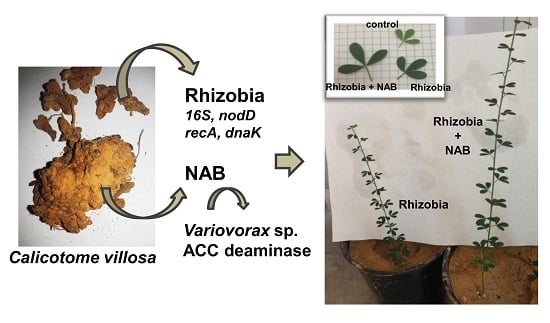
The ACC-Deaminase Producing Bacterium Variovorax sp. CT7.15 as a Tool for Improving Calicotome villosa Nodulation and Growth in Arid Regions of Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Localization of the Plants and Characteristics of the Soils
2.2. Isolation and Bacterial Growth
2.3. Genetic Diversity by BOX-PCR and Identification of Cultivable Bacteria
2.4. Determination of PGP Properties and Enzymatic Activities
2.5. Plant Inoculation and Growth
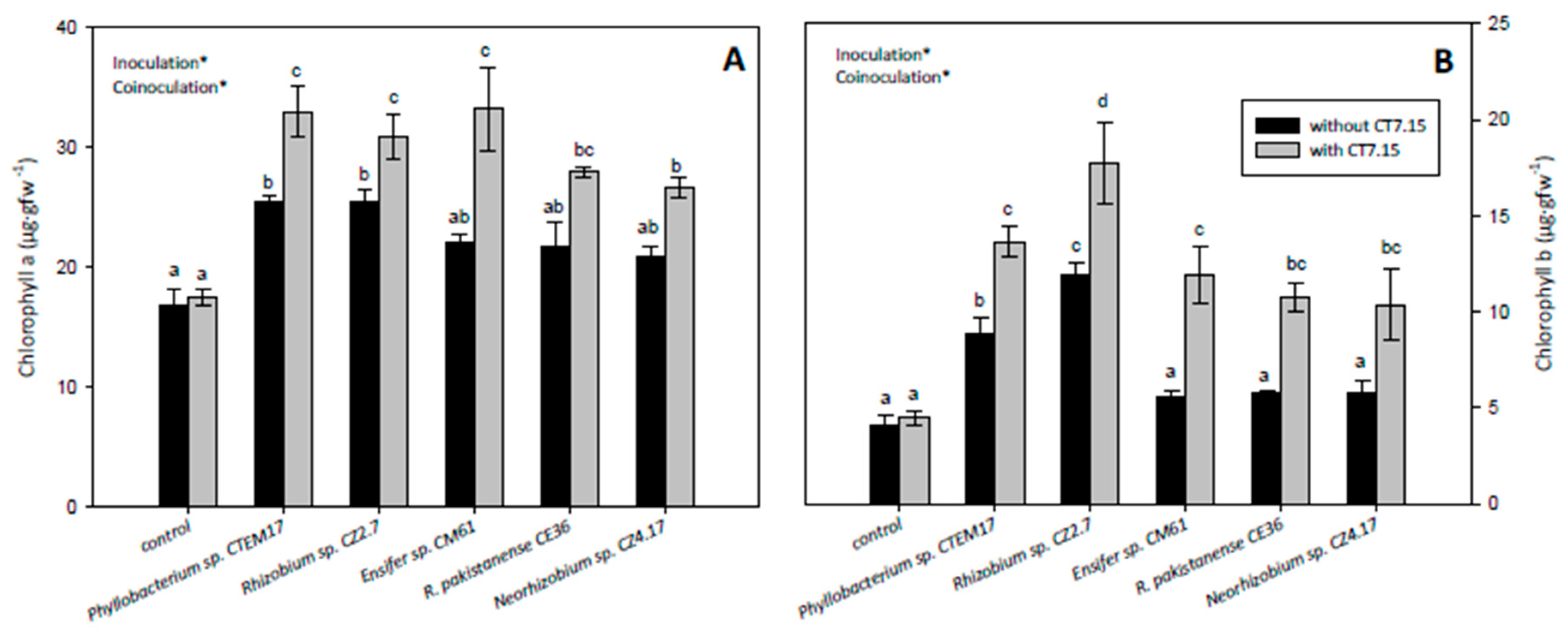
2.6. Photosynthetic Pigments
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biodiversity of Cultivable Bacteria Inhabiting C. villosa Nodules in Tunisian Arid Soils
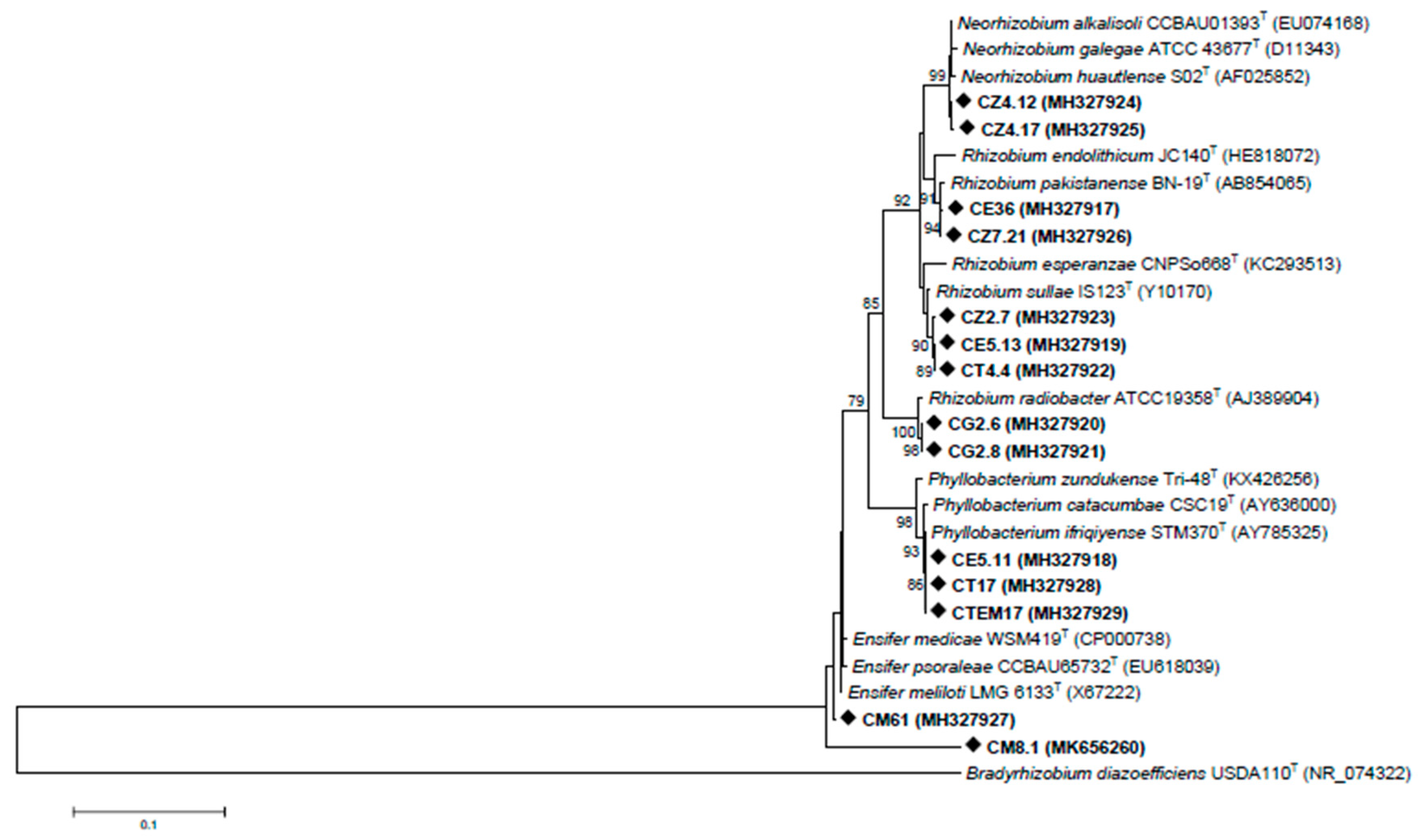
3.2. Rhizobia Isolated from C. villosa Nodules in Tunisian Arid Soils
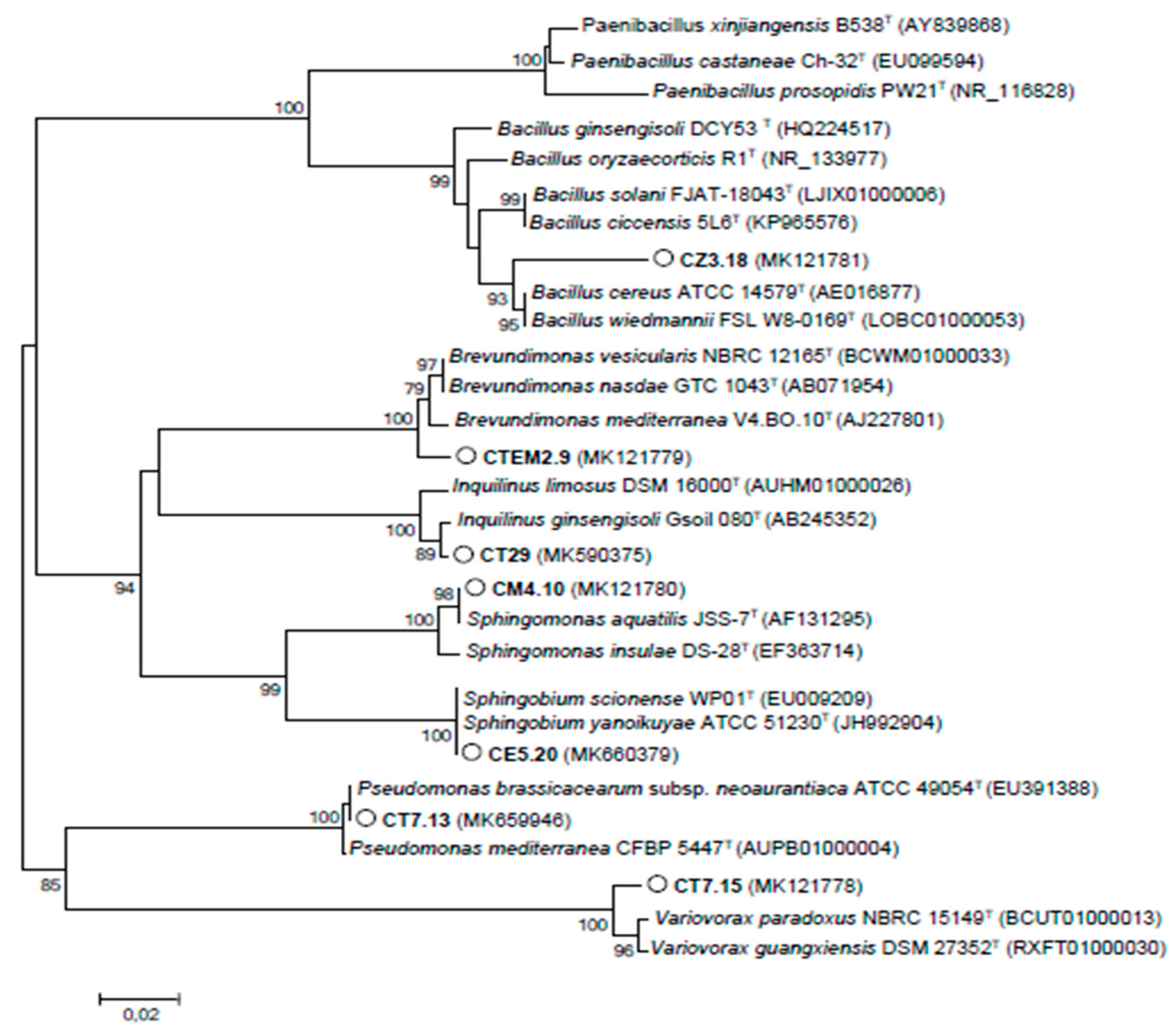
3.3. NAB Isolated from C. villosa Nodules in Tunisian Arid Soils
3.4. PGP Properties of the Isolates
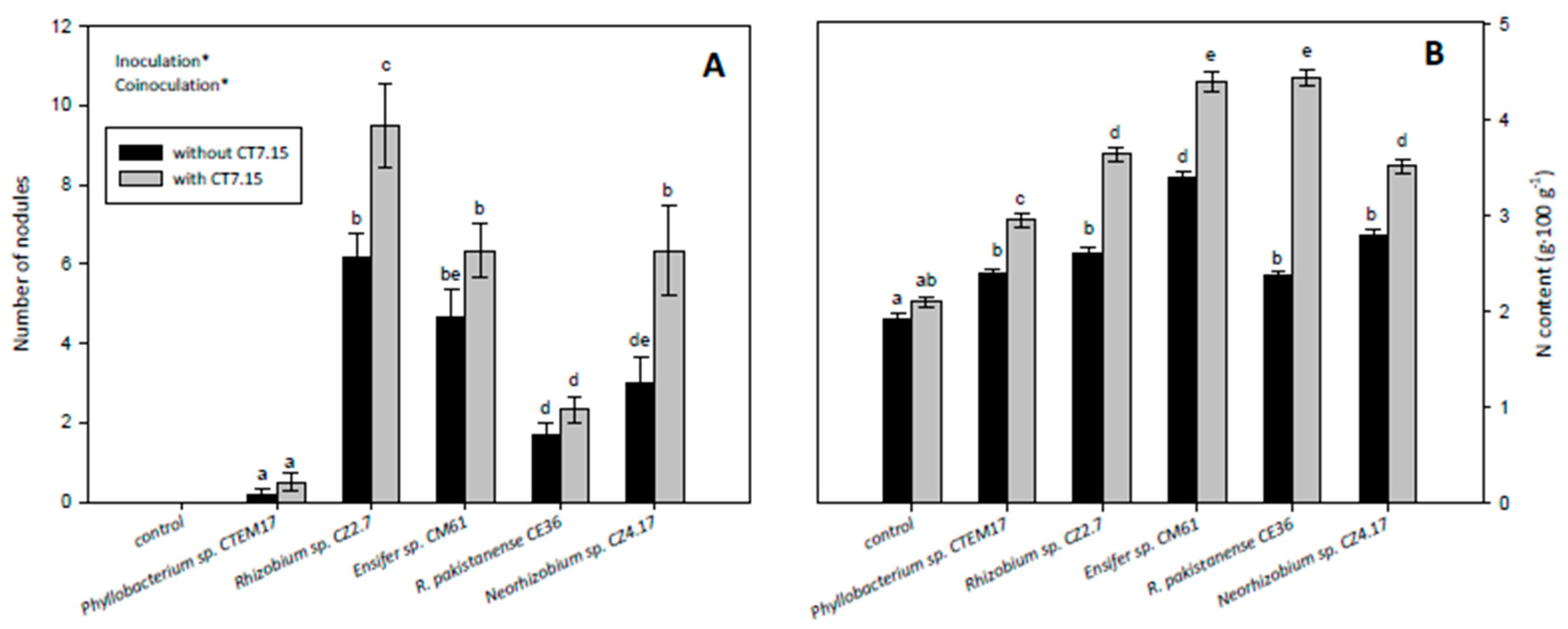
3.5. Co-Inoculation of C. villosa with Rhizobia and Variovorax sp. CT7.15 Strain Improves Plant Nodulation and Growth
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarhouni, M.; Ouled-Belgacem, A.; Henchi, B.; Neffati, M. A preliminary overview of the effects of seasonal drought and animal pressure around watering points on plant species using adaptative strategy analyses in the Tunisian arid zone. Ecol. Mediterr. 2006, 32, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Quezel, P.; Santa, S. Nouvelle Flore de L’Algérie et des Régions Désertiques Méridionales; Editions du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique: Paris, France, 1962; pp. 475–476.
- Greuter, W.; Burdet, H.M.; Long, G. Med.-Checklist 4: A Critical Inventory of Vascular Plants of the Circum Mediterranean Countries: Dicotyledones (Lauraceae Rhamnaceae); Genève Conservatoire et Jardin Botanique de la Ville de Genève: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, P.; Ramachandran, V.; Terpolilli, V. Rhizobia: From saprophytes to endosymbionts. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, M.; Lanza, A.; Bonni, M.L.; Marsala, S.; Puglia, A.M.; Quatrini, P. Diversity of rhizobia nodulating wild shrubs of Sicily and some neighboring islands. Arch. Microbiol. 2008, 190, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmi, A.; Boulila, F.; Bourebaba, Y.; Le Roux, C.; Belhadi, D.; De Lajudie, P. Phylogenetic diversity of Bradyrhizobium strains nodulating Calicotome spinosa in the Northeast of Algeria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhia, F.; Jeder, H.; Domergue, O.; Willems, A.; Cleyet-Marel, J.-C.; Gillis, M.; Dreyfus, B.; de Lajudie, P. Characterisation of wild legume nodulating bacteria (LNB) in the infra-arid zone of Tunisia. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 27, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhia, F.; Jeder, H.; Willems, A.; Gillis, M.; Dreyfus, B.; de Lajudie, P. Diverse bacteria associated with root nodules of spontaneous legumes in Tunisia and first report for nifH-like gene within the genera Microbacterium and Starkeya. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, S.E.; De Beuf, K.; Vekeman, B. A large diversity of non-rhizobial endophytes found in legume root nodules in Flanders (Belgium). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, G.; Patel, M.H.; Joshi, S.J. Isolation and characterization of nodule-associated Exiguobacterium sp. from the root nodules of fenugreek (Trigonella foenu-graecum) and their possible role in plant growth promotion. Int. J. Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 693982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Hidalgo, P.; Hirsch, A.M. The nodule microbiome: N2-Fixing rhizobia do not live alone. Phytobiomes 2017, 1, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, E.; Martínez-Hidalgo, P.; Carro, L.; Alonso, P.; Peix, A.; Trujillo, M.E.; Martínez-Molina, E. Nodular endophytes: An untapped diversity. In Beneficial Plant—Microbial Interactions: Ecology and Applications; González, B.R.M., González-López, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 214–236. [Google Scholar]
- Pandya, M.; Kumar, G.N.; Rajkumar, S. Invasion of rhizobial infection thread by non-rhizobia for colonization of Vigna radiata root nodules. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 348, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgadzaj, R.; James, E.K.; Kelly, S.; Kawaharada, Y.; de Jonge, N.; Jensen, D.B.; Madse, L.H.; Radutoiu, S. A legume genetic framework controls infection of nodules by symbiotic and endophytic bacteria. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanrewaju, O.S.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O. Mechanisms of action of plant growth promoting bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamalero, E.; Glick, B.R. Bacterial modulation of plant ethylene levels. Plant. Physiol. 2015, 169, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehboob, I.; Naveed, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Sessitsch, A. Potential of rhizosphere bacteria for improving Rhizobium-legume symbiosis. In Plant Microbe Symbiosis: Fundamentals and Advances; Arora, N.K., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Hidalgo, P.; Galindo-Villardón, P.; Trujillo, M.E.; Igual, J.M.; Martínez-Molina, E. Micromonospora from nitrogen-fixing nodules of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). A new promising plant probiotic bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6389. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, J.M. A manual for the practical study of root nodule bacteria. IBM Handb. 1970, 45, 440. [Google Scholar]
- Mesa, J.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Caviedes, M.A.; Redondo-Gomez, S.; Pajuelo, E.; Rodriguez-Llorente, I.D. Scouting contaminated estuaries: Heavy metal resistant and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in the native metal rhizoaccumulator Spartina maritima. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, J. Applied Multivariate Data Analysis; Springer Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 1, p. 621. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, R.; Velazquez, E.; Willems, A.; Vizcaino, N.; Subba-Rao, N.S.; Mateos, P.F.; Gillis, M.; Martinez-Molina, E. A new species of Devosia that forms a unique nitrogen-fixing root-nodule symbiosis with the aquatic legume Neptunia natans (L.f.) Druce. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5217–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.K.; Lim, Y.W. EzTaxon: A web based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, M.; Delaere, M.; Coopman, R.; de Vos, P.; Gillis, M.; Willems, A. Multilocus sequence analysis of Ensifer and related taxa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haukka, K.; Lindström, K.; Young, J.P. Three phylogenetic groups of nodA and nifH genes in Sinorhizobium and Mesorhizobium isolates from leguminous trees growing in Africa and Latin America. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenna, R.; Sugawara, H.; Koike, T.; Lopez, R.; Gibson, T.J.; Higgins, D.G.; Thompson, J.D. Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3497–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döebereiner, J. Isolation and identification of aerobic nitrogen-fixing bacteria from soil and plants. In Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry; Alef, K., Nannipieri, P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; pp. 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Buendía-Clavería, A.M.; Chamber, M.; Ruiz-Sainz, J.E. A comparative study of the physiological characteristics, plasmid content and symbiotic properties of different Rhizobium fredii strains. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1989, 12, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penrose, D.M.; Glick, B.R. Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol. Plant 2003, 118, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dyebinding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, J.P.; Prescott, L.M. Laboratory Exercises in Microbiology, 5th ed.; The McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; p. 466. [Google Scholar]
- Elbeltagy, A.; Nishioka, K.; Suzuki, H.; Sato, T.; Sato, Y.I.; Morisaki, H.; Mitsui, H.; Minamisawa, K. Isolation and characterization of endophytic bacteria from wild and traditionally cultivated rice varieties. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2000, 46, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, D.W.; Atkinson, E.M.; Long, S.R. Depolarization of alfalfa root hair membrane potential by Rhizobium meliloti Nod factors. Science 1992, 256, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 148, 350–382. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Tian, C.F.; Sui, X.H.; Chen, W.F.; Chen, W.X. Robust markers reflecting phylogeny and taxonomy of rhizobia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Romdhane, S.; Nasr, H.; Samba-Mbaye, R.; Neyra, M.; Ghorbal, M. Diversity of Acacia tortilis rhizobia revealed by PCR/RFLP on crushed root nodules in Tunisia. Ann. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 249–258. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdhi, M.; De Lajudie, P.; Mars, M. Phylogenetic and symbiotic characterization of rhizobial bacteria nodulating Argyrolobium uniflorum in Tunisian arid soils. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squartini, A.; Struffi, P.; Döring, H.; Selenska-Pobell, S.; Tola, E.; Giacomini, A.; Vendramin, E.; Velázquez, E.; Mateos, P.F.; Martinez-Molina, E.; et al. Rhizobium sullae sp. nov. (formerly ‘Rhizobium hedysari’), the root-nodule microsymbiont of Hedysarum coronarium L. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalid, R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ali, S.; Sui, X.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Amara, U.; Chen, W.; Hayat, R. Rhizobium pakistanensis sp. nov.; isolated from groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) nodules grown in rainfed Pothwar, Pakistan. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 107, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fterich, A.; Mahdhi, M.; Lafuente, A.; Pajuelo, E.; Caviedes, M.A.; Rodriguez-Llorente, I.D.; Mars, M. Taxonomic and symbiotic diversity of bacteria isolated from nodules of Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana in arid soils of Tunisia. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdhi, M.; Houidheg, N.; Mahmoudi, N.; Msaddak, A.; Rejili, M.; Mars, M. Characterization of rhizobial bacteria nodulating Astragalus corrugatus and Hippocrepis areolata in Tunisian Arid Soils. Polish J. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantelin, S.; Fischer-Le Saux, M.; Zakhia, F.; Béna, G.; Bonneau, S.; Jeder, H.; de Lajudie, P.; Cleyet-Marel, J.C. Emended description of the genus Phyllobacterium and description of four novel species associated with plant roots: Phyllobacterium bourgognense sp. nov.; Phyllobacterium ifriqiyense sp. nov.; Phyllobacterium leguminum sp. nov. and Phyllobacterium brassicacearum sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 827–839. [Google Scholar]
- Mhamdi, R.; Mrabet, M.; Laguerre, G.; Tiwari, R.; Aouani, M.E. Colonization of Phaseolus vulgaris nodules by Agrobacterium-like strains. Can. J. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrabet, M.; Mnasri, B.; Ben Romdhane, S.; Laguerre, G.; Aouani, M.E.; Mhamdi, R. Agrobacterium strains isolated from root nodules of common bean specifically reduce nodulation by Rhizobium gallicum. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 56, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, M.; Stepkowski, T.; Lotocka, B.; Malek, W. Phylogeny of nodulation genes and symbiotic properties of Genista tinctoria bradyrhizobia. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 186, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msaddak, A.; Durán, D.; Rejili, M.; Mars, M.; Ruiz Argüeso, T.; Imperial, J.; Palacios, J.; Rey, L. Diverse bacteria affiliated with the genera Microvirga, Phyllobacterium and Bradyrhizobium nodulate Lupinus micranthus growing in soils of Northern Tunisia. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2017, 83, e02820-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stępkowski, T.; Banasiewicz, J.; Granada, C.; Andrews, M.; Passaglia, L. Phylogeny and phylogeography of rhizobial symbionts nodulating legumes of the tribe Genisteae. Genes 2018, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinuesa, P.; León-Barrios, M.; Silva, C.; Willems, A.; Jarabo-Lorenzo, A.; Pérez-Galdona, R.; Werner, D.; Martínez-Romero, E. Bradyrhizobium canariense sp. nov.; an acid-tolerant endosymbiont that nodulates endemic genistoid legumes (Papilionoideae: Genisteae) from the Canary Islands, along with Bradyrhizobium japonicum bv. genistearum, Bradyrhizobium genospecies alpha and Bradyrhizobium genospecies beta. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaïch, K.; Bekki, A.; Bouras, N.; Holtz, M.D.; Soussou, S.; Mauré, L.; Brunel, B.; de Lajudie, P.; Cleyet-Marel, J.-C. Rhizobial diversity associated with the spontaneous legume Genista saharae in the northeastern Algerian Sahara. Symbiosis 2016, 71, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Díez, B.; Fajardo, S.; Puertas-Mejía, M.A.; de Felipe Mdel, R.; Fernández-Pascual, M. Stress tolerance, genetic analysis and symbiotic properties of root-nodulating bacteria isolated from Mediterranean leguminous shrubs in Central Spain. Arch. Microbiol. 2009, 191, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Laguerre, G.; Nour, S.M.; Macheret, V.; Sanjuan, J.; Drouin, P.; Amarger, N. Classification of rhizobia based on nodC and nifH gene analysis reveals a close phylogenetic relationship among Phaseolus vulgaris symbionts. Microbiology 2001, 147, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacovo, E.D.; Valentine, T.A.; Maluk, M.; Toorop, P.; Lopez del Egido, L.; Frachon, N.; Iannetta, P.P.M. Towards a characterisation of the wild legume bitter vetch (Lathyrus linifolius L. (Reichard) Bässler): Heteromorphic seed germination, root nodule structure and N-fixing rhizobial symbionts. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.H.; Wang, E.T.; Tan, Z.Y.; Zhu, M.E.; Chen, W.X. Rhizobium indigoferae sp. nov. and Sinorhizobium kummerowiae sp. nov.; respectively isolated from Indigofera spp. and Kummerowia stipulacea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Nick, G.; de Lajudie, P.; Eardly, B.D.; Suomalainen, S.; Paulin, L.; Zhang, X.; Gillis, M.; Lindström, K. Sinorhizobium arboris sp. nov. and Sinorhizobium kostiense sp. nov.; isolated from leguminous trees in Sudan and Kenya. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounsi-Hammami, S.; Le Roux, C.; Dhane-Fitouri, S.; de Lajudie, P.; Duponnois, R.; Jeddi, F.B. Genetic diversity of rhizobia associated with root nodules of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) in Tunisian calcareous soils. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 42, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinga, M.K.; Jaiswal, S.K.; Dakora, F.D. Presence of diverse rhizobial communities responsible for nodulation of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in South African and Mozambican soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 93, fiw236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hoque, M.S.; Broadhurst, L.M.; Thrall, P.H. Genetic characterization of root-nodule bacteria associated with Acacia salicina and A. stenophylla (Mimosaceae) across south-eastern Australia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aserse, A.A.; Räsänen, L.A.; Aseffa, F.; Hailemariam, A.; Lindström, K. Diversity of sporadic symbionts and nonsymbiotic endophytic bacteria isolated from nodules of woody, shrub, and food legumes in Ethiopia. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 10117–10134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, B.R. Promotion of plant growth by bacterial ACC deaminase. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2007, 26, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Poel, B.; Smet, D.; Van Der Straeten, D. Ethylene and hormonal crosstalk in vegetative growth and development. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Leubner-Metzger, G. Seed dormancy and the control of germination. New Phytol. 2006, 171, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.R.; Ecker, J.R. The ethylene gas signal transduction pathway: A Molecular Perspective. Annu. Rev. Gen. 1998, 32, 227–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaharoona, B.; Arshad, M.; Zahir, Z.A. Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria containing ACC-deaminase on maize (Zea mays L.) growth under axenic conditions and on nodulation in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 42, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, M.; Shimomura, T. Metabolism of 1-aminocyclopropane- 1-carboxylic acid. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1978, 42, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar]



| Coordinates | Ecosystem and Soil Characteristics | pH | Conductivity (µS/cm2) | Corg % | P2O5 % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1—Gabes | 33°46′ N, 10°5′ E | Oued bed, sandy gravel | 8.2 ± 0.3 | 19 ± 0.5 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | <0.005 |
| S2—Matmata | 33°29′ N, 10°4′ E | Oued bed, sandy gravel | 9.1 ± 0.4 | 48 ± 0.4 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | <0.005 |
| S3—Zarate | 33°41′ N, 10°21′ E | Sandy (protected area) | 8.3 ± 0.2 | 20 ± 0.6 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | <0.005 |
| S4—Medenine | 33°14′ N, 10°19′ E | Sandy gravel | 9.3 ± 0.2 | 32 ± 0.3 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | <0.005 |
| S5—Tataouine | 33°11′ N, 10°22′ E | Sandy gravel | 8.4 ± 0.3 | 29 ± 0.4 | 0.36 ± 0.02 | <0.005 |
| Strain | Accession No. | Related Species | Sequenced Fragment (bp) | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE36 | MH327917 | Rhizobium pakistanense | 928 | 98.99 |
| CE5.11 | MH327918 | Phyllobacterium ifriqiyense | 1029 | 99.70 |
| CE5.13 | MH327919 | Rhizobium sullae | 957 | 99.34 |
| CG2.6 | MH327920 | Rhizobium radiobacter | 1303 | 99.54 |
| CG2.8 | MH327921 | Rhizobium radiobacter | 1336 | 98.39 |
| CT4.4 | MH327922 | Rhizobium esperanzae | 1381 | 98.22 |
| CZ2.7 | MH327923 | Rhizobium esperanzae | 1360 | 97.41 |
| CZ4.12 | MH327924 | Neorhizobium alkalisoli | 1300 | 99.77 |
| CZ4.17 | MH327925 | Neorhizobium alkalisoli | 925 | 99.67 |
| CZ7.21 | MH327926 | Rhizobium pakistanense | 1017 | 98.80 |
| CM61 | MH327927 | Ensifer meliloti | 1020 | 99.51 |
| CT17 | MH327928 | Phyllobacterium catacumbae | 1432 | 95.36 |
| CTEM17 | MH327929 | Phyllobacterium ifriqiyense | 1382 | 96.44 |
| CT17.15 | MK121778 | Variovorax paradoxus | 1328 | 96.61 |
| CTEM29 | MK121779 | Brevundimonas sp. | 1100 | 97.36 |
| CM4.10 | MK121780 | Sphingomonas aquatilis | 1302 | 97.93 |
| CZ3.18 | MK121781 | Bacillus cereus | 889 | 97.64 |
| CT7.13 | MK659946 | Pseudomonas sp. | 979 | 96.78 |
| CM8.1 | MK656260 | Ensifer meliloti | 1049 | 90.14 |
| CE5.20 | MK660379 | Sphingomonas sp. | 1229 | 97.15 |
| CT29 | MK590375 | Inquilinus sp. | 1347 | 97.99 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bessadok, K.; Navarro-Torre, S.; Pajuelo, E.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Redondo-Gómez, S.; Caviedes, M.Á.; Fterich, A.; Mars, M.; Rodríguez-Llorente, I.D. The ACC-Deaminase Producing Bacterium Variovorax sp. CT7.15 as a Tool for Improving Calicotome villosa Nodulation and Growth in Arid Regions of Tunisia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040541
Bessadok K, Navarro-Torre S, Pajuelo E, Mateos-Naranjo E, Redondo-Gómez S, Caviedes MÁ, Fterich A, Mars M, Rodríguez-Llorente ID. The ACC-Deaminase Producing Bacterium Variovorax sp. CT7.15 as a Tool for Improving Calicotome villosa Nodulation and Growth in Arid Regions of Tunisia. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(4):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040541
Chicago/Turabian StyleBessadok, Khouloud, Salvadora Navarro-Torre, Eloísa Pajuelo, Enrique Mateos-Naranjo, Susana Redondo-Gómez, Miguel Ángel Caviedes, Amira Fterich, Mohamed Mars, and Ignacio D. Rodríguez-Llorente. 2020. "The ACC-Deaminase Producing Bacterium Variovorax sp. CT7.15 as a Tool for Improving Calicotome villosa Nodulation and Growth in Arid Regions of Tunisia" Microorganisms 8, no. 4: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040541
APA StyleBessadok, K., Navarro-Torre, S., Pajuelo, E., Mateos-Naranjo, E., Redondo-Gómez, S., Caviedes, M. Á., Fterich, A., Mars, M., & Rodríguez-Llorente, I. D. (2020). The ACC-Deaminase Producing Bacterium Variovorax sp. CT7.15 as a Tool for Improving Calicotome villosa Nodulation and Growth in Arid Regions of Tunisia. Microorganisms, 8(4), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040541