Contrasting Patterns of the Bacterial Communities in Melting Ponds and Periglacial Rivers of the Zhuxi glacier in the Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Illumina Miseq Sequencing
2.3. Network Construction and Characterization
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
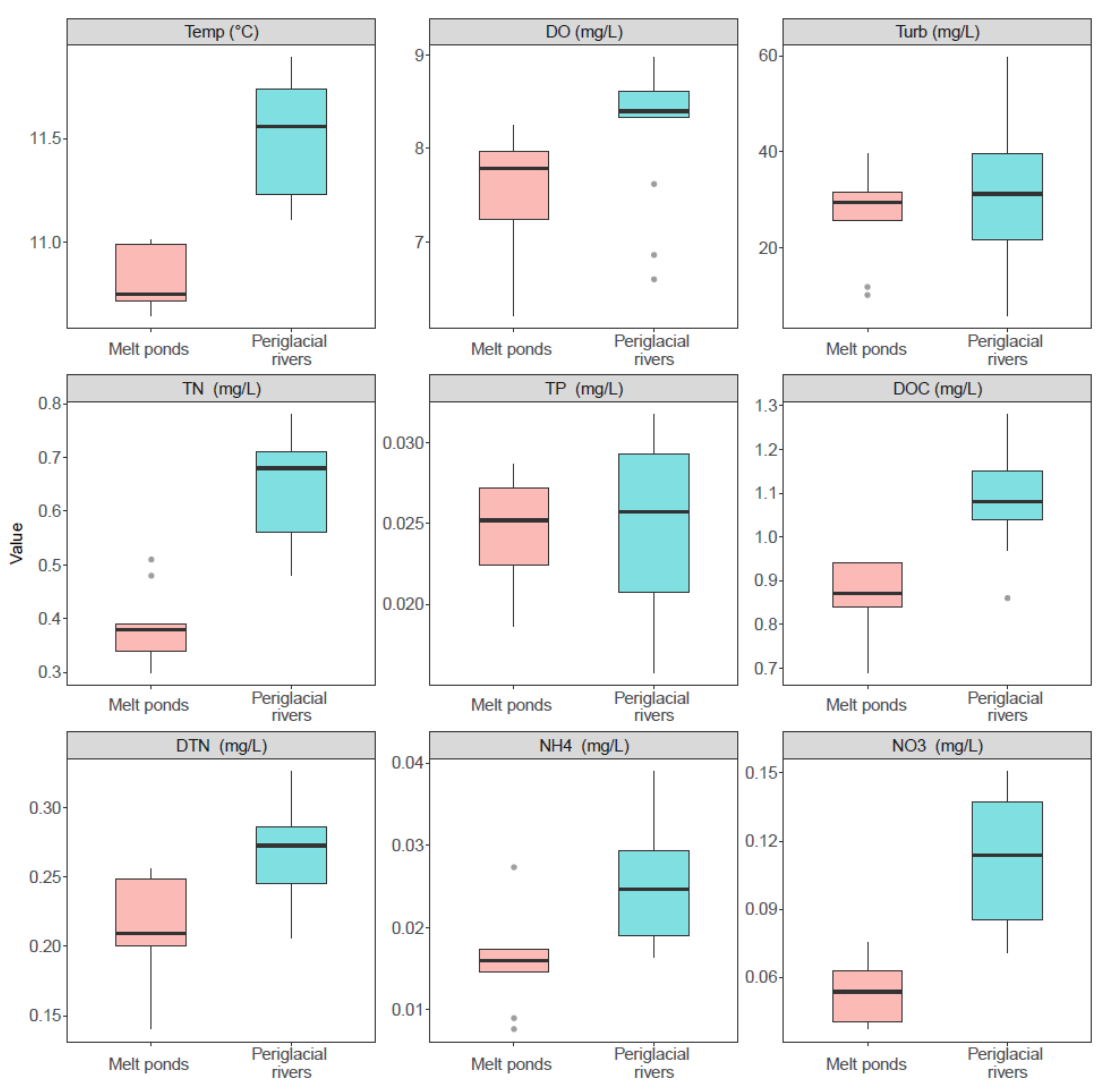
3.1. The Physicochemical Conditions in Melt Ponds and Periglacial Rivers
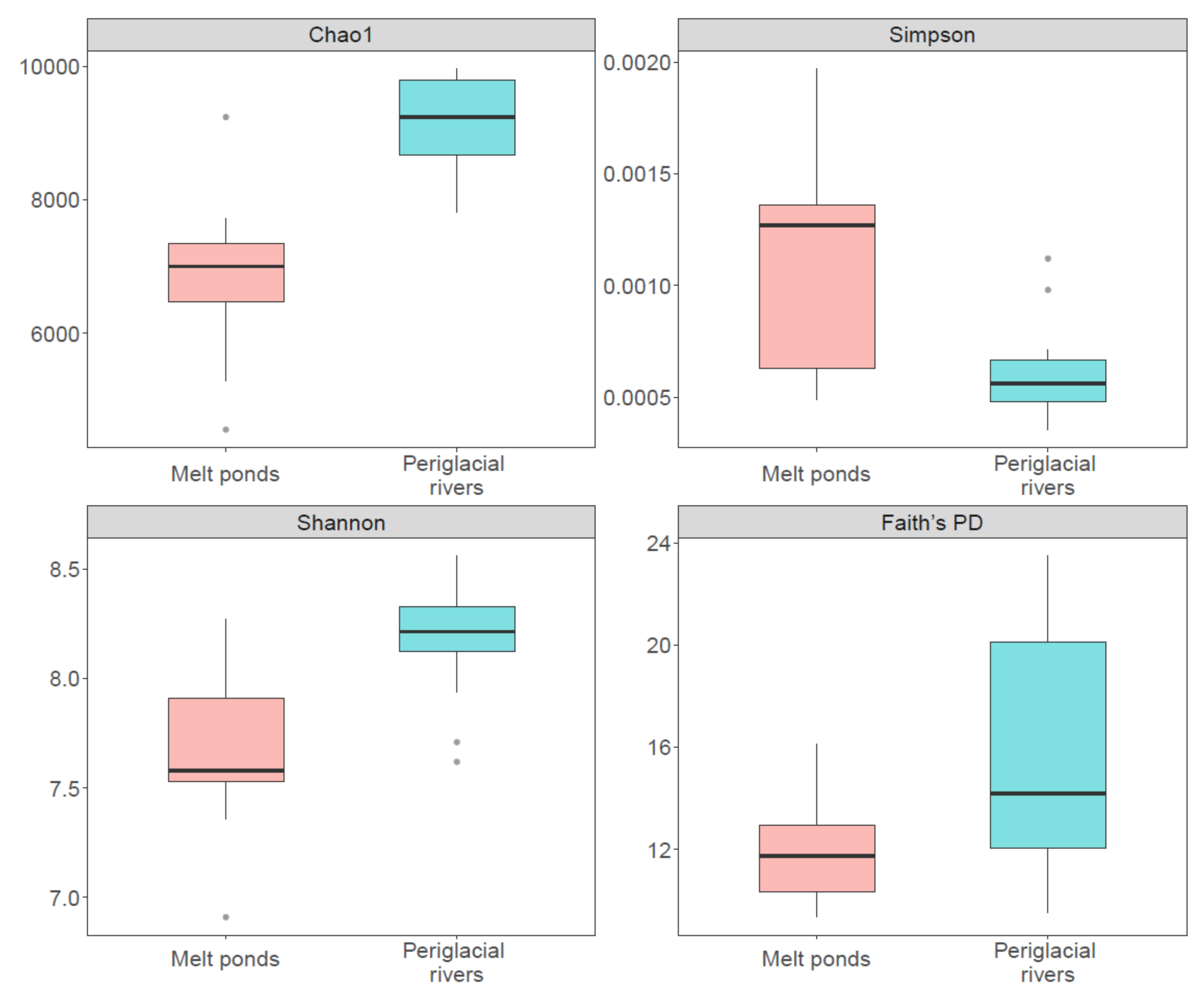
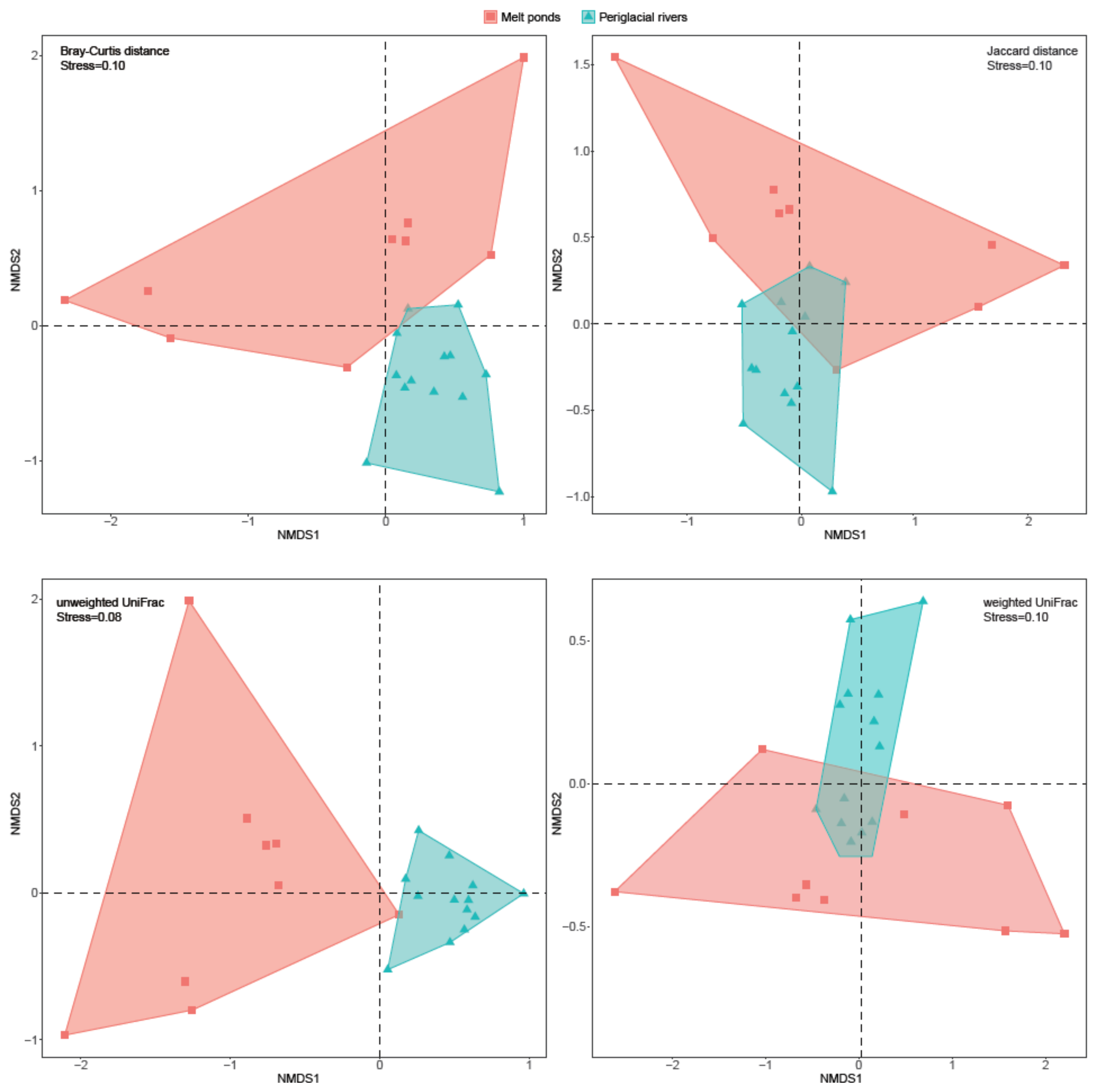
3.2. Diversity of Bacterial Communities between Melt Ponds and Periglacial Rivers
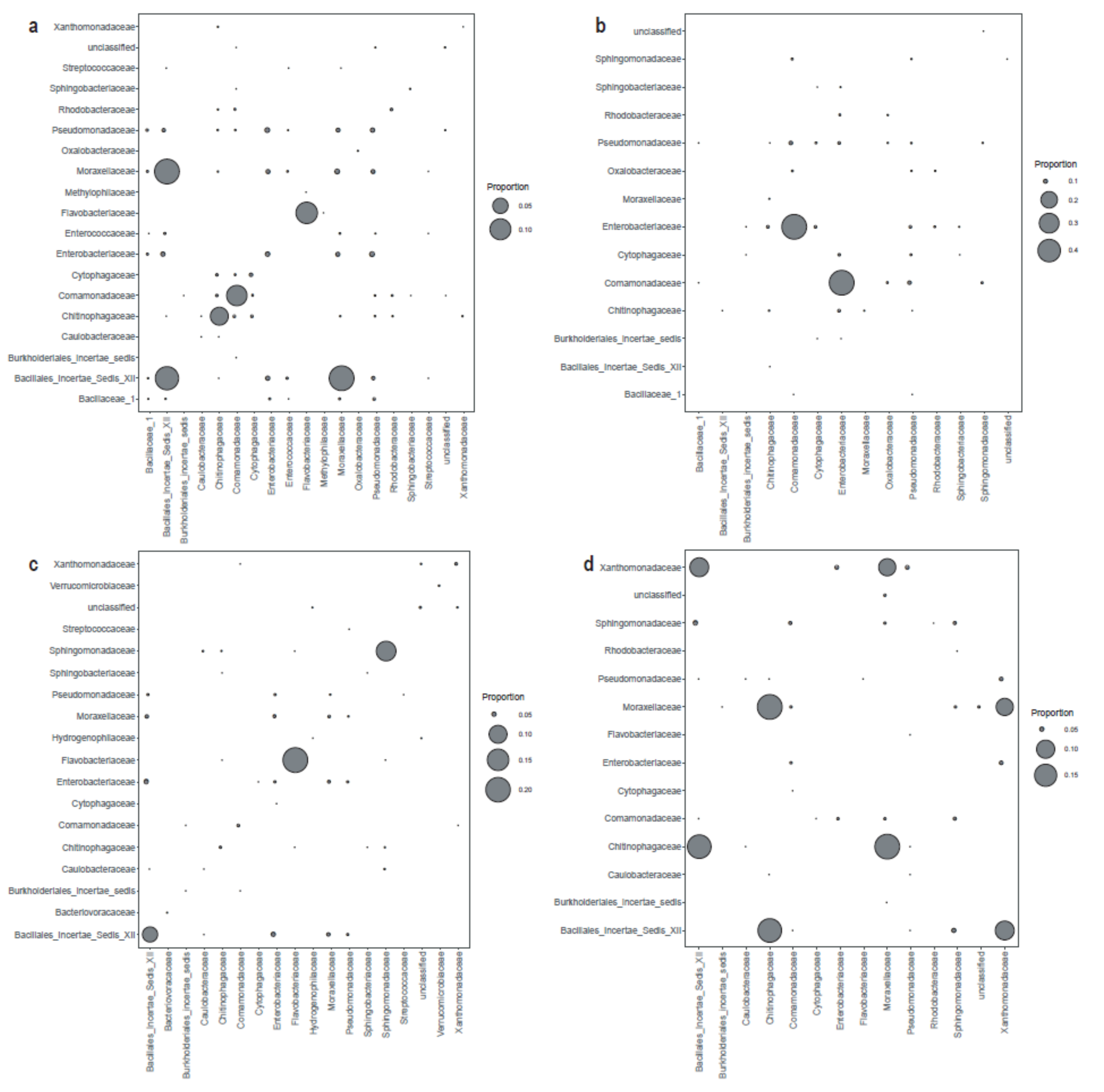
3.3. The Taxonomic Profile of the Bacterial Communities in Melt Ponds and Periglacial Rivers
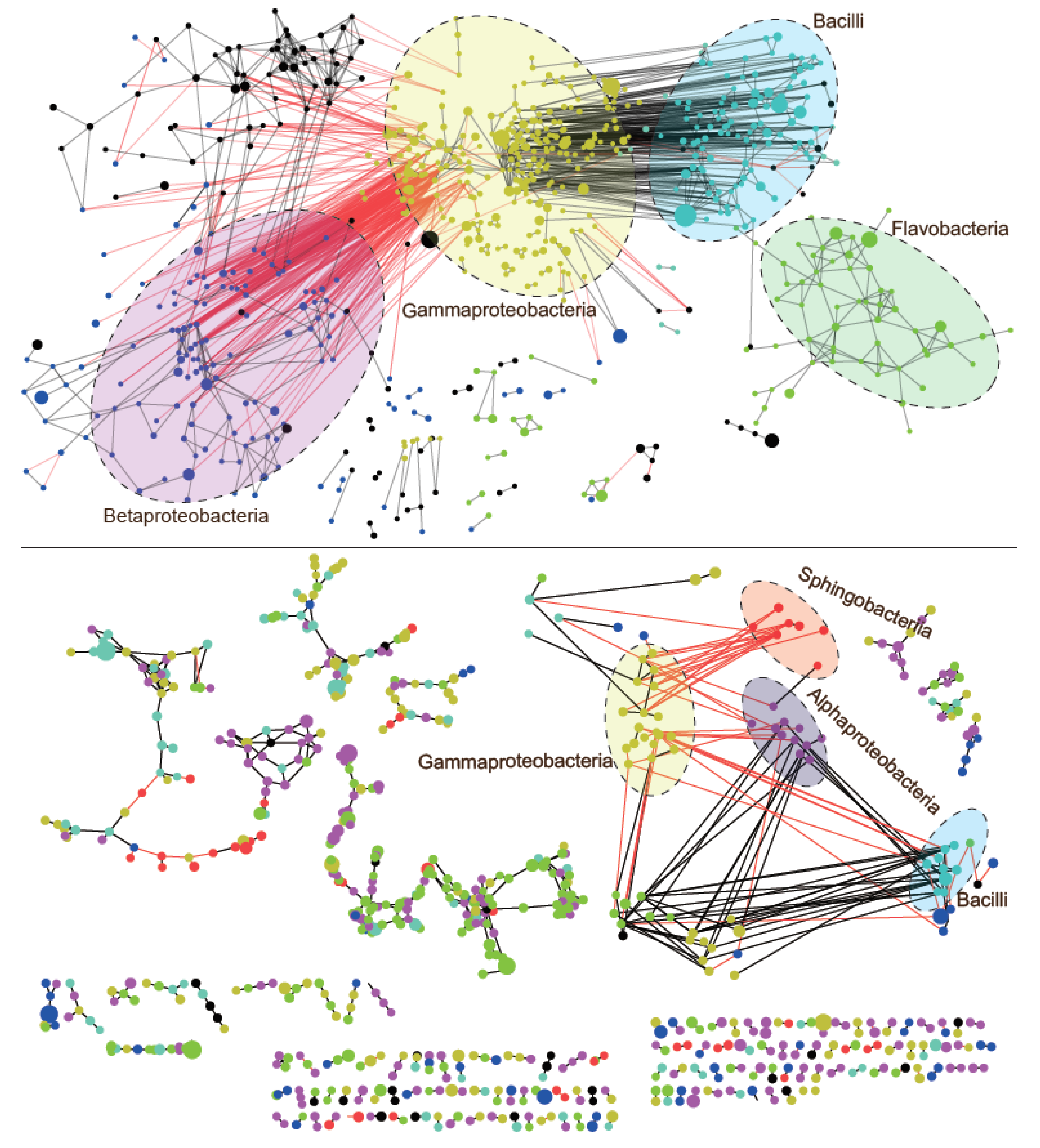
3.4. Architecture of Bacterial Co-Occurrence Network between Melt Ponds and Periglacial Rivers
4. Discussion
4.1. The Diversity and Composition Patterns between Melt Ponds and Periglacial Rivers
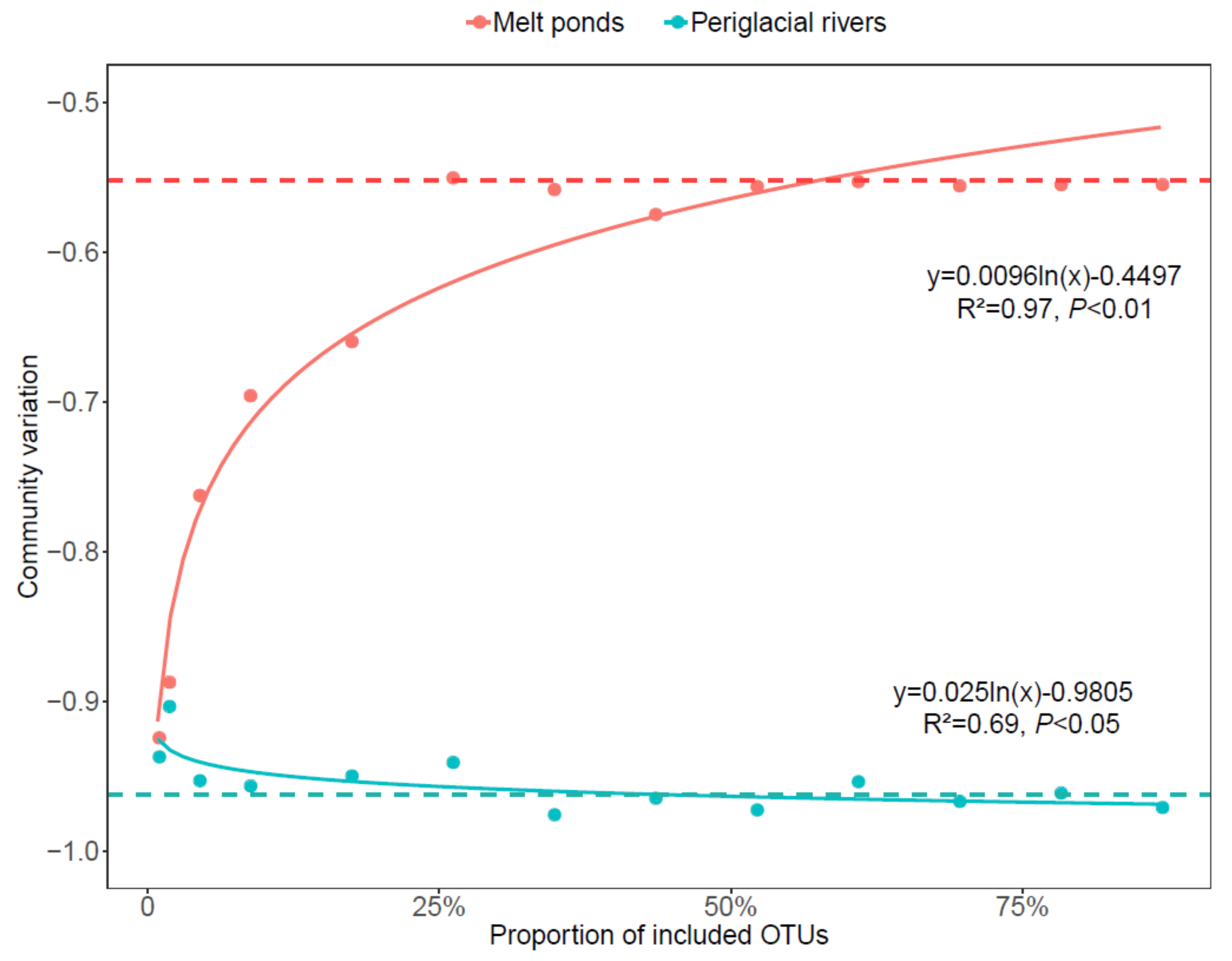
4.2. The Role of Rare Sub-Communities on the Bacterial Communities in Melt Ponds and Periglacial Rivers
4.3. Higher Competitive and Connected Network of Bacterial Communities in Melt Ponds than in Periglacial Rivers
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milner, A.M.; Khamis, K.; Battin, T.J.; Brittain, J.E.; Barrand, N.E.; Fuereder, L.; Cauvy-Fraunie, S.; Gislason, G.M.; Jacobsen, D.; Hannah, D.M.; et al. Glacier shrinkage driving global chagnes in downstream systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9770–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemp, M.H.; Frey, I.; Gärtner-Roer, I.; Nussbaumer, S.U.; Hoelzle, M.; Paul, F.; Haeberli, W.; Denzinger, F.; Ahlstrøm, A.P.; Anderson, B.; et al. Historically unprecedented global glacier decline in the early 21st century. J. Glaciol. 2015, 61, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, A.; Fujita, K. Contrasting glacier responses to recent climate change in high-mountain Asia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, B.J.; Zhu, L.P. Difference and cause analysis of water storage changes for glacier-fed and non-glacier-fed lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 93, 133399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, L.C.; Loose, B.; Heywood, K.J. Upper ocean distribution of glacial meltwater in the Amundsen Sea, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res-Ocean 2019, 124, 6854–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, K.N.; Isbel, J.L.; McHenry, L.; Limarino, C.O.; Moxness, L.D.; Schencman, L.J. A paleoclimatic reconstruction of the Carboniferous-Permian paleovalley fill in the eastern Paganzo Basin: Insights into glacial extent and deglaciation of southwestern Gondwana. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2019, 95, 102236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polashenski, C.; Perovich, D.; Courville, Z. The mechanisms of sea ice melt pond formation and evolution. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 17, C01001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneed, W.A.; Hamilton, G.S. Evolution of melt pond volume on the surface of the GreenlandIce Sheet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L03501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Stockwell, D.A.; Joo, H.M.; Son, Y.B.; Kang, C.K.; Whitledge, T.E. Phytoplankton production from melting ponds on Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C04030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, S.; McDonald, I.R.; Herbold, C.W.; Lee, C.K.; Niederberger, T.S.; Cary, C. Temporal, regional and geochemical drivers of microbial community variation in the melt ponds of the Ross Sea region, Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suren, A. Microfauna associated with algal mats in melt ponds of the Ross Ice Shelf. Polar Biol. 1990, 10, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, B.M.; Tiedje, J.M. Microbial reductive dehalogenation in Antarctic melt pond sediments. Antarct. Sci. 2007, 19, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segawa, T.; Takeuchi, N. Cyanobacterial communities on Qiyi glacier, Qilian Shan, China. Ann. Glaciol. 2010, 51, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, N.; Kohshima, S.; Seko, K. tructure, formation, and darkening process of albedo-reducing material (cryoconite) on a Himalayan glacier: A granular algal mat growing on the glacier. Arct. Antart. Alp. Res. 2001, 33, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam, I.; Charchuk, R.; Lange, B.; Beckers, J.; Haas, C.; Lanoil, B. Distinct bacterial assemblages reside at different depths in Arctic multiyear sea ice. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.J.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Joo, H.-M.; Jeong, J.Y.; Yang, E.J.; Kang, S.-H.; Yun, M.S.; Lee, S.H. In-situ measured carbon and nitrogen uptake rates of melt pond algae in the western Arctic ocean, 2014. Ocean Sci. J. 2018, 53, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsay, C.M.; Aguilar-Islas, A.; Fitzsimmons, J.N.; Hatta, M.; Jensen, L.T.; John, S.G.; Kadko, D.; Landing, W.M.; Lanning, N.T.; Morton, P.L.; et al. Dissolved and particulate trace elements in late summer Arctic melt ponds. Mar. Chem. 2018, 204, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptmann, A.L.; Markussen, T.N.; Stibal, M.; Olsen, N.S.; Elberling, B.; Bælum, J.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Jacobsen, C.S. Upstream freshwater and terrestrial sources are differentially reflected in the bacterial community structure along a small Arctic river and its estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster-Brown, J.G.; Hawes, I.; Jungblut, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Christenson, H.K. The effects of entombment on water chemistry and bacterial assemblages in closed cryoconite holes on Antarctic glaciers. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Vick-Majors, T.J.; Priscu, J.C.; Yao, T.D.; Kang, S.C.; Liu, K.S.; Cong, Z.Y.; Xiong, J.B.; Li, Y. Biogeography of cryoconite bacterial communities on glaciers of the Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turicchia, S.; Ventura, S.; Schütte, U.; Soldati, E.; Zielke, M.; Solheim, B. Biodiversity of the cyanobacterial community in the foreland of the retreating glacier Midtre Lovènbreen, Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 2005, 117, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gao, H.K. Ecological networks reveal contrasting patterns of bacterial and fungal communities in glacier-fed streams in Central Asia. Peer J. 2019, 7, e7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Song, H.F.; Lei, Y.B.; Korpelainen, H.; Li, C.Y. Distinct co-occurrence patterns and driving forces of rare and abundant bacterial sub-communities following a glacial retreat in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousset, A.; Bienhold, C.; Chatzinotas, A.; Gallien, L.; Gobet, A.; Kurm, V.; Küsel, K.; Rillig, M.C.; Rivett, D.W.; Salles, J.F.; et al. Where less may be more: how the rare biosphere pulls ecosystems strings. ISME J. 2017, 11, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skopina, M.Y.; Vasileve, A.A.; Pershina, E.V.; Pinevich, A.V. Diversity at low abundance: The phenomenon of the rare bacterial biosphere. Microbiology 2016, 85, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, H.; Jeppesen, E.; Meester, L.D.; Sommaruga, R. Changes in bacterioplankton community structure during early lake ontogeny resulting from the retreat of the Greenland Ice Sheet. ISME J. 2018, 12, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gao, H.K.; Elser, J.J. Longitudinal variation of microbial communities in benthic biofilms and association with hydrological and physicochemical conditions in glacier-fed streams. Freshw. Sci. 2017, 36, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boral, S.; Sen, I.S.; Ghosal, D.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, B.; Hemingway, J.D. Stable water isotope modeling reveals spatio-temporal variability of glacier meltwater contributions to Ganges River headwaters. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, L.; Singer, G.A.; Fasching, C.; Battin, T.J.; Besemer, K. Microbial biodiversity in glacier-fed streams. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.K.; Stibal, M.; Hawkings, J.R.; Mikkelsen, A.B.; Telling, J.; Kohler, T.J.; Gozdereliler, E.; Zarsky, J.D.; Wadham, J.L.; Jacobsen, C.S. Meltwater export of prokaryotic cells from the Greenland ice sheet. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Zeng, X.M.; Leavitt, S.W.; Wang, W.; An, W.; Xu, G.B.; Sun, W.Z.; Wang, Y.; Qin, D.H.; Ren, J.W. A 400-year tree-ring δ18O chronology for the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for inferring variations of the regional hydroclimate. Glob. Planet Chang. 2013, 104, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.C.; Tu, Q.Y. The standard methods for observation and analysis of lake eutrophication, 2nd ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 138–272. [Google Scholar]
- Sáenz, J.S.; Roldan, F.; Junca, H.; Arbeli, Z. Effect of the extraction and purification of soil DNA and pooling of PCR amplification products on the description ofbacterial and archaeal communities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1454–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. CoNet app: inference of biological association networks using Cytoscape. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.Z.; Shen, F.; Zeng, J.; Huang, R.; Yu, Z.B.; Wu, Q.L. Network analysis reveals seasonal variation of co-occurrence correlations between Cyanobacteria and other bacterioplankton. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: from network to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.K.; Chang, C.K. The Simes method for mulltiple hypothesis testing with positively dependent test statistics. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1997, 92, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The Igraph Software Package for Complex Network Research. Inter. J. Comp. Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.F.; He, Z.L.; Lou, F.; Zhou, J.Z. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumbo, F.; Paci, P.; Santoni, D.; Di-Paola, L.; Giuliani, A. GIANT: a cytoscape plugin for modular networks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.L. vegan2.0–2: Community Ecology Package. Available online: http://CRAN.Rproject.org/package = vegan (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrós-Alió, C. The Rare Bacterial Biosphere. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M.; Kraft, N.J.B.; Smith, K.G.; Vellend, M.; Inouye, B.D. Using null models to disentangle variation in community dissimilarity from variation in alpha-diversity. Ecosphere 2011, 2, art24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauvy-Fraunié, S.; Espinosa, R.; Andino, P.; Jacobsen, D.; Dangles, O. Invertebrate metacommunity structure and dynamics in an Andean glacial stream network facing climate change. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, A.M.; Brittain, J.E.; Castella, E.; Petts, G.E. Trends of macroinvertebrate community structure in glacierfed rivers in relation to environmental conditions: a synthesis. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1833–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhou, L.; He, X.T.; Jang, K.S.; Xiao, Y.L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, X.Y.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Brookes, J.D.; et al. Variability in Dissolved Organic Matter Composition and Biolability across Gradients of Glacial Coverage and Distance from Glacial Terminus on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. Artic. ASAP 2019, 53, 12207–12217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciok, A.; Budzik, K.; Zdanowski, M.K.; Gawor, J.; Grzesiak, J.; Decewicz, P.; Gromadka, R.; Bartosik, D.; Dziewit, L. Plasmids of psychrotolerant polaromonas spp. isolated from Arctic and Antarctic Glaciers—Diversity and role in adaptation to polar environments. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioks, A.; Dziewit, L.; Grzesiak, J.; Budzik, K.; Gorniak, D.; Zdanowski, M.K.; Bartosik, D. Identification of miniature plasmids in psychrophilic Arctic bacteria of the genus Variovorax. FEMS Microbiol. Ecology 2016, 92, fix043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.R.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.; Park, H.; Oh, T.J. Complete genome sequence of opine-utilizing Variovorax sp. strain PAMC28711 isolated from an Antarctic lichen. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 225, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertesz, M.A.; Kawasaki, A. Hydrocarbon-Degrading Sphingomonads: Sphingomonas, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium, and Sphingopyxis. In Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology; Timmis, K.N., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1693–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Zielińska, S.; Radkowski, P.; Ossowski, T.; Ludwig-Gałęzowska, A.; Łoś, J.M.; M, M.Ł. First insight into microbial community composition in a phosphogypsum waste heap soil. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2017, 64, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lòpez-Fernàndez, S.; Compant, S.; Vrhovsek, U.; Bianchedi, P.L.; Sessitsch, A.; Pertot, I.; Campisano, A. Grapevine colonization by endophytic bacteria shifts secondary metabolism and suggests activation of defense pathways. Plant Soil 2016, 405, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommaruga, R. When glaciers and ice sheets melt: consequences for planktonic organisms. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, A.; Maclsaac, H.J. Rare biosphere exploration using high-throughput sequencing: research progress and perspective. Conserv. Genet. 2015, 16, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Leff, J.W.; Fierer, N.; D’Angelo, H.; Bateman, C.; Gedallovich, S.M.; Gillikin, C.M.; Gradoville, M.R.; Mansor, P.; et al. Consequences of tropical forest conversion to oil palm on soil bacterial community and network structure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 112, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbrenner, I.A.; Cernava, T.; Erlacher, A.; Berg, G.; Grube, M. Differential sharing and distinct co-occurrence networks among spatially close bacterial microbia of bark, mosses and lichens. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2826–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Bai, C.R.; Cai, J.; Dai, J.Y.; Shao, K.Q.; Tang, X.M.; Gao, G. Co-occurrence network reveals the higher fragmentation of the bacterial communitiy in Kaidu River and its tributary in northwestern China. Microbes Environ. 2018, 33, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.; Widder, S. Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Frointer Microbiol. 2014, 5, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberán, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muismer, S.L.; Harmon, L.J. Predicting rates of interspecific interaction from phylogenetic trees. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röttjers, L.; Faust, K. From hairballs to hypotheses-biological insights from microbial networks. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zhong, J.X.; Yang, J.F.; Zhou, J.Z. Application of random matrix theory to microarray data for discovering functional gene modules. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 031924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiler, A.; Heinrich, F.; Bertilsson, S. Coherent dynamics and association networks among lake bacterioplankton taxa. ISME J. 2012, 6, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaffron, S.; Rehrauer, H.; Pernthaler, J.; von-Mering, C. A global network of coexisting microbes from environmental and whole-genome sequence data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milici, M.; Deng, Z.L.; Tomasch, J.; Decelle, J.; Wos-Oxley, M.L.; Wang, H.; Jáuregui, R.; Plumeier, I.; Giebel, H.-A.; Badewien, T.H.; et al. Co-occurrence analysis of microbial taxa in the Atlantic Ocean reveals high connectivity in the free-living bacterioplankton. Frointer Microbiol. 2016, 7, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Yao, X.; Wu, Y.; Han, W.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, X.; Shao, K.; Gao, G. Contrasting Patterns of the Bacterial Communities in Melting Ponds and Periglacial Rivers of the Zhuxi glacier in the Tibet Plateau. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040509
Hu Y, Yao X, Wu Y, Han W, Zhou Y, Tang X, Shao K, Gao G. Contrasting Patterns of the Bacterial Communities in Melting Ponds and Periglacial Rivers of the Zhuxi glacier in the Tibet Plateau. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(4):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040509
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yang, Xin Yao, Yuanyuan Wu, Wei Han, Yongqiang Zhou, Xiangming Tang, Keqiang Shao, and Guang Gao. 2020. "Contrasting Patterns of the Bacterial Communities in Melting Ponds and Periglacial Rivers of the Zhuxi glacier in the Tibet Plateau" Microorganisms 8, no. 4: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040509
APA StyleHu, Y., Yao, X., Wu, Y., Han, W., Zhou, Y., Tang, X., Shao, K., & Gao, G. (2020). Contrasting Patterns of the Bacterial Communities in Melting Ponds and Periglacial Rivers of the Zhuxi glacier in the Tibet Plateau. Microorganisms, 8(4), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040509







