The Duration of Increased Grain Feeding Affects the Microbiota throughout the Digestive Tract of Yearling Holstein Steers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction and Quality Check
2.4. Library Construction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.5. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
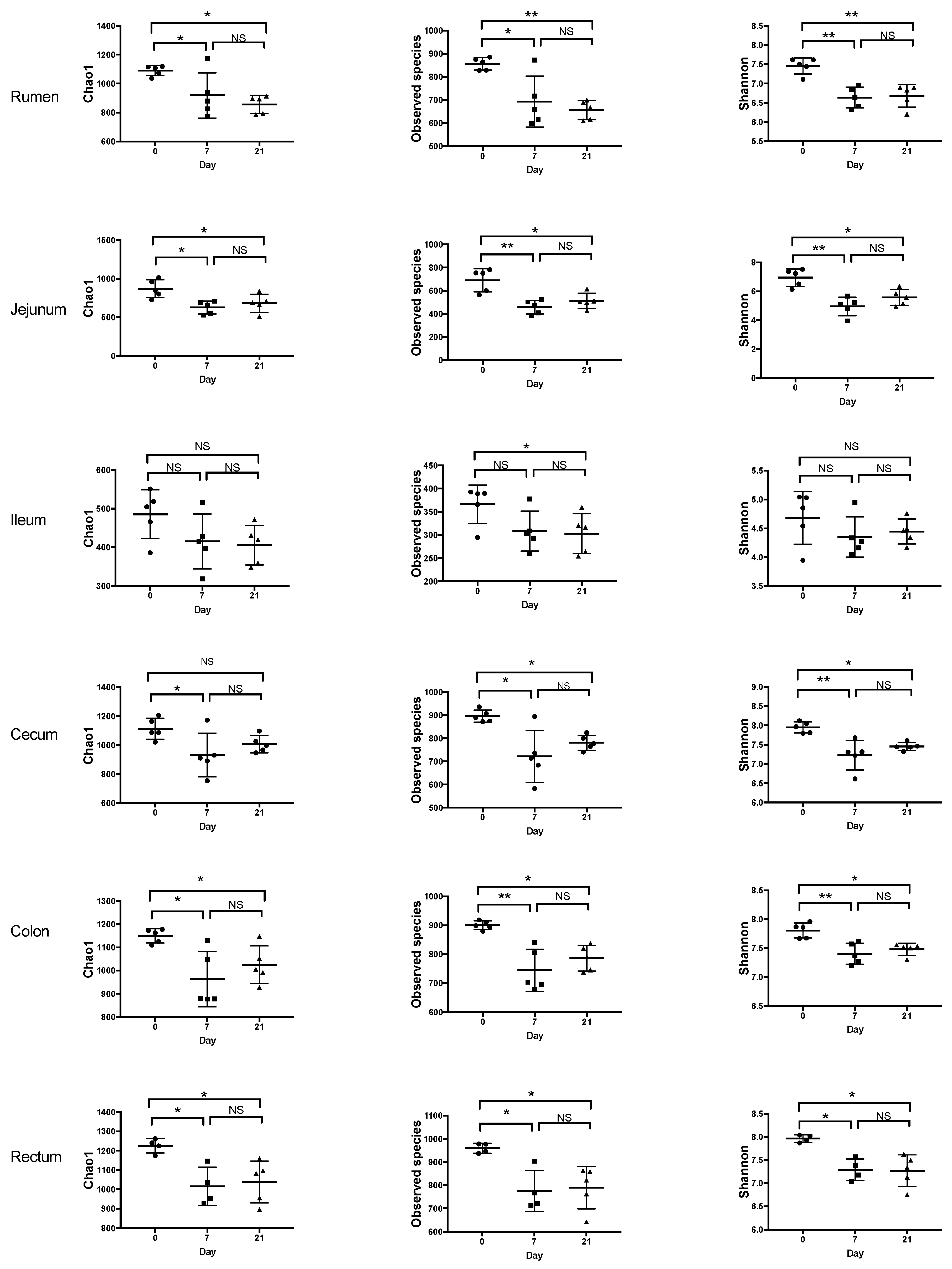
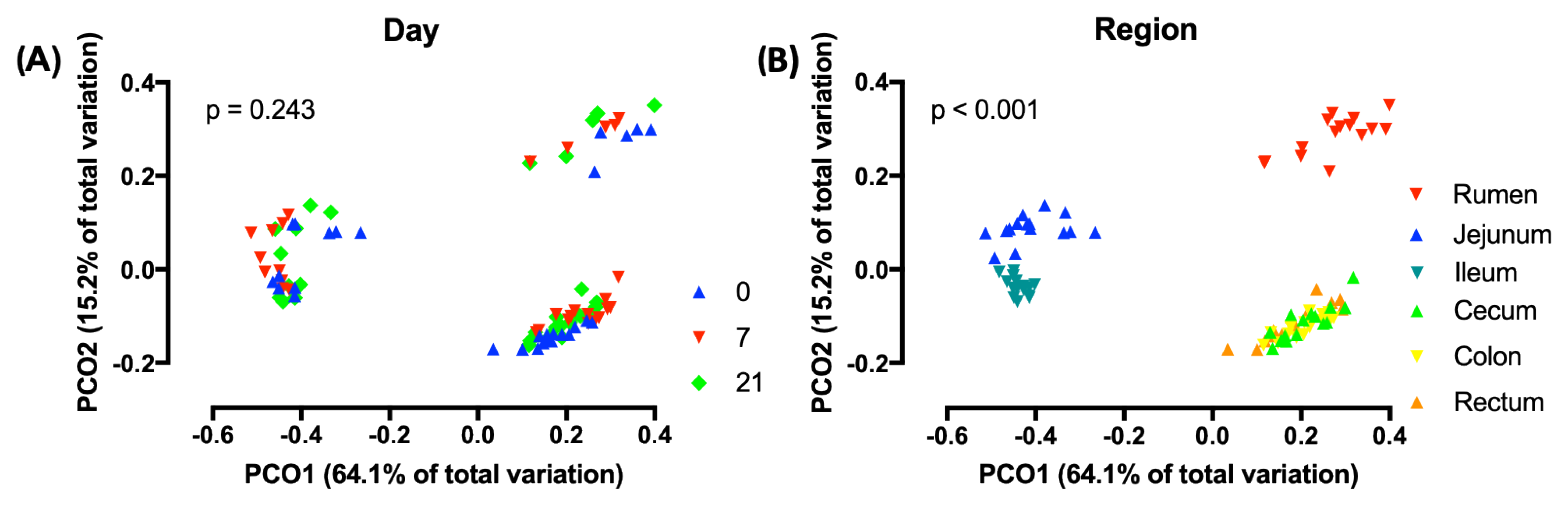
3.1. Effects of Treatment and Region of the Digestive Tract on the Richness and Diversity of Microbiota
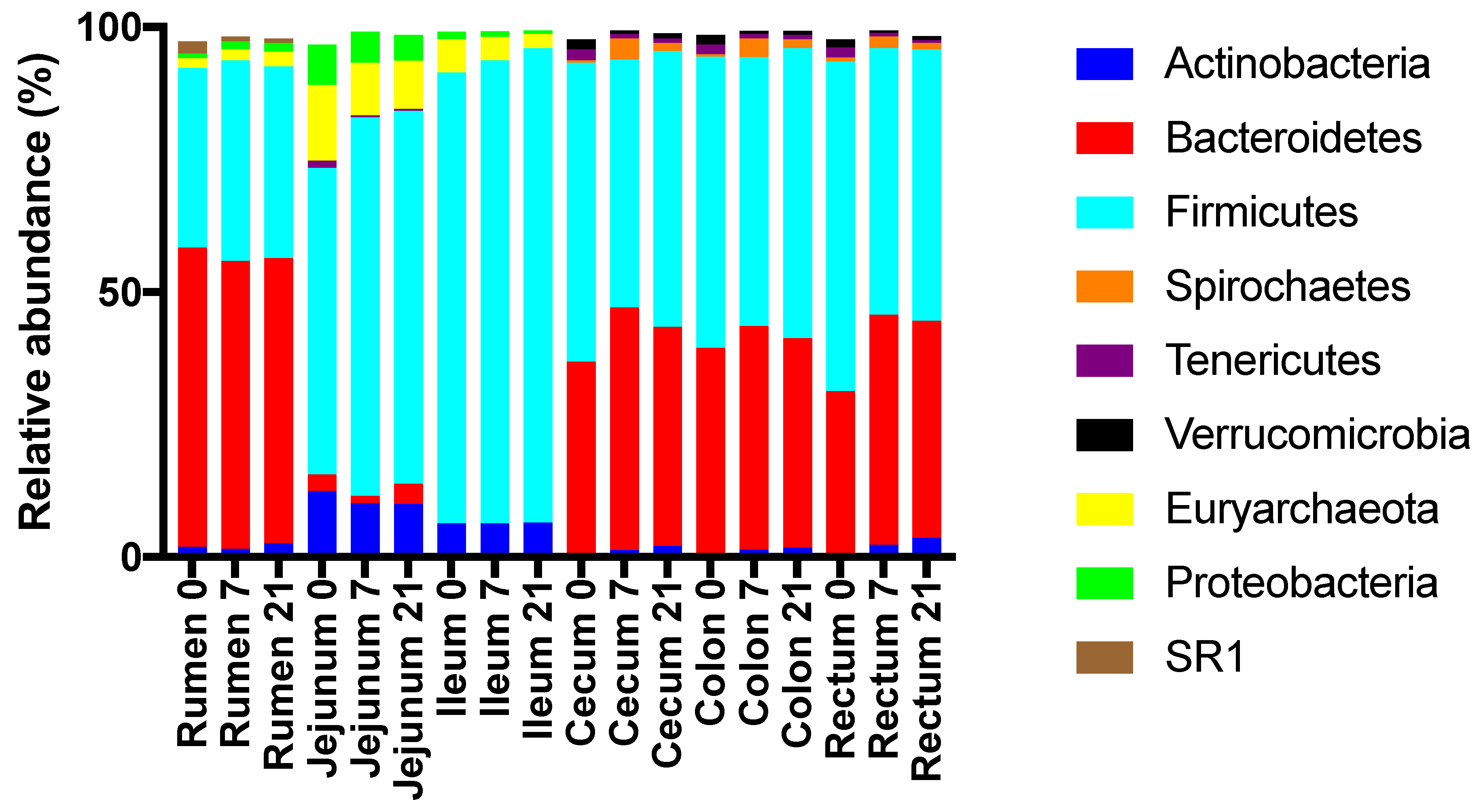
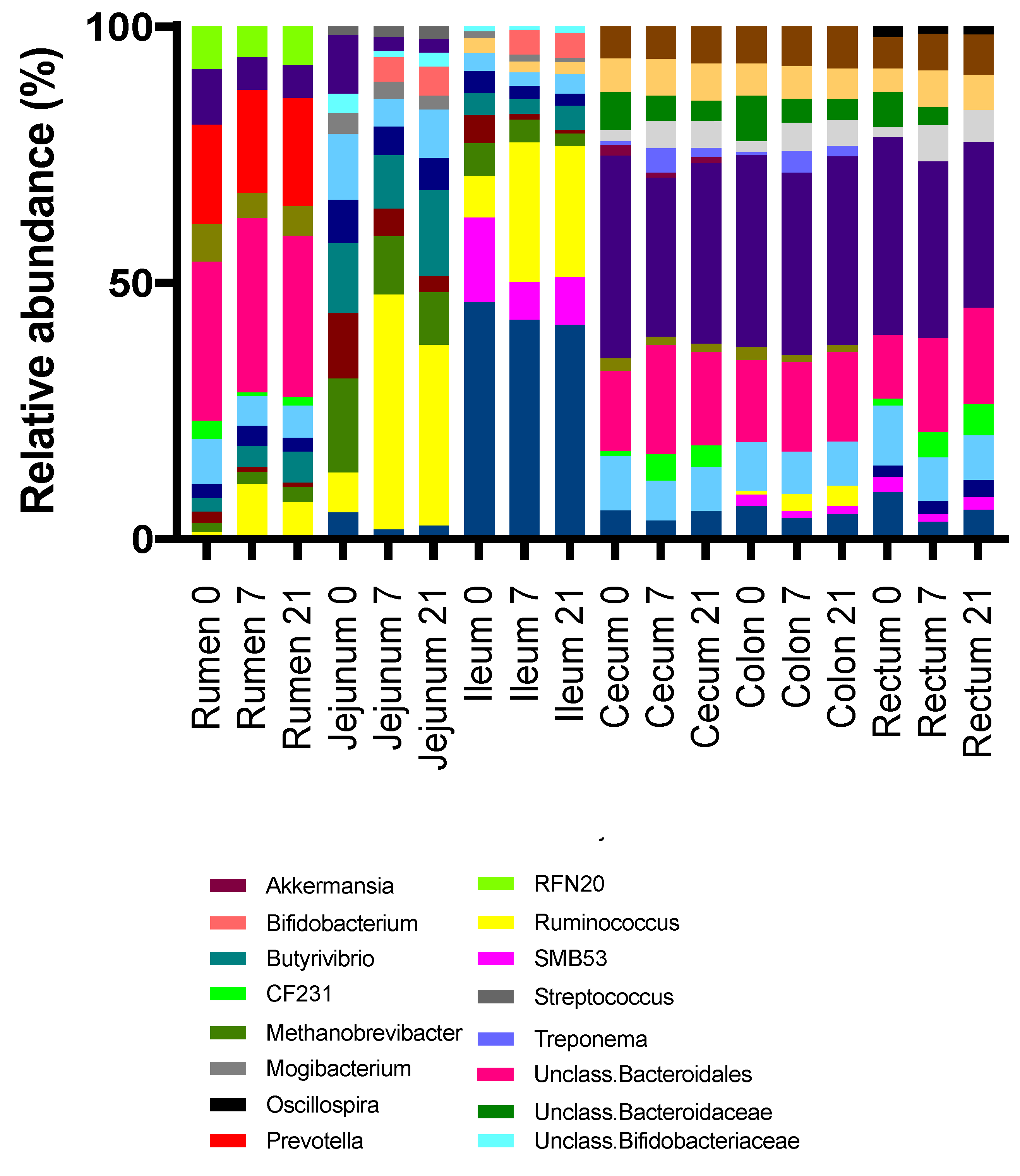
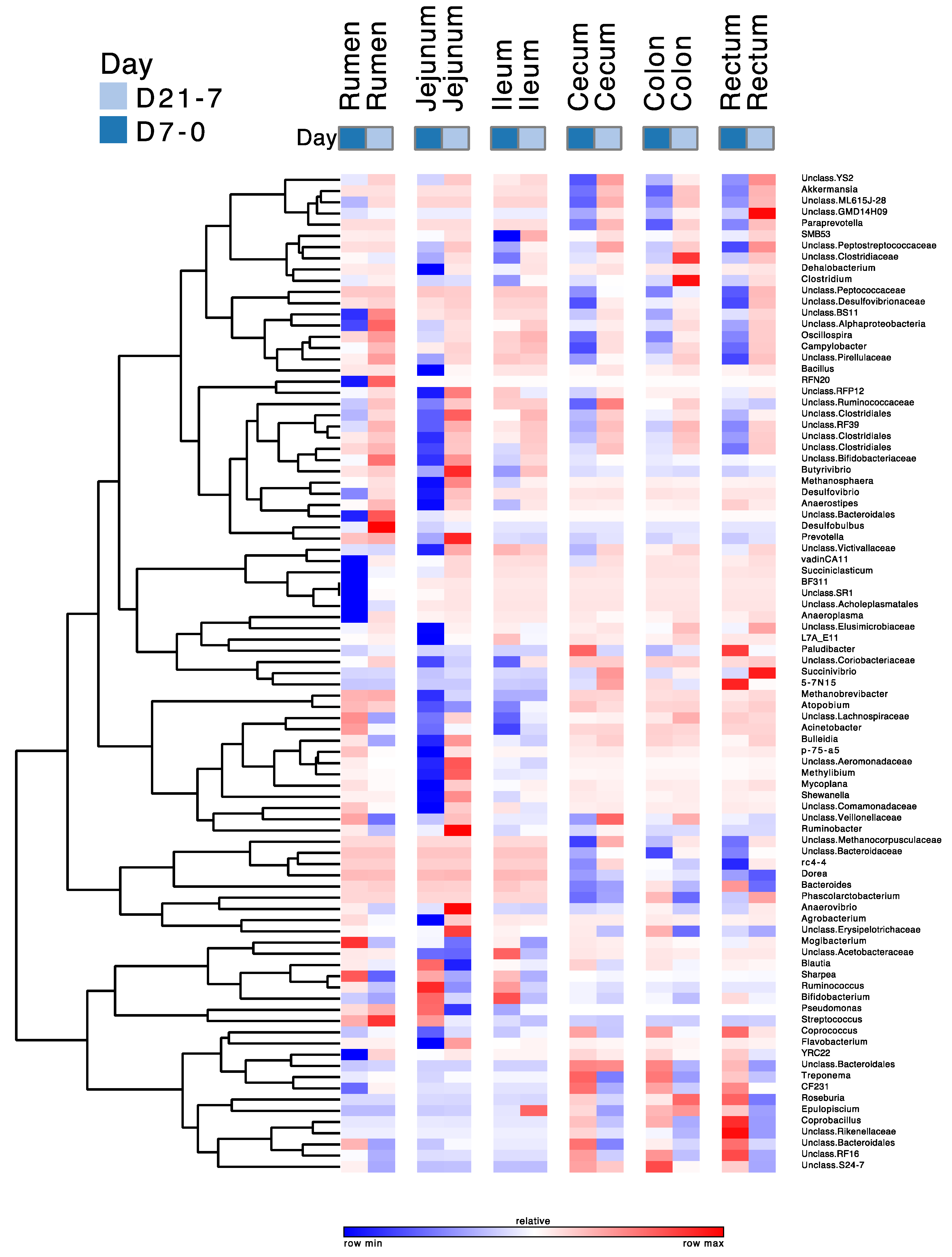
3.2. Effects of Treatment and Region on the Taxonomic Composition of the Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADF | Acid detergent fiber |
| CP | Crude protein |
| DM | Dry matter |
| NDF | Neutral detergent fiber |
| OM | Organic matter |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| SARA | Subacute ruminal acidosis |
References
- Plaizier, J.C.; Mesgaran, M.D.; Derakhshani, H.; Golder, H.; Khafipour, E.; Kleen, J.L.; Lean, I.; Loor, J.; Penner, G.; Zebeli, Q. Enhancing gastrointestinal health in dairy cows. Animal 2018, 12, s399–s418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.B.; Rychlik, J.L. Factors that alter rumen microbial ecology. Science 2001, 292, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleen, J.L.; Hooijer, G.A.; Rehage, J.; Noordhuizen, J.P. Subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA): A review. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 2003, 50, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaizier, J.C.; Khafipour, E.; Li, S.; Gozho, G.N.; Krause, D.O. Subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA), endotoxins and health consequences. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 172, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, R.M.; Schwaiger, T.; Penner, G.B.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Forster, R.J.; McKinnon, J.J.; McAllister, T.A. Characterization of the core rumen microbiome in cattle during transition from forage to concentrate as well as during and after an acidotic challenge. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.Y.; Zhang, R.Y.; Wang, D.S.; Zhu, W.Y. Impact of subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) adaptation on rumen microbiota in dairy cattle using pyrosequencing. Anaerobe 2013, 24, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, H.M.; Li, S.; Yoon, I.; Meale, S.J.; Azevedo, P.A.; Khafipour, E.; Plaizier, J.C. Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation products (SCFP) stabilize the ruminal microbiota of lactating dairy cows during periods of a depressed rumen pH. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, T.G.; Titgemeyer, E.C. Ruminal acidosis in beef cattle: The current microbiological and nutritional outlook. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, E17–E38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaizier, J.C.; Li, S.; Tun, H.M.; Khafipour, E. Nutritional models of experimentally-induced subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) differ in their impact on rumen and hindgut bacterial communities in dairy cows. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, A.; Azevedo, P.A.; Khafipour, E.; Plaizier, J.C. Effects of the dietary grain content on rumen and fecal microbiota of dairy cows. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2020. under review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafipour, E.; Li, S.; Tun, H.M.; Derakhshani, H.; Moossavi, S.; Plaizier, J.C. Effects of grain feeding on microbiota in the digestive tract of cattle. Anim. Front. 2016, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaizier, J.C.; Li, S.; Le Sciellour, M.; Schurmann, B.L.; Górka, P.; Penner, G.B. Effects of duration of moderate increases in grain feeding on endotoxins in the digestive tract and acute phase proteins in peripheral blood of yearling calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 7076–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurmann, B.L.; Walpole, M.E.; Górka, P.; Ching, J.C.; Loewen, M.E.; Penner, G.B. Short-term adaptation of the ruminal epithelium involves abrupt changes in sodium and short-chain fatty acid transport. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integ. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, R802–R816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmon, D.L.; Yamka, R.M.; Elam, N.A. Factors affecting intestinal starch digestion in ruminants: A review. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 84, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górka, P.; Schurmann, B.L.; Walpole, M.E.; Błońska, A.; Li, S.; Plaizier, J.C.; Kowalski, Z.M.; Penner, G.B. Effect of increasing the proportion of dietary concentrate on gastrointestinal tract measurements and brush border enzyme activity in Holstein steers. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4539–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CCAC. Canadian Council on Animal Care. Guidelines on the Care and Use of Farm Animals in Research, Teaching and Testing; CCAC: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Derakhshani, H.; Tun, H.M.; Cardoso, F.C.; Plaizier, J.C.; Khafipour, E.; Loor, J.J. Linking peripartal dynamics of rumen microbiota to dietary changes and production parameters. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masella, A.P.; Bartram, A.K.; Truszkowski, J.M.; Brown, D.G.; Neufeld, J.D. PANDAseq: Paired-end assembler for illumina sequences. BMC Bioinformat. 2012, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesianclassifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER v7: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C.M. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.4-1. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Callaway, T.R.; Dowd, S.E.; Edrington, T.S.; Anderson, R.C.; Krueger, N.; Bauer, N.; Kononoff, P.J.; Nisbet, D.J. Evaluation of bacterial diversity in the rumen and feces of cattle fed different levels of dried distillers grains plus solubles using bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 3977–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebeli, Q.; Metzler-Zebeli, B.U. Interplay between rumen digestive disorders and diet-induced inflammation in dairy cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressley, T.F.; Hall, M.B.; Armentano, L.E. Ruminant nutrition symposium: Productivity, digestion, and health responses to hindgut acidosis in ruminants. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 1120–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, C.; Crispie, F.; Lewis, E.; Reid, M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D. The rumen microbiome: A crucial consideration when optimising milk and meat production and nitrogen utilisation efficiency. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.B.; Muck, R.E.; Weimer, P.J. Quantitative analysis of cellulose degradation and growth of cellulolytic bacteria in the rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Zhu, W. The diversity of the fecal bacterial community and its relationship with the concentration of volatile fatty acids in the feces during subacute rumen acidosis in dairy cows. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaizier, J.C.; Li, S.; Danscher, A.M.; Derakshani, H.; Andersen, P.H.; Khafipour, E. Changes in microbiota in rumen digesta and feces due to a grain-based subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) challenge. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 74, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapio, I.; Fischer, D.; Blasco, L.; Tapio, M.; Wallace, R.J.; Bayat, A.R.; Ventto, L.; Kahala, M.; Negussie, E.; Shingfield, K.J.; et al. Taxon abundance, diversity, co-occurrence and network analysis of the ruminal microbiota in response to dietary changes in dairy cows. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, J.M.; D’Antonio, C.M. Elton revisited: A review of evidence linking diversity and invasibility. Oikos 1999, 1, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belanche, A.; Kingston-Smith, A.H.; Griffith, G.W.; Newbold, C.J. A multi-kingdom study reveals the plasticity of the rumen microbiota in response to a shift from non-grazing to grazing diets in sheep. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.C.; Purvis, H.T.; Najar, F.Z.; Sukharnikov, L.O.; Krehbiel, C.R.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Roe, B.A.; DeSilva, U. Rumen microbial population dynamics during adaptation to a high-grain diet. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7482–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, R.M.; Forster, R.J.; Yang, W.; McKinnon, J.J.; McAllister, T.A. Characterization of rumen bacterial diversity and fermentation parameters in concentrate fed cattle with and without forage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.N.; Jewell, K.A.; Freitas, F.S.; Benjamin, L.A.; Tótola, M.R.; Borges, A.C.; Moraes, C.A.; Suen, G. Characterizing the microbiota across the gastrointestinal tract of a Brazilian Nelore steer. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W. Characterising the bacterial microbiota across the gastrointestinal tracts of dairy cattle: Membership and potential function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez-Gonzalez, F.; Callaway, T.R.; Kizoulis, M.G.; Russell, J.B. Grain feeding and the dissemination of acid-resistant Escherichia coli from cattle. Science 1998, 281, 1666–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asma, Z.; Sylvie, C.; Laurent, C.; Jérôme, M.; Christophe, K.; Olivier, B.; Annabelle, T.M.; Francis, E. Microbial ecology of the rumen evaluated by 454 GS FLX pyrosequencing is affected by starch and oil supplementation of diets. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 504–514. [Google Scholar]
- Weimer, P.J. Redundancy, resilience, and host specificity of the ruminal microbiota: Implications for engineering improved ruminal fermentations. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitta, D.W.; Pinchak, W.E.; Dowd, S.; Dorton, K.; Yoon, I.; Min, B.R.; Fulford, J.D.; Wickersham, T.A.; Malinowski, D.P. Longitudinal shifts in bacterial diversity and fermentation pattern in the rumen of steers grazing wheat pasture. Anaerobe 2014, 30, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.S.; Renslow, R.S.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Lindemann, S.R. Integrating ecological and engineering concepts of resilience in microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plaizier, J.C.; Azevedo, P.; Schurmann, B.L.; Górka, P.; Penner, G.B.; Khafipour, E. The Duration of Increased Grain Feeding Affects the Microbiota throughout the Digestive Tract of Yearling Holstein Steers. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121854
Plaizier JC, Azevedo P, Schurmann BL, Górka P, Penner GB, Khafipour E. The Duration of Increased Grain Feeding Affects the Microbiota throughout the Digestive Tract of Yearling Holstein Steers. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(12):1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121854
Chicago/Turabian StylePlaizier, J. C., P. Azevedo, B. L. Schurmann, P. Górka, G. B. Penner, and E. Khafipour. 2020. "The Duration of Increased Grain Feeding Affects the Microbiota throughout the Digestive Tract of Yearling Holstein Steers" Microorganisms 8, no. 12: 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121854
APA StylePlaizier, J. C., Azevedo, P., Schurmann, B. L., Górka, P., Penner, G. B., & Khafipour, E. (2020). The Duration of Increased Grain Feeding Affects the Microbiota throughout the Digestive Tract of Yearling Holstein Steers. Microorganisms, 8(12), 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121854




