Republic of Guinea. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 2609–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, N.; Inaba, Y.; Akashi, H.; Miura, Y.; Shorthose, J.; Kurashige, K. Isolation of a new bovine ephemeral fever group virus. Aust. Vet. J. 1986, 63, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, M.; Inaba, Y.; Banjo, M.; Kubo, M. Isolation of Fukuoka virus, a member of the Kern Canvon serogroup viruses of the family Rhabdoviridae, from cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 1992, 32, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, M.; Saluzzo, J.F.; Digoutte, J.P.; Mattei, X. Identification du virus Nkolbisson par microscopie électronique. Ann. Inst. Pasteur Actual. 1987, 138, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Lin, X.-D.; Tian, J.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Chen, X.; Li, C.-X.; Qin, X.-C.; Li, J.; Cao, J.-P.; Eden, J.-S.; et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature 2016, 540, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metselaar, D.; Williams, M.C.; Simpson, D.I.; West, R.; Mutere, F.A. Mount Elgon bat virus: A hitherto undescribed virus from Rhinolophus hildebrandtii eloquens K. Anderson. Arch. Gesamte Virusforsch 1969, 26, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewick, S.; Agusto, F.; Calabrese, J.M.; Muturi, E.J.; Fagan, W.F. Epidemiology of La Crosse virus emergence, Appalachia Region, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Weger-Lucarelli, J.; Murrieta, R.A.; Fauver, J.R.; Garcia-Luna, S.M.; Prasad, A.N.; Black, W.C.; Ebel, G.D. Genetic drift during systemic arbovirus infection of mosquito vectors leads to decreased relative fitness during host switching. Cell Host. Microbe 2016, 19, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woelk, C.H.; Holmes, E.C. Reduced positive selection in vector-borne RNA viruses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 2333–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainwater-Lovett, K.; Pauszek, S.J.; Kelley, W.N.; Rodriguez, L.L. Molecular epidemiology of vesicular stomatitis New Jersey virus from the 2004-2005 US outbreak indicates a common origin with Mexican strains. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2042–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longdon, B.; Day, J.P.; Schulz, N.; Leftwich, P.T.; de Jong, M.A.; Breuker, C.J.; Gibbs, M.; Obbard, D.J.; Wilfert, L.; Smith, S.C.L.; et al. Vertically transmitted rhabdoviruses are found across three insect families and have dynamic interactions with their hosts. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2017, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, M.L.; Blohm, G.M.; Brooks, M.E.; Regan, K.L.; Brown, B.Y.; Barfield, M.; Holt, R.D.; Bolker, B.M. The prevalence and persistence of sigma virus, a biparentally transmitted parasite of Drosophila melanogaster. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2011, 13, 323–345. [Google Scholar]
- Longdon, B.; Jiggins, F.M. Vertically transmitted viral endosymbionts of insects: Do sigma viruses walk alone? Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 3889–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Teo, Y.-Y. Estimating time to the most recent common ancestor (TMRCA): Comparison and application of eight methods. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesi, N.; Kadjo, B.; Pourrut, X.; Leroy, E.; Pongombo Shongo, C.; Cruaud, C.; Hassanin, A. Molecular systematics and phylogeography of the tribe Myonycterini (Mammalia, Pteropodidae) inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear markers. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2013, 66, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olival, K.J.; Dick, C.W.; Simmons, N.B.; Morales, J.C.; Melnick, D.J.; Dittmar, K.; Perkins, S.L.; Daszak, P.; DeSalle, R. Lack of population genetic structure and host specificity in the bat fly, Cyclopodia horsfieldi, across species of Pteropus bats in Southeast Asia. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumptre, A.J.; Davenport, T.R.B.; Behangana, M.; Kityo, R.; Eilu, G.; Ssegawa, P.; Ewango, C.; Meirte, D.; Kahindo, C.; Herremans, M.; et al. The biodiversity of the Albertine Rift. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 134, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witsenburg, F.; Schneider, F.; Christe, P. Epidemiological traits of the malaria-like parasite Polychromophilus murinus in the Daubenton’s bat Myotis daubentonii. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaer, J.; Reeder, D.M.; Vodzak, M.E.; Olival, K.J.; Weber, N.; Mayer, F.; Matuschewski, K.; Perkins, S.L. Nycteria parasites of Afrotropical insectivorous bats. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, S.F.; Olival, K.J.; Kosoy, M.; Billeter, S.; Patterson, B.D.; Dick, C.W.; Dittmar, K. Global distribution and genetic diversity of Bartonella in bat flies (Hippoboscoidea, Streblidae, Nycteribiidae). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haelewaters, D.; Hiller, T.; Dick, C.W. Bats, bat flies, and fungi: A case of hyperparasitism. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S.J.; Hunter, M.S.; Zchori-Fein, E. The emerging diversity of Rickettsia. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Barrett, A.D.T. Transmission cycles, host range, evolution and emergence of arboviral disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, T.; Nikoh, N.; Koga, R.; Satô, M.; Tanahashi, M.; Meng, X.-Y.; Fukatsu, T. Reductive genome evolution, host-symbiont co-speciation and uterine transmission of endosymbiotic bacteria in bat flies. ISME J. 2012, 6, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, S.F.; Bush, S.E.; Patterson, B.D.; Dick, C.W.; Gruwell, M.E.; Dittmar, K. Evolution, multiple acquisition, and localization of endosymbionts in bat flies (Diptera: Hippoboscoidea: Streblidae and Nycteribiidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bat ID (§) | # of Flies | % Virus Pos. | Fly ID (1) | Virus ID | Fly ID (2) | Virus ID | Fly ID (3) | Virus ID | Fly ID (4) | Virus ID | Fly ID (5) | Virus ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BF1 | 0 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| BF2 | 0 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| BF3 | 4 | 50% | BF301 | KYAV−BF301 | BF302 | n/a | BF303 | KYAV−BF303 | BF304 | n/a | − | − |
| BF4 | 3 | 100% | BF401 | KYAV−BF401 | BF402 | BUGV | BF403 | KYAV−BF403 | − | − | − | − |
| BF5 | 0 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| BF6 | 2 | 100% | BF601 | KYAV−BF601 | BF602 | KYAV−BF602 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| BF7 | 5 | 100% | BF701 | KYAV−BF701 | BF702 | KYAV−BF702 | BF703 | KYAV−BF703 | BF704 | KYAV−BF704 | BF705 | KYAV−BF705 |
| BF8 | 3 | 67% | BF801 | KYAV−BF801 | BF802 | KYAV−BF802 | BF803 | n/a | − | − | − | − |
| BF9 | 3 | 67% | BF901 | KYAV−BF901 | BF902 | KYAV−BF902 | BF903 | n/a | − | − | − | − |
| BF10 | 2 | 50% | BF1001 | KYAV−BF1001 | BF1002 | n/a | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| BF11 * | 4 | 100% | BF1101 | KYAV−BF1101 | BF1102 | KYAV−BF1102 | BF1103 | KYAV−BF1103 | BF1104 | KYAV−BF1104 | − | − |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bennett, A.J.; Paskey, A.C.; Kuhn, J.H.; Bishop-Lilly, K.A.; Goldberg, T.L. Diversity, Transmission, and Cophylogeny of Ledanteviruses (Rhabdoviridae: Ledantevirus) and Nycteribiid Bat Flies Parasitizing Angolan Soft-Furred Fruit Bats in Bundibugyo District, Uganda. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050750
Bennett AJ, Paskey AC, Kuhn JH, Bishop-Lilly KA, Goldberg TL. Diversity, Transmission, and Cophylogeny of Ledanteviruses (Rhabdoviridae: Ledantevirus) and Nycteribiid Bat Flies Parasitizing Angolan Soft-Furred Fruit Bats in Bundibugyo District, Uganda. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(5):750. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050750
Chicago/Turabian StyleBennett, Andrew J., Adrian C. Paskey, Jens H. Kuhn, Kimberly A. Bishop-Lilly, and Tony L. Goldberg. 2020. "Diversity, Transmission, and Cophylogeny of Ledanteviruses (Rhabdoviridae: Ledantevirus) and Nycteribiid Bat Flies Parasitizing Angolan Soft-Furred Fruit Bats in Bundibugyo District, Uganda" Microorganisms 8, no. 5: 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050750
APA StyleBennett, A. J., Paskey, A. C., Kuhn, J. H., Bishop-Lilly, K. A., & Goldberg, T. L. (2020). Diversity, Transmission, and Cophylogeny of Ledanteviruses (Rhabdoviridae: Ledantevirus) and Nycteribiid Bat Flies Parasitizing Angolan Soft-Furred Fruit Bats in Bundibugyo District, Uganda. Microorganisms, 8(5), 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050750






