Advanced Strategies for Food-Grade Protein Production: A New E. coli/Lactic Acid Bacteria Shuttle Vector for Improved Cloning and Food-Grade Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Plasmids
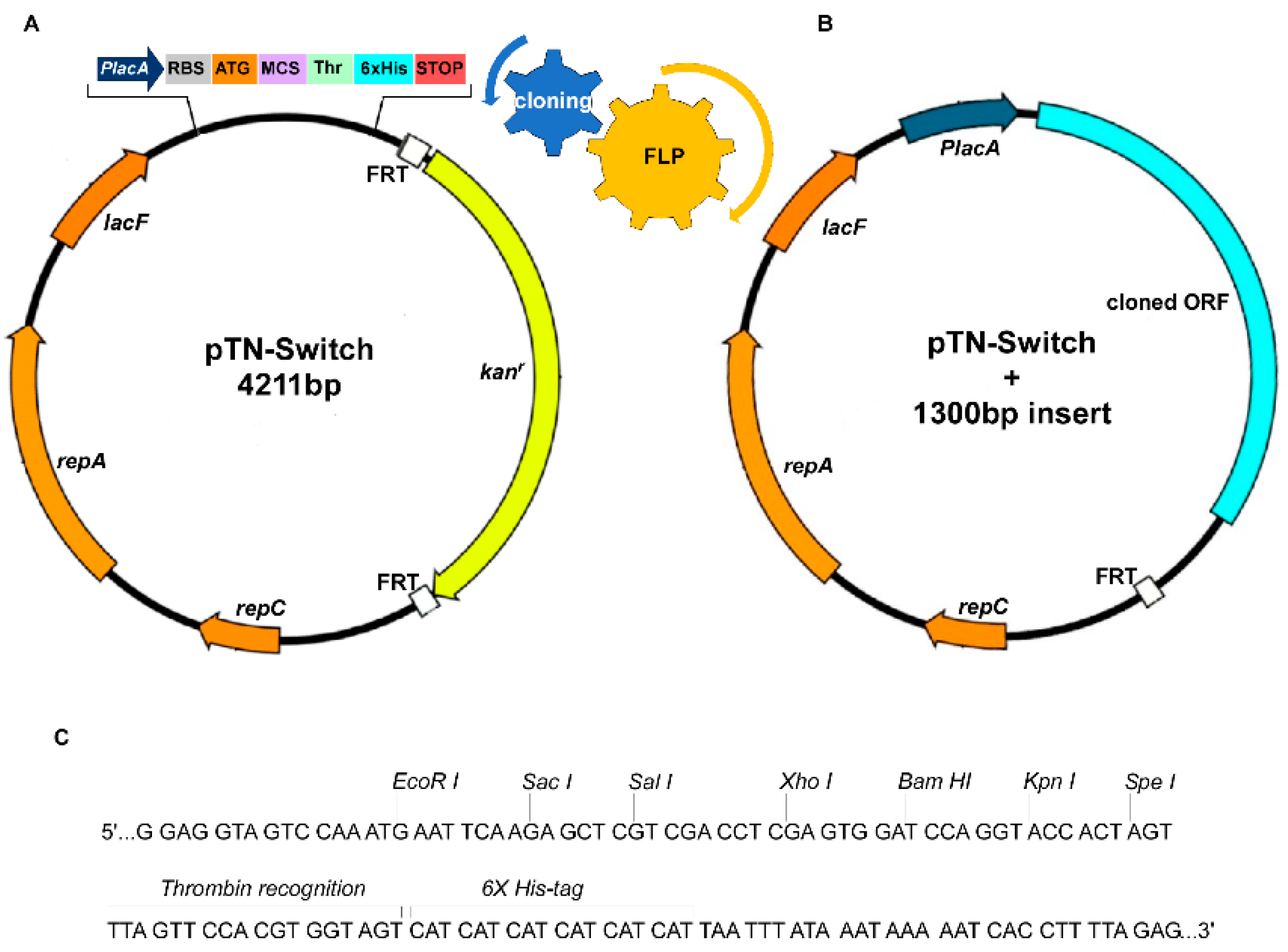
2.2. Plasmid Construction
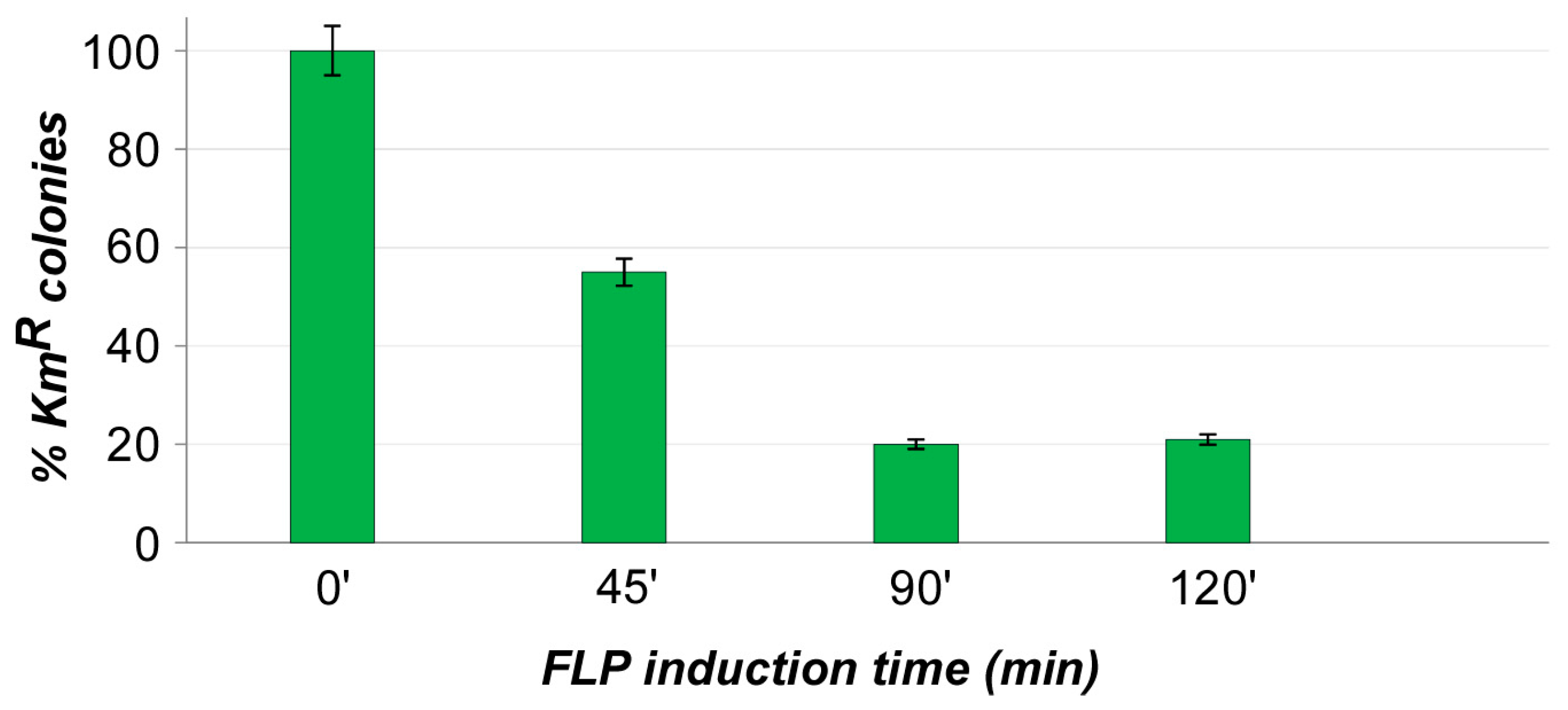
2.3. Cassette Removal Tests
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rygus, T.; Hillen, W. Inducible high-level expression of heterologous genes in Bacillus megaterium using the regulatory elements of the xylose-utilization operon. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1991, 35, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Nguyen, Q.A.; Ferreira, R.C.; Ferreira, L.C.S.; Tran, L.T.; Schumann, W. Construction of plasmid-based expression vectors for Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid 2005, 54, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.T.P.; Nguyen, H.D.; Schumann, W. Novel plasmid-based expression vectors for intra- and extracellular production of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 46, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malten, M.; Biedendieck, R.; Gamer, M.; Drews, A.-C.; Stammen, S.; Buchholz, K.; Dijkhuizen, L.; Jahn, D. A Bacillus megaterium plasmid system for the production, export and one-step purification of affinity tagged heterologous levansucrase from the growth medium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1677–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Hollmann, R.; Deckwer, W.D. Comparative proteomic analysis of high cell density cultivations with two recombinant Bacillus megaterium strains for the production of a heterologous dextransucrase. Proteome Sci. 2006, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Phan, T.T.; Schumann, W. Expression Vectors for the Rapid Purification of Recombinant Proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, W. Production of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 62, 137–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stammen, S.; Müller, B.K.; Korneli, C.; Biedendieck, R.; Gamer, M.; Franco-Lara, E.; Jahn, D. High-yield intra- and extracellular protein production using Bacillus megaterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 76, 4037–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Kimura, K.; Funane, K. Extracellular production of cycloisomaltooligosaccharide glucanotransferase and cyclodextran by a protease-deficient Bacillus subtilis host-vector system. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, C.; Zhang, H.W.; Song, D.G.; Xie, Y.G.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.Z. Expressing antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin-BF in Bacillus subtilis using SUMO technology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3651–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Su, L.; Duan, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, J. High-level extracellular protein production in Bacillus subtilis using an optimized dual-promoter expression system. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.; Huynh, P.; Truong, T.; Nguyen, H.A. Generic Protocol for Intracellular Expression of Recombinant Proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1586, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Landete, J.M. A review of food-grade vectors in lactic acid bacteria: From the laboratory to their application. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Guchte, M.; Penaud, S.; Grimaldi, C.; Barbe, V.; Bryson, K.; Nicolas, P.; Robert, C.; Oztas, S.; Mangenot, S.; Couloux, A.; et al. The complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus bulgaricus reveals extensive and ongoing reductive evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9274–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J. Mucosal vaccination and therapy with genetically modified lactic acid bacteria. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, V.B.; Saraiva, T.D.L.; Souza, B.M.; Zurita-Turk, M.; Azevedo, M.S.P.; De Castro, C.P.; Mancha-Agresti, P.; dos Santos, J.S.C.; Santos, A.C.G.; Faria, A.M.C.; et al. Development of a new DNA vaccine based on mycobacterial ESAT-6 antigen delivered by recombinant invasive Lactococcus lactis FnBPA+. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.B.; da Cunha, V.P.; Preisser, T.M.; Souza, B.M.; Turk, M.Z.; De Castro, C.P.; Azevedo, M.S.P.; Miyoshi, A. Lactococcus lactis carrying a DNA vaccine coding for the ESAT-6 antigen increases IL-17 cytokine secretion and boosts the BCG vaccine immune response. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, D.; Azevedo, M.; Innocentin, S.; Blugeon, S.; Lefévre, F.; Azevedo, V.; Miyoshi, A.; Courtin, P.; Chapot-Chartier, M.-P.; Langella, P.; et al. Immune response elicited by DNA vaccination using Lactococcus lactis is modified by the production of surface exposed pathogenic protein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurita-Turk, M.; Del Carmen, S.; Santos, A.C.G.; Pereira, V.B.; Cara, D.C.; Leclercq, S.Y.; de LeBlanc, A.D.; Azevedo, V.; Chatel, J.-M.; LeBlanc, J.G.; et al. Lactococcus lactis carrying the pValac DNA expression vector coding for IL-10 reduces inflammation in a murine model of experimental colitis. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancha-Agresti, P.; de Castro, C.P.; Dos Santos, J.S.C.; Araujo, M.A.; Pereira, V.B.; LeBlanc, J.G.; Leclercq, S.Y.; Azevedo, V. Recombinant Invasive Lactococcus lactis Carrying a DNA Vaccine Coding the Ag85A Antigen Increases INF-γ, IL-6, and TNF-α Cytokines after Intranasal Immunization. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, B.M.; Preisser, T.M.; Pereira, V.B.; Zurita-Turk, M.; de Castro, C.P.; da Cunha, V.P.; de Oliveira, R.P.; Gomes-Santos, A.C.; de Faria, A.M.C.; Machado, D.C.C.; et al. Lactococcus lactis carrying the pValac eukaryotic expression vector coding for IL-4 reduces chemically-induced intestinal inflammation by increasing the levels of IL-10-producing regulatory cells. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercenier, A.; Müller-Alouf, H.; Grangette, C. Lactic acid bacteria as live vaccines. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2000, 2, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pontes, D.S.; de Azevedo, M.S.P.; Chatel, J.-M.; Langella, P.; Azevedo, V.; Miyoshi, A. Lactococcus lactis as a live vector: Heterologous protein production and DNA delivery systems. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 79, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.; van der Vossen, J.M.; Venema, G. Construction of plasmid cloning vectors for lactic streptococci which also replicate in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 48, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Vos, W.M.; Kleerebezem, M.; Kuipers, O.P. Expression systems for industrial Gram-positive bacteria with low guanine and cytosine content. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1997, 8, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbouziane, B.; Ribelles, P.; Aubry, C.; Martin, R.; Kharrat, P.; Riazi, A.; Langella, P.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Development of a Stress-Inducible Controlled Expression (SICE) system in Lactococcus lactis for the production and delivery of therapeutic molecules at mucosal surfaces. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Montalbán-López, M.; Masuda, Y.; Kuipers, O.P. Zirex: A Novel Zinc-Regulated Expression System for Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4503–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, C.P.; Drumond, M.M.; Batista, V.L.; Nunes, A.; Mancha-Agresti, P.; Azevedo, V. Vector Development Timeline for Mucosal Vaccination and Treatment of Disease Using Lactococcus lactis and Design Approaches of Next Generation Food Grade Plasmids. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Zhu, H.; Shen, M.; Li, G.; Lu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Le, S.; Tan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Hu, F.; et al. Surface Display of Heterologous β-Galactosidase in Food-Grade Recombinant Lactococcus lactis. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. A food-grade approach for functional analysis and modification of native plasmids in Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cho, S.; Shin, J.; Cho, B.-K. Applications of CRISPR/Cas System to Bacterial Metabolic Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlec, A.; Strukelj, B. Novel applications of recombinant lactic acid bacteria in therapy and in metabolic engineering. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2009, 3, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlec, A.; Škrlec, K.; Kocjan, J.; Olenic, M.; Štrukelj, B. Single plasmid systems for inducible dual protein expression and for CRISPR-Cas9/CRISPRi gene regulation in lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosalbes, M.J.; Esteban, C.D.; Galán, J.L.; Pérez-Martínez, G. Integrative Food-Grade Expression System Based on the Lactose Regulon of Lactobacillus casei. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4822–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Ling, P.; Wang, F. Constructing a recombinant hyaluronic acid biosynthesis operon and producing food-grade hyaluronic acid in Lactococcus lactis. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCormick, C.A.; Griffin, H.G.; Gasson, M.J. Construction of a food-grade host/vector system for Lactococcus lactis based on the lactose operon. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 127, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platteeuw, C.; van Alen-Boerrigter, I.; van Schalkwijk, S.; de Vos, W.M. Food-grade cloning and expression system for Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar]
- de Ruyter, P.G.; Kuipers, O.P.; de Vos, W.M. Controlled gene expression systems for Lactococcus lactis with the food-grade inducer nisin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3662–3667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gu, P.; Yang, F.; Su, T.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Qi, Q. A rapid and reliable strategy for chromosomal integration of gene(s) with multiple copies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Garcia, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G. Techniques for chromosomal integration and expression optimization in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 2467–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.-F.; Sun, M.-Y.; Cui, L.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Xing, X.-H. Cre/loxP-Mediated Multicopy Integration of the Mevalonate Operon into the Genome of Methylobacterium extorquens AM1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 185, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, M.M. The FLP protein of the yeast 2-microns plasmid: Expression of a eukaryotic genetic recombination system in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 4223–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronostajski, R.M.; Sadowski, P.D. The FLP recombinase of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2 microns plasmid attaches covalently to DNA via a phosphotyrosyl linkage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1985, 5, 3274–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senecoff, J.F.; Bruckner, R.C.; Cox, M.M. The FLP recombinase of the yeast 2-micron plasmid: Characterization of its recombination site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 7270–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepanov, P.P.; Wackernagel, W. Gene disruption in Escherichia coli: TcR and KmR cassettes with the option of Flp-catalyzed excision of the antibiotic-resistance determinant. Gene 1995, 158, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.I.; Lennen, R.M.; Herrgård, M.J.; Nielsen, A.T. Seven gene deletions in seven days: Fast generation of Escherichia coli strains tolerant to acetate and osmotic stress. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliavia, M.; Nicosia, A.; Salamone, M.; Biondo, G.; Bennici, C.D.; Mazzola, S.; Cuttitta, A. Development of a fast DNA extraction method for sea food and marine species identification. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Perez, D.; Gunasekaran, S.; Orler, V.J.; Pfleger, B.F. A translation-coupling DNA cassette for monitoring protein translation in Escherichia coli. Metab. Eng. 2012, 14, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavia, M.; Cuttitta, A. Exploiting translational coupling for the selection of cells producing toxic recombinant proteins from expression vectors. BioTechniques 2016, 60, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| pNZ2122_680F | CAGGTACCACTAGTTTAGTTCCACGTGGTAGTCATCATCATCATCATCATTAATTTATAAATAAAAATCACCTTTTAGAG |
| pNZ2122_395R | AGTGGTACCTGGATCCACTCGAGGTCGACGAGCTCTTGAATTCATTTGGACTACCTCCTAAAT |
| pNZ2122/803ClaF | TCAAATCGATTCCACCAATTAAAGGACCGATAAC |
| pNZ2122/760SpeR | TCAACTAGTATTCTGCTCCCGCCCTTATG |
| pKD13_P1Cla | TCAAATCGATGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC |
| pKD13_P4Spe | TCAACTAGTGAATTAATTCCGGAGATCCATCGACGTGCAGTTC |
| pKD13_P1 | GTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC |
| pKD13_P41 | GAGATCCATCGACGTGCAGTTC |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tagliavia, M.; Nicosia, A. Advanced Strategies for Food-Grade Protein Production: A New E. coli/Lactic Acid Bacteria Shuttle Vector for Improved Cloning and Food-Grade Expression. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7050116
Tagliavia M, Nicosia A. Advanced Strategies for Food-Grade Protein Production: A New E. coli/Lactic Acid Bacteria Shuttle Vector for Improved Cloning and Food-Grade Expression. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(5):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7050116
Chicago/Turabian StyleTagliavia, Marcello, and Aldo Nicosia. 2019. "Advanced Strategies for Food-Grade Protein Production: A New E. coli/Lactic Acid Bacteria Shuttle Vector for Improved Cloning and Food-Grade Expression" Microorganisms 7, no. 5: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7050116
APA StyleTagliavia, M., & Nicosia, A. (2019). Advanced Strategies for Food-Grade Protein Production: A New E. coli/Lactic Acid Bacteria Shuttle Vector for Improved Cloning and Food-Grade Expression. Microorganisms, 7(5), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7050116






