Epidemiologic and Epizootic Data of Tularemia in the Past and in the Recent History in Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemic Investigations of Tularemia in Croatia—Efforts to Date
3. Epizooty of Tularemia
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Telford, S.R., 3rd; Goethert, H.K. Ecology of Francisella tularensis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CenterS for Disease Control and Prevention. Tularemia. Available online: https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/agentlist.asp (accessed on 25 May 2019).
- Dennis, D.T.; Inglesby, T.V.; Henderson, D.A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Ascher, M.S.; Eitzen, E.; Fine, A.D.; Friedlander, A.M.; Hauer, J.; Layton, M.; et al. Tularemia as a biological weapon: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2001, 285, 2763–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjodin, A.; Svensson, K.; Ohrman, C.; Ahlinder, J.; Lindgren, P.; Duodu, S.; Johansson, A.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Larsson, P.; Forsman, M. Genome characterisation of the genus Francisella reveals insight into similar evolutionary paths in pathogens of mammals and fish. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hestvik, G.; Warns-Petit, E.; Smith, L.A.; Fox, N.J.; Uhlhorn, H.; Artois, M.; Hannant, D.; Hutchings, M.R.; Mattsson, R.; Yon, L.; et al. The status of tularemia in Europe in a one-health context: A review. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 2137–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.; Oyston, P.C.; Green, M.; Titball, R.W. Tularemia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingry, L.C.; Petersen, J.M. Comparative review of Francisella tularensis and Francisella novicida. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, M.; Gyuranecz, M. Tularaemia: Clinical aspects in Europe. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyston, P.C. Francisella tularensis: Unravelling the secrets of an intracellular pathogen. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Database of the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu (accessed on 25 May 2019).
- Cerny, Z. Changes of the epidemiology and the clinical picture of tularemia in Southern Moravia (the Czech Republic) during the period 1936–1999. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 17, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Kleines, M. Two at one blow: Reemergence of tularemia in Upper Austria. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnvik, A. WHO Guidelines on Tularaemia. 2007.7, WHO/CDS/EPR/2007.7; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pilo, P. Phylogenetic Lineages of Francisella tularensis in Animals. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehringer, H.; Schacht, E.; Maylaender, N.; Zeman, E.; Kaysser, P.; Oehme, R.; Pluta, S.; Splettstoesser, W.D. Presence of an emerging subclone of Francisella tularensis holarctica in Ixodes ricinus ticks from south-western Germany. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013, 4, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubalek, Z.; Treml, F.; Halouzka, J.; Juricova, Z.; Hunady, M.; Janik, V. Frequent isolation of Francisella tularensis from Dermacentor reticulatus ticks in an enzootic focus of tularaemia. Med Vet. Entomol. 1996, 10, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreizinger, Z.; Hornok, S.; Dan, A.; Hresko, S.; Makrai, L.; Magyar, T.; Bhide, M.; Erdelyi, K.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Gyuranecz, M. Prevalence of Francisella tularensis and Francisella-like endosymbionts in the tick population of Hungary and the genetic variability of Francisella-like agents. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Yu, Z.J.; Wang, D.; Bronislava, V.; Branislav, P.; Liu, J.Z. The bacterial microbiome of field-collected Dermacentor marginatus and Dermacentor reticulatus from Slovakia. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubalek, Z.; Rudolf, I. Francisella tularensis prevalence and load in Dermacentor reticulatus ticks in an endemic area in Central Europe. Med Vet. Entomol. 2017, 31, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeske, K.; Tomaso, H.; Imholt, C.; Schulz, J.; Beerli, O.; Suchomel, J.; Heroldova, M.; Jacob, J.; Staubach, C.; Ulrich, R.G. Detection of Francisella tularensis in three vole species in Central Europe. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, A.; Schulze, C.; Kutzer, P.; Probst, C.; Hlinak, A.; Ochs, A.; Grunow, R. Tularaemia seroprevalence of captured and wild animals in Germany: The fox (Vulpes vulpes) as a biological indicator. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, M.; Heuner, K.; Jacob, D.; Grunow, R. Tularemia in Germany-A Re-emerging Zoonosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennebique, A.; Boisset, S.; Maurin, M. Tularemia as a waterborne disease: A review. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1027–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurcan, S. Epidemiology of tularemia. Balk. Med. J. 2014, 31, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunow, R.; Kalaveshi, A.; Kuhn, A.; Mulliqi-Osmani, G.; Ramadani, N. Surveillance of tularaemia in Kosovo, 2001 to 2010. Eur. Surveill. Bull. Eur. Sur Les Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reintjes, R.; Dedushaj, I.; Gjini, A.; Jorgensen, T.R.; Cotter, B.; Lieftucht, A.; D’Ancona, F.; Dennis, D.T.; Kosoy, M.A.; Mulliqi-Osmani, G.; et al. Tularemia outbreak investigation in Kosovo: Case control and environmental studies. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwibedi, C.; Birdsell, D.; Larkeryd, A.; Myrtennas, K.; Ohrman, C.; Nilsson, E.; Karlsson, E.; Hochhalter, C.; Rivera, A.; Maltinsky, S.; et al. Long-range dispersal moved Francisella tularensis into Western Europe from the East. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koene, M.; Rijks, J.; Maas, M.; Ruuls, R.; Engelsma, M.; van Tulden, P.; Kik, M.; Jooske, I.J.; Notermans, D.; de Vries, M.; et al. Phylogeographic Distribution of Human and Hare Francisella Tularensis Subsp. Holarctica Strains in the Netherlands and Its Pathology in European Brown Hares (Lepus Europaeus). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
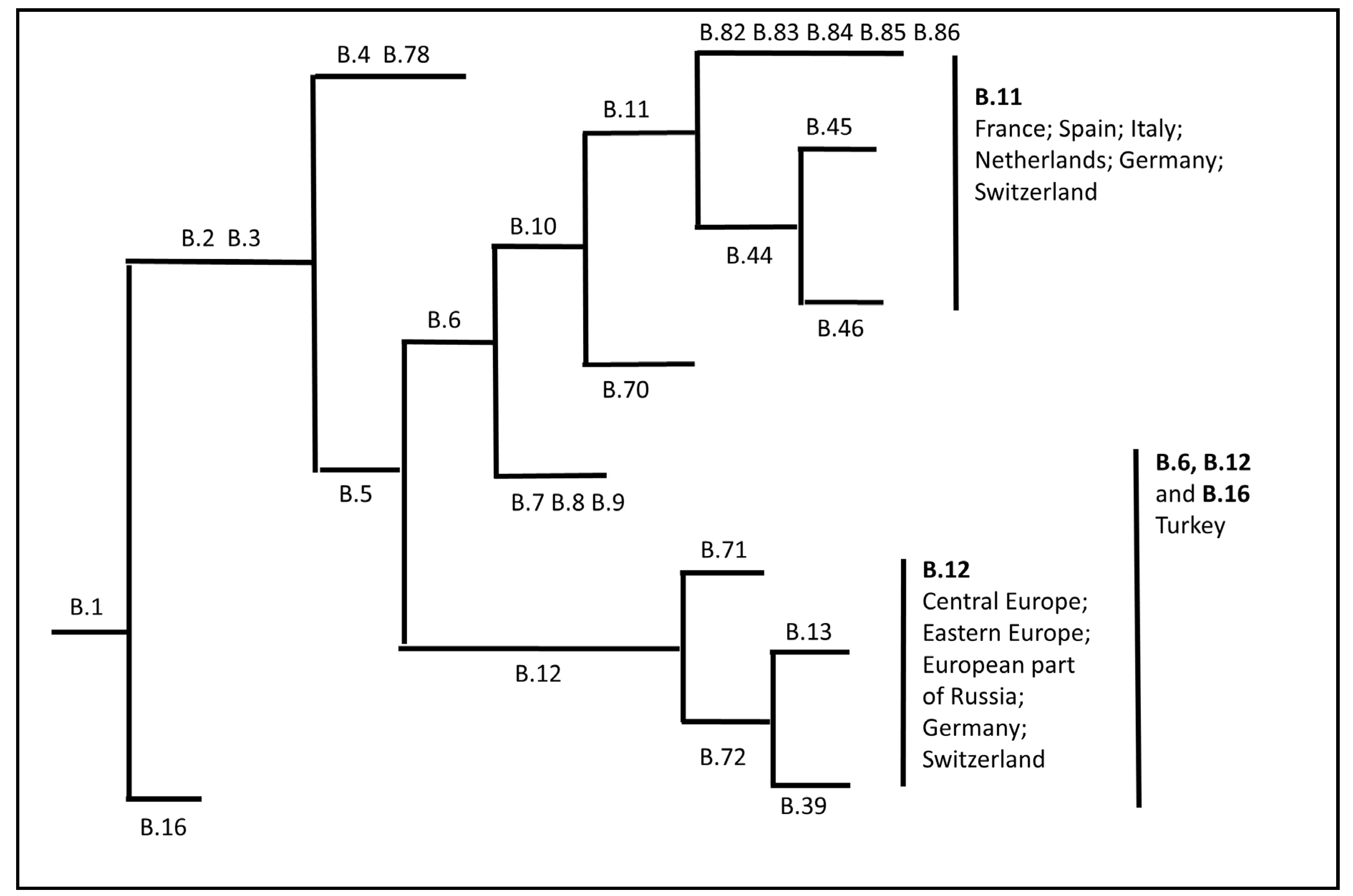
- Kreizinger, Z.; Erdelyi, K.; Felde, O.; Fabbi, M.; Sulyok, K.M.; Magyar, T.; Gyuranecz, M. Comparison of virulence of Francisella tularensis ssp. holarctica genotypes B.12 and B.FTNF002-00. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevin, M.; Girault, G.; Caspar, Y.; Cherfa, M.A.; Mendy, C.; Tomaso, H.; Gavier-Widen, D.; Escudero, R.; Maurin, M.; Durand, B.; et al. Phylogeography and Genetic Diversity of Francisella tularensis subsp. holarctica in France (1947-2018). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origgi, F.C.; Pilo, P. Francisella Tularensis Clades, B.FTN002-00 and B.13 Are Associated With Distinct Pathology in the European Brown Hare (Lepus europaeus). Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanturia, G.; Birdsell, D.N.; Kekelidze, M.; Zhgenti, E.; Babuadze, G.; Tsertsvadze, N.; Tsanava, S.; Imnadze, P.; Beckstrom-Sternberg, S.M.; Beckstrom-Sternberg, J.S.; et al. Phylogeography of Francisella tularensis subspecies holarctica from the country of Georgia. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morner, T.; Mattsson, R.; Forsman, M.; Johansson, K.E.; Sandstrom, G. Identification and classification of different isolates of Francisella tularensis. Zent. Veterinarmedizin. Reihe B J. Vet. Medicine. Ser. B 1993, 40, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsufjev, N.G.; Meshcheryakova, I.S. Infraspecific taxonomy of tularemia agent Francisella tularensis McCoy et Chapin. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 1982, 26, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vogler, A.J.; Birdsell, D.; Price, L.B.; Bowers, J.R.; Beckstrom-Sternberg, S.M.; Auerbach, R.K.; Beckstrom-Sternberg, J.S.; Johansson, A.; Clare, A.; Buchhagen, J.L.; et al. Phylogeography of Francisella tularensis: Global expansion of a highly fit clone. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2474–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borčić, B.; Gugić, F.; Kolić, J.; Tvrtković, N.; Bilić, V.; Bujas, S.; Nikolić, L. Nova (četvrta) epidemija tularemije u Srednjoj Posavini. Medicina 1975, 27, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Borčić, B. Epidemiološka Obilježja Tularemije u Njenim Prirodnim žarištima u Hrvatskoj. Disertacija; Sveučilište u Zagrebu: Zagreb, Croatia, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Heneberg, D.; Morelj, M.; Heneberg, N.; Mikes, M.; Doković, V.; Borčić, B.; Hrabar, A.; Išgum, M.; Đorđević, Z. Prvi rezultati istraživanja prirodnih žarišta tularemije na području Siska, Gušće, Popovca. Liječ. Vjesn. 1967, 89, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foshay, L. Prophylactic Vaccination Against Tularemia. Am. J. Clin. Path 1932, 2, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneberg, N.; Heneberg, Đ.; Borčić, B.; Peto, S.; Đorđević, Ž.; Išgum, M. Izrada i standardizacija jedne nove vrste intrakutanog tularina za retrogradnootkrivanje tularemične infekcije. Zbornik Radova VMA 1966, 1967, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Borčić, B.; Rudež, A.; Lasić, S.; Špalj, I.; Horvat, D.; Ferizović, Š.; Smok, I. Novi val tularemije u dugoselskom žarištu. Zdrav. Nov. 1968, 21, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Borčić, B. Some epidemiological and ecological characteristics of the tulaemia natural focus in the region of middle Posavina. In Proceedings of the VI International Congress of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases, Warszawa, Poland, 23–27 September 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Borčić, B. Atipična i asimptomatska tularemija u jednom aktivnom žarištu. In Proceedings of the Zbornika Radova III. Naučnog Sastanka Infektologa Jugoslavije, Portorož, Slovenia, 24–27 April 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Petričević, I.B.-K.M.; Breitenfeld, V.; Borčić, B.; Mažuran, D. Epidemija tularemije na području Dugog Sela i Vrbovca. Zdrav. Nov. 1968, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Mišić-Majerus, L.J.; Bujić, N.; Mađarić, V. Tularemija prenesena ubodom člankonožaca. Liječ. Vjesn. 1996, 118, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Brkić, I.; Borčić, B.; Aleraj, H. Tularemija u Petrinji. Vet. Stanica 1999, 129–192. [Google Scholar]
- Grgić, S.; Nikolić, J.; Čivljak, R.; Maretić, T.; Đaković Rode, O.; Lisić, M. Tifoidni oblik tularemije: Prikaz bolesnika. Infektološki Glas. 2011, 31, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Puljiz, I.; Vranjičan, Z.; Rakušić, S.; Jerković, L. Tularemija—prikaz bolesnika. Infektološki Glas. 2016, 36, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. Tularemia—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2016. Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/healthtopics/tularaemia/Pages/Annual-epidemiological-report-2016 (accessed on 17 November 2019).
- European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/tularaemia-annual-epidemiological-report-2018 (accessed on 17 November 2019).
- Ministry of Agriculture Veterinary and Food Safety Directorate. Program utvrđivanja prevalencije Francisella tularensis u Republici Hrvatskoj Zagreb, 2016. Available online: http://www.veterinarstvo.hr/UserDocsImages/Zdravlje_zivotinja/zoonoze_krpelji/PROGRAM%20TULAREMIJA%202018.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Croatian Institute of Public Health. Godišnje Izvješće o Zoonozama u Hrvatskoj za 2015./16. Godinu. Available online: https://www.hzjz.hr/sluzba-epidemiologija-zarazne-bolesti/godisnje-izvjesce-o-zoonozama-u-hrvatskoj/ (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Croatian Institute of Public Health. Communicable Diseases in Croatia 2016. Available online: https://www.hzjz.hr/en/news/communicable-diseases-in-croatia-in-2016/ (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Croatian Institute of Public Health. Communicable Diseases in Croatia 2017. Available online: https://www.hzjz.hr/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/ZBVHR_2017_Final.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Borcic, B.; Hrabar, A.; Dulic, B.; Tvrtkovic, N.; Bilic, V.; Mikacic, D. Ecological features of the tularemia natural focus in central Posavina (Croatia). Folia Parasitol. 1976, 23, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borčić, B.B.V.; Tvrtković, N. Tularemija u malih i divljih sisavaca. Vet Arh. 1975, 45, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Borcić, B.; Aleraj, B.; Žutić, M.; Mikačić, D. Uloga krpelja (Ixodidae) u podržavanju prirodnog žarišta tularemije u srednjoj Posavini. Vet. Arh. 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Tadin, A.; Tokarz, R.; Markotic, A.; Margaletic, J.; Turk, N.; Habus, J.; Svoboda, P.; Vucelja, M.; Desai, A.; Jain, K.; et al. Molecular Survey of Zoonotic Agents in Rodents and Other Small Mammals in Croatia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihelčić, M.; Habuš, J.; Vučelja, M.; Svoboda, P.; Kurolt, I.K.; Markotić, A.; Turk, N.; Margaletič, J.; Šantić, M. Prevalence of Francisella tuklarensis in the population of small mammals species in continental forests of Croatia. Šumarski List 2018, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Goethert, H.K.; Telford, S.R. Nonrandom distribution of vector ticks (Dermacentor variabilis) infected by Francisella tularensis. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, K.; Back, E.; Eliasson, H.; Berglund, L.; Granberg, M.; Karlsson, L.; Larsson, P.; Forsman, M.; Johansson, A. Landscape epidemiology of tularemia outbreaks in Sweden. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 ) was detected in 1964–1965 in localities around town Vrbovec. In 1974, the bacterium Francisella was detected in four different mammal species around town of Sisak: common vole (
) was detected in 1964–1965 in localities around town Vrbovec. In 1974, the bacterium Francisella was detected in four different mammal species around town of Sisak: common vole ( ), stripped field mouse (
), stripped field mouse ( ), common shrew and bicolored shrew (
), common shrew and bicolored shrew ( ). In the same area, in 1978, the bacterium was isolated from D. reticulatus ticks (
). In the same area, in 1978, the bacterium was isolated from D. reticulatus ticks ( ). Recent epizootic surveys reveal two mice positive for Francisella found in the locality of Draganić (2003–2011), and three positive mice collected on the locality of Lipovljani (2014–2016). Names of the cities and localities are labelled with upper case letters. Names of the rivers are labelled with lower case letters and italic. (Blank map adapted to source: https://d-maps.com/carte.php?num_car=5352&lang=en.
). Recent epizootic surveys reveal two mice positive for Francisella found in the locality of Draganić (2003–2011), and three positive mice collected on the locality of Lipovljani (2014–2016). Names of the cities and localities are labelled with upper case letters. Names of the rivers are labelled with lower case letters and italic. (Blank map adapted to source: https://d-maps.com/carte.php?num_car=5352&lang=en.
 ) was detected in 1964–1965 in localities around town Vrbovec. In 1974, the bacterium Francisella was detected in four different mammal species around town of Sisak: common vole (
) was detected in 1964–1965 in localities around town Vrbovec. In 1974, the bacterium Francisella was detected in four different mammal species around town of Sisak: common vole ( ), stripped field mouse (
), stripped field mouse ( ), common shrew and bicolored shrew (
), common shrew and bicolored shrew ( ). In the same area, in 1978, the bacterium was isolated from D. reticulatus ticks (
). In the same area, in 1978, the bacterium was isolated from D. reticulatus ticks ( ). Recent epizootic surveys reveal two mice positive for Francisella found in the locality of Draganić (2003–2011), and three positive mice collected on the locality of Lipovljani (2014–2016). Names of the cities and localities are labelled with upper case letters. Names of the rivers are labelled with lower case letters and italic. (Blank map adapted to source: https://d-maps.com/carte.php?num_car=5352&lang=en.
). Recent epizootic surveys reveal two mice positive for Francisella found in the locality of Draganić (2003–2011), and three positive mice collected on the locality of Lipovljani (2014–2016). Names of the cities and localities are labelled with upper case letters. Names of the rivers are labelled with lower case letters and italic. (Blank map adapted to source: https://d-maps.com/carte.php?num_car=5352&lang=en.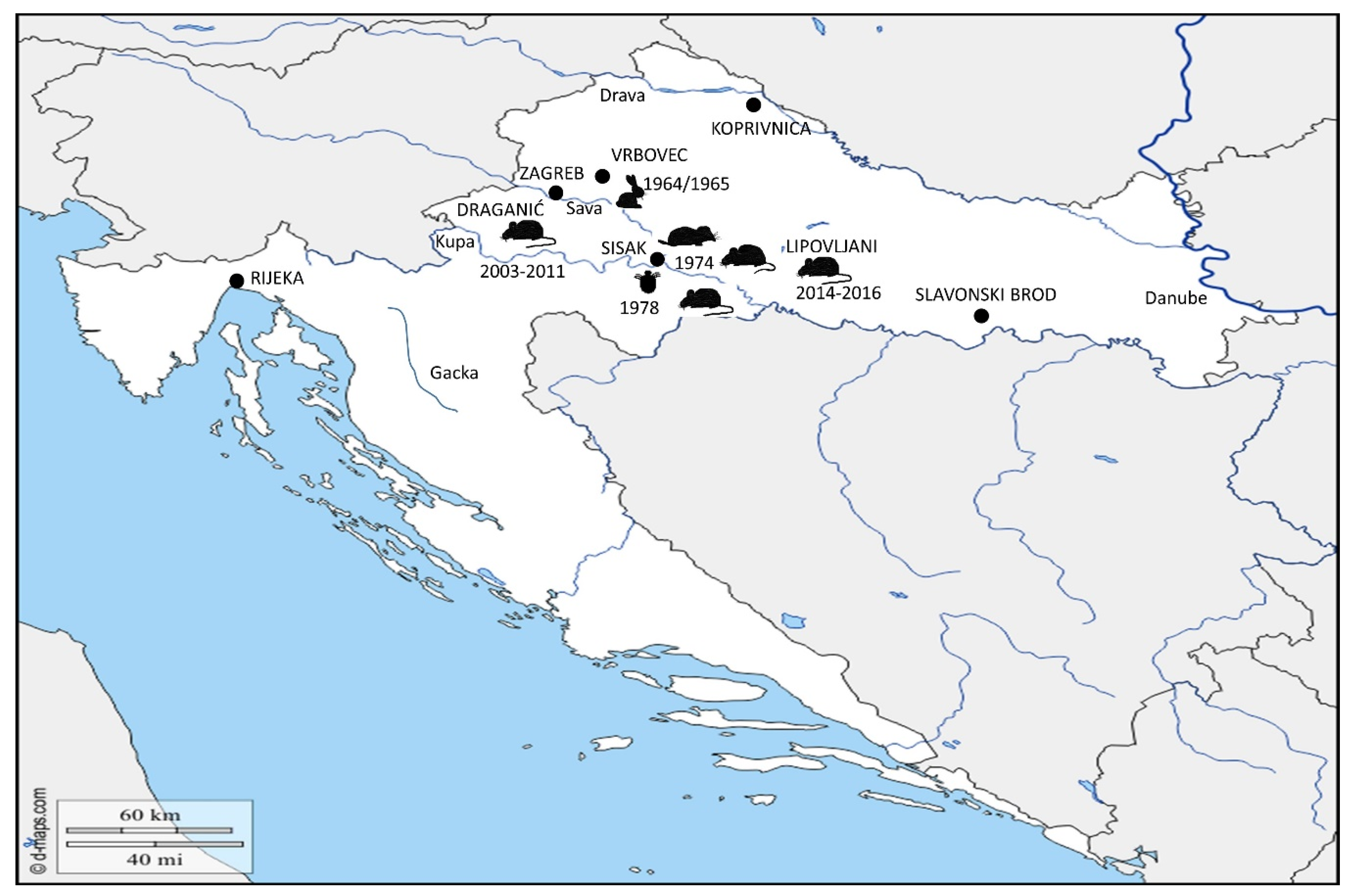
| Year | Number of Reported Cases |
|---|---|
| 2012 | 1 |
| 2013 | 2 |
| 2014 | 2 |
| 2015 | 13 |
| 2016 | 2 |
| 2017 | 3 |
| 2018 | 0 |
| Total | 23 |
| Animal Species | Number of Collected Animals | Number of F. tularensis Positive Animals |
|---|---|---|
| Apodemus flavicollis (yellow-necked mouse) | 3 | 0 |
| Apodemus agrarius (striped field mouse) | 87 | 3 |
| Apodemus sylvaticus (wood mouse) | 140 | 0 |
| Microtus arvalis (common vole) | 3 | 0 |
| Myodes (Clethryonomys) glareolus (bank vole) | 3 | 0 |
| Mus musculus (house mouse) | 2 | 0 |
| Crocidura leucodon (bicolored shrew) | 20 | 0 |
| Sorex araneus (common shrew) | 15 | 0 |
| Lepus europeus (European brown hare) | 10 | 1 |
| Vulpes vulpes (red fox) | 1 | 0 |
| Erinaceus (hedgehog) | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 285 | 4 |
| Animal Species | Number of Tested Animals | Number of F. tularensis Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| Microtus arvalis (common vole) | 87 | 4 |
| Apodemus agrarius (striped field mouse) | 70 | 4 |
| Apodemus sylvaticus (wood mouse) and Apodemus flavicollis (yellow-necked mouse) | 10 | 0 |
| Myodes (Clethryonomys) glareolus (bank vole) | 7 | 0 |
| Sorex araneus (common shrew) | 9 | 1 |
| Crocidura leucodon (bicolored shrew) | 22 | 3 |
| Mus musculus (house mouse) | 3 | 0 |
| Total | 208 | 12 |
| Species | Year | Total | % | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 1971 | 1972 | 1973 | 1974 | 1975 | 1976 | 1977 | 1978 | |||
| Ixodes ricinus | 402 | 2280 | 235 | 84 | 19 | 95 | 9 | 33 | 69 | 3226 | 7.4 |
| Dermacentor reticulatus | 0 | 1237 | 982 | 1831 | 579 | 2788 | 3177 | 2415 | 2261 | 15,270 | 35.1 |
| Dermacentor marginatus | 0 | 488 | 2585 | 5385 | 4965 | 4432 | 3194 | 2637 | 1270 | 24,960 | 57.3 |
| Undefined | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 76 | 76 | 0.2 |
| Total | 402 | 4005 | 3802 | 7300 | 5563 | 7315 | 6380 | 5085 | 3676 | 43,532 | 100.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihelčić, M.; Marečić, V.; Ožanič, M.; Kelava, I.; Knežević, M.; Šantić, M. Epidemiologic and Epizootic Data of Tularemia in the Past and in the Recent History in Croatia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050721
Mihelčić M, Marečić V, Ožanič M, Kelava I, Knežević M, Šantić M. Epidemiologic and Epizootic Data of Tularemia in the Past and in the Recent History in Croatia. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(5):721. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050721
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihelčić, Mirna, Valentina Marečić, Mateja Ožanič, Ina Kelava, Maša Knežević, and Marina Šantić. 2020. "Epidemiologic and Epizootic Data of Tularemia in the Past and in the Recent History in Croatia" Microorganisms 8, no. 5: 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050721
APA StyleMihelčić, M., Marečić, V., Ožanič, M., Kelava, I., Knežević, M., & Šantić, M. (2020). Epidemiologic and Epizootic Data of Tularemia in the Past and in the Recent History in Croatia. Microorganisms, 8(5), 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8050721






