Phylogenetic and Molecular Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bloodstream Infections in Northeast Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Analysis of Virulence and Resistance Genes
2.4. DNA Sequencing and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
2.5. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
3.1. Staphyloccocus spp. Strains Presented a High Resistance Profile Towards the Tested Antimicrobials
3.2. S. aureus Strains Isolated from Blood Infections Displayed a Diversity of Virulence and Resistance Genes
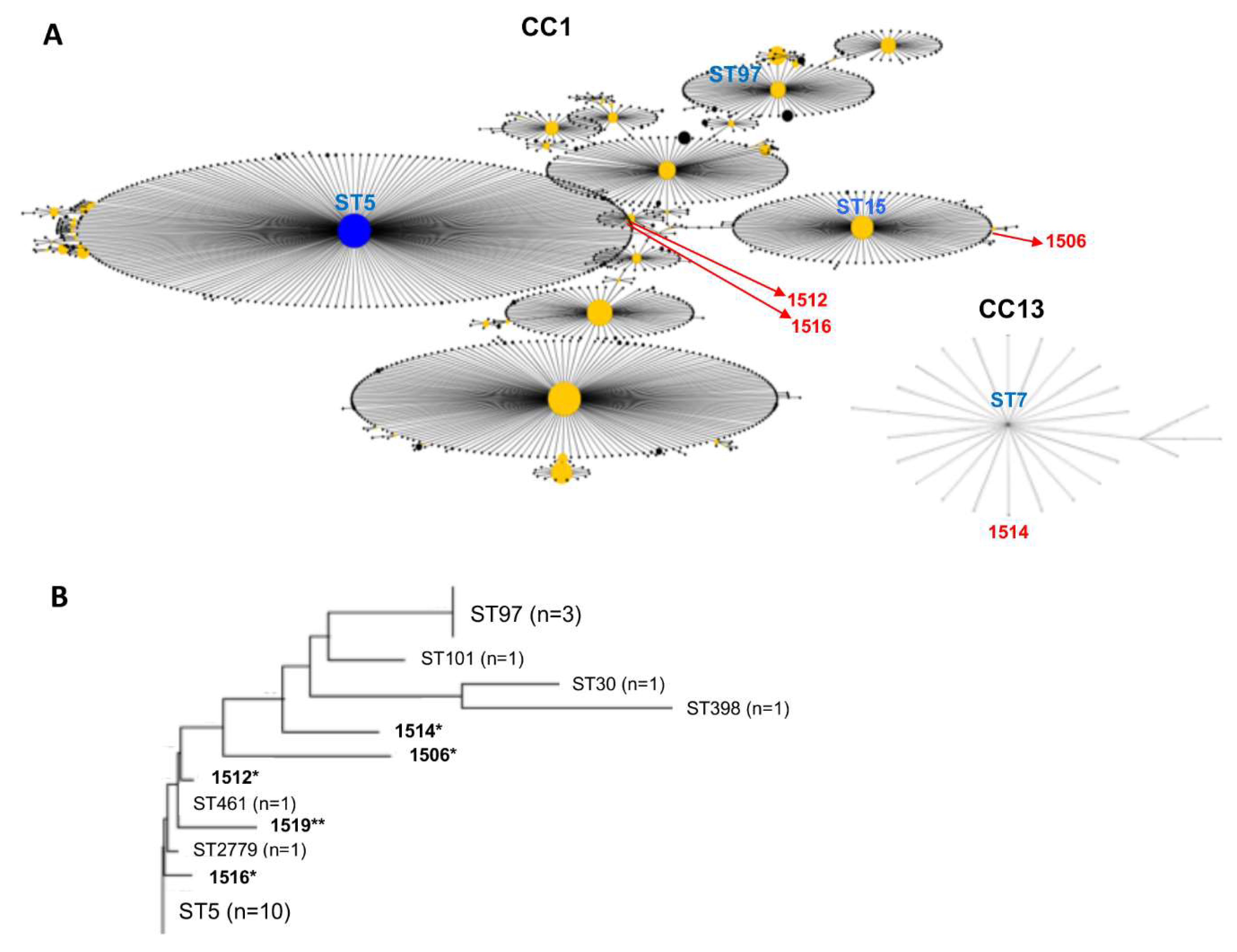
3.3. MLST Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrer, R.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Phillips, G.; Osborn, T.M.; Townsend, S.; Dellinger, R.P.; Artigas, A.; Schorr, C.; Levy, M.M. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: Results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opota, O.; Croxatto, A.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G. Blood culture-based diagnosis of bacteraemia: state of the art. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedrich, A.W. Control of hospital acquired infections and antimicrobial resistance in Europe: The way to go. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2019, 169, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafer, C.; Allison, J.; Hogue, A.; Huntington, M. Infectious Disease: Health Care-Associated Infections. Fp. Essent. 2019, 476, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pliakos, E.E.; Andreatos, N.; Ziakas, P.D.; Mylonakis, E. The Cost-effectiveness of Antimicrobial Lock Solutions for the Prevention of Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talan, D.A.; Krishnadasan, A.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Fosheim, G.E.; Limbago, B.; Albrecht, V.; Moran, G.J.; Group, E.M.I.N.S. Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus from skin and soft-tissue infections in US emergency department patients, 2004 and 2008. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laupland, K.B. Incidence of bloodstream infection: a review of population-based studies. Clin. Microbiol Infect. 2013, 19, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arias, C.A.; Reyes, J.; Carvajal, L.P.; Rincon, S.; Diaz, L.; Panesso, D.; Ibarra, G.; Rios, R.; Munita, J.M.; Salles, M.J.; et al. A Prospective Cohort Multicenter Study of Molecular Epidemiology and Phylogenomics of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia in Nine Latin American Countries. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Muir, T.W. Regulation of Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Mechanisms and Remaining Puzzles. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, K.D.; Foster, S.J.; Renshaw, S.A. Staphylococcus aureus: Setting its sights on the human innate immune system. Microbiology 2019, 165, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Li, M.; Hao, Z.; Shen, X.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Subinhibitory concentrations of resveratrol reduce alpha-hemolysin production in Staphylococcus aureus isolates by downregulating saeRS. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2018, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebic, V.; Budimir, A.; Aljicevic, M.; Mahmutovic Vranic, S.; Rebic, D. Panton-Valentine leukocidin and staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec characterization of community acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2019, 27, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Ganesh, V.K.; Hook, M. Adhesion, invasion and evasion: the many functions of the surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakakido, M.; Aikawa, C.; Nakagawa, I.; Tsumoto, K. The staphylococcal elastin-binding protein regulates zinc-dependent growth/biofilm formation. J. Biochem. 2014, 156, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Mukherjee, S.; Hsu, C.-H.; Davis, J.A.; Tran, T.T.T.; Yang, Q.; Abbott, J.W.; Ayers, S.L.; Young, S.R.; Crarey, E.T. MRSA and multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in US retail meats, 2010–2011. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, M.A.; Walsh, C.T. Antibiotics for emerging pathogens. Science 2009, 325, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: no ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seas, C.; Garcia, C.; Salles, M.J.; Labarca, J.; Luna, C.; Alvarez-Moreno, C.; Mejia-Villatoro, C.; Zurita, J.; Guzman-Blanco, M.; Rodriguez-Noriega, E.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections in Latin America: results of a multinational prospective cohort study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Blanco, M.; Mejía, C.; Isturiz, R.; Alvarez, C.; Bavestrello, L.; Gotuzzo, E.; Labarca, J.; Luna, C.M.; Rodríguez-Noriega, E.; Salles, M.J. Epidemiology of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Latin America. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omuse, G.; Zyl, K.N.; Hoek, K.; Abdulgader, S.; Kariuki, S.; Whitelaw, A.; Revathi, G. Molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from various healthcare institutions in Nairobi, Kenya: a cross sectional study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Rath, S.; Sahu, M.C.; Pattnaik, L.; Debata, N.K.; Padhy, R.N. Surveillance of infection status of drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an Indian teaching hospital. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2013, 3, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, G.A.; Harish, B.N.; Sujatha, S.; Vinothini, K.; Parija, S.C. Emergence of vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus species in southern India. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 911–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delgado, S.; Garcia, P.; Fernandez, L.; Jimenez, E.; Rodriguez-Banos, M.; del Campo, R.; Rodriguez, J.M. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains involved in human and bovine mastitis. Fems Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Deng, L.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Shang, Y.; Zhao, C.; et al. Superantigen gene profiles and presence of exfoliative toxin genes in community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Chinese children. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karahan, Z.C.; Dolapci, I.; Tekeli, A. Influence of reaction optimization on the results of PCR amplification of Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes among Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2009, 43, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boers, S.A.; van der Reijden, W.A.; Jansen, R. High-throughput multilocus sequence typing: bringing molecular typing to the next level. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.; Vu, B.G.; Stach, C.S.; Merriman, J.A.; Horswill, A.R.; Salgado-Pabon, W.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcus aureus beta-Toxin Mutants Are Defective in Biofilm Ligase and Sphingomyelinase Activity, and Causation of Infective Endocarditis and Sepsis. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.B.; Meyer, H.; Rogers, E.; Gilligan, P.H. Comparison of conventional susceptibility testing, penicillin-binding protein 2a latex agglutination testing, and mecA real-time PCR for detection of oxacillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3450–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, A.G.; Novais, S.G.; Marques, T.M.G.; Gonçalves, A.G. Prevalênca de Staphylococcus aureus resistente à meticilina (MRSA) em hospitais públicos e privados de São Luís, MA, Brasil. Rev. Ciências Da Saúde 2010, 12, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dulon, M.; Haamann, F.; Peters, C.; Schablon, A.; Nienhaus, A. MRSA prevalence in European healthcare settings: a review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Dai, Y.; Shang, J.; Li, M. Molecular Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Bovine Mastitis between 2014 and 2015. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, T.M.; Morgado, P.G.M.; Cavalcante, F.S.; Damasco, A.P.; Nouér, S.A.; dos Santos, K.R.N. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of heteroresistant and vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus from bloodstream infections in a Brazilian teaching hospital. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuinness, W.A.; Malachowa, N.; DeLeo, F.R. Vancomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salgado-Pabon, W.; Herrera, A.; Vu, B.G.; Stach, C.S.; Merriman, J.A.; Spaulding, A.R.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcus aureus beta-toxin production is common in strains with the beta-toxin gene inactivated by bacteriophage. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupieux, C.; Camus, C.; Lina, G.; Vandenesch, F.; Laurent, F.; Rasigade, J.P. Does beta-toxin production contribute to the cytotoxicity of hypervirulent Staphylococcus aureus? J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.; Kulhankova, K.; Sonkar, V.K.; Dayal, S.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Salgado-Pabon, W.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcal beta-Toxin Modulates Human Aortic Endothelial Cell and Platelet Function through Sphingomyelinase and Biofilm Ligase Activities. MBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreienbuehl, L.; Charbonney, E.; Eggimann, P. Community-acquired necrotizing pneumonia due to methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus secreting Panton-Valentine leukocidin: A review of case reports. Ann. Intensive Care 2011, 1, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, B.; Hussain, M.; Grundmeier, M.; Brück, M.; Holzinger, D.; Varga, G.; Roth, J.; Kahl, B.C.; Proctor, R.A.; Peters, G. Staphylococcus aureus panton-valentine leukocidin is a very potent cytotoxic factor for human neutrophils. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xu, L.; Tan, L.; Zhao, S.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, C.; Luo, X.; Li, S.; et al. Panton-Valentine Leucocidin (PVL) as a Potential Indicator for Prevalence, Duration, and Severity of Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tristan, A.; Ying, L.; Bes, M.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F.; Lina, G. Use of multiplex PCR to identify Staphylococcus aureus adhesins involved in human hematogenous infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4465–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bimanand, L.; Taherikalani, M.; Jalilian, F.A.; Sadeghifard, N.; Ghafourian, S.; Mahdavi, Z.; Mohamadi, S.; Sayehmiri, K.; Hematian, A.; Pakzad, I. Association between biofilm production, adhesion genes and drugs resistance in different SCCmec types of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from several major hospitals of Iran. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soltani, E.; Farrokhi, E.; Zamanzad, B.; Abadi, M.S.S.; Deris, F.; Soltani, A.; Gholipour, A. Prevalence and distribution of adhesins and the expression of fibronectin-binding protein (FnbA and FnbB) among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Shahrekord Hospitals. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fang, F.; Zhao, J.; Lou, N.; Li, C.; Huang, T.; Li, Y. Molecular characteristics and virulence gene profiles of Staphylococcus aureus causing bloodstream infection. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, O.; Merghni, A.; Elargoubi, A.; Rhim, H.; Kadri, Y.; Mastouri, M. Comparative study of virulence factors among methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downer, R.; Roche, F.; Park, P.W.; Mecham, R.P.; Foster, T.J. The elastin-binding protein of Staphylococcus aureus (EbpS) is expressed at the cell surface as an integral membrane protein and not as a cell wall-associated protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serray, B.; Oufrid, S.; Hannaoui, I.; Bourjilate, F.; Soraa, N.; Mliji, M.; Sobh, M.; Hammoumi, A.; Timinouni, M.; El Azhari, M. Genes encoding adhesion factors and biofilm formation in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Morocco. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowrishankar, S.; Kamaladevi, A.; Balamurugan, K.; Pandian, S.K. In vitro and in vivo biofilm characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from patients associated with pharyngitis infection. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, V.F.; Motta, C.C.; Soares, B.D.; Melo, D.A.; Coelho, S.M.; Coelho, I.D.; Barbosa, H.S.; Souza, M.M. Biofilm production and beta-lactamic resistance in Brazilian Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, J.S.; Burmolle, M.; Hansen, L.H.; Sorensen, S.J. The interconnection between biofilm formation and horizontal gene transfer. Fems Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguila-Arcos, S.; Alvarez-Rodriguez, I.; Garaiyurrebaso, O.; Garbisu, C.; Grohmann, E.; Alkorta, I. Biofilm-Forming Clinical Staphylococcus Isolates Harbor Horizontal Transfer and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.Y.; Chiueh, T.S.; Sun, J.R.; Tsao, S.M.; Lu, J.J. Molecular typing and phenotype characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from blood in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, W.K.; Han, L.Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, Q.Z.; Huangfu, Y.C.; Ni, Y.X. Epidemiological and genetic diversity of Staphylococcus aureus causing bloodstream infection in Shanghai, 2009–2011. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulgader, S.M.; Shittu, A.O.; Nicol, M.P.; Kaba, M. Molecular epidemiology of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Africa: A systematic review. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Yan, Z.Q.; Feng, D.; Luo, Y.P.; Wang, L.L.; Shen, D.X. Nosocomial bloodstream infection in patients caused by Staphylococcus aureus: Drug susceptibility, outcome, and risk factors for hospital mortality. Chin. Med. J. 2012, 125, 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Mehndiratta, P.L.; Bhalla, P. Typing of Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A technical review. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 30, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miko, B.A.; Hafer, C.A.; Lee, C.J.; Sullivan, S.B.; Hackel, M.A.; Johnson, B.M.; Whittier, S.; Della-Latta, P.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Lowy, F.D. Molecular characterization of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates in the United States, 2004 to 2010. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.C.; Wardyn, S.E. Human Infections with Staphylococcus aureus CC398. Curr. Env. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Uhl, J.R.; Cunningham, S.A.; Chia, N.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Sampathkumar, P.; Nelson, H.; Patel, R. Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in a single large Minnesota medical center in 2015 as assessed using MLST, core genome MLST and spa typing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Sun, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H. The Changing Pattern of Population Structure of Staphylococcus aureus from Bacteremia in China from 2013 to 2016: ST239-030-MRSA Replaced by ST59-t437. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowder, B.V.; Guinane, C.M.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Weinert, L.A.; Conway-Morris, A.; Cartwright, R.A.; Simpson, A.J.; Rambaut, A.; Nubel, U.; Fitzgerald, J.R. Recent human-to-poultry host jump, adaptation, and pandemic spread of Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19545–19550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyi, S.A.; Dupre, J.M.; Johnson, W.L.; Hoyt, P.R.; White, D.G.; Brody, T.; Odenwald, W.F.; Gustafson, J.E. Isolation and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains from a Paso del Norte dairy. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.C.; Guimaraes, F.F.; Manzi, M.P.; Budri, P.E.; Gomez-Sanz, E.; Benito, D.; Langoni, H.; Rall, V.L.; Torres, C. Molecular characterization and clonal diversity of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in milk of cows with mastitis in Brazil. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 6856–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nworie, A.; Onyema, A.S.; Okekpa, S.I.; Elom, M.O.; Umoh, N.O.; Usanga, V.U.; Ibiam, G.A.; Ukwah, B.N.; Nwadi, L.C.; Ezeruigbo, C.; et al. A Novel Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus t11469 and a Poultry Endemic Strain t002 (ST5) Are Present in Chicken in Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2936461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Noriega, E.; Seas, C.; Guzman-Blanco, M.; Mejia, C.; Alvarez, C.; Bavestrello, L.; Zurita, J.; Labarca, J.; Luna, C.M.; Salles, M.J.; et al. Evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones in Latin America. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e560–e566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Barkema, H.W.; Ali, T.; Liu, G.; Deng, Y.; Naushad, S.; Kastelic, J.P.; Han, B. Virulence gene profiles: alpha-hemolysin and clonal diversity in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine clinical mastitis in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meemken, D.; Blaha, T.; Tegeler, R.; Tenhagen, B.A.; Guerra, B.; Hammerl, J.; Hertwig, S.; Käsbohrer, A.; Appel, B.; Fetsch, A. Livestock Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LaMRSA) Isolated from Lesions of Pigs at Necropsy in Northwest Germany Between 2004 and 2007. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, e143–e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, W.; Strommenger, B.; Stanek, C.; Cuny, C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST398 in humans and animals, Central Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, C.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Benito, D.; Aspiroz, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage, virulence traits, antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and genetic lineages in healthy humans in Spain, with detection of CC398 and CC97 strains. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loo, I.; Huijsdens, X.; Tiemersma, E.; de Neeling, A.; van de Sande-Bruinsma, N.; Beaujean, D.; Voss, A.; Kluytmans, J. Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus of animal origin in humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Belkum, A.; Melles, D.C.; Peeters, J.K.; van Leeuwen, W.B.; van Duijkeren, E.; Huijsdens, X.W.; Spalburg, E.; de Neeling, A.J.; Verbrugh, H.A.; Dutch Working Party on, S.; et al. Methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 398 in pigs and humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoecke, H.; Piette, A.; De Leenheer, E.; Lagasse, N.; Struelens, M.; Verschraegen, G.; Dhooge, I. Destructive otomastoiditis by MRSA from porcine origin. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André Neto, E.D.; Pereira, R.F.A.; Snyder, R.E.; Machado, T.S.; André, L.S.P.; Cardoso, C.A.A.; Aguiar-Alves, F. Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clonal complex 398 with no livestock association in Brazil. Memórias Do Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2017, 112, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand-Lefevre, L.; Ruimy, R.; Andremont, A. Clonal comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from healthy pig farmers, human controls, and pigs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Gu, F.F.; Guo, X.K.; Ni, Y.X.; He, P.; Han, L.Z. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Childhood Pneumonia in Shanghai. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemiri, M.; Abbassi, M.S.; Couto, N.; Mansouri, R.; Hammami, S.; Pomba, C. Genetic characterisation of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from milk and nasal samples of healthy cows in Tunisia: First report of ST97-t267-agrI-SCCmecV MRSA of bovine origin in Tunisia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.Z.; Daum, R.S. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 616–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, H.; Takano, T.; Nishiyama, A.; Hung, W.-C.; Kuniyuki, S.; Shibuya, Y.; Reva, I.; Yabe, S.; Iwao, Y.; Higuchi, W. Evolution and virulence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-positive ST30 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the past 30 years in Japan. Biomed. Res. 2012, 33, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, Y.; Issartel, B.; Vanhems, P.; Fournet, J.-C.; Lina, G.; Bes, M.; Vandenesch, F.; Piémont, Y.; Brousse, N.; Floret, D. Association between Staphylococcus aureus strains carrying gene for Panton-Valentine leukocidin and highly lethal necrotising pneumonia in young immunocompetent patients. Lancet 2002, 359, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′ - 3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Size of PCR Product (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-lactamase (blaZ) | (F) ACTTCAACACCTGCTGCTTTC (R) TGACCACTTTTATCAGCAACC | 61 | 173 | [23] |
| Clumping factor A (clfA) | (F) GTAGGTACGTTAATCGGTT (R) CTCATCAGGTTGTTCAGG | 50 | 1548 | [23] |
| Collagen adhesin (can) | (F) AGTGGTTACTAATCATG (R) CAGGATAGATTGGTTTA | 45 | 1722 | [23] |
| Elastin-binding Protein (ebpS) | (F) CAATCGATAGACACAAATTC (R) CAGTTACATCATCATGTTTA | 50 | 506 | [23] |
| Exfoliative toxin A (eta) | (F) ACTGTAGGAGCTAGTGCATTTGT (R) TGGATACTTTTGTCTATCTTTTTCATCAAC | 55 | 190 | [24] |
| Exfoliative toxin B (etb) | (F) CAGATAAAGAGCTTTATACACACATTAC (R) AGTGAACTTATCTTTCTATTGAAAAACACTC | 55 | 612 | [24] |
| Fibronectin-binding protein A (fnbpA) | (F) CACAACCAGCAAATATAG (R) CTGTGTGGTAATCAATGTC | 50 | 1226 | [24] |
| Alpha-hemolysin (hla) | (F) CTGATTACTATCCAAGAAATTCGATTG (R) CTTTCCAGCCTACTTTTTTATCAGT | 55 | 209 | [24] |
| Beta-hemolysin (hlb) | (F) GTGCACTTACTGACAATAGTGC (R) GTTGATGAGTAGCTACCTTCAGT | 55 | 309 | [24] |
| Gama-hemolysin (hlg) | (F) GTCAAAGAGTCCATAATGCATTTAA (R) CACCAAATGTATAGCCTAAAGTG | 55 | 535 | [24] |
| Intracellular adhesion (icaA) | (F) GATTATGTAATGTGCTTGGA (R) ACTACTGCTGCGTTAATAAT | 50 | 770 | [23] |
| Methicillin resistance (mecA) | (F) GGTCCCATTAACTCTGAAG (R) AGTTCTGCAGTACCGGATTTTGC | 57 | 163 | [23] |
| Panton-valentine leucocidin (pvl) | (F) ATCAATAGGTAAAATGTCTGGACATGATCCA (R) GCATCAAATGTATTGGATAG AAAAGC | 55 | 433 | [25] |
| Serine-aspartate repeat-containing protein E (sdrE) | (F) CAGTAAATGTGTCAAAAGA (R) TTGACTACCAGCTATATC | 50 | 749 | [23] |
| Enterotoxin A (sea) | (F) GAAAAAAGTCTGAATTGCAGGGAACA (R) CAAATAAATCGTAATTAACCGAAGGTTC | 55 | 560 | [24] |
| Enterotoxin B (seb) | (F) ATTCTATTAAGGACACTAAGTTAGGGA (R) ATCCCGTTTCATAAGGCGAGT | 55 | 404 | [24] |
| Enterotoxin C (sec) | (F) GTAAAGTTACAGGTGGCAAAACTTG (R) CATATCATACCAAAAAGTATTGCCGT | 55 | 297 | [24] |
| Enterotoxin D (sed) | (F) GAATTAAGTAGTACCGCCCTAAATAATATG (R) GCTGTATTTTTCCTCCGAGAGT | 55 | 492 | [24] |
| Enterotoxin E (see) | (F) CAAAGAAATGCTTTAAGCAATCTTAGGC (R) CACCTTACCGCCAAAGCTC | 55 | 482 | [24] |
| Enterotoxin G (seg) | (F) AATTATGTGAATGCTCAACCCGATC (R) AAACTTATATGGAACAAAAGGTACTAGTTC | 55 | 642 | [24] |
| Enterotoxin H (she) | (F) CAATCACATCATATGCGAAAGCAG (R) CATCTACCCAAACATTAGCACC | 55 | 376 | [24] |
| Enterotoxin I (sei) | (F) CTCAAGGTGATATTGGTGTAGG (R) AAAAAACTTACAGGCAGTCCATCTC | 55 | 576 | [24] |
| Enterotoxin J (sej) | (F) TCAGAACTGTTGTTCCGCTAG (R) GAATTTTACCAYCAAAGGTAC | 55 | 138 | [24] |
| Siderophore compound transporter permease protein (sirB) | (F) CAGCTACGGCTACCGAAATA (R) CATTTTTGGGGGCTATTGTTGT | 61 | 399 | [23] |
| Virulence Factor Profile | Antibiotics Resistance Profile | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | ST | Isolates | blaZ | clfA | ebpS | fnbpA | hla | hlb | hlg | icaA | mecA | pvl | CIP | CLI | ERI | GEN | OXA | RIF | TEI | TRI |
| CC1 | 97 | 1522 | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 97 | 1523 | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − |
| CC1 | 97 | 1521 | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC17 | 101 | 1500 | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| CC2 | 30 | 1507 | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − |
| CC7 | 398 | 1520 | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| CC13 * | 5431 | 1514 | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 * | 5429 | 1506 | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 * | 5430 | 1512 | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 461 | 1509 | − | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 ** | 5433 | 1519 | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 2779 | 1502 | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| CC1 * | 5432 | 1516 | + | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1524 | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1518 | − | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | + |
| CC1 | 5 | 1517 | + | + | + | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1515 | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1501 | + | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1503 | − | − | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1505 | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1510 | − | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1511 | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CC1 | 5 | 1508 | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | − | + |
| Total | n % | 23 100% | 11 48% | 13 57% | 14 61% | 4 17% | 2 8% | 19 83% | 1 4% | 3 13% | 8 35% | 1 4% | 14 61% | 18 78% | 16 70% | 12 52% | 18 78% | 4 17% | 1 4% | 2 9% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monteiro, A.d.S.; Pinto, B.L.S.; Monteiro, J.d.M.; Ferreira, R.M.; Ribeiro, P.C.S.; Bando, S.Y.; Marques, S.G.; Silva, L.C.N.; Neto, W.R.N.; Ferreira, G.F.; et al. Phylogenetic and Molecular Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bloodstream Infections in Northeast Brazil. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070210
Monteiro AdS, Pinto BLS, Monteiro JdM, Ferreira RM, Ribeiro PCS, Bando SY, Marques SG, Silva LCN, Neto WRN, Ferreira GF, et al. Phylogenetic and Molecular Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bloodstream Infections in Northeast Brazil. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(7):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070210
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonteiro, Andrea de S., Bruna L. S. Pinto, Joveliane de M. Monteiro, Rômulo M. Ferreira, Patrícia C. S. Ribeiro, Silvia Y. Bando, Sirlei G. Marques, Luís C. N. Silva, Wallace R. Nunes Neto, Gabriella F. Ferreira, and et al. 2019. "Phylogenetic and Molecular Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bloodstream Infections in Northeast Brazil" Microorganisms 7, no. 7: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070210
APA StyleMonteiro, A. d. S., Pinto, B. L. S., Monteiro, J. d. M., Ferreira, R. M., Ribeiro, P. C. S., Bando, S. Y., Marques, S. G., Silva, L. C. N., Neto, W. R. N., Ferreira, G. F., Bomfim, M. R. Q., & Abreu, A. G. (2019). Phylogenetic and Molecular Profile of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Bloodstream Infections in Northeast Brazil. Microorganisms, 7(7), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070210






