Ethnic Differences Shape the Alpha but Not Beta Diversity of Gut Microbiota from School Children in the Absence of Environmental Differences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethic Approval and Consent to Participate
2.2. Study Site and Sampling
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing and Bioinformatic Analyses
2.6. Evaluation of Dietary Nutrition
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Subjects in the Three Ethnicity Groups
3.2. DNA Sequencing and Filtering
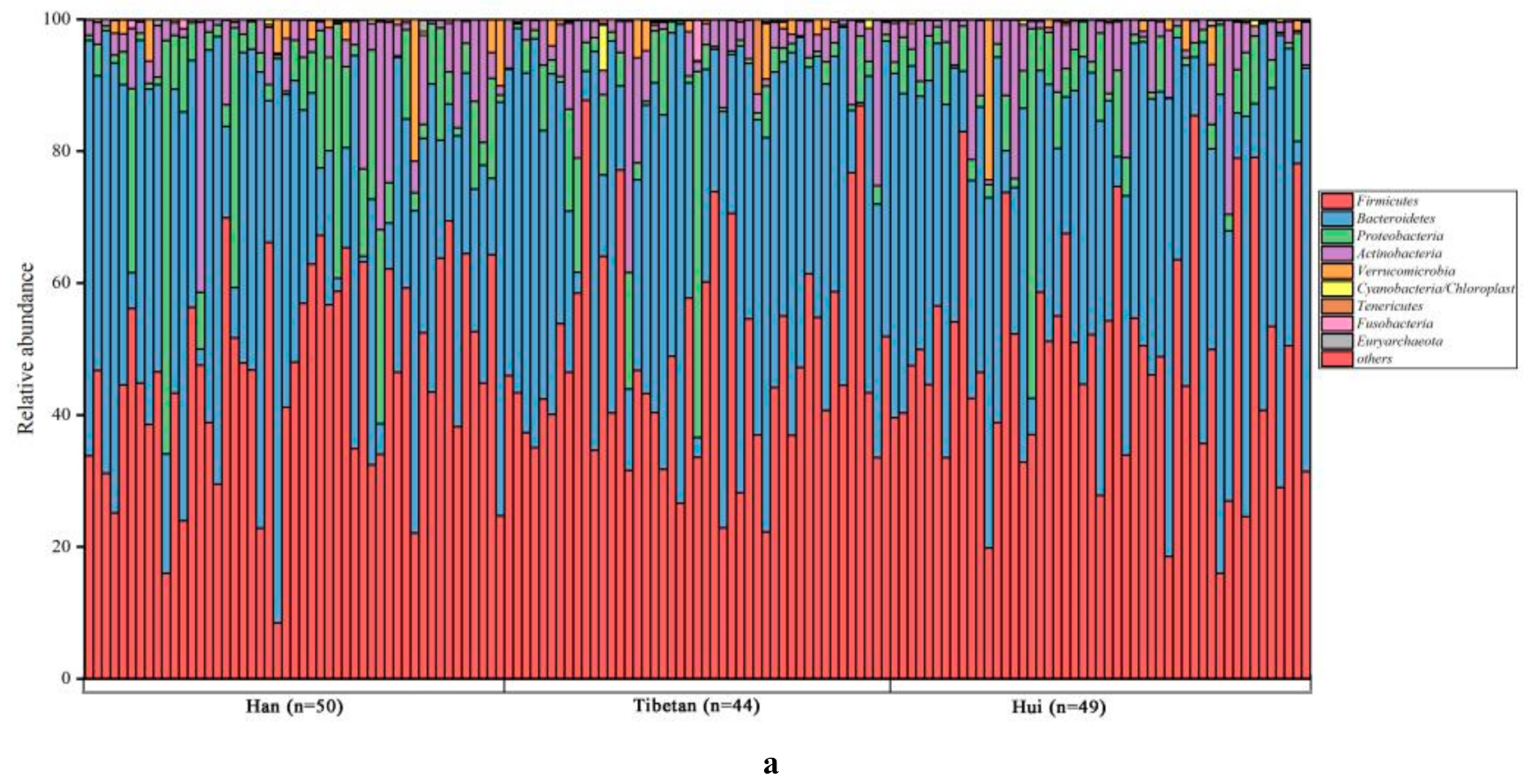
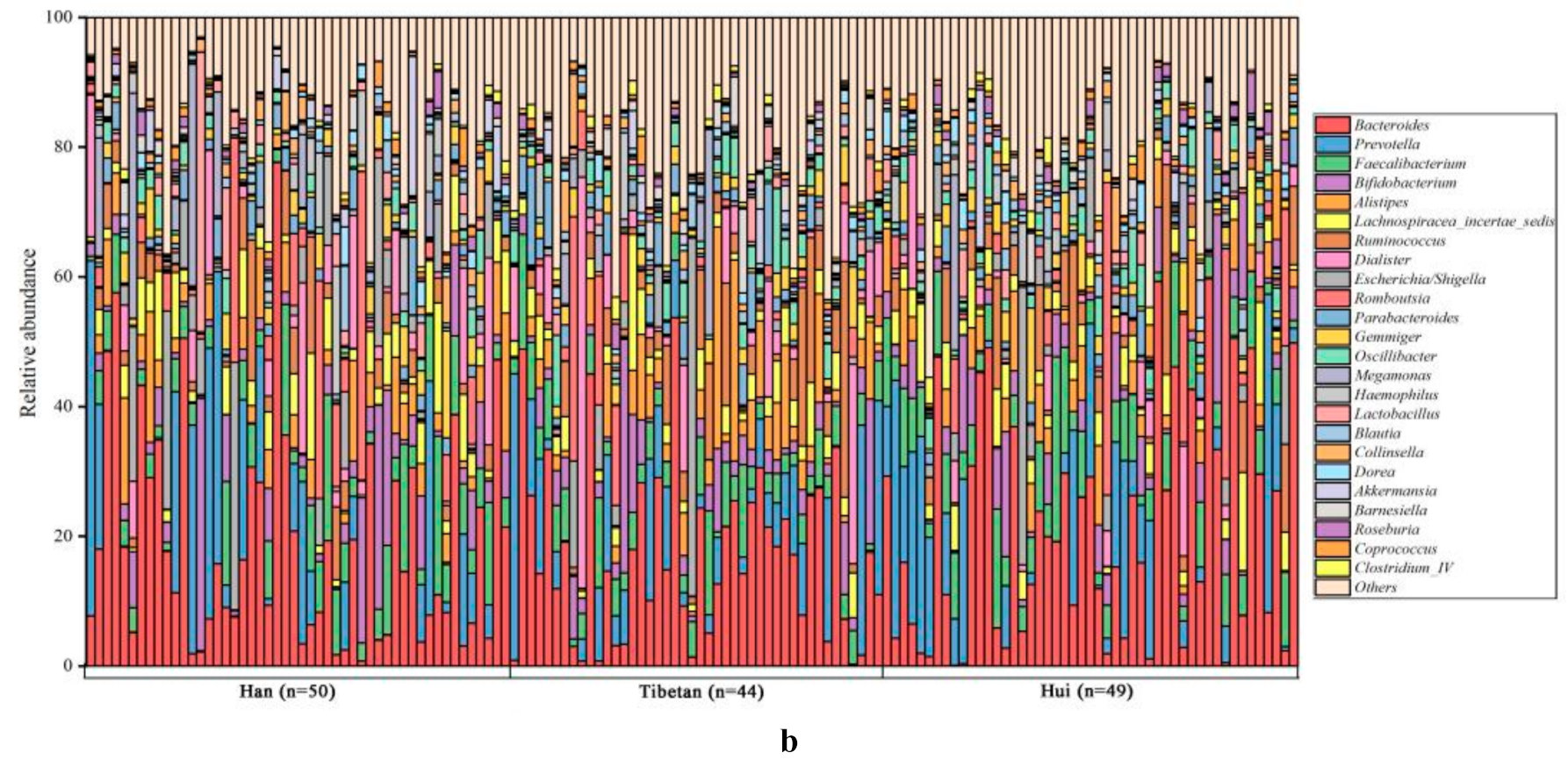
3.3. Bacterial Compositions of Fecal Samples
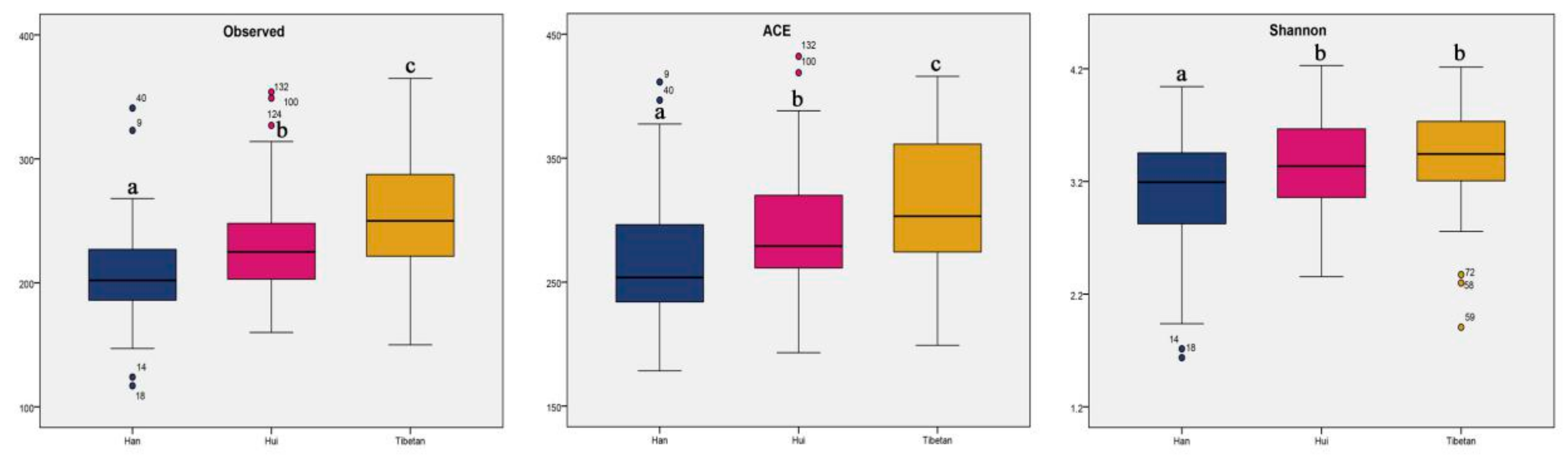
3.4. Alpha Diversity of Gut Microbes from the Three Ethnic Groups
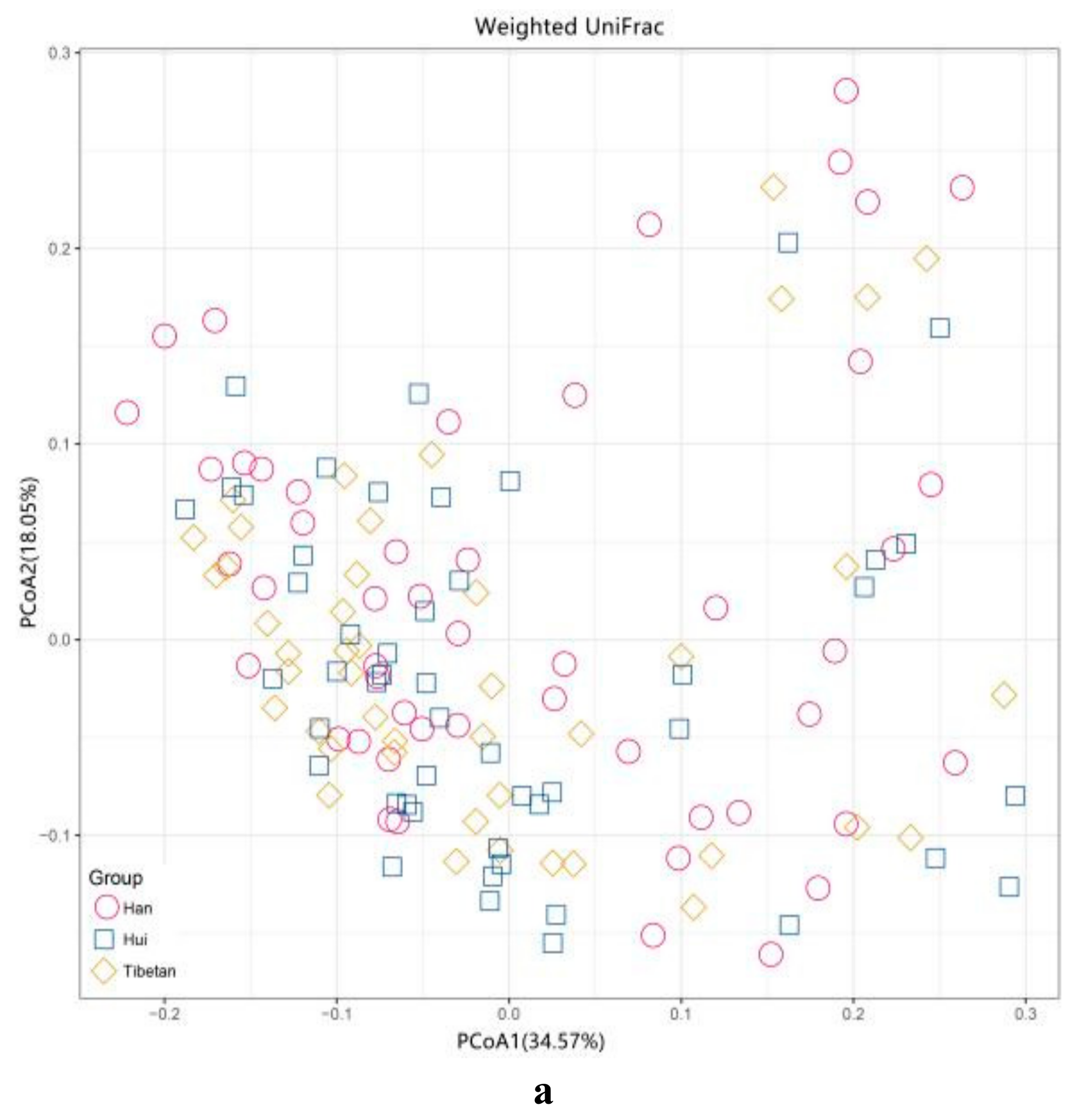
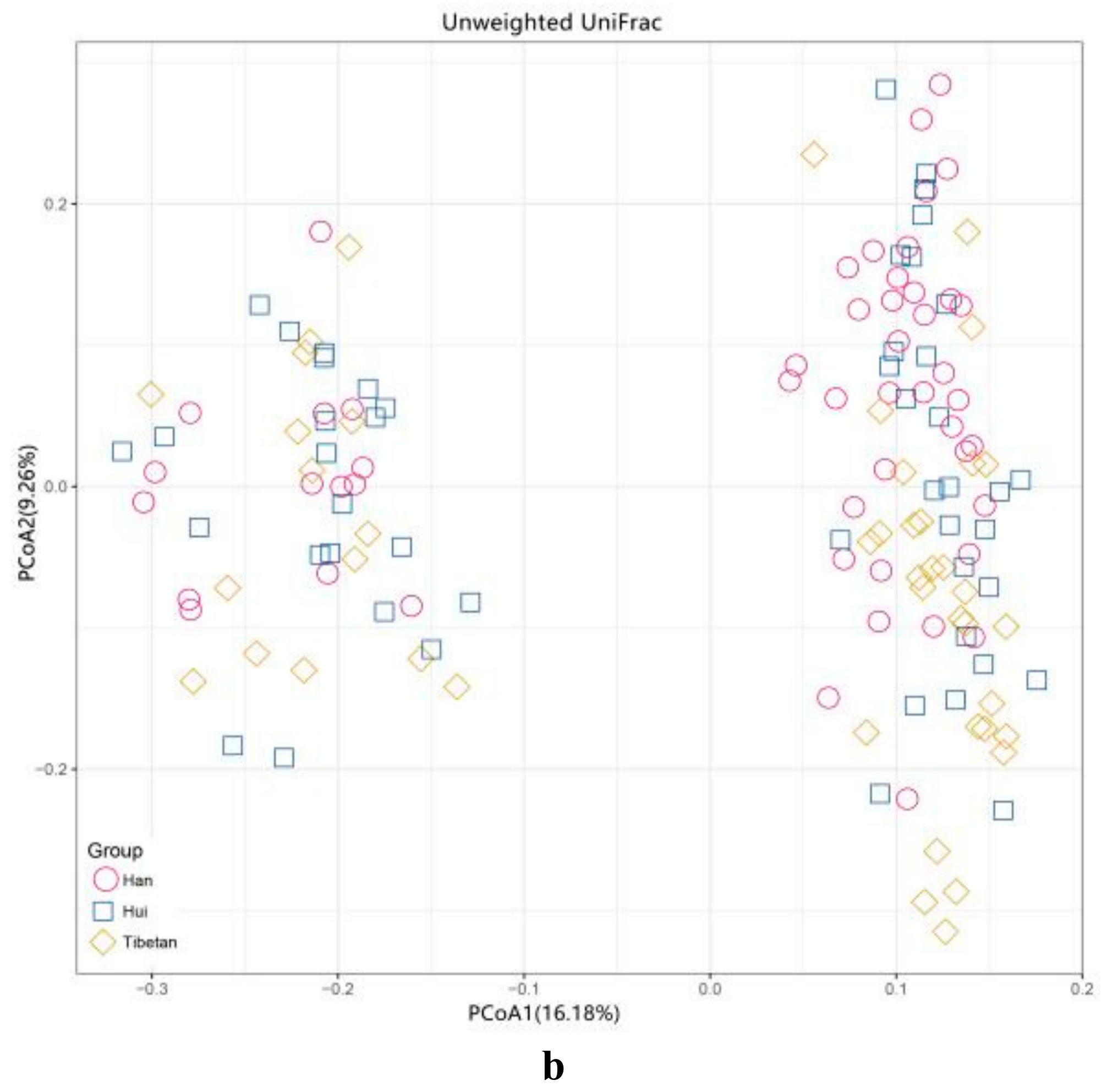
3.5. Beta Diversity of Gut Microbiota among the Three Ethnic Groups
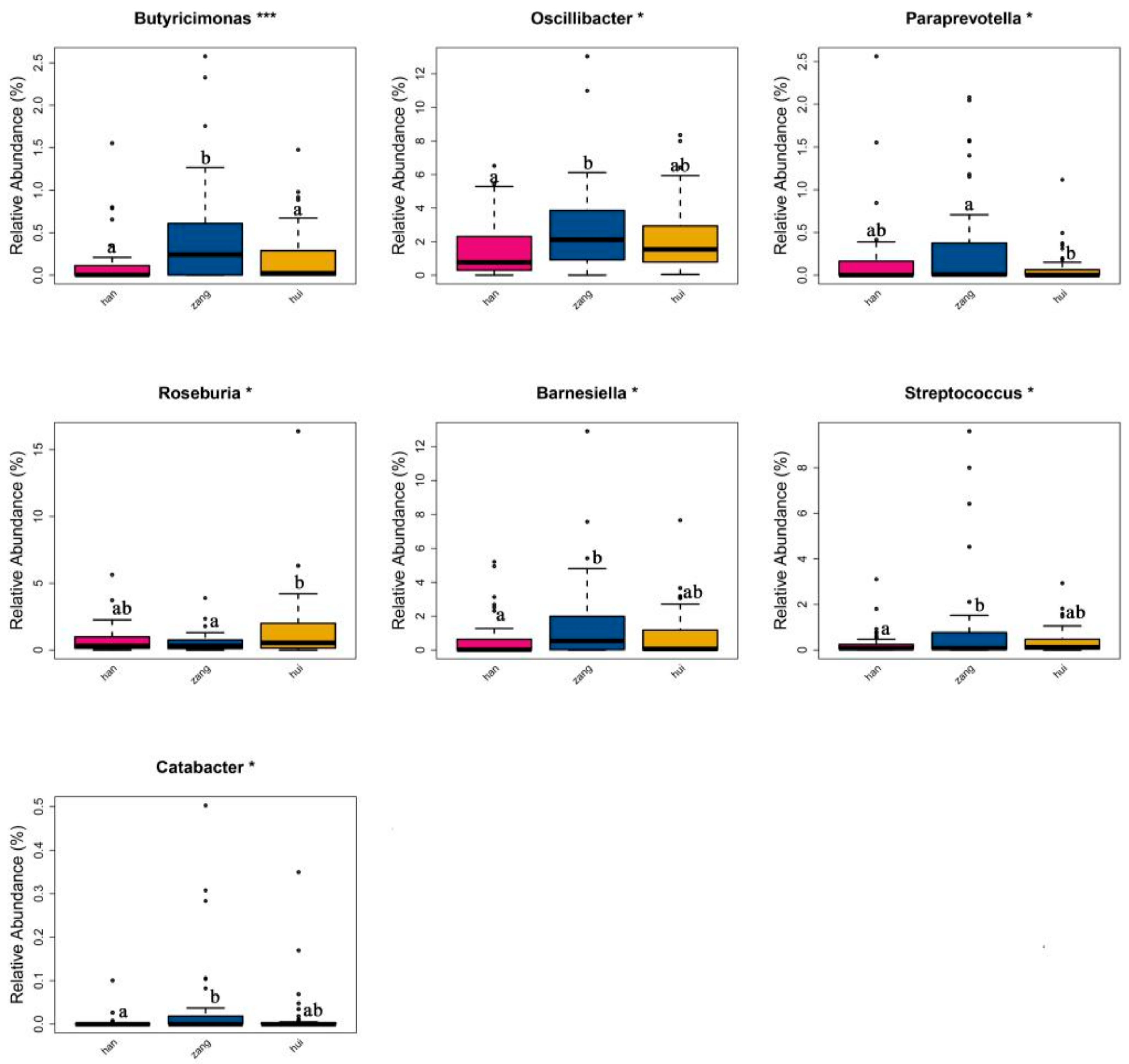
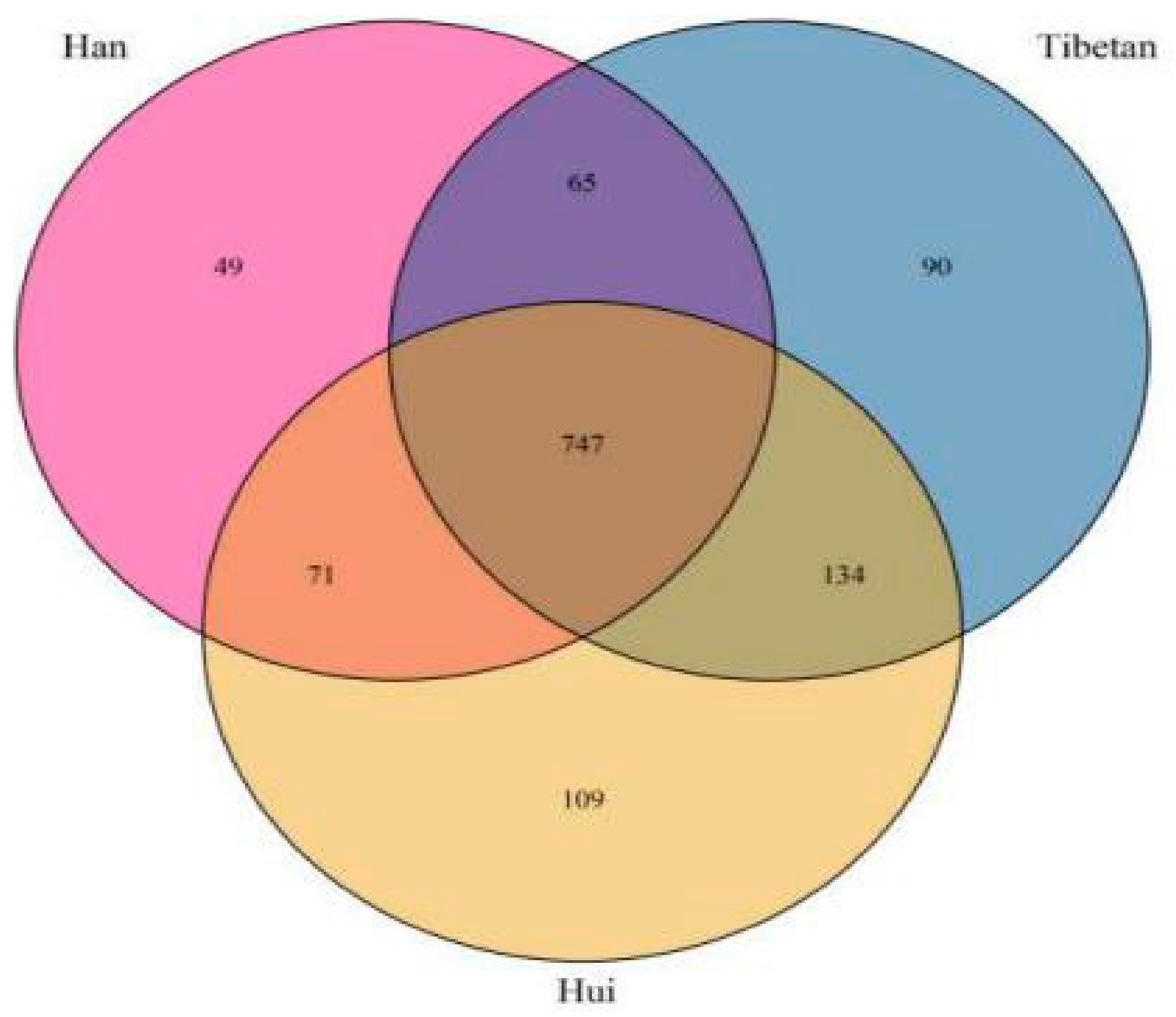
3.6. Microbial Signatures in Different Samples
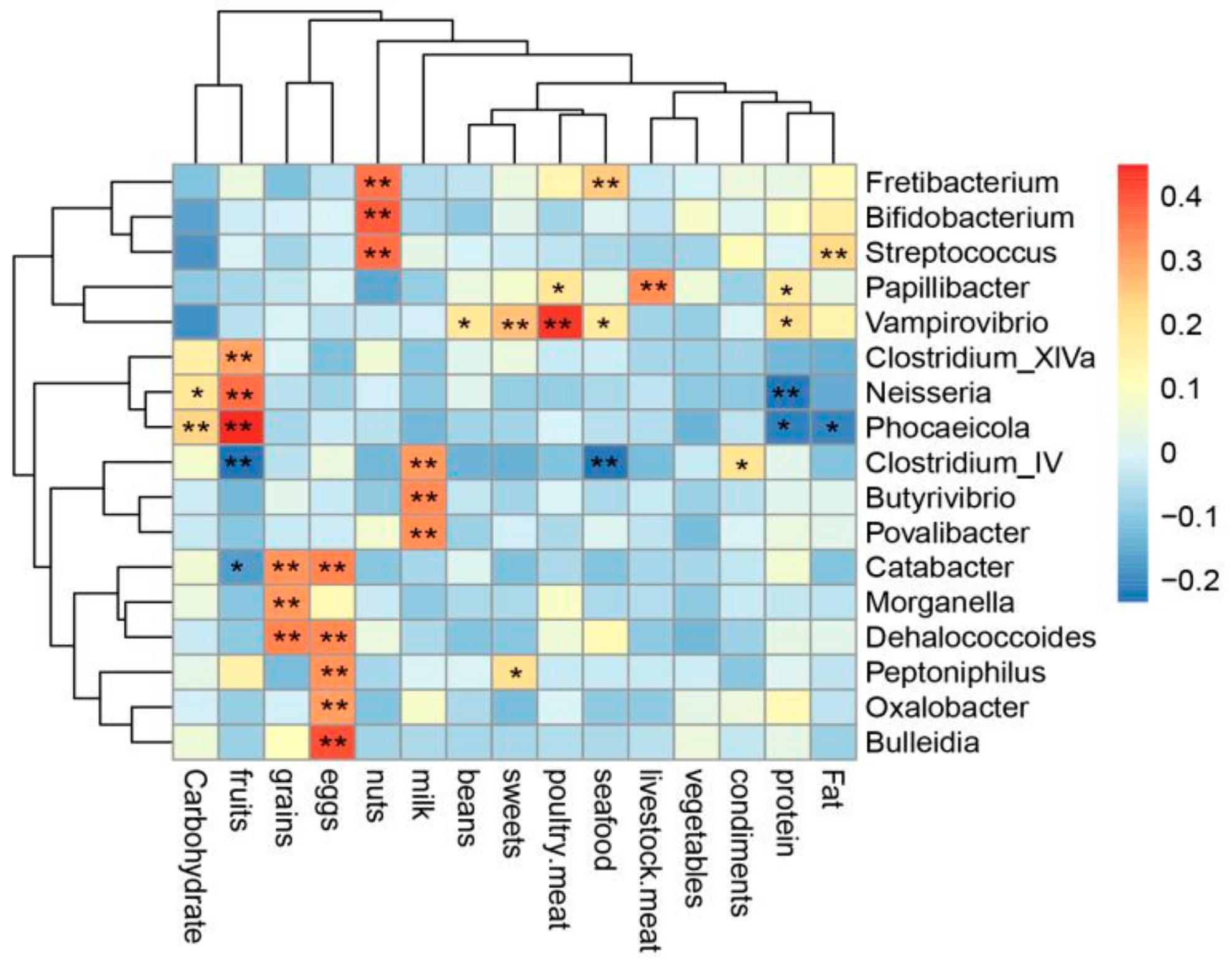
3.7. Correlation Analysis between Bacterial Genera and Diet
3.8. Change of Dietary Habits among the Three Ethnic Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ley, R.E.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 2006, 124, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.; Li, J.V.; Marchesi, J.R.; Nicholson, J.K. Gut microbiota composition and activity in relation to host metabolic phenotype and disease risk. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreiner, A.B.; Kao, J.Y.; Young, V.B. The gut microbiome in health and in disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Littman, D.R.; Macpherson, A.J. Interactions between the Microbiota and the Immune System. Science 2012, 336, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörmannsperger, G. Gut matters: Microbe-host interactions in allergic diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepage, P.; Häsler, R.; Spehlmann, M.E.; Rehman, A.; Zvirbliene, A.; Begun, A.; Ott, S.; Kupcinskas, L.; Doré, J.; Raedler, A. Twin Study Indicates Loss of Interaction Between Microbiota and Mucosa of Patients With Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, F.C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di, P.M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wu, W.; Zheng, H.-M.; Li, P.; McDonald, D.; Sheng, H.-F.; Chen, M.-X.; Chen, Z.-H.; Ji, G.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-D.-X.; et al. Regional variation limits applications of healthy gut microbiome reference ranges and disease models. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falony, G.; Joossens, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Wang, J.; Darzi, Y.; Faust, K.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Vandeputte, D.; et al. Population-level analysis of gut microbiome variation. Science 2016, 352, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisko, D.J.; Johnston, G.P.; Johnston, C.G. Effects of Dietary Yogurt on the Healthy Human Gastrointestinal (GI) Microbiome. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhernakova, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Schirmer, M.; Vatanen, T.; Mujagic, Z.; Vila, A.V.; Falony, G.; Vieira-Silva, S.; et al. Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity. Science 2016, 352, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschasaux, M.; Bouter, K.E.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Groen, A.K.; Herrema, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Bakker, G.J.; Attaye, I.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J.; et al. Depicting the composition of gut microbiota in a population with varied ethnic origins but shared geography. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, X. Comparative analyses of fecal microbiota in Tibetan and Chinese Han living at low or high altitude by barcoded 454 pyrosequencing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, L.; Zhang, Y. Spatial patterns of wet season precipitation vertical gradients on the Tibetan Plateau and the surroundings. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Dan, Z.; Gesang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Y.; Ren, Y.; Shi, Y.; Nie, Y. Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiota of Native Tibetan and Han Populations Living at Different Altitudes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensollen, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Blumberg, R.S. How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes the immune system. Science 2016, 352, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Dynamics and Stabilization of the Human Gut Microbiome during the First Year of Life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borre, Y.E.; O’Keeffe, G.W.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota and neurodevelopmental windows: Implications for brain disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Salazar, E.O.; Ortiz-Lopez, M.G.; Granados-Silvestre, M.L.A.; Palacios-Gonzalez, B.; Menjivar, M. Altered Gut Microbiota and Compositional Changes in Firmicutes and Proteobacteria in Mexican Undernourished and Obese Children. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E.; Fish, J.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Marsh, T.; Garrity, G.M.; et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: Improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D141–D145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colwell, R.K.; Chao, A.; Gotelli, N.J.; Lin, S.Y.; Mao, C.X.; Chazdon, R.L.; Longino, J.T. Models and estimators linking individual-based and sample-based rarefaction, extrapolation and comparison of assemblages. J. Plant Ecol. 2012, 5, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Huang, P.; Li, W.; Wang, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Yan, Z.; et al. Structural modulation of gut microbiota in life-long calorie-restricted mice. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Cho, M.S. Geography of Food Consumption Patterns between South and North China. Foods 2017, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Pan, X. China Food Composition, 2nd ed.; Peking University: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- McArdle, B.H.; Anderson, M.J. Fitting multivariate models to community data: A comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology 2001, 82, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnorr, S.L.; Candela, M.; Rampelli, S.; Centanni, M.; Consolandi, C.; Basaglia, G.; Turroni, S.; Biagi, E.; Peano, C.; Severgnini, M.; et al. Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Xue, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Cao, H.; et al. A phylo-functional core of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Ji, W.; Lin, B.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Xiong, X.; Fu, M.; Mipam, T.D.; Ai, Y.; Zeng, B.; et al. Correlations between gut microbiota community structures of Tibetans and geography. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, L.Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Gesudu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, J.; Huo, D.; Zhang, H. Characterization of Fecal Microbiota across Seven Chinese Ethnic Groups by Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariat, D.; Firmesse, O.; Levenez, F.; Guimarăes, V.D.; Sokol, H.; Doré, J.; Corthier, G.; Furet, J.P. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, H.N.; Collins, M.D. Proposal to restrict the genus Bacteroides (castellani and chalmers) to Bacteroides- fragilis and closely related species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1989, 39, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, G.T.; Macfarlane, S. Bacteria, Colonic Fermentation, and Gastrointestinal Health. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luying, P.; Zhong-Rong, L.; Green, R.S.; Holzman, I.R.; Jing, L. Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in CaCo-2 cell monolayers. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, I.; Ozawa, K.; Inoue, D.; Imamura, T.; Kimura, K.; Maeda, T.; Terasawa, K.; Kashihara, D.; Hirano, K.; Tani, T. The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Toh, H.; Hase, K.; Oshima, K.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Tobe, T.; Clarke, J.M.; Topping, D.L.; Suzuki, T. Bifidobacteria can protect from enteropathogenic infection through production of acetate. Nature 2012, 469, U543–U791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-J.; Park, S.-G.; Jang, H.B.; Choi, M.-G.; Park, K.-H.; Kang, J.H.; Park, S.I.; Lee, H.-J.; Cho, S.-H. Obesity Alters the Microbial Community Profile in Korean Adolescents. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Ha, C.W.Y.; Campbell, C.R.; Mitchell, A.J.; Dinudom, A.; Oscarsson, J.; Cook, D.I.; Hunt, N.H.; Caterson, I.D.; Holmes, A.J.; et al. Increased Gut Permeability and Microbiota Change Associate with Mesenteric Fat Inflammation and Metabolic Dysfunction in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daillere, R.; Vetizou, M.; Waldschmitt, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Isnard, C.; Poirier-Colame, V.; Duong, C.P.M.; Flament, C.; Lepage, P.; Roberti, M.P.; et al. Enterococcus hirae and Barnesiella intestinihominis Facilitate Cyclophosphamide-Induced Therapeutic Immunomodulatory Effects. Immunity 2016, 45, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeda, C.; Bucci, V.; Caballero, S.; Djukovic, A.; Toussaint, N.C.; Equinda, M.; Lipuma, L.; Ling, L.; Gobourne, A.; No, D.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Containing Barnesiella Species Cures Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecium Colonization. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le, P.D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Hui, S.; Huang, L. Healthy subjects differentially respond to dietary capsaicin correlating with the specific gut enterotypes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4681–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.L.; Hergert, N.; Rompato, G.; Lefevre, M. Whole Grain Oats Improve Insulin Sensitivity and Plasma Cholesterol Profile and Modify Gut Microbiota Composition in C57BL/6J Mice. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Wells, A.L.; Helmolz, K.; Nodet, C.; Molzer, C.; Leonard, C.; McKevith, B.; Thielecke, F.; Jackson, K.G.; Tuohy, K.M. Determination of the in vivo prebiotic potential of a maize-based whole grain breakfast cereal: A human feeding study. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Ahuja, V.; Paul, J. Fluctuations in butyrate-producing bacteria in ulcerative colitis patients of North India. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3404–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Shima, T.; Imaoka, A.; Kuwahara, T.; Momose, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yamasaki, S.; Saito, T.; Ohba, Y.; et al. Induction of Colonic Regulatory T Cells by Indigenous Clostridium Species. Science 2011, 331, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J. Fiber and Prebiotics: Mechanisms and Health Benefits. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, H.; Harris, J.; Lyon, E.; Beal, J.; Foey, A.D. Probiotics, Prebiotics and Immunomodulation of Gut Mucosal Defences: Homeostasis and Immunopathology. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1869–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-M. Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of Antimicrobial Substances Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Baikkimchi. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2014, 57, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Lin, Q.; Qu, J. Gut Microbiota in Tibetan Herdsmen Reflects the Degree of Urbanization. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Food Species | Han (n = 50) | Tibetan (n = 44) | Hui (n = 49) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intake (g) | Intake (g) | Intake (g) | |
| Grains | 156.25 (84.13–258.75) | 110.88 (69.50–237.75) | 115.00 (72.81–212.75) |
| Vegetables | 151.69 (63.04–305.75) ** | 87.81 (52.07–253.94) | 77.25 (33.61–121.55) |
| Fruits | 149.27 (74.82–278.94) ** | 103.67 (44.34–191.98) | 73.71 (22.30–158.95) |
| Poultry meat | 16.00 (3.67–37.52) | 20.35 (4.91–59.88) * | 10.58 (2.80–44.48) |
| Livestock meat | 3.05 (0.73–10.88) | 1.59 (0.00–6.26) | 4.58 (0.87–16.55) |
| Seafood | 2.78 (0.85–11.71) * | 1.67 (0.00–10.24) | 0.76 (0.00–4.97) |
| Milk | 94.00 (37.38–202.75) | 116.63 (50.00–282.38) | 61.75 (16.75–141.75) |
| Beans | 13 (0.00–53.25) | 11.75 (0.00–46.25) | 2.29 (0.00–20.25) |
| Eggs | 9.47 (0.00–21.20) | 11.36 (1.51–35.95) | 10.70 (0.81–26.68) |
| Nuts | 9.32 (1.87–28.82) | 8.55 (1.38–23.08) | 4.36 (1.28–15.40) |
| Condiments | 83.00 (38.75–194.00) | 63.13 (33.06–132.81) | 48.91 (11.19–291.56) |
| Sweets | 8.00 (1.50–27.38) | 10.13 (0.69–30.25) | 5.84 (1.68–35.63) |
| Nutrient | Han (n = 50) | Tibetan (n = 44) | Hui (n = 49) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (kcal) | 1945.12 (743.82–2768.64) | 1727.85 (1191.41–2636.43) | 1052.77 (818.14–2514.21) |
| Proteins (% energy) | 13.79 (11.12–18.90) | 13.04 (11.67–15.27) | 14.61 (11.04–17.73) |
| Fats (% energy) | 28.72 (20.61–38.75) | 33.93 (28.84–38.83) ** | 27.49 (17.83–35.95) |
| Carbohydrates (% energy) | 54.66 (47.96–64.18) | 51.55 (45.50–56.54) | 59.16 (46.63–69.18) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Long, D.; Yan, S.; Huang, W.; Long, R.; Huang, X. Ethnic Differences Shape the Alpha but Not Beta Diversity of Gut Microbiota from School Children in the Absence of Environmental Differences. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020254
Liu K, Zhang Y, Li Q, Li H, Long D, Yan S, Huang W, Long R, Huang X. Ethnic Differences Shape the Alpha but Not Beta Diversity of Gut Microbiota from School Children in the Absence of Environmental Differences. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(2):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020254
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ke, Yongling Zhang, Qinglin Li, Huan Li, Danfeng Long, Shijuan Yan, Wenjie Huang, Ruijun Long, and Xiaodan Huang. 2020. "Ethnic Differences Shape the Alpha but Not Beta Diversity of Gut Microbiota from School Children in the Absence of Environmental Differences" Microorganisms 8, no. 2: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020254
APA StyleLiu, K., Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Li, H., Long, D., Yan, S., Huang, W., Long, R., & Huang, X. (2020). Ethnic Differences Shape the Alpha but Not Beta Diversity of Gut Microbiota from School Children in the Absence of Environmental Differences. Microorganisms, 8(2), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020254





