Bioprospecting for Novel Halophilic and Halotolerant Sources of Hydrolytic Enzymes in Brackish, Saline and Hypersaline Lakes of Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Measurement of Physicochemical Parameters
2.2. Cultivation and Abundance Estimation of Halophilic and Halotolerant Microorganisms
2.3. Halophily and Halotolerance Assessment of the Isolates
2.4. Screening for Extracellular Enzyme Activities
2.5. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification of the 16S rRNA Gene
2.6. Gene Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Sampling Sites Description
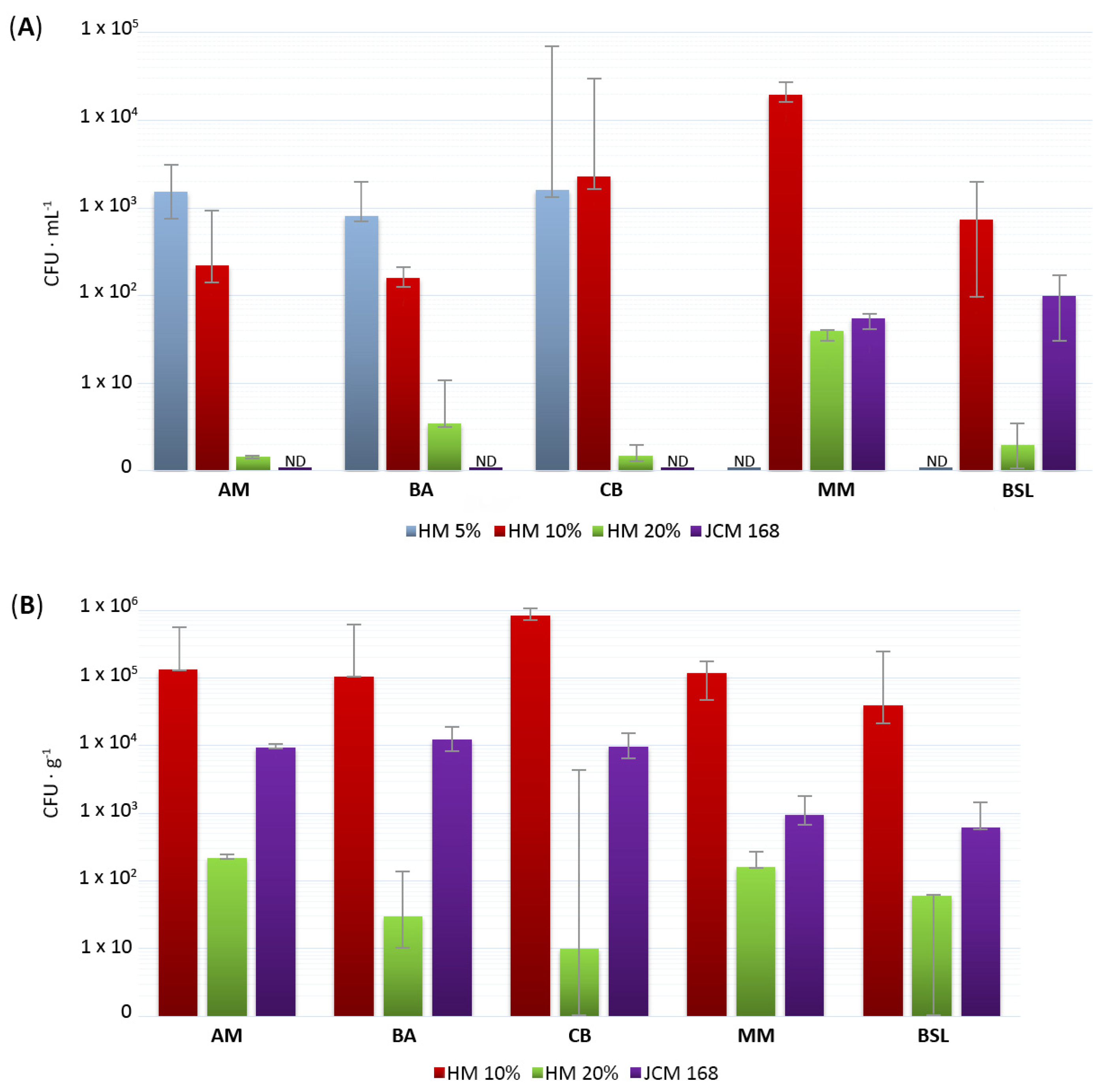
3.2. Abundance of Cultured Halophilic and Halotolerant Microorganisms
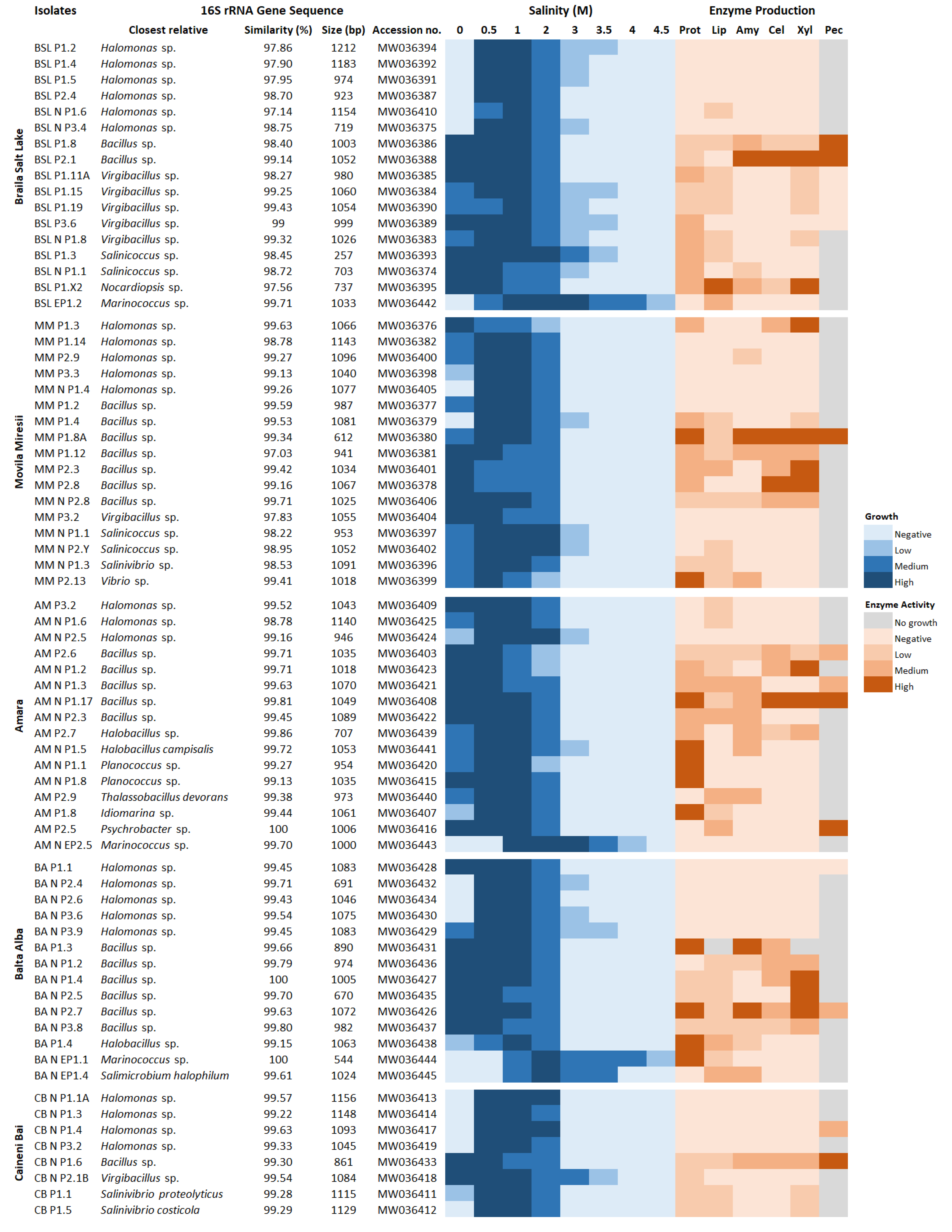
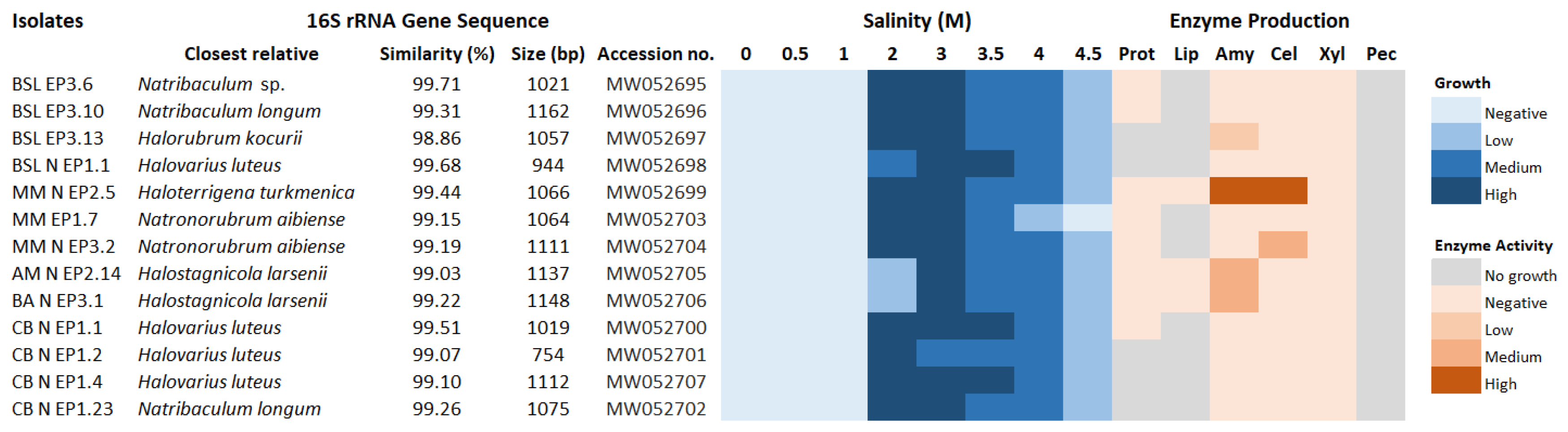
3.3. Halophily and Halotolerance of the Isolates
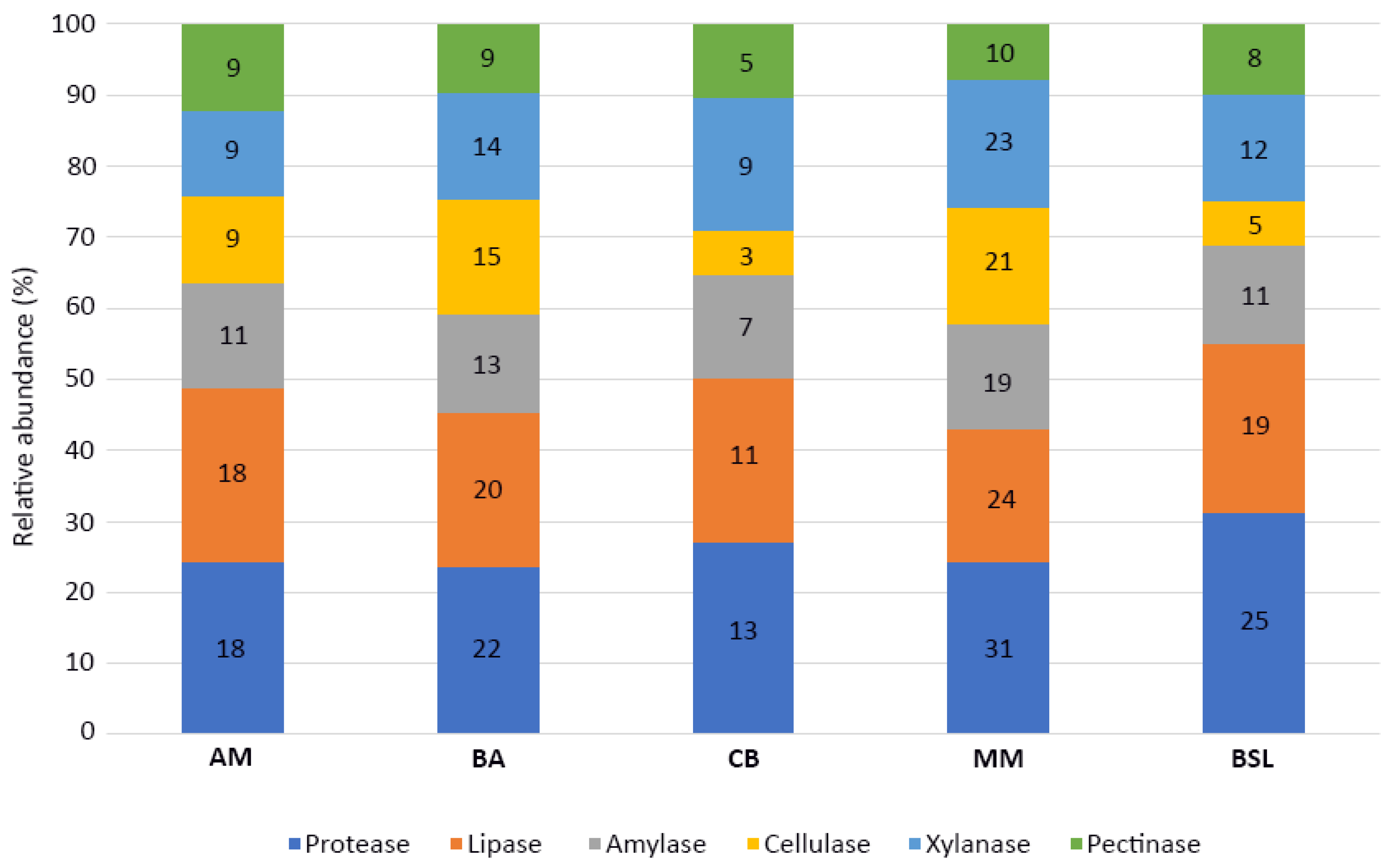
3.4. Production of Extracellular Hydrolytic Enzymes
3.5. Phylogenetic Affiliation of Bacterial and Archaeal Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oren, A. Diversity of Halophilic Microorganisms: Environments, Phylogeny, Physiology, and Applications. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGenity, T.J.; Oren, A. Hypersaline Environments. In Life at Extremes: Environments, Organisms and Strategies for Survival; Bell, E.M., Ed.; CAB International: Oxfordshire, UK, 2012; pp. 402–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Life in Hypersaline Environments. In Their World: A Diversity of Microbial Environments, Advances in Environmental Microbiology; Hurst, C.J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 301–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventosa, A.; Márquez, M.C.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; de la Haba, R.R. Taxonomy of Halophilic Archaea and Bacteria. In Advances in Understanding the Biology of Halophilic Microorganisms; Vreeland, R.H., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Plemenitaš, A.; Oren, A. Strategies of Adaptation of Microorganisms of the Three Domains of Life to High Salt Concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventosa, A.; de la Haba, R.R.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; Papke, R.T. Microbial Diversity of Hypersaline Environments: A Metagenomic Approach. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 25, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A. Halophilic Microbial Communities and Their Environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventosa, A.; Nieto, J.J. Biotechnological Applications and Potentialities of Halophilic Microorganisms. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 11, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Industrial and Environmental Applications of Halophilic Microorganisms. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Baffoe, D.K.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Halophile, an Essential Platform for Bioproduction. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 166, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chen, J.-C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G.-Q. Halophiles, coming stars for industrial biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.; Garbayo, I.; Vilchez, C.; Martinez-Espinosa, R.M. Haloarchaeal Carotenoids: Healthy Novel Compounds from Extreme Environments. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, P.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Ventosa, A. Halophiles and Their Biomolecules: Recent Advances and Future Applications in Biomedicine. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadeo, X.; López-Méndez, B.; Trigueros, T.; Laín, A.; Castaño, D.; Millet, O. Structural Basis for the Aminoacid Composition of Proteins from Halophilic Archea. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siglioccolo, A.; Paiardini, A.; Piscitelli, M.; Pascarella, S. Structural Adaptation of Extreme Halophilic Proteins through Decrease of Conserved Hydrophobic Contact Surface. BMC Struct. Biol. 2011, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoozegar, M.A.; Safarpour, A.; Noghabi, K.A.; Bakhtiary, T.; Ventosa, A. Halophiles and Their Vast Potential in Biofuel Production. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.-W.; Ge, H.-H.; Yi, Z.-W.; Zeng, R.-Y.; Zhang, G.-Y. Characterization of a Novel Psychrophilic and Halophilic β-1,3-Xylanase from Deep-Sea Bacterium, Flammeovirga pacifica Strain WPAGA1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Borgne, S.; Paniagua, D.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R. Biodegradation of Organic Pollutants by Halophilic Bacteria and Archaea. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 15, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathepure, B.Z. Recent Studies in Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Hypersaline Environments. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgareanu, V.A.C. The Protection and Management of Saline Lakes of Therapeutic Value in Romania. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1993, 2, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastescu, P. Lacurile din Romania—Limnologie Regionala; Editura Academiei: Bucuresti, Romania, 1971; pp. 100–236. [Google Scholar]
- Radulescu, C.; Dulama, I.D.; Stihi, C.; Ionita, I.; Chilian, A.; Necula, C.; Chelarescu, E.D. Determination of Heavy Metal Levels in Water and Therapeutic Mud by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Rom. J. Phys. 2014, 59, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Plesoianu, D.; Diaconescu, V. Amara, a Spa with an Extraordinary Natural Potential. Sci. Pap. Ser. Manag. Econ. Eng. Agric. Rural Dev. 2016, 16, 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Gheorghievici, L.; Gheorghievici, G.; Tanase, I. The Phytoplankton Composition Features of Five Romanian Pelogenous Ecosystems. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 14, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelarescu, E.D.; Radulescu, C.; Stihi, C.; Bretcan, P.; Tanislav, D.; Dulama, I.D.; Stirbescu, R.M.; Teodorescu, S.; Bucurica, I.A.; Andrei, R.; et al. Analysis of Elements in Lake Sediment Samples by PIXE Spectrometry. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2017, 406, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voicu, V.; Burtea, M.C.; Mocanu, V.; Dumitru, S. Seasonal Variation of Water Mineralisation Degree from Movila Miresii Lake and its Influence on Neighbouring Soils. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2017, 18, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Radulescu, C.; Bucurica, I.A.; Bretcan, P.; Chelarescu, E.D.; Tanislav, D.; Dulama, I.D.; Stirbescu, R.M.; Teodorescu, S. Complex Investigation of Unconsolidated Sediments of Romanian Plain Salt Lake. Rom. J. Phys. 2019, 64, 809. [Google Scholar]
- Moldoveanu, M.; Florescu, L.; Parpala, L.; Cojoc, R.; Enache, M. Romanian Salt Lakes: Some Physical-Chemical Features and Composition of Biological Communities. Muz. Olten. Craiova Olten. Stud. şi comunicări Ştiinţele Nat. 2015, 31, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Axinte, O.; Badescu, I.S.; Stroe, C.; Neacsu, V.; Bulgariu, L.; Bulgariu, D. Evolution of Trophic Parameters from Amara Lake. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 14, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Neagu, S.; Enache, M.; Cojoc, R. Extracellular Hydrolytic Activities of Halophilic Microorganisms Isolated from Balta Alba Salt Lake. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 19, 8951–8958. [Google Scholar]
- Ruginescu, R.M.; Cojoc, R.; Enache, M.; Lazar, V. Preliminary Characterization of a Cellulase Producing Bacterial Strain Isolated from a Romanian Hypersaline Lake. J. Environ. Prot. 2018, 9, 1066–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bulzu, P.-A.; Andrei, A.-Ş.; Salcher, M.M.; Mehrshad, M.; Inoue, K.; Kandori, H.; Beja, O.; Ghai, R.; Banciu, H.L. Casting Light on Asgardarchaeota Metabolism in a Sunlit Microoxic Niche. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, B.A. Chloride. In Drinking Water Chemistry: A Laboratory Manual; Hauser, B.A., Ed.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ventosa, A.; Quesada, E.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Ruiz-Berraquero, F.; Ramos-Cormenzana, A. Numerical Taxonomy of Moderately Halophilic Gram-Negative Rods. Microbiology 1982, 128, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Chen, F.; Liu, J. Halalkalicoccus subterraneus Sp. Nov., an Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Isolated from a Subterranean Halite Deposit. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauclare, P.; Natali, F.; Kleman, J.P.; Zaccai, G.; Franzetti, B. Surviving Salt Fluctuations: Stress and Recovery in Halobacterium salinarum, an Extreme Halophilic Archaeon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, E.R. Aseptic Laboratory Techniques: Plating Methods. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 63, e3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, D.J. Growth and Nutrition of Halophilic Bacteria. In The Biology of Halophilic Bacteria; Vreeland, R.H., Hochstein, L.I., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992; pp. 87–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rohban, R.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Ventosa, A. Screening and Isolation of Halophilic Bacteria Producing Extracellular Hydrolyses from Howz Soltan Lake, Iran. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menasria, T.; Aguilera, M.; Hocine, H.; Benammar, L.; Ayachi, A.; Si Bachir, A.; Dekak, A.; Monteoliva-Sánchez, M. Diversity and Bioprospecting of Extremely Halophilic Archaea Isolated from Algerian Arid and Semi-Arid Wetland Ecosystems for Halophilic-Active Hydrolytic Enzymes. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 207, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enache, M.; Itoh, T.; Kamekura, M.; Teodosiu, G.; Dumitru, L. Haloferax prahovense Sp. Nov., an Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Isolated from a Romanian Salt Lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, J.D.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Wolfenden, R.E.; Vicente, J.L.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Menconi, A.; Bielke, L.R.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez, G. Evaluation and Selection of Bacillus Species Based on Enzyme Production, Antimicrobial Activity, and Biofilm Synthesis as Direct-Fed Microbial Candidates for Poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, N.J.; Hermansson, M.; Wilén, B.-M. The Choice of PCR Primers Has Great Impact on Assessments of Bacterial Community Diversity and Dynamics in a Wastewater Treatment Plant. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Lee, G.H.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Verdonschot, R.C.M.; Vonk, J.A.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. Oxygen Drives Benthic-Pelagic Decomposition Pathways in Shallow Wetlands. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Meng, F.-W. ‘Red—The magic color for solar salt production’—But since When? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Porro, C.; Martín, S.; Mellado, E.; Ventosa, A. Diversity of moderately halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rubaye, M.T.S.; Al-Musawi, M.H.J.; Fakhari, J.; Hosseini, M. Screening and Characterization of Halophilic Bacteria With Industrial Enzymes from Salt Lake Razazah, Karbala, Iraq. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2017, 14, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, I.; Hassani, I.I.; l’Haridon, S.; Chalopin, M.; Hacène, H.; Jebbar, M. Characterization and Antimicrobial Potential of Extremely Halophilic Archaea Isolated from Hypersaline Environments of the Algerian Sahara. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 186–187, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orwa, P.; Mugambi, G.; Wekesa, V.; Mwirichia, R. Isolation of Haloalkaliphilic Fungi from Lake Magadi in Kenya. Heliyon 2020, 6, e02823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaitouni, L.B.D.; Anissi, J.; Sendide, K.; El Hassouni, M. Diversity of Hydrolase-Producing Halophilic Bacteria and Evaluation of Their Enzymatic Activities in Submerged Cultures. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.J. Growing Unculturable Bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 4151–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemzahi, A.; Makhdoumi, A.; Asoodeh, A. Culturable Diversity and Enzyme Production Survey of Halophilic Prokaryotes from a Solar Saltern on the Shore of the Oman Sea. J. Genet. Resour. 2020, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, Z.; Sura, M.; Roula, A.-M. Pectin Shows Antibacterial Activity against Helicobacter pylori. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, M.; Kumar, V.; Rana, V.; Tiwary, A.K. Aegle Marmelos Fruit Pectin for Food and Pharmaceuticals: Physico-Chemical, Rheological and Functional Performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zofou, D.; Shu, G.L.; Foba-Tendo, J.; Tabouguia, M.O.; Assob, J.-C.N. In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Salmonella Evaluation of Pectin Extracts and Hydrolysates from “Cas Mango” (Spondias Dulcis). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 3578402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, H.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, T. Extracellular Hydrolytic Enzyme Screening of Culturable Heterotrophic Bacteria from Deep-Sea Sediments of the Southern Okinawa Trough. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamekh, R.; Deniel, F.; Donot, C.; Jany, J.-L.; Nodet, P.; Belabid, L. Isolation, Identification and Enzymatic Activity of Halotolerant and Halophilic Fungi from the Great Sebkha of Oran in Northwestern of Algeria. Mycobiology 2019, 47, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menasria, T.; Monteoliva-Sánchez, M.; Benammar, L.; Benhadj, M.; Ayachi, A.; Hacène, H.; Gonzalez-Paredes, A.; Aguilera, M. Culturable Halophilic Bacteria Inhabiting Algerian Saline Ecosystems: A Source of Promising Features and Potentialities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, C.R. Bacillus subtilis and Its Relatives: Molecular Biological and Industrial Workhorses. Trends Biotechnol. 1992, 10, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, S.; Fujisawa, M. Industrial Applications of Alkaliphiles and Their Enzymes—Past, Present and Future. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, B.L.; Tabish, E.M.; Wolford, A.J.; Jones, D.L.; Butler, J.K.; Baxter, B.K. The Biogeography of Great Salt Lake Halophilic Archaea: Testing the Hypothesis of Avian Mechanical Carriers. Diversity 2018, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, K.J.; Cresswell-Maynard, T.D.; Nedwell, D.B.; McGenity, T.J.; Grant, W.D.; Timmis, K.N.; Embley, T.M. Isolation of Haloarchaea That Grow at Low Salinities. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomoiu, I.; Dumbravician, M.; Mohanu, M.; Enache, M.; Neagu, S.; Ruginescu, R.; Cojoc, R. Cleaning of Mural Paintings and Mortars: Review. Unpublished work; manuscript in preparation.
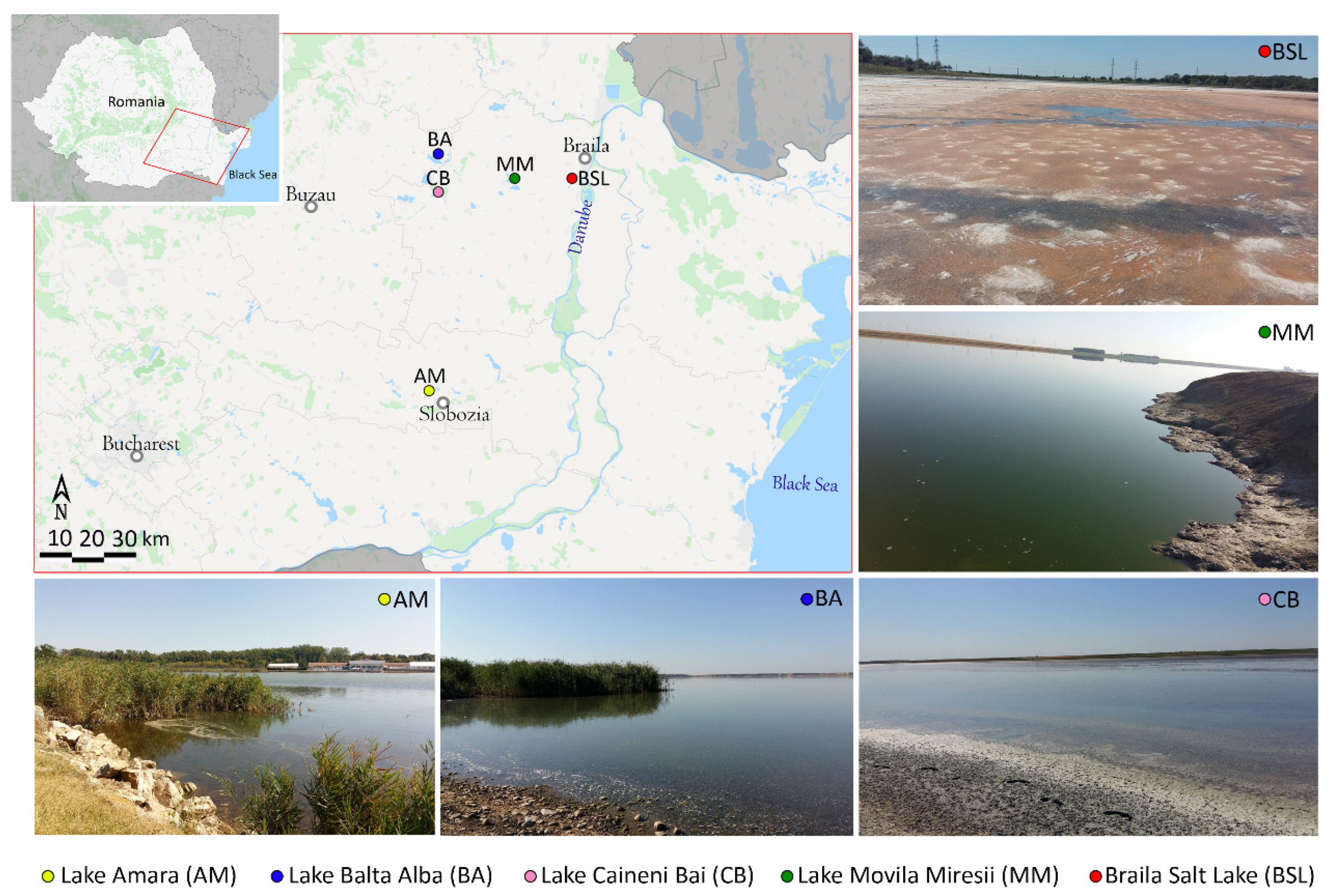

| Lake | pH | T (°C) | DO (mg·L−1) | ORP (mV) | EC (mS·cm−1) | Salinity (g·L−1) | Chloride (g·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM | 8.81 ± 0.3 | 25.49 ± 0.03 | 11.54 ± 1.29 | 12.67 ± 2.27 | 19.05 ± 0.25 | 11.31 ± 0.15 | 3.54 ± 0.07 |
| BA | 10.16 ± 0.25 | 24.4 ± 0.0 | 3.86 ± 0.19 | −158 ± 17.9 | 20.78 ± 0.18 | 12.36 ± 0.11 | 5.52 ± 0.07 |
| CB | 9.03 ± 0.23 | 29.96 ± 0.88 | 2.53 ± 1.81 | −220 ± 58.1 | 52.8 ± 8.98 | 35.67 ± 5.85 | 17.91 ± 0.87 |
| MM | 10.15 ± 0.26 | 22.87 ± 0.09 | 2.12 ± 0.51 | −94.7 ± 16.7 | 107.8 ± 0.2 | >70 * | 38.52 ± 0.54 |
| BSL | 8.05 ± 0.09 | 36.67 ± 2.75 | 0.71 ± 0.57 | −339 ± 43.9 | 168.1 ± 4.9 | >70 * | 150.5 ± 5.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruginescu, R.; Gomoiu, I.; Popescu, O.; Cojoc, R.; Neagu, S.; Lucaci, I.; Batrinescu-Moteau, C.; Enache, M. Bioprospecting for Novel Halophilic and Halotolerant Sources of Hydrolytic Enzymes in Brackish, Saline and Hypersaline Lakes of Romania. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121903
Ruginescu R, Gomoiu I, Popescu O, Cojoc R, Neagu S, Lucaci I, Batrinescu-Moteau C, Enache M. Bioprospecting for Novel Halophilic and Halotolerant Sources of Hydrolytic Enzymes in Brackish, Saline and Hypersaline Lakes of Romania. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(12):1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121903
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuginescu, Robert, Ioana Gomoiu, Octavian Popescu, Roxana Cojoc, Simona Neagu, Ioana Lucaci, Costin Batrinescu-Moteau, and Madalin Enache. 2020. "Bioprospecting for Novel Halophilic and Halotolerant Sources of Hydrolytic Enzymes in Brackish, Saline and Hypersaline Lakes of Romania" Microorganisms 8, no. 12: 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121903
APA StyleRuginescu, R., Gomoiu, I., Popescu, O., Cojoc, R., Neagu, S., Lucaci, I., Batrinescu-Moteau, C., & Enache, M. (2020). Bioprospecting for Novel Halophilic and Halotolerant Sources of Hydrolytic Enzymes in Brackish, Saline and Hypersaline Lakes of Romania. Microorganisms, 8(12), 1903. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121903







