Molecular Survey and Genetic Diversity of Hemoplasmas in Rodents from Chile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
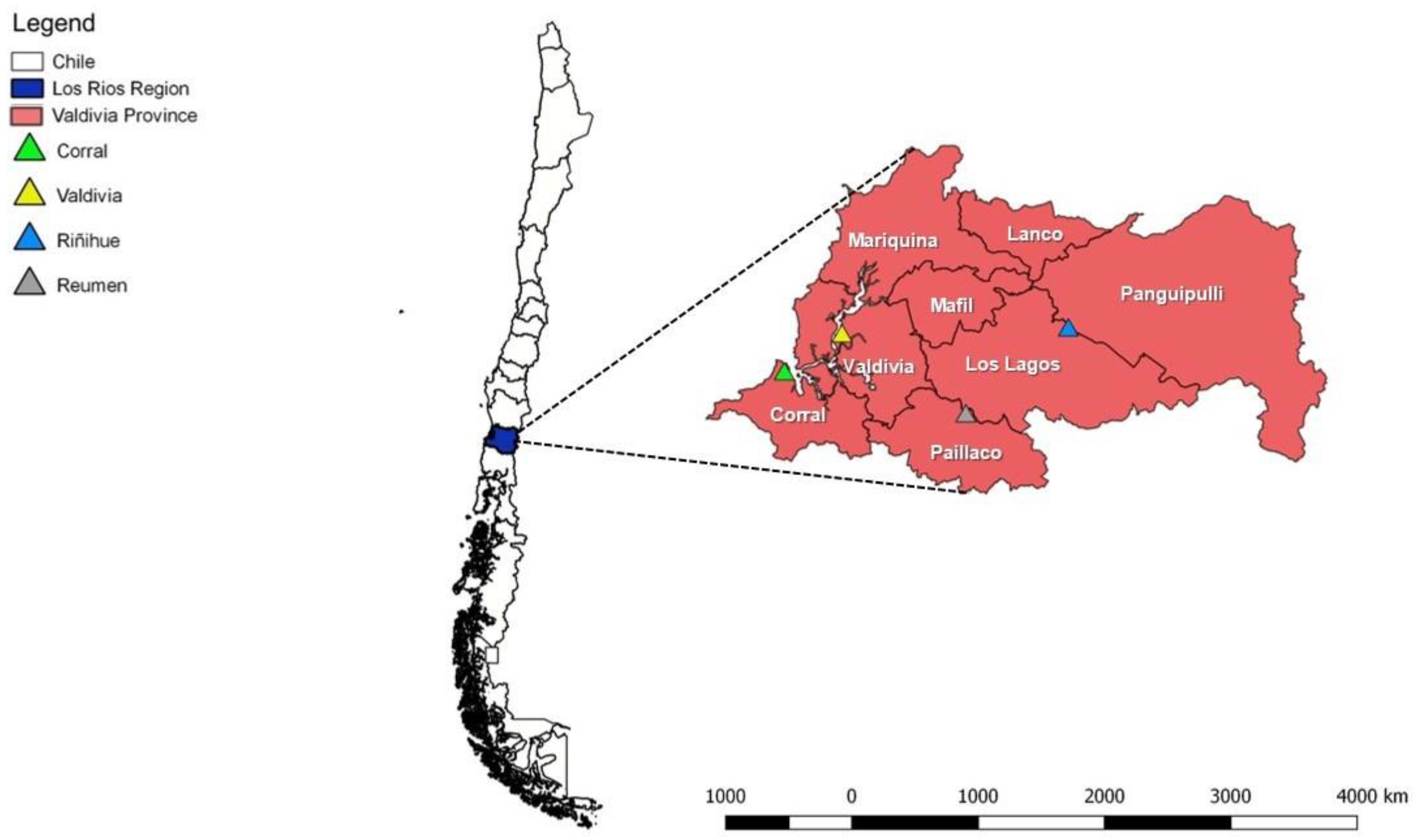
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Rodent Trapping and Sampling
2.3. DNA Extraction from Rodent Spleen Tissues
2.4. Endogenous PCR for Mammals
2.5. Molecular Detection of Hemotrophic Mycoplasma spp. 16S rDNA
2.6. BLAST Analysis
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Genotype Analysis
2.9. Splits Network Analysis
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rodents, Amplifiable DNA, and Hemoplasma Survey
3.2. BLAST Analysis
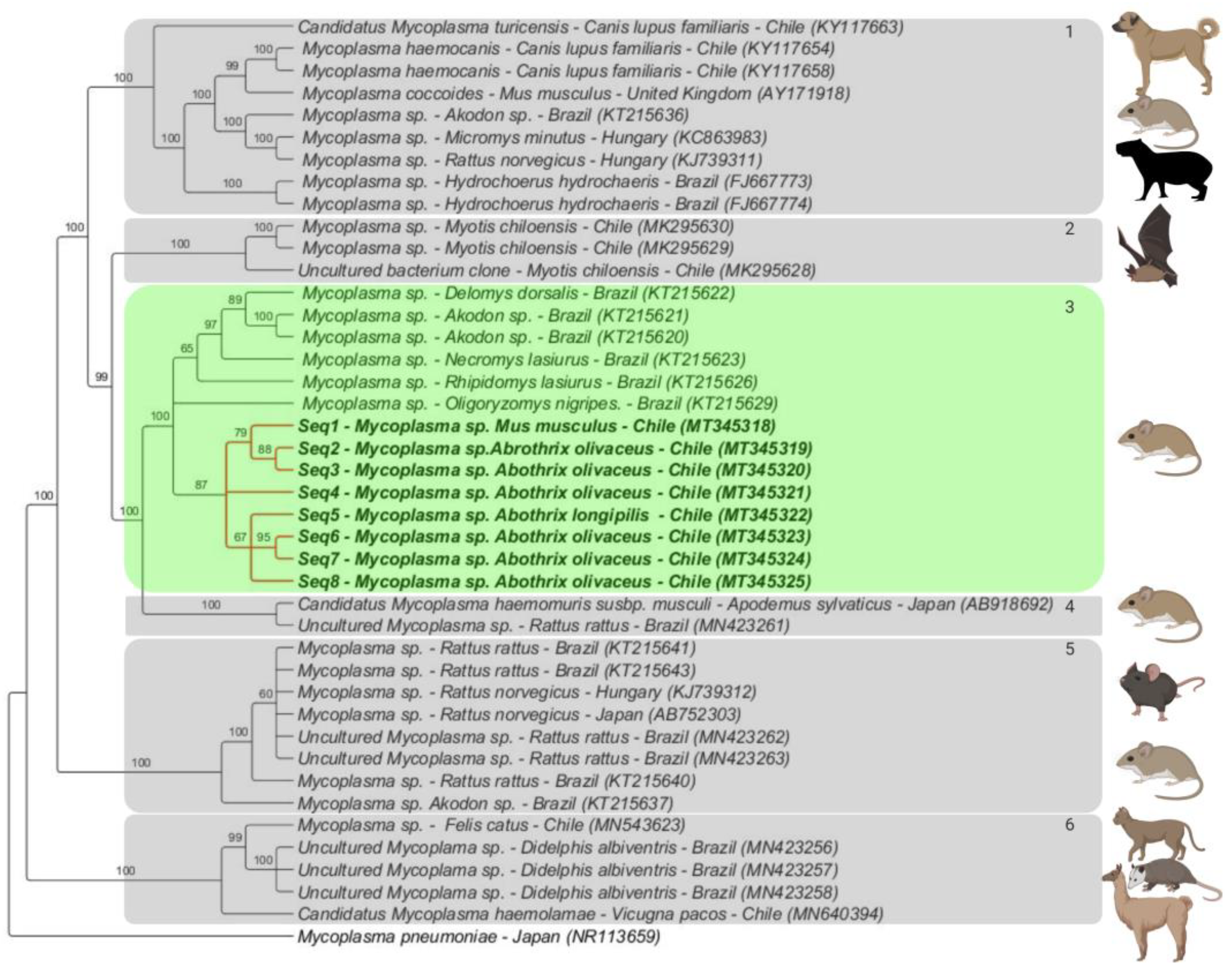
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
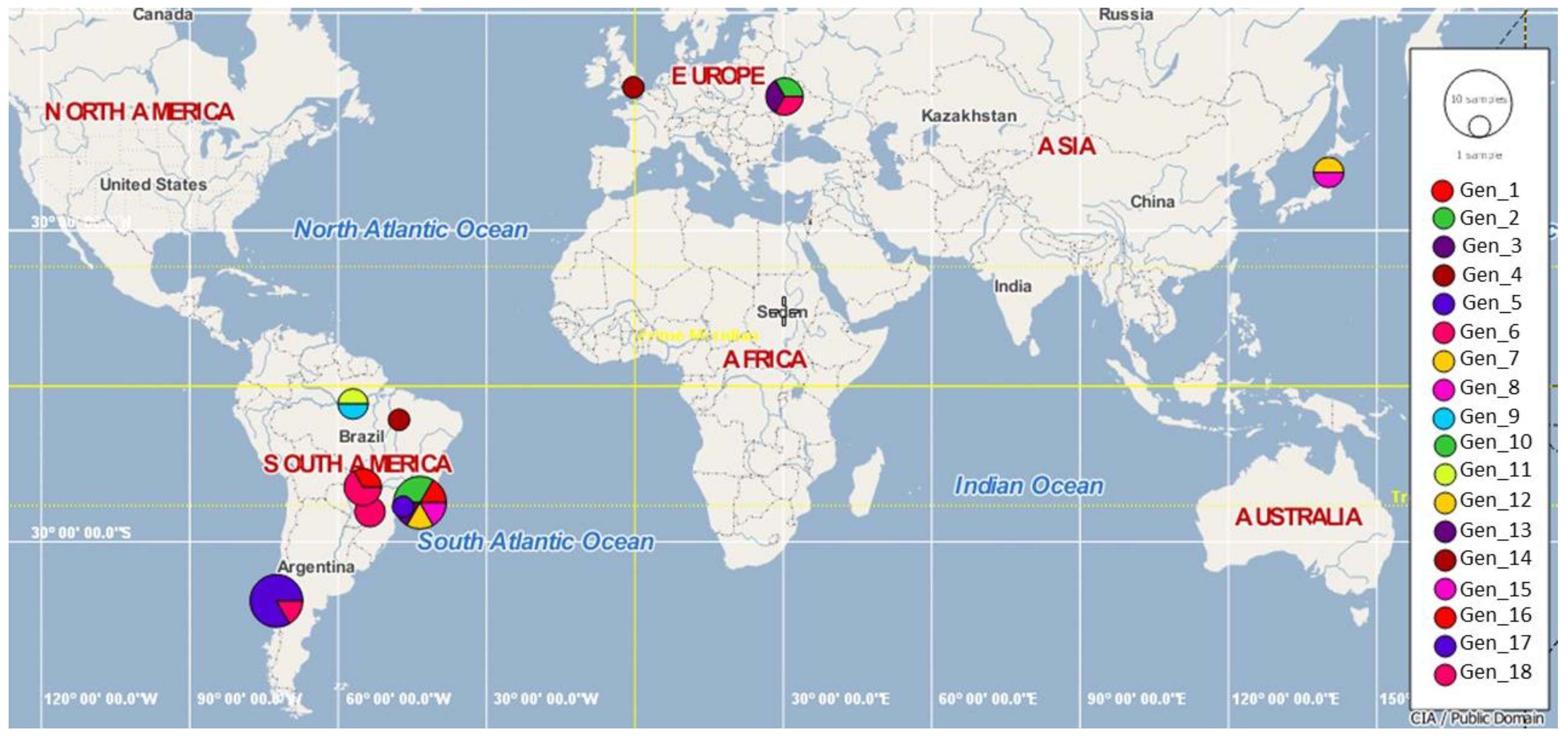
3.4. Genotype Analysis
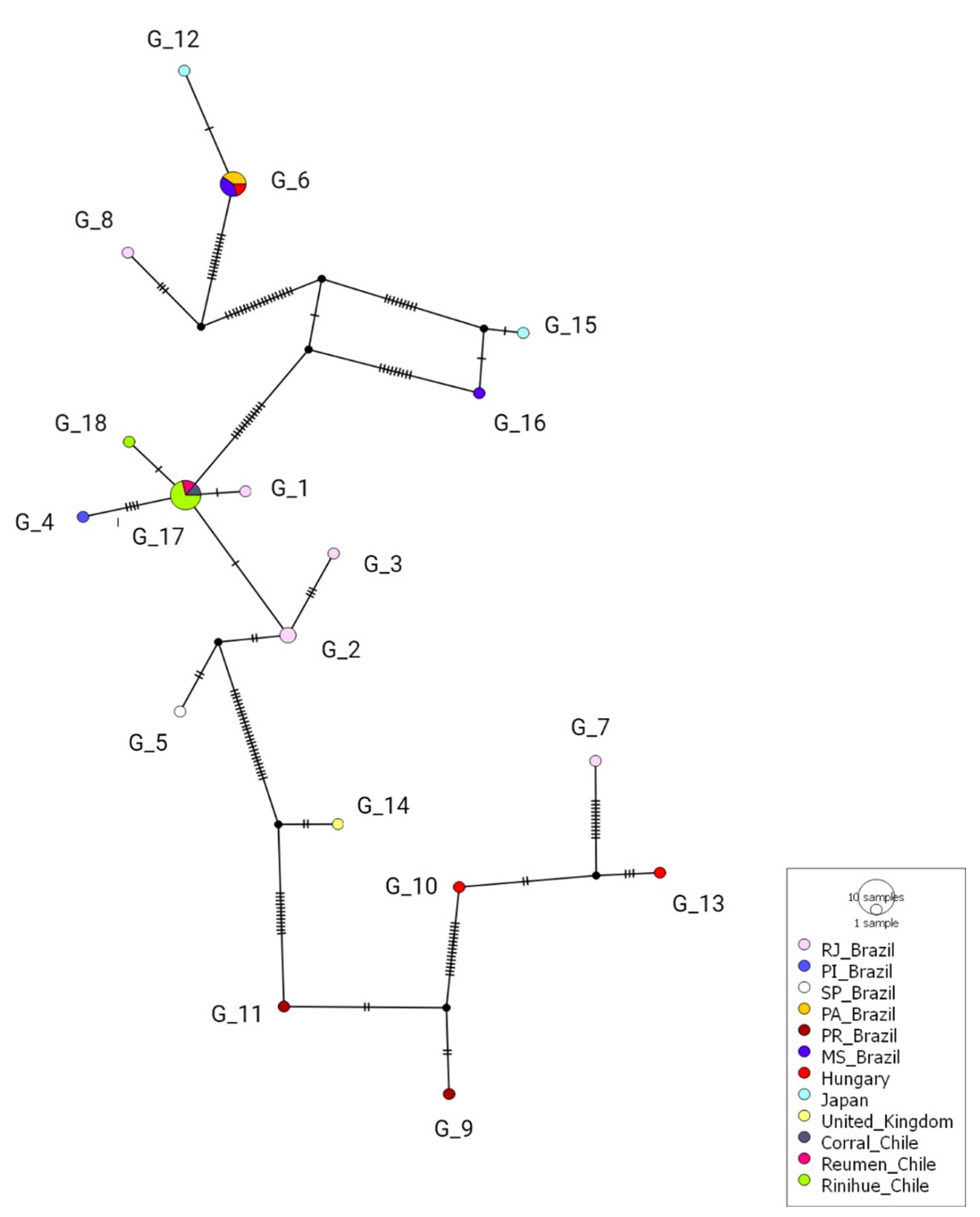
3.5. Splits Network Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neimark, H.; Johansson, K.E.; Rikihisa, Y.; Tully, J.G. Proposal to transfer some members of the genera Haemobartonella and Eperythrozoon to the genus Mycoplasma with descriptions of “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemofelis”, “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemomuris”, “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemosuis” and ’Candidatus Mycopl. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rikihisa, Y.; Kawahara, M.; Wen, B.; Kociba, G.; Fuerst, P.; Kawamori, F.; Suto, C.; Shibata, S.; Futohashi, M. Western immunoblot analysis of Haemobartonella muris and comparison of 16S rRNA gene sequences of H. muris, H. felis, and Eperythrozoon suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, M.R.N.; Vahedi, S.M.; Fatemeh, M. khan Haemotropic mycoplasmas (haemoplasmas): A review. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2014, 2, 1484–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Hall, W.T.; Sheffield, J.B.; Moore, D.H.; Hall, T. Fine structure of Haemobartonella muris as compared with Eperythrozoon coccoides and Mycoplasma pulmonis. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 90, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, S.C. Clinical observations on eperythrozoonosis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1979, 174, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoelzle, L. Development of a diagnostic PCR assay based on novel DNA sequences for the detection of Mycoplasma suis (Eperythrozoon suis) in porcine blood. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 93, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strait, E.L.; Hawkins, P.A.; Wilson, W.D. Dysgalactia associated with Mycoplasma suis infection in a sow herd. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2012, 241, 1666–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, S.; Peters, I.R.; Papasouliotis, K.; Cue, S.M.; Willi, B.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.J.; Knowles, T.G.; Day, M.J.; Helps, C.R. Description of outcomes of experimental infection with feline haemoplasmas: Copy numbers, haematology, Coombs’ testing and blood glucose concentrations. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, A.; Welc-Falęciak, R.; Bednarska, M.; Alsarraf, M.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Siński, E.; Behnke, J.M. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Stability and Dynamic Changes in the Haemoparasite Community of Bank Voles (Myodes glareolus) in NE Poland. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, K.M.; Goncarovs, K.O.; Thompson, C.A.; Halik, L.A.; Santos, A.P.; Guimaraes, A.M.S.; Feutz, M.M.; Holman, P.J.; Vemulapalli, R.; Messick, J.B. Identification of a Mycoplasma ovis-like organism in a herd of farmed white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in rural Indiana. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 41, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifiyazdi, H.; Nazifi, S.; Shirzad Aski, H.; Shayegh, H. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the causative agent of hemoplasma infection in small Indian Mongoose (Herpestes Javanicus). Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 37, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volokhov, D.V.; Hwang, J.; Chizhikov, V.E.; Danaceau, H.; Gottdenker, N.L. Prevalence, genotype richness, and coinfection patterns of hemotropic mycoplasmas in raccoons (Procyon lotor) on environmentally protected and urbanized barrier islands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00211–e00217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willi, B.; Filoni, C.; Catao-Dias, J.L.; Cattori, V.; Meli, M.L.; Vargas, A.; Martinez, F.; Roelke, M.E.; Ryser-Degiorgis, M.P.; Leutenegger, C.M.; et al. Worldwide Occurrence of Feline Hemoplasma Infections in Wild Felid Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, K.C.M.; Herrera, H.M.; Secato, C.T.; do Vale Oliveira, A.; Santos, F.M.; Rocha, F.L.; Barreto, W.T.G.; Macedo, G.C.; de Andrade Pinto, P.C.E.; Machado, R.Z.; et al. Occurrence and molecular characterization of hemoplasmas in domestic dogs and wild mammals in a Brazilian wetland. Acta Trop. 2017, 171, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.R.; Roque, A.L.R.; Matos, C.A.; de Jesus Fernandes, S.; Olmos, I.D.F.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R. Diversity and molecular characterization of novel hemoplasmas infecting wild rodents from different Brazilian biomes. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 43, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iso, T.; Suzuki, J.; Sasaoka, F.; Sashida, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Fujihara, M.; Nagai, K.; Harasawa, R. Hemotropic mycoplasma infection in wild black bears (Ursus thibetanus japonicus). Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 163, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarelli, P.E.; Elmore, S.A.; Jenkins, E.J.; Alisauskas, R.T.; Walsh, M.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G. Vector-borne pathogens in arctic foxes, Vulpes lagopus, from Canada. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 99, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; López-Roig, M.; Delicado, V.; Serra-Cobo, J.; Esperón, F. Widespread infection with hemotropic mycoplasmas in bats in Spain, including a hemoplasma closely related to “Candidatus Mycoplasma hemohominis”. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 39, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.C.; Cubilla, M.P.; de Moraes, W.; Cubas, Z.S.; Oliveira, M.J.; Estrada, M.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Sykes, J.E.; Lindsay, L.L.; Marcondes, M.; et al. Hemotropic Mycoplasma in a Free-ranging Black Howler Monkey (Alouatta caraya) in Brazil. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashida, H.; Sasaoka, F.; SuzukiI, J.; Watanabe, Y.; Fujihara, M.; Nagai, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Furuhama, K.; Harasawa, R. Detection of Hemotropic Mycoplasmas in Free-Living Brown Sewer Rats (Rattus norvegicus). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashida, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Rokuhara, S.; Nagai, K.; Harasawa, R. Molecular demonstration of hemotropic mycoplasmas in wild Japanese monkeys (Macaca fuscata). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2014, 76, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, S.; Földvári, G.; Rigó, K.; Meli, M.L.; Gönczi, E.; Répási, A.; Farkas, R.; Papp, I.; Kontschán, J.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. Synanthropic rodents and their ectoparasites as carriers of a novel haemoplasma and vector-borne, zoonotic pathogens indoors. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkenkamp, S.D.; Wescott, R.B. Arthropod transmission of Eperythrozoon coccoides in mice. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1988, 38, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fleer, K.A.; Foley, P.; Calder, L.; Foley, J.E. Arthropod vectors and vector-borne bacterial pathogens in Yosemite National Park. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Rodents of the Subfamily Caviinae (Hystricognathi, Caviidae) as Hosts for Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). Mastozoología Neotrop. 2010, 17, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Nava, S. Rodents of the subfamily Sigmodontinae (Myomorpha: Cricetidae) as hosts for South American hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) with hypotheses on life history. Zootaxa 2011, 2904, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Conrado, F.; do Nascimento, N.C.; dos Santos, A.P.; Zimpel, C.K.; Messick, J.B.; Biondo, A.W. Occurrence and identification of hemotropic mycoplasmas (Hemoplasmas) in free ranging and laboratory rats (Rattus norvegicus) from two Brazilian zoos. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.R.; Herrera, H.M.; Nantes, W.A.G.; Santos, F.M.; de Oliveira Porfírio, G.E.; Barreto, W.T.G.; de Macedo, G.C.; de Oliveira Assis, W.; Campos, J.B.V.; da Silva, T.M.V.; et al. Genetic diversity and lack of molecular evidence for hemoplasma cross-species transmission between wild and synanthropic mammals from Central-Western Brazil. Acta Trop. 2020, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Ronconi, A.; Cordeiro, N.; Bossi, D.; Bergallo, H.; Costa, M.; Balieiro, J.; Varzim, F. Blood parasites, total plasma protein and packed cell volume of small wild mammals trapped in three mountain ranges of the Atlantic Forest in Southeastern Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2007, 67, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.F.C.; Molento, M.B.; dos Santos, L.C.; Moraes, W.; Cubas, Z.S.; Santos, A.P.; Guimaraes, A.M.S.; Mohamed, A.; Barros Filho, I.R.; Biondo, A.W.; et al. Detection of a novel hemoplasma based on 16S rRNA gene DNA in captive and free-ranging capybaras (Hydrochaeris hydrochaeris). Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasawa, R.; Fujita, H.; Kadosaka, T.; Ando, S.; Rikihisa, Y. Proposal for ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemomuris subsp. musculi’ in mice, and ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemomuris subsp. ratti’ in rats. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, C.; Shemesh, M.; Garrido, M.; Messika, I.; Einav, M.; Khokhlova, I.; Tasker, S.; Hawlena, H. Haemoplasmas in wild rodents: Routes of transmission and infection dynamics. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 3714–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esch, G.W. Regulation of Parasite Populations: With Introd; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Ewald, P.W. The evolution of virulence: A unifying between and ecology parasitology. J. Parasitol. 2016, 81, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, Y.; Sasaoka, F.; Suzuki, J.; Watanabe, Y.; Fujihara, M. Prevalence of Hemoplasma Infection among Cattle in the Western Part of Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.M.; May, R.M. Coevolution of Hosts and Parasites. Parasitology 1982, 85, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, H.; Fujihara, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Ono, H.K.; Harasawa, R. A feline hemoplasma, “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum”, detected in dog in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.P.; Dos Santos, R.P.; Biondo, A.W.; Dora, J.M.; Goldani, L.Z.; De Oliveira, S.T.; De Sá Guimarães, A.M.; Timenetsky, J.; De Morais, H.A.; González, F.H.D.; et al. Hemoplasma infection in HIV-positive patient, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1922–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steer, J.A.; Tasker, S.; Barker, E.N.; Jensen, J.; Mitchell, J.; Stocki, T.; Chalker, V.J.; Hamon, M. A Novel Hemotropic Mycoplasma (Hemoplasma) in a Patient With Hemolytic Anemia and Pyrexia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, e147–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, E.N.; Tasker, S.; Day, M.J.; Warman, S.M.; Woolley, K.; Birtles, R.; Georges, K.C.; Ezeokoli, C.D.; Newaj-Fyzul, A.; Campbell, M.D.; et al. Development and use of real-time PCR to detect and quantify Mycoplasma haemocanis and “Candidatus Mycoplasma haematoparvum” in dogs. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Soto, F.; Sepúlveda, M.; Bittencourt, P.; Benevenute, J.L.; Ikeda, P.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R. Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii and B. henselae in dogs. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1202–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinborn-Astudillo, R.M.; Pau, N.; Tobar, B.Z.; Jaffe, D.A.; Boulouis, H.J.; Sepúlveda, P.; Müller, A.; Chomel, B.B. Bartonella Infection in Stray Dogs from Central and Southern Chile (Linares and Puerto Montt). Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, F.; Walker, R.; Sepulveda, M.; Bittencourt, P.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Müller, A. Occurrence of canine hemotropic mycoplasmas in domestic dogs from urban and rural areas of the Valdivia Province, southern Chile. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 50, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, V.; Islas, A.; Rivera, P.; Cruz, A.; Tardón, R. Mycoplasma haemominutum ” a través de PCR en gatos de la comuna de Chillán. Estudio preliminar. Mycoplasma haemofelis and “ Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum ” detection by PCR assay in cats of Chillán commune. Preliminar study. Hosp. Vet. 2011, 3, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Walker Vergara, R.; Morera Galleguillos, F.; Gómez Jaramillo, M.; Pereira Almosny, N.R.; Arauna Martínez, P.; Grob Behne, P.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Müller, A. Prevalence, risk factor analysis, and hematological findings of hemoplasma infection in domestic cats from Valdivia, Southern Chile. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 46, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristán, I.; Acuña, F.; Aguilar, E.; García, S.; López, M.J.; Cevidanes, A.; Cabello, J.; Hidalgo-Hermoso, E.; Johnson, W.E.; Poulin, E.; et al. Assessing cross-species transmission of hemoplasmas at the wild-domestic felid interface in Chile using genetic and landscape variables analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornquist, S.J.; Boeder, L.; Rios-Phillips, C.; Alarcon, V. Prevalence of Mycoplasma Haemolamae Infection in Peruvian and Chilean Llamas and Alpacas. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, J.; Altet, L.; Napolitano, C.; Sastre, N.; Hidalgo, E.; Dávila, J.A.; Millán, J. Survey of infectious agents in the endangered Darwin’ s fox (Lycalopex fulvipes): High prevalence and diversity of hemotrophic mycoplasmas. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; Cevidanes, A.; Sacristán, I.; Alvarado-Rybak, M.; Sepúlveda, G.; Ramos-Mella, C.A.; Lisón, F. Detection and Characterization of Hemotropic Mycoplasmas in Bats in Chile. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedenqvist, P.; Hellebrekers, L. Laboratory animal analgesia, anesthesia, and euthanasia. In Handbook of Laboratory Animal Science; Hau, J., Van Gerald, H., Eds.; CRC Press: Washintong, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 413–455. ISBN 0-8493-1086-5. [Google Scholar]
- Benavides, F.J.; Guénet, J.L. Biología y manejo reproductivo del ratón. Man. Genética Roedores Lab. Pricipios Básicos Apl. 2003, 1, 59–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, E.C.; Gontijo, C.M.; Cruz, I.; Melo, M.N.; Silva, A.M. Alternative PCR protocol using a single primer set for assessing DNA quality in several tissues from a large variety of mammalian species living in areas endemic for leishmaniasis. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2010, 105, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Compton, S.M.; Trull, C.L.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Mozayeni, B.R.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Infection with Hemotropic Mycoplasma Species in Patients with or without Extensive Arthropod or Animal Contact. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3237–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, V.V.C.; de Souza Ramos, I.A.; Herrera, H.M.; Mendes, N.S.; Calchi, A.C.; Campos, J.B.V.; Macedo, G.C.; Alves, J.V.A.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R. Occurrence and genetic diversity of hemoplasmas in beef cattle from the Brazilian Pantanal, an endemic area for bovine trypanosomiasis in South America. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 66, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, B.; Hillier, L.; Wendl, M.C.; Green, P. Base-Calling of Automated Sequencer Traces Using Phred. I. Accuracy Assessment. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Karsch-mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Wheeler, D.L. GenBank: Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D23–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Mrbayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for Inference of Large Phylogenetic Trees. In Proceedings of the Grid Computing Environments Workshop, GCE, New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Santorum, J.M.; Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Posada, D. jmodeltest.org: Selection of nucleotide substitution models on the cloud. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1310–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Buckley, T.R. Model Selection and Model Averaging in Phylogenetics: Advantages of Akaike Information Criterion and Bayesian Approaches Over Likelihood Ratio Tests. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöver, B.C.; Müller, K.F. TreeGraph 2: Combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioRender.com. Available online: https://biorender.com/ (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.; Snell, Q.; Walker, P.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K. TCS: Estimating Gene Genealogies Mark. In Proceedings of the 16th International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, Ft. Lauderdale, FL, USA, 15–19 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Huson, D.H. Splits Tree_analyzing and visualizing evolutionary data. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98, citeulike-article-id:691774. [Google Scholar]
- Kohn, M.A.; Senyak, J. Confidence Interval for a Proportion | Sample Size Calculators. Available online: http://sample-size.net/confidence-interval-proportion/ (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-Joining Networks for Inferring Intraspecific Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messick, J.B. Hemotrophic mycoplasmas (hemoplasmas): A review and new insights into pathogenic potential. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 33, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A. Detección de Mycoplasma haemofelis y “Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum” a través de PCR en gatos de la comuna de chillán. Hosp. Vet. 2005, 47, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm, R.R.; Mora, L.; Segovia, P. Haemobartonella Canis en un Caso Clínico. Av. Cienc. Vet. 1989, 4, 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Persichetti, M.F.; Pennisi, M.G.; Vullo, A.; Masucci, M.; Migliazzo, A.; Solano-Gallego, L. Clinical evaluation of outdoor cats exposed to ectoparasites and associated risk for vector-borne infections in southern Italy. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spotorno, A.; Palma, R.E.; Valladares, P. Biología de roedores reservorios de hantavirus en Chile. Rev. Chil. Infectol. 2000, 17, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.Y.T.; Himsworth, C.G. The secret life of the city rat: A review of the ecology of urban Norway and black rats (Rattus norvegicus and Rattus rattus). Urban Ecosyst. 2014, 17, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.J.; Hall, R.J. Too much of a good thing: Resource provisioning alters infectious disease dynamics in wildlife. Biol. Lett. 2014, 10, 20140309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliot, C.P. The insect vector for the natural transmission of eperythrozoon coccoides in mice. Science 1936, 84, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagawa, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Yokoyama, N.; Inokuma, H. Prevalence and Molecular Analyses of Hemotrophic Mycoplasma spp. (Hemoplasmas) Detected in Sika Deer (Cervus nippon yesoensis) in Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2014, 76, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harasawa, R. PCRApplication of nested PCR to detection of mycoplasmas. In Molecular and Diagnostic Procedures in Mycoplasmology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume II, pp. 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Huson, D.H.; Bryant, D. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshuillers, P.L.; Santos, A.P.; do Nascimento, N.C.; Hampel, J.A.; Bergin, I.L.; Dyson, M.C.; Messick, J.B. Complete Genome Sequence of Mycoplasma ovis Strain Michigan, a Hemoplasma of Sheep with Two Distinct 16S rRNA Genes. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, C.; Bai, Y.; Webb, C.; Kosoy, M. Bats are key hosts in the radiation of mammal-associated Bartonella bacteria. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer | Target Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplification Cycles | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRBP-CF-FWD | irbp | TCCAACACCACCACTGAGATCTGGAC |  | 35 cycles | 227 | Ferreira et al., 2010 |
| IRBP-CF-REV | GTGAGGAAGAAATCGGACTGGCC | |||||
| HemMyco16S-41s | 16S rRNA | GYATGCMTAAYACATGCAAGTCGARCG |  | 55 cycles | 800 | Maggi et al., 2013 |
| HemMyco16S-938as | CTCCACCACTTGTTCAGGTCCCCGTC | |||||
| Species | (bp) | N | VS | GC % | G | Gd (mean ± SD) | π (mean ± SD) | K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Mycoplasma spp. | 510 | 8 | 1 | 0.466 | 2 | 0.25 ± 0.180 | 0.0005 ± 0.0003 | 0.25 |
| B | Mycoplasma spp. | 876 | 36 | 112 | 0.462 | 18 | 0.94 ± 0.0006 | 0.068 ± 0.005 | 32.97 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alabí, A.S.; Monti, G.; Otth, C.; Sepulveda-García, P.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; de Mello, V.V.C.; Machado, R.Z.; André, M.R.; Bittencourt, P.; Müller, A. Molecular Survey and Genetic Diversity of Hemoplasmas in Rodents from Chile. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101493
Alabí AS, Monti G, Otth C, Sepulveda-García P, Sánchez-Hidalgo M, de Mello VVC, Machado RZ, André MR, Bittencourt P, Müller A. Molecular Survey and Genetic Diversity of Hemoplasmas in Rodents from Chile. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(10):1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101493
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlabí, Amir Salvador, Gustavo Monti, Carola Otth, Paulina Sepulveda-García, Melissa Sánchez-Hidalgo, Victória Valente Califre de Mello, Rosangela Zacarias Machado, Marcos Rogério André, Pedro Bittencourt, and Ananda Müller. 2020. "Molecular Survey and Genetic Diversity of Hemoplasmas in Rodents from Chile" Microorganisms 8, no. 10: 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101493
APA StyleAlabí, A. S., Monti, G., Otth, C., Sepulveda-García, P., Sánchez-Hidalgo, M., de Mello, V. V. C., Machado, R. Z., André, M. R., Bittencourt, P., & Müller, A. (2020). Molecular Survey and Genetic Diversity of Hemoplasmas in Rodents from Chile. Microorganisms, 8(10), 1493. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101493






